Decolorization of Melanoidin Using Sono–Fenton and Photo–Fenton Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Melanoidin Wastewater Synthesis
2.3. Fenton Process Experiment
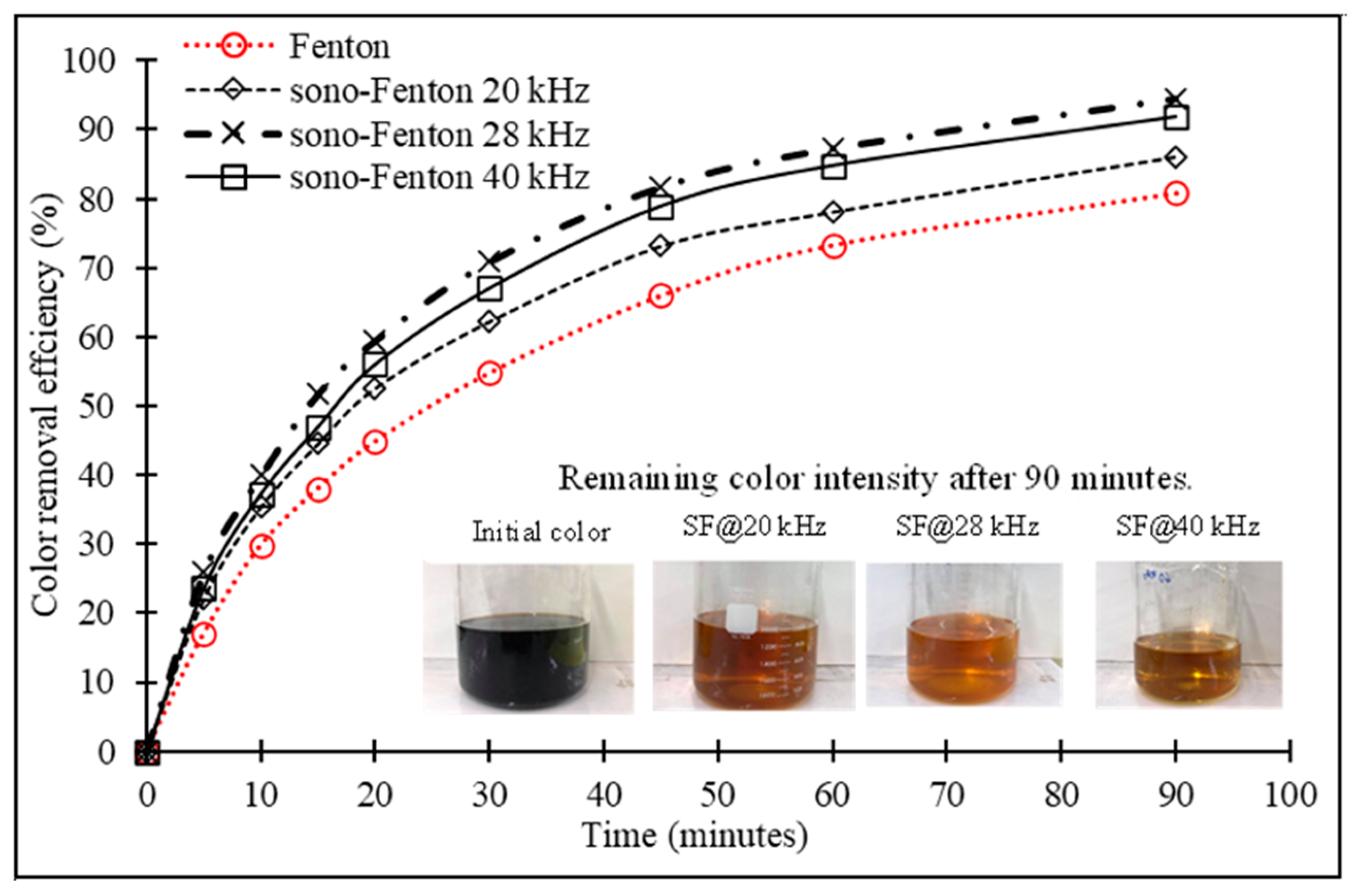
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Initial Fe2+ Dosage
3.2. Effect of Initial H2O2 Concentration
3.3. Effect of Initial pH
3.4. Optimization for Decolorization of Melanoidin Wastewater Using Sono–Fenton (Fe2+/H2O2/US) Process
3.5. Optimization for Decolorization of Melanoidin Wastewater Using Photo–Fenton Fe2+/H2O2/UV–C) Process
3.6. Optimization for Decolorization of Melanoidin Wastewater Using Sono–Photo–Fenton (Fe2+/H2O2/UV–C/US) Process
3.7. Kinetic Experiments
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsioptsias, C.; Petridis, D.; Athanasakis, N.; Lemonidis, I.; Deligiannis, A.; Samaras, P. Post-treatment of molasses wastewater by electrocoagulation and process optimization through response surface analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 164, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, R.; Bharagava, R.N.; Rai, V. Melanoidins as major colourant in sugarcane molasses based distillery effluent and its degradation. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4648–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumura, M.; Ohta, A.; Znad, H.T.; Kawase, Y. UV light assisted decolorization of dark brown colored coffee effluent by photo–Fenton reaction. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3775–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, D.; Adholeya, A. Biological approaches for treatment of distillery wastewater: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2321–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Pawar, R.; Mishra, S.; Tewari, A. Exploitation of marine cyanobacteria for removal of colour from distillery effluent. Indian J. Environ. Prot. 2001, 21, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Alavijeh, H.N.; Sadeghi, M.; Kashani, M.R.K.; Moheb, A. Efficient Chemical Coagulation-Electrocoagulation-Membrane Filtration Integrated Systems for Baker’s Yeast Wastewater Treatment: Experimental and Economic Evaluation. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2022, 3, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobya, M.; Delipinar, S. Treatment of the baker’s yeast wastewater by electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liakos, T.I.; Lazaridis, N.K. Melanoidin removal from molasses effluents by adsorption. J. Water Process. Eng. 2016, 10, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobya, M.; Gengec, E. Decolourization of melanoidins by a electrocoagulation process using aluminium electrodes. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 2429–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simaratanamongkol, A.; Thiravetyan, P. Decolorization of melanoidin by activated carbon obtained from bagasse bottom ash. J. Food Eng. 2010, 96, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Sirés, I.; Oturan, M.A. Electro–Fenton Process and Related Electrochemical Technologies Based on Fenton’s Reaction Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6570–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnajady, M.; Modirshahla, N.; Ghanbary, F. A kinetic model for the decolorization of C.I. Acid Yellow 23 by Fenton process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertugay, N.; Acar, F.N. Acar, Removal of COD and color from Direct Blue 71 azo dye wastewater by Fenton’s oxidation: Kinetic study. