Abstract
This manuscript addresses the issue of irrigation water management with high efficiency and effectiveness and focuses on systems associated with significant water losses, which is sprinkler irrigation. This article presents mathematical modeling that enables the application of precision irrigation using a gun sprinkler robot. The sprinkler robot was fabricated in the Faculty of Agriculture and Natural Resources workshop at As-wan University. The experiments were conducted using 12, 14, and 16 mm nozzle sizes and three gun heights, 1.25, 1.5, and 2 m, at three forward speeds, 25, 50, and 75 m/h. The results revealed that at nozzle 12, the actual wetted diameter would be less than the theoretical diameter by a percentage of 2–5%, while at nozzle 14, it ranged from 2 to 7%, but at nozzle 16, it increased from 6 to 9%. The values of evaporation and wind drift losses were always less than 2.8 mm. The highest efficiency was achieved at the lowest forward speed (25 m/h) and using a 1.5 m gun height. The highest water application efficiency was 81.8, 82.5, and 81.1% using nozzle 12, nozzle 14, and nozzle 16, respectively. Precise irrigation control using sensor and variable rate technology will be the preferred option in the future.
1. Introduction
The agricultural sector faces major challenges, especially water scarcity and climate change. This requires concerted efforts to create innovative solutions. These solutions are supposed to achieve maximum productivity with minimum water consumption. Sprinkler irrigation is justified by its ability to deliver water to crops, its adaptability to various terrains and soil types, its potential for water conservation, and its cost-effectiveness. It mimics rainfall, distributes water evenly, and reduces waste, which is critical for sustainable agriculture and landscaping. The traveler gun sprinkler can be adjusted to suit the specific needs of different crops and soil types, promoting water conservation and reducing waste. Compared to some other irrigation methods, such as drip irrigation, sprinkler systems are more economical to install and maintain. The utilization of traveler gun sprinklers has become an urgent requirement to address the ongoing water and energy shortages. One of the key sustainable development goals for developing countries is to ensure efficient water use within the agricultural sector. Rapid population growth, coupled with limited freshwater resources and arable land, is placing greater pressure on Egypt’s rural areas. Possibly one of the most crucial objectives of sustainable development for developing countries is to enhance the utilization of renewable energy sources in all sectors in general and the agricultural sector in particular and manage it optimally [1]. The non-judicious use of water at the farm level in traditional irrigation application methods is a present day concern across the world that can be resolved by enhancing application efficiency through the adoption of advanced irrigation techniques. Sprinkler irrigation is a method that has high application efficiency, which can be further increased when coupled with automation toward precision irrigation [2]. Ref. [3] highlighted that Egypt is experiencing a severe water shortage, a critical issue for agricultural irrigation. Ref. [4] noted that the primary source of water in Egypt is the Nile River; however, due to population growth and climate change, the available water resources are decreasing. The Nile provides over 98% of the water required for irrigation. Ref. [5] emphasized that the water used in agriculture in Egypt is increasing due to the growing demand for food driven by population growth. The demand for water in agriculture has reached approximately 63 billion cubic meters, which accounts for 82.9% of Egypt’s total water consumption. Ref. [6] pointed out that Egypt has a relatively small area of arable land, particularly in the Nile Valley and Delta, which comprises about 4% of Egypt’s total land area. Ref. [7] explained that Egypt’s per capita water resources are declining each year, with available water falling to 540 cubic meters per person. Ref. [8] predicted a significant decline in per capita water availability by 2030. Ref. [9] stated that the Egyptian government has taken steps to improve irrigation technology and water resource management through legislative and political support. Refs. [10,11] underscored the importance of improving irrigation systems and methods to enhance agricultural productivity and achieve environmental sustainability. Ref. [12] emphasized that these measures aim to reduce water wastage. Improving crop productivity and water efficiency can be significantly achieved by optimizing water distribution for irrigation and evaluating modern irrigation systems. Ref. [13] suggested that the Egyptian government is launching numerous initiatives to introduce water-saving methods to enhance the effectiveness of traditional irrigation systems, increasing production and improving water-use efficiency. Ref. [14] reported that water scarcity is the main yield limiting factor, where it is difficult to apply full crop water requirements to sustain maximal growth and yield. Therefore, it is very important to determine how to maintain optimum crop yields under water-deficient conditions. Ref. [15] stated that the traditional irrigation systems may provide unnecessary irrigation to one part of a field while leading to a lack of irrigation in other parts. Further development of irrigation systems is also necessary for increasing efficiency, productivity, and profitability of farming operations. Refs. [16,17] mentioned that sprinkler irrigation is one of the automated technologies currently practiced for frost protection for crops. Ref. [2] stated that sprinkler irrigation is a method that has high application efficiency, which can be further increased when coupled with automation toward precision irrigation. Recently, this has stimulated researchers to explore new irrigation technologies and strategies to improve water use efficiency. A brief overview of current irrigation technology is described in the following section.
Irrigation technologies include the following:
- Surface Irrigation:
This method involves flooding the field with water, furrow irrigation, and basin irrigation.
- 2.
- Sprinkler Irrigation:
Water is applied through a network of pipes and sprinklers, mimicking rainfall. It can be more efficient than surface irrigation, especially in undulating terrains. This method involves center pivot systems, hand-moved sprinkler systems, and gun sprinklers.
- 3.
- Micro-Irrigation:
This method delivers water directly to the plant’s root zone through a network of pipes. This method involves drip lines, drip tapes, and subsurface drip irrigation. Micro-irrigation is an irrigation method in which the water and nutrients required for crop growth are uniformly and accurately transported to the soil near the roots of crops at a small flow rate through a pipeline system and an irrigator installed on the final-stage pipeline [18].
- 4.
- Subsurface Irrigation:
Water is delivered to the root zone through a network of tubes buried beneath the soil surface. It can be particularly effective in sandy soils, where surface irrigation may not retain enough moisture. The optimized subsurface irrigation system is a super water-saving subsurface irrigation system developed to irrigate upland crops by soil capillarity. It is an environmentally friendly, solar-powered automatic irrigation method with minimum energy consumption and operational costs. In soils vulnerable to drought damage, it can outperform other irrigation methods [17].
- 5.
- Intelligent irrigation:
Recent developments include smart irrigation systems that use sensors, data analytics, and automation to deliver water precisely. These developments are based on the edge computing architecture and long-range radio communication technology, utilizing STM32 MCU, WH-101-L low-power LoRa modules, 4G modules, high-precision GPS, and other devices [19].
- 6.
- Precision Irrigation:
This approach leverages data from sensors, satellites, and weather forecasts to precisely tailor water distribution to specific areas of the field. Precision irrigation, defined as an efficient water allocation technique characterized by the optimal management and best collaboration of various factors of the irrigation process, attracts considerable attention in agricultural production and crop cultivation. Some frontier techniques, such as data-oriented irrigation management, performance-proven water allocation, and cloud-based irrigation control, are among the critical technologies capable of building a sustainable, integrative, and evolutionary irrigation system while providing the higher quality and efficiency needed for a full application of precision irrigation [16].
- 7.
