Abstract
Lung cancer is one of the deadliest cancers, responsible for more than 1.80 million deaths annually worldwide, and it is on the priority list of the WHO. In the current scenario, when cancer cells become resistant to drugs, making them less effective and leaving the patient in vulnerable conditions. To overcome this situation, researchers are constantly working on new drugs and medications that can help fight drug resistance and improve patients’ outcomes. In this study, we have taken five main proteins of lung cancer, namely RSK4 N-terminal kinase, guanylate kinase, cyclin-dependent kinase 2, kinase CK2 holoenzyme, and tumour necrosis factor-alpha, and screened the prepared Drug Bank library with 155,888 compounds against all using three Glide-based docking algorithms, namely HTVS, standard precision and extra precise, with a docking score ranging from −5.422 to −8.432 Kcal/mol. The poses were filtered with the MM\GBSA calculations, which helped to identify Imidazolidinyl urea C11H16N8O8 (DB14075) as a multitargeted inhibitor for lung cancer, validated with advanced computations such as ADMET and interaction pattern fingerprints. Further, it is proposed to optimise the compound with Jaguar and MD Simulation for at least 100 ns with NPT ensemble class to analyse the deviation and fluctuations and possible interactions for stability and experimental validation on the A549 cell line.
1. Introduction
This study is majorly focused on repurposing a drug that can act against multiple protein targets that have the slightest chance to develop resistance as there are various interacting residues. The possibility is significantly less as all the interacting residues have to go through the mutation, which is not easily possible, giving it less chance to develop resistance [1,2,3,4]. In lung cancer, many proteins participate directly and indirectly, and influencing their role can be a significant asset for multitargeted drug design. In lung and bladder cancer cells, RSK4 N-terminal kinase (PDBID: 6G77) promotes drug resistance and metastasis, and it is one of the essential proteins for the study because inhibiting it in vitro and in vivo in a tail vein injection model made tumour cells more susceptible to treatment and prevented metastasis [5]. The human guanylate kinase, or hGMPK (PDBID: 6NUI), is the only enzyme that produces cellular GDP, which is necessary for cellular viability and proliferation. Additionally, hGMPK has been given a crucial role in the metabolic activation of prodrugs that contain nucleoside analogues that are antiviral and antineoplastic. The production of the nucleotide building blocks of DNA, RNA, and cGMP depends on the hGMPK, and cancer cells have higher GTP levels [6]. The CDK2 gene in humans encodes the cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (PDBID: 1AQ1), also known as cell division protein kinase-2 or Cdk2. This gene produces an SER/THR protein kinase that belongs to the cyclin-dependent kinase family [7]. The casein kinase-2 holoenzyme (PDBID: 1JWH) is a protein serine/threonine kinase typically found in tetrameric complexes of two alpha catalytic subunits and two regulatory beta subunits. It is traditionally categorised as a messenger-independent protein kinase. It phosphorylates many substrates, regulates several signalling pathways, is connected to numerous human disorders in cancer, and controls nearly all malignant markers, which is best understood. Other prominent roles for CK2 in human infections include the usage of host cell CK2 by various viruses for their life cycles [8]. The tumour necrosis factor-alpha (PDBID: 1TNF) is the potent paracrine and endocrine modulator of inflammatory and immunological processes and regulates various types of cell growth and differentiation, and altered cells are destroyed explicitly, especially when combined with interferons [9]. All five of the above-cited kinases and proteins are crucial for developing lung cancer cells, and their continuous proliferation and finding a drug candidate that can potentially target them together can be a great asset.
