Abstract
Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) have emerged as viable alternatives to toxic organic solvents. The most intriguing aspect of these solvents is perhaps the widely varying physicochemical properties emerging from the changes in the constituents that form DESs along with their composition. Based on the constituents, a DES can be hydrophilic/polar or hydrophobic/non-polar, rendering a vastly varying spectrum of polarity a possibility. DESs formed by mixing urea (U) with hydrated lanthanide salts, lanthanum nitrate hexahydrate (La : U), cerium nitrate hexahydrate (Ce : U), and gadolinium nitrate hexahydrate (Gd : U), respectively, exhibit very high polarity as manifested via the probe-reported empirical parameters of dipolarity/polarizability (π*). The highest π* of 1.70 exhibited by the DES (Gd : U) in a 1 : 2 molar ratio is unprecedented. The π* ranges from 1.50 to 1.70 for these DESs, which is almost the highest reported for any solvent system. The π* decreases with an increasing amount of urea in the DES; however, the anomalous trends in H-bond donating acidity (α) and H-bond accepting basicity (β) appear to be due to the hydrated water of the lanthanide salt. The emission band maxima of the fluorescence probe of the “effective” dielectric constant (εeff) of the solubilizing media, pyrene-1-carboxaldehyde (PyCHO), in salt-rich DESs reflect higher cybotactic region dipolarity than that offered by water. Probe Nile red aggregates readily in these DESs to form non-fluorescent H-aggregates, which is a characteristic of highly polar solvents. The behavior of probe pyranine also corroborates these outcomes as the (lanthanide salt : urea) DES system supports the formation of the deprotonated form of the probe in the excited state. The (lanthanide salt : urea) DES system offers solubilizing media of exceptionally high polarity, which is bound to expand their application potential.
1. Introduction
Currently, the most emerged and prominent solvent class belonging to the area of green chemistry arguably comprises deep eutectic solvents (DESs). DESs are usually obtained by simply mixing two or more constituents in a particular molar ratio followed by gentle heating. In DESs, the thermodynamics of mixing ensures significant lowering of the normal freezing point compared to those of individual constituents [1,2,3,4,5]. While the application potential of DESs lies in their environmentally benign nature with negligible toxicity along with the low costs of the constituents and preparation, there is an escalated interest in academia due to the fact that a wide variety of physicochemical properties of these neoteric media are possible based on the identities of the constituents and their composition used to prepare these solvents [6,7,8,9,10]. Based on the chemical nature of the constituents, DESs are divided into several classes. In the formation of DESs, usually one component behaves as an H-bond donor (HBD), and the other behaves as an H-bond acceptor (HBA), leading to extensive H-bonding and other interactions (van der Waals, electrostatic, etc.) resulting in a liquid state under wide ranges of temperature and pressure [1,2,3,4,5].
DESs have been extensively investigated not only for their applications, but also for their physicochemical properties. Consequently, among other classifications, DESs may also be divided into “hydrophilic” and “hydrophobic” DESs, with “hydrophilic” DESs offering complete water miscibility and relatively high polarities [11,12]. DESs composed of a mixture of quaternary ammonium salt as an HBA with a suitable HBD have shown to possess relatively high polarity (as reported by several solvatochromic probes) in comparison to common solvents [13]. Extensive research has been carried out to characterize metal-based DESs by understanding their physicochemical properties with variations in the identity and composition of the constituents [14,15]. Kamlet-Taft parameters, in this context, have afforded the understanding of the H-bonding interactions that occur inside hydrated metal salt-based DESs [16,17,18,19]. Herein, we report our findings of exceptionally high probe-reported polarity exhibited by a set of type IV DESs constituting hydrated lanthanide metal salts as HBAs and urea as prototypical HBDs [14]. These DESs have recently been shown to support probe aggregation at unprecedented low concentrations [20]. Specifically, three (3) HBD urea-based DESs containing the HBA metal salts lanthanum nitrate hexahydrate (La : U), cerium nitrate hexahydrate (Ce : U), and gadolinium nitrate hexahydrate (Gd : U), respectively, are found to exhibit some of the highest probe-reported polarities in terms of the empirical Kamlet-Taft parameters of dipolarity/polarizability (π*) [21] and HBD acidity (α) [22] along with ET values [22]. The highly dipolar nature of the solubilization microenvironment offered by these DESs was further emphasized by the cybotactic region dipolarity of several fluorescence probes.
