Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a major cause of global mortality, underscoring the need for intelligent and accessible cardiac health monitoring. This paper proposes a non-wearable Internet-of-Medical-Things (IoMT) system combining real-time sensing, edge processing, and AI-driven diagnostics. Stationary sensors MAX30102 (heart rate, SpO2) and AD8232 (ECG) interfaced with micro-controller (ESP8266), processes data locally and feeds into the machine learning models trained on UCI Cleveland dataset. Random Forest and XGBoost achieved over 80% accuracy in predicting early cardiac risk. A Flask-SQLite web application provides role-based doctor/patient access, and a Natural Language Processing (NLP)-based interactive chatbot offers personalized guidance. The system delivers scalable, real-time, edge-enabled cardiac diagnostics without relying on wearable devices.
1. Introduction
According to the World Health Organization, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are reportedly the major cause of global mortality, affecting more than half a billion people and approximately 19.8 millions deaths in 2022, with 85% due to heart attack and stroke. In low- or middle-income countries, barriers such as limited access to healthcare facilities, high costs of diagnosis, and shortage of specialists make early diagnosis and treatment critical for the people with CVDs [1,2,3]. Traditional diagnosis methods involve either periodic in-clinic testing or Holter-based ECG monitoring that record continuous heart rhythms. The latter effectively diagnoses some CVDs that may be ignored in the absence of any symptoms [4]. However, the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing demand for personalized healthcare solutions require innovative technologies that can provide real-time, accurate and user-friendly health monitoring. In this context, the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) presents a promising opportunity to transform traditional healthcare into a more accessible, affordable, and proactive system [5,6].
IoMT enables a medical system to connect various smart devices, such as wearable sensors, medical examination instruments, and hospital assets, for establishing an information platform. These smart devices act as basic nodes in an IoMT system, collecting health data and transmitting it to the server for further processing and analysis [7]. When combined with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms, it can benefit prospective clinical trials to compare state-of-the-art procedures for risk stratification, precision diagnostics, and personalized medicines. Mobile health technologies improve the live monitoring of patients and the prediction of diseases without visiting health centers.
Several practical implementations demonstrating IoMT prototypes using connected and cost-efficient microcontrollers (ESP32/ESP8266) with Electrocardiography (ECG) Sensor and Pulse/PPG (Photoplethysmography) have been widely reported in the literature. These works establish the feasibility of integrating real-time cardiac activity monitoring with remote clinical access through sensors and cloud/server using Wi-Fi or Bluetooth [8,9,10,11,12]. The use of LoRA technology for data transmission of IoMT has proven to be both cost- and power efficient [13]. Some IoMT architectures utilize fog computing to meet latency and real-time requirements of CVD [14]. Recent research focuses on edge computing for cardiac monitoring and anomaly detection in a resource-constrained environment [15]. Various studies have proposed different ML algorithms capable of determining if a person has a CVD [16,17]. Authors in [18,19] suggest different AI/ML models that predict or learn CVDs by analyzing the sensor data. Rani et al. [20] proposed a hybrid ML algorithm based on Support Vector Machine (SVM), Random Forest (RF), Logistic Regression (LR), Naive Bayes (NB), and Adaboost. While Amit and Wilson [21] applied different ML algorithms such as, Decision Tree (DT), k-nearest neighbor (KNN), multi-layer perceptron (MLP), RF, NB, and SVM, for early prediction of CVDs based on IoMT data. An interactive chatbot can also serve as an integral part of the IoMT-based cardiac health monitoring system. It engages users in a one-on-one discussion and questionnaire about their health issues. The system is given data about health symptoms and with the aid of NLP, the chatbot guides the user to provide self-care and disease diagnosis [22]. Despite these advancements in IoMT technologies, there remain several limitations and research gaps that require a comprehensive solution for integrating these technologies into a user-friendly and proactive diagnostic system with real-time monitoring and predictive analytics using AI/ML models.
In this paper, we present a real-time IoMT-enabled solution designed for cardiac monitoring and predictive diagnostics, continuous and personalized healthcare, especially in underserved and remote areas. In contrast to most of the ESP-based cardiac IoMT prototypes based on single-lead sensors that limit diagnostic variability, we employ multi-modal sensors that collect real-time ECG, heart rate, and blood oxygen saturation (SpO2) measurements that enhance diagnostic accuracy. These sensors work on photoplethysmography technology- an optical technique that monitors consistency in blood volume, thereby allowing for screening and detecting the presence of CVDs. PPG measures oxygen saturation, blood pressure, and cardiac activity through a series of signals and peak detection to determine arterial irregularities [23,24]. The data streams are then wirelessly transmitted via an ESP8266 microcontroller to a web application for visualization and analysis. Furthermore, the system includes an ML pipeline trained on the Cleveland Heart Disease dataset [25] to assess heart disease risk. Further, an integrated AI-powered chatbot enhances patient engagement, providing recommendations based on symptoms and historical data. A comparative analysis of our proposed approach with existing IoMT solutions for CVD is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparative analysis of the proposed system with existing state-of-the-art IoMT for CVD.
2. System Design and Development
In this section, we present the components used to design the IoMT system and their interconnection for CVD monitoring.
The system design comprises three main parts:
- Microcontroller and sensors-based IoMT prototype;
- A Flask-SQLite web application provides role-based doctor/patient access, and a chatbot offers personalized guidance;
- A machine learning pipeline trained on the Cleveland Heart Disease dataset.
