Transcriptional Regulation of Salt Stress Tolerance in Triticum aestivum (Wheat): NAC Transcription Factors and Their Target Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of NAC Sequences
2.2. Transcription Factor Binding Site Prediction
2.3. Functional Gene Extraction
2.4. Mapping of DNA-Binding Residues in NAC Transcription Factors
2.5. Chromosomal Localization of NAC Genes
2.6. Protein Structure Prediction
2.7. Plant Growth Conditions and Treatments
2.8. Reverse Transcription-Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
3. Results
3.1. Identification of NAC Transcription Factors in the Wheat Genome
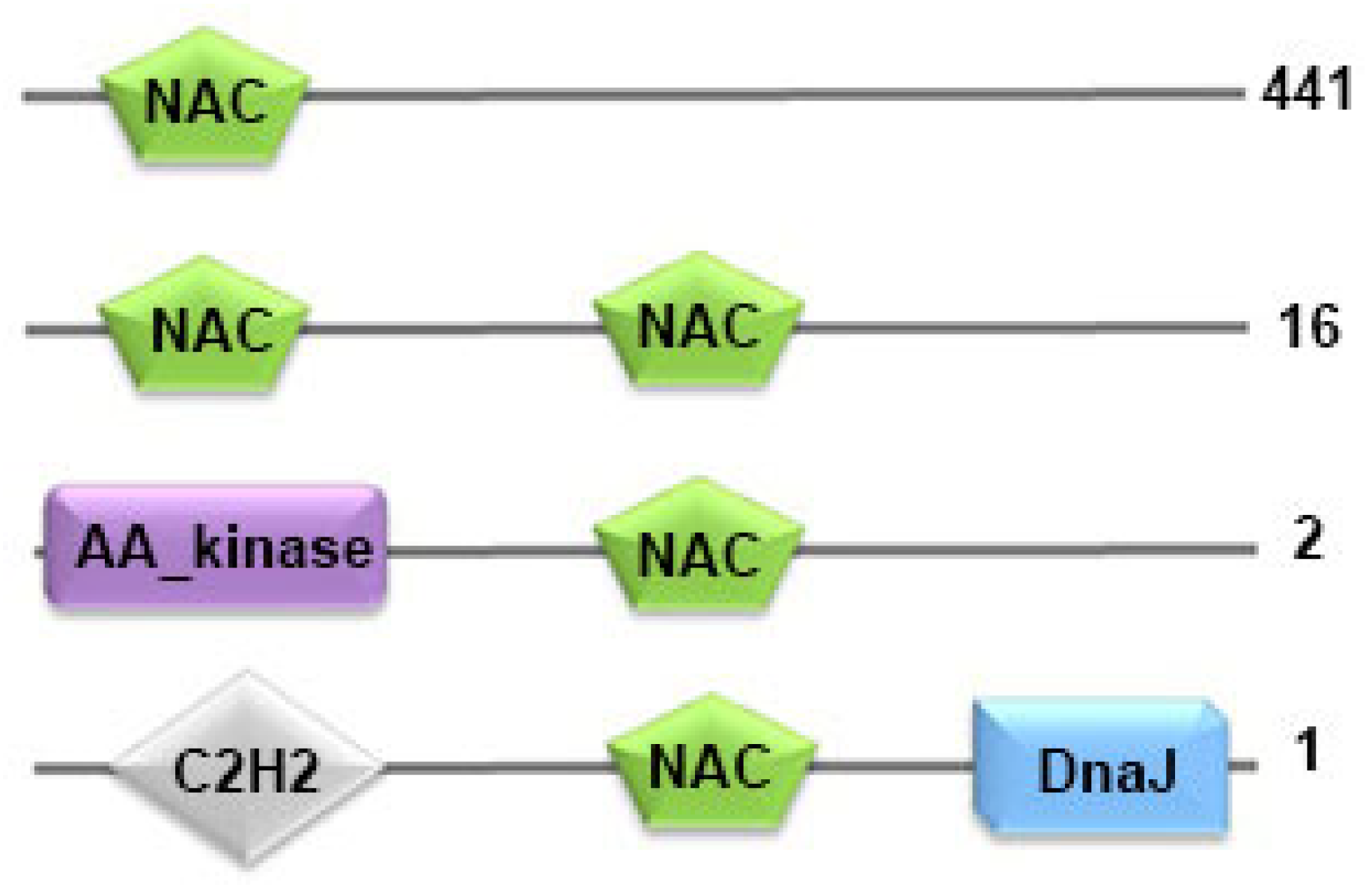
3.2. Domain Architecture of NAC Transcription Factors
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of NAC Transcription Factors
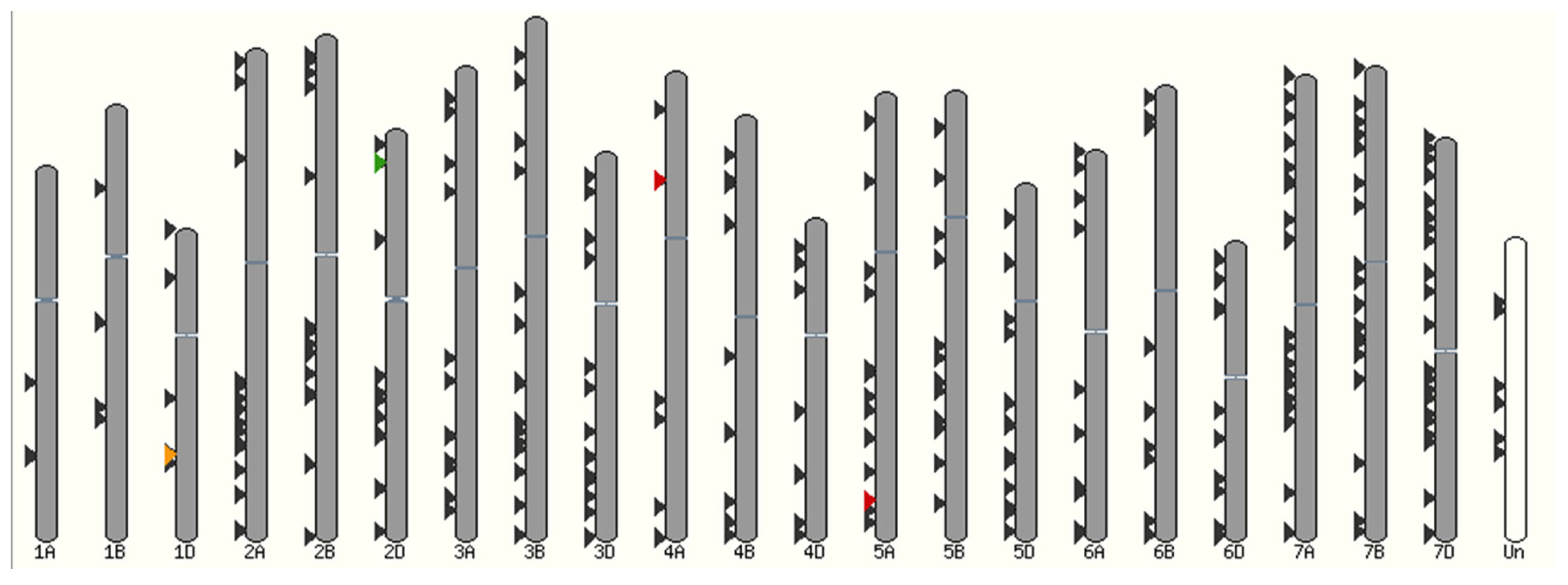
3.4. Chromosomal Location of NAC Transcription Factors
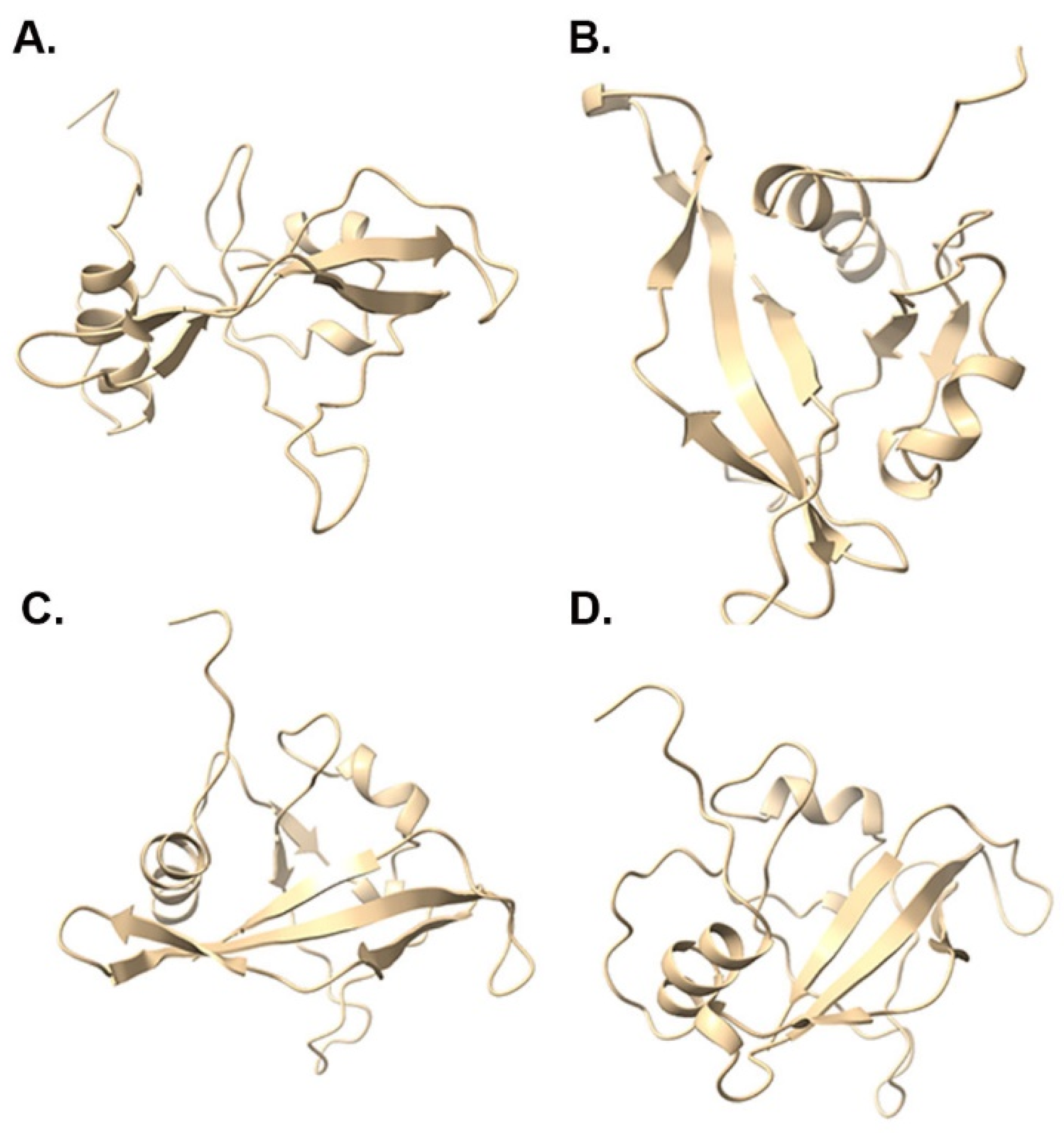
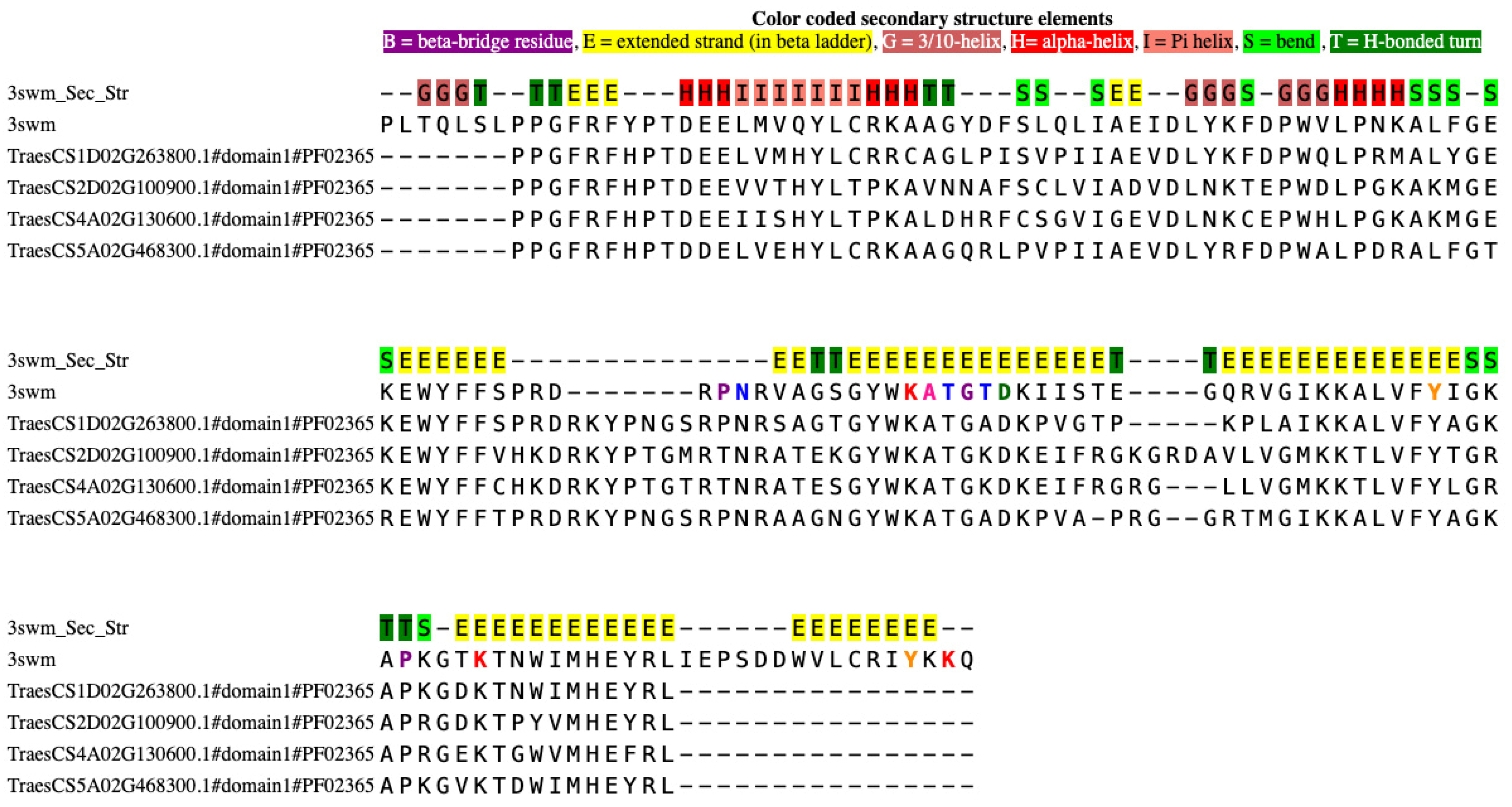
3.5. Protein Structure Prediction and DNA Binding Site Analysis
3.6. Identification and Extraction of Target Genes
3.7. NAC Family Gene Expression Under Salt Stress
3.7.1. NAC_1D Family
3.7.2. NAC_2D Family
3.7.3. NAC_4A Family
3.7.4. NAC_5A Family
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Chen, Z.; Marquis, M.; Averyt, K.; Tignor, M.; Miller, H. Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Group I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Summary for Policymakers; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- van de Wal, R.S.W.; Nicholls, R.J.; Behar, D.; McInnes, K.; Stammer, D.; Lowe, J.A.; Church, J.A.; DeConto, R.; Fettweis, X.; Goelzer, H.; et al. A high-end estimate of sea level rise for practitioners. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2022EF002751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.K. Impact of climate change on agriculture production and its sustainable solutions. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 2, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.; Muhammad, Z. Salinity: A Major Agricultural Problem—Causes, Impacts on Crop Productivity and Management Strategies, in Plant Abiotic Stress Tolerance: Agronomic, Molecular and Biotechnological Approaches; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 83–99. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, P.; Gill, R.; Ahlawat, S.; Anjum, N.A.; Sharma, K.K.; Ansari, A.A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Ramakrishna, A.; Chauhan, N.; Tuteja, N.; et al. Targeting the Redox Regulatory Mechanisms for Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crops. In Biochemical, Physiological and Molecular Avenues for Combating Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 151–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, A.; Skalicky, M.; Brestic, M.; Maitra, S.; Alam, M.A.; Abu Syed, M.; Hossain, J.; Sarkar, S.; Saha, S.; Bhadra, P.; et al. Consequences and mitigation strategies of abiotic stresses in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under the changing climate. Agronomy 2021, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandratos, N.; Bruinsma, J. FAO, World Agriculture Towards 2030/2050: The 2012 Revision. 