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1158–S1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, A.; Erden, G. Decolorization of a baker’s yeast industry effluent by Fenton oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 127, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunç, S.; Gürkan, T.; Duman, O. On-line spectrophotometric method for the determination of optimum operation parameters on the decolorization of Acid Red 66 and Direct Blue 71 from aqueous solution by Fenton process. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181–182, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, U.A.; Duong, T.T.; Ko, S.-Y.; Hussain, F.; Oh, S.-E. Optimization of Fenton process for removing TOC and color from swine wastewater using response surface method (RSM). J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, L.; Selvam, K.; Swaminathan, M. Photo–Fenton defluoridation of pentafluorobenzoic acid with UV–C light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2007, 188, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdad, F.; Younesi, H.; Bahramifar, N.; Hadavifar, M. Optimization of Fenton and photo–Fenton–based advanced oxidation processes for post–treatment of composting leachate of municipal solid waste by an activated sludge process. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 20, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalkaya, E.C.; Sengul, F. Application of Box–Wilson experimental design method for the photodegradation of bakery’s yeast industry with UV/H2O2 and UV/H2O2/Fe(II) process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaithambi, P.; Saravanathamizhan, R.; Matheswaran, M. Comparison of treatment and energy efficiency of advanced oxidation processes for the distillery wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 12, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, H.B. Sono–Fenton process for metronidazole degradation in aqueous solution: Effect of acoustic cavitation and peroxydisulfate anion. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 33, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basturk, E.; Karatas, M. Advanced oxidation of Reactive Blue 181 solution: A comparison between Fenton and Sono–Fenton process. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1881–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echavarría, A.P.; Pagán, J.; Ibarz, A. Melanoidins Formed by Maillard Reaction in Food and Their Biological Activity. Food Eng. Rev. 2012, 4, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W.-R. Melanoidins produced by the Maillard reaction: Structure and biological activity. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsiopoulou, N.G.; Liakos, T.I.; Lazaridis, N.K. Melanoidin chromophores and betaine osmoprotectant separation from aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 216, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Decolorization of the azo dye Reactive Black 5 by Fenton and photo-Fenton oxidation. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 71, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, C.; Chen, H.; Zeng, G.; Yu, G.; Guo, J. Removal of triazophos pesticide from wastewater with Fenton reagent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1028–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, M.; Mirbagheri, S.A.; Ye, F.; Dutta, J. Nano zero-valent iron on activated carbon cloth support as Fenton-like catalyst for efficient color and COD removal from melanoidin wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouasla, C.; Samar, M.E.-H.; Ismail, F. Degradation of methyl violet 6B dye by the Fenton process. Desalination 2010, 254, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, N.; Vabbina, P.K.; Pala, N. Sonochemistry: Science and Engineering. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 29, 104–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merouani, S.; Hamdaoui, O.; Rezgui, Y.; Guemini, M. Effects of ultrasound frequency and acoustic amplitude on the size of sonochemically active bubbles—Theoretical study. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotchie, A.; Grieser, F.; Ashokkumar, M. Effect of Power and Frequency on Bubble–Size Distributions in Acoustic Cavitation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 084302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, T.J.; Cobley, A.J.; Graves, J.E.; Morgan, D. New evidence for the inverse dependence of mechanical and chemical effects on the frequency of ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanapimmetha, A.; Srinophakun, P.; Amat, S.; Saisriyoot, M. Decolorization of molasses–based distillery wastewater by means of pulse electro–Fenton process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, F.; Santana, C.S.; Aguiar, A. Behavior of dihydroxybenzenes and gallic acid on the Fenton–based decolorization of dyes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, P.; Saha, S. Oxidation of direct dyes with hydrogen peroxide using ferrous ion as catalyst. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 31, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidney Santana, C.; Nicodemos Ramos, M.D.; Vieira Velloso, C.C.; Aguiar, A. Kinetic Evaluation of Dye Decolorization by Fenton Processes in the Presence of 3-Hydroxyanthranilic Acid. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, S.; Dashti, A.F.; Adnan, R. Applications of Fenton oxidation processes for decontamination of palm oil mill effluent: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 7302–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrades, F.; Saiz, S.; Garcia–Hortal, J.A.; García–Montaño, J. Degradation of Wheat Straw Black Liquor by Fenton and Photo–Fenton Processes. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008, 25, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Process | First-Order | Second-Order | BMG | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 1 (min−1) | R2 | k1 1 (min−1) | R2 | m 2 | b 3 | R2 | 1/m 4 | 1/b 5 | |
| Fenton | 0.0182 | 0.9659 | 0.0470 | 0.9974 | 26.7650 | 1.3434 | 0.9889 | 0.0374 | 0.7444 |
| SF @ 40 kHz. | 0.0270 | 0.9853 | 0.1108 | 0.9544 | 24.1070 | 1.1608 | 0.9798 | 0.0415 | 0.8615 |
| PF @ 60 W | 0.0296 | 0.8967 | 0.1998 | 0.9313 | 8.8821 | 1.3816 | 0.9839 | 0.1126 | 0.7238 |
| SPF @ 40 kHz and 60 W | 0.0242 | 0.7343 | 0.1206 | 0.4969 | 10.9350 | 1.4390 | 0.9643 | 0.0914 | 0.6949 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watcharenwong, A.; Kongka, K.; Kaeokan, A.; Chokejaroenrat, C.; Sakulthaew, C. Decolorization of Melanoidin Using Sono–Fenton and Photo–Fenton Processes. Waste 2023, 1, 455-467. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1020027
Watcharenwong A, Kongka K, Kaeokan A, Chokejaroenrat C, Sakulthaew C. Decolorization of Melanoidin Using Sono–Fenton and Photo–Fenton Processes. Waste. 2023; 1(2):455-467. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatcharenwong, Apichon, Kawintra Kongka, Anusara Kaeokan, Chanat Chokejaroenrat, and Chainarong Sakulthaew. 2023. "Decolorization of Melanoidin Using Sono–Fenton and Photo–Fenton Processes" Waste 1, no. 2: 455-467. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1020027
APA StyleWatcharenwong, A., Kongka, K., Kaeokan, A., Chokejaroenrat, C., & Sakulthaew, C. (2023). Decolorization of Melanoidin Using Sono–Fenton and Photo–Fenton Processes. Waste, 1(2), 455-467. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1020027