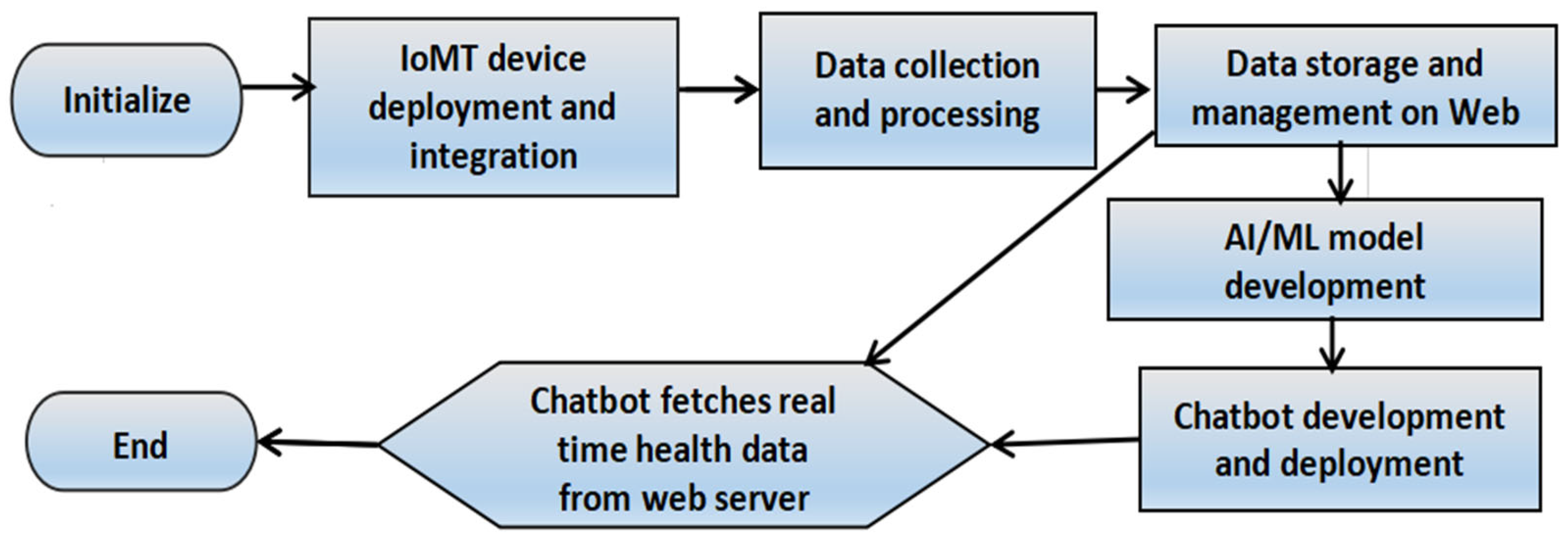
- Figure 1 represents the design of the proposed IoMT system.
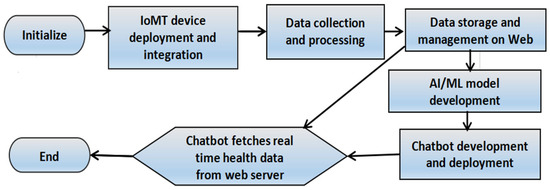 Figure 1. Methodology showing the process of system design.
Figure 1. Methodology showing the process of system design.
In the subsequent subsections, we discuss our system design in detail.
2.1. IoMT Prototype and System Design
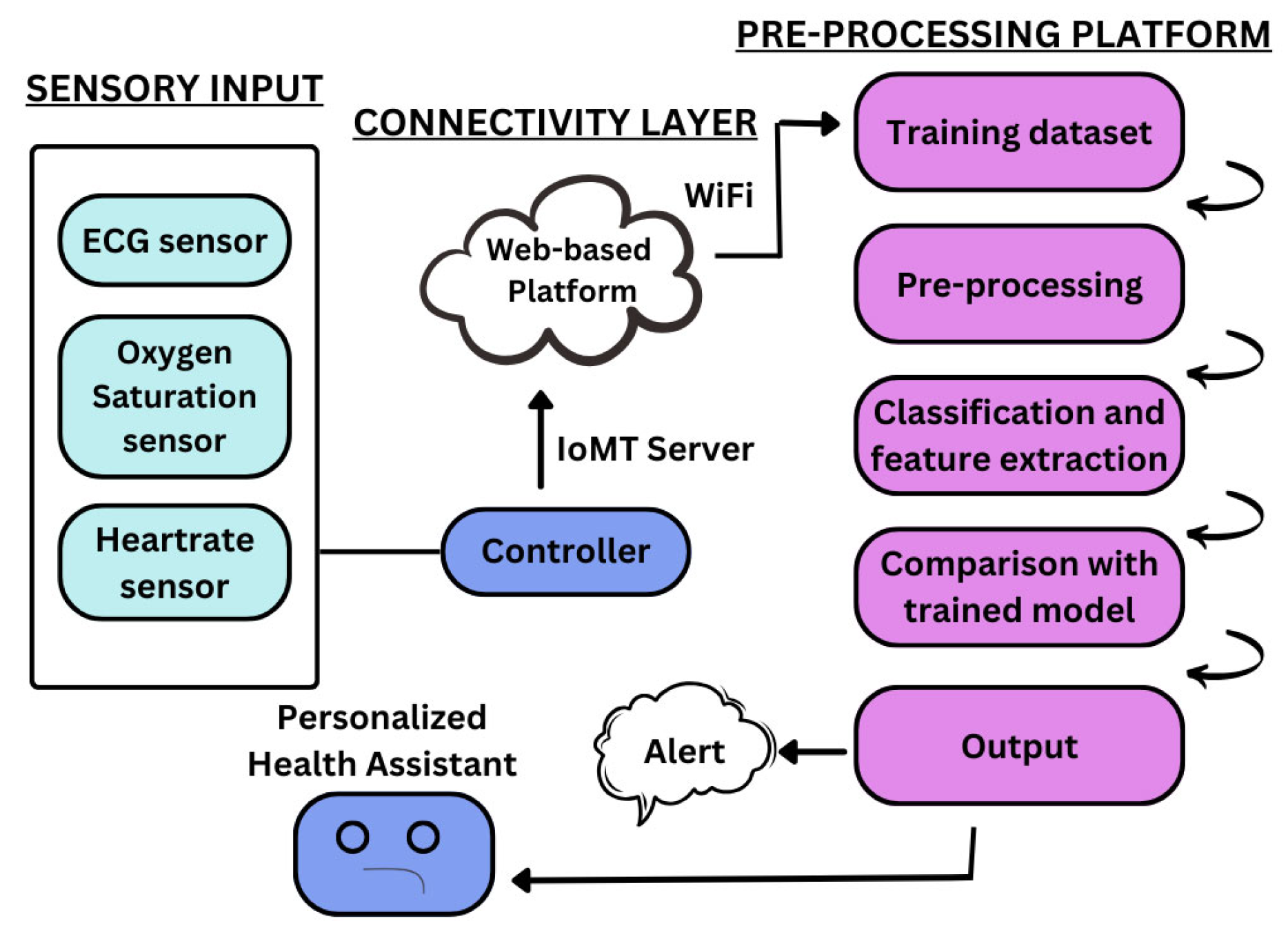
The proposed system is a real-time, personalized cardiac health monitoring platform as shown in Figure 2. It integrates biomedical sensors with a microcontroller, a lightweight backend, and a web-based user interface. The MAX30102 sensor is used for measuring heart rate and blood oxygen saturation (SpO2), while the AD8232 sensor captures ECG signals. These sensors are connected to the ESP8266 microcontroller, which collects the data and transmits it to a local host-based Flask server via HTTP requests over Wi-Fi. The MAX30102 and AD8232 is manufactured by Analog Devices, Inc., headquartered in Norwood, Massachusetts, USA. The ESP8266 is manufactured by Espressif Systems (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., based in Shanghai, China. All components were procured from a local supplier, General electronics, in Karachi, Pakistan.
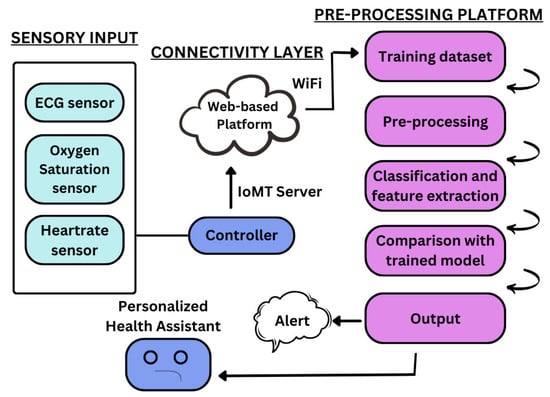
Figure 2.
Block diagram of the intelligent IoMT-based cardiovascular disease diagnosis system.