2012. Available online: www.fao.org/economic/esa (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Giraldo, P.; Benavente, E.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F.; Gimenez, E. Worldwide research trends on wheat and barley: A bibliometric comparative analysis. Agronomy 2019, 9, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesta, P.; Mora, F.; Del Pozo, A. Association mapping of drought tolerance indices in wheat: QTL-rich regions on chromosome 4A. Sci. Agric. 2019, 77, e20180153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Gong, Z.; Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, R.; Ge, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, R. Plants’ response to abiotic stress: Mechanisms and strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gan, S. AtNAP, a NAC family transcription factor, has an important role in leaf senescence. Plant J. 2006, 46, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.; Berk, K.; Aronsson, H. Evolution and identification of DREB transcription factors in the wheat genome: Modeling, docking and simulation of DREB proteins associated with salt stress. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 7191–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Lethin, J.; Blomberg, R.; Mousavi, H.; Aronsson, H. In silico based screening of WRKY genes for identifying functional genes regulated by WRKY under salt stress. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 83, 107131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, S.; Lethin, J.; Liu, X.; Pelc, J.; Zeng, P.; Hassan, S.; Aronsson, H. Genome-wide analysis of MYB transcription factors in the wheat genome and their roles in salt stress response. Cells 2023, 12, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.F.; Wu, S.H. Molecular events in senescing Arabidopsis leaves. Plant J. 2004, 39, 612–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sukumaran, S.; Viitanen, E.; Naik, N.; Hassan, S.; Aronsson, H. An Accurate Representation of the Number of bZIP Transcription Factors in the Triticum aestivum (Wheat) Genome and the Regulation of Functional Genes during Salt Stress. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 4417–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, F.; Maeta, E.; Terashima, A.; Kawaura, K.; Ogihara, Y.; Takumi, S. Development of abiotic stress tolerance via bZIP-type transcription factor LIP19 in common wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 891–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.B.; Foley, R.C.; Oñate-Sánchez, L. Transcription factors in plant defense and stress responses. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, M.; Ishida, T.; Fukaki, H.; Fujisawa, H.; Tasaka, M. Genes involved in organ separation in Arabidopsis: An analysis of the cup-shaped cotyledon mutant. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 841–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delessert, C.; Kazan, K.; Wilson, I.W.; Van Der Straeten, D.; Manners, J.; Dennis, E.S.; Dolferus, R. The transcription factor ATAF2 represses the expression of pathogenesis-related genes in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2005, 43, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souer, E.; van Houwelingen, A.; Kloos, D.; Mol, J.; Koes, R. The no apical meristem gene of Petunia is required for pattern formation in embryos and flowers and is expressed at meristem and primordia boundaries. Cell 1996, 85, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, K.; Takasaki, H.; Mizoi, J.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2012, 1819, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.N.; Ernst, H.A.; Leggio, L.L.; Skriver, K. NAC transcription factors: Structurally distinct, functionally diverse. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooka, H.; Satoh, K.; Doi, K.; Nagata, T.; Otomo, Y.; Murakami, K.; Matsubara, K.; Osato, N.; Kawai, J.; Carninci, P.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of NAC family genes in Oryza sativa and Arabidopsis thaliana. DNA Res. 2003, 10, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; He, H.; Chang, Y.; Miao, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Dong, F.; Xiong, L. Multiple roles of NAC transcription factors in plant development and stress responses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2025, 67, 510–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinge, M.; Boller, T. Differential induction of two potato genes, Stprx2 and StNAC, in response to infection by Phytophthora infestans and to wounding. Plant Mol. Biol. 2001, 46, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedus, D.; Yu, M.; Baldwin, D.; Gruber, M.; Sharpe, A.; Parkin, I.; Whitwill, S.; Lydiate, D. Molecular characterization of Brassica napus NAC domain transcriptional activators induced in response to biotic and abiotic stress. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 53, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.J.; Mu, R.; Cao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S. AtNAC2, a transcription factor downstream of ethylene and auxin signaling pathways, is involved in salt stress response and lateral root development. Plant J. 2005, 44, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.S.P.; Nakashima, K.; Sakuma, Y.; Osakabe, Y.; Qin, F.; Simpson, S.D.; Maruyama, K.; Fujita, Y.