Abstract
Maintaining Gymnophiona in captivity provides opportunities to study the behaviour and life-history of this poorly known Order, and to investigate and provide species-appropriate welfare guidelines, which are currently lacking. This study focuses on the terrestrial caecilian Herpele squalostoma to investigate its sensitivity to disturbances associated with routine husbandry needed for monitoring and maintaining adequate wellbeing in captivity. Fossorial caecilians gradually pollute their environment in captivity with waste products, and substrate must be replaced at intervals; doing so disturbs the animals directly and via destruction of burrow networks. As inappetence is frequently associated with stress in amphibians, the percentage consumption of offered food types, river shrimp (Palaemon varians) and brown crickets (Gryllus assimilis), was measured as an indicator of putative stress following three routine substrate changes up to 297 days post-substrate change. Mean daily variation in substrate temperatures were also recorded in order to account for environmental influences on food consumption, along with nitrogenous waste in tank substrate prior to a substrate change and fresh top soil in order to understand the trade-off between dealing with waste accumulation and disturbing animals. We found a significant negative effect of substrate disturbance on food intake, but no significant effect of prey type. Variations in daily soil temperatures did not have a significant effect on food intake, but mean substrate temperature did. Additionally, substrate nitrogenous waste testing indicated little difference between fresh and tank substrate. In conclusion, this study provides a basis from which to develop further welfare assessment for this and other rarely kept and rarely observed terrestrial caecilian species.
1. Introduction
Within zoos and other industries maintaining wild animals in captivity, there is a necessary balance to be struck between providing husbandry needs for captive animals and reducing negative effects that such provision may elicit [1]. Zoo licencing for the United Kingdom (UK), for example, outlines that animals should be checked twice daily while avoiding unnecessary stress or disturbance [2]. For some species, a frequency of twice daily checks is not feasible either due to the species’ natural history making them difficult to visually monitor e.g., fossorial, or because such checks are intrusive and cause significant stress to the animals. Most disturbances such as enclosure changes, handling and restraining, and transportation are temporary and create a short-term change in behavioural responses and glucocorticoid hormone production [3,4]. However, frequent negative events can cause chronic stress, which in turn causes negative morphological and behavioural responses. Chronic stress may be visible in amphibians through reduced feeding, behavioural inhibition or decreased activity, hiding, fearfulness, frequency of startle responses, stereotypies, raised or changed posture and/or displacement behaviours [5,6,7,8].
However, behavioural responses can often be difficult to interpret and a good understanding of what is deemed an appropriate response and what are abnormal or deleterious responses for both the individual and the species is needed [3,9]. Changes in activity or arousal can equally be caused by positive or negative stimuli, and these should be interpreted in the context of what might be typical for that species and for the situation. The frequency of arousing events is also expected to impact activity and behavioural responses. A good knowledge of the species’ natural history as well as individual animal history is needed to fully understand their husbandry needs [3], but for many rarely seen and understudied species this dearth of knowledge can create challenges for quantifying optimum requirements within captive settings.
One such group of little studied and poorly known animals are the elongated, limbless amphibians, caecilians (Order: Gymnophiona). There are about approximately 215 currently recognised species within the Order [10] with only six species currently being kept in zoos [11]. Many terrestrial caecilian species spend most of their lives in soil, making these animals difficult to monitor [12,13]. Alongside invertebrates, fossorial (burrowing) caecilian species may play an important part in engineering and maintaining ecosystems by influencing the structure of the soil and the distribution and cycling of organic matter [14,15,16,17]. However, caecilians are generally understudied, with most studies on fossorial vertebrate species focussing on burrowing mammals [15] in conjunction with a general overall bias away from studying amphibians [18]. Additionally, within amphibian research, caecilians, in general, are one of the least studied groups. As well as potentially providing direct benefits to species conservation, maintaining caecilians in captivity provides an opportunity to study various aspects of their biology, and develop and validate methods that can be used to understand and conserve them [13,19,20,21,22,23,24,25].
