Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to assess the association of diabetes mellitus and its medications with overall response (ORR) and mortality or cancer-specific survival (CSS) in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer receiving enfortumab vedotin monotherapy. Methods: This multicentre retrospective cohort study was designed according to the guidelines for the synthesis of qualitative research (ENTREQ). Eligible patients were adults (≥18) years treated with enfortumab vedotin monotherapy for metastatic urothelial cancer between June 2024 and January 2025. A total of 125 patients were reported across 11 centres. Results: The cohort included 93 males (74.4%) and 32 females (25.6%), with a mean age of 68.3 years (SD 9.3). The primary tumour site was the bladder in 109 (87.2%) cases and the upper tract (UTUC) in 16 (12.8%) cases. Interestingly, medication with metformin was significantly associated with cancer-specific mortality (37.9% versus 77.8%; p = 0.019), while patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus had a significantly better CSS (Log Rank = 0.004). Upon comparing only patients who already had diabetes mellitus and then received anti-diabetic medication, there was a significant association between patients with diabetes mellitus receiving metformin and a worse 3-month ORR (80.0% versus 55.6%; p = 0.039). Regarding the subpopulation of UTUC, cancer-specific mortality was significantly associated with metformin medication (p = 0.033). Conclusions: Despite recent reports that metformin has protective effects in urothelial cancer, our findings suggest that metformin use may be linked to worse responses and survival outcomes in patients treated with enfortumab vedotin monotherapy. Further research, particularly translational research into the underlying diabetic and pharmacologic pathways, is warranted.
1. Introduction
It is still controversial and under discussion whether diabetes mellitus or the use of antidiabetic drugs can increase the risk of bladder cancer or lead to its progression. Specifically, since the authorization of thiazolidinediones (glitazones), which have a PPAR-γ-agonistic effect, as oral antidiabetics around 20 years ago, there has been a controversy as to whether they increase the risk of bladder cancer or exacerbate its progression [1,2,3,4,5]. Furthermore, glitazones have a high cardiovascular risk profile, and due to this effect, currently pioglitazone is the only glitazone available for the oral treatment of diabetes mellitus in Western industrialized countries, and it is paramount in European countries [1,5].
However, the facts of this connection remain unclear to this day, and stringent proof of causality between PPAR-γ activation and the induction or progression of bladder cancer has not yet been achieved. On the contrary, there are even reports that PPAR-γ agonists have an antiproliferative effect on bladder tumour cells and could therefore even be used therapeutically [5,6,7]. In addition, at the American Association of Cancer Research (AACR) 2024 Bladder Cancer Congress, it was reported that glitazones can upregulate Nectin4 expression and thus may increase the therapeutic window of Nectin4-based therapies. The authors of an abstract presented there summarized this as follows: Modulating the PPAR-γ pathway increases Nectin4 expression, which we leveraged by rosiglitazone to increase targeting and anti-tumour efficacy of Nectin4-CAR-T cells. These preclinical results lay the foundation for the development of CAR-T therapies in bladder cancer and suggest rational drug combinations that may expand the therapeutic window of therapies targeting Nectin4 [5,8].
Enfortumab vedotin, an antibody–drug conjugate targeting Nectin4, has emerged as a promising agent in urothelial cancer, especially bladder cancer. Initially approved as monotherapy in the third-line setting based on the EV-201 (A Study of Enfortumab Vedotin for Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Bladder Cancer) trial, enfortumab vedotin has rapidly emerged as a cornerstone therapy [9,10,11,12].
Consequently, we performed a multicentre retrospective study in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer, bladder, and upper urinary tract tumours (UTUC) receiving enfortumab vedotin monotherapy. The initial planed primary aim was to assess the association of thiazolidinedione with overall response (ORR) and mortality or cancer-specific survival (CSS). The secondary aims were to assess the association of (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus, as well as first-line oral antidiabetic drugs (metformin, DDP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors), with ORR and death or CSS. A prespecified subgroup analysis of patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma was performed for sufficient datasets.
2. Materials and Methods
This retrospective cohort study was designed according to the guidelines for the synthesis of qualitative research (ENTREQ) found on equatornetwork.org [13]. Before starting the evaluation, we obtained the approval of the local ethics review board at RWTH Aachen University (EK 24-211 from 17 June 2024). Furthermore, the study was conducted in accordance with the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement for cohort studies [14].
