Abstract
Despite its high nutritional value, the residue obtained by cold pressing of the chia seeds (expeller) is still undervalued. Expeller is rich in proteins and fibers and contains about 7% omega-3 α-linolenic acid (ALA). Considering that chia seed has been reported to improve insulin resistance, among other cardiovascular risk factors, the aim of this work was to study the effects of a diet enriched with the expeller on a rabbit model of metabolic syndrome. A nutritional analysis of the expeller was evaluated. Rabbits were fed a standard diet (CD), a high-fat diet (HFD) and a HFD in which 20% of the calories from fat were replaced by the expeller (ED). At the end of the 6-week feeding period, clinical, biochemical, and vascular reactivity studies were performed. Results: The ED did not modify body weight or visceral fat, and reached to control fasting glucose (mg/dL; CD: 113 ± 3; HFD: 1261 ± 5; ED: 90 ± 7), insulin resistance (area under the curve of glucose tolerance, CD: 612 ± 23; HFD: 676 ± 17; ED: 517 ± 38), triglycerides (mg/dL CD: 113 ± 14; HFD: 192 ± 22; ED = 98 ± 22) and the TyG index (CD: 8.3 ± 0.2; HFD: 9.3 ± 0.3; ED: 8.28 ± 0.23). With respect to the vascular studies, a blunted norepinephrine response was found. In conclusion, the results showed a promising use of the expeller to develop functional foods that improve metabolic syndrome symptoms.
1. Introduction
Recycling and reuse are actions that allow the circularity of the system, with tasks that reintroduce residues as new inputs in the production circuits, adopting a circular production model []. The residue from chia seed (expeller) is a by-product obtained from the oil extraction of seeds by cold pressing []. The expeller has a high nutritional value due to its high content of proteins, fibers and minerals. In addition, the expeller has a residual content of 7–11% rich in omega-3 alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) oil []. However, this by-product is undervalued: it is often used for animal feed or marketed as crushed chia. To this date, some studies for adding value to expeller have been reported: the production of bioactive peptides with antioxidant properties by enzymatic hydrolysis with papain [] and the development of gluten-free premixes with buckwheat and chia flour for a bread product []. In the last years, the demand for functional foods has increased in developed economies as people look for a safer way to improve their general health and living. Functional foods are designed to meet the provision of basic nutrients as well as to offer the potential to enhance health or reduce the risk of diseases.
Metabolic syndrome (MS) identifies a subgroup of individuals with a shared pathophysiology who are at high risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD), a leading cause of death in the world []. In previous work, we have characterized a model of MS by feeding rabbits on a high-fat diet (HFD) for 6 weeks. This model shows normal body weight, hypertriglyceridemia, a reduction in the high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), an increase in visceral abdominal fat (VAF), fasting glucose (FG) and glucose intolerance. Furthermore, a HFD causes an early vascular dysfunction involving a proinflammatory status []. The beneficial effects of chia seeds on CVD risk factors have been widely studied. However, we recently reported that, in our experimental model of MS, the partial replacement of corn oil with chia oil has a partially beneficial effect on MS []. Thus, considering that expeller is an undervalued residue, despite its high nutritional value, and chia seed has been reported to improve insulin resistance, among other CVD risk factors, the aim of this work was to study the effects of a rich-in-expeller diet on a rabbit model of MS, validating its use as a functional food.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chia Expeller
The expeller was provided by NYNAGRO, a local chia seed and oil producer through its brand CHIA VITA (Tucumán, Argentina).
2.2. Animal Handling and Diets
The experimental protocols for this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee from the National University of Tucuman. All animal care and use programs were performed according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Institute of Health Publication, 8th edition, updated 2011). Eighteen male hybrid rabbits, 45 days after weaning, were individually housed in metal cages in a room under controlled conditions. The animals were randomized, separated, and fed with different diets for 6 weeks: regular rabbit chow (n = 6, control diet, CD); a CD supplemented with 18% fat (n = 6, high-fat diet, HFD), and a HFD in which 20% of the calories from fat were replaced by the expeller (n = 6, expeller diet, ED).
