Abstract
First of all, we show that any spherically symmetric galactic model with integrated mass profile as is physically correct close to the centre only provided that the circular velocity and the gravitational field as . Next, we apply this statement to a broad class of five-parameter spherical galactic models, including most of those used in astrophysics and cosmology. Specifically, we show that the Jaffe and Hernquist models can be trusted only for ( being the effective radius), while the Navarro–Frank–White (NFW) model cannot describe galaxies in the central region of regular clusters. We also briefly discuss the relevance of our result for the NFW profile of pure dark matter halos. However, we are unable to tell at which central distance the NFW model breaks down in either case, and this is a challenge for future investigations.
1. Introduction
Spherical analytic models are still ubiquitous in astrophysics and cosmology, ranging from globular clusters to galaxies, and from regular galaxy clusters to dark matter halos. Examples are many. While the Plummer sphere model [1] provides a good description of stars in globular clusters, the Jaffe [2] and Hernquist [3] models are routinely used to represent the stellar distribution in spheroidal elliptical galaxies and bulges. Further, the pseudo-isothermal profile (see, e.g., [4]) correctly describes the intermediate part of dark matter halos of spiral galaxies, while the Navarro–Frank–White (NFW) model [5] represents the galaxy distribution in regular clusters and provides a good analytic fit to the N-body simulations of pure dark matter halos within the standard CDM context.
The aim of the present paper is twofold. (1) We consider a generic spherically symmetric galactic model of radius r whose integrated mass profile —defined by Equation (1) below—is such that as . And we stress that—because of a statement that we are going to prove—the considered model is physically correct near the centre only provided that two conditions are satisfied: the circular velocity as and the gravitational field as (they are defined by Equations (5) and (6), respectively, below). (2) We apply such a statement to a broad class of five-parameter spherical galactic models, which includes most of those used in astrophysics and cosmology, in particular the three-parameter family of Dehnen profiles [6,7,8], the Jaffe, the Hernquist, and the pseudo-isothermal spherical models, as well as the NFW, the Plummer sphere, the modified Hubble [9], and the perfect sphere [10] profiles (observe that the models described in [6,8] coincide up to a simple rescaling of the radius).
Surprisingly, we have been unable to find our statement in books or papers. As a consequence, we have decided to publish it since it leads to new and important results, which are mentioned below.
The paper is organised as follows. In Section 2, we formulate and prove the statement in question, which has general validity, while in Section 3, we describe our broad class of five-parameter spherical galactic models. Section 4 is devoted to the application of the considered statement to a few galactic models from a purely mathematical point of view. We discover that for some of them, e.g., the Jaffe, Herquist, and NFW profiles, as the central distance decreases, the gravitational field monotonically decreases, becoming either nonvanishing in the centre (Hernquist, NFW) or infinite there (Jaffe). In Section 5, we analyze the Jaffe and Hernquist mass models for real spheroidal elliptical galaxies and bulges. We find that, when the Jaffe and Hernquist models are used to describe the stellar population of spheroidal elliptical galaxies and bulges, the presence of the central supermassive black hole (SMBH) avoids the above pathological behaviour in the neighbourhood of the centre. But we show that nonetheless both models can be trusted only for ( being the effective radius). In Section 6, we discuss the NFW model, in connection both with the distribution of galaxies in regular clusters and with pure dark matter halos. In either case, the NFW model loses its validity towards the centre, thereby failing to predict a central cusp. Finally, in Section 6, we draw our conclusions.
2. Formulation of the Statement
Before committing ourselves to any specific model described by a spherically symmetric density profile , we stress and prove a statement which ensures that any spherically symmetric galactic model makes sense close to the centre O.
