Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming much of society in a short time. Regardless of whether we know it, we interact with AI systems when we seek information online, shop, work, and engage with social media. AI has massive potential to promote human wellbeing but also poses considerable risks, as set out in an open letter signed by leaders in the field, such as Geoffrey Hinton, the “Godfather of AI”. This paper examines how AI can be used as a powerful tool to change pro-social behaviors as part of social marketing programs. We examine opportunities to build on existing efforts to use AI for pro-social behavior changes and the challenges and potential risks that AI may pose. The specific aims of the paper are to explore how AI can be used in social marketing policy, strategy development, and operational delivery. We also explore what this means for future social marketing practice. We present an overview of case studies from the social marketing field and the application of AI in the past, present, and future. We examine the following key question: can these new technologies can be used to promote social good, and if so, how? Through examples from policy, strategy development, operations, and research in social marketing, we examine how AI has been used and successfully applied to improve consumer outcomes and analyze its implications for social marketing. We conclude that AI has substantial promise but also poses some challenges and has potential negative impacts on efforts to promote pro-social behavior changes. Used well, AI may enable social marketers to more rapidly assess how to modify programs of action to ensure maximum efficiency and effectiveness. We suggest future research and programs within this field.
1. Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) conditions the environment in which people engage in behaviors ranging from consumer choices to decisions related to personal health and wellbeing. AI is rapidly transforming the choice architecture of consumer decisions. Dwivedi et al. [1] and Davenport et al. [2] have already emphasized the potential of AI in marketing, arguing that AI can transform business models, marketing strategies, sales processes, customer service options, and ultimately consumer behaviors. Also, Huang and Rust [3] proposed a framework for using AI in marketing. AI tools could assist or replace humans in performing different tasks, such as automating repetitive functions and activities as well as processing and analyzing data. Yet, AI can go beyond the improvement and mere execution of simple tasks and benefit society more in general. AI is already being used to undertake meta-reviews of behavioral science research to formulate a better understanding of the world’s scientific literature on behavior change intervention effectiveness and synthesize the results to answer the ‘big question’: what works, how well, compared with what, for what behavior, for whom, and in what setting [4].
These rapid changes extend to the domain of pro-social and behavioral changes, such as promoting vaccine uptake and healthy eating and preventing drug abuse. The application of AI will increasingly have major implications for how social change programs are implemented and evaluated.
For example, chatbots (i.e., internet-based computer programs designed to simulate conversations with human users) can encourage users to choose to engage in a weight loss program through personalized advice or to buy a specific health-related branded product or service. Generative AI (large-language, deep-learning models that can generate high-quality text, images, and other content based on the data they were trained to use) can frame choices by describing the benefits of a commercial offering for consumers or by persuasively presenting the potential risks of unhealthy behaviors, such as nicotine use. While several conceptual papers exist reflecting on the implications of AI for business and marketing [5], including digital and social media marketing [6,7,8], none have yet discussed its role in social marketing.
Social marketing has long worked to apply marketing concepts to promote behaviors and social changes. AI represents a powerful new tool for social marketing to improve human wellbeing. But it comes with challenges and potential pitfalls, as well as opportunities. For example, could a chatbot-focused weight loss program have unintended consequences by promoting other unhealthy behavior changes? Would such a chatbot have the ability to realize these consequences and correct its advice? Would a generative AI program to reduce nicotine use lead to a healthy lifestyle or to individuals choosing to use other substances? AI is another tool in the social marketer’s toolbox, and it is critical to understand how it can be used for social good while avoiding unintended harm [9]. AI, in addition, poses several broad social challenges and risks, including increased social isolation, the invasion of privacy, deep fake disinformation propagation, employment, and the promotion of social conflict [10].
This paper examines how AI can be used as a powerful tool to influence pro-social behaviors. We examine opportunities to build on existing efforts to use AI for behavior changes and explore the challenges and potential risks that AI may pose in the future. We build our argument according to the following structure. In Section 2 (background), we provide definitions of social marketing, AI, and AI’s potential benefits for social marketing, concluding with a set of guiding questions. In Section 3 (methods), we present social marketing as a guiding framework. Through this framework, we explore case studies, further described in Section 4, of how AI can be used in social marketing policy development, strategy development, and operational delivery and explain what this means for future social marketing practice. In Section 5, we discuss the risks and limitations of using this approach, as well as future opportunities for AI-enabled social marketing practice and research.
2. Background
2.1. What Is Social Marketing?
Social marketing has been defined as a methodology that “…seeks to develop and integrate marketing concepts with other approaches to influence behaviors that benefit individuals and communities for the greater Social good. It seeks to integrate research, best practice, theory, participant, and partnership insight, to inform the delivery of competition sensitive and segmented Social change programs that are effective, efficient, equitable and sustainable” [11].
Based on this definition, social marketing may be understood as a comprehensive and strategic approach to facilitating or maintaining social good. It takes a citizen-centered approach in which insights about what matters to people inform the development of effective and efficient social programs. Such programs may be focused on specific segments of society, such as disadvantaged or underrepresented groups, and aim to be broadly beneficial to the development of the whole of society.
Social marketing has been a widespread framework for promoting social and behavioral changes since at least the 1970s [12,13]. In the past two decades, the discipline has evolved into academic and professional associations, which culminated in the establishment of the International Social Marketing Association (iSMA), following the first World Social Marketing Conference held in 2008 in Brighton (UK). Since then, many regional organizations have joined the iSMA, whose network now includes the Australian Association of Social Marketing (AASM), the European Social Marketing Association (ESMA), the Pacific Northwest Social Marketing Association (PNSMA), the Social Marketing Association of North America (SMANA), the Latin American Social Marketing Association (LAMSO), and the African Social Marketing Association (ASMA). Further readings related to the history of social marketing are available [14,15].
