- Concept Paper
Engineered Microbial Consortium Embedded in a Biodegradable Matrix: A Triple-Action, Synthetic Biology Framework for Sustainable Post-Wildfire Restoration
- Markos Mathioudakis,
- Rafail Andreou and
- Spyros Gkelis
- + 16 authors
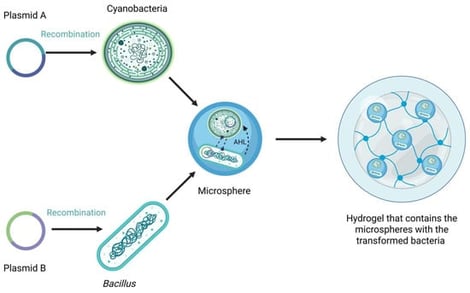
Wildfires are increasingly frequent and intense due to climate change, resulting in degraded soils with diminished microbial activity, reduced water retention, and low nutrient availability. In many regions, previously restored areas face repeated burning events, which further exhaust soil fertility and limit the potential for natural regeneration. Traditional reforestation approaches such as seed scattering or planting seedlings often fail in these conditions due to extreme aridity, erosion, and lack of biological support. To address this multifaceted problem, this study proposes a living, biodegradable hydrogel that integrates an engineered soil-beneficial microorganism consortium, designed to deliver beneficial compounds and nutrients combined with endemic plant seeds into a single biopolymeric matrix. Acting simultaneously as a biofertilizer, soil conditioner, and reforestation aid, this 3-in-1 system provides a microenvironment that retains moisture, supports microbial diversity restoration, and facilitates plant germination even in nutrient-poor, arid soils. The concept is rooted in circular economy principles, utilizing polysaccharides from food industry by-products for biopolymer formation, thereby ensuring environmental compatibility and minimizing waste. The encapsulated microorganisms, a Bacillus subtilis strain and a Nostoc oryzae strain, are intended to enrich the soil with useful compounds. They are engineered based on synthetic biology principles to incorporate specific genetic modules. The B. subtilis strain is engineered to break down large polyphenolic compounds through laccase overexpression, thus increasing soil bioavailable organic matter. The cyanobacterium strain is modified to enhance its nitrogen-fixing capacity, supplying fixed nitrogen directly to the soil. After fulfilling its function, the matrix naturally decomposes, returning organic matter, while the incorporation of a quorum sensing-based kill-switch system is designed to prevent the environmental escape of the engineered microorganisms. This sustainable approach aims to transform post-wildfire landscapes into self-recovering ecosystems, offering a scalable and eco-friendly alternative to conventional restoration methods while advancing the integration of synthetic biology and environmental engineering for climate resilience.
26 January 2026