Quantum Astronomy at the University and INAF Astronomical Observatory of Padova, Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
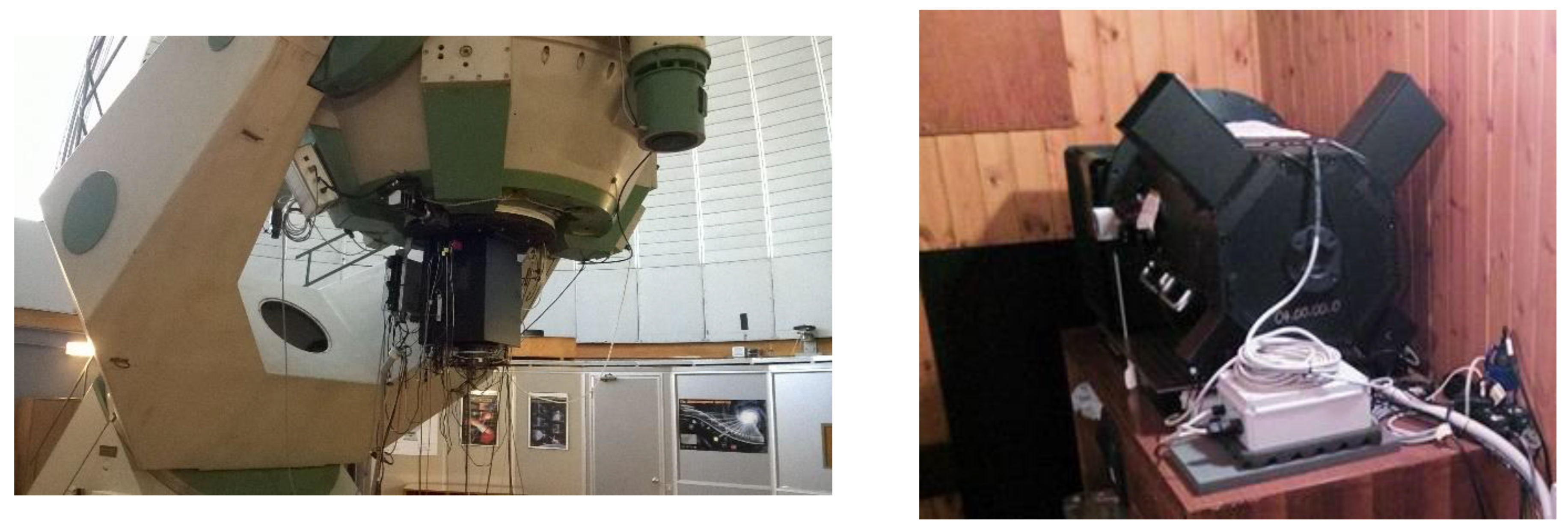
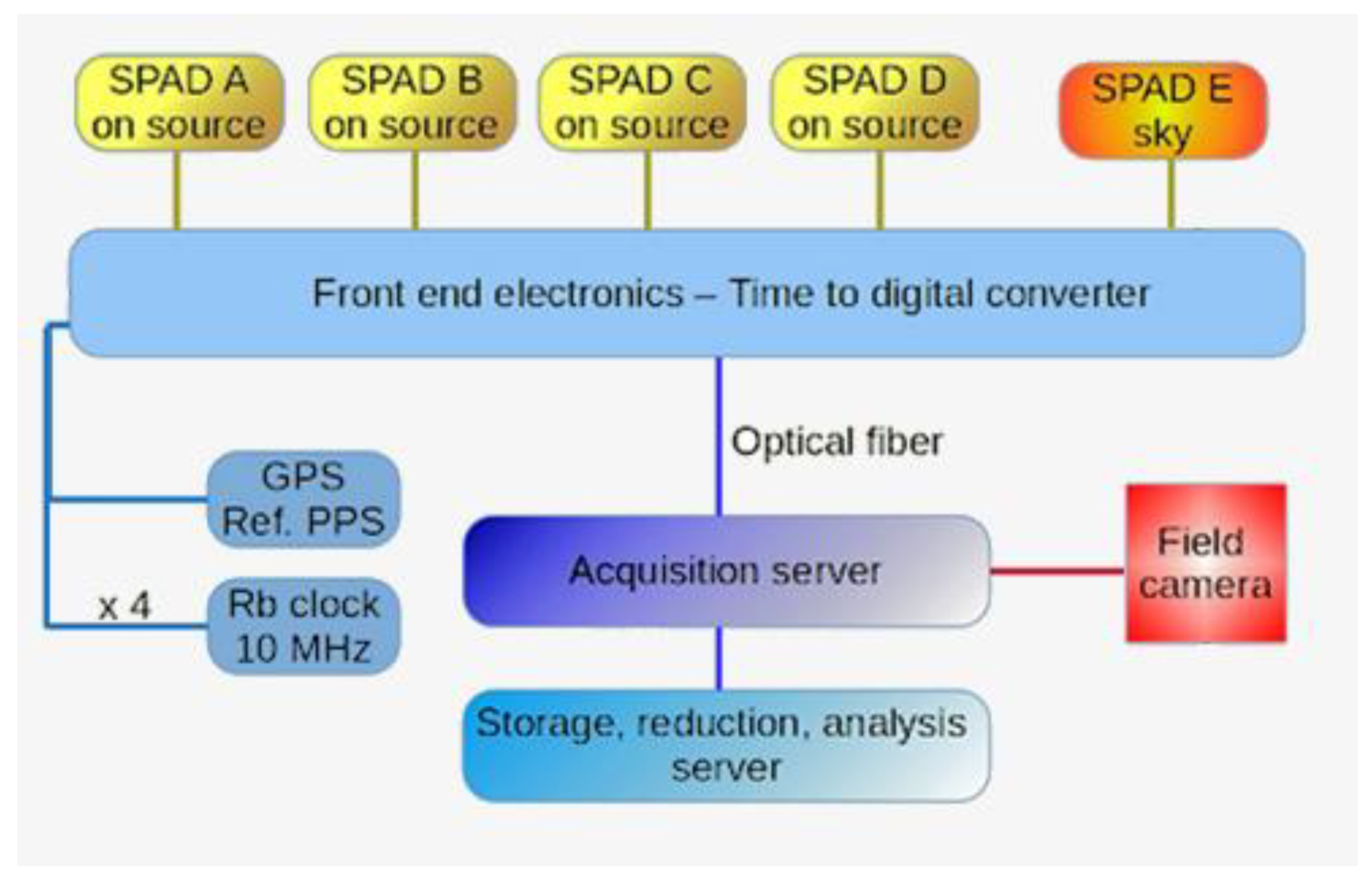
2. From QuantEye to AquEye and IquEye
