Abstract
Microorganisms such as methanogenic archaea play a key role in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) by breaking down organic matter and pollutants and producing methane, a potential renewable energy source. However, sulphate-reducing bacteria (SRB) compete with archaea for the same substrates under anaerobic conditions, lowering methane production and generating harmful hydrogen sulphide (H2S). Inhibiting SRB is therefore crucial to enhance methane yield and reduce toxic by-products. By means of manual screening of public databases (KEGG, BRENDA, PDB, PubChem) 12 potential inhibitors of SRB were found. After computational ecotoxicological assessment, four candidates were selected, and one of them experimentally increased methane production, demonstrating that SRB inhibition favours the anaerobic digestion of sludges. In order to further explore new candidates, Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship (QSAR) models were developed showing reliable predictive performance. These models enabled the virtual screening of COCONUT, a natural product database, identifying 73 potential SRB inhibitors. After an ecotoxicological assessment, five commercially available compounds remained. The identified candidates may reduce competition between SRB and methanogenic archaea, leading to higher methane production and supporting WWTPs in generating their own biogas. This would contribute to a circular economy and help mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
1. Introduction
Safe and clean water is one of the most basic human needs worldwide [1]. However, as the world population increases, water pollution is becoming a challenge for wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), due to the energy demands and the efficient treatment required to clean the effluents.
WWTPs perform at least two types of treatments: primary and secondary. The first one removes big floating objects, while the second treatment, led by microorganisms, eliminates inorganic and organic matter from wastewater. All these processes produce biosolids named sludge that must be treated. Wastewater treatment involves high energy consumption; for instance, in Europe, the overall WWTP’s electric use represents 0.8% of the total energy generated [2].
Anaerobic digestion of sludges removes pathogens and stabilises biosolids from wastewater treatments and has a very important role in the technical and economic management of WWTPs because it valorises volatile solids, generating methane-rich biogas, a renewable energy source. Anaerobic digestion stands out for its low energy demand and efficiency in processing the sewage sludge in comparison with other commonly used technologies in WWTPs [3]. Anaerobic digestion is a complex process (Figure 1A) resulting from a synergistic relationship between hydrolytic, fermentative acidogenic, and acetogenic bacteria and methanogens. Microorganisms collaborate to sequentially process the organic matter into acetate, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen. Then, methanogens take these substrates and generate methane, a potential source of energy [4].
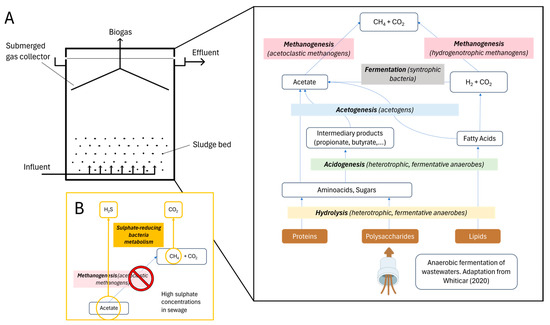
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the microbial consortium participating in anaerobic digestion. (A) Reactions occurring in the anaerobic tanks, adapted diagram adapted from Whiticar (2020) [5]. (B) SRB competence for the methanogenic substrate.
Generally, domestic wastewaters contain sulphate concentrations below 250 mg/L [6]; however, in some cases, the levels are higher due to industrial or natural factors, e.g., dyes or pharmaceuticals production, seawater intrusions, or soil composition [7,8]. The presence of high levels of sulphate leads to the competence of sulphate-reducing bacteria (SRB) with methanogens for the available substrates [9]. This phenomenon has been studied in nature [10,11], anaerobic tanks [9], and the human intestine [12]. In turn, the hydrogen sulphide (H2S), which is the final product of the sulphate-reducing metabolism, is detrimental to methanogens and other microbial species involved in anaerobic digestion (Figure 1B) [9,13,14]. This competition eventually results in a lower production of methane and a decrease in the efficiency of the organic processing that takes place in the anaerobic tanks. In addition, the H2S produced by SRB results in iron and steel corrosion [15] and represents a potential risk to human health and the environment, causing eye and respiratory irritation and being one of the causes of acid rain [16].
Co-digestion refers to the simultaneous digestion of two or more substrates to improve the economic viability of anaerobic digestion plants due to increased methane production. In the case of WWTPs, the sludge produced can be co-digested with agri-food waste to increase biogas production, maximising the existing facilities for anaerobic digestion and bringing additional organisational and economic benefits, besides the energy balance, for an environmentally friendly treatment of agri-food waste. This makes good use of existing infrastructures and substantially improves the energy balance of a WWTP, maximising renewable energy production as a step towards energy self-sufficiency and ultimately carbon neutrality [17]. However, a major challenge lies in the nature of many agri-food wastes, especially those with high protein content, as they often contain elevated concentrations of sulphates. This can promote sulphate-reducing metabolic pathways, increasing the activity of SRB, which compete with methanogens and produce H2S. Therefore, it is crucial for the proper management of co-digestion to monitor and properly manage sulphate levels in the digestion and co-digestion processes [18,19].
In addition, considering the global status of the climate crisis, novel approaches to optimise and improve energy efficiency are key in the endeavours to reduce industrial carbon footprints [20,21]. Circular economy strategies can align economic growth with the goal of reducing dependence on non-sustainable energy sources [22]. WWTPs play a central role in harnessing energy resources from wastewater, contributing to the efficient design of circular cities that could eventually mitigate the effects of climate change [21]. For instance, the recovery of chemical, hydraulic, and thermal energies from wastewater improves energy efficiency and reduces the environmental impacts caused by conventional treatment systems. Depending on the level of recovery, it could just supply energy to the WWTPs themselves or even the neighbourhood. However, the lack of public policies related to energy efficiency and government support is hindering this transformation [23]. Additionally, processed sludge offers a more sustainable way to produce fertilisers [24]. These examples represent some of the achievable measures in circular cities.
Prior to this work, some studies have focused on the issues caused by SRB such as oil, gas, and iron corrosion, resulting in emissions of H2S [15,25]. This gas, along with other sulphur species, is noxious to the environment and to human health [16]. Nevertheless, they remain key players in biogeochemical and biotechnological processes, for instance, the biomining of heavy metals or the bioremediation of sulphate-rich wastewaters [4,26]. Conventional SRB inhibitors, such as formaldehyde or antibiotics, could result in a bigger environmental issue due to the potential of SRB to develop resistance to these compounds. Alternative strategies have aimed to limit sulphate bioavailability by adding metallic salts, particularly iron salts. This is the solution traditionally used, as metallic salts were once relatively cheap; however, their cost is increasing and they have the disadvantage of adding metals to the digested sludge, which could affect the viability of their application as agricultural fertiliser. They are also hazardous substances due to their corrosiveness, which pose a risk to people during transport and handling. Other metallic salts, such as zinc and copper sulphide, have shown potent inhibitory activities against SRB [27]; however, they might affect the methanogenic archaea growth [28,29] or even disrupt the sludge structure and affect other phases of the consortium [30]. Additionally, molybdenum is an essential trace metallic atom present in different SRB enzymes. However, at high concentrations it is toxic to these bacteria, due to the inhibition of key proteins of their metabolism [31]. Therefore, the use of specific inhibitors is an optimal and efficient approach to tackle SRB growth in WWTPs. Exploration of endogenous ligands and their derivatives, as previously studied, can be a valid approach to identify novel inhibitors [32,33].
It has been described that SRB metabolism can be inhibited using chemical analogues of the endogenous ligands, such as sulphate, adenosine-5′-phosphosulphate (APS), and sulphite, which compete with the enzymatic activities, decreasing SRB growth [34]. Moreover, novel compounds with anti-SRB activities have been characterised, such as the synthetic diquaternary Schiff bases [35], but also, some natural products have an anti-SRB effect, as shown in the case of the lemongrass essential oil [36] or antimicrobial substances generated by fungi [37].
In summary, the endeavours in the field of SRB inhibition have focused solely on studying SRB without considering their effect on the methanogenic population and the quality of the sludge. Our aim is to consider the identification of SRB inhibitors that do not affect other populations present in the sludge. In this context, identifying novel bioactive compounds is a slow and expensive process that requires a huge experimentation effort in conventional laboratories. Computer-aided drug design methodologies are able to accelerate the discovery process, saving time and money by reducing experimentation on inactive compounds [38]. Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship (QSAR) is a widely used computational technique that allows to predict biological activities from a set of calculated descriptors that encode the chemical structures of the molecules. Therefore, QSARs need a training set of molecules with experimental data of the studied activity as well as the corresponding molecular structures. After cleaning and processing, the model is generated, choosing an algorithm that will fit the data. Once the model is generated, it can be applied to another set of molecules with unknown biological activities [38,39,40]. The potential of this technique has enabled the development of diverse models generated to identify novel antimicrobials, many of which were built from relevant specific chemical families [41,42], even peptides [43,44,45].
Herein, the use of computational approaches (a database search-driven approach and a virtual screening based on two QSAR models) to study potential SRB inhibitors to overcome the methanogenic competence in anaerobic digestors was proposed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of Candidate Compounds with SRB Inhibitory Potential
In order to identify the target SRB enzymes, a database search-driven approach was implemented, consisting of the combination of the information obtained from different sources to identify potential SRB inhibitors, as shown in Figure 2A.
2.1.1. Database Search-Driven Strategy
In order to identify specific targets for SRB, the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) PATHWAY Database (https://www.genome.jp/kegg/ accessed on 17 June 2023) [46], was employed, which contained around 10,000 genomes from different organisms, of which about 8000 are bacterial and 400 archaeal. The number of bacterial genomes currently stands at 9591, while the number of archaea genomes is 453. Then, the metabolic maps were tagged with a three-letter taxonomic identifier [47] before the selection of a single microorganism to represent the metabolic family of SRB and methanogens. To simplify this problem, two species were selected based on their presence in mesothermic and anaerobic conditions among the available organisms on KEGG. Thus, Methanosarcina acetivorans (KEGG organism prefix ‘mac’) and Desulfovibrio vulgaris strain Hildenborough (KEGG organism prefix ‘dvu’) were selected as representative methanogenic archaeon and sulphate-reducing bacterium, respectively. M. acetivorans is a metabolically versatile methanogenic archaeon able to use different substrates (acetate, methanol, methylamines or H2/CO2), thriving in varying environmental conditions and dominating under high organic loads [48]. In contrast, D. vulgaris is commonly used as a bacterial model to study sulphur metabolism. It reduces sulphate to hydrogen sulphide using lactate or H2/CO2 as electron donor, thus competing with methanogens for the substrates in WWTPs [49,50].
Then, the KEGG browser was employed to look for the sulphur pathway in D. vulgaris (with KEGG ID ‘dvu00920’) and in M. acetivorans (with KEGG ID ‘mac00920’). Both pathways were visualised and compared to identify the SRB-specific enzymes. Those enzymes that were absent in the methanogenic metabolism were selected as targets for further study.
Then, the following strategies were taken to select the SRB inhibitors: endogenous ligands of the target enzymes and other reported binding molecules were detected from (a) the Protein Data Bank (PDB) (https://www.rcsb.org/, accessed on 7 June 2023) [51] and (b) the Braunschweig Enzyme Database (BRENDA) (https://www.brenda-enzymes.org/, accessed on 15 March 2022) [52]. This way, common molecules between these enzymes could be found. In addition, PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 15 March 2022) [53] was also explored (c) to identify experimental data on SRB metabolism inhibition. Finally, the literature was reviewed (d) through the PubMed browser tool (PubMed, 2004; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 25 March 2024) using keywords such as ‘SRB inhibition’, the enzyme names, or ‘sulphur reduction’.
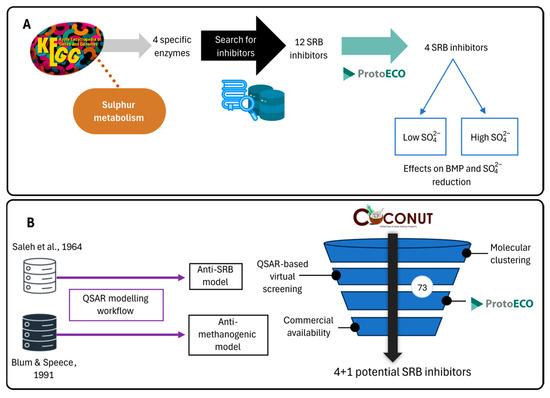
Figure 2.
Scheme of the workflow of the project. (A) Database search-driven approach and (B) QSAR models generation with data available from Salet et al. (1964) and Blum & Speece (1991) [54,55] and COCONUT screening.
2.1.2. QSAR Models Development
Following the workflow presented in Figure 2, the second approach was undertaken: QSAR-based virtual screening (Figure 2B).
Data Collection and Curation
After searching on PubMed and other literature databases, two research articles compiling inhibitory activities of 205 molecules against SRB (expressed in µg/mL) [54] and 128 against methanogenic archaea (expressed in µM) [55] were selected.
Datasets were then cleaned using an in-house Python (v3.9.18) (Python Software Foundation, https://www.python.org/, accessed on 23 September 2022) script, developed by ProtoQSAR, that removes inorganic and organometallic compounds, molecules with ‘forbidden’ atoms (those different to H, C, N, O, P, S, Si, F, Cl, Br, and I), and the counterions of the corresponding salts. Moreover, for the repeated molecules, if the standardised standard deviation of the experimental values was higher than 0.2, molecules were discarded; otherwise, the mean was calculated. Next, the units of the two activity datasets were transformed into pIC50, which is the negative logarithm of the Half Maximum Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) (nM) ().
Descriptors Calculation
Molecular descriptors are numerical representations of the composition and physicochemical properties of the encoded chemical structure. A total of 4678 descriptors (available groups of molecular descriptors presented in Table 1) were calculated using an in-house developed script written in Python. It calculates descriptors from RDKit (v2021.03.2) [56] and Mordred (v1.2.0) [57] packages, as well as descriptors described by Todeschini and Consonni [58].

Table 1.
List of the molecular descriptors categories calculated by WOTAN.
All the descriptors were subjected to an unsupervised feature reduction step to remove: (i) constant, infinite, and non-calculated values, and (ii) highly correlated values (considering correlation coefficients higher than 0.90). Also, the descriptors with empty values in more than 15% of the molecules were removed, and the rest of the empty values were calculated through k-Nearest Neighbours (kNNs). Afterwards, the molecular descriptors were standardised using the Standard Scaler approach implemented in Sci-Kit learn (v1.0.2) [59].