2.3. Preparation of Rich-in-Expeller Diet
The diet was prepared by replacing 10% of the daily calories ingested by the animal. An amount of expeller that replaced 10% of the total calories was incorporated into the balanced feed for rabbit (Ganave, Buenos Aires, Argentina). In summary, 100 g of rich-in-expeller food was prepared by adding 11.4 g of expeller (360 cal/100 g) into 84.8 g of the food matrix (balanced feed with 10% corn oil plus 8% lard added, 412 cal/100 g). Thus, a HFD and ED were isocaloric.
2.4. Proximate Composition of Expeller and Rich-in-Expeller Diet
The proximate composition was determined according to the Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). The crude fat was determined by continuous extraction in a Soxhlet extraction system (using an IVA glass extractor, Buenos Aires, Argentina), during 8 h using petroleum ether (fraction 60–80) as a solvent at 60 °C (AOAC 922.06).
The determination of ashes, was carried out in a muffle furnace brand ORL-Hornos Electricos, Lomas de Zamora, Buenos Aires, Argentina, model ORL-IV, at 550 °C (AOAC 923.03).
The crude protein content was determined by the Kjeldahl method (AOAC 984.13), using for digestion and subsequent distillation a Buchi K-435 equipment (Buchi Labortechnik, Flawil, Switzerland). To transform the nitrogen content obtained into protein, factor 6.25 was used. The moisture content was obtained by drying in an oven at 65 °C to a constant weight (AOAC 925.09).
2.5. Clinical and Biochemical Parameters
An intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test was performed two days before the end of the 6 weeks of feeding. At the end of the dietary intervention, food was withdrawn for 12 h. The rabbits were anesthetized, and the mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) was measured []. Blood samples were collected through the catheter inserted into the carotid artery. Plasma total cholesterol (TC), HDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides (TG) and FG were measured by using colorimetric reactions with commercial kits (Wiener, Rosario, Argentina). A midline incision was made in the rabbit using surgical techniques, and the adipose tissues from the abdominal areas were collected and weighed. The VAF and TyG indices were calculated [,].
2.6. Vascular Function Assessment
The aorta was carefully dissected, and the isometric contractile response was measured []. The endothelial function was checked by building a concentration–response curve (CRC) to acetylcholine (Ach, 10−8–10−5 M) in phenylephrine-precontracted aortic rings. Contractile responses to the vasoconstrictor agonists, angiotensin II (Ang II) and norepinephrine (NE), were checked. One group of arteries was exposed to increasing doses of Ang II (10−10–10−6 M), and the other group was exposed to increasing doses of NE (10−8–10−4 M) to construct a CRC. The KCl contractile response was also checked.
2.7. Statistical Analyses
The CRCs were fitted using a nonlinear interactive fitting program (GraphPad Prism 3.0; GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). The agonist potencies were calculated as pEC50 (negative logarithm of the molar concentration of an agonist producing 50% of the maximum response), and the maximum response was expressed as the Rmax (the maximum effect elicited by the agonist). The investigators were blinded to the treatment until the data analysis. The results are reported as a mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). The Shapiro and Wilk goodness-of-fit test was used to test for normal distribution. Statistically significant differences were calculated by the one-way analysis of variance (followed by Duncan’s post-test); p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Composition of Expeller and Rich-in-Expeller Diet
Table 1 shows the proximate composition of the expeller and ED.

Table 1.
Proximate composition of chia expeller and rich-in-expeller diet.
3.2. Clinical and Biochemical Parameters
At the end of the feeding trials (6 weeks), the animal body weights did not differ significantly among the groups (Table 2). The MAP was lower in the rabbits fed an ED than that in the other diet groups (Table 2). The FG, TyG index (Table 2) and area under the curve from the intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (AUCglu, nmol/Lxmin) were significantly lower in the ED than those of the HFD group (CD: 612 ± 23 vs. HFD = 676 ± 17 vs. ED = 517 ± 38; n = 6, p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA and Duncan’s post-test). Regarding the lipid profile, the ED significantly reduced the serum levels of TG and LDL-C with respect to the HFD. However, the ED did not modify VAF with respect to the HFD.