- Variable Rate Irrigation:
It is a technology that allows farmers to apply different amounts of water to different areas of a field, optimizing water use and potentially improving crop yields and water quality. It achieves this by adapting to the unique needs of various soil and crop conditions within a field, rather than applying water uniformly. Variable rate irrigation technology, matching appropriate irrigation applications to specific areas, could contribute to water savings compared to uniform rate irrigation at the field scale [15].
Ref. [20] clarified that sprinkler irrigation systems consume significant amounts of energy, accounting for 19% of annual energy consumption, 30% of total natural gas consumption, and 3.3 billion gallons of diesel fuel for pump pressure. According to [21], increasing the operating pressure from 0.45 MPa to 0.5 MPa is expected to lead to an 18% rise in energy costs. Therefore, reducing operating pressure slightly could lead to significant reductions in operational costs. Ref. [22] reported that one of the most used irrigation techniques for agriculture is sprinkler irrigation. Irrigation techniques have been used to increase agricultural output in arid areas and in locations where rainfall is the main factor in crop development. Sprinkling irrigation systems are used as part of irrigation system applications all around the world because of how convenient they are to use. Ref. [23] argued that lowering the operating pressure of the irrigation system while maintaining high irrigation efficiency is an essential approach to saving both water and energy to increase production. Ref. [24] confirmed that one common method to reduce energy consumption in irrigation systems is to decrease the operating pressure of the sprinkler system. However, recent studies indicate that reducing pressure may lead to a decrease in irrigation efficiency and coverage area. To address this issue, many studies have been conducted to enhance hydraulic performance by optimizing the operating pressure, nozzle selection, and optimal height [25]. Ref. [26] designed several different nozzles with varying height angles to achieve the best performance based on water distribution. Ref. [27] reported that the irrigation uniformity of sprinkler irrigation systems depends on many design factors such as nozzle type, nozzle diameter, operating pressure, and riser height. Refs. [28,29] confirmed that the optimal performance of rotating sprinklers is achieved by improving water distribution efficiency through careful selection of the operating pressure. Many irrigation equipment manufacturers are committed to developing low-pressure sprinklers, including quad sprinklers, rotary sprinklers, pivot sprinklers, among others [30]. Ref. [31] investigated the performance of a gun sprinkler system operated at various pressures (2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, and 5 kg/cm2) with different nozzle sizes and found that the wetting radius increased with the operating pressure. Ref. [32] evaluated the effectiveness of the gun sprinkler system using different operating pressures, observing that the covered area increased with higher operating pressures. The optimal operating pressure for nozzles with sizes of 10 mm and 12 mm was found to be 4.5 kg/cm2. Ref. [33] established relationships among pressures, discharge, and throw radius for an independent gun nozzle. The operating pressure can be adjusted based on soil type to achieve the desired precipitation rate. However, variations in discharge and throw radius with operating pressure depend on the nozzle type. It was found that the throw radius could be improved by adjusting the operating pressure. Ref. [34] stated that the water application rate and droplet kinetic energy are considered the most important indicators of soil erosion in sprinkler irrigation. However, little information is available relating sprinkler performance parameters to soil runoff, infiltration, and erosion. Ref. [35] concluded that using low-pressure sprinklers in agricultural irrigation has become an alternative way of reducing water and energy stress. For crops with higher water requirements, using low-pressure sprinklers means longer irrigation time is needed. The benefits associated with lower working pressure may be negated by the longer working time. Therefore, low-pressure sprinkler irrigation may be more applicable for crops with lower water requirements and for irrigation on sensitive crops and soils. So, the effects of the kinetic energy of low-pressure rotating sprinklers on soil water dynamics should be further investigated. Ref. [36] indicated that to overcome the problems of repeated sprinkling, a variable sprinkler irrigation system was developed. The variable sprinkler allows the pressure and flow to be changed with sprinkler rotation. Ref. [37] stated that in flood irrigation, 50–55% of water losses were noted in the field due to undulations and field application losses. Ref. [38] reported that more water is available with fewer application losses to crops by the new mobile sprinkler rain gun. By using a sprinkler rain gun, 72% of water can be saved with less operational cost in terms of fuel. The coefficient of uniformity is 80.2% with an application rate of 9.8 mm/h at 0.46 ha irrigated area, which showed a significant amount of water saving up to 978 m3 over losses. Ref. [39] indicated that sprinkler irrigation systems have been widely employed in different parts of the world states where water and energy have become limited and expensive; as a result, the conservation of water and energy resources is required to ensure the viability of pressurized irrigation systems. In recent decades, the increasing pressure on natural resources due to population growth and climate variability has further highlighted the need for efficient irrigation systems to ensure food security and sustainable water use. Considering the major technological innovations in previous studies compared to recent developments in irrigation systems, it has been shown that the sprinkler robot improves water efficiency. While traditional sprinkler irrigation systems suffer from significant water loss due to evaporation or runoff due to inaccuracies in water additionally [40,41], the sprinkler robot can move accurately and change the amount of water according to the moisture sensitivity, reducing waste and increasing water efficiency. The robot works to save energy and reduce costs compared to traditional irrigation systems because it often relies on high-energy petrol engines [42,43]. Future research should focus on enhancing irrigation system efficiency through advanced sensors and weather analytics, integrating additional renewable energy sources, and testing scalability across diverse urban environments [44]. So, the robot is equipped with intelligent sensors that enable it to automatically adjust the amount of added irrigation water based on data from moisture sensors. It can operate in multiple fields and stadiums and be able to irrigate different spaces with high precision, while fixed irrigation systems are difficult to move from one place to another, and the robot is lower in terms of manufacturing and maintenance costs than other irrigation systems. Because they use water efficiently and can increase crop yields in arid conditions, robotic sprinkler systems are essential for areas like Egypt. By automating irrigation, these systems increase irrigation accuracy and uniformity while lowering labor expenses and water waste. Additionally, they support sustainable agriculture by assisting farmers in adjusting to the problems posed by water scarcity and climate change. Therefore, this manuscript aims to enhance water-use efficiency using a sprinkler irrigation robot.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Description of Traveler Gun Sprinkler
Figure 1 shows the sprinkler robot used in this study during the preparation of the field experiments. The robot was manufactured in the Faculty of Agriculture and Natural Resources workshop at Aswan University to enhance water use efficiency in irrigation.
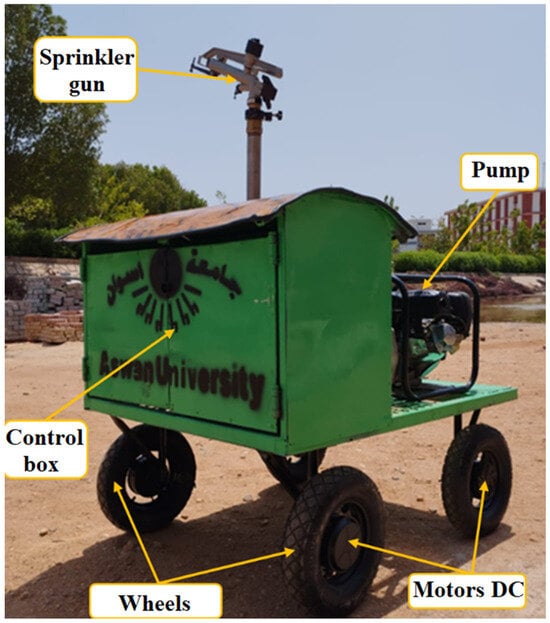
Figure 1.