Train/Validation Sets Splitting
After the first step of the molecular descriptors feature reduction, the curated entry dataset for the anti-methanogenic model was split into two groups: the train set (TS) and the validation set (VS). This method is commonly known as the holdout technique. The proportion of molecules assigned to each group was 3:1 for the TS and VS, respectively.
In the case of the sulphate-reducing bacteria model, the whole dataset was used to develop the model through 5-fold cross-validation (5-CV), due to the lack of sufficient data to build a valid model through the holdout method and ensure enough predictivity at the same time. In this method, the dataset is divided randomly into five groups; one of those groups is used as the test set, and the model is trained with the remaining four groups. This process is repeated five times, and the metrics are averaged.
Feature Selection and Model Generation
Three different algorithms to select the most relevant set of descriptors to model the data using an own developed pipeline were evaluated: Recursive Feature Elimination [60], Feature importance [61], and Permutation Importance [62].
For model generation, a total of sixteen regression machine learning algorithms available in Python were tested in order to find the most appropriate model, including linear models (Linear regression, Ridge, Lasso, etc.), Supported Vector Machine models (Supported Vector Regression, Nu Support Vector Regression), Tree models (Random Forest, Extra Trees, etc.), and others (Ada Boost Regression, Light Gradient-Boosting Machine, kNN, etc.).
Model Evaluation
To evaluate the models, the correlation coefficient (R2), Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Mean Square Error (MSE) were calculated (Equations (1)–(3)), and a 10-fold cross-validation (10-CV) was applied to evaluate the performance of the models [63].
where n = number of values; yi = observed value for the ith data point = predicted value for the ith data point; and = mean of the y values.
Applicability Domain (AD) Assessment
Three different methods were used to calculate the AD of the models: Tanimoto coefficient, Euclidean distance, and leverage. A molecule is considered to be within the AD of the model if it is inside by at least one of those methods. The Jaccard–Tanimoto coefficient measures the structural similarity of two molecules by calculating a set of fingerprints (the MACCS fingerprints in our case) for each compound and comparing them. The coefficient ranges from 0 to 1, with values closer to 1 indicating greater similarity. Following the recommendations for random MACCS fingerprints [64], a threshold of 0.528 was applied. Compounds with similarity values above this threshold relative to any molecule in the TS are considered to be within the AD. The Euclidean distance is a measure of the length of the vector between two points within a given space. Pairwise Euclidean distances between all molecules in the training set are calculated, and the threshold value is set by the maximum distance within this set. A molecule is considered to fall within the AD if its maximum distance from any training point is less than or equal to the defined threshold [65]. Finally, the leverage method uses the distance to the structural centroid of the TS to assess whether a molecule falls within the AD [66]. The leverage value for each substance is determined by the number of descriptors (p) and the number of substances in the TS (n), and the threshold value to consider a target substance inside the AD is defined by 3·(p/n) [67].
2.2. Integration on a Web-Based Server
The models were integrated onto the ChemoPredictionSuite website (https://chemopredictionsuite.com, accessed on 1 October 2025), a web-based server formed by different predictive modules, using Django framework (v2.1.5.) [68].
2.3. COCONUT Virtual Screening
The COlleCtion of Open Natural prodUcTs (COCONUT) gathers around 400,000 natural products, making it the only available database with such a level of data (https://coconut.naturalproducts.net/, accessed on 4 April 2022) [69].
This database was chosen to perform the screening and obtain predictions of anti-SRB and anti-methanogenic activities. The database was processed to make it easier to work with it and accelerate the later screening. This reduction consisted of a similarity-based clustering that finally resulted in the most varied compounds. First, to identify each compound, MACCS fingerprints were calculated using RDKit (v2021.03.2). Later, the clustering of the molecules was performed using the density-based OPTICS (Ordering Points To Identify the Clustering Structure) method with the Jaccard index as the metric to evaluate molecular similarity, implemented in Scikit-learn. This process resulted in 43,338 structurally varied molecules to perform the virtual screening.
Once the predictions were obtained, the AD was evaluated (see the corresponding Materials and Methods, Section 2) in both QSAR models for each molecule predicted by using three different methods: Euclidean distance, Tanimoto index, and leverages. Those outside the AD were discarded, retaining only reliable data. Then, a threshold of IC50 ≤ 5 mM was used as a positivity criterion (i.e., molecules with concentrations below the threshold were considered as “positives” and the rest as “negatives”). The molecules predicted as toxic (predicted IC50 ≤ 5 mM) for SRB and non-toxic (predicted IC50 > 5 mM) for methanogenic archaea were selected.
2.4. Ecotoxicological Predictions
To ensure the environmental safety of the potential candidates of SRB inhibition, from both approaches (database search and QSAR-based virtual screening), ecotoxicological predictions were performed on them using the activated sludge respiration inhibition model of the ProtoPRED module called ‘ProtoECO’ (https://protopred.protoqsar.com/ProtoECO_info, accessed on 20 January 2025). Technical details can be consulted on the corresponding QMRF, containing the QSAR model metrics, the confusion matrix, and further information (https://protopred.protoqsar.com/static/brochures/ProtoECO_sludge_inhibition_brochure.pdf, accessed on 1 October 2025).
2.5. Experimental Evaluation of the Effects of the Selected Anti-SRB Candidates on Methane
Once the compounds that had an inhibitory capacity against SRB but were safe for methane-producing microorganisms had been selected, assays were conducted to determine their effect on both metabolic pathways. For this purpose, biomethanation tests were performed in the presence of a biodegradable substrate and with an excess of the electron acceptor SO42− to promote sulphate reduction.
To further evaluate the effect of the anti-SRB compounds, the sludge was characterised by analysing pH, conductivity, dry matter, volatile matter, chemical oxygen demand (COD), total, partial and intermediate alkalinity, acidity, sulphate, and iron. All parameters were determined according to the Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater [70].
Biochemical methane potential (BMP) assays were carried out under mesophilic conditions (35 ± 1 °C) for 200 h, considering two time windows, by using the AMPTS II system (Bioprocess Control, Lund, Sweden) equipped with 500 mL glass reactors and a gas flowmeter and a CO2 trap, following the procedure described by Angelidaki et al. [71]. The inoculum consisted of anaerobic sludge collected from a wastewater treatment plant full-scale digester. A substrate-to-inoculum ratio (S/I) of 0.50 g VSsubstrate/g VSinoculum was selected, corresponding to the addition of 0.55 g of volatile solids, to ensure sufficient methanogenic activity and to avoid overload or intermediate accumulation, while remaining within the recommended range for anaerobic biodegradability assays. The biogas produced was passed through a CO2 trap prior to volume measurement so that the recorded gas corresponded only to methane. Reactors were operated with intermittent mixing at 80% intensity, applying cycles of 500 s stirring followed by 30 s pauses, with direction reversal at each cycle to promote homogeneous conditions. All conditions were performed in triplicate. To see the effect of sulphate reduction on methanogenesis, methane production was monitored for 48 h, and results were expressed as CH4 volume at standard conditions (0 °C, 1 atm) per unit of volatile solids added (mL CH4/g VS). First, methane production was evaluated at 40 h, since previous studies have shown that the majority of hydrogen sulphide is generated during the first 24–48 h of anaerobic digestion [72,73]. These values enabled the early effect of each inhibitor on sulphate reduction to be detected. The assays were then maintained until the instantaneous methane production rate dropped below 0.1 Nml/min, a condition reached after 200 h in all replicates, which allowed the potential cumulative toxicity on the methanogenic biomass to be assessed [74]. The tests were considered complete when the instantaneous methane production of each sample equalled that of the control. Subsequently, stability parameters, including dry matter (%DM), volatile matter (%VM), total, partial, and intermediate alkalinity, and their ratios, were analysed to confirm adequate degradation and to assess process stability in anaerobic digestion [75]. Theoretical maximum methane production based on the COD load was also indicated. The stoichiometric relationship between COD removal and methane generation has been well established, with 1 g of COD destroyed corresponding to approximately 0.35 L CH4 at standard temperature and pressure (STP) [76].
In total, six experimental conditions were assessed. First, a control was established in triplicate, in which the inoculum was fed only with sludge; this blank was considered the reference for maximum methane production. A second blank included the addition of sulphate as an electron acceptor to stimulate SRB activity and evaluate its impact on methanogenic performance. The difference between both blanks reflects the effect of sulphate reduction, as it has been reported that SRB outcompete methanogens under non-limiting sulphate concentrations due to their kinetic and thermodynamic advantages [72,74,77,78]. Conversely, in low-sulphate environments, methanogens tend to dominate.
Finally, the four selected compounds were tested, also in triplicate, by adding a single dose of each inhibitor in the presence of sludge and sulphate. Table 2 summarises the experimental conditions applied in each replicate. In summary, three groups of experimental conditions were evaluated, all in triplicate: (i) a blank without sulphate (representing the maximum methanogenic potential), (ii) a blank with sulphate (representing methanogenic potential under SRB competition), and (iii) individual assays with sulphate and one inhibitor. Reported values correspond to the mean of the replicates.

Table 2.
Outline of the experimental approach for the validation of the reagents under study. Each condition is performed in triplicate with a theoretical maximum BMP (based on COD) of 220 Nm3/kg and an organic load of 0.945 g.
2.6. Statistical Analysis of the Experimental Results
Methane production accumulated was analysed across treatments using two-sided Welch’s t-tests versus the sulphate-supplemented control (Sludge+ SO42−). To control the family-wise error rate, Holm correction was applied to p-values from all pairwise comparisons. Data are reported as means and deviation. Confidence intervals of 95% and Cohen’s d are provided to convey uncertainty and effect size. This uniform procedure was applied identically to all treatments.
Statistical analyses were performed in Python (v3.11) using pandas, SciPy, and statsmodels libraries. Data processing, normalisation, and statistical testing scripts were developed specifically for this study to ensure full reproducibility.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of SRB-Specific Enzymes
Different strategies were used (as showed in Figure 2) to find relevant candidate molecules.
As a first result, four different candidate enzymes were found: ATPs (Adenosine triphosphate sulfurylase, EC 2.7.7.4); APSr (Adenosine phosphosulphate reductase, EC 1.8.99.2); cysC/APSK (Adenosine phosphosulphate kinase, EC 2.7.1.25); and DSR (Dissimilatory sulphite reductase, EC 1.8.99.5; formerly named desulphorubidine, EC 1.8.99.3) (Figure 3). These four enzymes were selected as the target of our study to inhibit the sulphate-reducing activity.
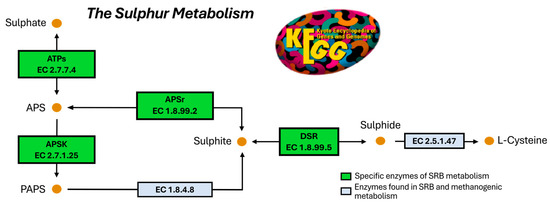
Figure 3.
Scheme of the sulphur metabolism KEGG reference pathway map diagram, coloured to represent the specific SRB-enzymes (in green) and the enzymes found in both SRB and methanogenic metabolisms (in light blue). The arrows represent the different reactions (a double-headed arrow denotes a reversible reaction) catalysed by the represented enzymes. ATPs (Adenosine triphosphate sulfurylase), APSr (Adenosine phosphosulphate reductase), cysC/APSK (Adenosine phosphosulphate kinase), and DSR (Dissimilatory sulphite reductase).