People and governments worldwide apply social marketing to develop and deliver programs to solve big problems like health promotion, disease prevention, family planning, environmental protection, economic development, crime reduction, election participation, and compliance with laws and regulations, among others. Social marketing is now standard practice among multi-lateral development agencies and in many national governments as it has a demonstrated track record of success and a growing base of evidence of its effectiveness [6,16,17].
At its core, social marketing is fundamentally about influencing human behavior in a way that is beneficial, acceptable to, and valued by citizens. Evolutionary psychologists such as Buss [18] and many economists agree that one key reason for the development of the human species has been our focus on mutuality and cooperation [16]. Both drivers of human development involve mutually beneficial exchanges and actions to influence the behavior of others for their own good and the group’s good. It has also been persuasively argued by Ridley [19] that trade and exchanges are fundamental aspects of what it is to be human.
2.2. Artificial Intelligence
In this paper, we define AI as a set of tools (i.e., digital computers or computer-controlled robots) that can perform tasks commonly associated with intelligent human beings, that is, learning, reasoning, problem solving, creating content, and using language. These are the core areas of research in AI [20,21].
Chatbots have come a long way since their inception in 1966. The original chatbot named “Eliza”, created by Joseph Weizenbaum at MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, marked a significant milestone towards automated customer engagement and interaction. Following this innovation, early rule-based conversational chatbots like “Parry” and “A.L.I.C.E” enabled organizations to transform their CX capabilities by delivering responses to predefined commands in real time [22].
Machine learning, natural language processing technologies, and large language models have led to the rapid development of advanced chatbots in recent years. In marketing, so-called “Intelligent systems” have been used to manage industrial marketing issues for the past two decades, according to a historical overview offered by Martinez-Lopez and Casillas [23]. Most AI applications relate to definitions of segments and business markets, managing customer and channel relationships, organizing supply chains, leveraging data for business intelligence, making decisions about pricing and communication strategies, and innovating products and services.
Now, chatbots can understand and respond to user inputs more extensively and effectively. Intelligent chatbots like Microsoft Cortana, Google Assistant, Amazon Alexa, and Apple Siri have recently spurred this paradigm shift, enabling analyses of patterns in large datasets and the training of these devices based on past interactions to deliver more accurate yet contextually relevant responses.
Recently, breakthroughs like deep learning, neural networks, and generative AI (e.g., ChatGPT) have significantly improved chatbot capabilities. For example, generative AI can engage humans in richer and more personalized conversations through a better understanding of speech formation, user intent, context, and nuances in language [24].
Generative AI unlocks new dimensions in customers’ and, in the case of governments, citizens’ engagement experience by generating human-like text, images, audio, and other outputs based on patterns and human prompts. Businesses across all industries are seeing generative AI as a next-gen approach to artificial intelligence, enabling them to automate both mundane and complex tasks [25,26].
Generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google BARD, and other large language models have dramatically improved how chatbots interact and converse more realistically and convincingly with users. GPTs can generate a structured human-sounding response to a natural language query and engage in conversations with a human user. As a result, companies could rely on these tools to interact with consumers by learning what they want or need and responding accordingly. This could enhance the consumers’ decision-making capabilities and deliver more personalized customer experiences.
2.3. How Is AI Relevant to Social Marketing?
Given the aforementioned principles underlying social marketing and the rapid growth, development, and growing influence of AI, it is time to address three fundamental questions: (1) How can social marketing harness the power of AI to promote social good? (2) What challenges and opportunities do AI technologies present to social marketer? (3) How does AI impact the framework and theoretical foundations underlying the field of social marketing?
AI’s use in marketing is not new, insomuch that a definition of AI marketing exists. “AI marketing” is defined as the process of leveraging AI tools and methods such as data models, algorithms, and machine learning to produce and interpret consumer insights that marketers can use to optimize spending and resource allocation, customize content, and personalize the consumer journey (source).
Social marketers have always sought to harness the power of marketing concepts and principles, as succinctly captured in the concept of the “4 Ps” of marketing (place, price, product, and promotion), and treated behavior as the outcome of interest, as opposed to sales in the case of commercial enterprises. Deep engagement is essential to both commercial and social marketing, and thus, chatbots, GPTs, and new AI technologies can serve the same essential functions in promoting pro-social behavior changes and the promotion of human wellbeing as well as economic growth and wealth creation.
There are six key benefits to applying AI as part of social marketing programs:
- Personalized, tailored support;
- Increased scale and reach;
- Increased engagement;
- Maintaining interest in a topic;
- Trend spotting and rapid response;
- Building communities of interest and providing support.
First, AI can increase the customization and tailoring of social marketing offerings. For example, GPT interactions with beneficiary audiences may identify preferences (e.g., which user benefits might promote engagement in a weight loss program) that would increase the perceived relevance and value of an offer; the tool might suggest the user access a local community to engage with or incentives to join local gyms or cooking clubs.
AI can also support market segmentation. For example, social media chatbots can use publicly available data to identify specific subgroups of interest based on combinations of psychographic (lifestyle), demographic, and behavioral data based on each user’s social media activity trails [27]. By identifying more refined audience segments and using lifestyle trend data on consumer preferences, social marketing can become more precise, provide personalized, tailored support, and deliver content that is more likely to promote social and behavioral changes.