The sprinkler robot during the preparation of the field experiments.
The design features include its simplicity and ease of use, and the fact that its components are made from locally available materials, which makes it both cost-effective and accessible. Also, it is controlled remotely by four motorized wheels. The sprinkler is supplied with irrigation water by a pump attached to the sprinkler cart. The pump is connected to the water source located at the field head by a drawn hose. The hose-drawn traveler has a 1.5-inch diameter and a 200 m long polyvinyl chloride hose. The gun with a 16 mm nozzle and an operating pressure of 400 kPa is mounted in the center of the car to keep the traveler sprinkler balanced during the operation. The forward speed will be adjusted before operation according to the soil moisture content.
2.2. The Main Components
The sprinkler consists of four main components, which are summarized as follows:
2.2.1. Frame
The frame was fabricated from welded iron square bars 40 mm width × 40 mm height × 2 mm thickness and 30 mm width × 30 mm height × 1 mm thickness. The frame was covered with sheet metal 1 mm thick. The rectangular-shaped frame was formed at 550 mm in height, 1200 mm in length, and 900 mm in width. The frame has four pneumatic ground wheels (400 × 8) distributed at the corners.
2.2.2. Power Source
The power source was four DC motors. Each motor was attached to the sprinkler’s ground wheel. The capacity of each motor was 350 W. These motorized wheels are responsible for controlling the forward speed of the sprinkler. They are programmed according to field operating conditions.
2.2.3. Control Box
The control box attached to the sprinkler car contained the electronic circuits responsible for controlling the sprinkler operation. Also, it contained three batteries. Two lithium-ion batteries (36 V, 4400 mA) were used as an alternative power source for the DC motor, and the third (12 V, 2200 mA) was used for running the electronic circuits. These batteries could be recharged using solar panels if necessary.
2.2.4. Sprinkler Irrigation System
The sprinkler system consists of a pump (2 inches, 23 m3/h) mounted on the car. A 7-horsepower gasoline engine was used to power the pump. The pump was used to draw irrigation water from the source through a hose drawn behind the sprinkler. The pump was connected to the sprinkler gun (D = 1.5 in) with galvanized iron pipes. These connections make it possible to control the gun height from the ground. The sprinkler gun incorporates a range of nozzles with varying heights to create different spray patterns, ensuring efficient water distribution over a wide coverage area.
The nozzle sizes used during the experiments are shown in Figure 2. The throw angle of sprinkler guns is an engineering factor that affects water distribution and irrigation efficiency. This angle determines the distance that water can reach, and therefore the coverage of the target area. The throw angle is usually between 30° and 45°. These angles allow for wide coverage of the target area while maintaining an even water distribution. An angle less than 30° may result in limited coverage of the target area. In comparison, an angle greater than 45° may result in increased evaporation before the water reaches the soil, thus reducing irrigation efficiency.
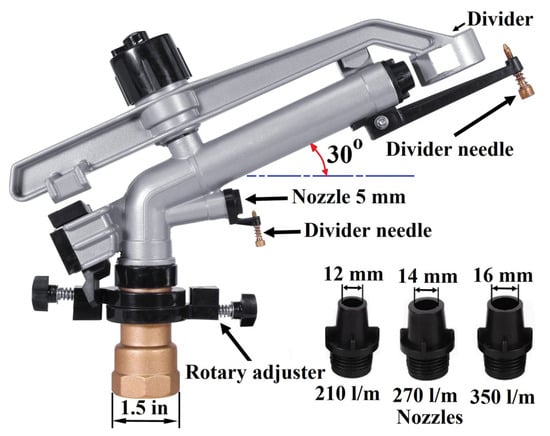
Figure 2.
The nozzle sizes used during the experiments.
2.3. Location and Experimental Conditions
The experiments were conducted in July 2024 at Aswan University stadium, Egypt, which is located approximately 85 m above sea level, at 24.088 degrees north latitude and 32.899 degrees east longitude. This gun sprinkler irrigated the stadium (110 × 70 m), as shown in Figure 3. The experimental soil is classified as sandy soil. During the experiments, the temperature ranged from 33° to 39° and the average relative humidity was 47%. Currently, the stadium is irrigated with a fixed sprinkler system. The experiments were conducted in a still, windless climate and no wind speeds were recorded.
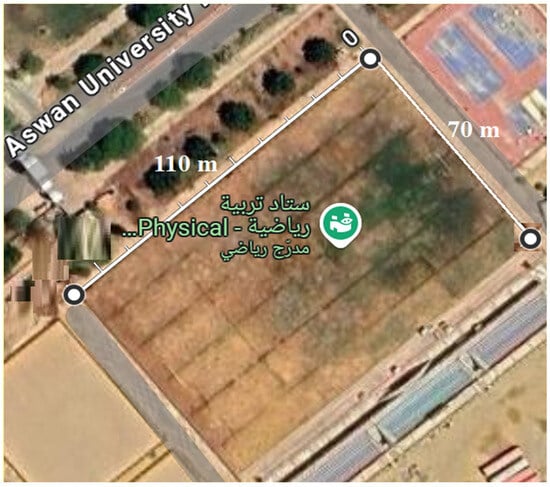

Figure 3.
Experimental area map.
2.4. Working Principle
Figure 4 shows the working principle of the traveler gun sprinkler during field experiments. The field experiments were carried out in a field with sandy soil on a relatively flat topography. This field was the subfield inside Aswan University. First, the starting point coordinates are determined according to the nozzle size, forward speed, and the required overlap ratio. Based on this, the irrigation path dimensions within the field are determined. Second, the gun sprinkler is programmed to move without sprinkling until it reaches the starting point coordinates. The gun sprinkler pulls the water hose from the reel and then connects the other end to the main water line valve. At the starting point, the sprinkler stops for a specific time and irrigation is carried out at this point without movement. This stage is considered a fixed sprinkler irrigation system. After this specified time, the sprinkler starts moving at a forward speed. This forward speed will determine the time the sprinkler stops for irrigation at the starting point to achieve regular irrigation in the entire field after irrigation is completed. Irrigation is conducted with a 180-degree sprinkling angle against the direction of sprinkler movement. The hose reel was responsible for twisting the hose behind the sprinkler during the irrigation. The experiments were conducted under 4 bar pressure.
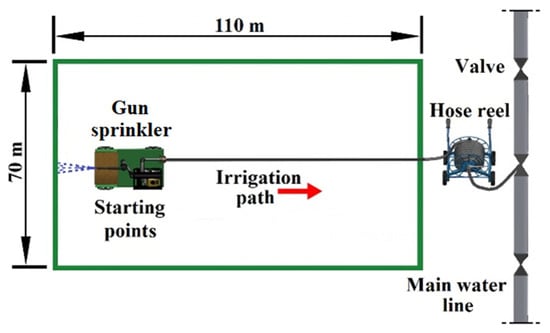
Figure 4.
