Cell-Free Mitochondrial DNA in Cell Culture Supernatant: Fragment Size Analysis and FBS Contamination Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Primers
2.4. qPCR and PCR Assays
2.5. DNA Quantification and Primer Efficiency
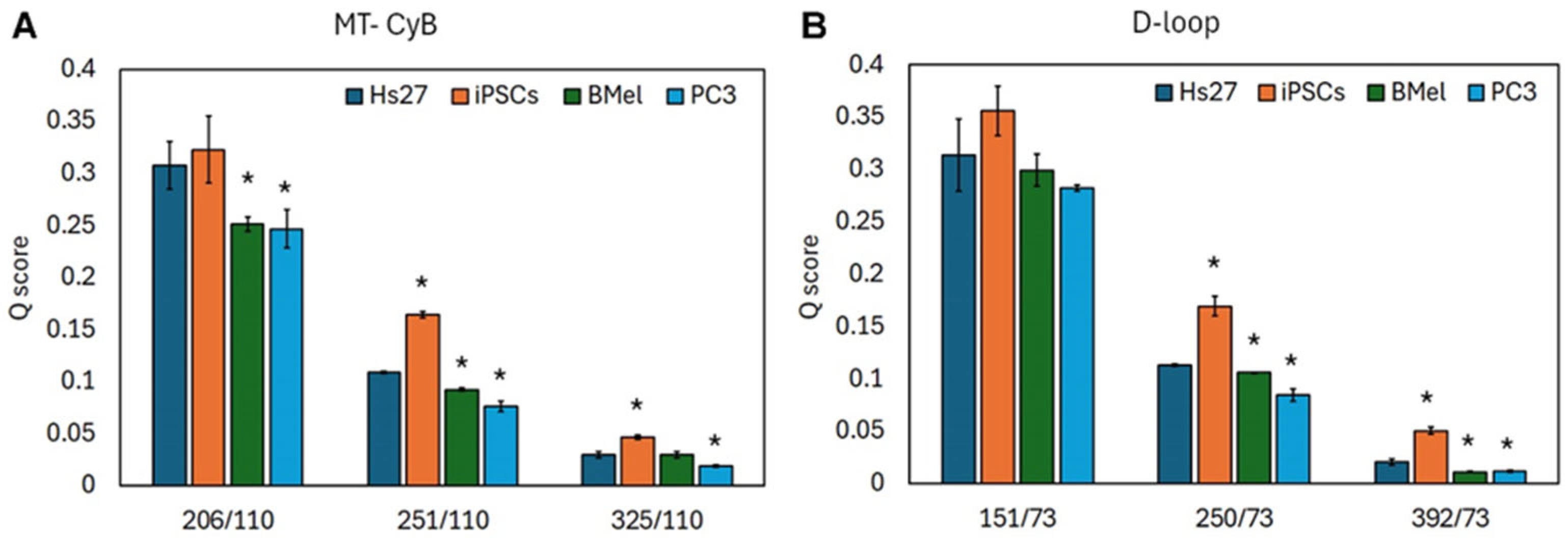
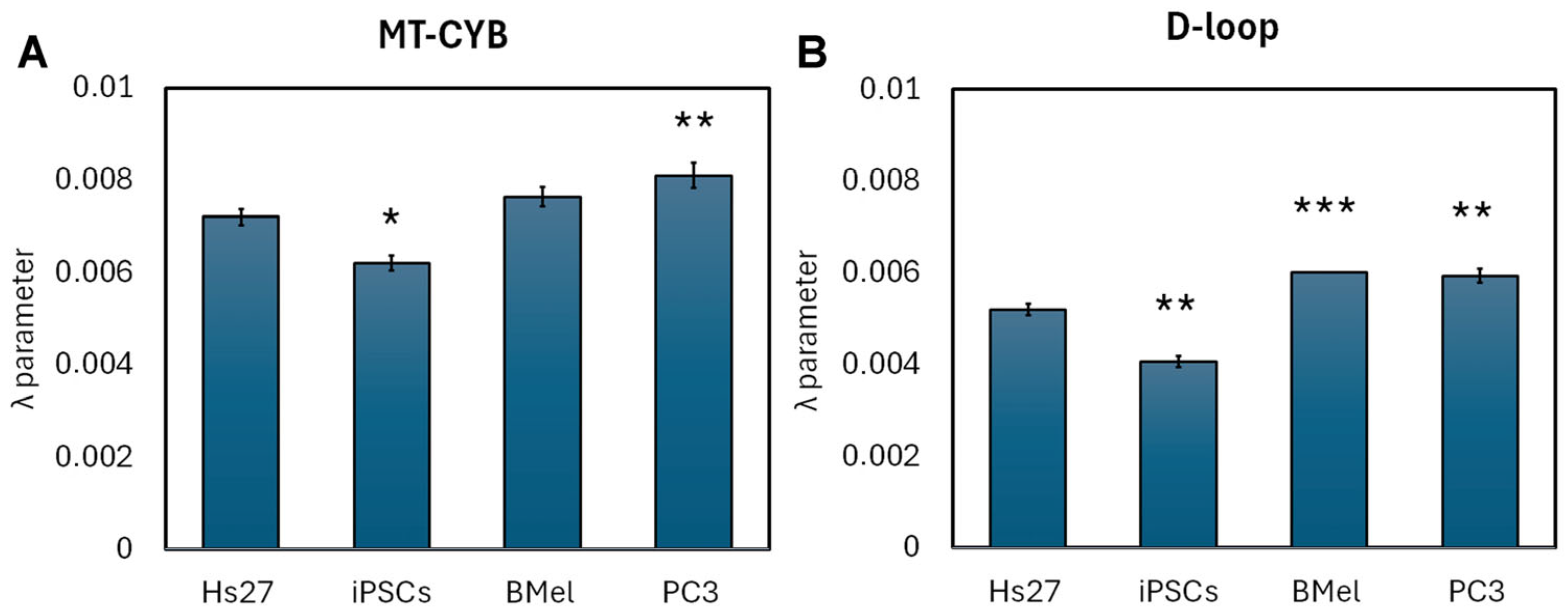
2.6. Evaluation of cf-mtDNA Fragmentation
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
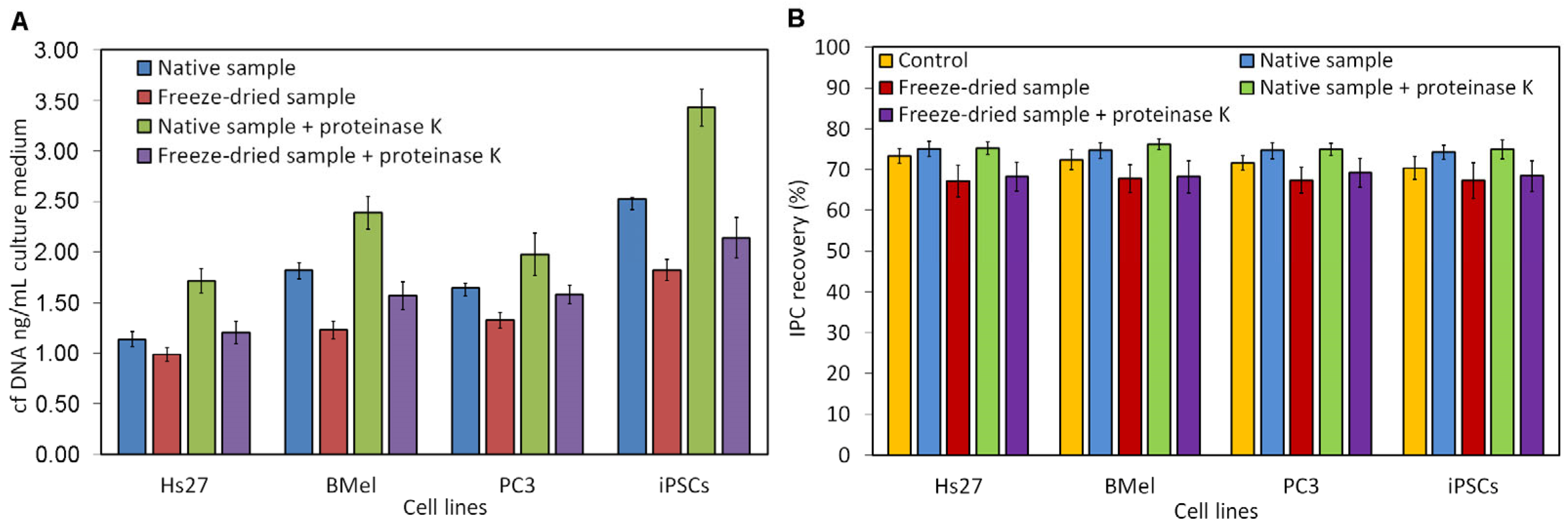
3.1. Optimization of cfDNA Extraction
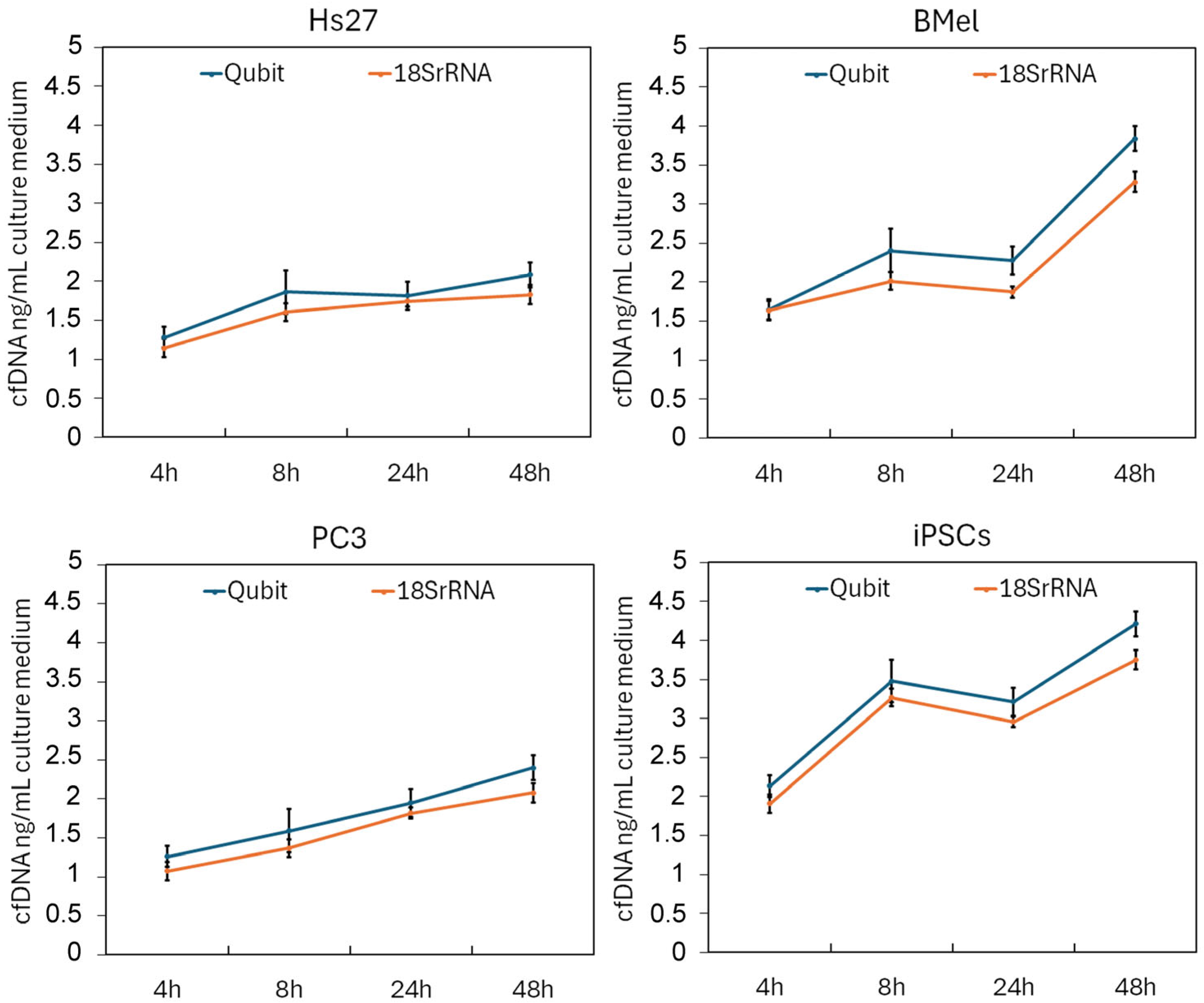
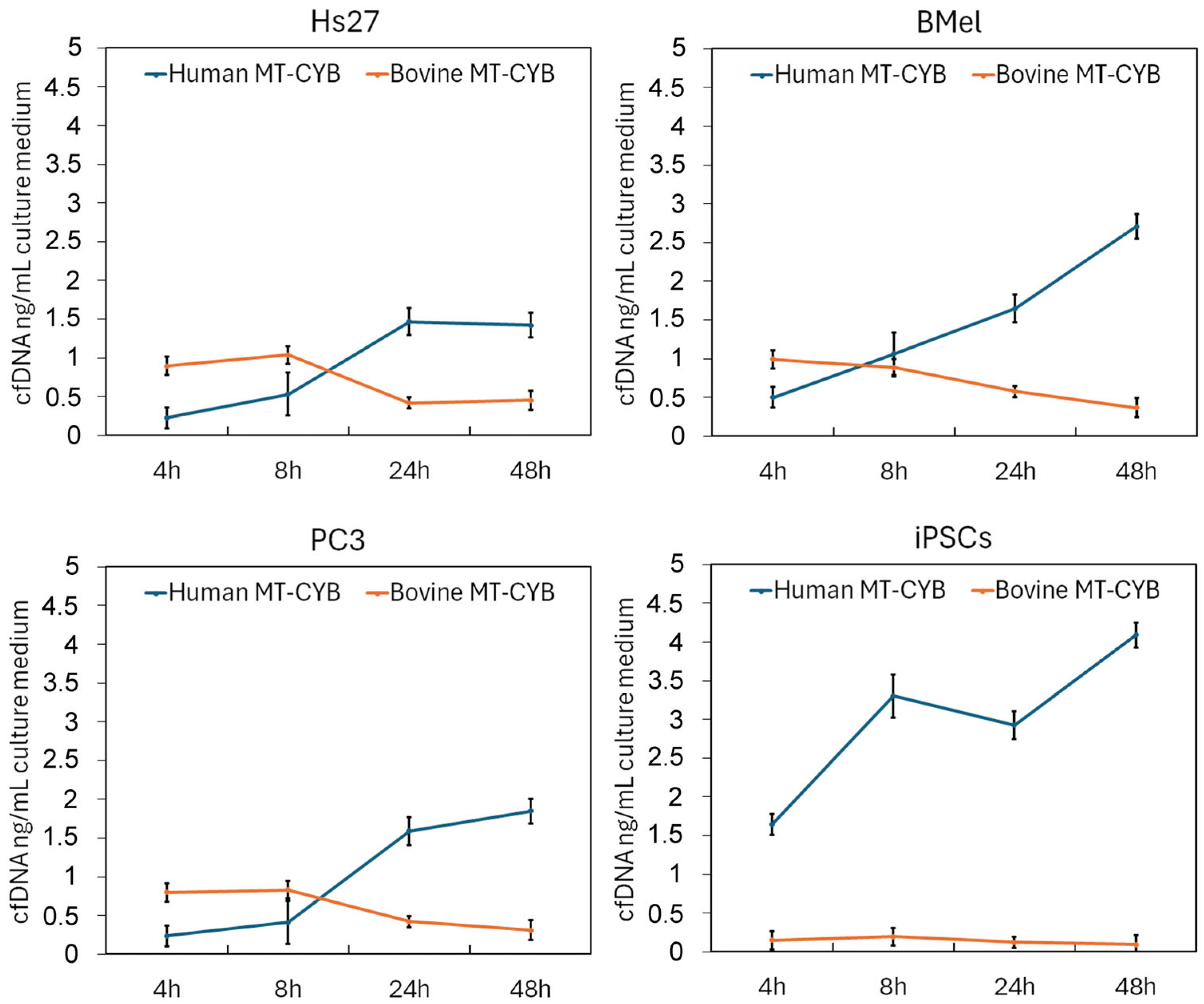
3.2. Quantification of cfDNA and Assessment of Bovine DNA Contamination
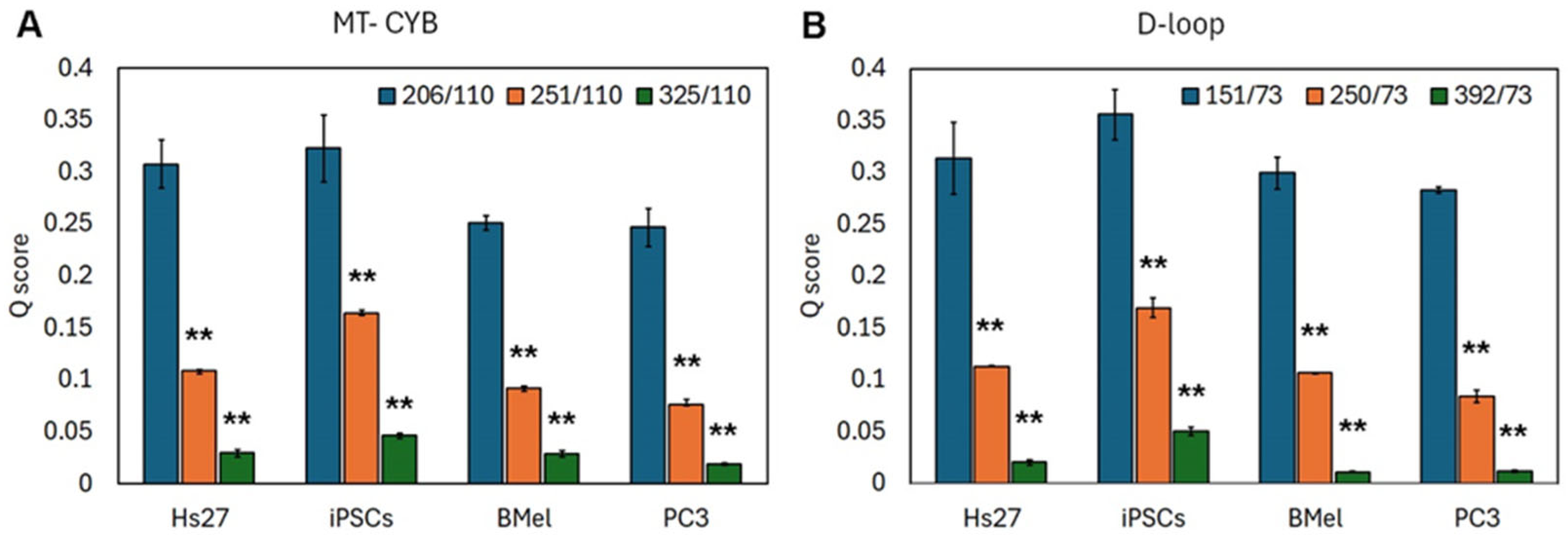
3.3. cf DNA Fragmentation Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filatova, A.A.; Alekseeva, L.A.; Sen’kova, A.V.; Savin, I.A.; Sounbuli, K.; Zenkova, M.A.; Mironova, N.L. Tumor- and Fibroblast-Derived Cell-Free DNAs Differently Affect the Progression of B16 Melanoma In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronkhorst, A.J.; Ungerer, V.; Holdenrieder, S. The Emerging Role of Cell-Free DNA as a Molecular Marker for Cancer Management. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2019, 17, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, S.M.; Yekula, A.; Khanna, P.; Hsia, T.; Gamblin, A.S.; Ekanayake, E.; Escobedo, A.K.; You, D.G.; Castro, C.M.; Im, H.; et al. The Liquid Biopsy Consortium: Challenges and Opportunities for Early Cancer Detection and Monitoring. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 101198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-Villanueva, M.; Hidalgo-Pérez, L.; Rios-Romero, M.; Cedro-Tanda, A.; Ruiz-Villavicencio, C.A.; Page, K.; Hastings, R.; Fernandez-Garcia, D.; Allsopp, R.; Fonseca-Montaño, M.A.; et al. Cell-Free DNA Analysis in Current Cancer Clinical Trials: A Review. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, H.; Melnikova, V.O.; Kosco, K.; Woodward, B.; More, S.; Pingle, S.C.; Weihe, E.; Park, B.H.; Tewari, M.; Erlander, M.G.; et al. Monitoring Daily Dynamics of Early Tumor Response to Targeted Therapy by Detecting Circulating Tumor DNA in Urine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4716–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, H.; Nykin, D.; Bui, N.; Quan, D.; Gomez, G.; Woodward, B.; Venkatapathy, S.; Duttagupta, R.; Fung, E.; Lippman, S.M.; et al. Cell-Free DNA from Ascites and Pleural Effusions: Molecular Insights into Genomic Aberrations and Disease Biology. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Avssn, R.; Chittela, R.K. A Phenol-Chloroform Free Method for cfDNA Isolation from Cell Conditioned Media: Development, Optimization and Comparative Analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2024, 687, 115454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, H.; Long, Y.; Li, P.; Gu, Y. The Main Sources of Circulating Cell-Free DNA: Apoptosis, Necrosis and Active Secretion. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 157, 103166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.W.L.; Chan, K.C.A.; Sun, H.; Jiang, P.; Su, X.; Chen, E.Z.; Lun, F.M.F.; Hung, E.C.W.; Lee, V.; Wong, J.; et al. Nonhematopoietically Derived DNA Is Shorter than Hematopoietically Derived DNA in Plasma: A Transplantation Model. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straver, R.; Oudejans, C.B.M.; Sistermans, E.A.; Reinders, M.J.T. Calculating the Fetal Fraction for Noninvasive Prenatal Testing Based on Genome-wide Nucleosome Profiles. Prenat. Diagn. 2016, 36, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.C.; Blumenfeld, Y.J.; Chitkara, U.; Hudgins, L.; Quake, S.R. Analysis of the Size Distributions of Fetal and Maternal Cell-Free DNA by Paired-End Sequencing. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungerer, V.; Bronkhorst, A.J.; Van Den Ackerveken, P.; Herzog, M.; Holdenrieder, S. Serial Profiling of Cell-Free DNA and Nucleosome Histone Modifications in Cell Cultures. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, R. Size Profile of Cell-Free DNA: A Beacon Guiding the Practice and Innovation of Clinical Testing. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4737–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.; Baranova, A.; Butler, T.; Spellman, P.; Mileyko, V. Non-Random Fragmentation Patterns in Circulating Cell-Free DNA Reflect Epigenetic Regulation. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, S.; Gurioli, G.; De Giorgi, U.; Conteduca, V.; Tedaldi, G.; Calistri, D.; Casadio, V. Cell-Free DNA as a Diagnostic Marker for Cancer: Current Insights. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 6549–6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Fleischhacker, M.; Rabien, A. Cell-Free DNA in the Blood as a Solid Tumor Biomarker—A Critical Appraisal of the Literature. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonekamp, N.A.; Larsson, N.-G. SnapShot: Mitochondrial Nucleoid. Cell 2018, 172, 388–388.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marom, S.; Blumberg, A.; Kundaje, A.; Mishmar, D. mtDNA Chromatin-like Organization Is Gradually Established during Mammalian Embryogenesis. iScience 2019, 12, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerts, M.J.A.; Timmermans, E.C.; Van De Stolpe, A.; Vossen, R.H.A.M.; Anvar, S.Y.; Foekens, J.A.; Sleijfer, S.; Martens, J.W.M. Tumor-Specific Mitochondrial DNA Variants Are Rarely Detected in Cell-Free DNA. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Pol, Y.; Moldovan, N.; Ramaker, J.; Bootsma, S.; Lenos, K.J.; Vermeulen, L.; Sandhu, S.; Bahce, I.; Pegtel, D.M.; Wong, S.Q.; et al. The Landscape of Cell-Free Mitochondrial DNA in Liquid Biopsy for Cancer Detection. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, M.; Peng, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W.; Lan, X. Novel Technologies in cfDNA Analysis and Potential Utility in Clinic. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 33, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, E.W.I.; Brahmer, A.; Ehlert, T.; Kluge, K.; Philippi, K.F.A.; Boedecker, S.C.; Weinmann-Menke, J.; Simon, P. Validating Quantitative PCR Assays for cfDNA Detection without DNA Extraction in Exercising SLE Patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaide, M.; Cheung, M.; Hillman, J.; Rassekh, S.R.; Deyell, R.J.; Batist, G.; Karsan, A.; Wyatt, A.W.; Johnson, N.; Scott, D.W.; et al. Evaluating the Quantity, Quality and Size Distribution of Cell-Free DNA by Multiplex Droplet Digital PCR. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitenc, M.; Grebstad Tune, B.; Melheim, M.; Atneosen-Åsegg, M.; Lai, X.; Rajar, P.; Solberg, R.; Baumbusch, L.O. Assessing Nuclear versus Mitochondrial Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA) by qRT-PCR and Droplet Digital PCR Using a Piglet Model of Perinatal Asphyxia. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval, A.P.; Khromova, A.S.; Blagodatskikh, K.A.; Zhitnyuk, Y.V.; Shtykova, Y.A.; Alferov, A.A.; Kushlinskii, N.E.; Shcherbo, D.S. Application of PCR-Based Approaches for Evaluation of Cell-Free DNA Fragmentation in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1101179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronkhorst, A.J.; Wentzel, J.F.; Aucamp, J.; Van Dyk, E.; Du Plessis, L.; Pretorius, P.J. Characterization of the Cell-Free DNA Released by Cultured Cancer Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungerer, V.; Bronkhorst, A.J.; Uhlig, C.; Holdenrieder, S. Cell-Free DNA Fragmentation Patterns in a Cancer Cell Line. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aucamp, J.; Calitz, C.; Bronkhorst, A.J.; Wrzesinski, K.; Hamman, S.; Gouws, C.; Pretorius, P.J. Cell-Free DNA in a Three-Dimensional Spheroid Cell Culture Model: A Preliminary Study. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 89, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kong, P.; Ma, G.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.; Xia, T.; Xie, H.; Zhou, W.; Wang, S. Characterization of the Release and Biological Significance of Cell-Free DNA from Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 43180–43191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, B.; Warton, K.; Ford, C.E. Endogenous Cell-Free DNA in Fetal Bovine Serum Introduces Artifacts to in Vitro Cell-Free DNA Models. BioTechniques 2022, 73, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuwono, N.L.; Warton, K.; Ford, C.E. The Influence of Biological and Lifestyle Factors on Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Blood Plasma. eLife 2021, 10, e69679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Huang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yi, X.; Zhu, J.; Wu, W. Analysis of Cf-mtDNA and Cf-nDNA Fragment Size Distribution Using Different Isolation Methods in BV-2 Cell Supernatant of Starvation-Induced Autophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.F.; Junqueira-Neto, S.; Pinheiro, J.; Machado, J.C.; Costa, J.L. Induction of Apoptosis Increases Sensitivity to Detect Cancer Mutations in Plasma. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 127, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronkhorst, A.J.; Ungerer, V.; Holdenrieder, S. Comparison of Methods for the Quantification of Cell-Free DNA Isolated from Cell Culture Supernatant. Tumor Biol. 2019, 41, 1010428319866369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulou, M.; Karaglani, M.; Balgkouranidou, I.; Pantazi, C.; Kolios, G.; Kakolyris, S.; Chatzaki, E. Circulating