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Co-expression of the stress-inducible zinc finger homeodomain ZFHD1 and NAC transcription factors enhances expression of the ERD1 gene in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007, 49, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Dai, M.; Yao, J.; Xiao, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, L. Overexpressing a NAM, ATAF, and CUC (NAC) transcription factor enhances drought resistance and salt tolerance in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12987–12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uauy, C.; Distelfeld, A.; Fahima, T.; Blechl, A.; Dubcovsky, J. A NAC gene regulating senescence improves grain protein, zinc, and iron content in wheat. Science 2006, 314, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Sanz-Burgos, A.P.; Guo, H.; García, J.A.; Gutiérrez, C. GRAB proteins, novel members of the NAC domain family, isolated by their interaction with a geminivirus protein. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 39, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.-P.; Bower, N.I.; McIntyre, C.L.; Riding, G.A.; Kazan, K.; Shorter, R. TaNAC69 from the NAC superfamily of transcription factors is up-regulated by abiotic stresses in wheat and recognises two consensus DNA-binding sequences. Funct. Plant Biol. 2006, 33, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.-Y.; Deng, L.; Cai, G.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Zhao, J.; Huang, L.-L.; Kang, Z.-S. Characterization of a novel wheat NAC transcription factor gene involved in defense response against stripe rust pathogen infection and abiotic stresses. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 3703–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, F.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Qi, T.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, R.; Yi, R.; He, J.; et al. Genome-wide survey and functional verification of the NAC transcription factor family in wild emmer wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, Z.; Pan, W.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, H.; Li, X.; Xing, L.; Jia, H.; She, K.; Nie, X. Genome-wide identification, evolution and expression analysis of NAC gene family under salt stress in wild emmer wheat (Triticum dicoccoides. L). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Tang, X. NAC transcription factors in plant multiple abiotic stress responses: Progress and prospects. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xia, P. NAC transcription factors as biological macromolecules responded to abiotic stress: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308 Pt 1, 142400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrill, P.; Harrington, S.A.; Uauy, C. Genome-wide sequence and expression analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in polyploid wheat. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 3019–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Geng, H.; Cui, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, D. Functional analysis of wheat NAC transcription factor, TaNAC069, in regulating resistance of wheat to leaf rust fungus. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 604797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, C.; Zhuang, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Yan, Y.; Xu, H.; Ma, C.; et al. A wheat NAC transcription factor, TaNAC018-7D, regulates seed dormancy and germination by binding to the GA biosynthesis gene TaGA7ox-A1. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2025, 233, 106130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Guo, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Shi, W.; Xia, G.; Fu, D.; et al. WheatOmics: A platform combining multiple omics data to accelerate functional genomics studies in wheat. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 1965–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.; Haleemath Sameer, S.; Töpel, M.; Aronsson, H. MSALigMap—A Tool for Mapping Active-Site Amino Acids in PDB Structures onto Known and Novel Unannotated Homologous Sequences with Similar Function. Life 2022, 12, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, E.C.; Goddard, T.D.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Pearson, Z.J.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Tools for structure building and analysis. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lethin, J.; Byrt, C.; Berger, B.; Brien, C.; Jewell, N.; Roy, S.; Mousavi, H.; Sukumaran, S.; Olsson, O.; Aronsson, H. Improved salinity tolerance-associated variables observed in EMS mutagenized wheat lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lethin, J.; Shakil, S.S.M.; Hassan, S.; Sirijovski, N.; Töpel, M.; Olsson, O.; Aronsson, H. Development and characterization of an EMS-mutagenized wheat population and identification of salt-tolerant wheat lines. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, H.; Bruning, B.; Van Straten, G.; Almås, Å.R.; Lethin, J.; Naik, N.; Hassan, S.; Olsson, O.; Aronsson, H. Effects of increasing salinity by drip irrigation on total grain weight show high yield potential of putative salt-tolerant mutagenized wheat lines. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerin, C.; Roche, J.; Allard, V.; Ravel, C.; Mouzeyar, S.; Bouzidi, M.F. Genome-wide analysis, expansion and expression of the NAC family under drought and heat stresses in bread wheat (T. aestivum L.). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, S.A.; Yang, A.W.H.; Sasse, A.; Cowley, G.; Albu, M.; Caddick, M.X.; Morris, Q.D.; Weirauch, M.T.; Hughes, T.R. Similarity regression predicts evolution of transcription factor sequence specificity. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Das Gupta, M.; Joseph, A.P.; Chatterjee, N.; Srinivasan, N.; Nath, U. Identification of specific DNA binding residues in the TCP family of transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1174–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Li, F.; Mei, F.; Chen, N.; Kang, Z. Regulatory changes in TaSNAC8-6A are associated with drought tolerance in wheat seedlings. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1078–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Yang, Q.; Liu, S.; Chen, X. Comparative transcriptome analysis of resistant and susceptible wheat in response to Rhizoctonia cerealis. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Krishnappa, G.; Kumar, S.; Devate, N.B.; Rathan, N.D.; Kumar, S.; Mishra, C.N.; Ram, S.; Tiwari, R.; Parkash, O.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies novel loci and candidate genes for rust resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, L.J.; Ortega, S.F.; Harper, A.L. Identification of candidate regulators of the response to early heat stress in climate-adapted wheat landraces via transcriptomic and co-expression network analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1252885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.J.; Chen, D.; Lynne Mclntyre, C.; Fernanda Dreccer, M.; Zhang, Z.-B.; Drenth, J.; Kalaipandian, S.; Chang, H.; Xue, G.-P. Heat shock factor C2a serves as a proactive mechanism for heat protection in developing grains in wheat via an ABA-mediated regulatory pathway. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.; Wilkinson, M.; Lowe, C.; Xu, J.; Hughes, D.; Hassall, K.L.; Hassani-Pak, K.; Amberkar, S.; Noleto-Dias, C.; Ward, J.; et al. Novel molecules and target genes for vegetative heat tolerance in wheat. Plant-Environ. Interact. 2022, 3, 264–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samtani, H.; Sharma, A.; Khurana, P. Overexpression of HVA1 enhances drought and heat stress tolerance in Triticum aestivum doubled haploid plants. Cells 2022, 11, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Ding, L.; Nie, Y.; Li, F.; Ma, Z.; et al. The E3 ligase TaGW2 mediates transcription factor TaARR12 degradation to promote drought resistance in wheat. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 605–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, R.; Safi, M.T.; Ahmadzai, W.; Sato, K.; Kawaura, K. Comparative transcriptome analysis of synthetic and common wheat in response to salt stress. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xia, Z.; Zhou, C.; Wang, G.; Meng, X.; Yin, P. Insights into salinity tolerance in wheat. Genes 2024, 15, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Peng, K.; Lou, G.; Ren, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Xing, J.; Song, C.; Cang, J. Transcriptome analysis of the winter wheat Dn1 in response to cold stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-P.; Huang, Y.W.; Chen, I.H.; Shenkwen, L.L.; Hsu, Y.H.; Tsai, C.H. Plasma membrane-associated cation-binding protein 1-like protein negatively regulates intercellular movement of BaMV. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 4765–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qin, L.; Sun, X.; Zhao, S.; Yu, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, M. Salt stress-induced changes in soil metabolites promote cadmium transport into wheat tissues. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 127, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasileva, K.V.; Vasquez-Gross, H.A.; Howell, T.; Bailey, P.; Paraiso, F.; Clissold, L.; Simmonds, J.; Ramirez-Gonzalez, R.H.; Wang, X.; Borrill, P.; et al. Uncovering hidden variation in polyploid wheat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E913–E921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Chang, J.; Chen, M.; Li, K.; Yang, G.; He, G. TaNAC29, a NAC transcription factor from wheat, enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, F.; Horie, T. A conserved primary salt tolerance mechanism mediated by HKT transporters: A mechanism for sodium exclusion and maintenance of high K+/Na+ ratio in leaves during salinity stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, B.; Akpınar, B.A.; Alaux, M.; Algharib, A.M.; Sehgal, D.; Ali, Z.; Aradottir, G.I.; Batley, J.; Bellec, A.; Bentley, A.R.; et al. Capturing wheat phenotypes at the genome level. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 851079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.-X.; Chen, S.-Y.; He, Y.-H.; Xu, Y.-P.; Yang, J.; Cai, X.-Z. Fine-tuning of the dual-role transcription factor WRKY8 via differential phosphorylation for robust broad-spectrum plant immunity. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 101072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Hoehenwarter, W.; Scheel, D.; Lee, J. Phosphorylation of the CAMTA3 transcription factor triggers its destabilization and nuclear export. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 1056–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, M.-K.; Zeng, J.; Chen, L.; Huang, W. Transcriptional activation and repression in the plant circadian clock: Revisiting core oscillator feedback loops and output pathways. Plant Commun. 2025, 6, 101415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, C.D.; Debray, K.; Herwegh, D.; Develtere, W.; Impens, L.; Schaumont, D.; Vandeputte, W.; Aesaert, S.; Coussens, G.; De Boe, Y.; et al. BREEDIT: A multiplex genome editing strategy to improve complex quantitative traits in maize. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 218–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| NAC Transcription Factors (TFs) and Their Target Genes (TGs) | Gene ID | Molecular Function | Biological Processes |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAC_1D (TF) | TraesCS1D02G263800 | DNA binding | regulation of transcription |