2. Materials and Methods
Hydrated metal salts [lanthanum nitrate hexahydrate (La), cerium nitrate hexahydrate (Ce), and gadolinium nitrate hexahydrate (Gd)] and urea were chosen as the DES constituents and were obtained with the highest purity ≥ 99% from Sigma-Aldrich and SRL Enterprises, respectively. N,N-Diethyl-4-nitroaniline (DENA) and 4-nitroaniline (NA) (Figure 1) were used as absorbance probes in this work. DENA and NA were obtained from Frinton Laboratories and Spectrochem Co. Ltd.(Hainesport, NJ, USA), respectively, while Pyridin-N-oxide (PyO, 95%), Pyrene-1-carboxyldhyed (PyCHO, 99%), 9-diethylamino-5-benzo[a]phenoxazinone (Nile red, ≥98%, HPLC), and 8-hydroxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid (pyranine, 99%) (Figure 1) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). These were used without any further purification.
Figure 1.
The molecular structures of the solvatochromic probes used in this work.
DESs with mixtures of (La : U), (Ce : U), and (Gd : U) were prepared by simply mixing the lanthanide salts (all ≥ 99+% purity) with urea (>99.9% purity) at permissible (in the context of DES formation) molar composition ranges (1 : 3 to 1 : 7 for La : U, 1 : 3.5 to 1 : 7 for Ce : U, and 1 : 2 to 1 : 7 for Gd : U). At several compositions, simply mixing the two solid constituents resulted in liquid-state DESs under ambient conditions (no heating was required). All UV-vis molecular absorbance and fluorescence as well as NMR spectroscopic probes were dissolved in the DESs, and the probe responses were acquired using adequate sampling and data collection techniques using appropriate instrumentation.
Stock solutions of probes were prepared by dissolving a precalculated amount of the respective probe in ethanol and storing it at 4 ± 1 °C in pre-cleaned brown-amber glass vials. Mettler Toledo AB104-S balance was used to weigh the proper amount of probe with an accuracy of ±0.0001 g. A prerequisite amount of the prepared stock solution was taken in a 1 cm2 quartz cuvette. Grade 1 nitrogen gas was used to evaporate the ethanol. The UV-visible absorbance spectra of all samples were collected by using Lambda 35 double-beam spectrophotometer (purchased from PerkinElmer) containing a photomultiplier tube (PMT) detector with a flexible deuterium and a Xe lamp as a light source. The required amount of DESs under investigation was transferred to the cuvette. Dissolution of the probes in DESs was confirmed using the linearity of the absorbance versus the concentration plot. The 13C of 250 mM PyO dissolved in La : U-based DESs was obtained on Brucker 500 MHz (DPX-500) NMR spectrometers(Billerica, Massachusetts, USA). CDCl3 was used as internal reference, and the sample was taken in the sealed capillary inside the same NMR tube (consists of CDCl3). The steady-state fluorescence spectra were obtained using an FLS1000 spectrometer(Livingston, West Lothian, UK) with emission monochromators (STGM325-M) and grating excitation (STGM325-X) containing a 450 W xenon arc lamp as the radiation source, a red PMT detector, and a temperature controller (a Quantum Northwest Luma 40). All parts of the instrument are product of Quantum Northwest, Inc. (Libert Lake, WA, USA). The spectrometer was bought from Edinburgh Instruments, Ltd. Appropriate blank was subtracted from the emission and excitation spectra before analysis. Data analysis was accomplished using SigmaPlot v14.5. A Horiba-Jobin Yvon Fluorocube time-correlated single-photon counting (TCSPC) fluorimeter was used to measure the fluorescence lifetime of the selected probe. Samples were also characterized through Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) absorbance data, which were acquired on a double-beam spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies Cary 660 ATR, Santa Clara, CA, USA) from 4000 to 400 cm−1.