AI can expand the reach of social marketing by enabling large-scale campaigns using digital media platforms at scale and at a low cost. For example, advanced chatbots can interact with thousands of social media users and engage them in interventions and research, deliver customized content based on their preferences, keep them engaged, and promote long-term participation in behavior change campaigns. AI can do much more than a human social media manager can possibly do in a day to respond to and engage with their community.
AI can increase engagement with social marketing through interactivity, two-way and multi-channel communication, and opportunities to engage with products in different places and at low price points. For example, generative AI can help address issues related to competition with unhealthy behaviors by examining large datasets, identifying human user patterns, and developing offers of exchanges that are more beneficial than those offered by the competition. We provide examples of this kind of approach in the next section. In particular, the ability of AI to learn through interactions with people provides an opportunity to continually refresh messages, offerings, and incentives. For example, using a gamification (i.e., the use of game theory to enhance engagement with a program or consumer offer) approach, continuous learning can help beneficiaries of social marketing programs stay engaged and campaigns achieve a greater impact beyond the duration of a program [28].
Generative AI can also enable campaigns to remain fresh and provide novel offerings, for example, by generating new content derived from consumers’ feedback and comments. In addition, large datasets of comments can be analyzed to identify new trends, for example, data on how users engage with new social media platforms, games, and service offerings and create tailored offerings.
Digital platforms such as social media have the inherent feature of interactivity and the potential to engage participants and populations in the context of their social networks, thus building a sense of identification and connection with the intervention. This can be accomplished through ‘gamification’ features, such as virtual incentives and rewards and through social role modelling by individuals that are appealing and aspirational for the audience. Digital platforms, like social media, provide the opportunity for participant co-creation (i.e., content co-generated by users and investigators) [29]. Generative AI tools could be fed social media content to generate further content or understand trends in consumers’ opinions and behaviors.
The purpose of this paper is to explore in more depth how social marketing may be able to harness AI technologies by engaging and learning from beneficiaries about how to create more effective offerings and services and tailoring behavior to influence efforts to achieve personal and community social development and improvement. The key question is, can these new technologies be used to promote social good [9]? And if so, how? We use the social marketing framework to present case examples.
3. Methods
3.1. The Social Marketing Framework
The new global-consensus social marketing concepts developed through a wide-ranging consensus-building exercise sponsored by the International Social Marketing Association and now endorsed by all current social marketing associations in 2017 set out a single central principle of social marketing and six core concepts that define its practice. The central social marketing principle is the creation of social and personal good. This is the central purpose of social marketing [30]. To deliver this principle, social marketing applies six core concepts. These six concepts are set out in Figure 1.
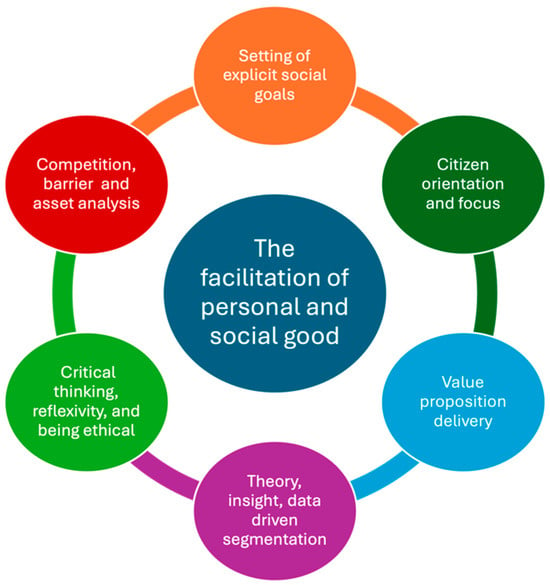
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the social marketing principle (at the center) and concepts (adapted from iSMA et al., 2017) [31].
Social marketing also applies a wide range of methods that are not unique and are applied in other approaches to social and behavioral changes, for example, the use of systematic planning and evaluation. What the social marketing conceptual model does is identify a hierarchy of relevance and importance about the key attributes and distinguishing features of social marketing. This helps practitioners promote and identify good social marketing practices [32]. AI is a new tool in the practitioner’s toolbox, and the challenge is to identify opportunities to effectively apply AI’s many capabilities to enhance social marketing, outlined above, to improve the effectiveness of social marketing in achieving equitable and ethical social and behavior changes.
These key concepts provide an overarching framework that guides the development of all social marketing strategy, programs, and campaigns. Social marketing draws on the use of a wide range of behavioral theories to promote human wellbeing but also assesses factors that underlie the receptivity of audiences to behavioral influence programs such as economic conditions, as well as cultural and social norms.
The social marketing framework has a place for AI as a technology and methodology for promoting social and behavior change. For example, receptivity to message and product offerings can be enhanced through rich customization through generative AI interactions with specific audiences and insights from large dataset analyses. Behavior changes (the product to a social marketer) can be precisely targeted based on data on human user preferences. Place, price, and promotional efforts can be matched with behavior changes based on generative AI interactions and resulting data to maximize social marketing effectiveness. These efforts can integrate the predictive theoretical models and constructs to build upon the social marketing framework.