| Calcium-dependent protein kinase (TG) | TraesCS2A02G456100 | ATP binding, calcium ion binding, calmodulin binding, protein kinase activity | protein phosphorylation, intracellular signal transduction |
| Hsp70 (TG) | TraesCS1D02G284000 | ATP binding, ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone | Stress response |
| NAC_2D (TF) | TraesCS2D02G100900 | DNA binding | regulation of transcription |
| bZIP transcription factor (TG) | TraesCS3D02G364900 | DNA binding | regulation of transcription |
| HKT8 (TG) | TraesCS4D02G361300 | cation transmembrane transporter activity | cation transport, transmembrane transport, metal ion transport |
| NAC_4A (TF) | TraesCS4A02G130600 | DNA binding | regulation of transcription |
| Non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase (TG) | TraesCS7B02G279300 | protein kinase activity, ATP binding | protein phosphorylation, signal transduction |
| NAC_5A (TF) | TraesCS5A02G468300 | DNA binding | regulation of transcription |
| Plant cadmium resistance 2 (TG) | TraesCS3B02G214000 | unknown | unknown |
| Plasma membrane-associated cation-binding protein 1 (TG) | TraesCS3B02G183300 | anchored component of plasma membrane | cellular response to stimulus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Sukumaran, S.; Abedin, T.; Sayed, M.A.; Hassan, S.; Aronsson, H. Transcriptional Regulation of Salt Stress Tolerance in Triticum aestivum (Wheat): NAC Transcription Factors and Their Target Genes. Crops 2025, 5, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops5060081
Liu X, Sukumaran S, Abedin T, Sayed MA, Hassan S, Aronsson H. Transcriptional Regulation of Salt Stress Tolerance in Triticum aestivum (Wheat): NAC Transcription Factors and Their Target Genes. Crops. 2025; 5(6):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops5060081
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xin, Selvakumar Sukumaran, Tanvir Abedin, Md. Abu Sayed, Sameer Hassan, and Henrik Aronsson. 2025. "Transcriptional Regulation of Salt Stress Tolerance in Triticum aestivum (Wheat): NAC Transcription Factors and Their Target Genes" Crops 5, no. 6: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops5060081
APA StyleLiu, X., Sukumaran, S., Abedin, T., Sayed, M. A., Hassan, S., & Aronsson, H. (2025). Transcriptional Regulation of Salt Stress Tolerance in Triticum aestivum (Wheat): NAC Transcription Factors and Their Target Genes. Crops, 5(6), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops5060081