3. Results and Discussion
Well-established UV–vis molecular absorbance probes, N,N-diethyl-4-nitroaniline (DENA) [21] and 4-nitroaniline (NA) [23] (Figure 1), were employed to obtain the dipolarity/polarizability (π*) and H-bond accepting (HBA) basicity (β) of the three DESs at several different compositions using the following expressions:
where ῡDENA and ῡNA are the lowest energy absorbance band maxima of the probes DENA and NA, respectively, in kK units (1000 cm−1 = 1 kK). Our attempts to obtain the ET values [that subsequently afford HBD acidity (α)] using Reichardt’s betaine dyes 30 and 33, the most used probes for this purpose, were futile as both of these dyes were insoluble in our DESs or due to the protonation of –O−; these dyes did not exhibit lowest-energy intramolecular charge-transfer absorbance bands. Schneider et al. [24] used pyridine-N-oxide (PyO) (Figure 1) as a probe to characterize the HBD acidity (α) of several solvents using 13C NMR chemical shifts with the following equations:
where d24 is the difference (in ppm) of the 13C NMR chemical shifts () of carbon 2 with respect to that of carbon 4 of PyO. The correlation between α was thus estimated, and the α from Reichardt’s dye () was established by Freire’s [22] group recently as follows:
supporting the suitability of PyO as an alternative probe to characterize the HBD acidity of the solvents. It was further shown that the [22] and [22] single-parameter polarity scales can be subsequently obtained using the following equations:
and
The absorbance spectra and the respective absorbance maxima of DENA and NA in all three DESs at all investigated compositions are presented in Figure S1 and Table S1, respectively (the representative spectra within DESs (Gd : U) at 1 : 2 and 1 : 7 molar ratios are shown in Figure 2). With the increase in the amount of urea in all three DES systems, a significant hypsochromic shift in the DENA wavelength maxima is clearly observed. While similar to DENA, the NA wavelength maxima depends, to some extent, on the identity of the lanthanide metal, interestingly, and contrary to DENA, the band maxima of NA are statistically the same irrespective of the amount of urea in the DES system. The 13C NMR scans of PyO within (La : U) at 1 : 3 and 1 : 7 molar ratios are presented in Figure 3 as representatives (others ratios are shown in Figure S2). It is to be noted that (Ce : U) based DESs appear to react with PyO, and due to the high number of unpaired electrons in Gd, the 13C NMR of PyO in (Ce : U) and (Gd : U) DESs could not be obtained. The values of the empirical parameters π*, β, α, and , estimated from Equations (1)–(6) for the applicable DES systems, are presented in Table 1 and Table 2. A careful examination of the empirical parameters listed in Table 1 and Table 2 reveals that π*, , and α decrease, while β increases monotonically as the relative amount of urea is increased within a DES system.
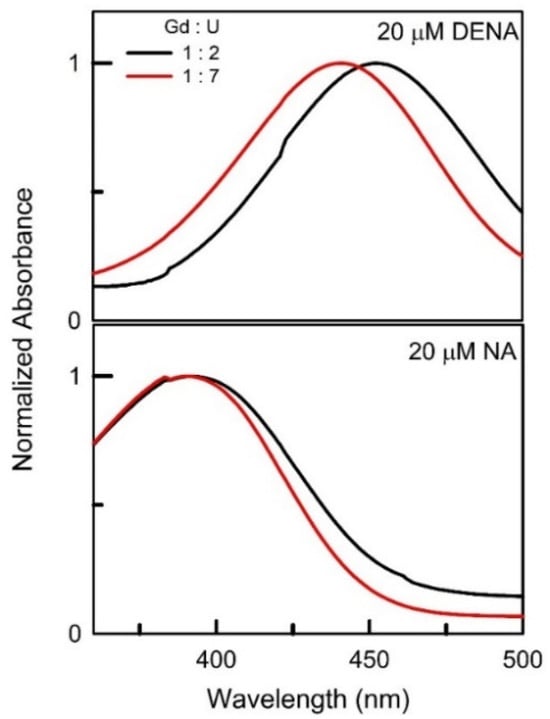
Figure 2.
Representative absorbance spectra of 20 ± 2 μM DENA and 20 ± 2 μM NA within DESs (Gd : U) at 1 : 2 and 1 : 7 molar ratios.
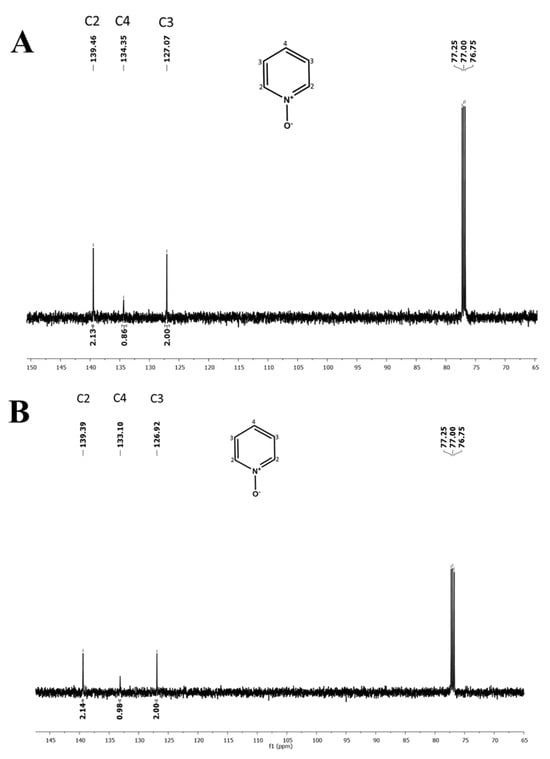
Figure 3.
Representative 13C NMR spectra of 250 ± 5 mM PyO within DESs (La : U) at 1 : 3 (A) and 1 : 7 (B) molar ratios.

Table 1.