In this work, we studied the Congo caecilian (Herpele squalostoma), a fossorial caecilian from lowland forests and agricultural habitats across Nigeria, Cameroon, Central African Republic, mainland Equatorial Guinea and Bioko Island, Gabon, Congo, and the western Democratic Republic of Congo, with possible records in Angola [26]. Herpele squalostoma is reported to be locally abundant and sporadically traded (in large numbers on occasion) in the commercial international pet trade [12,20,27]. Despite this reported abundance, little is known about the ecology of this species [28]. Listed as Least Concern [26], H. squalostoma is not threatened, however this species can act as an analogue model to develop caecilian husbandry techniques to apply to more threatened taxa [29]. Currently this species is poorly represented in zoological collections that may aid in natural history research, with only 13 animals maintained between two institutions [11]. Due to the fossorial nature of this, and most, caecilian species it is difficult to monitor and assess behavioural responses that could inform welfare provisions within captive settings [13]. Prey consumption where food items are placed on the surface is one of the few visual and external measures of wellbeing for this study species.
This study evaluates the effects of disturbance from three substrate change events on the food consumption in H. squalostoma. We propose the proportion of prey consumption is a suitable, non-invasive, measure of putative stress in that species. Through this work, we aim to better understand the susceptibility of H. squalostoma to environmental disturbance and provide evidence to inform best husbandry practices that reduce negative welfare impacts and ensure that these needs are met.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Models, Experimental Design, and Data-Collection
Four H. squalostoma of unknown sex and age were maintained at the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) London Zoo, on loan as part of a collaborative project with the Natural History Museum’s Herpetology Research Group. Animal lengths ranged from 51.5–56.9 cm (as of February 2021) indicating that all animals were of adult age, though the exact ages are unknown. The enclosure was designed to mimic descriptions and photographs of wild habitat [9,28,29]. They were housed as a group in a 135 cm L × 71 cm H × 60.5 cm W glass enclosure (Custom Aquaria, Rushden, UK) with a substrate depth of 30 cm at the front of the tank, sloping upwards to a depth of 43 cm at the rear which was intended to improve the visitors view and the aesthetic of the enclosure. The enclosure had a small open column of water in the back right corner at a depth of 16–21 cm, permeable via a cork barrier to the substrate layer and planted with Radican Sword (Echinodorus muricatus). This allowed for a permanent layer of water in the base of the enclosure, ensuring the substrate layer retained moisture. Grasses (Carex morrowii and C. m. variegata) were planted in the terrestrial areas to provide surface cover, substrate structure and root structures for egg clutches to be laid around [30,31,32]. The substrate consisted of topsoil with buried masses of dried leaves of mixed tree species, cork tubes lined with clay and branches to provide potential nest sites.
Substrate minimal and maximal daily temperatures were recorded with a digital probe thermometer (ETI Ltd., Worthing, UK) at approximately 20 cm substrate depth from the surface, enabling us to approximate daily mean substrate temperatures as (Tmin + Tmax)/2 (thereafter referred to as “average temperature”), and the daily range of substrate temperature variation (Tmax–Tmin) on feeding days. Readings of maximum and minimum temperatures were taken only once per day. The room climate control provided ambient temperatures aligning with climate data for Yaounde, Cameroon based on field study sites [30]. Outdoor temperatures and sunlight influenced the substrate temperatures somewhat because the public-facing side of the tank is within 2 cm of the room show window.
The caecilians were fed a diet consisting of defrosted river shrimp (Palaemon varians) kept whole or halved if >2 cm total length; defrosted, gut-loaded, killed adult brown crickets (Gryllus assimilis); and small live worms (Dendrobaena sp.). Weights of whole shrimp were c. 0.3 g and brown crickets c. 0.5 g. This was designed to replicate the wild diet within the confines of what we can reasonably source [33,34]. Each prey type was given independently on a set schedule alternating between food types, and the animals were fed three times per week (Monday, Wednesday, and Friday) between 8:30 a.m.–5 p.m., most often before 12 p.m. Shrimp or crickets (Shrimp, Max = 54, Min = 12, Median = 27; Cricket, Max = 45, Min = 12, Median = 25) were offered on feed days, placed near burrow entrances to increase accessibility for the animals. The remaining number of prey items were counted the following day before being discarded. Live Dendrobaena worms were offered once per week on a set feed day but were excluded from this study as they could not be counted and removed without substantial disturbance to the animals. The number of prey items offered were relatively the same quantity irrespective of the number of tunnel entrances available, which greatly reduced post-substrate change. Because the quantity and size of the prey items offered varied between feed days, the proportionate consumption was calculated. Food intake was recorded after every non-worm feed, with a total of 147 observations over the course of our study, which lasted a total of 598 days (from 7 February 2020 to 27 September 2021).