The system is designed to be compact and cost-effective, allowing patients to continuously monitor their cardiac activity. The collected data is stored in a SQLite database on the server machine, making it retrievable for visualization and analysis. This end-to-end system enables seamless communication between hardware and software components without requiring any third-party cloud integration.
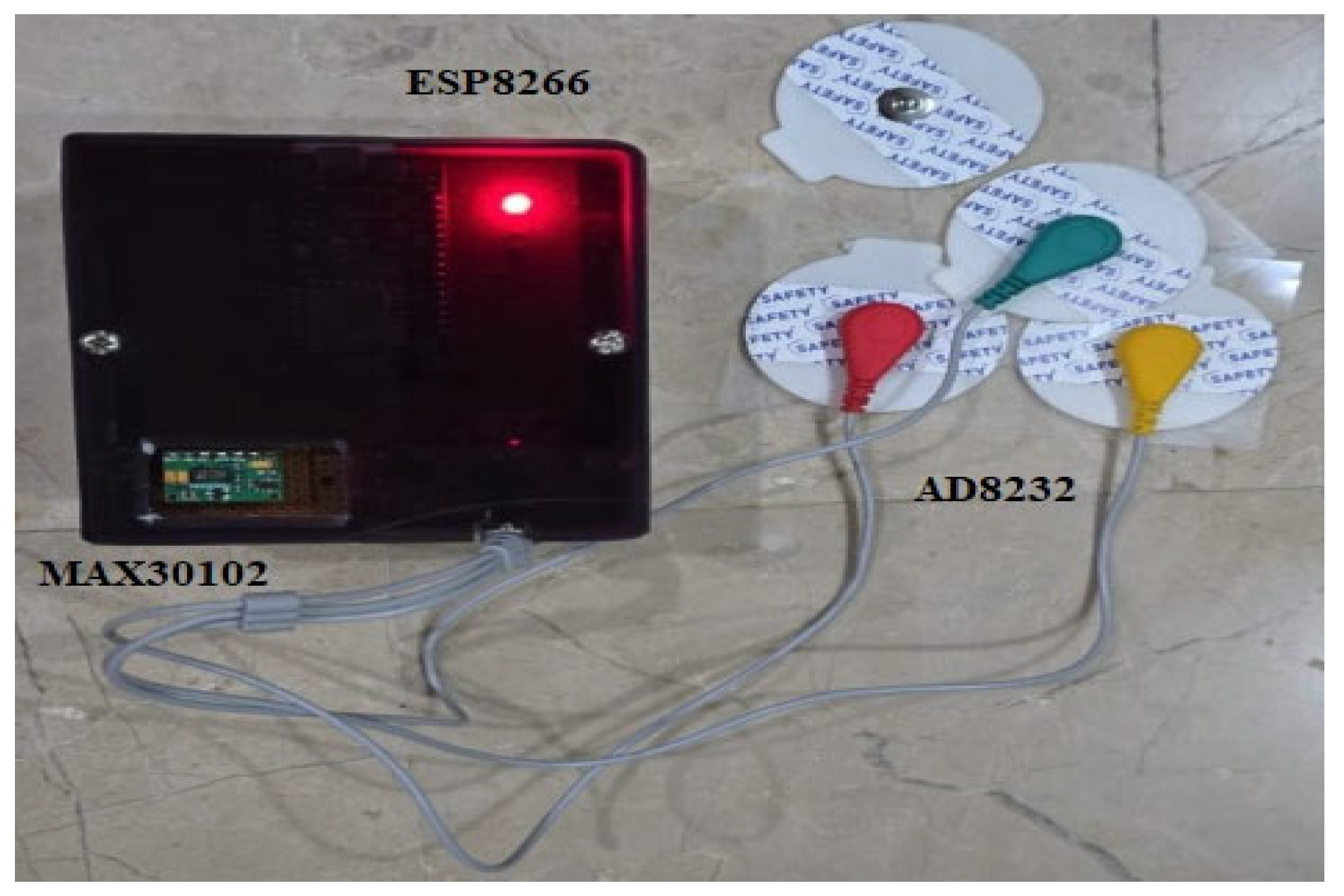
Data is acquired as physiological signals from the MAX30102 and AD8232 sensors through physical contact. The user touches their finger sensor, which measures fluctuations in blood volume, employing PPG for measurement of heart rate and SpO2. For ECG monitoring, sticky electrodes attached to the AD8232 sensor are applied to the user’s chest to capture the heart’s electrical activity. The two sensors are connected to the ESP8266 microcontroller, and the readings are viewed in the serial monitor via the Arduino IDE. The developed prototype is shown in Figure 3. The system does not automatically send data to the web interface; rather, the readings obtained are recorded and entered manually into the web dashboard for further visualization and storage in the local SQLite database. This half-automated solution enables system validation and functional testing prior to shifting to real-time transmission in subsequent versions. It also provides users with full control over when and where data is stored and logged.
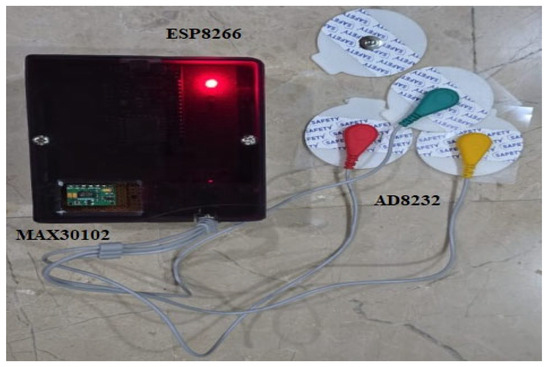
Figure 3.
Prototype with MAX30102 and AD8232 sensors with ESP8266 on vero board for real-time health monitoring.