Dipolarity/polarizability (π*) and HBA basicity (β) of (Ln : U)-based DESs at 298.15 K.

Table 2.
HBD acidity values (α’s), and , of (La : U) DESs at 298.15K.
There are two highly unusual aspects associated with these probe-reported empirical parameters that clearly emerge. First and foremost, the values of the polarity indicators, π* and , are exceptionally high—they are almost the highest reported for any solvent system (π* ranges from 1.50 to 1.70, and ranges from 1.29 to 1.42). In comparison, for choline chloride (ChCl)-based DESs, the reported π* is 1.23 for (ChCl : U :: 1 : 2) [11], 1.373 for (ChCl : citric acid :: 1 : 1) [25], and 1.406 for (ChCl : ZnCl2 :: 1 : 2) [25]. The highest π* for any DES that we could find in the literature is 1.671 for (betaine : citric acid :: 1 : 1) [25] under ambient conditions. Clearly, these (lanthanide salt : urea) based DESs offer exceptionally high dipolarity/polarizability, especially at compositions with a high metal salt content. This further manifests in the unprecedented high values [ of 1.42 for (La : U :: 1 : 3) is the highest, and we could not find comparable values for any solvent system in the literature]. The exceptionally high probe-reported polarity of these (lanthanide salt : urea) DESs can be effectively utilized in chemical synthesis and separation along with many other applications.
The second unusual aspect of the data is as follows: The decreases in π* and with an increasing relative amount of urea is easy to comprehend as urea, the neutral constituent, is increased, and lanthanide salt, the ionic constituent, is decreased. However, surprisingly, α shows a decrease and β shows an increase as the HBD constituent urea is increased (and HBA salt is decreased) within the DES system. This is tentatively attributed to the presence of hydrated water in the system, which contributes significantly to the HBD acidity, and as the relative amount of hydrated metal salt decreases, the α also decreases (while most of the urea is involved in the H-bonding interaction). A slight increase in β as the relative amount of urea is increased in the DES system appears to be a complex interplay of the interactions involving salt, hydrated water, and urea. Further experimentation in our research labs is ongoing to obtain insights into this observation. It is also noteworthy that for these DESs, the α values are fairly high [e.g., 1.77 for (La : U :: 1 : 3)], if not the highest [>2.00 for DESs constituted of (ChCl : D-sorbital :: 1 : 2), (ChCl : citric acid :: 1 : 1), (ChCl : lactic acid :: 1 : 1), (betaine : glycerol :: 1 : 2), (betaine : citric acid :: 1 : 1), and (betaine : urea :: 1 : 2)] [25]. Surprisingly, the β values of these lanthanide : urea DESs are significantly lower in comparison to those of other DES systems [among the reported β values of DESs, only (ChCl : urea : ethylene glycol :: 1 : 1 : 1) (β = 0.000), (ChCl : ethylene glycol : formamide :: 1 : 1 : 1) (β = 0.000), and (betaine : citric acid :: 1 : 1) (β = 0.012) exhibit such low H-bond accepting basicity] [25].
In order to corroborate these unusually high probe-reported polarities of lanthanide salt/urea DESs, we explored the behavior of judiciously selected fluorescence probes within these DESs. First, a wavelength-shift fluorescence probe pyrene-1-carboxaldehyde (PyCHO), which provides information about the “effective” dielectric constant (εeff) of solubilizing media [26], is used to assess the polarity of (lanthanide salt : urea) DESs. PyCHO exhibits a well-structured emission band in non-polar solvents, which becomes broad and structureless as polarity is increased [27]. The strong dependency of the PyCHO emission spectra on εeff is mirrored by a gradual bathochromic shift with an increase in εeff in the medium [26]. As expected, the emission spectra and band maxima of PyCHO in (lanthanide salt : urea) DESs presented in Figure 4 (the emission spectra for other DESs at all of the investigated compositions are presented in Figure S3) show a broad structureless band with a gradual bathochromic shift with a decrease in the amount of urea, suggesting an increasing polarity (or “effective” dielectric constant). More importantly, the emission band maxima of PyCHO in (lanthanide salt : urea) DES systems are in the range of 472–486 nm (Table 3), while for other hydrophilic ChCl-based DESs, the values lie in the 452–460 nm range [28]. The emission maxima for these DESs, particularly at a lower (Ln : U) molar ratio, are even higher than those reported in water (ca. 475 nm) [28], implying that the εeff value of these DES systems are higher than those of water. These outcomes clearly demonstrate the unusually high polarity surrounding the probe cybotactic region for PyCHO when dissolved in these type IV (Ln : U) DESs and corroborate the outcomes of the empirical polarity parameters discussed above.