3.2. Identification of SRB-Specific Inhibitors
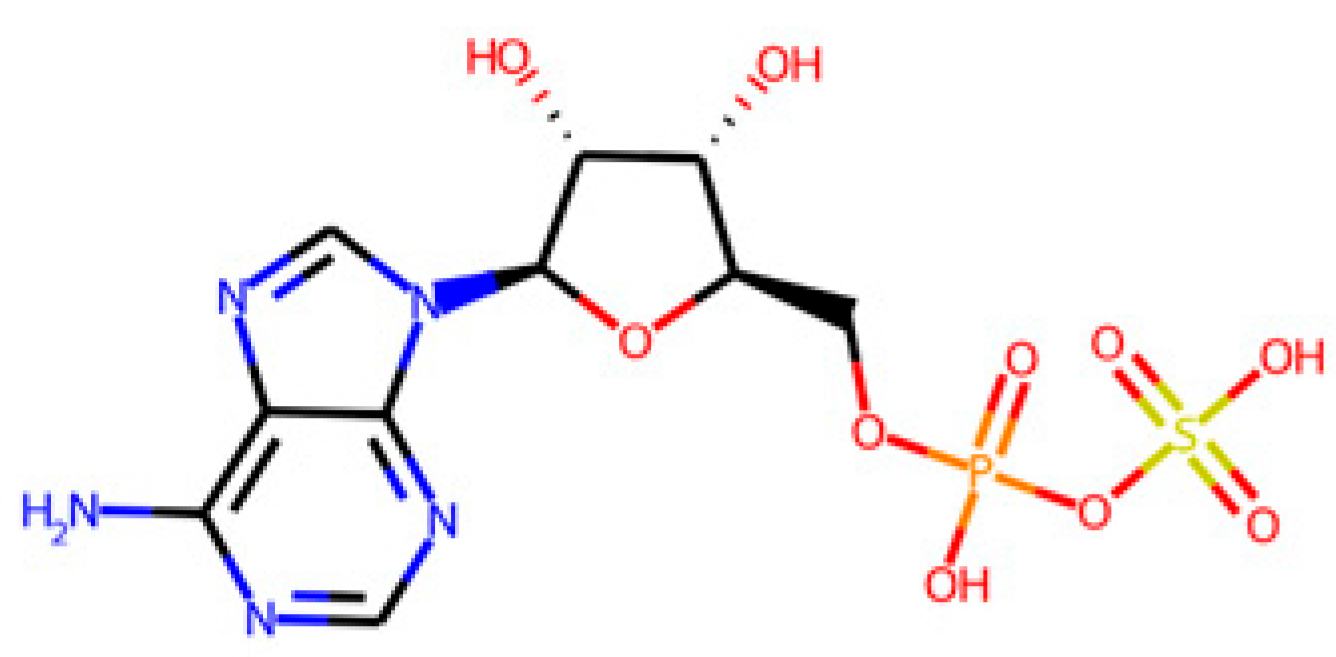
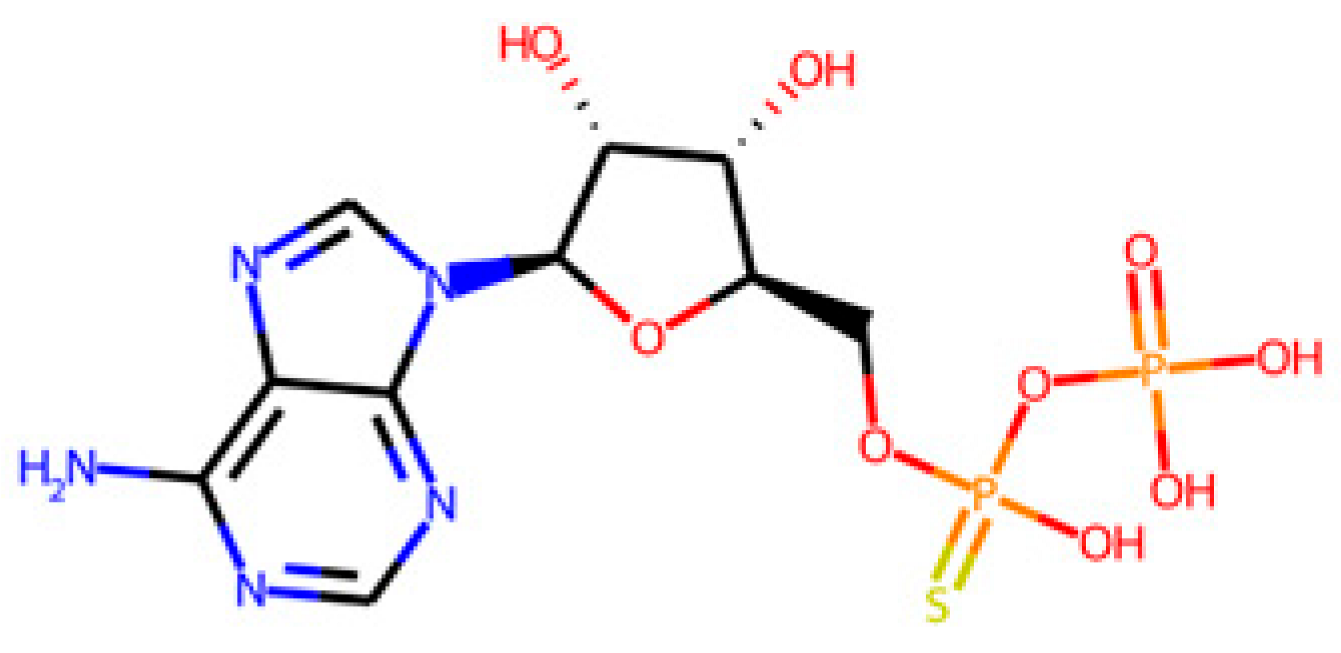
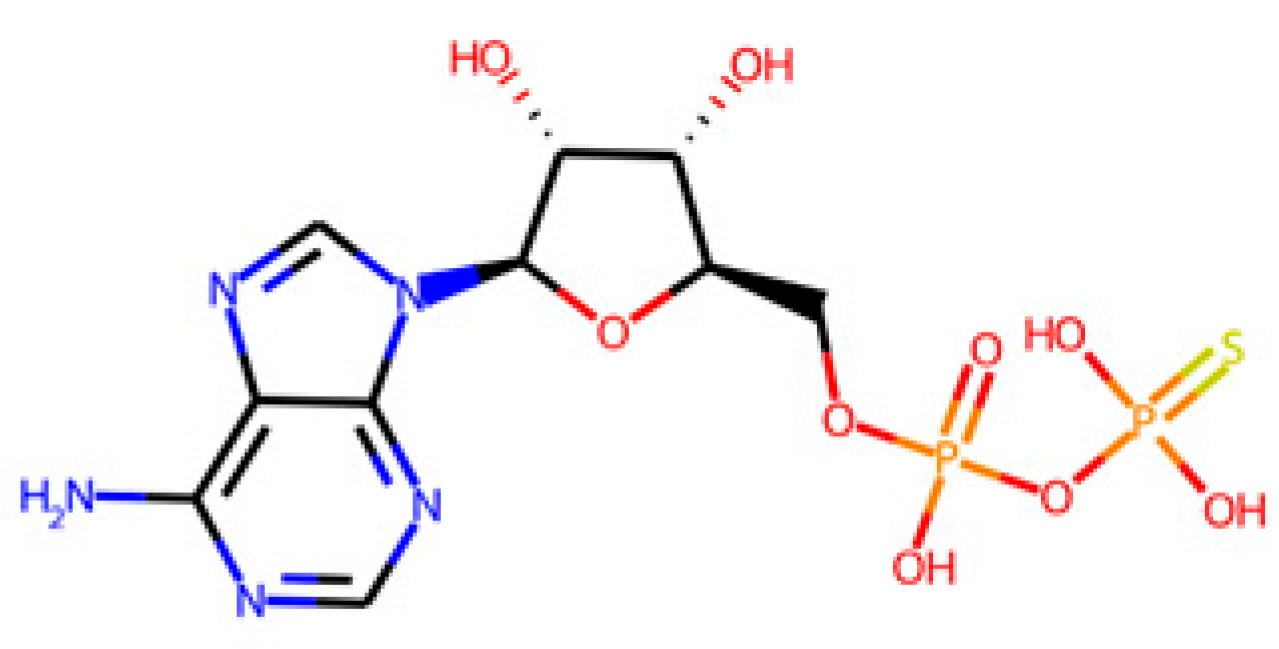
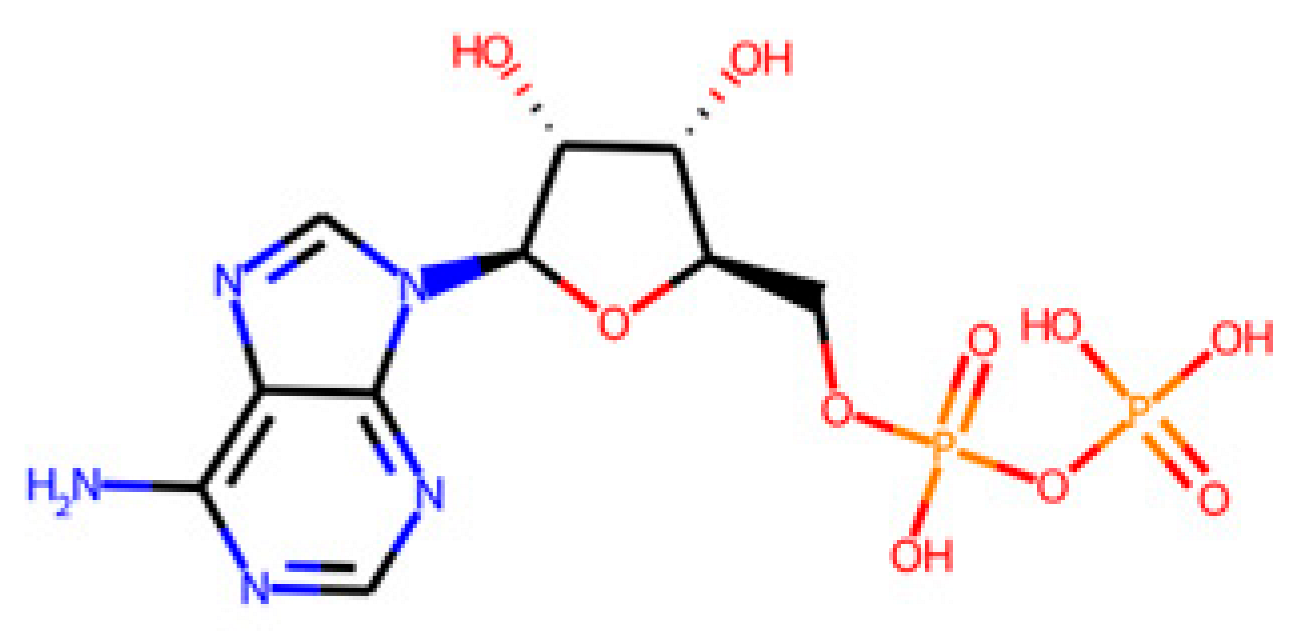
After identifying the target enzymes and following the workflow presented in Figure 1A, the search of the corresponding ligands of the identified target enzymes in the PDB database yielded a common substrate, the adenosine-5′-phosphosulphate (APS). APS is shared with APSr, ATPs, and APSK enzymes but not with the DSR enzyme, as shown in Figure 4 and Table 3.
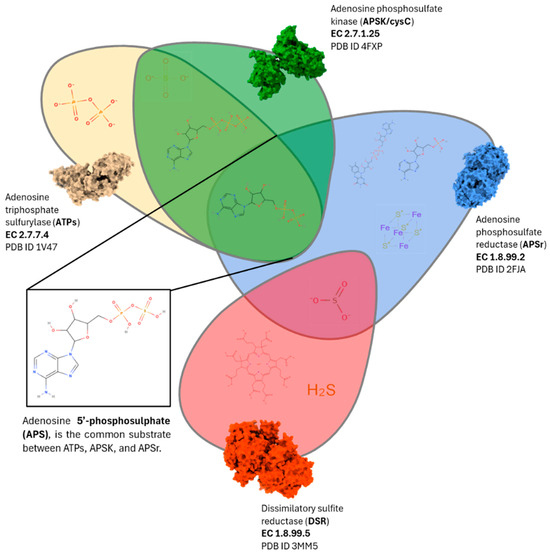
Figure 4.
Representation of the different natural substrates of the four target SRB-specific enzymes and the common ligand (APS) for ATPs, APSK, and APSr. The shown substrates correspond to those presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Main information of the identified SRB-specific enzymes and their ligands. The common endogenous ligand is underlined.
PubChem database searching allowed us to find the bioassay record AID 440574 (available at https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/440574, accessed on 7 November 2023), which consisted of the study of the binding affinity of 24 different substances to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis APSr [32]. Among them, the APS and six APS derivatives were characterised to have a Kd ≤ 10 µM.
Then, specific inhibitors present in scientific publications and public databases were sought.BRENDA contains information about enzymes and the metabolic pathways they are involved in, as well as inhibitors and endogenous ligands [79]. When searching in BRENDA, a study performed to screen 400 compounds, included in the panel Pathogen Box assembled by the Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV), was found [80]. The authors identified two inhibitors of the APSK from Entamoeba histolytica. Finally, three compounds were extensively studied as inhibitors of two of the enzymes of the SRB metabolism: APSr and ATPs [81,82].
They were taken into account along with the above-selected compounds, and in sum, they amount to 12 potential SRB inhibitors (Table 4).

Table 4.
Main characteristics of the molecular candidates.
Intending to ensure the safety of these 12 selected compounds, available information in the CLP database was first checked (ECHA’s Classification, Labelling and Packaging Regulation on Chemicals Inventory, https://echa.europa.eu/es/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database, accessed on 6 November 2024). Both BHT (available online: https://echa.europa.eu/es/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/24787, accessed on 6 November 2024) and BHA (available online: https://echa.europa.eu/es/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/19604, accessed on 6 November 2024) are reported to be non-readily biodegradable and cause aquatic toxicity, while none of the APS derivatives or the MMV compounds have been classified under CLP regulation.
Then, in order to avoid the use of compounds with inhibitory effects on sludge, the compounds with no experimental data available on this endpoint were subjected to the prediction of their potential capacity to inhibit activated sludge respiration, by using a proprietary model (https://protopred.protoqsar.com, accessed on 6 November 2024). Among all the substances tested, MMV676512, MMV676409 (substances retrieved from the BRENDA), and ABTS were predicted to inhibit activated sludge respiration, while APS and its derivatives were predicted to be non-inhibitors.