The working principle of the sprinkler robot during field experiments.
2.5. Theoretical and Mathematical Analysis
Figure 5 shows a schematic diagram of the field gun operation simulation parameters. The values of the parameters related to the theoretical and mathematical analysis for the field irrigation are shown in Table 1.
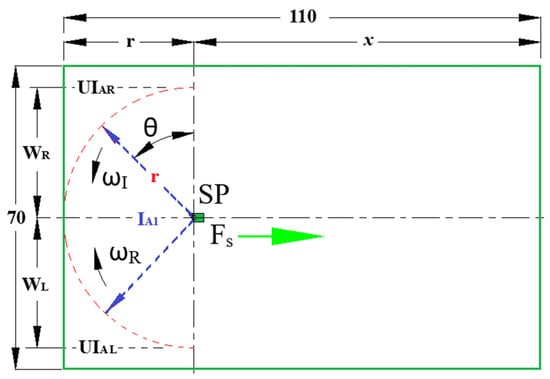
Figure 5.
A schematic diagram of the field gun operation simulation parameters.

Table 1.
Values of parameters related to theoretical and mathematical analysis.
To deduce the mathematical relationships of the working principle of the traveler gun sprinkler, it is assumed that flowing water from the nozzle has three properties:
1. Constant pressure (P = 4 bar).
2. Constant discharge (Q, m3/s).
3. Constant wetting radius (r, m). The wetting radius is the distance between the gun nozzle and the maximum point in the field that the irrigation water flow can reach.
When the sprinkler reaches the starting point coordinates inside the field, water begins to flow from the nozzle at an angle (θ = 0). It is the angle formed by the path of the water flowing from the nozzle with the horizontal axis. The sprinkler stops at this point and the angle (θ) changes with time to give the rotational speed (ω).
When the gun is rotated 180 degrees, the irrigated area (Ia1) can be estimated from the following equation:
But the sprinkler is supposed to cover the rectangular irrigation area whose dimensions are r × Wd. Thus, an unirrigated area (UIa) will be created at the corners of the experimental plot. This area can be estimated from the following equation:
This equation is used to program the sprinkler to move at another coordinate point that enables it to irrigate this area. The irrigation area covered by the sprinkler as it moves backward is abstractly defined as a “rectangle”. This rectangle (the experimental field) represents the irrigated area as the sprinkler moves by wheel motors from the starting point toward the end of the field. The forward speed (Fs, m/s) is estimated by the rate of change in displacement (x, m) to time (T, s) using the following equation:
The irrigated area (Ia2, m2) at any time (T, s) can be estimated from the following equation:
But this area changes with the change in time from T0 to T1 according to the following equation:
The volume of irrigation water (V, m3) added at time (T, s) is estimated from the following equation:
But this volume changes with the change in time from T0 to T1 according to the following equation:
From Equations (6) and (8), the applied water depth (Da, m) can be obtained from the following equations:
The water volume that reaches each side varies depending on how long the sprinkler is directed to the left or right during its movement. The total spray time (T) is the time it takes the gun to rotate through the double angular interval (covering the area on both sides of the gun line). Therefore, the spray time is divided into (TL), which is the time during which the gun is directed toward the left side, and (TR), the time during which the gun is directed toward the right side. The total irrigation time is estimated from the following equation:
The gun irrigates with a constant discharge (Q, m3/h) on both sides.
The volume of irrigation water for the right side (VR, m3) and the volume of irrigation water for the left side (VL, m3) are estimated from the following equations:
Therefore, by Equations (10), (14) and (15), it is possible to deduce the applied water depth on each side (DaR and DaL, m) through the following equations:
The average applied water depth is calculated from the following equation:
Looking at Equations (10) and (18), the water depth depends on the discharge and forward speed of the gun sprinkler. The forward speed of the gun can be estimated from the following equations:
Through Equation (20), the required forward speed can be determined; the wheel motors will be programmed according to the applied depth targeted for each crop.
Under the assumption that the effect of longitudinal transition between adjacent irrigation paths was negligible, this modeling can be repeated for each longitudinal path independently. However, in the case of a comprehensive mathematical analysis, the effect of the overlap ratio of irrigation paths on the field performance of the sprinkler will be shown. This mathematical modeling enables the application of variable rate technology for precise control in field irrigation using gun sprinklers. It helps to improve water distribution in the field and reduce losses, especially when using gun sprinklers to irrigate large areas. Also, it will open up the possibility of controlling this sprinkler to work as a fixed and traveling sprinkler. Thus, it combines the advantages of fixed and traveling irrigation systems.
2.6. Technical Detail and the Robotic System’s Functionality
The sprayer robot’s navigation system and path determination represent the positioning system and the construction of a location map at the same time. Once the sensors measure field moisture, the robot uses simultaneous localization and mapping algorithms to create a map of the field environment, taking into account the overlap ratio and water application rate. With the map in hand, it can plan its optimal path from its initial location to the target destination (the irrigation start point). Path planning algorithms take into account various factors, such as obstacle avoidance, travel distance, forward speed, and adjacent path interference to plan the most efficient route. Furthermore, the centering point can be varied to cover the irrigation of field corners and irregular areas. As the robot moves, it continuously tracks its own position relative to the given environment. Localization algorithms can use sensor data and a cognitive map to determine the robot’s precise location. Once the path is planned and the location is determined, the robot’s control system (automated wheels) takes over the movement. This system executes the necessary actions to propel the robot along the planned path, ensuring smooth and reliable movement. Robot localization refers to a robot’s ability to determine its position and orientation within a frame of reference. Path planning is an effective extension of localization, requiring the robot’s current position and the position of its target location to be determined, both within the same frame of reference or coordinates. Irrigation performance will vary with robotic control to provide the possibility of reducing water loss through surface runoff and irrigating lands with uneven surfaces and difficult topography. Furthermore, the precise control of water application in small quantities and at close intervals with high efficiency and controlled irrigation water distribution can be achieved. Labor use can be minimized and human error reduced in the management of other fixed sprinkler irrigation systems. The development of a robotic sprinkler system that is characterized by simple technology, reliability, ease of maintenance, availability of spare parts, and accessibility to farmers, especially in developing countries, will positively impact agricultural production and the efficiency of irrigation water use, and reduce irrigation costs by up to 40% compared to other systems such as surface irrigation and fixed sprinkler irrigation.
2.7. Experimental Variables
Some important engineering factors have been determined that directly affect robot performance. Variables of the experiments are as follows:
2.7.1. Gun Nozzles
According to [35], it is necessary to select the nozzles adapted to the working pressure of the sprinkler irrigation system. Thus, it is not recommended to equip the sprinkler with a large nozzle under low working pressure. The nozzles give different discharge rates and wetting diameters (Wdth). To match operating pressure, the experiments were carried out by using 12, 14, and 16 mm nozzle sizes.