2.2. Backend and Web Interface
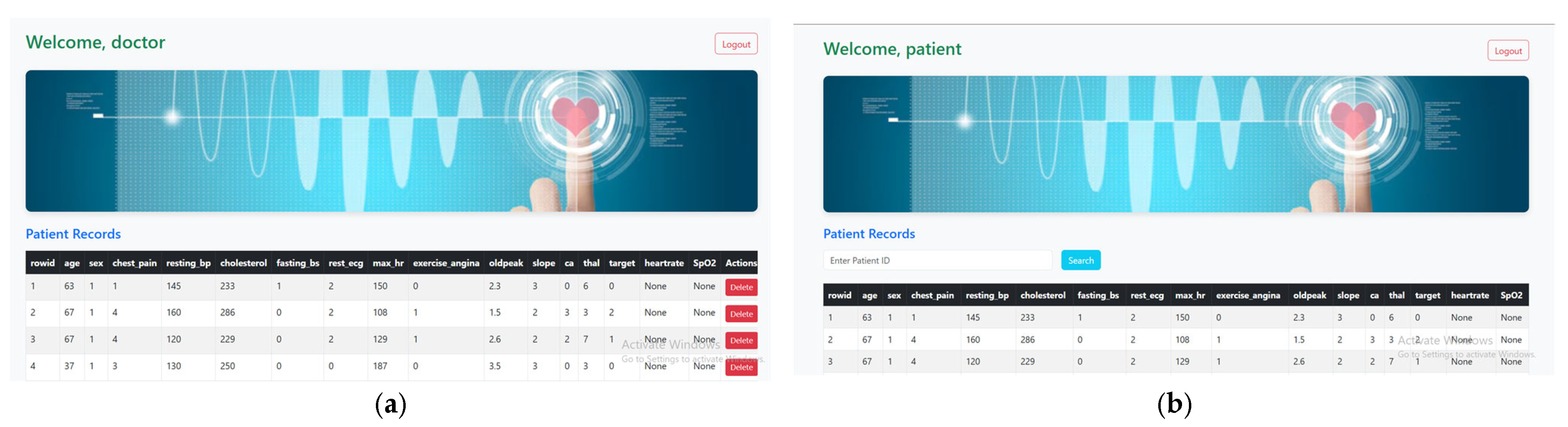
The backend system is developed using the Python Flask 3.1.0 framework and functions as a REST API to manage cardiac health data. It is hosted on a local machine with Wi-Fi capability, enabling communication between the web interface and backend services. The physiological data, including heart rate, SpO2, and ECG values, is captured using sensors and displayed on the Arduino IDE’s serial monitor. This data is then manually entered into the system via a secure web interface. The backend stores all health data in a local SQLite database, which includes patient ID, timestamps, and corresponding health parameters. The frontend is built using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript and allows doctors and patients to log in. Doctors can add or delete patient records, while patients can view their individual health information. The system runs on Wi-Fi within a local network environment and is accessible via web browser, making it convenient for use in clinics, labs, or controlled setups without requiring internet-based cloud services. Figure 4a shows a form for adding new patient data. The form has fields like age, sex, cholesterol, chest pain type, heart rate, and SpO2. Figure 4b shows the patient dashboard, where the table is read-only with a search bar at the top. The patient enters their Patient ID and clicks search. If the ID matches a record in the database, that record is shown. If not, an error message is displayed.