2. Methods
2.1. Protein Preparation and Ligand Library Collection and Preparation
The proteins were identified through literature reviews and searched for in https://www.rcsb.org/ for 3D protein structures [10]. We identified RSK4 N-terminal kinase (PDBID: 6G77) [5], human guanylate kinase or hGMPK (PDBID: 6NUI) [6], cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (PDBID: 1AQ1) [7], casein kinase-2 holoenzyme (PDBID: 1JWH) [8], and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (PDBID: 1TNF) [9]. All five proteins were downloaded and imported to Schrodinger’s Maestro workspace for preparation optimisation and minimisation. The protein preparation workflow (PPW) was used to prepare the proteins [10,11,12]. First, 6G77 contains a dimer of two chains and two ligands bound to each chain with solvents and two zinc metals; only chain A was kept, and everything else was removed. In 6NUI, only chain A was found and kept the same, while in 1AQ1, chain A was found with solvents and ligands, so we removed the solvent before preparations. Next, 1JWH contains four chains with ligands, solvents and metal zinc and phosphates, and each was removed except chain A and the bound ligand, while in the case of 1TNF, we kept only chain A out of four chains. In the preprocess tab of PPW, we capped the termini of each protein, filled missing side chains, assigned bond orders to the CCD database, replaced hydrogen, and created zero bond orders and disulphide bonds [12]. Termini oxygen was added to protein chains, converted selenomethionines to methionine, filled missing loops with Prime, generated the hetero state with Epik at pH 7 ± 2 and set only one state best to process further [13,14]. In the optimisation of hydrogen bond assignments tab, sample water orientation and used crystal symmetry to obtain the best-fitted state and minimised hydrogen of altered species and used PROPKA for the optimisation. Further, in the minimisation and delete water tab, converge heavy atoms to RMSD 0.30 Å, delete water beyond 5 Å to the ligand, and minimise with the OPLS4 force field [15].
At the same time, the complete Drug Bank library from http://go.drugbank.com/ was downloaded [16,17]. The LigPrep tool was used to prepare the ligand library, where we browsed the complete library and kept the filter size to 500 atoms and beyond that was dropped, and the below 500 atoms ligands were initially minimised with the OPLS4 forcefield [15,18]. The ionisation was kept generating possible states at a target pH of 7 ± 2 while using the Epik and adding the metal binding states, including the original state and desalt, to generate tautomers [13]. The stereoisomer computations were kept retaining specified chiralities and generating 32/ligand in the SDF file that generated 1,55,888 ligand states.
2.2. Glide Grid Generation and Multitargeted Molecular Docking