The inclusion criteria were adult patients over 18 years receiving enfortumab vedotin monotherapy for metastatic urothelial cancer. If the inclusion criteria were met, there were no further exclusion criteria.
All relevant patient data, like patient history and demographic characteristics, and all relevant clinical data, e.g., comorbidities, medication, or pathological data, were collected. From June 2024 until January 2025, 10 university medical centres and 1 tertiary care centre reported 125 patients.
For the assessment of response, the radiological RECIST criteria version 1.1 were used [15]. According to these criteria, overall response rate (ORR) is defined as the proportion of patients who have a partial or complete response to therapy; it does not include stable disease and is a direct measure of drug tumoricidal activity [16]. Additionally, CSS is defined as the time from randomization or treatment initiation to patient death caused by the index cancer, whether due to the original tumour or to a second primary tumour of the same cancer type [17].
For each numerical variable, the numerical distribution was preliminarily assessed by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Descriptive statistics were made with means and standard deviations for normal distribution or with medians and IQRs for non-parametric data. For parametric continuous variables, Student’s t test was used, and for parametric categorical variables, the chi-square test or the Fisher exact test was used. For non-parametric data, the Mann–Whitney U test was used for categorical and continuous variables. Kaplan–Meier plots were used to estimate the median CSS, and univariate comparisons were performed using the log rank test. All reported p-values were based on a two-sided hypothesis, and p < 0.05 was considered to be significant. All statistical calculations were performed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences 29.0 software (SPSS Inc., IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characterization of the Study Population
One-hundred twenty-five patients from ten university medical centres and from one tertiary care centre were included in this analysis. Ninety-three (74.4%) were male and thirty-two (25.6%) were female. The mean age of the population was 68.3 (SD 9.3) years. The origin of the tumour was the bladder in 109 (87.2%) cases and the upper tract in 16 (12.8%) cases. All patients had high-grade disease and 59 (47.2%) had primary metastatic disease. Overall, the patients were in good condition, with a mean ECOG performance status of 0.7 (SD 0.8). Most patients (n = 80; 64.0%) were on third-line therapy. Furthermore, only 25 (20.0%) patients received neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Regarding the differences between urothelial bladder cancer and UTUC, there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of age (p = 0.428), gender (p = 0.075), primary metastatic disease (p = 0.405), ECOG performance status (0.814), and therapy line (p = 0.525). However, UTUC presented at significantly higher T stages (clinically and pathologically) (p = 0.003). These differences are illustrated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of bladder cancer and UTUC regarding demographic characterization.
3.2. Diabetes Mellitus, Antidiabetic Drugs, and Response Rates
Concerning diabetes mellitus, 24 patients (19.2%) had the disease; 10 (8.0%) were also insulin-dependent, 9 (7.2%) received metformin, 5 (4.0%) received a DDP-4 inhibitor, and 7 (5.6%) received a SGLT2 inhibitor, but no one had a thiazolidinedione as their medication.
After 3 months of therapy, ORR was 61.6%, and after 6 months, it was 40.0%. The median duration of response was 5 months (IQR 3.0–6.0). The median follow-up time was 7 months (IQR 5.0–10.0). Fifty-one patients (40.8%) had already died due to their malignant disease. These survival parameters apply for the whole study population.
Table 2 illustrates the association of diabetes and its medication with the parameters of response (patients without the parameter versus patients with the parameter). Interestingly, in this situation, only the medication with metformin is significantly associated with cancer-specific mortality (p = 0.019).

Table 2.
Association of diabetes parameters with parameters of response (comparison of patients without the parameter versus patients with the parameter).
Figure 1 shows the differences in CSS in patients with or without diabetes parameters (analysing the whole population). Of note, there was significant difference in CSS between patients with and without insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (Log Rank = 0.004).
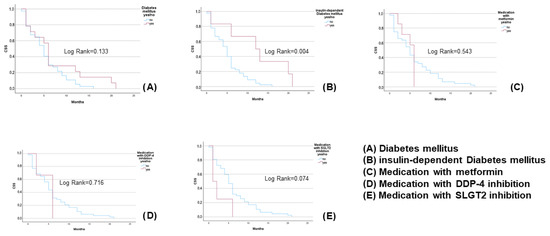
Figure 1.