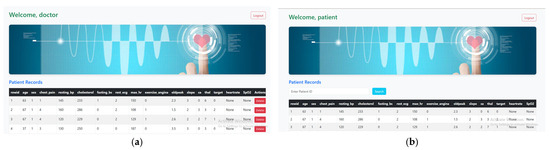
Figure 4.
Role-based dashboards to access specific heart disease features designed (a). Doctor dashboard with patient records, (b). Patient dashboard.
2.3. Machine Learning Model Deployment
The machine learning-based cardiac disease prediction system follows a structured workflow starting with the widely used UCI Cleveland Heart Disease dataset [27], for benchmarking in cardiovascular risk research. Data preprocessing involves handling missing values, encoding categorical attributes, and normalizing features with StandardScaler to improve model convergence and performance. Feature selection retains only the most informative attributes, reducing complexity while improving interoperability. The dataset is split into training and testing sets, and five algorithms—Logistic Regression, Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, k-Nearest Neighbors, and XGBoost—are evaluated using accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score [28]. For performance optimization, we performed hyperparameter tuning via GridSearchCV and Bayesian Optimization, with 10-fold cross-validation [29]. For real-time deployment, the optimized model is integrated into an IoT-enabled healthcare framework using AD8232 and MAX30102 sensors connected via ESP8266, transmitting data to a backend system for analysis, with a chatbot delivering instant diagnostic insights to support continuous cardiac health monitoring. The following five supervised learning models were trained and evaluated [15].
2.4. Chatbot Integration for Cardiovascular Diagnostic Support
This work combines a domain-specific chatbot with an AI/ML-powered IoMT system that deals specifically with cardiac diagnostics. It is developed with Python and the Falcon-7B-Instruct model through Hugging Face on Google Colab. The chatbot connects user inputs to relevant health information by examining real-time sensor data and answering in natural language. The chatbot is implemented with the following technical stack:
- Model: Falcon-7B-Instruct (Hugging Face Transformer-based Large Language Model);
- Frameworks: PyTorch 2.1.0 (model inference), Hugging Face Transformers 4.36.2;
- Environment: Google Colab with GPU acceleration;
- APIs/Libraries: Requests (HTTP), web-based API for real-time data integration.
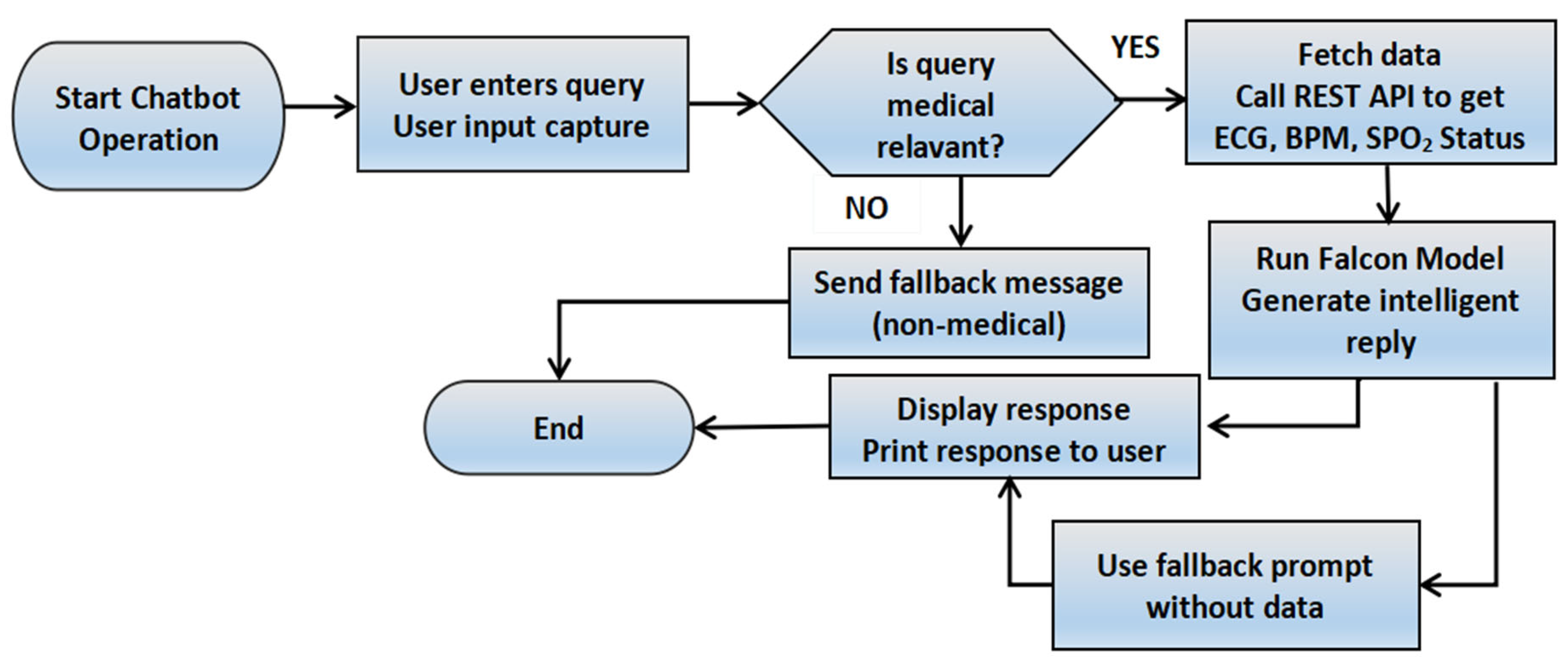
Figure 5 demonstrates the procedure of user input and chatbot response to answer cardiac queries.