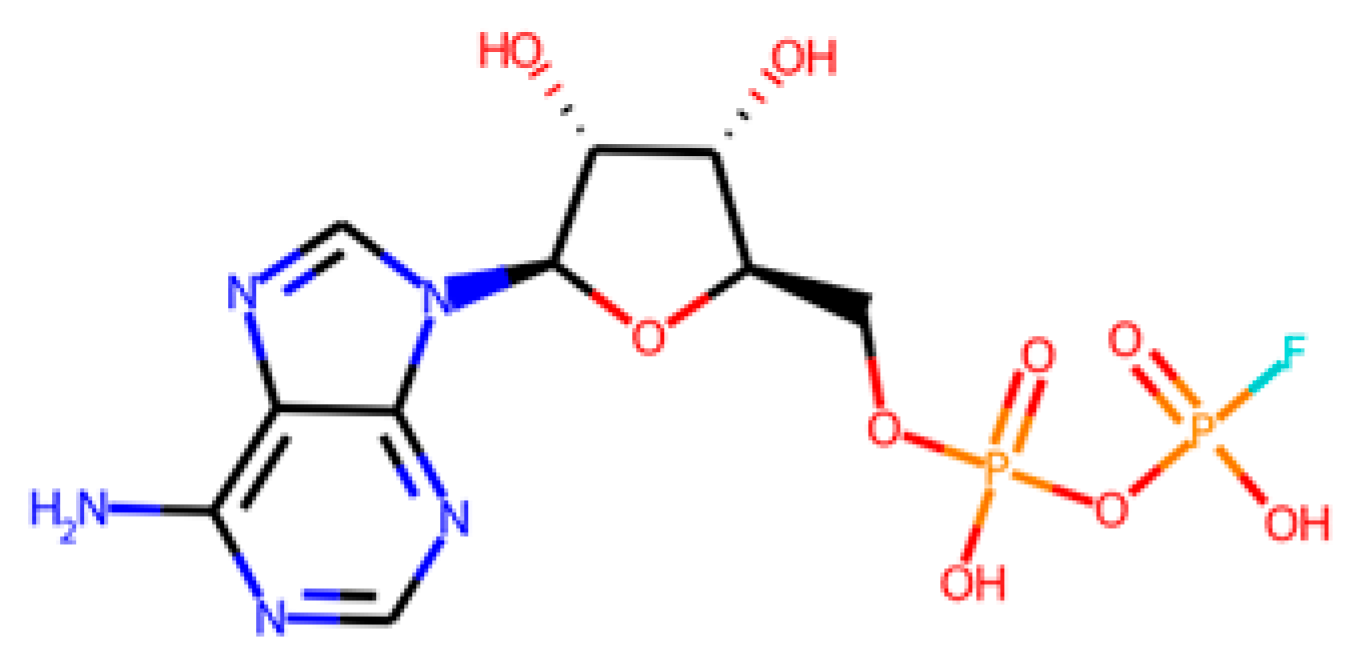
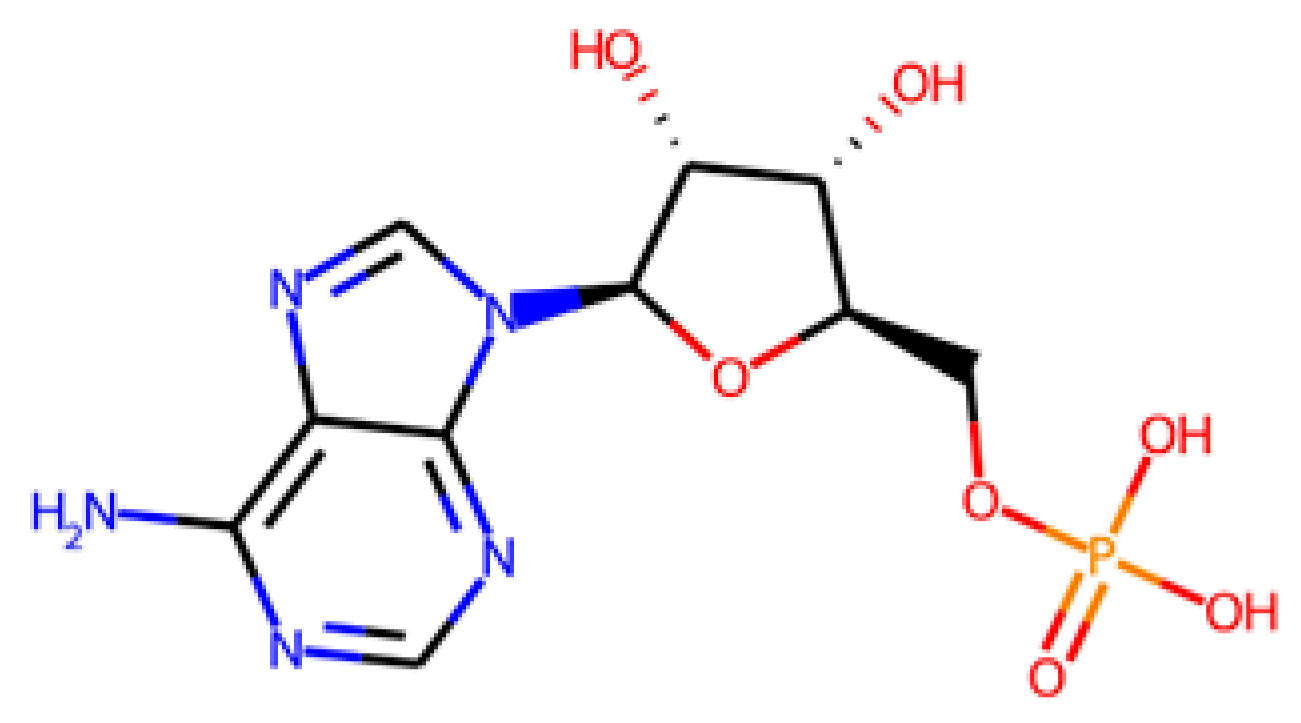
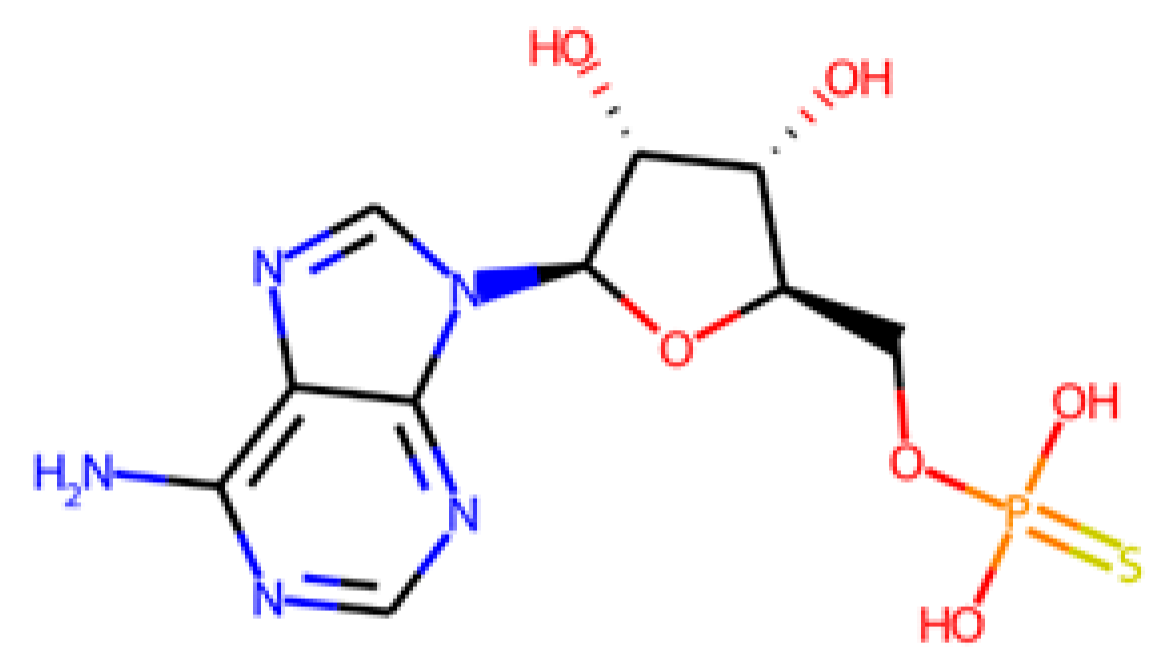
Eventually, it was decided to select four molecules to be tested. On the one hand, ADP (APS-deriv3) and AMP (APS-deriv5) were chosen because they were predicted to have no effect on activated sludge respiration. Although it has been previously reported that endogenous molecules can have some toxicity [83,84], in this case no evidence of toxicity was found for any of them. On the other hand, ABTS and BHT were chosen because, despite their toxic effects, they have been shown to be efficient inhibitors of APSr and ATPs at low concentrations [81,82] and could serve as a reference to compare other anti-SRB agents.
3.3. Evaluation of the Effect of SRB Inhibitors on Methane Production
After the identification of the compounds, their effectiveness in inhibiting SRB and their impact on the BMP of the sludge were evaluated. All compounds were tested at equivalent concentrations (50 µM) of the target substances. To this end, anaerobic respirometry assays were conducted to determine the BMP of sludge from a WWTP.
The average results of the replicates are presented in Figure 5, which shows the cumulative methane production curves during the first 48 h of the assay for each compound, compared with the blanks with and without sulphate. Methane production in the presence of AMP and ABTS was similar to that observed in the sludge + SO4 blank, whereas the addition of BHT caused a pronounced decrease in methane production, indicating a potential toxic effect on metabolic groups involved in methanogenesis.
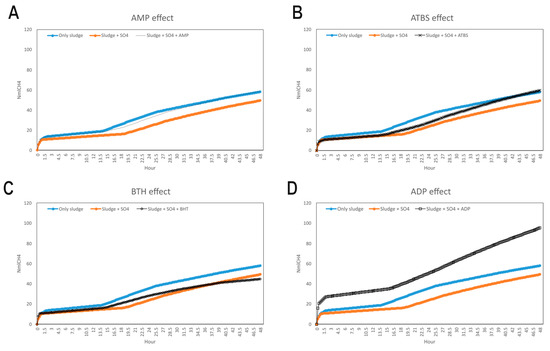
Figure 5.
Evolution of average methane production. Methane production of the two blanks is shown in blue (without sulphate addition) and orange (with sulphate addition). The cumulative methane production for each tested compound is shown in black: (A) AMP, (B) ABTS, (C) BHT, and (D) ADP.
Table 5 shows the characterisation of the sludge and the inoculum under low sulphate concentration conditions.

Table 5.
Characterisation of the feed sludge and inoculum for the validation test at low sulphate concentration.
The addition of SO42− in the blank without inhibitors (orange line in Figure 5) resulted in a 29% reduction in methane production compared with the blank without sulphate (blue line in Figure 5). This decrease is consistent with previous reports describing methane reductions of up to 92% following sulphate addition, attributed both to competition between SRB and methanogens for common substrates and to the toxic effects of H2S on methanogenic archaea [72,74].
In contrast, AMP (Figure 5A) showed methanogenic activity close to the maximum potential, indicating that its addition partially counteracted the inhibition caused by sulphate. Additionally, ADP increases the methane production in comparison with the blank (Figure 5D). This positive effect may be explained by the selective inhibition of critical enzymes in the dissimilatory sulphate reduction pathway, such as ATPs, APSK, APSr, and DSR, whose activity is essential to convert sulphate into H2S [85,86]. Interference with these enzymes would block the use of sulphate as an electron acceptor, thereby reducing both competition for H2 and acetate and the accumulation of toxic H2S, which explains the partial recovery of BMP.
Table 6 presents the maximum BMP obtained for the replicate fed exclusively with sludge and without sulphate addition, which was taken as the 100% reference value. The same tables also report the biodegradability indices, calculated from the final methane production at the end of the assays and expressed relative to the activity of the blank.

Table 6.
Maximum BMP for sludge without sulphate addition.
As shown in Table 7 and Figure 6, BHT reduced methanogenic activity by 55%, compared to the blank without sulphate, exceeding even the inhibition observed in the sulphate blank. This pattern suggests a non-specific adverse effect, possibly related to toxicity towards methanogenic archaea or other microbial groups, rather than to the selective inhibition of the sulphate reduction pathway. Previous studies have highlighted that undissociated H2S is highly toxic to methanogens, as it can freely diffuse through cell membranes and disrupt key enzymatic systems [74], suggesting that BHT may enhance these toxic effects or interfere directly with enzymes such as DSR [85].

Table 7.
Biodegradability indexes for each tested condition.
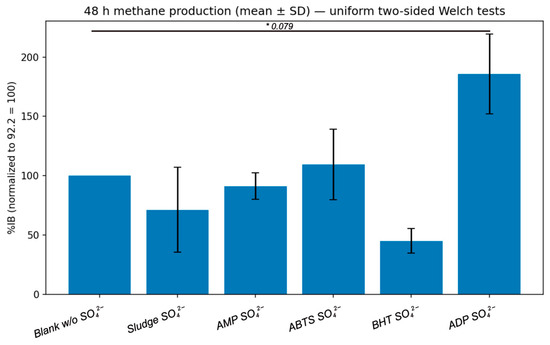
Figure 6.
Statistical analysis performed on the resulting biodegradability indexes for each condition. Statistical differences between conditions were assessed using two-sided Welch’s t-tests with Holm correction; asterisk indicates p < 0.1.
In contrast, in the case of ADP, methane production was abnormally high, reaching values 86% above the blank, which is greater than expected for the applied organic load in batch assays. This behaviour could be attributed to cell lysis phenomena, providing additional substrate to the system, as well as to the partial inhibition of the initial sulphate activation steps (ATPs and APSK), thereby limiting APS availability and diverting electron flow back to methanogenesis [85,86]. This dual explanation, extra substrate from lysis and inhibition of sulphate reduction, would account for the unusually high methane production observed.
The average analytical results (Table 8) confirmed these trends: COD concentrations were higher in all assays with inhibitors, whereas acidity was lower in the case of BHT, consistent with the reduced methane yield and suggesting a general toxic effect on the microbial biomass involved in acidogenesis. In contrast, the accumulation of acids in the replicates supplemented with ADP indicates a possible metabolic imbalance, likely reflecting a shift in the acidogenic–methanogenic equilibrium.

Table 8.
Mean analytic results from the reactors used in the assays. Both controls and the four studied products are included. AMP, ABTS, BHT, and ADP samples correspond to Sludge + SO42− + the respective tested molecule.
3.4. QSAR Models Development and Integration on a Web-Based Server
Once the inhibition of SRB had been confirmed to favour methane production, we wanted to explore the possibility of employ computational techniques to expand the list of candidate compounds. To do so, two QSAR models have been developed to predict specific inhibitory capacity against SRB and methanogenic archaea.
Two different datasets were collected, as described in the Materials and Methods, Section 2, and processed following the workflow described in Figure 7. Briefly, datasets were collected and subjected to a curation step. Curated data was split into two subsets (75%/25%), where the former subset was used to develop the model, and the latter was used to validate it. On the other hand, a QSAR model for anti-SRB was developed using a 5-CV strategy, due to the low number of compounds.
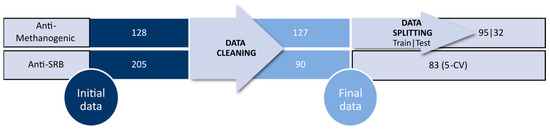
Figure 7.
Database description. The initial inhibitory data against each group of microorganisms go through a cleaning step.
Table 9 summarises the main characteristics (number of descriptors and algorithm used) and the metrics, evaluated by 10-fold CV, for each QSAR model.

Table 9.
Metrics of the regression predictive models of antimicrobial activity against methanogenic archaea and sulphate-reducing bacteria.
In order to improve the usability of these models as a predictive tool, a web-based server was developed, and the models were integrated into an online platform (available at https://chemopredictionsuite.com/SulfaTOX, accessed on 25 February 2025). The SulfaTOX module is divided into two sections, as shown in Figure 8: input molecule(s) and model selection. The server accepts different file inputs (.csv, .txt, .xlsx, etc.) and single molecules can be introduced by SMILES, CAS number, or by drawing. Altogether, the SulfaTOX tool allows the user to screen large datasets, to choose both predictive models or to be used as a single predictor of anti-SRB or anti-methanogenic activity, and to obtain all the prediction results in a single file.
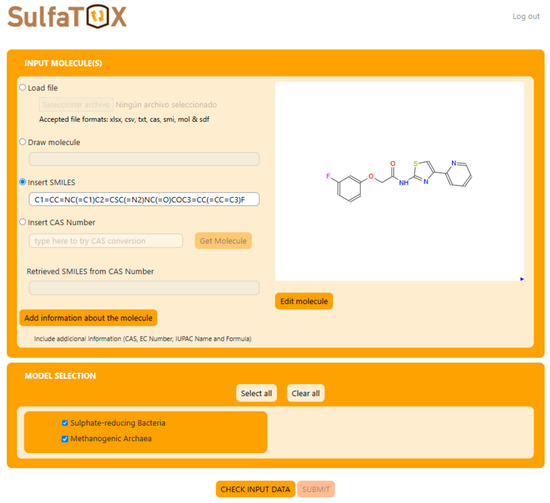
Figure 8.
Graphic User Interface (GUI) of integrated SulfaTOX models on the ChemoPredictionSuite platform, displaying the MMV676409 molecule as an example.