Substrate changes for the study caecilians are typically performed every six to eight months to minimise frequent disturbance to animals and burrow structures while providing adequate environmental needs, for example by preventing the build-up of nitrogenous waste to detrimental levels. Due to an interruption from the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, which created staff shortages and increased pressure on staff workload, a substrate change was postponed and occurred approximately ten months (297 days) after the previous change. During substrate changes the animals are caught, placed into separate plastic 9 L Really Useful Boxes (Really Useful Products Ltd., Castleford, UK) filled nearly full with tank substrate, to allow the animals to burrow, before being visually checked, weighed, and photographed for subsequent morphological measurements via ImageJ (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij, accessed on 21 September 2021) [35]. The enclosure was then stripped with all old substrate discarded and replaced with fresh 25 L bags of topsoil (B&Q, London, UK) that was pre-warmed to the same temperature as the enclosure substrate. Plants and furnishings were retained and replaced in the enclosure with the new substrate. Caecilians were then reintroduced to the enclosure by placing them on the surface of the new substrate. Substrate change duration were between four to five hours and animals were not fed while contained in the Really Useful Boxes. A subsequent change occurred within the usual time frame at around seven months (218 days) from the last change. Substrate changes were carried out on 26 November 2019, 21 April 2020 and 16 February 2021.
Substrate samples were taken from the tank during the removal of the substrate on the day of the most recent substrate change, and of fresh substrate taken directly from the bags of topsoil, provided by the supplier. Samples were taken from three locations within the tank, and from three different randomly selected bags of fresh substrate. Samples were only taken once, during this most recent change, and results did not include previous substrate changes. Samples of 10 g substrate were suspended in 100 mL reverse osmosis (RO) water before being filtered through coffee filter paper (Filtropa Unbleached Coffee Filter Papers, Size 4) overnight at a temperature of 0.3–0.5 °C. The sample water was removed with a pipette so as not to disturb the final sediment layer. This was tested with Salifert profitest (Duiven, Netherlands) nitrate water tests and Palintest (Gateshead, UK) ammonia and nitrite water tests using a Palintest Interface photometer 7500. The concentration of ammonia, nitrite and nitrate was recorded to assess waste build up in the substrate and the mean test results were calculated per condition. These variables were also measured against the RO water to control for any nitrogenous waste contamination.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
A full generalized linear mixed model (GLMM) was built with a binomial error distribution and a logit link function [36] for the proportion of food items eaten as the response variable, to test for the effect of temperatures on amount consumed. Days since the last substrate change, the food type (crickets or shrimps), the daily mean temperature, and the daily range of temperature variation were tested as covariates, and the substrate change number was implemented as a random effect to control for differences in intercepts due to repeated measures on the same group of individuals [37]. Using a frequentist hypothesis testing approach, the significance of each covariate was tested using Walt z-tests to determine the best structure for our final model. Our final model’s assumptions were verified graphically (Appendix A, Figure A1) and its fit was assessed using Bolker’s dispersion estimate and marginal and conditional R2 metrics [38]. Parameter estimates were all calculated using Laplace approximation [39]. Analyses were conducted using the packages lme4 [40] and MuMIn [41] in the software R version 4.1.0 [42] and is available in open-access at https://github.com/LeaFieschiMeric/substrate_change_in_herpele (accessed on 28 October 2021).
3. Results
The daily variation in temperature and the type of food provided did not have a significant difference on the proportion of food items consumed (respectively, z = 0.031, p-value = 0.975; z = 0.851, p-value = 0.394). However, average temperature has a significantly negative effect on the food intake (z = −3.424, p-value < 0.05, Figure 1A). The proportion of food eaten significantly increases with time since last substrate change (z = 7.624, p-value < 0.05, Figure 1B).