The receptor Grid Generation tool was used to generate the grids on each protein individually, and for the case of 1AQ1 and 1JWH, the native ligand site was selected, while in the case of proteins with no ligand, such as 6G77, 6NUI, and 1TNF, the complete protein residues were selected under grid for blind docking to find the best docking poses [19]. For the molecular docking, we used the virtual screening workflow (VSW) tool, where we browsed the prepared ligand library as a ligand source, used the combined input files, and redistributed them for sub-jobs [11]. In the filter tab, QikProp and Lipinski’s rules were checked to ensure only ligands satisfying the criteria of drug candidates pass to the following screening level, and then prepared girds were added [20]. In the docking tab, we used the Epik state penalties for the docking and the screening with the High Throughput Virtual Screening (HTVS), Standard Precision (SP) Docking, and Extra Precise (XP) Docking and then the poses were post-processed with the Molecular Mechanics-based Generalised Born Surface Area (MM\GBSA) calculations [11]. The flexible docking strategy was used where only the top 5% of data from HTVS were passed to SP, and 10% of the SP was passed to XP. The minimisation from XP was performed after docking and generated up to 4 poses from each compound state, and then 100% of compounds were passed to the MM\GBSA computations [3,4].
2.3. ADMET and Interaction Fingerprinting Analysis
The compound’s ADMET was computed using the QikProp and Schrodinger’s maestro and produced the number of amidine, acid, amide, rotor, rtvFG, CNS, mol MW, dipole, SASA, FOSA, FISA, PISA, WPSA, donor hydrogen bonds, accepter hydrogen bonds, and % of human oral absorption, with Lipinski’s rule of 5 and 3 [20] and have computed many more ADMET values. Furthermore, molecular interaction patterns or fingerprints are a summary of the interactions between a drug and a set of proteins, and they are often used in drug discovery and development to predict the potential therapeutic effects and side effects of a drug. The interaction fingerprint tool generated the fingerprints among the proteins and identified the compound Imidazolidinyl urea. The receptor–ligand complexes were generated after merging them individually. Then, we selected any contact option and aligned the sequences while keeping 6G77 as a reference sequence to define the N and C terminal of the protein and generate the fingerprints. The complete matrix was then plotted for any contact, ligand display property was selected for the docking score and coloured the main plot to the residue number sequences to identify initial and ending residues. Further, only interacting residues were taken to eliminate the noise and understand it better while taking the count of ligand interactions and count of residue interaction to understand which amino acids are participating more from which protein with the ligand [11].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Interaction Analysis
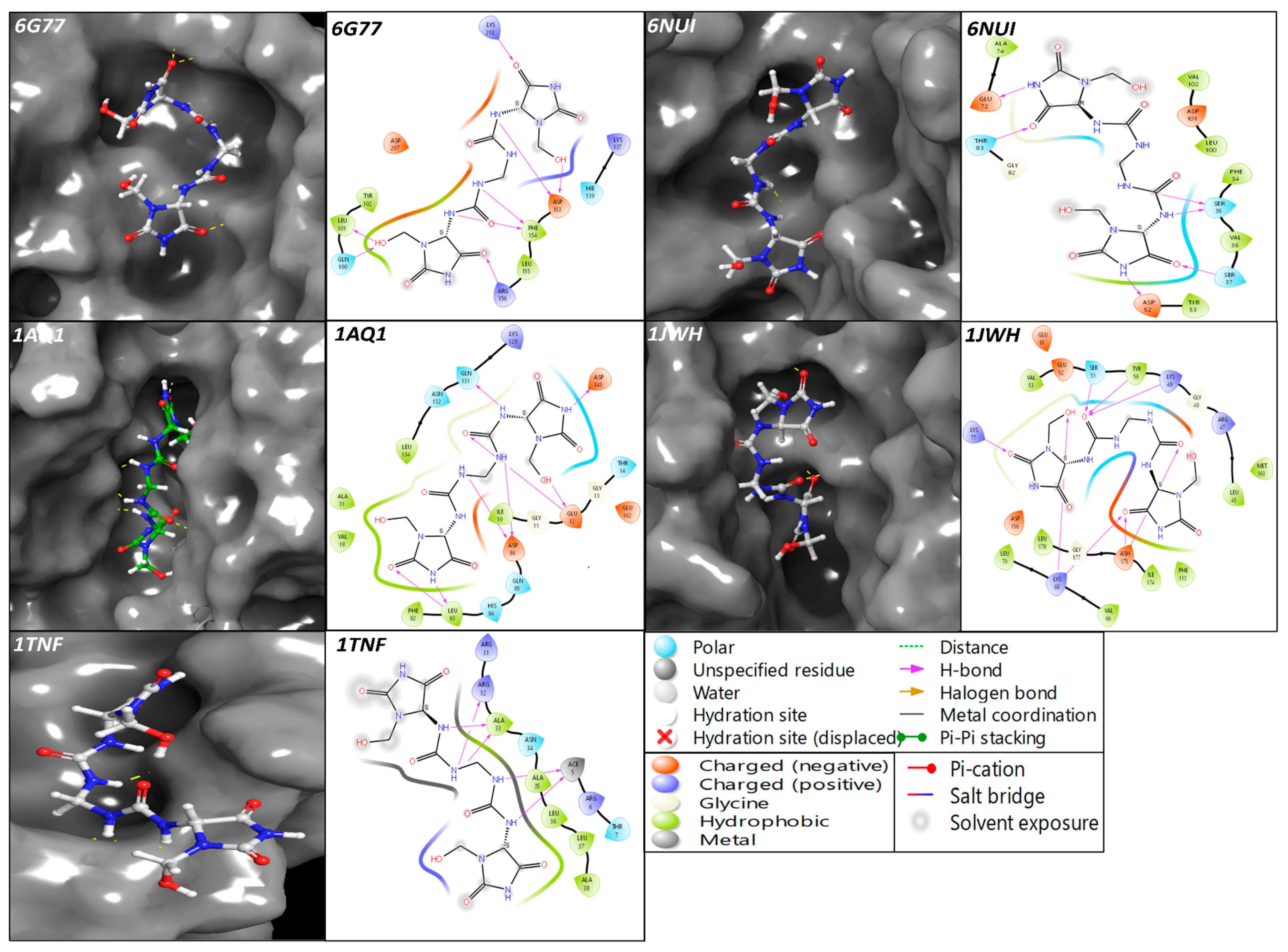
The multitargeted potency of the drugs has been identified with extra-precise docking and MM\GBSA computations through individual sampling and computations in sheets with the help of produced scores. The RSK4 N-terminal kinase (PDBID: 6G77) in the complex with Imidazolidinyl urea has formed eight hydrogen bonds among the LYS213, ARG156 and O atom, and GLN100, LEU101, ASP153 and OH atoms, and ASP153, PHE154, and NH atoms (Figure 1) while producing the docking score of −6.723 Kcal/mol and MM\GBSA score of −34.67 Kcal/mol (Table 1). The human guanylate kinase or hGMPK (PDBID: 6NUI) in the complex with Imidazolidinyl urea has formed six hydrogen bonds among the O atom and THR83 and SER37, and NH atoms and ASP52, SER35, and GLU72 (Figure 1), while producing the docking score of −7.147 (Kcal/mol) and MM\GBSA score of −48.55 (Kcal/mol) (Table 1). The cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (PDBID: 1AQ1) in the complex with Imidazolidinyl urea has produced eight hydrogen bonds among the ASP145, GLN131, ASP86, LEU83 and NH atoms, and LEU83, GLU12 with O atoms and GLU12 have also interacted with OH atoms (Figure 1) while producing the docking score of −7.945 Kcal/mol and MM\GBSA score of −42.95 Kcal/mol (Table 1). The casein kinase-2 holoenzyme (PDBID: 1JWH) in the complex with Imidazolidinyl urea has formed eight hydrogen bonds among the ASH175, LYS68, LYS77, LYS49, TYR50, SER51 and O atoms, and LYS68 and OH atoms (Figure 1) while producing the docking score of −6.635 Kcal/mol and MM\GBSA score of −42.82 Kcal/mol (Table 1). The tumour necrosis factor-alpha (PDBID: 1TNF) in the complex with Imidazolidinyl urea has formed five hydrogen bonds among the ALA33, ARG32 and ACE5 with NH atoms (Figure 1) while producing the docking score of −5.422 Kcal/mol and MM\GBSA score of −38.16 Kcal/mol (Table 1). The overall molecular docking and Prime MM\GBSA results are beyond satisfaction regarding the scoring and the number of hydrogen bonds. The H-bonds play a significant role in the binding affinity among the Imidazolidinyl urea and the proteins, and it significantly influences the conformation and stability of a protein-ligand complex and increases its affinity for the protein. The Glide searches for potential binding sites on the protein and generates a list of possible poses for the ligand, and then evaluates the stability of each pose by calculating the energy of the complex pose with the lowest energy considered for further analysis because of their stability and best fit for the protein–ligand complex.
Figure 1.
Showing the ligand interaction diagram (LID) with 3D snaps to clarify where the ligand is binding to the proteins and 2D representation study the interacting atoms, residues with types and bonds.

Table 1.
Showing the docking score (Kcal/mol), MM\GBSA score (Kcal/mol), and other important computations produced during the molecular docking process.
3.2. ADMET and Interaction Pattern Identification
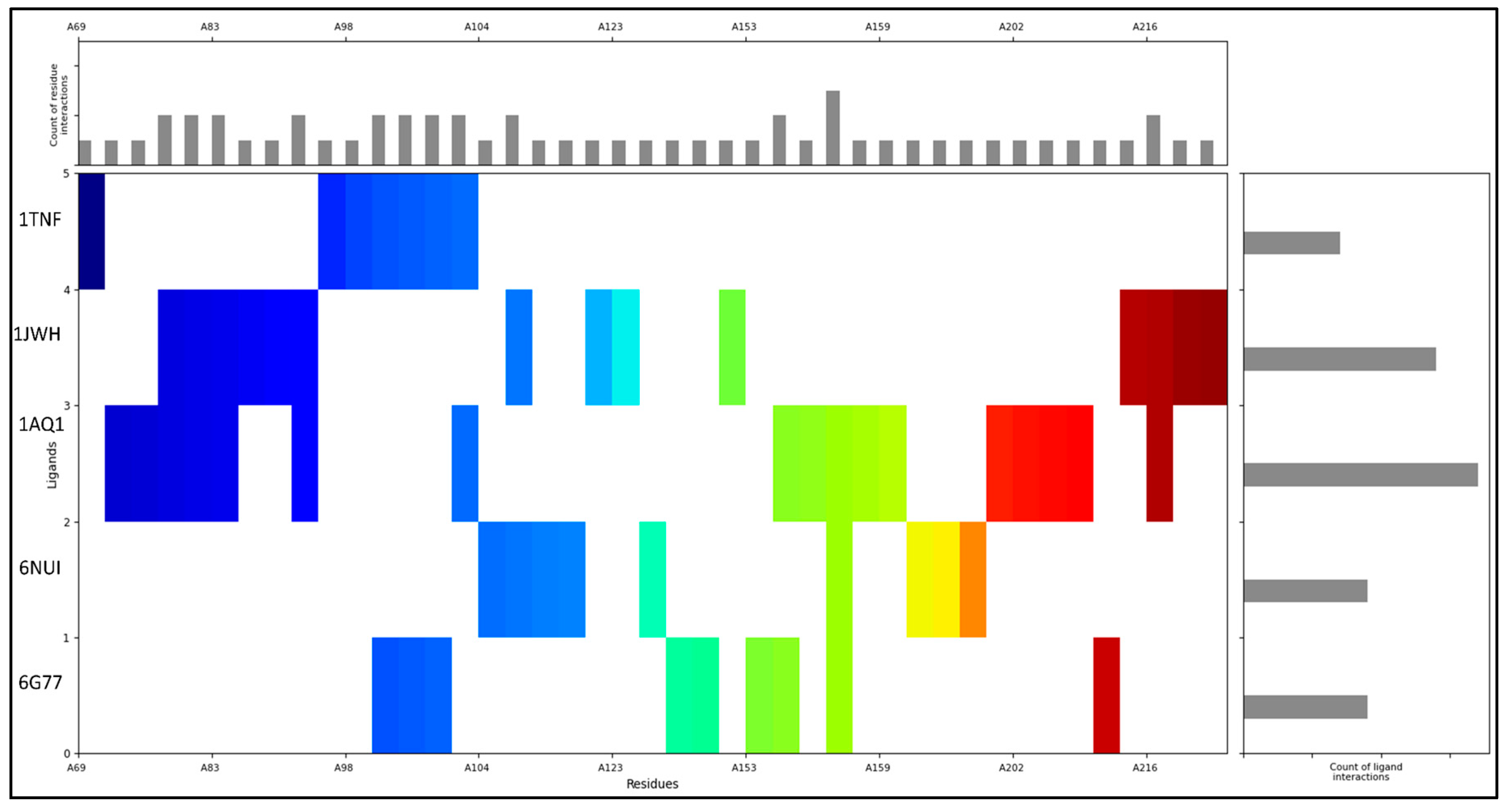
The ADMET properties were computed with the help of the QikProp tool, and the same values were used to filter against the compounds with Lipinski’s rules. The compound has obtained five stars out of five, as the ADMET values perfectly match the standard values and with the lowest toxicity. Imidazolidinyl urea has zero amines, amidine, acid, amide, rotor, and rtvFG and is inactive for the central nervous system. The compound’s molecular weight is 388.296, and the atom numbers are below 500 atoms and can be considered among the novel drug candidates. The dipole, SASA, FOSA, FISA and volume of the compounds are 13.717, 590.656, 162.601, 428.055, and 1034.87, respectively, while the PISA and WPSA values are zero. Additionally, the compound