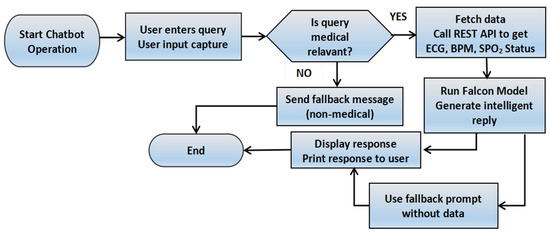
Figure 5.
Chatbot flowchart with medical query handling and sensor-based response generation.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. System Performance
The system prototype was tested in a controlled environment. ECG signals from the AD8232 were successfully captured and displayed in near-real time. Heart rate and SpO2 data from the MAX30102 were recorded consistently, though with some sensitivity to finger placement. Web interface performance was smooth under local hosting conditions. Real-time updates were displayed on the dashboard with minimal latency. The database allowed efficient storage and retrieval of patient data. The chatbot accurately understood queries related to chest pain, fatigue, dizziness, and other heart-related symptoms. Responses were relevant, context-aware, and aligned with model predictions.
3.2. Evaluation of Machine Learning Models
After training, each ML model is evaluated on an 80:20 train-test split. The evaluation metrics for all models are summarized in Table 2. For each ML model, we evaluated performance using three main metrics: precision, recall, and F1-score. These are especially important in healthcare because wrong predictions, like missing a real case or giving a false alarm, can have serious effects on a patient’s health. Precision measures how many of the cases predicted as heart disease were correct, helping reduce false positives. Recall tells us how many real heart disease cases the model was able to catch, which is very important to avoid missing patients who need help. The F1-score combines both precision and recall into one value and is useful when the dataset has uneven numbers of cases. In our results, the RF model showed the highest accuracy of around 83%, followed by XGBoost with about 82%. LR gave an average performance. SVM had high recall, meaning it identified more real cases, but its precision was lower, which means it also had more false alarms. These evaluations helped us choose the best model for safer and more reliable heart disease prediction.

Table 2.
Table comparing accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score for the five ML models.
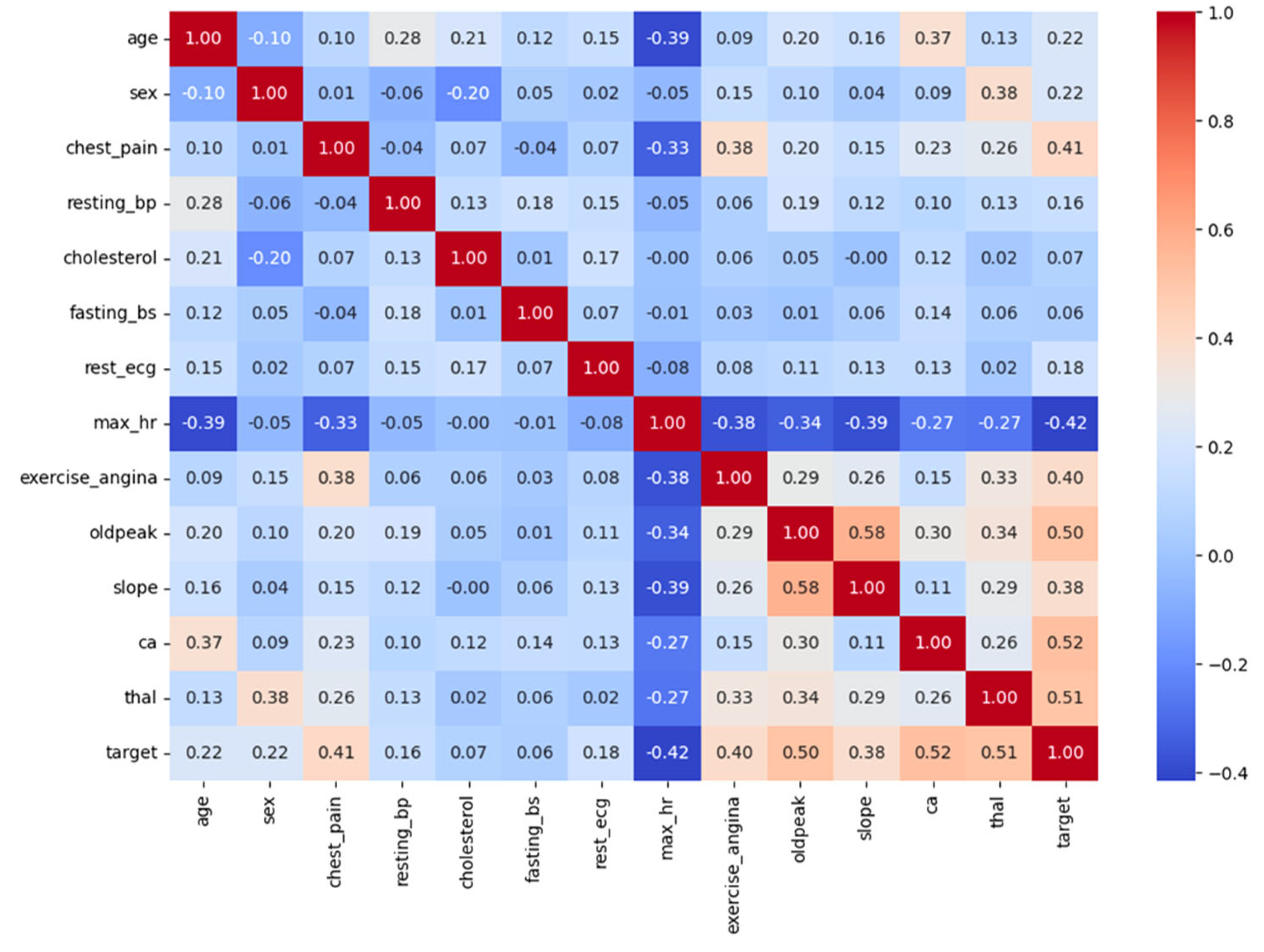
Figure 6 reflects a correlation heatmap that shows how different features in the dataset relate to each other and to the presence of heart disease (target). The values range from −1 to +1. A value close to +1 means a strong positive correlation, meaning both features increase together. A value close to −1 shows a strong negative correlation, meaning that as one feature increases, the other decreases. A value near 0 means little or no correlation. Important features identified by the models include the following: Chest pain type (cp), Age, Maximum heart rate achieved (thalach), Serum cholesterol (chol), depression induced by exercise (oldpeak). From the heatmap, we can see that features like cp, slope, ca, and thal have strong correlations with the target variable, meaning they are likely to be important in predicting heart disease. For example, cp has a positive correlation of 0.43 with heart disease, suggesting certain chest pain types are common in patients with CVD. On the other hand, maximum heart rate (max_hr) has a negative correlation of −0.42 with the target, meaning a lower max heart rate is often linked to heart disease. This kind of heatmap is very helpful in identifying which features are most useful for model building. It also helps avoid multicollinearity, when two features are too similar, by showing which features are highly correlated with each other. For example, slope and oldpeak or ca and thal show moderate-to-strong correlation, which is worth considering during feature selection.
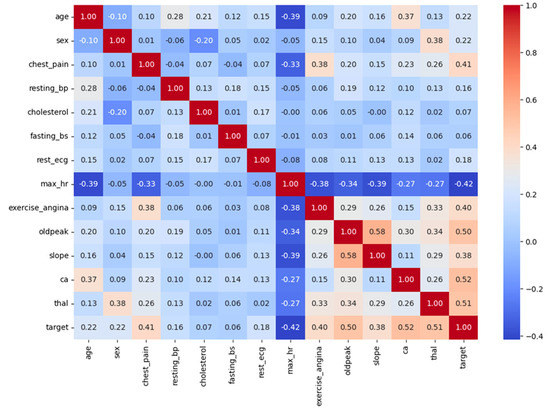
Figure 6.
Heatmap of feature correlations and target relationships.
4. Conclusions