2.7.2. Forward Speed
According to [39], the forward speed of the traveler gun sprinkler during field irrigation varies from 25.4 to 82.9 m per hour, depending on the field’s topography, the type of crop, and the climatic operating conditions. Therefore, the field experiments were conducted at three forward speeds of the gun sprinkler: 25, 50, and 75 m per hour.
2.7.3. Gun Height
In the standard specifications of the gun, the throw angle was 30°. It was stipulated that the gun height should not exceed 2 m from the ground to reduce the effect of the wind. Figure 6 shows the sprinkler tested at three different gun heights (h) above the soil surface: 1.25, 1.5, and 2 m.
Figure 6.
The sprinkler tested at three different heights of the gun.
2.8. Experimental Design
Irrigation experiments were carried out in a test field. This field was the subfield of Aswan University. The experiments were conducted at a constant pressure of 4 bars. To measure water application depth, 48 catch cans were placed at a grid spacing of 5 × 5 m. The experiment begins by placing the sprinkler robot on the opposite side of the field, at the location of the water valves, and directing it toward the hose reel to supply water. The robot is programmed to move within the field without irrigation until it stops at the starting point. The coordinates of this point change according to the nozzle size, forward speed, overlap ratio, and the desired water application rate for the crop. From this point, the field irrigation process begins using the following techniques:
2.8.1. Fixed Irrigation
In this case, the operating system is considered a fixed irrigation system. The robot stays at this point to irrigate. Irrigation time at the starting point was estimated from Equation (21), which changes according to experimental variables. Equation (21) was derived from Equation (4) in the mathematical analysis. Water flows from the gun to complete the irrigation at a 180-degree angle. At this stage, the effect of experimental variables (nozzle sizes and gun height) on the actual application rate and wetted diameter was studied.
2.8.2. Traveling Irrigation
After the specified irrigation time is completed, the robot immediately starts moving to complete the irrigation process for the test field. In this case, the irrigation process is similar to a travel irrigation system. This technology is unique among automated irrigation systems, combining the advantages of fixed and travel irrigation in one system. This technology allows precise control of travel irrigation systems to apply variable irrigation rates. At the end of this experiment, the collected water was measured to estimate the water depth under the specified operating conditions.
The experiment was repeated by reprogramming the robot with different operating conditions to study the effect of experimental variables (gun nozzles, forward speeds, and gun heights) on the average collected water depth.
2.9. Measurements
2.9.1. Irrigation Time at Starting Point
The sprinkler stop time at the start point for fixed irrigation before moving to irrigate the rest of the plot is estimated from the following equation:
where:
- Tsp is the sprinkler stop time at start point (h).
- r is the wetting radius (m).
- is the forward speed (mph).
2.9.2. The Theoretical Application Rate
The theoretical application rate was calculated by the following equation:
where:
- Arth is the theoretical application rate (mm/h).
- Qth is the theoretical discharge of the sprinkler (m3/h).
- L is the length of the path to be irrigated by the gun (m).
- Wd is the wetted diameter (m).
2.9.3. The Actual Application Rate
When using the actual discharge measured in field experiments, the actual application rate can be calculated by the following equation:
where:
- Arac is the actual application rate (mm/h).
- Qdac is the actual discharge of the sprinkler (m3/h).
- Wdac is the actual wetted diameter.
2.9.4. The Average Applied Water Depth
The average applied water depth was estimated according to the time required to irrigate the field with dimensions W × L by the following equation:
where:
- Da is the depth of applied water (mm).
- Arth is the theoretical application rate (mm/h).
- T is the time required to irrigate the field (h).
The following equation estimated the time required:
where:
- T is the time required (h).
- L is the length of the path to be irrigated by the gun (m).
- Fs is the forward speed of the robot during field irrigation (m/h).
2.9.5. The Average Collected Water Depth
A total of 48 catch cans were placed at a grid spacing of 5 × 5 m for the measurement of the depth of water application, as shown in Figure 7. The volume of water collected in the catch cans was measured to determine the average collected water depth, Dc (mm).

Figure 7.
Field experiments to estimate average collected water depth.
2.9.6. Evaporation and Wind Drift Losses
Evaporation and wind drift losses (EWDL, mm) were determined using the following equation:
2.9.7. Water Application Efficiency
Water application efficiency (Aeff.) was calculated by the following equation:
3. Results
3.1. The Theoretical Application Rate
The experiments were carried out at a pressure of 4 bar and the theoretical discharges (Qth) of the sprinkler were 12.6, 16.2, and 21 m3/h while the actual discharges (Qth) were 11.6, 14.5, and 18.9 m3/h for nozzle sizes 12, 14, and 16, respectively. The theoretical application rates were 2.29, 2.68, and 3.18 mm/h for nozzle sizes 12, 14, and 16, respectively.
3.2. Effect of Gun Heights on Actual Wetted Diameter and Application Rate
The wetted diameter was estimated using three different heights to study the effect of gun heights on the actual application rate. The actual wetted diameter depends on the sprinkler height regardless of the forward speed. The actual wetted diameter was determined at specific gun heights, as shown in Table 2. The results revealed that at nozzle 12, the actual wetted diameter would be less than the theoretical diameter by a percentage of 2–5%, while at nozzle 14, it ranged from 2 to 7%, but at nozzle 16, it increased from 6 to 9%.

Table 2.
Actual wetted diameter at gun heights.
The actual application rates are determined based on actual wetted diameters and discharges. Figure 8 shows the effect of gun heights on the actual application rate.
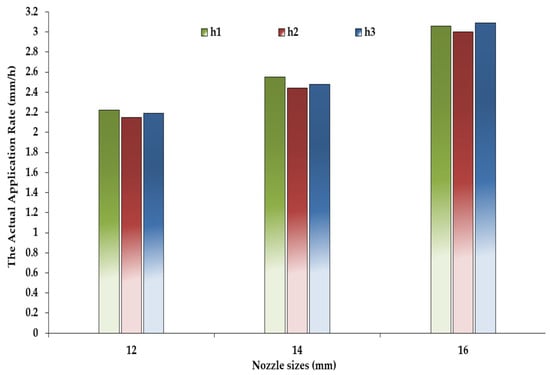
Figure 8.
Effect of gun heights on actual application rate.
The data indicated that the actual application rates were directly proportional to the nozzle size when the gun was operated at constant pressure. The lack of wind during the experiments may have led to the gun height not having a major effect on the actual application rate.
3.3. Irrigation Time at Starting Point
Table 3 shows the time required for fixed and traveling irrigation under experimental conditions. The data showed that the irrigation time at the starting point ranged from 20 to 72 min according to nozzle sizes, forward speed, and wetting diameters. These results are used to program the sprinkler at the start to determine the starting point coordinates and the stopping time required for fixed irrigation.

Table 3.
Time required for fixed and traveling irrigation under experimental conditions.
3.4. Effect of Some Engineering Factors on Sprinkler Robot Performance
Table 4 summarizes the results obtained for the effect of some engineering factors on the traveler gun sprinkler performance.

Table 4.
The effect of some engineering factors on sprinkler robot performance.