STATEMENT:
Suppose that an arbitrary spherically symmetric galactic model defined by the density profile has integrated mass profile
such that
Then, in order for the considered mass model to be physically correct near the centre, the following two conditions should be met:
where denotes the modulus of the circular velocity
while is minus the modulus of the gravitational field
respectively (for these definitions see, e.g., [9]), and G is the Newton constant. Although our statement should belong to the scientific background of any astrophysics or cosmologists, for the reader’s convenience we prove it. The circular velocity is a vector always tangent to a circle of radius r centred in O (which should not be confused with the rotation velocity). When r shrinks to 0, such a tangent direction becomes meaningless, and so must vanish by symmetry. Let us next address the gravitational field , whose direction is radially oriented with respect to O, supposing further that a test particle of mass m is present in O. What is the force acting on ? In order to settle this issue, we start by focusing our attention on an infinitesimal volume at distance r from O, which pulls with a force equal to . But for any , there is an equal volume at the same distance r from O but in the opposite direction with respect to O of the same size and mass—owing to the spherical mass distribution—which pulls with the same force as before but in the opposite direction. As a result, the total force arising from both and acting on vanishes. And since the same reasoning can be used for any pair of infinitesimal volumes on opposite sides of O because of spherical symmetry, we end up with the conclusion that no net force acts on . Hence, the central gravitational field must vanish. So, our statement is proved. Therefore, whenever condition (2) is met but one of the conditions (3) or (4) is not, then the considered mass model loses its physical meaning in the neighbourhood of the centre.
3. A Five-Dimensional Class of Spherically Symmetric Galactic Models
In order to be definite, we focus our attention on galactic models which are defined by the following mass density
where , a are arbitrary positive constants, and , , are arbitrary parameters. Models of this sort are mentioned but not thoroughly discussed by Mo, van den Bosch, and White [11] (see also [9]).
We shall see that for some of them, behaves as for , but this fact does not bother us, since realistic astronomical systems are spatially bounded with radius , and hence the considered mass models should be cut at . Of course, such a truncation can affect other properties of the models, like, for instance, isothermality in the case of the regular isothermal sphere [9]. In addition, we shall encounter models which exhibit a central density profile which is called a central core, whereas other models display a h, namely they have as . A priori, nobody worries about a central cusp, since an infinite central density is not against any physical principle; indeed, the density is merely a derived quantity which cannot be directly measured, and what matters are the integrated mass profile, the circular velocity, and the gravitational field. Only and are directly measurable quantities.
Actually, the main point behind the present analysis is that—given a certain density profile —it cannot absolutely be taken for granted that the observable quantities and possess a physically sensible behaviour towards the centre. Surprisingly, even though several properties of some models included in the considered family have been carefully analyzed, close to the centre, so far insufficient attention has been paid to the circular velocity and no attention whatsoever to the gravitational field (with the exception of the regular isothermal sphere [9]).
We should mention that after this paper was nearly finished, we became aware of the exhaustive analysis of the same class of models described by Equation (7) carried out in 1996 by Zhao [12]. Nevertheless, the overlap between the two papers is nearly vanishing, since Zhao also does not consider the central behaviour of the gravitational field . As far as notations are concerned, the reader can recover Zhao’s counterpart of our Equation (7) by the replacements , , and .
4. Mathematical Discussion
Starting from Equation (7), the integrated mass profile reads
whose explicit form is
where is the confluent hypergeometric function of the second kind. Correspondingly, the circular velocity and the gravitational field are defined by Equations (5) and (6), respectively. So, all we need to know is .
Specifically, our task is to explicitly investigate the behaviour of , and as for the above-mentioned models, even though our strategy can straightforwardly be extended to any spherically symmetric galactic model and in particular to Equation (7) with arbitrary values of , , and .
In view of the forthcoming analysis, it is therefore instrumental to evaluate , , and as for , , and in specific ranges. We start with the case , , and . Correspondingly, we find
while
and
for any value of in the above range. Next, we address the case , , and . Accordingly, we obtain
regardless of the values of in the specified range. As a consequence, in the present case, conditions (2)–(4) happen to be automatically satisfied.
Finally, we proceed to apply these results to the previously considered models. Schematically, our results are as follows.
- 1.
- 2.
- Dehnen models—They correspond to , , . The integrated mass profile is
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- Pseudo-isothermal sphere—It corresponds to , , . The integrated mass profile is
- 6.
- Modified Hubble profile—It corresponds to , , . The integrated mass profile is
- 7.
- Perfect sphere model—It corresponds to , , . The integrated mass profile is
- 8.
- Plummer sphere model—It corresponds to , , . The integrated mass profile is
We can obtain some of the previous results—in the particular case of the models described by Equation (7)—by enforcing condition (4) with the help of Equations (1) and (6). Whence,
Observe that the left-hand side of Equation (21) is an indeterminate form . So, by employing the de L’Hôpital’s rule, we find
Inserting next the expression of from Equation (7), we obtain the condition
which is met for . As discussed above, for , as , and for we find as . Note that if with , condition (4) is satisfied, since as but diverges as .