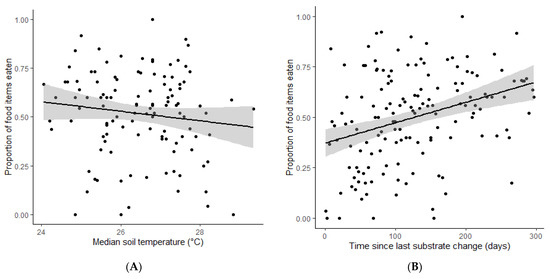
Figure 1.
Scatterplots of the proportion of food items eaten by captive Herpele squalostoma depending on the significant regression parameters: (A) the average substrate temperature and (B) the time since the substrate was last changed.
Average substrate temperatures ranged from 23.3 °C to 30.4 °C with a daily substrate temperature variation of 0.1–5.8 °C on feeding days. The room climate control provided ambient temperatures between 25.7–33.3 °C day-time maximum and 20.9–30.5 °C night-time minimum. Outdoor temperatures and sunlight influenced the substrate temperatures somewhat as the public-facing side of the tank is within 2 cm of the room show window.
Our final model includes the time since last substrate change and the average temperature as covariates, and the substrate change number as a random effect. The graphical assessment of the residuals (Appendix A, Figure A1) and the conditional R2 (Table 1) in our final model suggest an acceptable fit.

Table 1.
Regression parameters estimates on the log-odds scale, with their standard errors and z-values, for all covariates used in our final model, along with odds-ratios (OR) and confidence intervals given on the scale of the linear predictor. Model fit is acceptable according to the estimated measures of variance and dispersion.
Every subsequent day after a substrate change, the proportion of food intake increases by 1.004, showing a cumulative increase of the proportion of food eaten over time after a substrate change. Conversely, for every 1 °C increase in the substrate temperature the caecilians consume 1.11 times less food.
Tests for ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate (mg/L) were carried out for tank substrate at 218 days after a substrate change and for fresh substrate from three random bags of commercially bought topsoil (Table 2). Water tests for the RO water used to suspend the substrate samples showed a mean ammonia of 0 mg/L (N = 1), nitrite of 0.01 mg/L (N = 1) and mean nitrate of 0 mg/L (N = 1).

Table 2.
Concentrations of ammonia, nitrite and nitrate (mg/L) for tank substrate (at 218 days after the previous substrate change) and fresh substrate. Mean, median, range and N values are recorded.
Following the previous substrate change delayed by COVID mitigations and staff work demands, when removed from the enclosure all caecilians were considered healthy and increased in length and weight. Therefore, it is unlikely this prolonged period of an additional 2 months between changes had any visual detrimental effects.
4. Discussion
The complete destruction of the burrow systems of captive Herpele squalostoma in this study after a substrate change created an expected reduction in consumption due to the lack of accessibility to the surface and prey items left on the surface of the substrate (i.e., shrimp and crickets but not worms). However, this study shows that after the animals had re-built new burrow exits, consumption of the river shrimp and crickets remained reduced for an extended period. The exact timescale of the re-formation of burrow exits was not measured but anecdotally 1–2 exits were formed within a week and several exits ranging across at least half of the tank we made around 4–6 weeks after a substrate change occurred. This suggests that the disturbance from substrate changes did not only create short-term physical barriers to consumption but also longer-term psychological or behavioural barriers.
This species’ natural history and the quantity of prey they typically consume in the wild is unknown. Therefore, low consumption is a relative term. In our study, we observe a large range of variation in the proportion of food eaten (we record values from 0 to 100% of offered items consumed) with a mean of 50% of offered items consumed. Indeed, these proportions are directly influenced by the total number of items offered, which varied greatly. There seems to be a plateau in the number of items eaten (maximum number of items eaten = 38, although maximum number of items offered = 54), corresponding to a mean of 9.4 items per individual. On average, 13.5 items were eaten in total, which corresponds to slightly more than 3 food items per individual. There was no trend in the number of items offered over time indicating that trends in consumption were not related to food increasing or decreasing over time. Future studies should use a fixed total number of food items proposed every day and try to determine typical food consumption per individual instead of in a group. Statistical tests confirm a significant effect of the length of time after a substrate change with percentage consumption with a cumulative increase over time post-disturbance. Daily variations in temperature did not significantly affect percentage of consumption. The average substrate temperatures did have a significant effect, with these individuals feeding less at higher temperatures.