3. Astrophysical Results
3.1. Optical Pulsar Light Curves
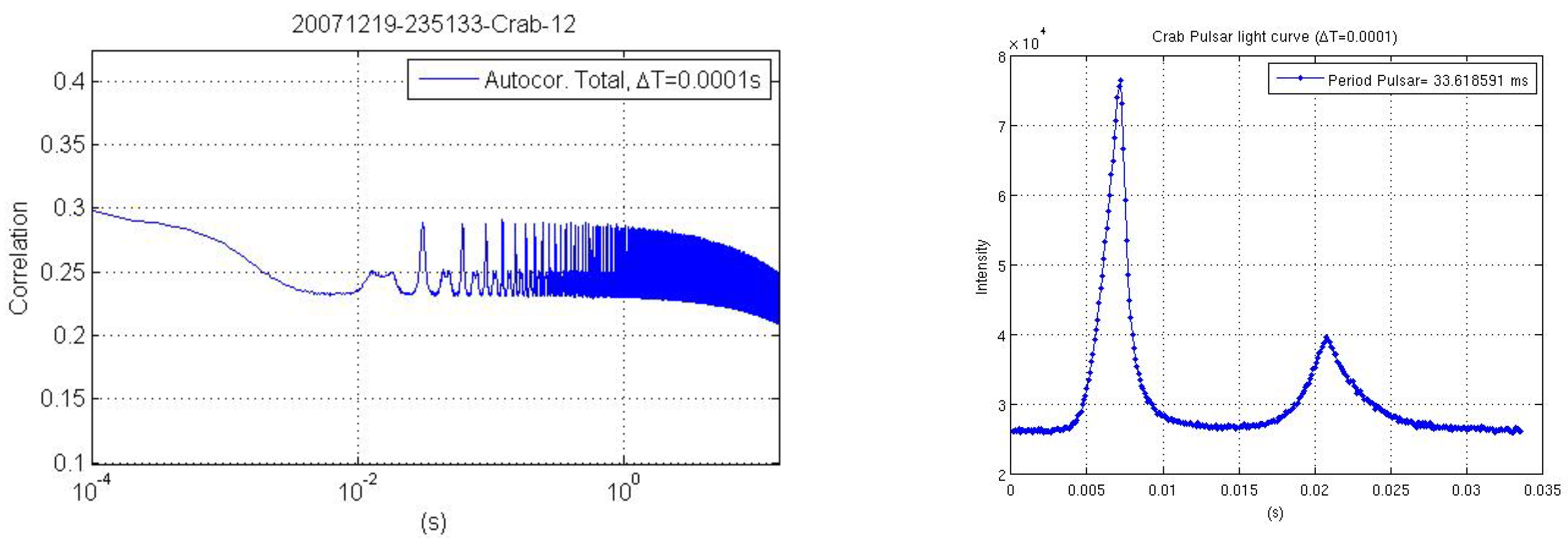
3.1.1. The Crab Nebula Pulsar
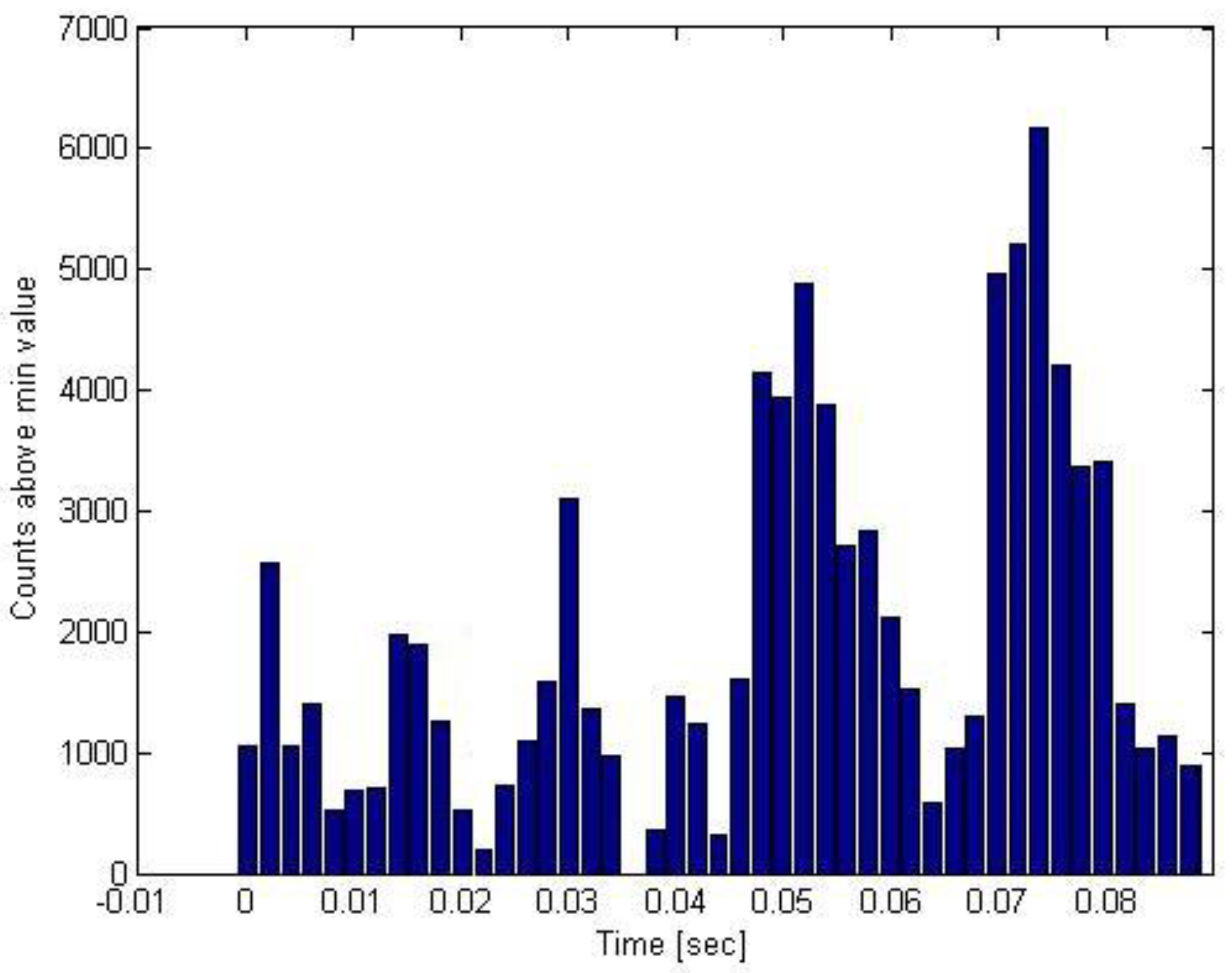
3.1.2. PSR B0540-69
3.1.3. Vela Pulsar
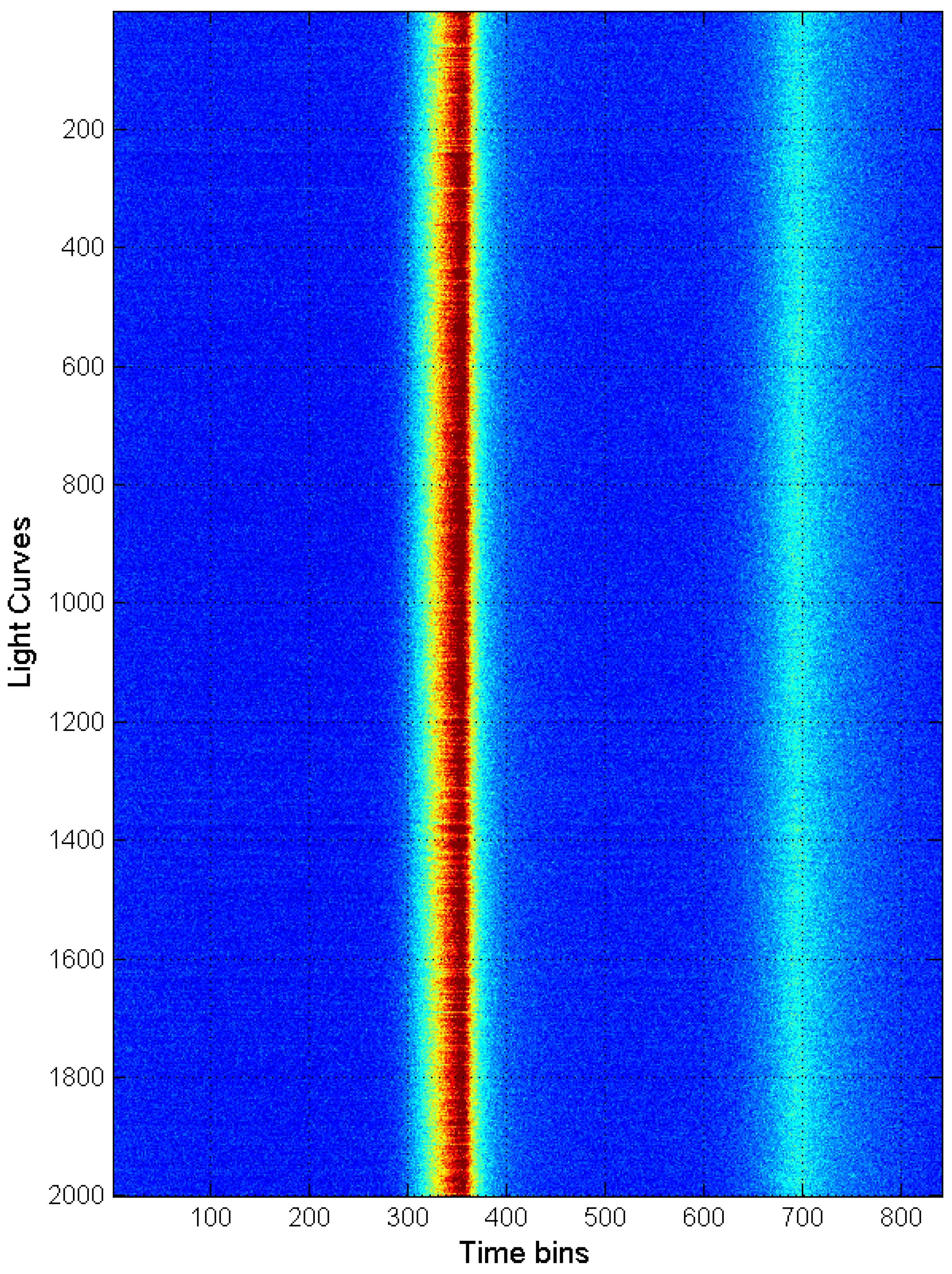
3.1.4. PSR J1023+0038