5. Real Spheroidal Ellipticals and Bulges
The analysis carried out so far is formal in nature, since it merely refers to specific abstract models. For instance, models describing the stellar distribution inside spheroidal elliptical galaxies and bulges are invalid close to the centre because of the presence of an SMBH (for a review, see [13]). Nevertheless, our previous results are important because they are alarm bells that some models can be pathological also beyond the SMBH. Below, we will carefully analyze the behaviour of such models in their realistic context.
Some relationships exist in the literature between the SMBH mass and the properties of the host galaxies. One of them has been obtained by Magorrian et al. [14]:
with denoting the ‘hot’ stellar component of the host galaxy. Incidentally, from Equation (24), it follows that the value of for ellipticals is much larger than that for spirals. Another tight relation links to the central one-dimensional velocity dispersion of the host bulge
where the values of the two parameters A and depend on the considered sample. Out of several studies, we select three of them. We stress that the most critical point is the actual definition of and a careful discussion thereof can be found in [15].
- Gebhardt et al. (2000) find and [16]. These authors choose the definition of within the slit aperture of length , where is the bulge effective radius.
- Merritt and Ferrarese (2001) obtain and [17]. They use the standard definition to evaluate inside .
- Tremaine et al. (2002) obtain and [15]. They estimate with a variety of techniques.
The Dehnen models—and in particular the Jaffe and Hernquist models—have routinely been used to represent the stellar distribution within spheroidal elliptical galaxies and bulges (just to quote a few papers out of so many, see Refs. [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]).
Let us therefore discuss the effect of the central SMBH on a generic Dehnen model. Here, the relevant quantity is the dynamical radius , where the gravitational fields of the SMBH and of the host galaxy are equal [9]. We neglect the dark matter, because the central region of ellipticals and bulges is believed to be baryon-dominated. It is then trivial to find that is given by
but since the term inside the square brackets is obviously much larger than 1—by defining —Equation (26) boils down to the following approximate expression:
Thus, we conclude that the Dehnen models can make sense for a galactocentric distance larger than as provided by Equations (26) or (27) (more about this later).
As a next step, we focus our attention on the Jaffe and Hernquist models. Since for the Jaffe model [2] and for the Hernquist model [3], by specializing Equation (27) to these cases, we obtain
and
for the Jaffe and Hernquist models, respectively. So, only for galactocentric distances larger than either or can the Jaffe or the Hernquist model be regarded as a realistic description of the stellar population of spheroidal ellipticals and bulges.
Incidentally, a slightly different discussion of the Hernquist model is contained in [9] (see Figure 4.20), where—denoting by the luminous mass of the galaxy—for and , it is found that and , respectively.
Henceforth, we prefer to work with the dimensionless quantities defined as follows:
- (1)
- Radial distance: .
- (2)
- Mass density: .
- (3)
- Integrated mass profile: .
- (4)
- Square circular velocity: .
- (5)
- Gravitational field: .
We will replace by for the NFW model.
We are now in a position to assess the validity of the Jaffe and Hernquist models. Because we are interested in investigating in great detail what happens around the centre, we plot , , and versus in logarithmic scales in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively.
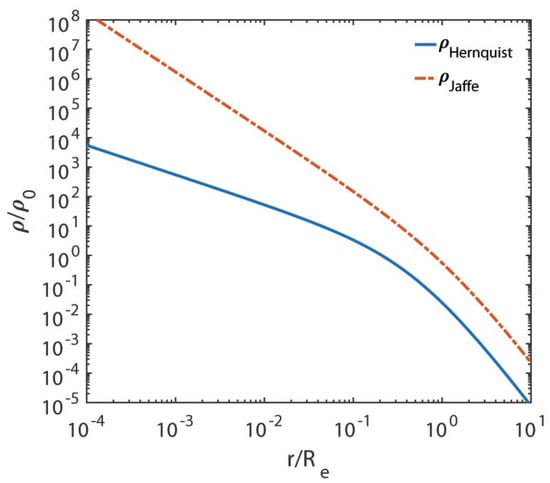
Figure 1.
We report on the vertical axis and on the horizontal axis, both in logarithmic scale.