3.5. Validation of QSAR Models and Identification of Novel Compounds
The first step was to evaluate the predictive capacity of our models on the molecules that were experimentally tested (Table 10). The predicted anti-SRB and anti-methanogenic activities are interpreted based on two concentration criteria: low activity is considered below or equal to an inhibitory activity of 5 mM; otherwise, it is considered high activity. The predictions for ABTS and BHT are in agreement with the experimental results, as they are able to inhibit both microbial groups. In the case of ADP, it is efficiently predicted for SRB, whereas no conclusion can be drawn for its potential inhibition against methanogenic archaea, as the compound falls outside the AD of the model. In the case of AMP, the model predicts AMP as inactive, despite having a slight positive effect on methane production in the experimental result.

Table 10.
Results of the prediction of selected molecules by the SulfaTOX server.
In order to find new compounds with the ability to inhibit SRB, but not methanogenic archaea, the COCONUT database was screened using the SulfaTOX web server. COCONUT is an open database of natural products which comprises a collection of around 400,000 chemical compounds of diverse natural origins and represents one of the most complete and structurally varied databases of this kind. Furthermore, including the COCONUT screening in the pipeline would allow us to find more sustainable and innovative compounds [87,88].
Figure 9 shows the workflow used for virtual screening. First, 73 molecules were selected from the COCONUT virtual screening for their low activity (inhibitory activity > 5 mM) against methanogenic archaea and high activity against SRB (inhibitory activity ≤ 5 mM) (Figure 9A). The 73 molecules were then subjected to ecotoxicity predictions using the ProtoECO module, and every molecule with an unfavourable prediction (based on the ecotoxicological criteria applied, see Materials and Methods, Section 2) was discarded. Only nine candidates remained safe according to the ProtoECO predictions, from which four were commercially available (Figure 9B).
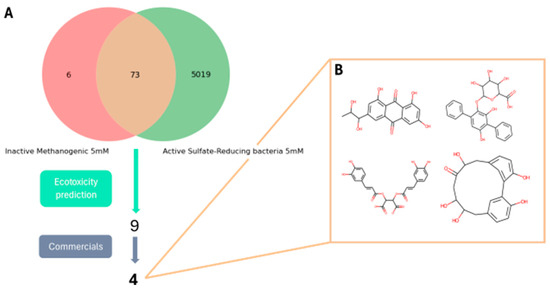
Figure 9.
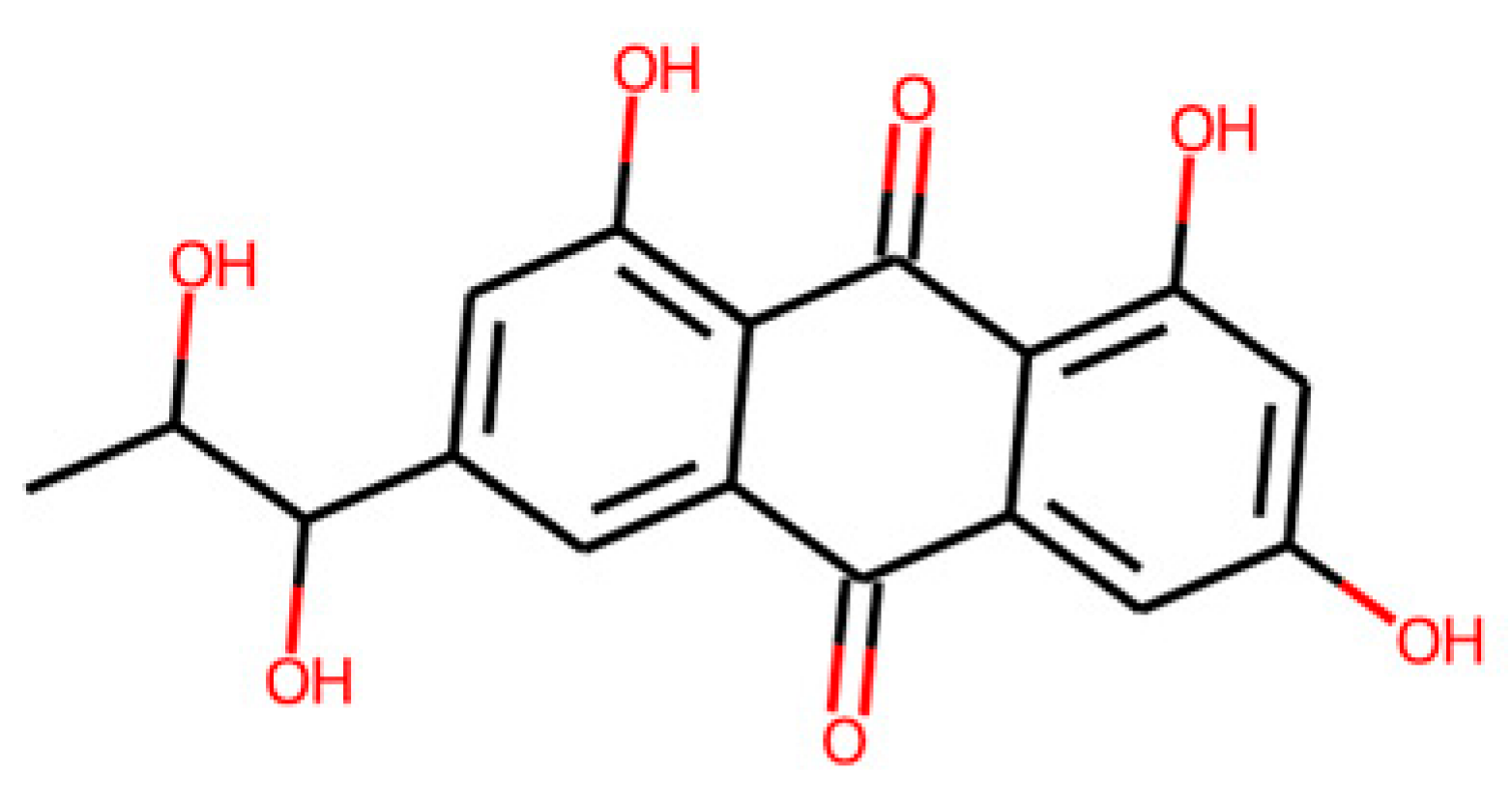
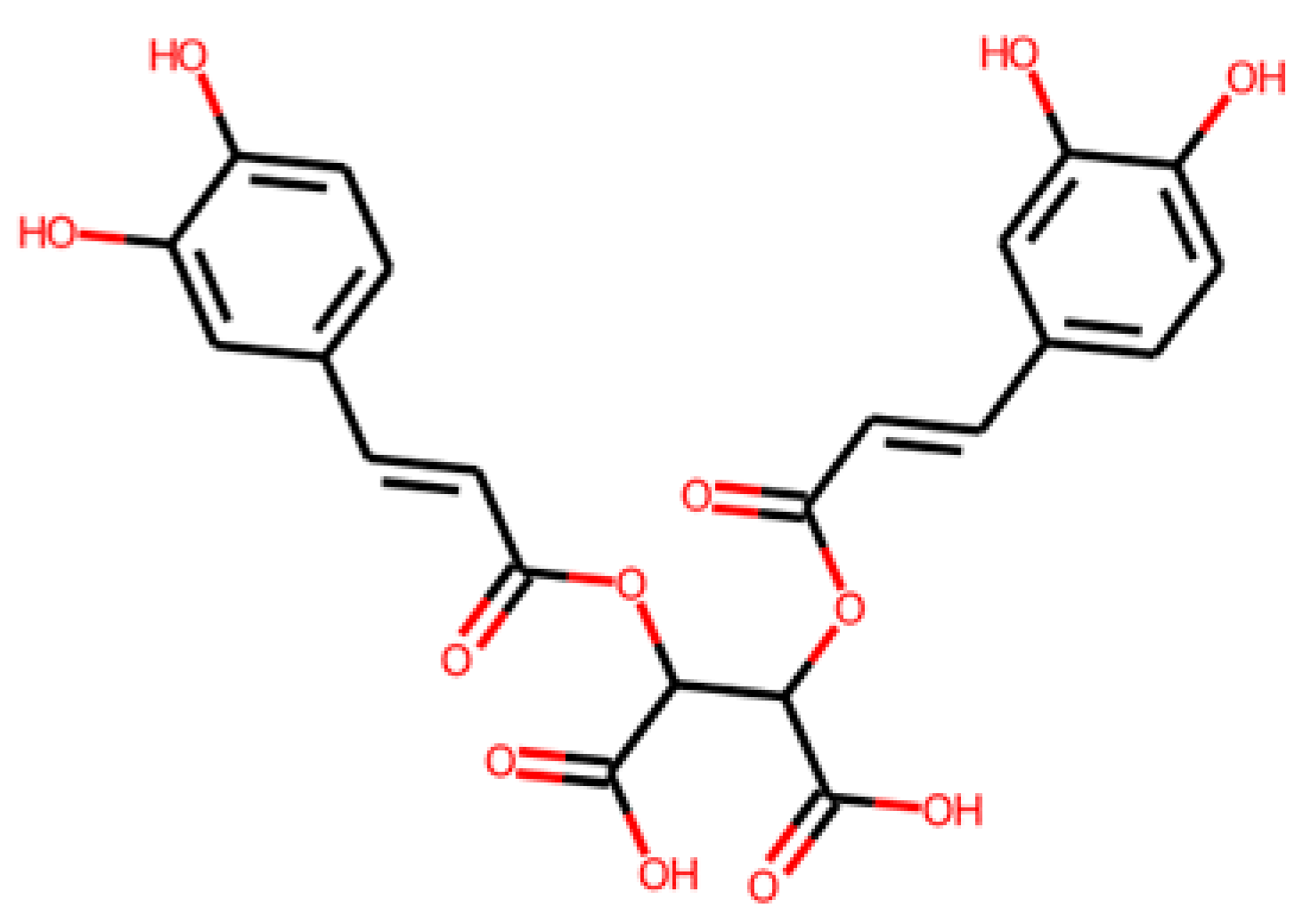
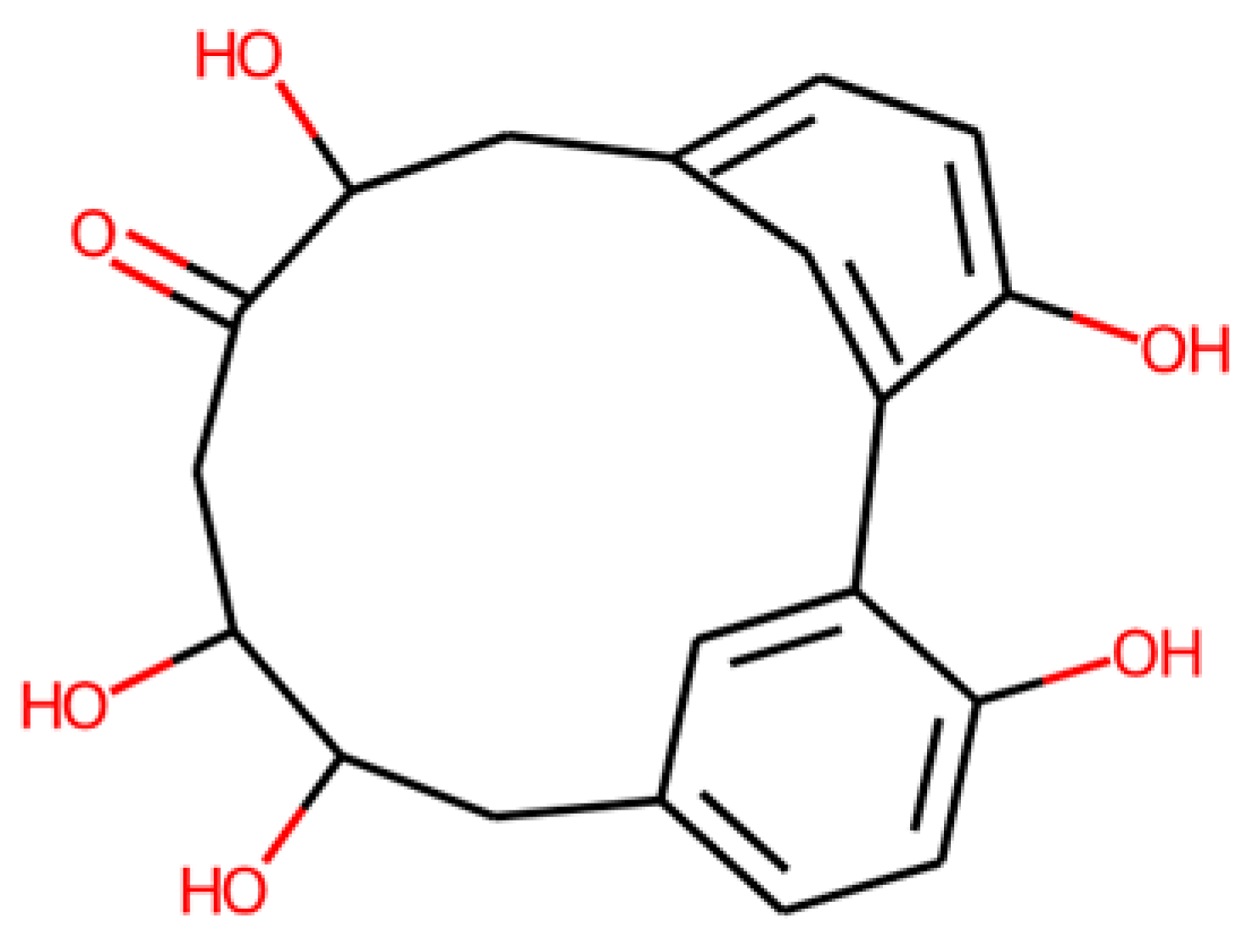
Virtual screening results and further selection. (A) COCONUT virtual screening pipeline. (B) Molecular structures of the four final candidates from the COCONUT virtual screening.