3.2. Using AI in Relation to Each Element of the SM Framework
There are several ways that AI can be used in social marketing practice pertaining to each element of the social marketing framework; in some cases, it is already being used as such. Let us consider each of the six main components of the social marketing framework. For example, consider theory, insight, data, and evidence-informed audience segmentation. One essential element of this component is how audiences for social marketing efforts may be divided or segmented to maximize the impact of offerings on outcomes such as behavior changes. How could AI be used to better understand and analyze data from audiences to improve customer experience and campaign effectiveness? Answer: AI can analyze large quantities of data rapidly to identify audience segments and trends based on demographic characteristics but also psychographics (attitudes, beliefs, and lifestyle choices) and actual behavior, such as responding to online social media posts or engaging with social and or commercial offers online. In this way, AI can use large data, such as those from social media platforms reflecting consumer choices and preferences, to most effectively reach and impact consumers via messages, products/services, placements, and pricing schemes.
Also, consider competition analysis. AI can be used to analyze the prevalence of competing behaviors and existing prices, placements, and promotions in both commercial and social marketplaces.
Product, service, and social program innovation teams are increasingly dependent on understanding (in near real time) consumers’ preferences and motivations, how they are talking about products and brands, and even broader trends that are important to product development, go-to-market, and brand equity strategies. As brands need to get closer to the customer and do so more efficiently by reconciling redundancies in tools (like social listening, finding the voice of the customer, and text or sentiment analytics), many are rethinking their approaches to gathering and activating consumer insights—and the role of social media data as a whole. Online conversations from social media sites, blogs, and forums have become critical sources of insight that provide authentic, unprompted consumer feedback. Brands can use both online and offline conversations to drive better business decisions at scale.
AI will ultimately impact the social marketing framework and how campaigns are researched, designed, implemented, and evaluated. It will also impact policy development, strategy development, and operational and delivery management. In the following, we provide several case studies to illustrate how the framework has been and can be used to integrate AI in the future.
4. Case Studies
In the following, we present case studies of how AI has been used in social marketing. One central feature of these case studies and the main premise of our approach is that AI can best be used to enhance marketing and social marketing efforts through human–machine interaction and teams. As Sandro Kaulartz, Chief Research Officer within Ipsos Social Intelligence Analytics service line puts it, “Machine intelligence does a great job in laying the foundations, helping us navigate between complex contextual layers—not easily available to the human eye. But human-machine teams unlock this potential—and deliver scale, speed, and accuracy to have confidence in results” [33].
Our overall thesis is that AI can be a powerful tool to enhance social marketing and increase its effectiveness in promoting social good and behavior changes at different levels, depending on the focus of the social marketing action at hand. According to French and Blair-Stevens [34], these levels include: (a) policy development, (b) strategy development, and (c) operational delivery.
Social marketing concepts as outlined in this paper should be used to inform the development of AI systems designed to define a range of citizens insights and values that are gathered and synthesized to inform social policy selection. Social marketers will also be able to use these insights to rapidly capture and synthesize understanding about potential intervention policies and strategy. See Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of case studies.
4.1. AI in Policy Development
Governmental policy is informed by multiple strands of evidence, insight, and data, as well as risk assessments, feasibility assessments, and public opinion. This array of intelligence streams is currently assessed and weighed by ministers and civil servants using standards, expert advice, and political considerations. Most governments are accelerating their AI research activity and investment in policy enhancement. There are a growing number of governmental AI policy-focused case studies and interventions globally [35]. Many of these initiatives and experiments are focused on influencing behavior [36] and/or increasing the efficiency of systems and workers to promote public good. A good example is an AI model in the field of energy consumption developed by the United Kingdom’s government.
The UK uses machine learning clustering techniques to collect and analyze data from digital electricity meters to develop an automated AI model to predict which types of electrical home appliances are used and when. By doing so, the system predicts power consumption needs and patterns. This information allows public utilities to predict future energy needs and enables social marketing programs to be developed and targeted to encourage citizens to power their homes more smartly. This approach helps to reduce costs to citizens and overconsumption, which reduces climate change [17].
Social marketers play a significant role in this context, especially in supporting governments and public servants to develop appropriate strategies and endorse citizen-centric approaches. Strategic social marketing has been applied to policy development in various contexts since the early days of the discipline [34]. For example, several scholars have argued that social marketing principles could be applied to public health policy processes (Crawshaw 2013) [37] to enhance successful policy development and implementation. “Upstream social marketing” is a concept that embodies the essence of social marketers trying to influence policymakers’ decisions (and behaviors) to create systems that could foster community and individual behavior changes (see for example: Gordon [13], Key and Czaplewski [27], and Kennedy et al. [38]).
There is currently no single algorithm or process that leads to optimum policy decision making. Yet, Haddad et al. [4] suggest four ways in which AI can help governments develop policies. First, AI can help deliver faster, cheaper, and higher-quality public services, increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of policy and policy selection and evaluation. Second, AI can write policies in a way that resonates with citizens’ voices. The power of such AI enabled systems is that they are rooted in a deep and ongoing understanding of citizen expectations and their views about relevant social, economic, health, and environmental issues. These insights will increasingly empower governments and other policy development institutions to more efficiently select optimal policy interventions, track their impact, and if necessary, modify policies accordingly. Third, AI can help design budgets that minimize public spending and maximize returns. Fourth, AI can facilitate the work of public servants, freeing their time to unlock their creative and strategic potential—rather than focusing on daunting administrative tasks. The prerequisite is that governments set “clear [21], targeted, and public aspirations for their use of AI”, followed by the appropriate selection of AI-driven projects, monitored against the projects’ goals and overarching strategies. AI is being used to track and synthesize changing societal trends, values, sentiment, and behaviors in near real time (see the model suggested by Milano, O’Sullivan, and Gavanelli [39]). Generative AI has the potential to be able to gather and assess such diverse streams of intelligence and suggest policy options with the greatest chance of being effective, feasible, and broadly acceptable to citizens. The case below shows how AI could be used to “crunch” big data to synthesize policy options and make recommendations.