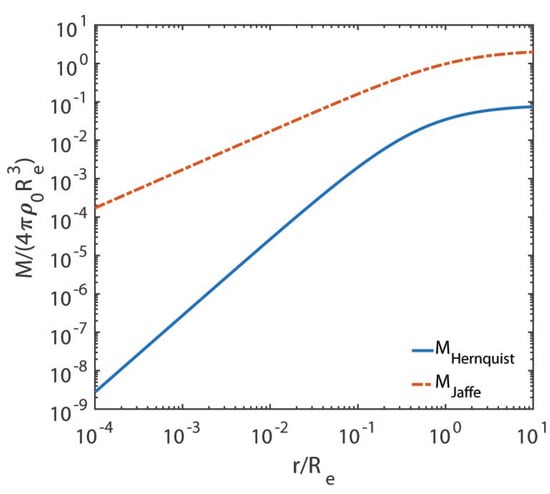
Figure 2.
We show on the vertical axis and on the horizontal axis, both in logarithmic scale.
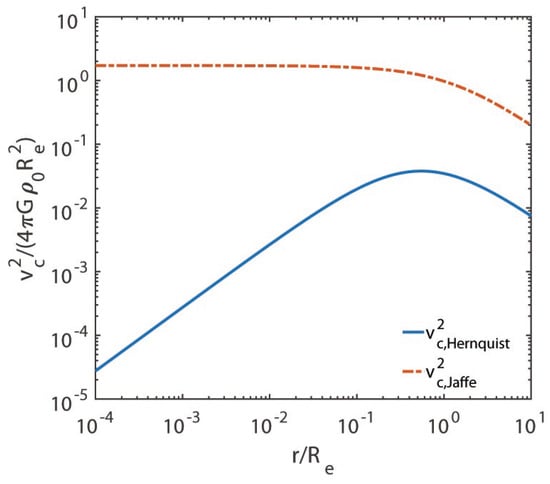
Figure 3.
We exhibit on the vertical axis and on the horizontal axis, both in logarithmic scale.
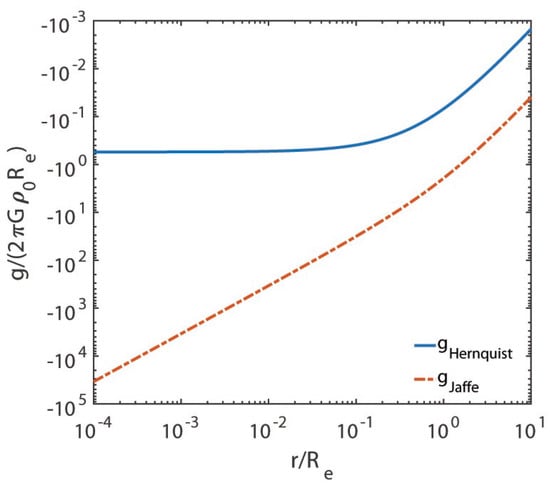
Figure 4.
We report on the vertical axis and on the horizontal axis, both in logarithmic scale.
The departure from similarity of the two models takes place around , where it starts to become larger and larger as the galactocentric distance becomes smaller and smaller. Moreover, the circular velocity curve for the Hernquist model is physically very well-behaved, while for the Jaffe model, it is not. In addition, the gravitational field does not show any turn towards 0 for either model (this is not evident for the Jaffe model from Figure 4 due to its small size, but we have seen in Section 4 that ).
Fortunately, we can make sense out of such behaviour by recalling that historically both models have been devised in order to reproduce the De Vaucouleurs surface brightness profile upon projection, assuming a constant mass-to-light ratio. Accordingly, their shape should nearly coincide at, say, , as indeed takes place in the considered figures. We are thus led to guess that both models fail to fit the De Vaucouleurs law in projection for . A check of our guess can be obtained by projecting these models onto the sky. The results are shown in Figure 5.
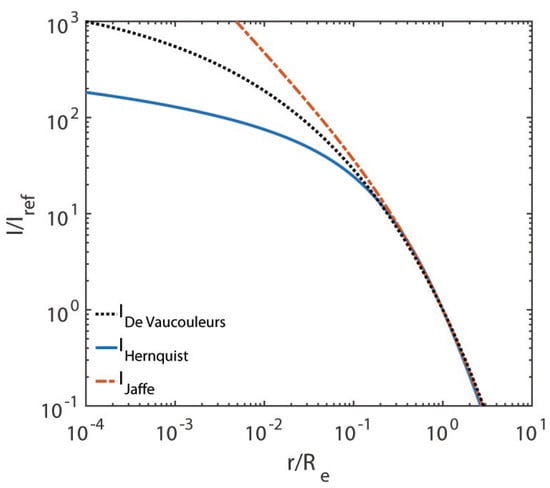
Figure 5.