3.4.1. The Average Applied Water Depth
It was estimated according to the time required for irrigation to achieve the theoretical application rates. It was inversely proportional to the forward speed of the sprinkler at the nozzle sizes. The data in Table 4 indicated that when the sprinkler gun’s forward speed was changed to 25, 50, and 75 m/h using nozzle 12, the water depth was observed to be 10.08, 5.04, and 3.34 mm, respectively. But this change will inevitably vary with the size of the nozzle. The applied depth depends on the crop water requirement. Crop water requirements encompass the total amount of water used in evapotranspiration. An irrigation system aims to achieve this depth by pre-planning the irrigation operation and adjusting the engineering factors associated with the irrigation system used. The overlap ratio, irrigation time, and number of irrigations per day are the main factors that achieve the targeted depth.
3.4.2. Evaporation and Wind Drift Losses and Water Application Efficiency
From Table 4, the values of evaporation and wind drift losses were always less than 2.8 mm. Previous studies indicated that evapotranspiration is significantly affected by global climatic changes as an essential component of both climate and hydrological cycles. The results indicated that the highest efficiency was achieved at the lowest forward speed (25 m/h) and using a 1.5 m gun height. The highest water application efficiency values were 81.8, 82.5, and 81.1% using nozzle 12, nozzle 14, and nozzle 16, respectively.
3.4.3. The Average Collected Water Depth
Experiments have shown that increasing the nozzle size significantly affects the average collected water depth at the sprinkler heights. The optimum depth is determined according to the crop water requirement. In this study, the water requirement of the landscape field is estimated at 11.65 mm/day. Figure 9 shows the average collected water depths as a function of forward speed using three nozzles at a sprinkler height of 1.25 m.
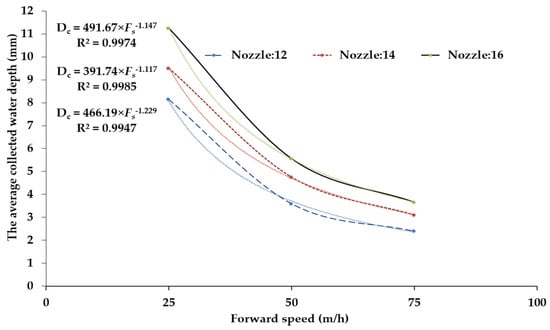
Figure 9.
The average collected water depth as a function of forward speed using three nozzles at a sprinkler height of 1.25 m.
The results pointed out that nozzle 12 had the lowest average collected water depth at all forward speeds but the collected water depth increased from 2.4 to 8.15 mm with a decrease in forward speed from 75 to 25 m/h. Likewise, nozzle 16 had the maximum average collected water depth at all forward speeds and the collected water depth increased from 3.66 to 11.25 mm with a decrease in forward speed from 75 to 25 m/h. The following equations were derived using curve fitting:
Figure 10 shows the collected water depths as a function of forward speed using three nozzles at a sprinkler height of 1.5 m. The nozzle 12 gave the lowest average collected water depth at all forward speeds but the collected water depth increased from 2.71 to 8.25 mm with a decrease in forward speed from 75 to 25 m/h. Likewise, nozzle 16 had the maximum average collected water depth at all forward speeds and the collected water depth increased from 3.75 to 11.35 mm with a decrease in forward speed from 75 to 25 m/h.
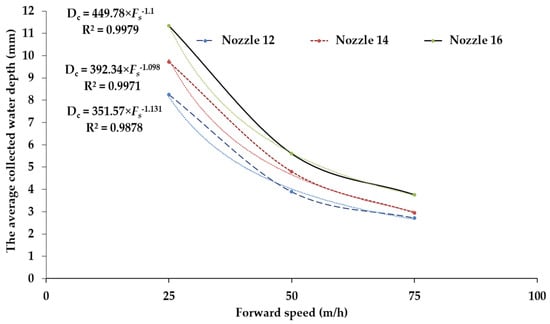
Figure 10.
The average collected water depth as a function of forward speed using three nozzles at a sprinkler height of 1.5 m.
The following equations were derived using curve fitting:
Figure 11 shows the average collected water depths as a function of forward speed using three nozzles at a sprinkler height of 2 m.
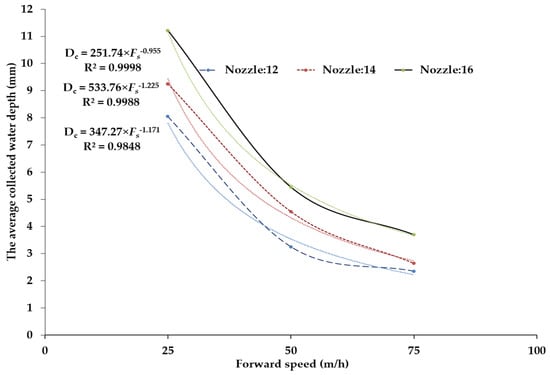
Figure 11.
The average collected water depth as a function of forward speed using three nozzles at a sprinkler height of 2 m.
The nozzle 12 had the lowest average collected water depth at all forward speeds but the collected water depth increased from 2.35 to 8.05 mm with a decrease in forward speed from 75 to 25 m/h. Likewise, nozzle 16 had the maximum average collected water depth at all forward speeds and the collected water depth increased from 3.7 to 11.21 mm with a decrease in forward speed from 75 to 25 m/h.
The following equations were derived using curve fitting:
The relationships shown in Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11 indicate that the collected water depth and forward speed were highly correlated and the correlation coefficient was very high and closer to 1 “R2 = 0.99 or 0.98”. So, the correlation between Da and Fs was strong. As a result, the forward speed required to reach the necessary average collected water depth can be easily found using these equations.
The depth of water application can be changed easily by varying the forward speed of the sprinkler and gun height. In addition, the depth of water application can also be changed by controlling the water application time. Thus, the flexibility of operation and control of engineering factors will allow the application of any desired average water depth for each crop under different field conditions. This is one of the special features that must be available in advanced irrigation systems.
4. Discussion
This robot is designed to provide a range of powerful features aimed at optimizing the irrigation process by combining a fixed and a travel irrigation system into one automated system. This manuscript presents mathematical relationships that govern the operation of the robot to meet different water requirements of crops. The results of this study are consistent with previous studies [45] in steady-state irrigation. Also, it focused on the precision irrigation of the left and right sub-sectors. This can be repeated separately in each sector, assuming that the longitudinal transition between adjacent sectors have little effect on irrigation, as previous studies have indicated [45]. The evaporation and wind drift losses are consistent with [46,47,48] for this type of loss. However, wind conditions were negligible during the experiments. For instance, ref. [47] demonstrated that evaporation and wind drift losses were similar for both system options (line of sprinklers and gun-sprinkler), presenting significant differences only for the lowest machine velocity. The time required for fixed and traveling irrigation was determined under experimental conditions, so it is recommended to schedule irrigation water through the use of automated irrigation systems. The yield can be directly affected by the time factor that determines the water amount and the interval between irrigations. Intelligent irrigation systems extend the time plants are watered, allowing them to saturate and produce an efficient crop. Extending the time between irrigations or applying too little irrigation water each time can reduce crop productivity, which prior research has validated [49]. For example, a study [50] confirmed that irrigation water deficit had a negative effect on wheat crops. Changing environmental conditions and a shortage of water demand a system that can manage irrigation efficiently. Further development of wireless sensor applications in agriculture is also necessary for increasing the efficiency, productivity, and profitability of farming operations [51,52]. Intensive research and development are recommended to identify current shortcomings in irrigation processes and methods. Future research directions will focus on integrating variable rate technology, the Internet of Things, and satellite mapping to enhance robot performance. Furthermore, precise irrigation control using sensor technology will be the preferred option in the future. Spreading awareness of the use of these systems will improve irrigation and its applications to achieve maximum operational efficiency.