The build-up of nitrogenous wastes in the substrate is one of the main concerns when providing adequate captive welfare and when determining the length between substrate changes in this species, because high levels of nitrogenous waste can have detrimental health effects for amphibians [43,44], such as increased mucous production, change in skin pigmentation as well as immunosuppression and increased vulnerability to disease [45]. Recommended nitrogenous waste concentrations for amphibians are <0.2 mg/L ammonia, <1.0 mg/L nitrites and <50 mg/L nitrates (both tank soil and fresh substrate in this study fall within these acceptable parameters) [46].
The nitrogenous substrate tests indicate that there is a small difference between values between substrate 218 days after the previous change and fresh substrate. Therefore, to reduce the disruptive effects of substrate changes, the frequency of substrate changes could be reduced in this captive group. Further experimentation needs to be carried out to determine the maximum time between changes before substrate quality becomes detrimental, but routine substrate tests could be used to inform substrate change frequency in the same way as is used as standard to inform aquarium water changes. In addition, the levels of nutrients in fresh, commercially bought topsoil is on average, slightly higher in all nitrogenous waste value concentrations. However, the concentration is also more variable between bags provided by suppliers, and the plants in this enclosure most likely reduced the build-up of nitrogenous waste and/or reduced the higher ammonia values from the fresh substrate [44]. Further experiments could be done to compare sparsely and heavily planted enclosures and the speed at which nitrogenous wastes build up over the same time periods. It is noted that some caecilians may favour and thrive in nutrient-rich substrates. For example, Siphonops annulatus is highly associated with organically rich, fertile, and humid soils in cabruca cacao plantations [17]. However, this preference for nutrient-rich microhabitats may be explained by humidity, temperature, or abundance of prey rather than nutrient richness, though cannot be confirmed. However, as the detrimental levels of nitrogenous waste for specifically caecilians are unknown and preference of soil richness varies between species, the natural history and wild habitat of each species should be considered when determining disturbance from substrate change frequency.
Some caecilian species might have (semi-) permanent burrow structures; therefore, the removal and disturbance of substrate could potentially be more detrimental to these species than those that do not have such permanent burrow structures [15,47,48]. Boulengerula boulengeri, for example, are more abundantly encountered during digging than during other sampling methods such as pitfall traps and visual surveys on the forest floor surface [49], possibly suggesting the use of permanent burrows in a particular soil depth range [50]. However, the movement of this species between burrows and the frequency and duration of use is unknown to confirm whether these are permanently used. Some species may show large home areas such as Gegeneophis ramaswamii which have been shown to have large movements in and out of a sampled study area of 100 m2 [15]. Other species are epigeic for at least some part of the time, for example ichthyophiids or scolecomorphids [48,51]. Some caecilians may tolerate disturbed habitats; population densities of B. taitanus were greater in agricultural land than in forest [49]. The particular species’ natural history is important to consider because disturbances in captivity to tunnels systems may have stronger welfare implications to some species over others.
Another variable that may also impact the determination of substrate change frequency is the preferred compression and hardness of the substrate [22]. Additionally, burrow permanence is likely dictated by soil type. The substrate is a basic factor in terrestrial caecilian husbandry; however, there is little data on preferences in the wild or in captivity [22]. For some species, it may be beneficial to have relatively frequent substrate changes if they prefer softer, less compacted substrate. Additionally, the composition of some softer substrates, such as wood pulp-based substrates like Megazorb Animal Bedding (Northern Crop Driers, Melbourne, York, UK) which has been used to house terrestrial caecilians [22,25], will decompose faster or allow for a faster build-up of nitrogenous wastes. Artificial paper-based substrates do not support live plant growth and accumulate bacterial growth much more rapidly [52]. The more rapid decomposition of some substrates again raises the dilemma of balancing the minimisation of disturbance and destruction of burrows against providing preferred substrate hardness or types and substrate chemical parameters. It has been noted that both Geotrypetes seraphini and Microcaecilia unicolor favoured Megazorb over coir in choice chambers [22,25].