We show the projected Jaffe and Hernquist models as well as the De Vaucouleurs law versus , both in logarithmic scale. In all cases, is the dimensionless surface brightness.
We see that Figure 5 beautifully shows that indeed both the Jaffe and Hernquist models can be trusted only for , if we want to stick to a constant luminous mass-to-light ratio for (our conversion from surface mass density to surface brightness has been performed by assuming ). Taking these models seriously in the range , an unphysical gradient in would necessarily show up, which could be confused with a colour/metallicity gradient or a gradient of the total mass-to-light ratio , which might in turn be erroneously interpreted as evidence for dark matter.
6. NFW Model
Let us come back to the NFW profile, whose explicit form is
which we plot versus in Figure 6. Moreover, we obtain the dimensionless square circular velocity and the dimensionless gravitational field by employing Equations (5) and (6), respectively. Note that in Equations (5), (6) and (16) we have made the replacement .
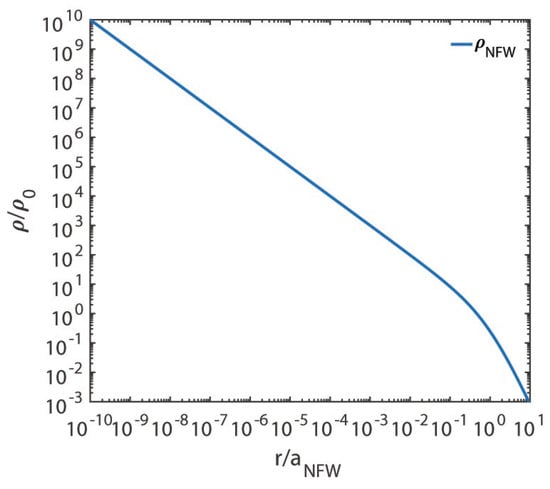
Figure 6.
We exhibit on the vertical axis and on the horizontal axis, both in logarithmic scale.
These quantities are plotted versus in Figure 7 and Figure 8. While the behaviour of shown in Figure 7 looks physical and in agreement with our statement, the behaviour of exhibited in Figure 8 implies that this is not the case. Hence, the NFW model fails close enough to the centre. We stress that the situation is presently worse as compared to the one discussed in Section 5, since we have no handle to tell at which distance from the centre the NFW model breaks down.
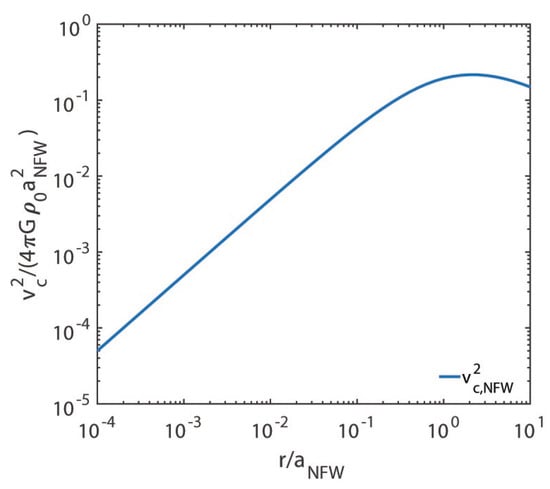
Figure 7.
We report on the vertical axis and on the horizontal axis, both in logarithmic scale.
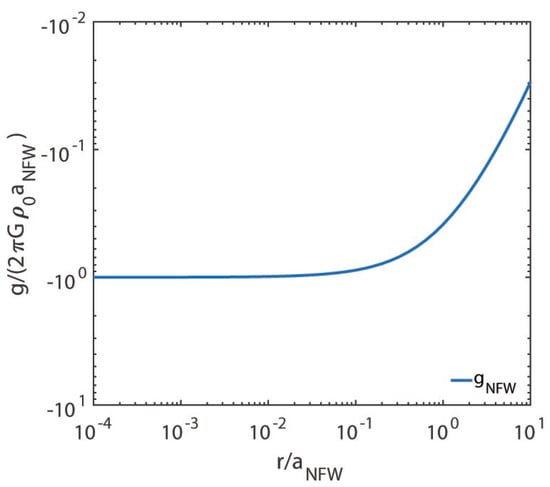
Figure 8.