Cell-free DNA Release in Vitro: Kinetics, Size Profiling, and Cancer-related Gene Methylation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14079–14089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layek, S.S.; Kanani, S.; Doultani, S.; Gohil, T.; Patil, S.; Sudhakar, A.; Raval, K.B.; Kuppusamy, K.; Gorani, S.; Raj, S.; et al. Analyzing Cell-Free Genomic DNA in Spent Culture Media: Noninvasive Insight into the Blastocysts. Glob. Med. Genet. 2024, 11, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Rodriguez, M.; Diez-Juan, A.; Jimenez-Almazan, J.; Martinez, S.; Navarro, R.; Peinado, V.; Mercader, A.; Meseguer, M.; Blesa, D.; Moreno, I.; et al. Origin and Composition of Cell-Free DNA in Spent Medium from Human Embryo Culture during Preimplantation Development. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Lambie, M.; Yu, C.W.; Stambolic, V.; Waldron, J.N.; Bratman, S.V. Senescence, Necrosis, and Apoptosis Govern Circulating Cell-Free DNA Release Kinetics. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Ito, J.; Shirasuna, K.; Kuwayama, T.; Iwata, H. Comparative Analysis of Cell-Free DNA Content in Culture Medium and Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number in Porcine Parthenogenetically Activated Embryos. J. Reprod. Dev. 2020, 66, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deig, C.R.; Thowe, R.T.; Frye, E.D.; Chin-Sinex, H.J.; Mendonca, M.S.; Lautenschlaeger, T. In Vitro Cell-Free DNA Quantification: A Novel Method to Accurately Quantify Cell Survival after Irradiation. Radiat. Res. 2018, 190, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Shen, X.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Fetal bovine serum, an important factor affecting the reproducibility of cell experiments. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golshan, M.; Dortaj, H.; Rajabi, M.; Omidi, Z.; Golshan, M.; Pourentezari, M.; Rajabi, A. Animal origins free products in cell culture media: A new frontier. Cytotechnology 2025, 77, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Chan, C.W.M.; Chan, K.C.A.; Cheng, S.H.; Wong, J.