5. Conclusions
In this article, a mathematical model was derived based on the theoretical analysis of the sprinkler robot’s performance in the field under the influence of some engineering factors. Some important equations were obtained that determine the forward speed of the sprinkler, water application time, and the average applied water depth on both sides of the gun sprinkler under different operating conditions. Using curve fitting, equations were obtained that determine the forward speed of the sprinkler to achieve the required depth using three sprinkler heights. The results of using three nozzle sizes under constant pressure confirmed that the actual application rates were directly proportional to the nozzle size. The applied depth was estimated according to the time required for irrigation to achieve the theoretical application rates. It was inversely proportional to the forward speed of the sprinkler at the nozzle sizes. Also, the throw radius of the traveler gun sprinkler was found to be affected by gun heights. An irrigation system aims to achieve this depth by pre-planning the irrigation operation and adjusting the engineering factors associated with the irrigation system used. The overlap ratio, irrigation time, and number of daily irrigations are the main factors that achieve the targeted depth. Engineering factors effecting gun sprinkler performance are viewed as the scientific approach and cornerstone of future strategies for developing gun sprinkler irrigation systems. Notably, developing sprinkler irrigation systems, especially the gun sprinkler, will make it widely used with different soil types. This will enhance the practical utility of gun sprinkler irrigation. It will open the way for more studies to rediscover the effect and role of irrigation with gun sprinkler systems to improve soil properties in general and saline–alkaline soils in particular because salinity is the most harmful factor that seriously reduces plant productivity [53]. Rain-simulating irrigation systems may play a role in soil leaching and influencing the properties of saline–alkali soils. It may help remove dissolved salts and possibly improve soil conditions, a discovery that deserves further study. Overall, this manuscript will provide useful insights into the significance of developing and innovating a more advanced sprinkler irrigation system that combines the features of both traveler and fixed irrigation systems and shows high reliability under different operating conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.E. and M.R.; methodology, N.E. and S.I.; software, R.M. and M.R.; validation, S.I., H.T., and M.R.; formal analysis, N.E.; resources, M.R. and D.W.; data curation, N.E., H.T., and R.M.; writing—original draft preparation, N.E.; writing—review and editing, S.S.; supervision, N.E., S.I., H.T., and R.M.; project administration, S.S. and D.W.; funding acquisition, D.W and S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development of reclamation technology and equipment for saline-alkali land (Project number: WSR2023093); Integrated Demonstration of High-Yield Cultivation and Mechanization Technology for Saline-Alkali Land Oil Crops (project number: SDNYXTTG-2024-15); Key Technology Innovation and Industrialization of Saline-Alkali Soil Cultivation and Plowing Joint Equipment (project number: 2024CGZH14); and the Creation of key components for efficient tillage equipment for saline-alkali land (project number: Y20240055).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the manuscript; further inquiries can be directed to the authors.
Acknowledgments
“The Yellow River Delta Intelligent Agricultural Machinery Equipment Industry Research Academy Board of Directors” is acknowledged by the authors for providing invaluable advice and assistance during M.R.’s PhD thesis. The authors also convey their appreciation to the funders for their financial assistance and their kind contribution of time and expertise, both of which were crucial to the successful completion of the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Elkaoud, N.S.M.; Kassem, M.R.; Tarabye, H.H.; Adam, M.S. Promoting Food Security and Sustainability with A Transportable Indirect Evaporative Solar Pre-Cooler. Rev. Fac. Nac. Agron. Medellín 2024, 77, 10865–10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhdary, J.N.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y.; Pan, X.; Hussain, Z.; Javaid, M.; Rizwan, M. Advances in Sprinkler Irrigation: A Review in the Context of Precision Irrigation for Crop Production. Agronomy 2024, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, M.; El Deen, G. The Efficiency Using of Water Resources Under the Environmental Effects in Arab Republic of Egypt. Assiut J. Agric. Sci. 2006, 37, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayan, M.B.; Ismail, S.M.; Mahmoud, R.K.; Taraby, H.H.H. Field evaluation of a prototype self-drawn sprinkler irrigation. Arch. Agric. Sci. J. 2022, 5, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Abu-Ross, A.; Assail, I.; Mansour, R. Estimation of the Economic and Productive Efficiency of Maize Crop Under Different Irrigation Conditions in Beheira Governorate. J. Product. Dev. 2022, 27, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y. Unspeakable Ecology: Eco-Science and Environmental Awareness Through Thick Inquiries, 1910S–1980S. Twent.-Century China 2022, 47, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.H.M.; Makled, S.M.; Elsabea, A.M.R. Current Demand for Water Resources in Egyptian Agriculture. Arab Univ. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 27, 1291–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shahed, M.A. An Analytical Economic Study for the Optimal Use of Irrigation Water in Egyptian Agriculture. Aquat. Sci. Fish Resour. 2022, 3, 34–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeldin, M. Challenges of water resources management in Egypt and solution opportunities. Constr. Sci. Educ. 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Eissa, M.A.; Rekaby, S.A.; Hegab, S.A.; Ragheb, H.M. Effect of deficit irrigation on drip-irrigated wheat grown in semi-arid conditions of Upper Egypt. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 1576–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, A.M.; Zekry, A.A.; Hassan, A.Y. Innovative Solar Photovoltaic Solutions for Water-Efficient Irrigation: A Comprehensive Algorithmic Approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 34th Conference of Open Innovations Association (FRUCT), Riga, Latvia, 15–17 November 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, E.M.A. Can irrigation water saving options cope with water scarcity in Egypt? Environ. Sci. Agric. Food Sci. 2020, 6, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, S.M. The development of water markets in China: Progress, peril, and prospects. Water Policy 2014, 17, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.A.; Rekaby, S.A.; Hegab, S.A.; Ragheb, H.M. Optimum rate of nitrogen fertilization for drip-irrigated wheat under semi-arid conditions. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Ding, F.; Yan, H. Evaluation of variable rate irrigation management in forage crops: Saving water and increasing water productivity. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 275, 108020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xiong, J.; Xiao, J. Water Allocation and Integrative Management of Precision Irrigation: A Systematic Review. Water 2020, 12, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunarathna, M.H.J.P.; Sakai, K.; Nakandakari, T.; Kazuro, M.; Onodera, T.; Kaneshiro, H.; Uehara, H.; Wakasugi, K. Optimized Subsurface Irrigation System (OPSIS): Beyond Traditional Subsurface Irrigation. Water 2017, 9, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wang, R.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Xiong, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M. Effects of Different Micro-Irrigation Methods on Water Use and the Economic Benefits of an Apple–Soybean Intercropping System. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, L.; Ni, J.