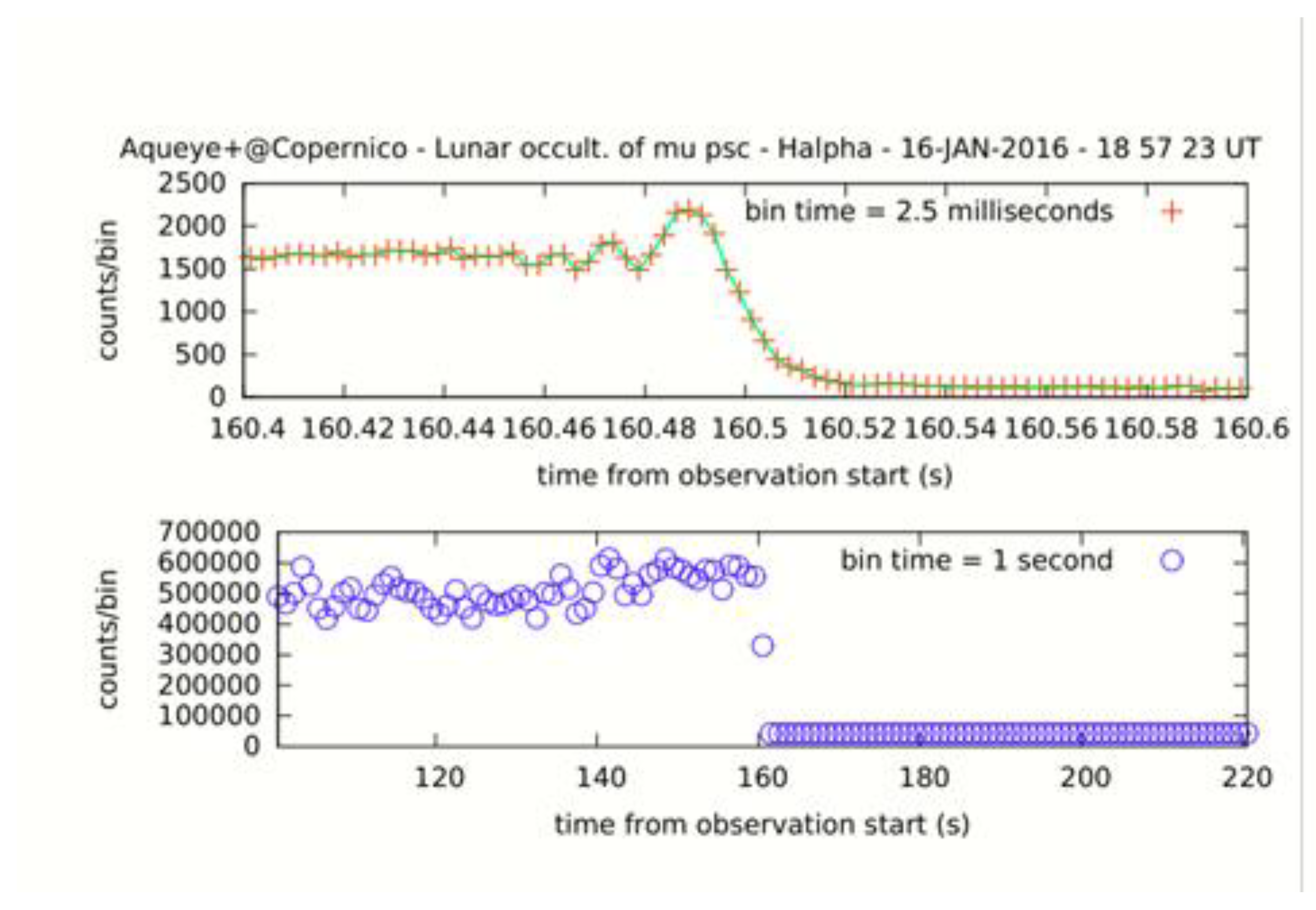
3.2. Lunar Occultations
3.3. Stellar Intensity Interferometry
- Rather relaxed geometric accuracy, meaning that precisions of centimeters are required for making an intensity interferometry measurement, to be compared with the fraction of wavelength (sub-micron in visible light) needed for realizing classical phase interferometers.
- For the same reason, there is no need to have telescope mirrors with high optical quality; the actual, most stringent limitation is to minimize the amount of stray light/background on the sensor.
- Negligible sensitivity to seeing conditions (on timescales as short as fractions of a ns, the atmospheric turbulence is essentially frozen), so that there is no need to use adaptive optics.