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Wong, G.L.H.; Chan, S.L.; Mok, T.S.K.; Chan, H.L.Y.; et al. Lengthening and Shortening of Plasma DNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1317–E1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, F.; Wang, S.; Jiao, H.; Dang, M.; Zhou, K.; Guo, W.; Guo, S.; Zhang, H.; Song, W.; et al. Aberrant Fragmentomic Features of Circulating Cell-Free Mitochondrial DNA as Novel Biomarkers for Multi-Cancer Detection. EMBO Mol. Med. 2024, 16, 3169–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdas, E.; Stawski, R.; Kaczka, K.; Nowak, D.; Zubrzycka, M. Altered Levels of Circulating Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, S.; Limanaqi, F.; Ferese, R.; Biagioni, F.; Campopiano, R.; Centonze, D.; Fornai, F. Ccf-mtDNA as a Potential Link Between the Brain and Immune System in Neuro-Immunological Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Li, D.Y.; Guo, X.; Cao, H.Y.; Chen, Y.B.; Zhou, F.; Ge, N.J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, S.S.; Zhao, Z.; et al. NGS-Based Profiling Reveals a Critical Contributing Role of Somatic D-Loop mtDNA Mutations in HBV-Related Hepatocarcinogenesis. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakova, O.; Kussainova, A.; Kakabayev, A.; Aripova, A.; Baikenova, G.; Izzotti, A.; Bersimbaev, R. The Level of Free-Circulating mtDNA in Patients with Radon-Induced Lung Cancer. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakova, O.; Kausbekova, A.; Kussainova, A.; Kalibekov, N.; Serikbaiuly, D.; Bersimbaev, R. Involvement of Circulating Cell-Free Mitochondrial DNA and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Lung Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 22, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, Q.; Su, J.; Li, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Z.; Han, J. Quantitative Detection of Circulating MT-ND1 as a Potential Biomarker for Colorectal Cancer. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 21, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.; Zhou, Q.; Dao, D.Y.; Lo, Y.M.D. Circulating Biomarkers in the Diagnosis and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Wang, S.; Feng, Z.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, H.; Guo, X.; Xing, J.; Liu, Y. Circulating Cell-Free mtDNA as a New Biomarker for Cancer Detection and Management. Cancer Biol. Med. 2023, 21, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfigli, A.; Cesare, P.; Volpe, A.R.; Colafarina, S.; Forgione, A.; Aloisi, M.; Zarivi, O.; Poma, A.M.G. Estimation of DNA Degradation in Archaeological Human Remains. Genes 2023, 14, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, H.; Wu, W.; Geng, S.; Zhong, G.