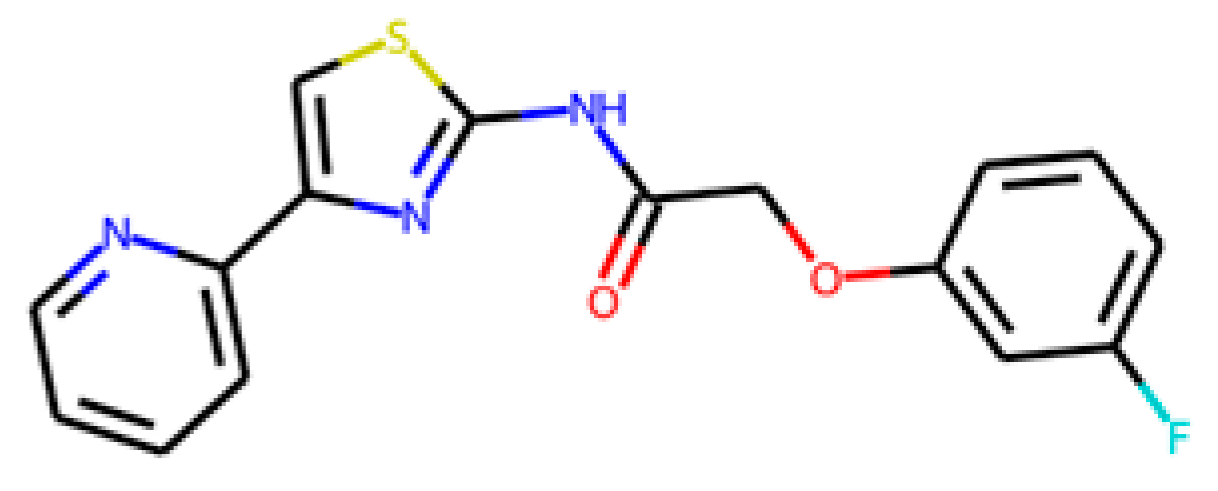
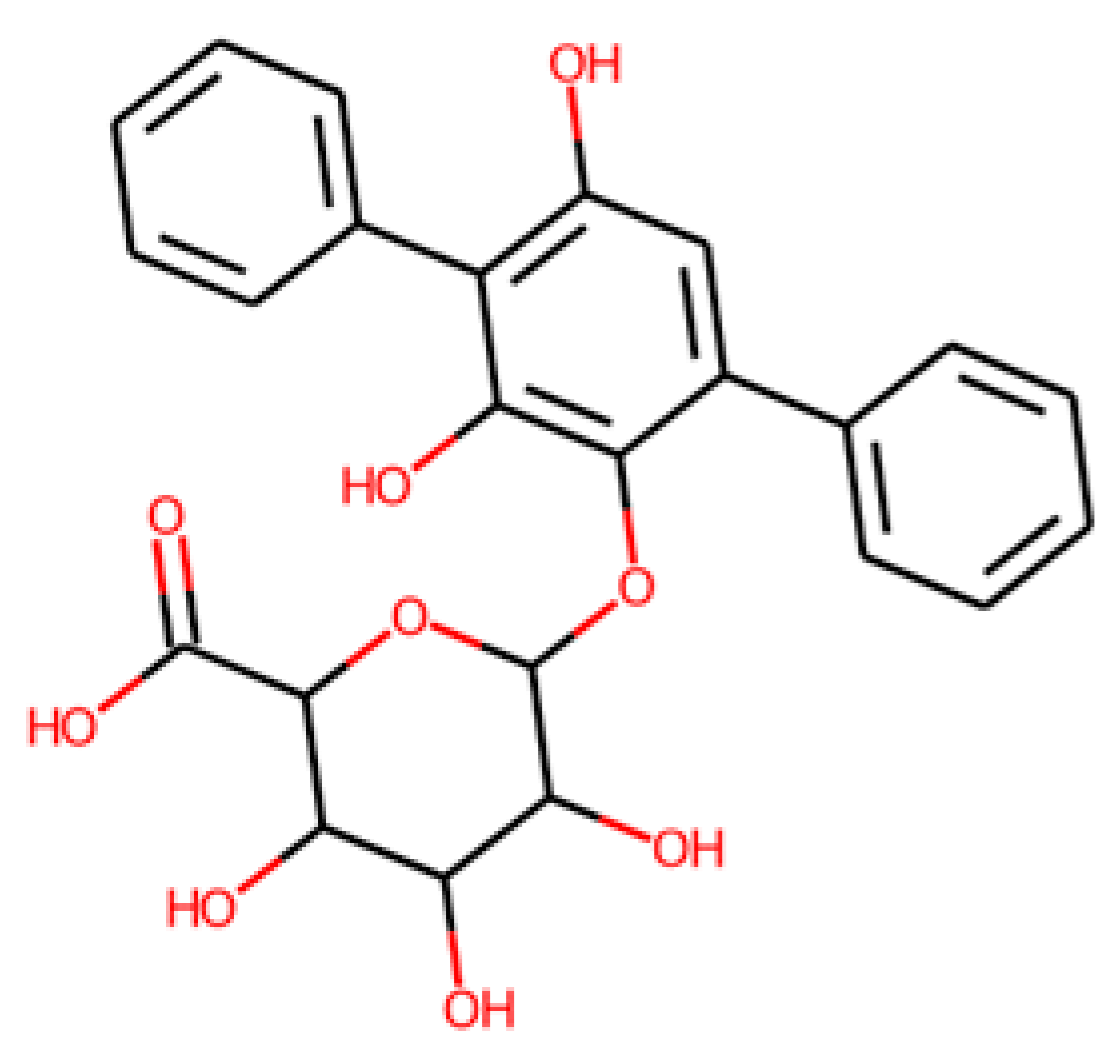
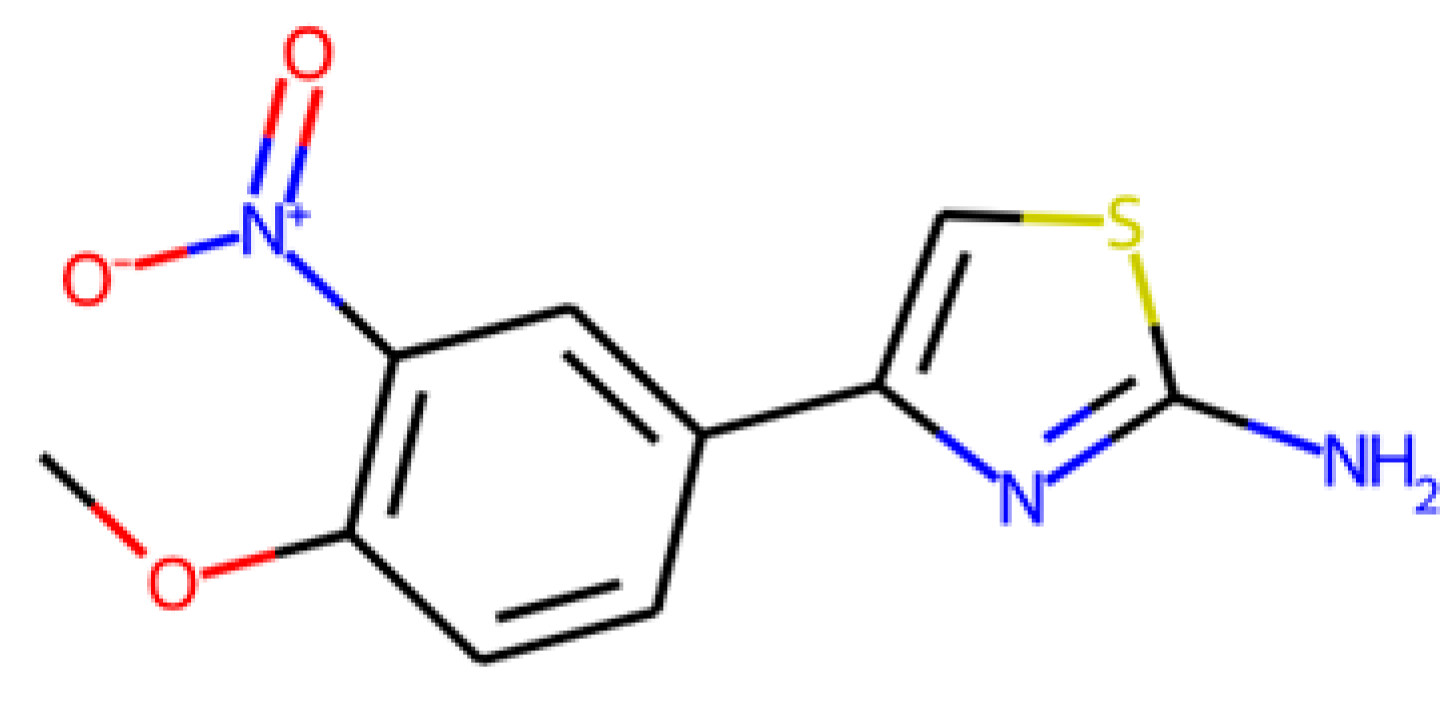
In order to expand the list of candidate compounds, analogues of the nine selected molecules that could be commercially available were searched. We were able to find a substance with PubChem CID 738793 that was an analogue of CNP0458120 (Figure 10).
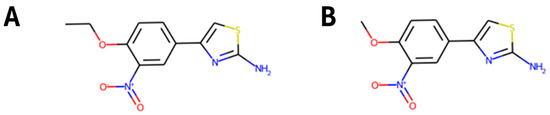
Figure 10.
Molecular representation of molecule with COCONUT identifier CNP0458120 (A) and its structural analogue, with PubChem CID 738793 (B).
It is important to note that the server identified molecules with benzene groups, a functional group also present in BHT, as well as multiple hydroxy groups, as in the case of AMP and ADP (molecular representations in Table 11). Moreover, CNP0458120 contains the aminothiazole group, which is usually found in some families of antimicrobial agents [89,90].

Table 11.
Main identifiers of molecular candidates from the COCONUT virtual screening.
This strategy ultimately yielded five potential SRB inhibitors, shown in Table 11.
4. Discussion
Microbial methane production in WWTPs is a promising methodology for green bio-gas production. However, this production could be affected by the competitive relationship existing between methanogenic archaea and sulphate-reducing bacteria, reducing the efficiency of anaerobic digestion and producing a dangerous and corrosive gas. As a possible strategy, inhibition of SRB can help to favour methane production. This inhibition reduces the competition for substrates such as acetate or hydrogen, potentially recovering the methanogenic activity, yet it also may disrupt the redox balance and the syntrophic interactions. The outcome depends on how the inhibitors affect the SRB population and the rest of microbial species in the anaerobic system. It is also essential to consider the accumulation of toxic intermediates. In microbial syntrophic relationships, community changes and environmental perturbations can lead to compensating mechanisms. These mechanisms can inhibit or promote certain metabolic pathways [91]. Therefore, whole-picture approaches which consider all the species in the consortium should be taken and are key for understanding the complexity of these systems.
In the present work, through the combination of a database search-driven approach and QSAR-based virtual screening, nine candidates for sulphate-reduction inhibition have been identified—four and five molecules, respectively—that might inhibit SRB without interfering with methanogenic metabolism.
The database search-driven strategy yielded 12 diverse molecules whose specific anti-SRB activities were reported. From the selected molecules that were subjected to experimental testing (ADP, AMP, ABTS, and BHT), only ADP efficiently increased methane production, successfully optimising the levels of this gas in the reactors. However, BHT and ABTS showed an eventual decrease in methane production. It is important to note that the BMP values obtained are lower than the theoretical values, mainly for the following reasons First, the theoretical value assumes the complete conversion of all the substrate carbon into CH4; however, some carbon is transformed into CO2, since biogas production involves several metabolic pathways and not just methanogenesis (see Figure 1). Second, the biogas generated in the tests was passed through a CO2 trap before measurement, so only the methane fraction generated was quantified. Third, the equilibrium between CH4 and CO2 depends on the predominant microbial pathways at any given time, since bacteria and archaea compete for electron acceptors and substrates. This microbial competition can modify the percentage of CH4 and CO2 in the generated biogas (for example, it depends on the proportion of acetoclastic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens participating in the process). Finally, to verify the effect of the compounds on sulphate reduction, the CH4 values used for comparison between replicates were those obtained at 48 h, an insufficient time to achieve complete methane conversion. This short duration was chosen to capture the initial effect of sulphate reduction, whose kinetics are faster than those of methanogenesis, thus allowing for comparison of the effect on methanogenesis among the different replicates analysed.
As mentioned previously, the higher methane production might be explained by potential pleiotropic effects, affecting several enzymes from the sulphur metabolism. This could lead to the alteration of the levels of metabolic intermediates and promote higher levels of methane. Additionally, ADP is structurally closer to APS, PAPS, and other metabolites involved in the sulphur metabolism than AMP, BHT, or ABTS, performing better in the competition for the enzymes against their endogenous ligands. However, nucleotides such as AMP have been reported to deregulate energetic metabolic pathways (i.e., tricarboxylic acid cycle) and have been proposed as a therapeutic complement to antibiotics in tackling infections caused by Gram-negative resistant bacteria [92]. Therefore, the observed effect of AMP could be optimised with another inhibitor. The exact mechanisms through which these compounds affect methanogenesis remain unclear. However, it has already been reported that some additives can affect the sludge structure and interfere with different phases of the anaerobic consortium, ultimately leading to reduced methane yields. For instance, Pasciucco et al. reported that aluminium-based coagulants modified sludge characteristics and inhibited methane production during anaerobic digestion, probably by disrupting hydrolysis and acidogenesis phases [30]. These findings highlight the need for more global approaches to better understand microbial and physicochemical interactions in sludge systems.
It is important to recognise that this study represents a first approximation, establishing the computational and experimental feasibility of the inhibition strategy. ADP demonstrated high efficacy with an 86% increase in methane production, which could mean high production on a real scale, resulting in direct energy savings. The effective use of the compounds studied at relatively low concentrations and in single doses (e.g., 50 µM tested in the assays) suggests that the operational cost is manageable. The price of the products is currently high, as they have been produced on demand, but it is foreseeable they could be substantially cheaper when manufactured on a larger industrial scale, which will offset the initial costs associated with smaller-scale synthesis. Likewise, it is necessary to analyse on a larger scale the economic savings resulting from increased methane production.
The successful and selective inhibition of SRB presents ecological, energetic, and economic advantages, promoting a shift to a circular economy and sustainable model in the WWTP sector. In addition to the increase in methane production, SRB inhibition directly addresses the significant issues derived from the H2S generation. This gas can not only affect the methanogens but also damage the structural integrity of the facilities and reduce the useful life of cogeneration engines, entailing additional costs for their removal. The reduction in the SRB enzymes activity (e.g., ATPs, APSK, and APSr) thus greatly diminishes the production and accumulation of H2S. Traditional control strategies, such as the addition of metal salts, can compromise the quality and the potential valorisation of the digested sludge as agricultural fertiliser. The identification and validation of selective and non-ecotoxic candidates is essential to have alternative control strategies.
The capacity of a QSAR model to distinguish between active and inactive compounds mainly depends on the molecular descriptors used to encode the chemical information [93]. Understanding the role of the selected descriptors allows us to draw a clear relationship between certain structural and physicochemical characteristics and the biological activity of interest and comprehend the underlying mechanisms. Among the descriptors employed in the generation of the anti-SRB QSAR model (Supplementary Materials Table S1) and in the generation of the anti-methanogenic QSAR model (Supplementary Materials Table S2), we found that most descriptors are low-explainable and complex molecular descriptors, such as the 3D-MoRSe series. This may be due to the heterogeneity of the employed dataset used to develop the model, as it contains compounds that affect different targets [54,55]. Such a limitation could be overcome through more specific investigations on both microorganism targets in future studies.