Table 2.
Clinical and biochemical parameters.
3.3. Effects of Diets on Acetylcholine Relaxation Responses
Ach-relaxation was significantly lower in the arteries from the HFD and ED groups than that in the arteries from the CD group (CD-Rmax: 60 ± 4% vs. HFD-Rmax: 43 ± 5% vs. ED: 49 ± 2%; n = 13; p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA and Duncan’s post-test).
3.4. Effect of Diets on Contractile Response to Agonists
The Rmax to Ang II was similar in all diet groups. However, pEC50 was higher in the arteries from the EDs than that of the arteries from HFDs (CD: 7.82 ± 0.08 vs. HFD: 8.13 ± 0.06 vs. ED = 8.25 ± 0.09, n = 8, p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA and Duncan’s post-test). Thus, a shift to the left of the curve was found (Figure 1).
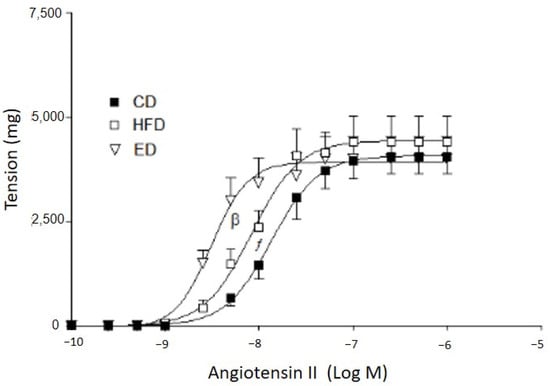
Figure 1.
Concentration–response curve to angiotensin II. CD: regular diet; HFD: high-fat diet; ED: expeller diet. β p < 0.05 indicates statistically significant differences between pEC50 of arteries from rabbits fed on ED and the other diet groups (one-way ANOVA). ƒ p < 0.05 indicates statistically significant differences between pEC50 of arteries from rabbits fed on HFD and CD (one-way ANOVA).
The Rmax to NE was significantly decreased in the arteries from the ED group as compared to the other diet groups (Figure 2). The contractile response to KCl was higher in the arteries from HFD than that of CD. The ED did not normalize the contractile response to KCl (CD: 3907 ± 270 vs. HFD: 6743 ± 500 mg vs. ED: 5668 ± 695 mg; n = 7; p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA and Duncan’s post-test).
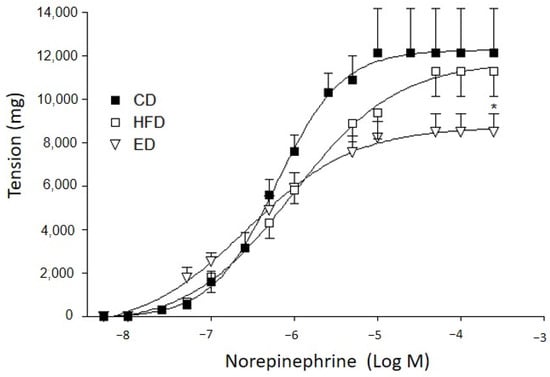
Figure 2.
Concentration–response curve to norepinephrine. CD: regular diet; HFD: high-fat diet; ED: expeller diet. * p < 0.05 indicates statistically significant differences between Rmax of arteries from animals fed on ED and the other diet groups (one-way ANOVA).