Differences in CSS between diabetic and non-diabetic patients with or without diabetes parameters, for the whole population.
Comparing only patients who already had diabetes mellitus and then received the special anti-diabetic medication, there was no significant difference in 3-month ORR (p = 0.404), 6-month ORR (p = 0.876), and CSS (p = 0.889) in the insulin-dependent diabetes group. Furthermore, there was no significant difference in 3-month ORR (p = 0.202) and CSS (p = 0.134) in those who received metformin; in 3-month ORR (p = 0.088), 6-month ORR (p = 0.770), and CSS (p = 0.203) in those receiving a DDP-4 inhibitor; or in 3-month ORR (p = 0.406), 6-month ORR (p = 0.811), and CSS (p = 0.445) in those receiving a SGLT2 inhibitor. Interestingly, there was a significant association between patients with diabetes mellitus receiving metformin and a worse 3-month ORR (80.0% versus 55.6%; p = 0.039).
3.3. Subgroup Analysis of UTUC
Due to the significantly higher T stages in UTUC, a comprehensive subgroup analysis was performed. Overall, 16 patients with a mean age of 66.1 (SD 9.7) years were included. Nine patients were (56.3%) were male and seven (43.7%) were female. Furthermore, six patients (37.5%) had primary metastatic disease, and the majority of the patients (n = 8; 50.0%) were also on their third therapy line. Regarding diabetes mellitus, three (18.8%) had the disease; one (6.3%) was also insulin-dependent, one (6.3%) received metformin, two (12.5%) received a DDP-4 inhibitor, and one (6.3%) received a SGLT2 inhibitor, but no one had a thiazolidinedione as their medication.
After 3 months, ORR was 62.5%, and after 6 months, it was 37.2%. The median duration of response was 4 months (IQR 3.0–6.0). There was no significant difference in the duration of response between bladder cancer and UTUC (p = 0.092).
Eight patients (50.0%) had already died due to their malignant disease. Additionally, there was no significant difference in CSS between the bladder cancer and UTUC groups (Log Rank = 0.418).
However, there was no significant association between diabetes parameters and ORR after three or six months, nor CSS, in the UTUC group, with one exception: cancer-specific mortality was only significantly associated with metformin medication in the UTUC group (p = 0.033).
4. Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, we performed the first multicentre analysis of diabetes mellitus and its medication in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer receiving enfortumab vedotin monotherapy. In our opinion, it is very difficult to analyze glitazones in this context, since they are used as a second-line therapy in diabetes mellitus, especially because of their unfavourable cardiovascular risk profile [5,6,8]. Consequently, while the hypothesis that glitazones may expand the therapeutic window of Nectin4-targeted therapies is mechanistically intriguing, it remains speculative and requires further experimental and translational validation.
4.1. Metformin and Cancer-Specific Outcomes
Interestingly, we found that metformin use was significantly associated with cancer-specific mortality in the whole cohort and with significantly worse 3-month ORR in diabetic patients. Additionally, metformin use was significantly associated with cancer-specific mortality in UTUC. These findings contrast with recent reports suggesting that metformin has positive effects on bladder cancer outcomes and prognosis [18,19,20,21,22].
van Hattum et al. performed a systematic review and meta-analysis on the effect of metformin on bladder cancer incidence and outcomes. They reviewed 13 studies including 3,315,320 patients on the risk of developing bladder cancer after metformin exposure, as well as 9 studies including 4006 patients on the oncological outcomes of patients with bladder cancer. Metformin did not alter bladder cancer incidence (HR 0.97, 95% CI 0.87–1.09) or oncological outcomes for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), but it was associated with a reduced risk of recurrence (HR 0.52, 95% CI 0.32–0.84), cancer-specific mortality (HR 0.58, 95% CI 0.43–0.78), and overall mortality (HR 0.66, 95% CI 0.47–0.92) in muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). However, the authors noted significant bias and heterogeneity among the studies, leading them to conclude that the role of metformin in bladder cancer prevention and treatment remains unclear [23].