can donate 2.5 hydrogen bonds and accept 8.9 hydrogen bonds. Further, an extended table (Table 2) is provided to understand each compound descriptor against the standard values. The interaction fingerprints of the compound were computed to understand the compound’s diversity of the interacting residues. Imidazolidinyl urea has interacted with the protein with the middle and ending residues RSK4 N-terminal kinase (6G77) and the human guanylate kinase or hGMPK (6NUI) while with cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (1AQ1), casein kinase-2 holoenzyme (1JWH) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (1TNF), it has interacted with the initial residues. ARG156 from 6G77, 6NUI and 1AQ1 was the most interacting residue that formed three interactions and then GLN181, GLY82, SER83, VAL87, GLN100, LEU101, TYR102, ALA103, LYS105, PHE154, and ASP216 are the ones that formed at least two interactions among the selected proteins. Additionally, 1AQ1 is the protein that has formed the most interaction, and then 1JWH, followed by 6NUI, 6G77 and 1TNF, with the Imidazolidinyl urea (Figure 2).

Table 2.
Showing the ADMET properties produced by QikProp with descriptors.
Figure 2.
Showing the interaction fingerprints of interacting atoms with residues of Imidazolidinyl urea and RSK4 N-terminal kinase (6G77), human guanylate kinase or hGMPK (6NUI), cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (1AQ1), casein kinase-2 holoenzyme (1JWH) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (1TNF) with the ligand and residue interaction counts. The C and N terminals are shown with different colours to make it clear with the interaction, and the counts are plotted adjacent to the PDBs.
4. Conclusions
The treatment of lung cancer has come a long way in recent years, thanks to modern drug designing techniques that allowed us to create more effective and safer drugs and reduce the risk of drug resistance. By using targeted drug therapies and allosteric regulators, we can improve the effectiveness of the drugs and reduce the risk of side effects. However, it is easier to develop resistance to this strategy. We have also seen several breakthroughs in the past years, giving us hope for a more effective treatment for lung cancer. In this study, we have identified Imidazolidinyl urea, which is used as a cosmetic preservative and is an antimicrobial compound that effectively acts against multiple protein targets and has the potency to reduce cancer cells. The molecular docking, fingerprinting with interaction patterns, and MM\GBSA calculation helped to understand the multitargeted potency of the compound.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ECB2023-14138/s1
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, data collection/curation, analysis, writing and extensive editing of the first draft, S.A.; Computational resources, reviewing and editing, supervision, K.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
No funding was provided to support the project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Since this study is entirely in silico, ethical obligations are not applicable because they do not involve humans or other organisms directly.