CitizenLab
A crowdsourcing tool called ‘CitizenLab’ [40], developed by a technology company based in Belgium, allowed policymakers to analyze previously collected citizen attitudes and views about climate change, fostering community engagement. CitizenLab’s platform allowed the collection of over 1700 ideas or options from citizens and, through its advanced analytic capabilities, translated the ideas into fifteen priority policies that the public was asked to vote on. This is what discriminative AI can do: synthesize and make sense of a large amount of data.
4.2. AI in Strategy Development
Social marketing is a field of research and practice deeply rooted in strategic planning processes (see, for example, Lee and Kotler [6]). Regardless of the approaches and planning frameworks used, social marketers act as strategic thinkers designing strategies for social and behavior changes (French and Blair-Stevens [34]). AI can help in different phases of the planning process, for example, by analyzing data for a situational analysis, defining social issues, understanding audiences by analyzing their values expressed through social media, analyzing consumer behaviors, etc. AI tools can also be leveraged to validate formative research findings, generate key messages, and improve campaign relevance and, ultimately, effectiveness. The case study below shows how AI could be used to generate and disseminate key messages.
4.2.1. Wikaytek
Wikaytek is a platform to disseminate reliable information among vulnerable populations with limited literacies [41]. This project targeted Syrian refugees living in Lebanon and was aimed to disseminate COVID-19-related information by repurposing social media content to WhatsApp. The service pulled information from reliable sources, such as the World Health Organization, UNICEF, and other international organizations, and diffused protective information via social media (mostly on the X platform, formerly known as Twitter). The service allowed an operator to select the messages, automatically translate them into Arabic, and produce an audio version of the text using Google’s text-to-speech feature. The translated text and audio content were then sent to a WhatsApp group of participants, with a connection available through application programming interfaces (APIs). The project was evaluated through a pilot study targeting Syrian refugee women living in a suburban area of the capital city Beirut. The qualitative and quantitative evaluations demonstrate that the users appreciated receiving information that was already verified and came from credible sources in a format that was acceptable and accessible to them (audio).
The Wikaytek project has been extended and expanded to serve the needs of the Jordanian Red Crescent and Lebanese Red Cross to disseminate messages in remote areas. A novel “Community Health Promotion Platform” incorporates generative AI features to create health promotion and health protection videos showcasing operators of two organizations talking about specific issues and disseminating audiovisual content via WhatsApp. Generative AI tools are used to compose textual messages, translate them into Arabic, and generate videos using an avatar resembling an official spokesperson from credible institutions in the respective countries.
4.2.2. COVID-19 Vaccination Promotion in Nigeria
Social media presents both risks and opportunities. It is a key vector of mis- and disinformation, but it also offers great opportunities for reaching diverse audiences with accurate health information. To leverage this potential, Agha et al. [42], explored drivers of COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and combated vaccine hesitancy, including on social media, as part of planning for a coordinated behavior change campaign in Nigeria. In-depth qualitative interviews were conducted with representatives of social media outreach organizations and influencers. The study provided valuable insights for leveraging social media networks to promote vaccine acceptance. Influencers shared important recommendations for building social media momentum and engaging different types of social media actors. Finally, the study also revealed great potential for an approach to designing the next generation of effective social media based social and behavioral change campaigns.
Using Rogers’ diffusion of innovation theory (Rogers, 2003) [43], the subsequent campaign targeted reluctant, but persuadable, health care providers (HCPs) who were expected to have the potential to speed vaccine uptake (diffusion) to a wider base of the persuadable, yet vaccine-hesitant population. The campaign used the Facebook social media platform, local social influencers, and paid and earned impressions to disseminate messages targeting key predictors of vaccine hesitancy (e.g., the “5 C’s” [8]). Influencers were trained to apply several “Implementation Practice Models,” including the Opportunity, Ability, Motivation (OAM) framework; the Capacity, Opportunity, Motivation, Behavior (COM-B) model; the East, Attractive, Social, and Timely (EAST) model; and the Fogg behavior model [44]. They also received ongoing technical assistance and content creation assistance from local and international advertising firms and the management of Facebook’s advertising platform to boost their messages.
4.3. AI in Operational Delivery
Social marketing plans also include implementation and evaluation components, rendering the application of strategies more tangible, measurable, and linked to impact (see Lee and Kotler [6]). Social marketers can leverage AI to assist in implementing these strategies, in monitoring and evaluating activities, and in developing actual intervention content.
Evaluation of Large-Scale, Multicomponent Campaigns Using Advanced Conversational Chatbots
AI has potential to enhance the effectiveness of behavior change interventions. Recent studies have identified several ways that AI has been and may in the future be used in multiple behavior change domains, including nicotine and tobacco control, nutrition and physical activity, and vaccination, among others [45]. Predictive analytics have focused on predicting weight loss, intervention adherence, dietary lapses, and emotional eating. Studies have focused on evaluating AI-assisted behavior change interventions that instantaneously collect behavioral data, optimize prediction models for behavioral lapse events, and enhance behavioral self-control through adaptive and personalized nudges/prompts [46]. Recent studies integrate many of these AI features into one learning app that can provide customized advice and encouragement for behavior changes based on the usage patterns of participants [47].