We show on the vertical axis and on the horizontal axis, both in logarithmic scale.
6.1. NFW Model and Regular Galaxy Clusters
Nowadays, the overall distribution of galaxies in regular clusters is believed to be well-described by an NFW model with , where denotes the virial radius and the galaxy concentration ranges from [33] to [34]. Unfortunately, the galaxy distribution in the central region is more uncertain. According to Adami et al., the luminosity profile of the brightest galaxies is significantly cusped in the centre of the clusters (regardless of the redshift), whereas the luminosity profile of the fainter galaxies is significantly better fitted by a cored model [35]. But Lin et al. claim that all galaxies are distributed according to a model (7) with , , , and , which is almost indistinguishable from an NFW profile [36]. However, according to our result, the galaxy distribution cannot be represented by an NFW profile all the way down to the centre.
6.2. NFW Model and Dark Matter Halos
It has been well-known since 1997 that the NFW profile provides the classic analytic fit to the N-body simulations of pure collisionless cold dark matter particles [5]. Within this context, we have , where is the radius where the overdensity is 200 times larger than the mean cosmic density—currently considered as the virial radius—while is the halo concentration parameter, which depends on both the halo mass and its redshift [11]. But for the present analysis, we do not need to commit ourselves to any specific value. So, its validity rests upon simulations, and even the most recent simulations are unable to probe the central region inside about from the centre. Therefore, it is presently totally unclear whether our result applies in this context. Only future N-body simulations of pure dark matter halos with resolution much better than about will show whether the NFW persists very close to the centre. If it turns out to be the case, our result would apply.
We stress that these considerations make sense only in the absence of baryons. Unfortunately, over the years, several astrophysicists and cosmologists have blindly applied the NFW model to real galaxies, finding no cusp where they expected to discover it, namely in bulgeless galaxies, like galaxies with low surface brightness and dwarf galaxies (see, e.g., [37,38] and references therein). Actually, since 1986 [39], it has been known that baryons strongly affect the dark matter halo—which can either collapse or expand—thereby invalidating the NFW profile (see, e.g., [40,41], and for a review, see [42]).
7. Conclusions
We have first stressed and proved the general statement according to which any spherically symmetric galactic model whose integrated mass profile as is physically correct in the neighbourhood of the centre, only provided that the circular velocity as , and the gravitational field as . We have next applied the considered statement to models from a class of five-parameter self-gravitating spherical galactic models, which are most frequently used in astrophysics and cosmology, like the Hernquist, Jaffe, and NFW models.
As is well-known, the stellar population of spheroidal elliptical galaxies and of bulges are often described by either the Jaffe model or the Hernquist model. We have shown that in both cases—even taking the central SMBH into account—they can be trusted only for galactocentric distances larger than about 0.2 effective radii.
We have next addressed the distribution of galaxies in regular clusters, which is believed to be well-represented by an NFW model, with suitable values of the parameters. We have demonstrated that such a description must break down towards the centre, thereby avoiding the central cusp, which is instead predicted by the NFW model. Unfortunately, we have no idea where such a failure starts to takes place. This is a challenge for future improved photometric studies which can determine the stellar profile in the innermost region, thereby resolving the issue.
Finally, we have considered the NFW model in connection with pure dark matter halos. In this case, if future N-body simulations with resolution much better than about show that the NFW persists very close to the centre of pure dark matter halos, then our result would apply. As stated above, the baryonic infall drastically changes the nature of the halo—making it either contracting or expanding—so that the NFW profile becomes obsolete for real galaxies. We remark that such behaviour has started to be systematically investigated by employing models of the form (7) for suitable values of the parameters not considered here (see, e.g., [43,44]). We plan to extend the present analysis to this very interesting case in a future publication.