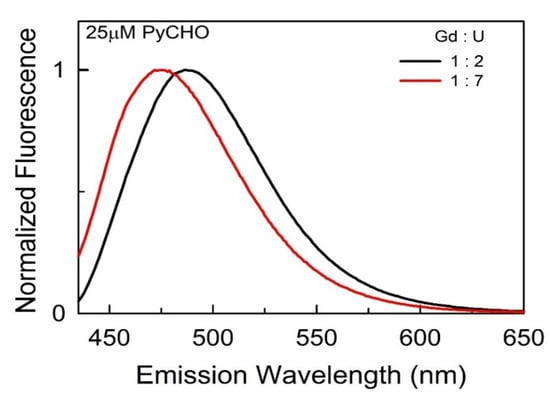
Figure 4.
Representative emission spectra of 25 ± 2 μM PyCHO ( within DESs (Gd : U) at 1 : 2 and 1 : 7 molar ratios.

Table 3.
Emission wavelength maxima ( of 25 ± 2 μM PyCHO in (Ln : U)-based DESs at 298.15 K.
Next, we used the popular fluorescent twisted intramolecular charge-transfer (TICT) probe 9-diethylamino-5-benzo[a]phenoxazinone, commonly called Nile red [29], which, due to its planer structure and poor solubility, is known to form aggregates in an aqueous (and highly polar) medium [29]. The fluorescence spectral response of Nile red reveals unique solute–solute interactions when solubilized in (lanthanide salt : urea) DESs. Most interestingly, the absorbance and excitation spectra of Nile red are different from each other; the excitation maxima of the probe, particularly for (Ce : U) and (Gd : U) DESs, are significantly hypsochromically shifted compared to the absorbance maxima (Figure S4 and Table 4), clearly implying probe aggregation within these DESs. Furthermore, the spectral maxima strongly depend on the composition of a given DES system (highlighted in Figure 5) compared to (Gd : U :: 1 : 2), and the absorbance and excitation maxima of Nile red in a (Gd : U :: 1 : 7) are significantly blue-shifted (~28 and ~25 nm, respectively). Overall, the unusual behavior of Nile red within these metal DESs indicates the formation of H-aggregates. The hypothesis of the formation of H-aggregates in DESs is further supported by the absence of the characteristic sharp bathochromically shifted emission spectra for the J-aggregates, indicating the Nile red aggregates formed within these DESs to be non-emissive H-aggregates [30]. The presence of aggregates was further confirmed using resonance light scattering (RLS). It was observed that with the increase in the concentration of Nile red, the intensity of the band at ca. 642 nm is increased in (Ln : U :: 1 : 7) DESs (Figure S5). The hydrophobic nature of Nile red and its poor solubility in water combined with π-π stacking interactions of the planar structure contribute to its aggregation to form non-emissive H-aggregates [29,31]. We believe the exceptionally high polarity of these DESs leads to the aggregation of Nile red in lanthanide salt + urea DESs. Finally, it is noteworthy that the emission maxima of Nile red vary from 658 nm to 677 nm in these DESs (Table 4), which is considerably bathochromic compared to other DESs, ionic liquids, and polar solvents (emission maxima ≤ 580 nm) [28,32]. This enormous difference in emission maxima could be a combined effect of the very high polarity of the (lanthanide salt : urea) DESs (leading to lower energy emission bands) and the fact that emission originates from the aggregates of the probe.

Table 4.
Absorbance ( 10 ± 1 μM), excitation ( 25 ± 2 μM), and emission ( 25 ± 2 μM) wavelength maxima of Nile red in (Ln : U)-based DESs at 298.15 K.
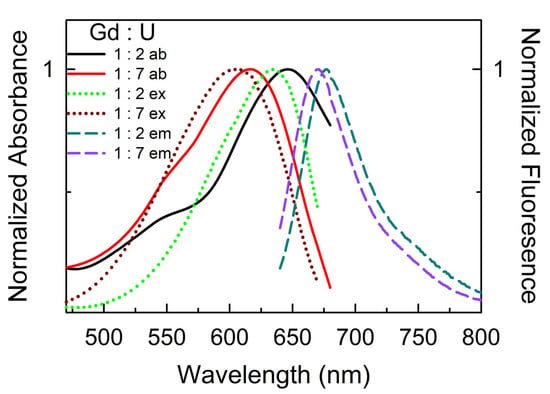
Figure 5.
Representative absorbance (ab, 10 ± 1 μM), excitation (ex, 25 ± 2 μM), and emission (em, 25 ± 2 μM) spectra of Nile red dissolved in DESs (Gd : U) at 1 : 2 and 1 : 7 molar ratios.