Large-scale, multicomponent social marketing campaigns can leverage AI to achieve behavior changes. AI-enabled promotions with machine learning and chatbot functionality can respond to user behavior and habits with prompts/nudges, advice, suggestions for adapted nutrition and physical activities, self-monitoring, and incentives. Campaign offerings can function as a kind of “personal assistant” that gets to know the user and provides recommendations based on their preferences and use of the app’s functions over time. These are learning systems that provide customized responses based on users’ consumption of content such as videos, achievement of goals, and badges, as well as self-monitoring and engagement with the participant community (social support).
For example, Evans et al. conducted a nationwide evaluation of social media content designed to promote COVID-19 vaccination and to complement research on a nationwide vaccination promotion campaign in Nigeria run in 2022 [48]. The campaign followed a theory of change model, described earlier, based on the Diffusion of Innovation theory, social norms theory, and the Motivation, Opportunity, Ability (MOA) framework [49,50,51]. The campaign aimed to influence individuals who were uncertain about vaccination as the theory of change posited that they could be persuaded to vaccinate. Data were collected through a novel intervention delivery and data collection platform through social media, and this study demonstrates the capability and potential of new social-media-based data collection techniques.
The study found that pro-vaccination social norms and vaccination rates increased, and vaccine hesitancy decreased, among participants randomized to the social media intervention study arm. Social media campaigns are a promising approach to increasing vaccination at scale in LMICs, and social norms are an important factor in promoting vaccination, which is consistent with social norms theory [52].
5. Discussion
In the table below, we provide a summary of the opportunities of and risks of the use of AI in social marketing applications related to policy or strategy development and operational delivery. In the following paragraphs, we elaborate on these opportunities, risks, and limitations, and provide some suggestions for future applications and approaches. See Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of AI opportunities and risks in social marketing.
5.1. Opportunities Presented by AI and How These Can Be Maximized
AI clearly offers tremendous possibilities to social marketing in its ability to help in identifying priority populations, expand our ability to reach them, and provide personalized and highly tailored interactions with human beings. The ability of AI to learn from its interactions with humans creates new opportunities to provide fresh offerings that will maintain interest, engagement, and incentives and overcome obstacles to long-term participation in behavior change initiatives typically required to achieve lasting change [53].
5.2. Risks Presented by AI and How These Can Be Mitigated
Additionally, ethical and moral aspects linked to the use of AI need to be fully understood. For instance, AI-based response biases due to programmers’ biases [22], users’ and audiences’ technological/media illiteracies, and the potential for inequalities in users and audiences, etc., need to be understood. AI has known biases based on the data available to it, such as from the internet. For example, stereotypical depictions of specific population groups may produce unintended negative effects and indeed even reduce the effectiveness of social marketing efforts. Social marketers need to develop the ability to use AI tools in ways that maintain high standards of professional ethics [54].
5.3. Limitations
There is a need for capability and capacity development in the application of AI within social marketing. In particular, social marketers need to understand and develop skills in employing AI in campaigns. This requires continuing professional education and experience using AI, to gain knowledge and a hands-on capacity to understand both what works and what does not work when using AI for behavior changes. AI is only as good as the data available to it and what it acquires through active operation (machine learning). Social marketers need to understand this and employ AI with an eye to its level of machine learning and developed capacity at a given point in a campaign. AI may improve as it is iteratively applied to a social change problem, such as overcoming vaccine hesitancy. As the system becomes more capable, social marketers can expand its application, understanding what the system can and cannot do at a specific point in its learning, development, and the implementation of a behavior change program.
5.4. Future Directions
One recommended future direction is to examine the relative effectiveness of AI responses/feedback compared to humans in designing social marketing solutions. A future research study could compare programs using either or both approaches and compare the relative effectiveness of each in achieving behavior change outcomes. This could also potentially be accomplished through a computer simulation approach.
Furthermore, AI can be used to optimize the right mix of social marketing interventions. As we have explored in this paper, AI will increasingly assist those applying social marketing concepts. One of the key social marketing concepts that AI will improve is the selection of what ‘forms’ and ‘types’ of intervention should be deployed to assist people in taking up and maintaining positive health behaviors [55].
The crux of the challenge is how to discern, based on theory, citizen insight and evidence, as well as what mix of ‘forms’ and ‘types’ of social program interventions will work in which situation with a specific target audience. In some cases, we may need to critically engage people in understanding a problem and helping to solve it, or we might set out to ‘nudge’ people into adopting a behavior [39]. In other circumstances, we may need to apply disincentives to dissuade bad behavior, such as smoking in the workplace. There are then several different ‘forms’ and ‘types’ of intervention that can be used to influence health-related behaviors. Assessing the efficiency, effectiveness, and acceptability of different elements of a social marketing intervention mix will be assisted by real-time data gathering, supplemented by data from intervention tracking and evaluation studies. These AI-assisted activities may also be enhanced using AI to conduct rolling meta-reviews of scientific, economic, and social studies.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we presented the case for using AI to enhance the impact and efficiency of social marketing. We have outlined examples of when AI could help and facilitate the work of social marketers operating at policy, strategy, and operational delivery levels. AI, and specifically generative AI, is likely to become an integral aspect of social marketing practice [37,56]. However, its application and, just as importantly, the interpretation of its recommendations and actions will need close supervision by those people deploying it. To this end, those applying AI in social marketing should take into account published ethical and professional standards guidance as well as the AI-specific good practice guidance and legislation that will emerge over the next few years.