These conflicting results raise the following question: What could be the reasons for this “metformin paradox”? Regarding bladder cancer and diabetes mellitus, especially metformin, a lot of confounders must be taken into account, including demographic and lifestyle factors (age, sex, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, physical activity), factors specifics to diabetes (type of diabetes mellitus (type I or II), its medical therapy, including medication combinations, and the patient’s metabolic situation), and factors concerning the bladder cancer itself (NMIBC, MIBC, metastatic disease, histological subtypes, and treatment variants, especially immune-modulating drugs) [18,19,20,22,23]. Thus, there might be constellations of patient populations in whom metformin has positive effects and of some others in whom it has negative effects on bladder cancer. Therefore, further research should address all these confounders, particularly given the global prevalence of diabetes mellitus and obesity [24,25].
Notably, another idea must be added to this particular discussion: it is important to distinguish between metformin’s potential role in bladder cancer development and its interaction with cancer therapy. This represents two distinct research questions:
- –
- Firstly, is metformin a driver of carcinogenesis in bladder cancer?
- –
- Secondly, does metformin’s interaction with bladder cancer treatment lead to worse response or outcomes?
4.2. Insulin-Dependent Diabetes and Hyperglycaemia
Additionally, we reported that patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus had a significant better CSS. This is an interesting and new result, and the explanation is not quite obvious and is in contrast to other data. Unfortunately, we must assume that this is only a confounding factor, since in the EV-201 trial, hyperglycaemia was one of the most frequent grade 3 adverse events: hyperglycaemia was identified as one of the serious adverse events potentially leading to death by metabolic acidosis. One fatal case was described: an obese patient (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) without baseline hyperglycaemia who developed treatment-related grade 4 hyperglycaemia and had metabolic acidosis [9].
Understanding why patients treated with enfortumab vedotin develop hyperglycaemia and whether this contributes to outcomes is clinically important—especially since the combination of enfortumab vedotin and pembrolizumab is now a first-line therapy for metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Interestingly, in the first report of the German GARDIANS project providing real-world data about the treatment of enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab, hyperglycaemia was not one of the most frequent adverse events, and no treatment-related fatal event occurred [26]. However, these are only first retrospective data with a short follow-up period and so, at least in our opinion, the diabetes mellitus/hyperglycaemia/obesity complex must be further studied in this context. Investigations should also consider the other confounders mentioned. However, it should be noted that death due to hyperglycaemia would manifest as an event in overall survival (OS), but chronic hyperglycaemia and metabolic acidosis might lead to worse therapy responses. In this context, we would like to emphasize the importance of precise documentation and the correct use of definitions in oncology studies, especially in retrospective analyses.
4.3. Considerations for the UTUC Subgroup
Looking at the UTUC subgroup, the topic must also be contextualized in light of the considerable heterogeneity in clinical practice guidelines. Different practices in diagnosis and treatment might have influenced our results in a significant way. As shown in a recent systematic comparison, substantial differences exist in recommendations and management across guidelines. This lack of standardization may contribute to variability in treatment responses and highlights the need for further research tailored specifically to this population [27]. Additionally, in our UTUC population, the interpretation of outcomes, particularly the observed association between metformin use and cancer-specific mortality, may be affected by upstream treatment variability. A recent systematic review confirmed that, while neoadjuvant systemic therapy may improve pathological response, its benefit over adjuvant therapy is still unclear, and patient selection remains challenging [28]. Such inconsistency in pre-treatment strategies could have influenced both response to enfortumab vedotin and overall prognosis in this subgroup.
4.4. Study Limitations
This study has several limitations. Unfortunately, we could not address our initial first study aim regarding glitazones due to the fact that none of the patients in our cohort received glitazones. Furthermore, the retrospective study design, low incidence—unfortunately also for metformin—and event rates may have led to selection bias. Due to these low event rates, we did not consider diabetic combination therapies. Additionally, and due to the retrospective study design, we were not able to analyze several important parameters, like glycaemic control (HbA1c, glucose levels), duration and dose of metformin, renal function, corticosteroid use, or pre-treatment strategies, especially in UTUC. In our opinion, future investigations should address these confounding factors and may perform multivariate analyses. Finally, with the recent shift to first-line therapy with enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab, further research is needed in the context of combination therapy.