Informed Consent Statement
Both authors agree to submit the manuscript in the conference proceeding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, for providing computational resources and software solutions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no potential competing interest or conflict of interest.
References
- Ahmad, S.; Bano, N.; Qazi, S.; Yadav, M.K.; Ahmad, N.; Raza, K. Multitargeted molecular dynamic understanding of butoxypheser against SARS-CoV-2: An in silico study. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2022, 17, 1934578X221115499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Pasha Km, M.; Raza, K.; Rafeeq, M.M.; Habib, A.H.; Eswaran, M.; Yadav, M.K. Reporting dinaciclib and theodrenaline as a multitargeted inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2: An in-silico study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, Y.S.; Mashraqi, M.M.; Alzamami, A.; Alturki, N.A.; Ahmad, S.; Alharthi, A.A.; Alshamrani, S.; Asiri, S.A. Unveiling the multitargeted potential of N-(4-Aminobutanoyl)-S-(4-methoxybenzyl)-L-cysteinylglycine (NSL-CG) against SARS CoV-2: A virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzamami, A.; Alturki, N.A.; Alghamdi, Y.S.; Ahmad, S.; Alshamrani, S.; Asiri, S.A.; Mashraqi, M.M. Hemi-Babim and Fenoterol as Potential Inhibitors of MPro and Papain-like Protease against SARS-CoV-2: An In-Silico Study. Medicina 2022, 58, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysostomou, S.; Roy, R.; Prischi, F.; Thamlikitkul, L.; Chapman, K.L.; Mufti, U.; Peach, R.; Ding, L.; Hancock, D.; Moore, C.; et al. Repurposed floxacins targeting RSK4 prevent chemoresistance and metastasis in lung and bladder cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaba4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Shah, P.P.; Ban, D.; Trigo-Mouriño, P.; Carneiro, M.G.; DeLeeuw, L.; Dean, W.L.; Trent, J.O.; Beverly, L.J.; Konrad, M.; et al. Solution structure and functional investigation of human guanylate kinase reveals allosteric networking and a crucial role for the enzyme in cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 11920–11933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, A.M.; Noble, M.E.; Tunnah, P.; Brown, N.R.; Johnson, L.N.; Endicott, J.A. Protein kinase inhibition by staurosporine revealed in details of the molecular interaction with CDK2. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niefind, K.; Guerra, B.; Ermakowa, I.; Issinger, O. Crystal structure of human protein kinase CK2: Insights into basic properties of the CK2 holoenzyme. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 5320–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eck, M.J.; Sprang, S.R. The structure of tumor necrosis factor-α at 2.6 Å resolution: Implications for receptor binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 17595–17605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.W.; Beran, B.; Bi, C.; Bluhm, W.F.; Dimitropoulos, D.; Goodsell, D.S.; Prlic, A.; Quesada, M.; Quinn, G.B.; Westbrook, J.D.; et al. The RCSB Protein Data Bank: Redesigned web site and web services. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39 (Suppl. S1), D392–D401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger Release. 1: Maestro; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017; p. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger Release. 4: Protein Preparation Wizard; Epik, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 2018-3. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger Release. 1: Epik; Schrödinger Release: New York, NY, USA, 2020; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger Release. 1: Prime; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Wu, C.; Ghoreishi, D.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Damm, W.; Ross, G.A.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Russell, E.; Von Bargen, C.D.; et al. OPLS4: Improving Force Field Accuracy on Challenging Regimes of Chemical Space. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 4291–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A Major Update to the DrugBank Database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramlal, A.; Ahmad, S.; Kumar, L.; Khan, F.N.; Chongtham, R. From Molecules to Patients: The Clinical Applications of Biological Databases and Electronic Health Records. In Translational Bioinformatics in Healthcare and Medicine; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 107–125. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger Release. 2: LigPrep; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger Release. 4: Glide; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018; p. 757. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger Release. 1: QikProp; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020; p. 329. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).