Nevertheless, some of the captured descriptors are directly related to structural features or specific functional groups. Our anti-SRB QSAR model identified the ‘N-079’ descriptor (i.e., counts the presence of nitrogen atoms charged positively in the molecules). It has been reported that quaternary ammonium salts are antimicrobial molecules with great potential, known for adsorbing to the bacterial membranes due to the cationic charge [94]. Moreover, molecules with charged nitrogen could be competing for the active site of the enzymes involved in sulphur metabolism. The model also identified the descriptor SLogP_VSA3 (which captures the contributions of specific atom type to the surface area and therefore the local lipophilicity). This descriptor reflects the relevance of the passive intake of compounds through lipidic membranes in the case of SRB, which are commonly Gram-negative bacteria. In the case of the anti-methanogenic QSAR model, the following seven molecular descriptors presented a high explainability: ‘H-052’, ‘O-059’, ‘B03[N-O]’, ‘B03[N-Cl]’, ‘F04[O-Cl]’, ‘nRCOO’, and ‘nAl_OH’. Together, these descriptors indicate the presence of hydroxyl, carboxylic, and chloro-substituted groups, suggesting that these species may have a potential relationship with the inhibitory activity against methanogenic archaea. Indeed, some studies have reported inhibition of methanogens by halogenated compounds such as 2-bromoethanesulfonate or bromochloromethane, and diverse carboxylic acids like pterin-6-carboxylic acid [95,96]. The combination of these atom-centred descriptors and functional groups with some complex 3D descriptors likely captures the conformational and electronic diversity required to interfere with the metabolic pathways or membrane integrity of these microorganisms.
In summary, despite the fact that previous QSAR models have been used to describe the inhibition of SRB-related enzymes or methanogenic microorganisms [97,98], it is remarkable that this is the first time, to the best of our knowledge, that SRB and methanogenic microorganisms have both been taken into account in a single tool to identify safe and specific candidates against this type of bacteria and archaea. Moreover, robust and competent performances were accomplished. They were able not only to successfully screen a subset from the COCONUT database and confirm some of the results of the experimental studies, but also to identify significant functional groups such as aminothiazole, hydroxide, or aromatic groups, molecular elements widely present among common and novel antimicrobials [35,89,90,99]. Despite the limited amount of data, the QSAR models showed acceptable performance and successfully captured functional groups or substructures present in known antimicrobial agents. However, more diverse data is needed, and this could mean an improvement of the QSAR models in the future, trying to enhance not only the predictive ability of the model but also enlarge the chemical space in which the model is reliable. In addition, ecotoxicological predictions were also incorporated, because industrial optimisation should go hand in hand with environmental safety in circular economies.
Little has been studied concerning the inhibition of SRB through modelling techniques, especially QSAR models. Of particular note are the molecular docking studies on SRB proteins that have helped in the identification of novel SRB inhibitors [81,82,100]. In them, dos Santos et al. selected APSr and ATPs as inhibition targets of SRB and identified some compounds with inhibitory activities that were of interest in our work. From that point, the approaches presented in this work contribute to refinement and better selection of potential candidates by taking into account the likely inhibition of methanogenesis, as has been studied [28,55,101], by some of the previously studied molecules.
Other studies have also applied computational tools in the identification of antimicrobials with different applications, such as industrial biocidal control [100,102,103] or clinical disinfection [104]. Some combine QSAR modelling with docking and molecular dynamics, like the work by Ye et al. [105] on Streptococci or the one by Tejera et al. [103]. Other works, like this study, focus on QSAR modelling, like Abdullahi et al. [102], to identify potential antimicrobials. Both strategies are equally valid, and in fact the results indicate that they serve as successful approaches to discover novel molecules with antimicrobial potential after experimental validation [100,106,107,108]. The experimental validation has an essential role in improving the in silico methodology and evaluating the efficiency of the predicted candidates in a real context.
Based on the results obtained, other types of inhibitors, such as synthetic molecules, could be further explored, and the already selected inhibitors could be further studied using different techniques, such as molecular modelling approaches. All of this would add to the knowledge of wastewater microbiology, and we hope to contribute to a shift towards a more sustainable paradigm. Briefly, the combination of available published data and computational tools has shown the potential of QSAR models in the identification of novel molecules of interest in the field of environmental chemistry. With the opportunity to test some of the compounds, the computational evidence of the generated models was supported.
5. Conclusions
This work efficiently demonstrate that the approach of inhibiting SRB can be efficiently applied in bioreactors to increase the production of methane by reducing the competition between SRB and methanogenic microorganisms present in the sludge. Moreover, this study underscores different strides made in harnessing the potential of computational tools within the field of environmental chemistry through the utilisation of QSAR models. Notably, the models presented in this work hold promise for screening large databases.
The nine carefully selected compounds, some of which exhibited inhibitory activity against sulphate-reducing bacteria while remaining safe for methanogens and non-ecotoxic, represent an alternative to the proposed inhibitors in WWTPs and also as candidates in oil and gas corrosion scenarios. Some of the compounds still need to be validated. This crucial step ensures the reliability and accuracy of their performance.
The prospective application of ADP (or molecules that act through the same mechanism of action) in WWTPs emerges as a potential solution for reducing hydrogen sulphide emissions. Furthermore, it opens avenues for a more sustainable utilisation of energy, helping in the transition towards a circular economy paradigm.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040128/s1, Table S1: Selected molecular descriptors for the anti-SRB QSAR model generation and their description; Table S2: Selected molecular descriptors for the anti-methanogenic QSAR model generation and their description.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.T.-C., M.J.T.M., Á.B.-S., R.G. and E.S.-C.; Data curation, D.T.-C., C.L., Á.B.-S. and E.S.-C.; Formal analysis, D.T.-C., M.J.T.M., Á.B.-S. and E.S.-C.; Funding acquisition, Á.B.-S. and R.G.; Investigation, D.T.-C., L.E.C., P.S.-C., C.L., M.J.T.M., Á.B.-S., P.G. and E.S.-C.; Methodology, D.T.-C., L.E.C., C.L., Á.B.-S. and E.S.-C.; Project administration, P.S.-C., Á.B.-S. and R.G.; Resources, Á.B.-S. and R.G.; Software, D.T.-C., L.E.C. and E.S.-C.; Supervision, L.E.C., Á.B.-S. and E.S.-C.; Validation, D.T.-C., Á.B.-S. and E.S.-C.; Visualisation, D.T.-C. and M.J.T.M.; Writing—original draft, D.T.-C., L.E.C., M.J.T.M., Á.B.-S. and E.S.-C.; Writing—review and editing, D.T.-C., L.E.C., P.S.-C., C.L., M.J.T.M., Á.B.-S., P.G., R.G. and E.S.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is part of the project SulfaTOX, which has received funding from the Generalitat Valenciana and IVACE (Valencian Institute for Business Competitiveness) through the programme of research and development in cooperation, PIDCOP-CV-2022 (grant IDs: IMIDCA/2022/29 and IMIDCA/2022/36). This project is cofounded with the European Union.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Public Entity of Wastewater Sanitation (EPSAR) of the Valencian Community (Spain), attached to the Department of Agriculture, Rural Development, Climate and Ecological Transition, owner of the WWTPs.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors David Talavera-Cortés, Rafael Gozalbes, and Eva Serrano-Candelas were employed by the company ProtoQSAR SL; authors Laureano E. Carpio, Patricia Serrano-Candelas, and Rafael Gozalbes were employed by the company MolDrug AI Systems SL; and authors Carlos Lafita López, M José Tárrega Marti, Ángela Baeza-Serrano, and Pau Granell Muñoz were employed by the company Global Omnium Medio Ambiente SL.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ABTS | 3-ethyl-2-[(3-ethyl-6-sulfo-1,3-benzothiazol-2-ylidene)hydrazinylidene]-1,3-benzothiazole-6-sulfonic acid |
| ADP | Adenosine DiPhosphate |
| AMP | Adenosine MonoPhosphate |
| APS | Adenosine-5′-PhosphoSulphate |
| APSK | Adenosine PhosphoSulphate Kinase |
| APSr | Adenosine PhosphoSulphate reductase |
| ATPs | Adenosine TriPhosphate sulfurylase |
| BHA | 2-tert-butyl-4-methoxyphenol |
| BHT | 2,6-ditert-butyl-4-methylphenol |
| BMP | Biochemical Methane Potential |
| BRENDA | Braunschweig Enzyme Database |
| COCONUT | COlleCtion of Open Natural prodUcTs |
| COD | Chemical Oxygen Demand |
| DSR | Dissimilatory Sulphite Reductase |
| H2S | Hydrogen sulphide |
| IC50 | Half Maximum Inhibitory Concentration |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MSE | Mean Square Error |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| QSAR | Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship |
| SRB | Sulphate-Reducing Bacteria |
| TS | Train Set |
| VS | Validation Set |
| WWTP | Wastewater Treatment Plant |
References
- UN-Water. Summary Progress Update 2021: SDG 6—Water and Sanitation for All; UN-Water: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ganora, D.; Hospido, A.; Husemann, J.; Krampe, J.; Loderer, C.; Longo, S.; Moragas Bouyat, L.; Obermaier, N.; Piraccini, E.; Stanev, S.; et al. Opportunities to improve energy use in urban wastewater treatment: A European-scale analysis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 044028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettinga, G. Anaerobic digestion and wastewater treatment systems. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1995, 67, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitton, G. Wastewater Microbiology, 4th ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Whiticar, M.J. The Biogeochemical Methane Cycle. In Hydrocarbons, Oils and Lipids: Diversity, Origin, Chemistry and Fate; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 669–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hudaib, B. Treatment of real industrial wastewater with high sulfate concentrations using modified Jordanian kaolin sorbent: Batch and modelling studies. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülsen, T.; Hsieh, K.; Batstone, D.J. Saline wastewater treatment with purple phototrophic bacteria. Water Res. 2019, 160, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushkevych, I.; Vítězová, M.; Vítěz, T.; Bartoš, M. Production of biogas: Relationship between methanogenic and sulfate-reducing microorganisms. Open Life Sci. 2017, 12, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozuolmez, D.; Na, H.; Lever, M.A.; Kjeldsen, K.U.; Jørgensen, B.B.; Plugge, C.M. Methanogenic archaea and sulfate reducing bacteria co-cultured on acetate: Teamwork or coexistence? Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 136098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, K.J.; Nedwell, D.B.; Embley, T.M. Analysis of the Sulfate-Reducing Bacterial and Methanogenic Archaeal Populations in Contrasting Antarctic Sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Cummings, J.H.; Macfarlane, G.T. Competition for hydrogen between sulphate-reducing bacteria methanogenic bacteria from the human large intestine. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1988, 65, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirasawa, J.S.; Sarti, A.; Del Aguila, N.K.S.; Varesche, M.B.A. Application of molecular techniques to evaluate the methanogenic archaea and anaerobic bacteria in the presence of oxygen with different COD:Sulfate ratios in a UASB reactor. Anaerobe 2008, 14, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjansson, J.K.; Schönheit, P. Why do sulfate-reducing bacteria outcompete methanogenic bacteria for substrates? Oecologia 1983, 60, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enning, D.; Garrelfs, J. Corrosion of iron by sulfate-reducing bacteria: New views of an old problem. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone Rubright, S.L.; Pearce, L.L.; Peterson, J. Environmental toxicology of hydrogen sulfide. Nitric Oxide 2017, 71, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinardell, S.; Astals, S.; Koch, K.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Dosta, J. Co-digestion of sewage sludge and food waste in a wastewater treatment plant based on mainstream anaerobic membrane bioreactor technology: A techno-economic evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 124978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, T.Y.; Cha, G.C.; Seo, Y.C.; Jeon, C.; Choi, S.S. Effect of COD/sulfate ratios on batch anaerobic digestion using waste activated sludge. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2008, 14, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, A.; Ueki, K.; Matsuda, K. Effect of sulfate reduction on methanogenesis in the anaerobic digestion of animal waste. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 1988, 34, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maktabifard, M.; Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Szulc, P.; Mousavizadegan, M.; Xu, X.; Zaborowska, E.; Li, X.; Mąkinia, J. Net-zero carbon condition in wastewater treatment plants: A systematic review of mitigation strategies and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 185, 113638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiho, S.; Wessberg, N.; Pippuri-Mäkeläinen, J.; Mäki, E.; Sokka, L.; Parviainen, T.; Nikinmaa, M.; Siikavirta, H.; Paavola, M.; Antikainen, M.; et al. Creating a Circular City–An analysis of potential transportation, energy and food solutions in a case district. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knäble, D.; de Quevedo Puente, E.; Pérez-Cornejo, C.; Baumgärtler, T. The impact of the circular economy on sustainable development: A European panel data approach. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 34, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrispim, M.C.; Scholz, M.; Nolasco, M.A. Biogas recovery for sustainable cities: A critical review of enhancement techniques and key local conditions for implementation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 103033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maktabifard, M.; Zaborowska, E.; Makinia, J. Energy neutrality versus carbon footprint minimization in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 300, 122647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basafa, M.; Hawboldt, K. Reservoir souring: Sulfur chemistry in offshore oil gas reservoir fluids. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2018, 9, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri Novair, S.; Biglari Quchan Atigh, Z.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; Shu, W.; Price, G.W. The role of sulphate-reducing bacteria (SRB) in bioremediation of sulphate-rich wastewater: Focus on the source of electron donors. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 184, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utgikar, V.P.; Harmon, S.M.; Chaudhary, N.; Tabak, H.H.; Govind, R.; Haines, J.R. Inhibition of sulfate-reducing bacteria by metal sulfide formation in bioremediation of acid mine drainage. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhania, I.P.; Robinson, J.P. Heavy metal inhibition of methanogenesis by Methanospirillum hungatei GP1 (Heavy metal inhibition; Methanospirillum; methanogenesis). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1984, 22, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, L.M.; Stams, A.J.M.; Sousa, D.Z. Methanogens, sulphate and heavy metals: A complex system. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 537–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasciucco, F.; Pasciucco, E.; Castagnoli, A.; Iannelli, R.; Pecorini, I. Comparing the effects of Al-based coagulants in waste activated sludge anaerobic digestion: Methane yield, kinetics and sludge implications. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, K.C.; Woodards, N.A.; Xu, H.; Barton, L.L. Reduction of molybdate by sulfate-reducing bacteria. BioMetals 2009, 22, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.A.; Bhave, D.P.; Carroll, K.S. Identification of critical ligand binding determinants in Mycobacterium tuberculosis adenosine-5′-phosphosulfate reductase. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5485–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, G.J.; Mayville, P.; Muir, T.W.; Novick, R.P. Rational design of a global inhibitor of the virulence response in Staphylococcus aureus based in part on localization of the site of inhibition to the receptor-histidine kinase, AgrC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13330–13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeva, M.K.; Coates, J.D. Specific inhibitors of respiratory sulfate reduction: Towards a mechanistic understanding. Microbiology 2019, 165, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, N.A.; Altalhi, A.A.; Saleh Mohamed, N.E.; Kana, M.T.H.A.; Mohamed, E.A. Growth Inhibition of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria during Gas and Oil Production Using Novel Schiff Base Diquaternary Biocides: Synthesis, Antimicrobial, and Toxicological Assessment. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 40098–40108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenblum, E.; de Goulart, F.R.V.; de Rodrigues, I.A.; Abreu, F.; Lins, U.; Alves, P.B.; Blank, A.F.; Valoni, É.; Sebastián, G.V.; Alviano, D.S.; et al. Antimicrobial action and anti-corrosion effect against sulfate reducing bacteria by lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus) essential oil and its major component, the citral. AMB Express 2013, 3, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa JPda Tibúrcio, S.R.G.; Marques, J.M.; Seldin, L.; Coelho, R.R.R. Streptomyces lunalinharesii 235 prevents the formation of a sulfate-reducing bacterial biofilm. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Melo, M.C.R.; Maasch, J.R.M.A.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Accelerating antibiotic discovery through artificial intelligence. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, T.W.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Netzeva, T.I. The present status of QSAR in toxicology. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 2003, 622, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, T.A.; Nunes-Alves, A.; Mazzolari, A.; Ruggiu, F.; Wei, G.W.; Merz, K. The (Re)-Evolution of Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship (QSAR) Studies Propelled by the Surge of Machine Learning Methods. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 5317–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anquetin, G.; Greiner, J.; Mahmoudi, N.; Santillana-Hayat, M.; Gozalbes, R.; Farhati, K.; Derouin, F.; Aubry, A.; Cambau, E.; Vierling, P. Design, synthesis and activity against Toxoplasma gondii, Plasmodium spp., and Mycobacterium tuberculosis of new 6-fluoroquinolones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 41, 1478–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appell, M.; Compton, D.L.; Evans, K.O. Predictive Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship Modeling of the Antifungal and Antibiotic Properties of Triazolothiadiazine Compounds. Methods Protoc. 2021, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenssen, H.; Fjell, C.D.; Cherkasov, A. Hancock REW: QSARmodeling computer-aided design of antimicrobial peptides. J. Pept. Sci. 2008, 14, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toropova, M.A.; Veselinović, A.M.; Veselinović, J.B.; Stojanović, D.B.; Toropov, A.A. QSAR modeling of the antimicrobial activity of peptides as a mathematical function of a sequence of amino acids. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2015, 59, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, M.H.; Orozco, R.Q.; Rezende, S.B.; Rodrigues, G.; Oshiro, K.G.N.; Cândido, E.S.; Franco, O.L. Computer-Aided Design of Antimicrobial Peptides: Are We Generating Effective Drug Candidates? Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurade, M.B.; Saha, S.; Salama, E.S.; Patil, S.M.; Govindwar, S.P.; Jeon, B.H. Acetoclastic methanogenesis led by Methanosarcina in anaerobic co-digestion of fats, oil and grease for enhanced production of methane. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Hýžová, B.; Vítězová, M.; Rittmann, S.K.M.R. Microscopic Methods for Identification of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria from Various Habitats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, T.; Lovley, D.R. Desulfovibrio vulgaris as a model microbe for the study of corrosion under sulfate-reducing conditions. mLife 2022, 1, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, F.C.; Koetzle, T.F.; Williams, G.J.B.; Meyer, E.F.; Brice, M.D.; Rodgers, J.R.; Kennard, O.; Shimanouchi, T.; Tasumi, M. The protein data bank: Acomputer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 112, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomburg, I.; Hofmann, O.; Baensch, C.; Chang, A.; Schomburg, D. Enzyme data and metabolic information: BRENDA, a resource for research in biology, biochemistry, and medicine. Gene Funct. Dis. 2000, 1, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1373–D1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.M.; Macpherson, R.; Miller, J.D.A. The Effect of Inhibitors on Sulphate Reducing Bacteria: A Compilation. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1964, 27, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, D.J.W.; Speece, R.E. A database of chemical toxicity to environmental bacteria its use in interspecies comparisons correlations. Res. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1991, 63, 198–207. [Google Scholar]
- Landrum, G.; Tosco, P.; Kelley, B.; Sriniker; Ric, G.; Vianello, R.; NadineSchneider; Dalke, A.; N, D.; Kawashima, E.; et al. RDKit. Available online: https://www.rdkit.org (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Moriwaki, H.; Tian, Y.S.; Kawashita, N.; Takagi, T. Mordred: A molecular descriptor calculator. J. Cheminform. 2018, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todeschini, R.; Consonni, V. Molecular Descriptors for Chemoinformatics. In Molecular Descriptors for Chemoinformatics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–252. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jeong, J.C. Enhanced recursive feature elimination. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA 2007), Cincinnati, OH, USA, 13–15 December 2007; pp. 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 3149–3157. [Google Scholar]
- Altmann, A.; Toloşi, L.; Sander, O.; Lengauer, T. Permutation importance: A corrected feature importance measure. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.; Portlock, T.; Nyaga, D.M.; O’Sullivan, J.M. A review of model evaluation metrics for machine learning in genetics and genomics. Front. Bioinform. 2024, 4, 1457619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrum, G. Thresholds for “Random” in Fingerprints the RDKit Supports—RDKit Blog. Available online: https://rdkit.blogspot.com/2013/10/fingerprint-thresholds.html (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Zhang, Z.; Sangion, A.; Wang, S.; Gouin, T.; Brown, T.; Arnot, J.A.; Li, L. Chemical Space Covered by Applicability Domains of Quantitative Structure-Property Relationships and Semiempirical Relationships in Chemical Assessments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3386–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benigni, R.; Bossa, C. Mechanisms of Chemical Carcinogenicity and Mutagenicity: A Review with Implications for Predictive Toxicology. 2011. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/cr100222q (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Sahigara, F.; Mansouri, K.; Ballabio, D.; Mauri, A.; Consonni, V.; Todeschini, R. Comparison of different approaches to define the applicability domain of QSAR models. Molecules 2012, 17, 4791–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foundation, D.S. Django. 2019. Available online: https://www.djangoproject.com/ (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- Sorokina, M.; Merseburger, P.; Rajan, K.; Yirik, M.A.; Steinbeck, C. COCONUTonline: Collection of Open Natural Products database. J. Cheminform. 2021, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA/AWWA/WEF: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Angelidaki, I.; Alves, M.; Bolzonella, D.; Borzacconi, L.; Campos, J.L.; Guwy, A.J.; Kalyuzhnyi, S.; Jenicek, P.; Van Lier, J.B. Defining the biomethane potential (BMP) of solid organic wastes and energy crops: A proposed protocol for batch assays. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, N.; Wagner, A.O.; Illmer, P. Effect of sulfate addition on carbon flow and microbial community composition during thermophilic digestion of cellulose. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 4605–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Cheng, H.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, C.; Chen, C.; Liu, W.; Ding, C.; Li, Z.; et al. Enhanced methane production by alleviating sulfide inhibition with a microbial electrolysis coupled anaerobic digestion reactor. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lens, P.N.L.; Visser, A.; Janssen, A.J.H.; Hulshoff Pol, L.W.; Lettinga, G. Biotechnological Treatment of Sulfate-Rich Wastewaters. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 28, 41–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, L.E.; Boyle, W.C.; Converse, J.C. Improved alkalimetric monitoring for anaerobic digestion of high-strength wastes. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1986, 58, 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Barthakur, A.; Bora, M.; Singh, H.D. Kinetic Model for Substrate Utilization and Methane Production in the Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Feeds. Biotechnol. Prog. 1991, 7, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stams, A.J.M. Metabolic interactions between anaerobic bacteria in methanogenic environments. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1994, 66, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdel, F. Microbiology and Ecology of Sulphate and Sulphur Reducing Bacteria. In Biology of Anaerobic Organisms; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 456–486. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, A.; Jeske, L.; Ulbrich, S.; Hofmann, J.; Koblitz, J.; Schomburg, I.; Neumann-Schaal, M.; Jahn, D.; Schomburg, D. BRENDA, the ELIXIR core data resource in 2021: New developments and updates. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D498–D508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi-Ichi, F.; Ishikawa, T.; Tam, V.K.; Deloer, S.; Hamano, S.; Hamada, T.; Yoshida, H. Characterization of Entamoeba histolytica adenosine 5′-phosphosulfate (APS) kinase; validation as a target and provision of leads for the development of new drugs against amoebiasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, E.S.; De Souza, L.C.V.; De Assis, P.N.; De Almeida, P.F.; Ramos-De-Souza, E. Souring control in fluid samples of oil industry using a multiple ligand simultaneous docking (MLSD) strategy. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2015, 33, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, E.S.; Gritta, D.H.S.; De Almeida, J.S. Analysis of interactions between potent inhibitors of ATP sulfurylase via molecular dynamics. Mol. Simul. 2016, 42, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, B.P.; Bottiglieri, T.; Arning, E.; Ziegler, M.G.; Hansen, L.A.; Masliah, E. Elevated S-adenosylhomocysteine in Alzheimer brain: Influence on methyltransferases cognitive function. J. Neural Transm. 2004, 111, 547–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Spears, M.E.; Carlisle, A.E.; Kim, D. Endogenous toxic metabolites and implications in cancer therapy. Oncogene 2020, 39, 5709–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postgate, J.R. The Sulphate-Reducing Bacteria; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y. A new method for the simultaneous enhancement of methane yield and reduction of hydrogen sulfide production in the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A. The impact of natural products upon modern drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynendaele, E.; Furman, C.; Wielgomas, B.; Larsson, P.; Hak, E.; Block, T.; Van Calenbergh, S.; Willand, N.; Markuszewski, M.; Odell, L.R.; et al. Sustainability in drug discovery. Med. Drug Discov. 2021, 12, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Sikdar, P.; Bairagi, M. Recent developments of 2-aminothiazoles in medicinal chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 109, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minickaitė, R.; Grybaitė, B.; Vaickelionienė, R.; Kavaliauskas, P.; Petraitis, V.; Petraitienė, R.; Tumosienė, I.; Jonuškienė, I.; Mickevičius, V. Synthesis of Novel Aminothiazole Derivatives as Promising Antiviral Antioxidant Antibacterial Candidates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Dai, X.; Xu, Y. Microbial Community and Metabolic Pathways in Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Solid Wastes: Progress, Challenges and Prospects. Fermentation 2025, 11, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, Z.; Maituersong, Z.; Wang, T.; Su, Y. Adenosine Monophosphate as a Metabolic Adjuvant Enhances Antibiotic Efficacy against Drug-Resistant Bacterial Pathogens. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratov, E.N.; Bajorath, J.; Sheridan, R.P.; Tetko, I.V.; Filimonov, D.; Poroikov, V.; Oprea, T.I.; Baskin, I.I.; Varnek, A.; Roitberg, A.; et al. QSAR without borders. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3525–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S.; Xu, Y.; Nie, W.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, T.; Chen, P. Quaternary Ammonium Salts: Insights into Synthesis and New Directions in Antibacterial Applications. Bioconjug. Chem. 2023, 34, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.; Park, T.; Kim, M.; Yu, Z. Rumen methanogens mitigation of methane emission by anti-methanogenic compounds substances. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGurrin, A.; Maguire, J.; Tiwari, B.K.; Garcia-Vaquero, M. Anti-methanogenic potential of seaweeds seaweed-derived compounds in ruminant feed: Current perspectives risks future prospects. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eric, S.; Cvijetic, I.; Zloh, M. 3D-QSARstudy of adenosine 5’-phosphosulfate (APS) analouges as ligands for APSreductase. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2021, 86, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, D.J.W.; Speece, R.E. Quantitative structure-activity relationships for chemical toxicity to environmental bacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1991, 22, 198–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemek, J.; Valent, M.; Pódová, M.; Košíková, B.; Joniak, D. Antimicrobiai properties of aromatic compounds of plant origin. Folia Microbiol. 1987, 32, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, E.S.; De Souza, L.C.V.; De Assis, P.N.; Almeida, P.F.; Ramos-De-Souza, E. Novel potential inhibitors for adenylylsulfate reductase to control souring of water in oil industries. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 32, 1780–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Meng, Q.; Yu, Z. Effects of Methanogenic Inhibitors on Methane Production and Abundances of Methanogens and Cellulolytic Bacteria in In Vitro Ruminal Cultures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, M.; Uzairu, A.; Shallangwa, G.A.; Mamza, P.A.; Ibrahim, M.T. Computational modelling of some phenolic diterpenoid compounds as anti-influenza A virus agents. Sci. Afr. 2023, 19, e01462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejera, E.; Munteanu, C.R.; López-Cortés, A.; Cabrera-Andrade, A.; Pérez-Castillo, Y. Drugs Repurposing Using QSAR, Docking and Molecular Dynamics for Possible Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Protease. Molecules 2020, 25, 5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodyna, D.; Kovalishyn, V.; Semenyuta, I.; Blagodatnyi, V.; Rogalsky, S.; Metelytsia, L. Imidazolium ionic liquids as effective antiseptics disinfectants against drug resistant, S. aureus: In silico and in vitro studies. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2018, 73, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Yang, X.; Ma, C. QSAR, Docking Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies of Sigmacidins as Antimicrobials against Streptococci. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouarab-Chibane, L.; Forquet, V.; Lantéri, P.; Clément, Y.; Léonard-Akkari, L.; Oulahal, N.; Degraeve, P.; Bordes, C. Antibacterial properties of polyphenols: Characterization and QSAR (Quantitative structure-activity relationship) models. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 440698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izmailyan, R.; Matevosyan, M.; Khachatryan, H.; Shavina, A.; Gevorgyan, S.; Ghazaryan, A.; Tirosyan, I.; Gabrielyan, Y.; Ayvazyan, M.; Martirosyan, B.; et al. Discovery of new antiviral agents through artificial intelligence: In vitro and in vivo results. Antiviral Res. 2024, 222, 105818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, H.; Wu, J.; Turville, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Valtchev, P.; Schindeler, A.; Dehghani, F. Virtual screening and in vitro validation of natural compound inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 119, 105574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).