Finally, we used a popular amphiphilic fluorescence probe 8-hydroxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid (pyranine) [33], an arylsulfonate with an −OH group, and a planer aromatic ring that undergoes excited-state proton transfer (ESPT) depending on the environment of media [33]. This probe is highly sensitive to its cybotactic region, and depending on the polarity of the surrounding milieu, it can exist in two different forms, protonated (ROH) and deprotonated (RO¯) [34,35]. The emission spectra of pyranine in three (lanthanide salt : urea) DES systems are presented in Figure S6; representative spectra are shown in Figure 6. Based on the literature, the emission band with maxima appearing at 450 (±5) nm characterizing the excited protonated form (ROH*) is the dominant form when the relative amount of urea in the DES is smaller. However, increasing the amount of urea in our DES system results in the appearance of a shoulder at a long wavelength (ca. 515 nm), which is due to the emergence of the deprotonated form of pyranine (RO−*). The ESPT to the DES at higher relative urea amounts is further supported by the excited-state intensity decay [I(t)] measurements. The I(t) acquired at both 450 nm and 515 nm in all the investigated (Ln : U) DESs and the associated global fit decay parameters are reported in Table S2. Importantly, it is observed that at low urea concentrations, the decay fits best to a single exponential function at both wavelengths, implying the presence of only the ROH*, whereas at higher urea concentrations, the decay starts to show a better fit to a double exponential decay function, with one of the recovered pre-exponential factors being negative, implying that the process takes place after excitation. It has been reported earlier that pyranine readily undergoes ESPT in a methanol–urea mixture; as the urea amount is increased, more and more RO−* is formed [36]. The formation of UH+ is proposed to facilitate the deprotonation of pyranine in its excited state [36]. We believe an increase in the HBA basicity (β) of the media with an increasing urea is responsible for the enhanced deprotonation of pyranine as the urea is increased in the DES system. Clearly, the complex interplay of high polarity and the HBA basicity of (lanthanide salt : urea) DES systems controls the photophysical behavior of the probe pyranine.
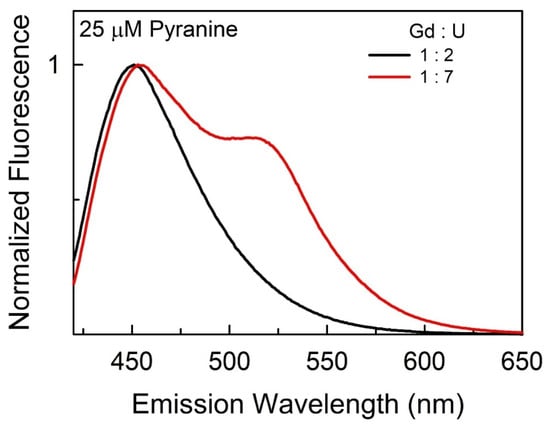
Figure 6.
Representative emission spectra of 25 ± 2 μM pyranine ( dissolved in DESs (Gd : U) at 1 : 2 and 1 : 7 molar ratios.
In order to obtain insights into the interactions between Ln salt and urea as the DES is formed in the absence of any external probe, the FTIR absorbance spectral signature of a representative DES (Gd : U :: 1 : 2) is compared with that of Gd(NO3)3.6H2O and urea, respectively (Figure 7 and Table S3 [37,38]). Significant shifts in the relevant band maxima of the Gd salt as well as urea upon the formation of DES corroborate the presence of strong interspecies interactions within the DES. These interactions appear to be responsible in affording the significantly high polarity to these DESs. In a seminal work, Edler’s group reported very high surface tension and density along with low viscosity and glass transition temperatures associated with similar DESs [39]. The existence of strongly bonded but fluxional oligomeric polyanions and polycations was put forth. It was stated that the excess of the molecular component in the DESs resulted in an intercalating H-bonded nanostructure possessing water and urea. It may be proposed that such structuring may result in a highly polar cybotactic region as exhibited by the optical probes.
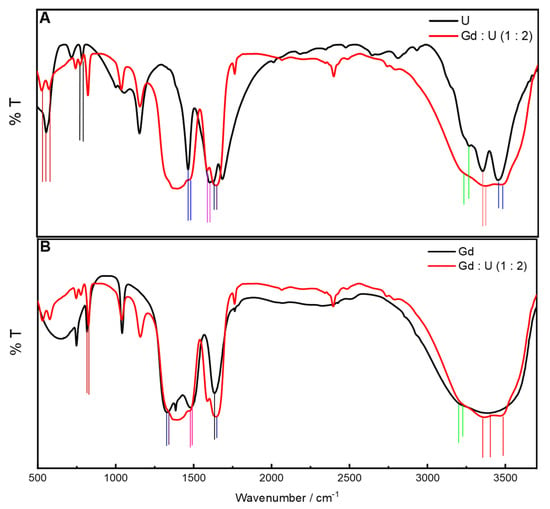
Figure 7.