In the field of policy development and selection, AI will have an important role to play in enhancing the systematic review of what policy options should be developed through a process of assembling from diverse streams of intelligence plausible and acceptable policy options. AI will also enhance the stream’s optimum selection of the best mix of intervention modalities to deploy. AI’s contribution to assessing the immediate and ongoing impact of interventions at an operational level will also enable social marketers to more rapidly assess how to modify programs of action to ensure maximum efficiency and effectiveness.
Finally, there is a need for more research on how best to apply AI in social marketing to maximize behavioral impacts. Funding agencies, such as the National Institutes of Health in the USA and the National Institute of Health Research in the UK, should specifically focus their funding efforts on how to harness AI for social and behavior changes. This will enable practitioners to apply research lessons learned to realize population-level benefits of AI-enabled social marketing at scale.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.D.E., M.B. and J.F.; methodology, W.D.E., M.B. and J.F.; validation, W.D.E., M.B. and J.F.; investigation, W.D.E., M.B. and J.F.; resources W.D.E., M.B. and J.F.; writing—original draft preparation, W.D.E.; writing—review and editing, W.D.E., M.B. and J.F.; visualization, M.B.; supervision, W.D.E.; project administration, W.D.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Hughes, L.; Ismagilova, E.; Aarts, G.; Coombs, C.; Crick, T.; Duan, Y.; Dwivedi, R.; Edwards, J.; Eirug, A.; et al. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 57, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, T.; Guha, A.; Grewal, D.; Bressgott, T. How artificial intelligence will change the future of marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2020, 48, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-H.; Rust, R.T. A strategic framework for artificial intelligence in marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2020, 49, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, R.; Sunstein, C. Nudge: Improving Decisions about Health, Wealth and Happiness; Yale University: New Haven, CT, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, A.F.S.; Laurindo, F.J.B.; Spinola, M.M.; Goncalves, R.F.; Mattos, C.A. The strategic use of artificial intelligence in the digital era: Systematic literature review and future research directions. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 57, 102225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Kotler, P. Social Marketing: Behavior Change for Good; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, K.; Gupta, R. Application of AI Technology in Modern Digital Marketing Environment. World J. Entrep. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 17, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, L.M. Towards adopting AI techniques for monitoring social media activities. Sustain. Eng. Innov. 2021, 3, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, T.; Athaluri, S.A.; Singh, S. ChatGPT in medicine: An overview of its applications, advantages, limitations, future prospects, and ethical considerations. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1169595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslej, N.; Fattorini, L.; Brynjolfsson, E.; Etchemendy, J.; Ligett, K.; Lyons, T.; Manyika, J.; Ngo, H.; Niebles, J.C.; Parli, V.; et al. The AI Index 2023 Annual Report. AI Index Steering Committee, Institute for Human-Centered AI; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, April 2023; Available online: https://aiindex.stanford.edu/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/HAI_AI-Index-Report_2023.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- Global Consensus Definition of Social Marketing. 2014. Available online: https://europeansocialmarketing.org/social-marketing-definition-translations/#:~:text=The%20Global%20Consensus%20Definition%20of%20Social%20Marketing%3A,for%20the%20greater%20social%20good (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Grier, S.; Bryant, C.A. Social marketing in public health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2005, 26, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R. Unlocking the potential of upstream social marketing. Eur. J. Mark. 2013, 47, 1525–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, J. The Importance of Social Marketing History. Soc. Mark. Q. 2015, 4, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, J.; Gordon, R. Strategic Social Marketing: For Behaviour and Social Change; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Using Data from Electricity Meters to Predict Energy Consumption. 2019. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/case-studies/using-data-from-electricity-meters-to-predict-energy-consumption (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- French, J. History of Social marketing. In The Palgrave Encyclopedia of Social Marketing; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, D. Evolutionary Psychology: The New Science of the Mind; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ridley, M. The Rational Optimist: How Prosperity Evolves. Brock Educ. J. 2012, 21, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, I.H. AI-Based Modeling: Techniques, Applications and Research Issues towards Automation, Intelligent and Smart Systems. SN Comput. Sci. 2022, 3, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, J.; Abat, M.; Mourtada, A.; Rawson, S.; Faddoul, A. AI for Governments. Available online: https://www.oliverwyman.com/our-expertise/insights/2020/oct/ai-for-governments.html (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- Chakraborty, C.; Pal, S.; Bhattacharya, M.; Dash, S.; Lee, S.-S. Overview of Chatbots with special emphasis on artificial intelligence-enabled ChatGPT in medical science. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1237704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, F.J.; Casillas, J. Artificial intelligence-based systems applied in industrial marketing: An historical overview, current and future insights. Indust. Market. Manag. 2013, 4, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, L.; Baglivo, F.; Arzilli, G.; Privitera, G.P.; Ferragina, P.; Tozzi, A.E.; Rizzo, C. ChatGPT and the rise of large language models: The new AI-driven infodemic threat in public health. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1166120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temsah, M.