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Jiang, X. Research and Development of an IoT Smart Irrigation System for Farmland Based on LoRa and Edge Computing. Agronomy 2025, 15, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, Z.; Chen, R.; Yang, T.; Tian, Z. Experimental Study on Droplet Characteristics of Rotating Sprinklers with Circular Nozzles and Diffuser. Agriculture 2022, 12, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhesmaeili, O.; Montero, J.; Laserna, S. Analysis of water application with semi-portable big size sprinkler irrigation systems in semi-arid areas. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 163, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Fordjour, A.; Dwomoh, F.A.; Lewballah, J.K.; Ofosu, S.A.; Liu, J.; Oteng, J. Experimental study on the effects of pressure loss on uniformity, application rate and velocity on different working conditions using the dynamic fluidic sprinkler. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, N.; Audsley, E.; Brodt, S.; Garnett, T.; Henriksson, P.; Kendall, A.; Kramer, K.J.; Murphy, D.; Nemecek, T.; Troell, M. Energy Intensity of Agriculture and Food Systems. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2011, 36, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.; Grove, I.; Peets, S.; Norton, T. Advanced Monitoring and Management Systems for Improving Sustainability in Precision Irrigation. Sustainability 2017, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, M.; Yang, W. Drop size distribution of fixed spray-plate sprinklers with two-dimensional video disdrometer. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2014, 148, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.; Guo, C.; Han, W.; Yao, X.; Sun, Y. Optimization of impact sprinkler sub-nozzle parameters of elevation angle and position. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, M.; Hassan, S.B.; Yusof, K.B.W. Effect of combination factors of operating pressure, nozzle diameter and riser height on sprinkler irrigation uniformity. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 695, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, K.H.; Kissiinger, J.A.; Farrens, G.P.; Borneman, J. Performance and Water Conservation Potential of Multi-Stream, Multi-Trajectory Rotating Sprinklers for Landscape Irrigation. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2006, 23, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semananda, N.P.K.; Ward, J.D.; Myers, B.R. A Semi-Systematic Review of Capillary Irrigation: The Benefits, Limitations, and Opportunities. Horticulturae 2018, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.S.; Lima, L.A.; Colombo, A.; Caldeira, A.C.D.M.; Faria, F.H.D.S. Water distribuition characteristics and soil loss of LEPA Quad-Spray emitter nozzles. Eng. Agric. 2013, 33, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuyttens, D.; Baetens, K.; De Schampheleire, M.; Sonck, B. Effect of nozzle type, size and pressure on spray droplet characteristics. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 97, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Pradeep, K.B.; Begum, S.G.; Kumar, K.A.; Sumathi, P. Feasibility studies on raingun method of irrigation system in groundnut. Agric. Eng. Today 2021, 45, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedkar, D.D.; Gorantiwar, S.D.; Adsul, S.U. Studies on Pressure-Discharge and Pressure-Radius of Throw Relationships for Rainguns. J. Agric. Res. Technol. 2014, 39, 469–475. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Song, Z. Critical Factors Influencing Soil Runoff and Erosion in Sprinkler Irrigation: Water Application Rate and Droplet Kinetic Energy. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 283, 108299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, X. Effects of Pressure and Nozzle Size on the Spray Characteristics of Low-Pressure Rotating Sprinklers. Water 2020, 12, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Lu, Y.; Hu, H.; Hu, Y. Review and Research Prospects on Sprinkler Irrigation Frost Protection for Horticultural Crops. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 326, 112775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmak, S.; Odhiambo, L.O.; Kranz, L.W.; Eisenhauer, D. EC732. Irrigation Efficiency and Uniformity, and Crop Water Use Efficiency. Biol. Syst. Eng. Pap. Publ. 2011, 451. Available online: https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/biosysengfacpub/451 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Yaseen, M.U.; Saddique, G.; Ashraf, M.; Yasmeen, Z.; Ahmad, S. Design, development and testing of mobile sprinkler rain gun for smart irrigation in arid zone-based crops. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 57, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, L.C.; Flores, J.H.N.; Fuga, E.C.; Nörenberg, B.G.; Beskow, S.; de Oliveira, H.F.E.; do Prado, G.; Colombo, A. Modeling Water Distribution Uniformity of Medium-Sized Sprinklers Using Artificial Neural Networks. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Hui, X.; Li, M.; Xu, Y. Development in sprinkler irrigation technology in China. Irrig. Drainage. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatheendrdasan, R.K.; Arathy, J.; Rubasree, M.; Shimola, C.M.; Rajeswari, R. Evaluation of a Traveller Sprinkler System with Various Nozzles. Water Product. J. 2020, 1, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Tang, Y.; Tang, L. Energy consumption analysis of hydraulic turbine of JP75 hose reel irrigator. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng. 2016, 34, 1008–1012, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Wu, P.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, X.; Xu, H. Construction and application of mobile spraying uniformity model of hard hose traveler. Trans. CSAE 2016, 32, 130–137, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, M.A.; Abdelkader, T.K.; Sayed, H.A.A.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Atia, M.F. Design and evaluation of a solar powered smart irrigation system for sustainable urban agriculture. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penzotti, G.; Rizzini, D.L.; Caselli, S. A planning strategy for sprinkler-based variable rate irrigation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 212, 108126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, K.D.; Kohl, R.A.; DeBoer, D.W. Measurement of low-pressure sprinkler evaporation loss. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.L.; Serralheiro, R.; Santos, N. Improving irrigation performance in hose-drawn traveller sprinkler systems. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 96, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, A.N.; Zabady, F.I.; Hassan, A.M.; Elmashad, M.M. Study of Temporal Changes in Subsurface Drainage in Land-Scape. Al-Azhar J. Agric. Eng. 2024, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, K.M.; El-Gamal, T.T.; Abu El-Khair, R.; Osama, M.; El-Naser, A.; Khaled, H. Implications of different irrigation water qualities on crop production: A case study of Sharkia Governorate. Al-Azhar J. Agric. Eng. 2023, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeen, S.A.; El-Sayed, M.M. Influence of compost and canal clay scouring on sandy soil properties and wheat productivity under irrigation water regime. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2021, 10, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chikangaise, P.; Shi, W.; Chen, W.H.; Yuan, S. Review of intelligent sprinkler irrigation technologies for remote autonomous system. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Issaka, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, P.; Chen, C. Overview of emerging technologies in sprinkler irrigation to optimize crop production. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaousmail, M.; Nili, M.S.; Brik, R.; Saadouni, M.; Yousif, S.K.M.; Omer, R.M.; Osman, N.A.; Alsahli, A.A.; Ashour, H.; El-Taher, A.M. Improving the Tolerance to Salinity Stress in Lettuce Plants (Lactuca sativa L.) Using Exogenous Application of Salicylic Acid, Yeast, and Zeolite. Life 2022, 12, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).