- Correlation is performed at the measured signal level, which can be a current or, as in our case, a string of photon time tags; for this, just an accurate time reference is needed, and there is no need for ad-hoc optical links between telescopes to realize interference between the optical light beam, as with phase interferometers.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbieri, C.; Da Deppo, V.; D’Onofrio, M.; Dravins, D.; Fornasier, S.; Fosbury, R.; Naletto, G.; Nilsson, R.; Occhipinti, T.; Tamburini, F.; et al. QuantEYE, the quantum optics instrument for OWL. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2005, 1, 506–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barbieri, C.; Dravins, D.; Occhipinti, T.; Tamburini, F.; Naletto, G.; Da Deppo, V.; Fornasier, S.; D’Onofrio, M.; Fosbury, R.A.E.; Nilsson, R.; et al. Astronomical applications of quantum optics for extremely large telescopes. J. Mod. Opt. 2007, 54, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, C.; Naletto, G.; Tamburini, F.; Occhipinti, T.; Giro, E.; D’Onofrio, M. From QuantEYE to AquEYE—Instrumentation for Astrophysics on Its Shortest Timescales, High Time Resolution Astrophysics. Phelan, D., Ryan, O., Shearer, A., Eds.; Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-1-4020-6517-0. [Google Scholar]
- Occhipinti, T.; Zampieri, L.; Naletto, G.; Barbieri, C. Quantum astronomy: Scientific background, technologies, achieved results, and future developments. SPIE Proc. 2018, 10548, 105481K. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, F.; Anzolin, G.; Umbriaco, G.; Bianchini, A.; Barbieri, C. Overcoming the Rayleigh Criterion Limit with Optical Vortices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 163903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzolin, G.; Tamburini, F.; Bianchini, A.; Umbriaco, G.; Barbieri, C. Optical vortices with starlight. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 488, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, C.; Tamburini, F.; Anzolin, G.; Bianchini, A.; Mari, E.; Sponselli, A.; Umbriaco, G.; Prasciolu, M.; Romanato, F.; Villoresi, P. Light’s Orbital Angular Momentum and Optical Vortices for Astronomical Coronagraphy from Ground and Space Telescopes. Earth Moon Planets 2009, 105, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, Z.; Min, C.; Fu, X.; Liu, Q.; Gong, M.; Yuan, X. Optical vortices 30 years on: OAM manipulation from topological charge to multiple singularities. Light. Sci. Appl. 2019, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanbury, B.R. The Intensity Interferometer: Its Application to Astronomy; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, C.; Naletto, G.; Occhipinti, T.; Facchinetti, C.; Verroi, E.; Giro, E.; Di Paola, A.; Billotta, S.; Zoccarato, P.; Bolli, P.; et al. AquEYE, a single photon counting photometer for astronomy. J. Mod. Opt. 2009, 56, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naletto, G.; Barbieri, C.; Occhipinti, T.; Capraro, I.; Di Paola, A.; Facchinetti, C.; Verroi, E.; Zoccarato, P.; Anzolin, G.; Belluso, M.; et al. Iqueye, a single photon-counting photometer applied to the ESO new technology telescope. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 508, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, L.; Naletto, G.; Barbieri, C.; Verroi, E.; Ceribella, G.; D’Alessandro, M.; Farisato, G.; Di Paola, A.; Zoccarato, P. Aqueye+: A new ultrafast single photon counter for optical high time resolution astrophysics. SPIE Proc. 2015, 9504, 95040C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, L.; Naletto, G.; Barbieri, C.; Burtovoi, A.; Fiori, M.; Spolon, A.; Ochner, P.; Lessio, L.; Umbriaco, G.; Barbieri, M. (Very) Fast astronomical photometry for meter-class telescopes. Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skaln. Pleso 2019, 49, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zampieri, L.; Germanà, C.; Barbieri, C.; Naletto, G.; Čadež, A.; Capraro, I.; Di Paola, A.; Facchinetti, C.; Occhipinti, T.; Ponikvar, D.; et al. The Crab pulsar seen with AquEYE at Asiago Cima Ekar observatory. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Germanà, C.; Zampieri, L.; Barbieri, C.; Naletto, G.; Čadež, A.; Calvani, M.; Barbieri, M.; Capraro, I.; Di Paola, A.; Facchinetti, C.; et al. Aqueye optical observations of the Crab Nebula pulsar. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 548, A47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.; Shearer, A.; Stappers, B.; Barbieri, C.; Naletto, G.; Zampieri, L.; Verroi, E.; Gradari, S. Crab Pulsar: Enhanced Optical Emission During Giant Radio Pulses. New Horiz. Time-Domain Astron. Proc. Int. Astron. Union IAU Symp. 2012, 285, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, L.; Čadež, A.; Barbieri, C.; Naletto, G.; Calvani, M.; Barbieri, M.; Verroi, E.; Zoccarato, P.; Occhipinti, T. Optical phase coherent timing of the Crab nebula pulsar with Iqueye at the ESO New Technology Telescope. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 2813–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Čadež, A.; Zampieri, L.; Barbieri, C.; Calvani, M.; Naletto, G.; Barbieri, M.; Ponikvar, D. What brakes the Crab pulsar? Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 587, A99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, G.B.; Edwards, R.T.; Manchester, R.N. TEMPO2, a new pulsar-timing package—I. An overview. MNRAS 2006, 369, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.T.; Hobbs, G.B.; Manchester, R.N. TEMPO2, a new pulsar timing package—II. The timing model and precision estimates. MNRAS 2006, 372, 1549–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanwal, D. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 1999.