4.5. Mechanistic Considerations
There remains, again, an essential question, even if the interaction between Nectin4 and diabetic pathways is still a hypothesis, as mentioned above: What is the pathophysiology behind Nectin4’s interaction with diabetic pathways? Firstly, we think that it is worthwhile to explore the interaction of Nectin4 with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PARP-γ) inhibition and related diabetic pathways [5,8]. The proteome analysis by Shahid et al. provides a first clue for the description of the interaction of the signalling pathways: in a characterization of the global proteome of human bladder cells treated with the PPAR-γ agonist pioglitazone, they identified 95 upregulated and 29 downregulated proteins (absolute log2 fold change >0.58 and p value < 0.05) [29]. This suggests intersecting signalling cascades between anti-diabetic agents and urothelial cancer cells.
Secondly, it is essential to understand the connection of metabolic factors, such as obesity, hyperglycaemia, insulin resistance, and elevated growth factor, with steroid hormone levels, oxidative stress, and an increased activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the development or progression of bladder cancer. This may aid in promoting individualized medicine. For instance, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DDP-4) inhibition has been postulated to increase the risk of metastasis through the induction of CXCL12/CXCL4, which activates mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR), promoting epithelial–mesenchymal transcription [30]. Elucidating this complex problem will require extensive translational research but is important given the rise in individualized targeted therapies and the global burden of diabetes mellitus and obesity.
5. Conclusions
In summary, our retrospective analysis suggests that metformin use may be associated with a reduced therapeutic efficacy of enfortumab vedotin in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma, but these are still exploratory results. These findings highlight the need for further investigation—particularly translational studies—to elucidate the underlying biological interactions between antidiabetic agents and urothelial tumour biology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.S., B.K. and J.K.; methodology, L.S. and A.U.; software, L.S.; validation, L.S., B.K. and J.K.; formal analysis, L.S. and A.U.; investigation, all authors; resources, L.S., B.K. and J.K.; data curation, L.S., B.K. and J.K.; writing—original draft preparation, L.S., B.K., A.U. and J.K.; writing—review and editing, all authors; visualization, all authors; supervision, L.S., B.K. and J.K.; project administration, L.S., B.K. and J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Before starting the evaluation, we obtained the approval of the local ethics review board at RWTH Aachen University (EK 24-211 from 17 June 2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was not mandatory due to the retrospective study design.
Data Availability Statement
All study data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all participating centres, including the study nurses, who provided the patient data and supported this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ripamonti, E.; Azoulay, L.; Abramovicz, M.; Platt, R.W.; Siussa, S. A systematic review of observational studies of the association between pioglitazone use and bladder cancer. Diabet. Med. 2019, 36, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehtälä, J.; Khanfir, H.; Bennett, D.; Ye, Y.; Korhonen, P.; Hoti, F. Pioglitazone use and risk of bladder cancer: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetol. Int. 2019, 10, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.M.; Kwok, C.S.; Chen-Turner, C.; Maduakor, C.A.; Singh, S.; Loke, Y.K. Thiazolidinediones and associated risk of bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 78, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.H. A review on thiazolidinediones and bladder cancer in human studies. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part. 2014, 32, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneidewind, L.; Sommerhalder, B.; Willi, D.; Rönnau, C.; Uhlig, A.; Kiss, B. Association of glitazones and bladder cancer: A rapid review. Urologie 2025, 64, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, R.; Matsuyama, M.; Segawa, Y.; Hase, T.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Tsuchida, T.; Wada, S.; Kawahito, Y.; Sano, H.; Nakatani, T. Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) in human urinary bladder carcinoma and growth inhibition by its agonists. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 104, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumber, S.A.; Tate, T.; Al-Ahmadi, H.; Chen, X.; Choi, W.; Basar, M.; Lu, C.; Viny, A.; Batourina, E.; Li, J.; et al. Rosiglitazone and trametinib exhibit potent anti-tumor activity in a mouse model of muscle invasive bladder cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Delavan, H.M.; Zhu, J.; Kasap, C.; Yip, E.; Lodha, R.; Sheng-You, L.; Porten, S.; Friedlander, T.; Koshkin, V.; et al. Modulating the PPARγ pathway to augment NECTIN4-targeting chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy. In Proceedings of the AACR Special Conference on Bladder Cancer: Transforming the Field, Charlotte, NC, USA, 17–20 May 2024; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, E.Y.; Petrylak, D.P.; O´Donnel, P.H.; Lee, J.L.; van der Heijden, M.S.; Loriot, Y.; Stein, M.N.; Necchi, A.; Kojima, T.; Harrison, M.R.; et al. Enfortumab vedotin after PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors in cisplatin-ineligible patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma (EV-201): A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, S.; Hirose, K.; Masuda, H. Enfortumab Vedotin with or Without Pembrolizumab in Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e250250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.E.; Powles, T.; Sonpavde, G.P.; Loriot, Y.; Duran, I.; Lee, J.L.; Matsubara, N.; Vulsteke, C.; Castellano, D.; Mamtani, R.; et al. EV-301 long-term outcomes: 24-month findings from the phase III trial of enfortumab vedotin versus chemotherapy in patients with previously treated advanced urothelial carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, T.; Valderrama, B.P.; Gupta, S.; Bedke, J.; Kikuchi, E.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Iyer, G.; Vulsteke, C.; Park, S.H.; Shin, S.J.; et al. Enfortumab Vedotin and Pembrolizumab in Untreated Advanced Urothelial Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, A.; Flemming, K.; McInnes, E.; Oliver, S.; Craig, J. Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: ENTREQ. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2012, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaruz, L.C.; Socinski, M.A. The clinical viewpoint: Definitions, limitations of RECIST, practical considerations of measurement. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2629–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, N.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. A comparison of relative survival and cause-specific survival methods to measure net survival in cancer populations. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 4773–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ren, W.; Zhou, X.; Long-Fei, L.; He-Qun, C.; Xiong-Bing, Z. Association of metformin intake with bladder cancer risk and oncologic outcomes in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, M.S.; Cripps, R. Diabetes Mellitus and Increased Risk of Cancer: Focus on Metformin and the Insulin Analogs. Pharmacotherapy 2010, 30, 1159–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondergaard, C.S.; Esquivel, P.N.; Dalamaga, M.; Magkos, F. Use of Antihyperglycemic Drugs and Risk of Cancer in Patients with Diabetes. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 25, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Xue, D.; Wang, K.; Zhang, F.; Shi, J.; Jia, B.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, H.; et al. Metformin exerts an antitumor effect by inhibiting bladder cancer cell migration and growth and promoting apoptosis through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. BMC Urology 2022, 22, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, F.; Rajati, F.; Sarokhani, D.; Babandpour, M.; Moradinazar, M. The Relationship between Metformin Consumption and Cancer Risk: An Updated Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2023, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Hattum, J.W.; de Ruiter, B.M.; Oddens, J.R.; de Reijke, T.M.; Wilmink, J.W.; Molenaar, R.J. The Effect of Metformin on Bladder Cancer Incidence and Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Bladder Cancer 2022, 8, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elleisy, M.; Zettl, H.; Dräger, D.L.; Hakenberg, O.W. The Impact of Diabetes and Antidiabetics on the Obesity Paradox in Renal Cell Cancer. Urol. Int. 2024, 109, 311–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elleisy, M.; Zettl, H.; Dräger, D.L.; Hakenberg, O.W. The Impact of Diabetes and Antidiabetics on Uro-Oncological Disease Outcomes: A Single-Center Experience. Urol. Int. 2025, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschaebitz, S.; Casuscelli, J.; Büttner, T.; Darr, C.; Volk, A.-L.; Hennig, M.; Holzwarth, N.; Zengerling, F.; Dib, M.; Schlack, K.; et al. Enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma: First results on outcomes and safety in a German multicenter real-world patient cohort (GUARDIANS). J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfo, S.D.; Cilio, S.; Aveta, A.; Wu, Z.; Cerrato, C.; Napolitano, L.; Lasorsa, F.; Lucarelli, G.; Verze, P.; Siracusano, S.; et al. Upper Tract Urothelial Cancer: Guideline of Guidelines. Cancers 2024, 16, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Paul, A.; Raman, J.D.; Necchi, A.; Psutka, S.P.; Buonerba, C.; Zargar, H.; Black, P.C.; et al. Neoadjuvant systemic therapy in patients undergoing nephroureterectomy for urothelial cancer: A multidisciplinary systematic review and critical analysis. Minerva Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 74, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Kim, M.; Yeon, A.; Jin, P.; Kim, W.-K.; You, S.; Kim, J. Pioglitazone Alters the Proteomes of Normal Bladder Epithelial Cells but Shows No Tumorigenic Effects. Int. Neurourol. J. 2020, 24, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, M. Diabetes, Antidiabetic Medications and Cancer Risk in Type 2 Diabetes: Focus on SGLT-2 Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).