Author Contributions
M.R. and G.G. have equally contributed, read, and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. Data curation, writing, visualization: all sections have been written by both authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
M.R. acknowledges the financial support by an INFN grant. The work of G.G. is supported by a contribution from the grant ASI-INAF 2015-023-R.1.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data used in this paper can be requested from the authors of the quoted papers.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Magda Arnaboldi, Patrizia Caraveo, Luca Ciotti, Ortwin Gerhard, and Andrea Macciò for useful discussion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Plummer, H.C. On the Problem of Distribution in Globular Star Clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1911, 71, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, W.A. Simple model for the distribution of light in spherical galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1983, 202, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernquist, L. An Analytical Model for Spherical Galaxies and Bulges. Astrophys. J. 1990, 356, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, S.M. Dark matter in spiral galaxies. I. Galaxies with optical rotation curves. Astron. J. 1986, 91, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.F.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M. A Universal Density Profile from Hierarchical Clustering. Astrophys. J. 1997, 490, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnen, W. A Family of Potential-Density Pairs for Spherical Galaxies and Bulges. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1993, 265, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnen, W.; Gerhard, O.E. Two-integral models for oblate elliptical galaxies with cusps. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1994, 268, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaine, S.; Richstone, D.O.; Byun, Y.-I.; Dressler, A.; Faber, S.M.; Grillmair, C.; Kormendy, J.; Lauer, T.R. A family of models for spherical stellar systems. Astron. J. 1994, 107, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binney, J.; Tremaine, S. Galactic Dynamics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- de Zeeuw, P.T. Elliptical galaxies with separable potentials. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1985, 216, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.; van den Bosch, F.; White, S. Galaxy Formation and Evolution; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.S. Analytical models for galactic nuclei. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1996, 278, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormendy, J.; Richstone, D. Inward Bound—The Search For Supermassive Black Holes In Galactic Nuclei. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1995, 33, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magorrian, J.; Tremaine, S.; Richstone, D.; Bender, R.; Bower, G.; Dressler, A.; Faber, S.M.; Gebhardt, K.; Green, R.; Grillmair, C.; et al. The Demography of Massive Dark Objects in Galaxy Centers. Astron. J. 1998, 115, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaine, S.; Gebhardt, K.; Bender, R.; Bower, G.; Dressler, A.; Faber, S.M.; Filippenko, A.V.; Green, R.; Grillmair, C.; Ho, L.C.; et al. The Slope of the Black Hole Mass versus Velocity Dispersion Correlation. Astrophys. J. 2002, 574, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, K.; Bender, R.; Bower, G.; Dressler, A.; Faber, S.M.; Filippenko, A.V.; Green, R.; Grillmair, C.; Ho, L.C. A Relationship between Nuclear Black Hole Mass and Galaxy Velocity Dispersion. Astrophys. J. 2000, 539, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, D.; Ferrarese, L. The M•-σ Relation for Supermassive Black Holes. Astrophys. J. 2001, 547, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rix, H.-W.; de Zeeuw, P.T.; Cretton, N.; van der Marel, R.P.; Carollo, C.M. Dynamical Modeling of Velocity Profiles: The Dark Halo around the Elliptical Galaxy NGC 2434. Astrophys. J. 1997, 488, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, X.; Gilmore, G. Inferring Dark Halo Structure from Observed Scaling Law of Late-Type Galaxies and LSBs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 294, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cappellari, M.; Bacon, R.; Bureau, M.; Damen, M.C.; Davies, R.L.; De Zeeuw, P.T.; Emsellem, E.; Falcón-Barroso, J.; Krajnovic, D.; Kuntschner, H.; et al. The SAURON project - IV. The mass-to-light ratio, the virial mass estimator and the Fundamental Plane of elliptical and lenticular galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 366, 1126. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Kochanek, C.S. The Baryon Fractions and Mass-to-Light Ratios of Early-Type Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2007, 671, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciotti, L.; Morganti, L. Two-Component Galaxy Models: The Effect of Density Profile at Large Radii on the Phase-Space Consistency. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 303, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Samurovic, S. Dynamical Constant Mass-to-Light Ratio Models of NGC 5128. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 514, A95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ragone-Figueroa, C.; Granato, G.L. Puffing up Early-Type Galaxies by Baryonic Mass Loss: Numerical Experiments. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 414, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortora, C.; Napolitano, N.R.; Romanowsky, A.J.; Jetzer, P. Central Dark Matter Trend in Early-Type Galaxies. Mem. Della Soc. Astron. Ital. Suppl. 2012, 9, 302. [Google Scholar]