FTIR absorbance spectra of urea (U, panel A), Gd(NO3)3.6H2O (Gd, panel B), and DES (Gd : U :: at 1 : 2) (panels A and B), respectively, under ambient conditions. Vertical lines represent shift in maxima when going from neat constituent to DES.
4. Conclusions
We reported our findings that DESs composed of lanthanide salt + urea exhibit polarity (via empirical dipolarity/polarizability, π*, and/or parameters, emission maxima of PyCHO, aggregation by Nile red, and prototropism by pyranine) that is higher than that of any reported solvent system in the literature, especially for lanthanide salt-rich DES systems. The unusually high polarity of these DESs is attributed to lanthanide salt as well as the hydrated water of the salt. The polarity can be effectively tuned by varying the relative amount of lanthanide salt and urea within the DES. The hydrated water of the salt, obtained via controlling H-bonding, plays a decisive role in controlling the HBD acidity, α, and HBA basicity, β, as the composition of the DES, i.e., the lanthanide salt-to-urea ratio, is changed. These DES systems open new avenues of applications where high cybotactic region polarity is desired.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/liquids4030028/s1, Figure S1: Absorbance spectra of 20 ± 2 μM DENA and 20 ± 2 μM NA dissolved in Ln:U-based DESs at room temperature; Figure S2: 13C NMR spectra of 250 ± 5 mM PyO within La : U at 1 : 4 (Panel A), 1 : 5 (Panel B), and 1 : 6 (Panel C) molar ratios; Figure S3: Fluorescence emission spectra of 25 ± 2 μm PyCHO ( dissolved in Ln : U-based DESs at room temperature; Figure S4: Absorbance spectra of 10 ± 1 μM Nile red and fluorescence excitation spectra of 25 ± 2 μM Nile red dissolved in Ce : U-based (panel A) and Gd : U-based (panel B) DESs at room temperature; Figure S5: RLS spectra of Nile red with variation in concentration dissolved in Ln : U-based (1 : 7) DESs at room temperature. Figure S6: Emission spectra of 25 ± 2 μM pyranine ( dissolved in Ln : U-based DESs at room temperature; Table S1: Absorbance wavelength (/nm) of 20 ± 2 μM DENA and 20 ± 2 μM NA dissolved in Ln : U-based deep eutectic solvent at room temperature. Table S2: Recovered excited-state intensity decay parameters for pyranine (= 450 nm, 515 nm; excitation with 404 nm violet laser diode) dissolved in Ln : U-based DES at room temperature by using global fit; Table S3: FTIR absorbance band maxima of urea, Gd(NO3)3.6H2O, and DES (Gd : U) at 1 : 2 molar ratios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization, Writing—Original Draft, and Data Collection, A.P.; Data Collection, V.K.; Writing—Review and Editing, Supervision, Resources, and Project Administration, S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was generously funded by the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, EMR-II (CSIR-EMR-II), GoI through a grant to Siddharth Pandey [grant number 01(3043)/21/ EMR-II]. The authors gratefully acknowledge the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), GoI for providing funding [grant no. CRG/2021/000602] for the UV-vis spectrophotometer. We would also like to thank the Central Research Facility at IIT Delhi for providing the NMR measurements.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
Anushis Patra would like to acknowledge the Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Government of India for his Senior Research Fellowship (SRF).