There are several limitations to this study due to the lack of available knowledge on this species’ natural history, the concealment of the usual behavioural indicators for assessing welfare due to their fossorial nature. Additionally, this study provides an indicator of group behaviour rather than individual behaviour; therefore, individual welfare cannot be assessed, and changes may not benefit all individuals equally [1]. Results may have skewed if one individual behaved largely different than its counterparts. However, as the study animals have been housed as a group for a long period and because no known recorded measure of welfare is currently available for this species, or any other caecilian in captivity, tracking food consumption changes in relation to disturbance does provide a basis to assess welfare on a group level. Furthermore, the overdispersion and the moderate conditional R2 of our model indicate that it does not capture all the variation observed in the data. Other untested factors could explain some of the variability in the proportion of food eaten in H. squalostoma, and the feeding response cannot be used alone to predict putative welfare state. Indeed, the total amount of food items given (which ranged from 12–54) and their changing distribution within the enclosure could have introduced variation into the data. Food was positioned near tunnel entrances/exits, but consumption may have been affected by the proximity of the caecilians to these positions and their activity under the surface. Additionally, other covariates that may have impacted percentage consumption, such as ambient air humidity, were not tested here.
Zoo legislation in the UK calls for the daily check of all animals under a zoo’s care, without causing unnecessary stress or disturbance [2]. Due to the fossorial nature of H. squalostoma, there are limitations on how frequently the animals can be checked and in how activity and stress can be monitored and assessed remotely to aid in welfare assessment tools. More research is needed to learn about this rarely maintained species, but this study demonstrates that simple captive experiments can provide opportunities for evidence-based husbandry and to improve the knowledge and welfare provision in captive caecilians.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.C.C., C.J.M. and B.T.; methodology, K.C.C., C.J.M. and B.T.; formal analysis, L.F.-M.; investigation, K.C.C.; data curation, K.C.C. and F.S.; writing—original draft preparation, K.C.C. and L.F.-M.; writing—review and editing, D.J.G., K.C.C., F.S., B.T. and M.W.; supervision, B.T. and C.J.M.; project administration, K.C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, due to only naturally occurring behaviours being recorded during routine husbandry.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Analyses are available in open-access at https://github.com/LeaFieschiMeric/substrate_change_in_herpele (accessed on 1 December 2021).
Acknowledgments
We thank all members of the Herpetology team at ZSL London Zoo who assisted in the husbandry of the animals in this work and inputted into the data collection; in addition to the authors, Daniel Kane, Joe Capon, Unnar Ævarsson and Charlotte Ellis, and to Lewis Rowden for support in internal administration processes.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Figure A1.
Graphical check of the final model’ assumptions using Pearson’s residuals against (A) fitted values and against the two covariates -the time since the last substrate change (B) and the median temperature (C) and QQ-plot of the residuals (D). The absence of pattern suggests that assumptions of homoscedasticity and normality of model residuals are verified.
References
- Whitham, J.C.; Wielebnowski, N. New directions for zoo animal welfare science. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2013, 147, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of the Environment, Transport and the Regions. Secretary of State’s Standards of Modern Zoo Practice; Department of the Environment, Transport and the Regions: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Van Waeyenberge, J.; Aerts, J.; Hellebuyck, T.; Pasmans, F.; Martel, A. Stress in wild and captive snakes: Quantification, effects and the importance of management. Vlaams Diergeneeskd. Tijdschr. 2018, 87, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, E.J.; Forsburg, Z.R.; Davis, D.R.; Gabor, C.R. Non-invasive methods for measuring and monitoring stress physiology in imperiled amphibians. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, K.N.; Tromborg, C.T. Sources of stress in captivity. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 102, 262–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, C.; Arena, P.; Lindley, S.; Jessop, M.; Steedman, C. Assessing reptile welfare using behavioural criteria. Practice 2013, 35, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossie, T.J.; Ferland-Raymond, B.; Burness, G.; Murray, D.L. Morphological and behavioural responses of frog tadpoles to perceived predation risk: A possible role for corticosterone mediation? Ecoscience 2010, 17, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woody, S.M.; Santymire, R.M.; Cronin, K.A. Posture as a Non-Invasive Indicator of Arousal in American Toads (Anaxyrus americanus). J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2021, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benn, A.L.; McLelland, D.J.; Whittaker, A.L. A review of welfare assessment methods in reptiles, and preliminary application of the welfare quality® protocol to the pygmy blue-tongue skink, Tiliqua adelaidensis, using animal-based measures. Animals 2019, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, D.R. Amphibian Species of the World: An Online Reference; Version 6.1; American Museum of Natural History: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Available online: https://amphibiansoftheworld.amnh.org/index.php (accessed on 17 August 2021). [CrossRef]
- Species360. 2021. Available online: www.Species360.org (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Gower, D.J.; Wilkinson, M. The conservation biology of caecilians. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.; Michaels, C.J.; Gower, D.J.; Wilkinson, M. The use of visible implant elastomer to permanently identify caecilians (Amphibia: Gymnophiona). Herpetol. Bull. 2019, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P.; Bignell, D.; Lepage, M.; Wolters, V.; Roger, P.A.; Ineson, P.O.W.H.; Heal, O.W.; Dhillion, S. Soil function in a changing world: The role of invertebrate ecosystem engineers. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 1997, 33, 159–193. [Google Scholar]
- Measey, G.J.; Gower, D.J.; Oommen, O.V.; Wilkinson, M. A mark–recapture study of the caecilian amphibian Gegeneophis ramaswamii (Amphibia: Gymnophiona: Caeciliidae) in southern India. J. Zool. 2003, 261, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.T.; Loader, S.P.; Gower, D.J. Trophic ecology of East African caecilians (Amphibia: Gymnophiona), and their impact on forest soil invertebrates. J. Zool. 2006, 269, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jared, C.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Wilkinson, M.; Delabie, J.H. Conservation of the caecilian Siphonops annulatus (Amphibia, Gymnophiona) in Brazilian cacao plantations: A successful relationship between a fossorial animal and an agrosystem. Agrotrópica 2015, 27, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, X.; Shine, R.; Lourdais, O. Taxonomic chauvinism. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2002, 17, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.C. Feeding in caecilians. In Feeding: Form, Function and Evolution in Tetrapod Vertebrates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 149–166. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, M.; Müller, H.; Gower, D.J. On Herpele multiplicata (Amphibia: Gymnophiona: Caeciliidae). Afr. J. Hepatol. 2003, 52, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Maddock, S.T.; Lewis, C.J.; Wilkinson, M.; Day, J.J.; Morel, C.; Kouete, M.; Gower, D.T. Non-lethal DNA sampling for caecilian amphibians. Herpetol. J. 2014, 24, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Tapley, B.; Bryant, Z.; Grant, S.; Kother, G.; Feltrer, Y.; Masters, N.; Strike, T.; Gill, I.; Wilkinson, M.; Gower, D.J. Towards evidence-based husbandry for caecilian amphibians: Substrate preference in Geotrypetes seraphini (Amphibia: Gymnophiona: Dermophiidae). Herpetol. Bull. 2014, 129, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Rendle, M.E.; Tapley, B.; Perkins, M.; Bittencourt-Silva, G.; Gower, D.J.; Wilkinson, M. Itraconazole treatment of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd) infection in captive caecilians (Amphibia: Gymnophiona) and the first case of Bd in a wild neotropical caecilian. J. Zoo Aquar. Res. 2015, 3, 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Flach, E.J.; Feltrer, Y.; Gower, D.J.; Jayson, S.; Michaels, C.J.; Pocknell, A.; Rivers, S.; Perkins, M.; Rendle, M.E.; Stidworthy, M.F.; et al. Postmortem findings in eight species of captive caecilian (Amphibia: Gymnophiona) over a ten-year period. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2020, 50, 79–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatley, C.; Tapley, B.; Michaels, C.J. Substrate preference in the fossorial caecilian Microcaecila unicolor (Amphibia: Gymnophiona, Siphonopidae). Herpetol. Bull. 2020, 152, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group. Herpele squalostoma. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: E.T59565A16958011. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T59565A16958011.en (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Wilkinson, M.; Sherratt, E.; Starace, F.; Gower, D.J. A new species of skin-feeding caecilian and the first report of reproductive mode in Microcaecilia (Amphibia: Gymnophiona: Siphonopidae). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouete, M.T.; Ndeme, E.S.; Gower, D.J. Further observations of reproduction and confirmation of oviparity in Herpele squalostoma (Stutchbury, 1836) (Amphibia: Gymnophiona: Herpelidae). Herpetol. Notes 2013, 6, 583–586. [Google Scholar]