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Long, G.; Ren, Q.; Luan, Y.; et al. Circulating Cell-Free DNA Fragmentation Is a Stepwise and Conserved Process Linked to Apoptosis. BMC Biol. 2023, 21, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, H.; Seo, Y.; Kakizaki, E.; Kozawa, S.; Muraoka, E.; Yukawa, N. Identification of DNA of Human Origin Based on Amplification of Human-Specific Mitochondrial Cytochrome b Region. Forensic Sci. Int. 2005, 152, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.B.; Gallati, S.; Schaller, A. qPCR-Based Mitochondrial DNA Quantification: Influence of Template DNA Fragmentation on Accuracy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 423, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamimuzzaman, M.; Le Tourneau, J.J.; Unni, D.R.; Diesh, C.M.; Triant, D.A.; Walsh, A.T.; Tayal, A.; Conant, G.C.; Hagen, D.E.; Elsik, C.G. Bovine Genome Database: New Annotation Tools for a New Reference Genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D676–D681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiff, S.; Glennon, M.; Lyng, J.; Smith, T.; Shilton, N.; Maher, M. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Detection of Bovine DNA in Meat and Bone Meal Samples. J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavlick, M.F. Development of a Universal Internal Positive Control. BioTechniques 2018, 65, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poma, A.; Cesare, P.; Bonfigli, A.; Volpe, A.R.; Colafarina, S.; Vecchiotti, G.; Forgione, A.; Zarivi, O. A qPCR-Duplex Assay for Sex Determination in Ancient DNA. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deagle, B.E.; Eveson, J.P.; Jarman, S.N. Quantification of Damage in DNA Recovered from Highly Degraded Samples—A Case Study on DNA in Faeces. Front. Zool. 2006, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Hashida, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsubara, T.; Ohtsuka, T.; Suzawa, K.; Maki, Y.; Soh, J.; Asano, H.; Tsukuda, K.; et al. Estimation of Age-Related DNA Degradation from Formalin-Fixed and Paraffin-Embedded Tissue According to the Extraction Methods. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 2683–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primes | Sequenza Primers 5′-3′ | Product (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| FORW_CYB_1091 | AACCATCGTTGTATTTCAACT | 1091 |