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, D.V.; Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Sustainable Media for Nanoscale and Functional Materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: Properties, Applications, and Perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbous, Y.P.; Hayyan, M.; Hayyan, A.; Wong, W.F.; Hashim, M.A.; Looi, C.Y. Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Biotechnology and Bioengineering—Promises and Challenges. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 105–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Syntheses, Properties and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents—Solvents for the 21st Century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal-Abidin, M.H.; Hayyan, M.; Ngoh, G.C.; Wong, W.F. Doxorubicin Loading on Functional Graphene as a Promising Nanocarrier Using Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent Systems. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 1656–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruesgas-Ramón, M.; Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Durand, E. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) for Phenolic Compounds Extraction: Overview, Challenges, and Opportunities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Dietz, C.H.J.T.; Warrag, S.E.E.; Kroon, M.C. The Curious Case of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Story on the Discovery, Design, and Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 10591–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.C.; Mecerreyes, D. Emerging Ionic Soft Materials Based on Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 8465–8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Pandey, S. Solvatochromic Probe Behavior within Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Effect of Temperature and Water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 14652–14661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Su, E. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: The New Generation of Green Solvents for Diversified and Colorful Applications in Green Chemistry. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.Q.; Abbasi, N.M.; Anderson, J.L. Deep Eutectic Solvents in Separations: Methods of Preparation, Polarity, and Applications in Extractions and Capillary Electrochromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1633, 461613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khokhar, V.; Dhingra, D.; Pandey, S. Effect of Temperature and Composition on Density and Dynamic Viscosity of (Lanthanide Metal Salts + Urea) Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Tahir, S.; Khalid, A.R.; Hanif, M.A.; Abbas, Q.; Zahid, M. Breaking New Grounds: Metal Salts Based-Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Applications- a Comprehensive Review. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 2421–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Liu, Y.; Meng, J.; Cheng, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, H. Multiple Hydrogen Bond Coordination in Three-Constituent Deep Eutectic Solvents Enhances Lignin Fractionation from Biomass. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 2711–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Meng, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, S.; Wang, L.; Xia, Q.; Yu, H. Room Temperature Dissolving Cellulose with a Metal Salt Hydrate-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 272, 118473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, D.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Fang, G.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y. Selective Degradation of Hemicellulose and Lignin for Improving Enzymolysis Efficiency via Pretreatment Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 376, 128937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Sun, C.; Hu, Y.; Xia, C.; Sun, F.; Zhang, Z. Reaction Characteristics of Metal-Salt Coordinated Deep Eutectic Solvents during Lignocellulosic Pretreatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, V.; Kumar, M.; Pandey, S. Pyrene Aggregation at Unprecedented Low Concentrations in (Lanthanide Metal Salt + Urea) Deep Eutectic Solvents. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Abboud, J.L.; Taft, R.W. The Solvatochromic Comparison Method. 6. The π* Scale of Solvent Polarities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 6027–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, P.P.; Passos, H.; Gomes, J.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Alternative Probe for the Determination of the Hydrogen-Bond Acidity of Ionic Liquids and Their Aqueous Solutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 11011–11016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Taft, R.W. The Solvatochromic Comparison Method. I. The β-Scale of Solvent Hydrogen-Bond Acceptor (HBA) Basicities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, H.D.; Badrieh, Y.; Migron, Y.; Marcus, Y. Hydrogen Bond Donation Properties of Organic Solvents and Their Aqueous Mixtures from 13C NMR Data of Pyridine-N-Oxide. Z. Phys. Chem. 1992, 177, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojeicchowski, J.P.; Abranches, D.O.; Ferreira, A.M.; Mafra, M.R.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Using COSMO-RS to Predict Solvatochromic Parameters for Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 10240–10249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanasundaram, K.; Thomas, J.K. Solvent-Dependent Fluorescence of Pyrene-3-carboxaldehyde and Its Applications in the Estimation of Polarity at Micelle-Water Interfaces. J. Phys. Chem. 1977, 81, 2176–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, K.W.; Acree, W.E. Estimation of the Effective Dielectric Constant of Cyclodextrin Cavities Based on the Fluorescence Properties of Pyrene-3-Carboxaldehyde. Appl Spectrosc 1988, 42, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Rai, R.; Pal, M.; Pandey, S. How Polar Are Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.K.; Kamada, K.; Ohta, K. Spectroscopic Studies of Nile Red in Organic Solvents and Polymers. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1996, 93, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniasih, I.N.; Liang, H.; Mohr, P.C.; Khot, G.; Rabe, J.P.; Mohr, A. Nile Red Dye in Aqueous Surfactant and Micellar Solution. Langmuir 2015, 31, 2639–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Behera, R.K.; Behera, P.K.; Mishra, B.K.; Behera, G.B. Cyanines during the 1990s: A Review. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 1973–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspan, P.; Fowler, S.D. Spectrofluorometric Studies of the Lipid Probe, Nile Red. J. Lipid Res. 1985, 26, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolbert, L.M.; Solntsev, K.M. Excited-State Proton Transfer: From Constrained Systems to “Super” Photoacids to Superfast Proton Transfer. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, J.F.; Wyatt, P.A.H. Acid-Base Properties of Electronically Excited States of Organic Molecules. Adv. Phys. Org. Chem. 1976, 12, 131–221. [Google Scholar]
- Förster, T. Primary Photophysical Processes. Pure Appl. Chem. 1973, 34, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htun, T. Excited-State Proton Transfer in Nonaqueous Solvent. J. Fluoresc. 2003, 13, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdadolnik, J.; Maréchal, Y. Urea and Urea–Water Solutions—An Infrared Study. J. Mol. Struct. 2002, 615, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.L.; Irish, D.E. Interactions in Lanthanide Systems. I. A Raman and Infrared Study of Aqueous Gadolinium Nitrate. J. Chem. Phys. 1971, 54, 4479–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, O.S.; Bowron, D.T.; Edler, K.J. Structure and Properties of “Type IV” Lanthanide Nitrate Hydrate:Urea Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 4932–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).