- Golden, A.; Shearer, A.; Redfern, R.M.; Beskin, G.M.; Neizvestny, S.I.; Neustroev, V.V.; Plokhotnichenko, V.L.; Cullum, M. High speed phase-resolved 2-d UBV photometry of the Crab pulsar. A&A 2000, 363, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, R.W.; Miller, A.J.; Cabrera, B.; Nam, S.W.; Martinis, J.M. Phase-resolved Crab Studies with a Cryogenic Transition-Edge Sensor Spectrophotometer. ApJ 2001, 563, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, A.; Stappers, B.; O’Connor, P.; Golden, A.; Strom, R.; Redfern, M.; Ryan, O. Enhanced Optical Emission During Crab Giant Radio Pulses. Science 2003, 301, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosterbroek, T.; de Bruijne, J.H.J.; Martin, D.; Verhoeve, P.; Perryman, M.A.C.; Erd, C.; Schulz, R. Absolute timing of the Crab Pulsar at optical wavelengths with superconducting tunneling junctions. A&A 2006, 456, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oosterbroek, T.; Cognard, I.; Golden, A.; Verhoeve, P.; Martin, D.D.E.; Erd, C.; Schulz, R.; Stüwe, J.A.; Stankov, A.; Ho, T. Simultaneous absolute timing of the Crab pulsar at radio and optical wavelengths. A&A 2008, 488, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słowikowska, A.; Kanbach, G.; Kramer, M.; Stefanescu, A. Optical polarization of the Crab pulsar: Precision measurements and comparison to the radio emission. MNRAS 2009, 397, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceribella, G. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Padova, Padova, Italy, 2015.
- Gradari, S.; Barbieri, M.; Barbieri, C.; Naletto, G.; Verroi, E.; Occhipinti, T.; Zoccarato, P.; Germanà, C.; Zampieri, L.; Possenti, A. The optical light curve of the LMC pulsar B0540-69 in 2009. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 412, 2689–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fermi LAT Collaboration; Ackermann, M.; Albert, A.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Barbieri, C.; Bastieri, D.; Bellazzini, R.; Bissaldi, E.; et al. An extremely bright gamma-ray pulsar in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Science 2015, 350, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignani, R.P.; Shearer, A.; De Luca, A.; Marshall, F.E.; Guillemot, L.; Smith, D.A.; Rudak, B.; Zampieri, L.; Barbieri, C.; Naletto, G.; et al. The First Ultraviolet Detection of the Large Magellanic Cloud Pulsar PSR B0540–69 and Its Multi-wavelength Properties. Astrophys. J. 2019, 871, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolon, A.; Zampieri, L.; Burtovoi, A.; Naletto, G.; Barbieri, C.; Barbieri, M.; Patruno, A.; Verroi, E. Timing analysis and pulse profile of the Vela pulsar in the optical band from Iqueye observations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 482, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, L.; Burtovoi, A.; Fiori, M.; Naletto, G.; Spolon, A.; Barbieri, C.; Papitto, A.; Ambrosino, F. Precise optical timing of PSR J1023+0038, the first millisecond pulsar detected with Aqueye+ in Asiago. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2019, 485, L109–L113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtovoi, A.; Zampieri, L.; Fiori, M.; Naletto, G.; Spolon, A.; Barbieri, C.; Papitto, A.; Ambrosino, F. Spin-down rate of the transitional millisecond pulsar PSR J1023+0038 in the optical band with Aqueye+. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2020, 498, L98–L103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illiano, G.; Papitto, A.; Ambrosino, F.; Zanon, A.M.; Zelati, F.C.; Stella, L.; Zampieri, L.; Burtovoi, A.; Campana, S.; Casella, P.; et al. Investigating the origin of optical and X-ray pulsations of the transitional millisecond pulsar PSR J1023+0038. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 669, A26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassanelli, T.; Naletto, G.; Codogno, G.; Barbieri, C.; Verroi, E.; Zampieri, L. New technique for determining a pulsar period: Waterfall principal component analysis. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 663, A106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommel, F.L.; Braga-Ribas, F.; Desmars, J.; Camargo, J.I.B.; Ortiz, J.L.; Sicardy, B.; Vieira-Martins, R.; Assafin, M.; Santos-Sanz, P.; Duffard, R.; et al. Stellar occultations enable milliarcsecond astrometry for Trans-Neptunian objects and Centaurs. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 644, A40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, L.; Richichi, A.; Naletto, G.; Barbieri, C.; Burtovoi, A.; Fiori, M.; Glindemann, A.; Umbriaco, G.; Ochner, P.; Dyachenko, V.V.; et al. Lunar Occultations with Aqueye+ and Iqueye. Astron. J. 2019, 158, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labeyrie, A.; Lipson, S.G.; Nisenson, P. An Introduction to Optical Stellar Interferometry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dravins, D.; LeBohec, S.; Jensen, H.; Nuñez, P.D. Optical intensity interferometry with the Cherenkov Telescope Array. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 43, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naletto, G.; Zampieri, L.; Barbieri, C.; Barbieri, M.; Verroi, E.; Umbriaco, G.; Favazza, P.; Lessio, L.; Farisato, G. A 3.9 km baseline intensity interferometry photon counting experiment. SPIE Proc. 2016, 9980, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capraro, I.; Barbieri, C.; Naletto, G.; Occhipinti, T.; Verroi, E.; Zoccarato, P.; Gradari, S. Quantum astronomy with Iqueye. SPIE Proc. 2010, 7702, 77020M. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, L.; Naletto, G.; Barbieri, C.; Barbieri, M.; Verroi, E.; Umbriaco, G.; Favazza, P.; Lessio, L.; Farisato, G. Intensity Interferometry with Aqueye+ and Iqueye in Asiago. SPIE Proc. 2016, 9907, 9907–9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, M.; Barbieri, C.; Zampieri, L.; Naletto, G.; Burtovoi, A. Measurement of the second-order g(2) correlation function of visible light from Vega in photon counting mode. SPIE Proc. 2021, 11835, 118350D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, L.; Naletto, G.; Burtovoi, A.; Fiori, M.; Barbieri, C. Stellar intensity interferometry of Vega in photon counting mode. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 506, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuderi, S.; Giuliani, A.; Pareschi, G.; Tosti, G.; Catalano, O.; Amato, E.; Antonelli, L.; Gonzàles, J.B.; Bellassai, G.; Bigongiari, C.; et al. The ASTRI Mini-Array of Cherenkov telescopes at the Observatorio del Teide. J. High Energy Astrophys. 2022, 35, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellone, S.; Bigongiari, C.; Burtovoi, A.; Cardillo, M.; Catalano, O.; Franceschini, A.; Lombardi, S.; Nava, L.; Pintore, F.; Stamerra, A.; et al. ASTRI Mini-Array core science at the Observatorio del Teide. J. High Energy Astrophys. 2022, 35, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, L.; Bonanno, G.; Bruno, P.; Gargano, C.; Lessio, L.; Naletto, G.; Paoletti, L.; Rodeghiero, G.; Romeo, G.; Bulgarelli, A.; et al. A stellar intensity interferometry instrument for the ASTRI Mini-Array telescopes. SPIE Proc. 2022, 12183, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbieri, C.; Naletto, G.; Zampieri, L. Quantum Astronomy at the University and INAF Astronomical Observatory of Padova, Italy. Astronomy 2023, 2, 180-192. https://doi.org/10.3390/astronomy2030013
Barbieri C, Naletto G, Zampieri L. Quantum Astronomy at the University and INAF Astronomical Observatory of Padova, Italy. Astronomy. 2023; 2(3):180-192. https://doi.org/10.3390/astronomy2030013
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbieri, Cesare, Giampiero Naletto, and Luca Zampieri. 2023. "Quantum Astronomy at the University and INAF Astronomical Observatory of Padova, Italy" Astronomy 2, no. 3: 180-192. https://doi.org/10.3390/astronomy2030013
APA StyleBarbieri, C., Naletto, G., & Zampieri, L. (2023). Quantum Astronomy at the University and INAF Astronomical Observatory of Padova, Italy. Astronomy, 2(3), 180-192. https://doi.org/10.3390/astronomy2030013