- Tortora, C.; Napolitano, N.R.; Romanowsky, A.J.; Jetzer, P. Stellar Mass-to-Light Ratio Gradients in Galaxies: Correlations with Mass. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 418, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lingam, M.; Nguyen, P.H. The Double-Power Approach to Spherically Symmetric Astrophysical Systems. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 440, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eadie, G.M.; Eadie, G.M.; Harris, W.E.; Widrow, L.M. Estimating the Galactic Mass Profile in the Presence of Incomplete Data. Astrophys. J. 2015, 806, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrova, I.; Lokas, E.L. Galaxies with Prolate Rotation in Illustris. Astrophys. J. 2017, 850, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoldan, A.; Lucia, G.D.; Xie, L.; Fontanot, F.; Hirschmann, M. Structural and Dynamical Properties of Galaxies in a Hierarchical Universe: Sizes and Specific Angular Momenta. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 481, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Nicola, S.; Saglia, R.P.; Thomas, J.; Dehnen, W.; Bender, R. Non-parametric Triaxial Deprojection of Elliptical Galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravita, C.; Ciotti, L.; Pellegrini, S. Jeans Modeling of Axisymmetric Galaxies with Multiple Stellar Populations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 506, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, R.G.; Yee, H.K.C.; Ellingson, E.; Morris, S.L.; Abraham, R.; Gravel, P.; Pritchet, C.J.; Smecker-Hane, T.; Hartwick, F.D.A.; Hesser, J.E.; et al. The Average Mass Profile of Galaxy Clusters. Astrophys. J. 1997, 485, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Marel, R.P.; Magorrian, J.; Carlberg, R.G.; Yee, H.K.C.; Ellingson, E. The Velocity and Mass Distribution of Clusters of Galaxies from the CNOC1 Cluster Redshift Survey. Astron. J. 2000, 119, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, C.; Mazure, A.; Ulmer, M.P.; Savine, C. Central matter distributions in rich clusters of galaxies from z∼0 to z∼0.5. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 371, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Mohr, J.J.; Stanford, S.A. K-Band Properties of Galaxy Clusters and Groups: Luminosity Function, Radial Distribution, and Halo Occupation Number. Astrophys. J. 2004, 610, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.J.; Simon, J.D.; Fabricius, M.H.; van den Bosch, R.C.E.; Barentine, J.C.; Bender, R.; Gebhardt, K.; Hill, G.J.; Murphy, J.D.; Swaters, R.A.; et al. Dwarf galaxy dark matter density profiles inferred from stellar and gas kinematics. Astrophys. J. 2014, 789, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-H.; Hunter, D.A.; Brinks, E.; Elmegreen, B.G.; Schruba, A.; Walter, F.; Rupen, M.P.; Young, L.M.; Simpson, C.E.; Johnson, M.C.; et al. High-resolution mass models of dwarf galaxies from little things. Astron J. 2015, 149, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, G.R.; Faber, S.M.; Flores, R.; Primack, J.R. Contraction of Dark Matter Galactic Halos due to Baryonic Infall. Astrophys. J. 1986, 301, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollet, E.; Macció, A.V.; Dutton, A.A.; Stinson, G.S.; Wang, L.; Penzo, C.; Gutcke, T.A.; Buck, T.; Kang, X.; Brook, C.; et al. NIHAO—IV: Core Creation and Destruction in Dark Matter Density Profiles across Cosmic Time. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 456, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macció, A.V.; Crespi, S.; Blank, M.; Kang, X. NIHAO— XXIII. Dark Matter Density Shaped by Black Hole Feedback. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 495, L46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontzen, A.; Governato, F. Cold Dark Matter Heats Up. Nature 2014, 506, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekel, A.; Ishai, G.; Dutton, A.A.; Macciò, A.V. Dark-Matter Halo Profiles of a General Cusp/Core with Analytic Velocity and Potential. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 468, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, J.; Jiang, F.; Dekel, A.; Cornuault, N.; Ginzburg, O.; Koskas, R.; Lapiner, S.; Dutton, A.; Macciò, A.V. The Dekel-Zhao profile: A mass-dependent dark-matter density profile with flexible inner slope and analytic potential, velocity dispersion, and lensing properties. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 499, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).