This paper presents an end-to-end, real-time cardiac health monitoring system that integrates wearable biomedical sensors, wireless data transmission, machine learning, and a chatbot interface. The proposed solution is low-cost, scalable, and suitable for deployment in remote or underserved regions. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, especially techniques like Random Forest and XGBoost, we achieved an accuracy of up to 85%, with further improvement through hyperparameter tuning and Bayesian optimization. The chatbot enhances usability, making the system patient-friendly. With future enhancements such as mobile application integration, cloud deployment, and stronger security protocols, this system has the potential to redefine how cardiac healthcare is delivered, making it smarter, faster, and more accessible.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.M., A.K., H.N. and B.K.; methodology, H.M., A.K., H.N. and B.K.; software, A.K., H.N. and B.K.; validation, A.K., H.N. and B.K.; formal analysis, H.M., A.K., H.N. and B.K.; investigation, A.K., H.N. and B.K.; resources, A.K., H.N. and B.K.; writing—original draft preparation, H.M., A.K., H.N. and B.K.; writing—review and editing, H.M.; visualization, A.K., H.N. and B.K.; supervision, H.M.; project administration, H.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used is publicly available at https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/heart+Disease (accessed on 29 November 2024).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to the Department of Telecommunications Engineering, NED University of Engineering and Technology, Karachi, Pakistan, for providing the necessary facilities and support to carry out this work as a Final Year Design Project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Di Cesare, M.; Perel, P.; Taylor, S.; Kabudula, C.; Bixby, H.; Gaziano, T.A.; McGhie, D.V.; Mwangi, J.; Pervan, B.; Narula, J.; et al. The Heart of the World. Glob. Heart 2024, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Mensah, G.A.; Fuster, V.; Murray, C.J.L.; Roth, G.A. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risks, 1990–2022. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 2350–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndreas, S.; Bothner, U.; De La Hoz; Kloer, I.; Trampisch, M.; Alter, P. Post Hoc Holter ECG Analysis Olodaterol Formoterol Moderate-to-Very-Severe COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2020, 15, 1955–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldahiri, A.; Alrashed, B.; Hussain, W. Trends in Using IoT with Machine Learning in Health Prediction System. Forecasting 2021, 3, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, I.; Campo-Valera, M.; Rodríguez, J.-V.; Lok Woo, W. IoMT Innovations in Diabetes Management: Predictive Models Using Wearable Data. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 121994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Internet of Medical Things: A Systematic Review. Neurocomputing 2023, 557, 126719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Li, Y.; Nabeed, T.; Rahman, M.T. Remote Monitoring of Heart Rate and ECG Signal Using ESP32. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Advanced Electronic Materials, Computers and Software Engineering (AEMCSE), Changsha, China, 26–28 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Palamar, A.; Palamar, M.; Osukhivska, H. Real-Time Health Monitoring Computer System Based on Internet of Medical Things. In Proceedings of the ITTAP’2023: 3rd International Workshop on Information Technologies: Theoretical and Applied Problems, Ternopil, Ukraine, 22–24 November 2023; pp. 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, V.-N.; Coboi, A.; Nam, D.D.; Vien, L.G.; Thai, P.D. Design of ECG Circuit and Patient Remote Monitoring System Using MQTT Protocol for ECG Signals. J. Basic Appl. Res. Int. 2024, 30, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.-A.T.; Vo, B.-T.; Pham, V.-N.; Ba, Q.-H.D.; Nguyen, T.-N.; Ha, M.-H.; Kim, D.-T. Patient Remote Monitoring System Using MQTT Protocol for ECG Signals. In Proceedings of the 2024 9th International Conference on Integrated Circuits, Design, and Verification (ICDV), Hanoi, Vietnam, 6–7 June 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.; Al-awlaqi, A.A.H.M.; Li, M.; O’Grady, M.; Gu, X.; Wang, J.; Cao, N. Wearable IoT Enabled Real-Time Health Monitoring System. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2018, 2018, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L. The IoT-Based Heart Disease Monitoring System for Pervasive Healthcare Service. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 112, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon, J.A.; Guerra-Ojeda, S.; Carrascosa, C.; Julian, V. An IoT and Fog Computing-Based Monitoring System for Cardiovascular Patients with Automatic ECG Classification Using Deep Neural Networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hizem, M.; Bousbia, L.; Ben Dhiab, Y.; Aoueileyine, M.O.-E.; Bouallegue, R. Reliable ECG Anomaly Detection on Edge Devices for Internet of Medical Things Applications. Sensors 2025, 25, 2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhirud, N.; Tataale, S.; Randive, S.; Nahar, S. A Literature Review Chatbots Healthcare Domain. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 8, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Hannan, A.; Cheema, S.M.; Pires, I.M. Machine Learning-Based Smart Wearable System for Cardiac Arrest Monitoring Using Hybrid Computing. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 87, 105519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, J.-W.; Zang, G.-Y.; Pu, J. The Primary Use of Artificial Intelligence in Cardiovascular Diseases: What Kind of Potential Role Does Artificial Intelligence Play in Future Medicine? J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Yin, Y.; Yang, Q.; Huo, T. Artificial Intelligence in Cardiovascular Diseases: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Kumar, R.; Ahmed, N.M.O.S.; Jain, A. A Decision Support System for Heart Disease Prediction Based upon Machine Learning. J. Reliab. Intell. Environ. 2021, 7, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, A.; Jeberson, W. Diagnosis of Heart Disease Using Internet of Things and Machine Learning Algorithms. In Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Computing, Communications, and Cyber-Security, Gujarat, India, 6–7 February 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 691–702. ISBN 9789811607325. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, F.A.; Shakil, G.S.; Iqbal, S.S.M.; Sajid, S.T.A. Self-Diagnosis Medical Chatbot Using Artificial Intelligence. In Algorithms for Intelligent Systems; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 587–593. ISBN 9789811567063. [Google Scholar]
- Sadad, T.; Bukhari, S.A.C.; Munir, A.; Ghani, A.; El-Sherbeeny, A.M.; Rauf, H.T. Detection of Cardiovascular Disease Based on PPG Signals Using Machine Learning with Cloud Computing. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1672677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, G.M. Photoplethysmography (PPG) for Heart Disease. Available online: https://www.news-medical.net/health/Photoplethysmography-(PPG)-for-Heart-Disease.aspx (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Lee, H.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, S.P.; Park, J.; Park, I.H.; Youk, H. Substantiation and Effectiveness of Remote Monitoring System Based on IoMT Using Portable ECG Device. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva-Tsaneva, G.; Cheshmedzhiev, K.; Tsanev, Y.-A.; Dechev, M.; Popovska, E. Healthcare Monitoring Using an Internet of Things-Based Cardio System. IoT 2025, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UCI Machine Learning Repository. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/45/heart+disease (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Srinivasan, S.; Gunasekaran, S.; Mathivanan, S.K.; Malar M.B., B.A.; Jayagopal, P.; Dalu, G.T. An Active Learning Machine Technique Based Prediction of Cardiovascular Heart Disease from UCI-Repository Database. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohan, D.; Reddy, G.P.; Kumar, Y.V.P.; Prakash, K.P.; Reddy, C.P. An Extensive Experimental Analysis for Heart Disease Prediction Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).