-H.; Aljamaan, F.; Malki, K.H.; Alhasan, K.; Altamimi, I.; Aljarbou, R.; Bazuhair, F.; Alsubaihin, A.; Abdulmajeed, N.; Alshahrani, F.S.; et al. ChatGPT and the Future of Digital Health: A Study on Healthcare Workers’ Perceptions and Expectations. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarifis, A.; Cheng, X. The Five Emerging Business Models of Fintech for AI Adoption, Growth and Building Trust. In Business Digital Transformation; Zarifis, A., Ktoridou, D., Efthymiou, L., Cheng, X., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Qadri, M.A.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Applications for Marketing: A Literature-Based Study. Int. J. Intell. Netw. 2022, 3, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, T.M.; Czaplewski, A.J. Upstream social marketing strategy: An integrated marketing communications approach. Bus. Horizons 2017, 60, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurisz, N.; Ćwiklicki, M.; Żabiński, M.; Canestrino, R.; Magliocca, P. Co-Creation in Health 4.0 as a New Solution for a New Era. Healthcare 2023, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S. Social Marketing’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT): A Commentary. Soc. Mark. Q. 2019, 25, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Social Marketing Association; European Social Marketing Association; Australian Association of Social Marketing; Asociación Latinoamericana de Mercadeo Social. Global Consensus on Social marketing Principles, Concepts, and Techniques. 2017. Available online: https://smana.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/ESMA-AASM-SMANA-endorsed-Consensus-Principles-and-concepts-paper.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- French, J.; Deshpande, S.; Evans, W.; Obregon, R. Key Guidelines in Developing a Pre-Emptive COVID-19 Vaccination Uptake Promotion Strategy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Understanding Your Consumers with AI in the Market Research. 2022. Available online: https://www.ipsos.com/en/understanding-your-consumers-ai-market-research (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- French, J.; Blair-Stevens, C. Using social marketing to develop policy, strategy, and operational synergy. Soc. Market. Public Health Theory Pract. 2010, 1, 67–79. [Google Scholar]
- Hello, World: Artificial Intelligence and Its Use in the Public Sector; OECD: Paris, France, 2019; Volume 36. [CrossRef]
- Tools for Trustworthy AI: A Framework to Compare Implementation Tools for Trustworthy AI Systems; OECD: Paris, France, 2021.
- Crawshaw, P. Public health policy and the behavioural turn: The case of social marketing. Crit. Soc. Policy 2013, 33, 616–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.-M.; Kemper, J.A.; Parsons, A.G. Upstream social marketing strategy. J. Soc. Mark. 2018, 8, 258–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, M.; O’Sullivan, B.; Gavanelli, M. Sustainable Policy Making: A Strategic Challenge for Artificial Intelligence. AI Mag. 2014, 35, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citizen Lab. Build Stronger Democracies by Making Public Decision Making More Inclusive, Participatory and Responsive. Available online: https://www.impact.citizenlab.co/ (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Semaan, J.; Farah, C.; Harb, R.A.; Bardus, M.; Germani, A.; Elhajj, I.H. Tackling the COVID-19 infodemic among Syrian refugees in Lebanon: Development and evaluation of the “Wikaytek” tool. Digit. Health 2023, 9, 20552076231205280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, S.; Chine, A.; Lalika, M.; Pandey, S.; Seth, A.; Wiyeh, A.; Seng, A.; Rao, N.; Badshah, A. Drivers of COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake amongst Healthcare Workers (HCWs) in Nigeria. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Willmott, T.J.; Pang, B.; Rundle-Thiele, S. Capability, opportunity, and motivation: An across contexts empirical examination of the COM-B model. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michie, S.; Thomas, J.; Mac Aonghusa, P.; West, R.; Johnston, M.; Kelly, M.P.; Shawe-Taylor, J.; Hastings, J.; Bonin, F.; O’mara-Eves, A. The Human Behaviour-Change Project: An artificial intelligence system to answer questions about changing behaviour. Wellcome Open Res. 2020, 5, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, H.S.J. The Use of Artificial Intelligence-Based Conversational Agents (Chatbots) for Weight Loss: Scoping Review and Practical Recommendations. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2022, 10, e32578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, H.S.J.; Ang, W.H.D.; Lau, Y. The potential of artificial intelligence in enhancing adult weight loss: A scoping review. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 1993–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, W.D.; Bingenheimer, J.B.; Long, M.; Ndiaye, K.; Donati, D.; Rao, N.M.; Akaba, S.; Nsofor, I.; Agha, S. Outcomes of a social media campaign to promote COVID-19 vaccination in Nigeria. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearing, J.W.; Cox, J.G. Diffusion Of Innovations Theory, Principles, And Practice. Health Aff. 2018, 37, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cislaghi, B.; Heise, L. Using social norms theory for health promotion in low-income countries. Health Promot. Int. 2018, 34, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cislaghi, B.; Heise, L. Theory and practice of social norms interventions: Eight common pitfalls. Glob. Health 2018, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.T.; Prentice, D.A. Changing norms to change behavior. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2016, 67, 339–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Aonghusa, P.; Michie, S. Artificial Intelligence and Behavioral Science through the Looking Glass: Challenges for Real-World Application. Ann. Behav. Med. 2020, 54, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Social Marketing Statement of Ethics. 2023. Available online: https://isocialmarketing.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/5/2022/10/iSMA-Social-Marketing-statement-of-ethics.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- French, J. Why nudging is not enough. J. Soc. Mark. 2011, 1, 54–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Májovský, M.; Černý, M.; Kasal, M.; Komarc, M.; Netuka, D. Artificial Intelligence Can Generate Fraudulent but Authentic-Looking Scientific Medical Articles: Pandora’s Box Has Been Opened. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e46924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).