| REV_CYB_1091 | ACTTGTCCAATGATGGTAAAAGG | |
| FORW_CYB | AACCGCCTTTTCATCAATCG | |
| REV_CYB_110 | GTAGGAAGAGGCAGATAAAGAATATTGAG | 110 |
| REV_CYB_206 | TGAAGGCTGTTGCTATAGTTGCA | 206 |
| REV_CYB_251 | TGGCCCCTCAGAATGATATTTG | 251 |
| REV_CYB_325 | GTAGCCTCCTCAGATTCATTGAACT | 325 |
| FORW_HVR_807 | ATGTCTGCACAGCCGCTTTC | 807 |
| REV_HVR_807 | TGTGTGTTCAGATATGTTAAAGCCA | |
| FORW_D-loop | GCCACAGCACTTAAACACATCTCT | |
| REV_D-loop_73 | TGAAATCTGGTTAGGCTGGTGTTAG | 73 |
| REV_D-loop_151 | GTATGGGAGTGGGAGGGGA | 151 |
| REV_D-loop_250 | GGGGGTGTCTTTGGGGT | 250 |
| REV_D-loop_392 | TGGAACGGGGATGCTTG | 392 |
| FORW_CYB_Bovine | CTACTGACACTCACATGAATTGG | 99 |
| REV_CYB_Bovine | CACTAGGATGAGGAGAAAGTATAGG | |
| FORW_18SrRNA | CGAACGTCTGCCCTATCAACTT | 61 |
| REV_18SrRNA_61 | ACCCGTGGTCACCATGGTA | |
| FORW_IPC | CGCGAGATACACTGCCAGAA | 65 |
| REV_IPC | GACCACAGCCAGATTAAATTTACCA | |
| OLIGO_IPC | 5′CGCGAGATACACTGCCAGAAATCCGCGTGATTACGAGTCGTGGTAAATTTAATCTGGCTGTGGTC3′ 3′GCGCTCTATGTGACGGTCTTTAGGCGCACTAATGCTCAGCACCATTTAAATTAGACCGACACCAG5′ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cesare, P.; Colafarina, S.; Bonfigli, A.; Volpe, A.R.; Aloisi, M.; Zarivi, O.; Poma, A.M.G. Cell-Free Mitochondrial DNA in Cell Culture Supernatant: Fragment Size Analysis and FBS Contamination Assessment. DNA 2025, 5, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5030041
Cesare P, Colafarina S, Bonfigli A, Volpe AR, Aloisi M, Zarivi O, Poma AMG. Cell-Free Mitochondrial DNA in Cell Culture Supernatant: Fragment Size Analysis and FBS Contamination Assessment. DNA. 2025; 5(3):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5030041
Chicago/Turabian StyleCesare, Patrizia, Sabrina Colafarina, Antonella Bonfigli, Anna Rita Volpe, Massimo Aloisi, Osvaldo Zarivi, and Anna Maria Giuseppina Poma. 2025. "Cell-Free Mitochondrial DNA in Cell Culture Supernatant: Fragment Size Analysis and FBS Contamination Assessment" DNA 5, no. 3: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5030041
APA StyleCesare, P., Colafarina, S., Bonfigli, A., Volpe, A. R., Aloisi, M., Zarivi, O., & Poma, A. M. G. (2025). Cell-Free Mitochondrial DNA in Cell Culture Supernatant: Fragment Size Analysis and FBS Contamination Assessment. DNA, 5(3), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5030041