4. Discussion
In previous work, we demonstrated that the replacement of 3% corn oil with chia oil into HFD reduces the TG levels and improves endothelial dysfunction []. The increase in plasmatic ALA levels may account for these effects. Data from the literature report the beneficial effect of chia seeds on insulin resistance []. Unexpectedly, chia oil worsened FG and insulin resistance in our model of MS. Dietary fiber is strongly related to the prevention of chronic diseases, such as hypercholesterolemia, diabetes and obesity. Taking into account that a high fiber content has been found in chia expeller [], we hypothesized that an ED might improve FG and insulin resistance in our model. The results from rabbits fed on an ED showed that TG reached the control levels and reduced FG, insulin resistance and the TyG index. These parameters are key CVD risk factors characterizing MS. In addition, the MAP was decreased in rabbits fed on an ED. Chia seed hydrolysates have been found to inhibit ACE []. This may be the mechanism explaining the reduction in MAP. However, while the expeller protein content was high, the protein content in the ED was similar to that of the CD []. This means further studies on protein composition should be carried out to clarify this point. Furthermore, ACE inhibition induces the upregulation of the Ang II receptors (AT1) as a compensatory mechanism. As the in vitro isometric contractions evaluate Ang II-AT1 receptor binding pharmacologically, we hypothesized that AT1 receptor upregulation might account for the increasing Ang II sensitivity found in the arteries of rabbits fed on an ED. Regarding the contractile response to NA, ED reduced the Rmax with respect to the other groups. Considering that insulin blunts sympathetic vasoconstriction [], this effect of an ED may be related to the improvement of insulin sensitivity.
5. Conclusions
The results showed promising use of the expeller to develop functional foods that improve metabolic syndrome symptoms.
Author Contributions
S.J.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Resources, Funding Acquisition, Writing-Reviewing and Editing; G.A.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing; A.V.: Methodology, Investigation, Formal Analysis. Analia Rossi: Methodology, Investigation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by: PICT 2015/1164 (ANCyT-Argentina); PIUNT G621 (SCAIT, Argentina) and by institutional funds from Instituto Superior de Investigaciones Biológicas (INSIBIO). Furthermore, present work was supported by grant Ia ValSe-Food-CYTED (119RT0567).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee from the National University of Tucuman, Argentina, Approval number: 021/2019; Date: 15 November 2019; Date endorsed: 23 March 2021) according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Institute of health Publication 8th edition, updated 2011).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, Susana Jerez, upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Agustina Gonzalez Colombres for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Industrial. El Valor de los Residuos: Distintos Modos de Reducir, Reutilizar, Reciclar y Revalorizar Residuos Industriales, 1st ed.; Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Industrial: Buenos Aires, Argentine, 2016; Available online: https://www.inti.gob.ar/publicaciones/descargac/1 (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Cotabarren, J.; Rosso, A.; Tellechea, M.; García-Pardo, J.; Rivera, J.L.; Obregón, W.D.; Parisi, M.G. Adding value to the chia (Salvia hispanica L.) expeller: Production of bioactive peptides with antioxidant properties by enzymatic hydrolysis with Papain. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitani, M.; Spotorno, V.; Nolasco, S.; Tomas, M. Physicochemical and functional characterization of by-products from chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seeds of Argentina. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 45, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronel, E.; Guiotto, E.; Aspiroz, M.; Tomas, M.; Nolasco, S.; Capitani, M. Development of gluten-free premixes with buckwheat and chia flours: Application in a bread product. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 141, 110916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Zerdan, B.M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, G.; Roco, J.; Medina, A.; Sierra, L.; Medina, M.; Jerez, S. High fat diet-induced metabolically obese and normal weight rabbit model shows early vascular dysfunction: Mechanisms involved. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón, G.; Medina, A.; Martin Alzogaray, F.; Medina, M.; Roco, J.; Jerez, S. Partial replacement of corn oil with chia oil into a high fat diet produces either beneficial and deleterious effects on metabolic and vascular alterations in rabbits. PharmaNutrition 2020, 14, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, A.G.; D’Alessandro, M.E.; Hein, G.J.; Oliva, M.E.; Lombardo, Y.B. Dietary chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.) rich in alpha-linolenic acid improves adiposity and normalises hypertriacylglycerolaemia and insulin resistance in dyslipaemic rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Pablo-Osorio, B.; Mojica, L.; Urías-Silvas, J.E. Chia Seed (Salvia hispanica L.) Pepsin Hydrolysates Inhibit Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme by Interacting with its Catalytic Site. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limberg, J.K.; Soares, R.N.; Power, G.; Harper, J.L.; Smith, J.A.; Shariffi, B.; Jacob, D.W.; Manrique-Acevedo, C.; Padilla, J. Hyperinsulinemia blunts sympathetic vasoconstriction: A possible role of β-adrenergic activation. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2021, 320, R771–R779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).