- Michaels, C.J.; Gini, B.F.; Preziosi, R.F. The importance of natural history and species-specific approaches in amphibian ex-situ conservation. Herpetol. J. 2014, 24, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Channing, A.; Rödel, M.O. Field Guide to the Frogs & Other Amphibians of Africa; Penguin Random House: Cape Town, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kouete, M.T.; Wilkinson, M.; Gower, D.J. First reproductive observations for Herpele Peters, 1880 (Amphibia: Gymnophiona: Herpelidae): Evidence of extended parental care and maternal dermatophagy in H. squalostoma (Stutchbury, 1836). Int. Sch. Res. Notices 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupfer, A.; Maxwell, E.; Reinhard, S.; Kuehnel, S. The evolution of parental investment in caecilian amphibians: A comparative approach. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 119, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Measey, G.J.; Gower, D.J.; Oommen, O.V.; Wilkinson, M. A subterranean generalist predator: Diet of the soil-dwelling caecilian Gegeneophis ramaswamii (Amphibia; Gymnophiona; Caeciliidae) in southern India. C. R. Biol. 2004, 327, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouete, M.T.; Blackburn, D.C. Dietary partitioning in two co-occurring caecilian species (Geotrypetes seraphini and Herpele squalostoma) in Central Africa. Integr. Org. Biol. 2020, 2, obz035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ImageJ. Image Processing and Analysis in Java. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Bolker, B.M.; Brooks, M.E.; Clark, C.J.; Geange, S.W.; Poulsen, J.R.; Stevens, M.H.H.; White, J.S.S. Generalized linear mixed models: A practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, R.B.; Anderson, M.J. Remedies for pseudoreplication. Fish. Res. 2004, 70, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.C. Extension of Nakagawa & Schielzeth’s R2GLMM to random slopes models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 944–946. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raudenbush, S.W.; Yang, M.L.; Yosef, M. Maximum likelihood for generalized linear models with nested random effects via high-order, multivariate Laplace approximation. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2000, 9, 141–157. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, K. Mu-MIn: Multi-model inference. R Package Version 1.43.17. 2020. Available online: http://R-Forge.R-project.org/projects/mumin/ (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Rouse, J.D.; Bishop, C.A.; Struger, J. Nitrogen pollution: An assessment of its threat to amphibian survival. Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentini, A.M. 34. Husbandry and care of amphibians. In Zookeeping; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2013; pp. 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Densmore, C.L.; Green, D.E. Diseases of amphibians. ILAR J. 2007, 48, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odum, R.A.; Zippel, K.C. Amphibian water quality: Approaches to an essential environmental parameter. Int. Zoo Yearb. 2008, 42, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhies, M.R. Vertebrate burrows. In The Study of Trace Fossils; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1975; pp. 325–350. [Google Scholar]
- Gower, D.J.; Loader, S.P.; Moncrieff, C.B.; Wilkinson, M. Niche separation and comparative abundance of Boulengerula boulengeri and Scolecomorphus vittatus (Amphibia: Gymnophiona) in an East Usambara forest, Tanzania. Afr. J. Herpetol. 2004, 53, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Measey, G.J. Are caecilians rare? An east African perspective. J. East Afr. Nat. Hist. 2004, 93, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kupfer, A.; Wilkinson, M.; Gower, D.J.; Müller, H.; Jehle, R. Care and parentage in a skin-feeding caecilian amphibian. J. Exp. Zool. Part A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2008, 309, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupfer, A.; Nabhitabhata, J.; Himstedt, W. Life history of amphibians in the seasonal tropics: Habitat, community and population ecology of a caecilian (genus Ichthyophis). J. Zool. 2005, 266, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, C.J.; Preziosi, R.F. Clinical and naturalistic substrates differ in bacterial communities and in their effects on skin microbiota in captive fire salamanders (Salamandra salamandra). Herpetol. Bull. 2020, 151, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).