Antibody Delivery into the Brain by Radiosensitizer Nanoparticles for Targeted Glioblastoma Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
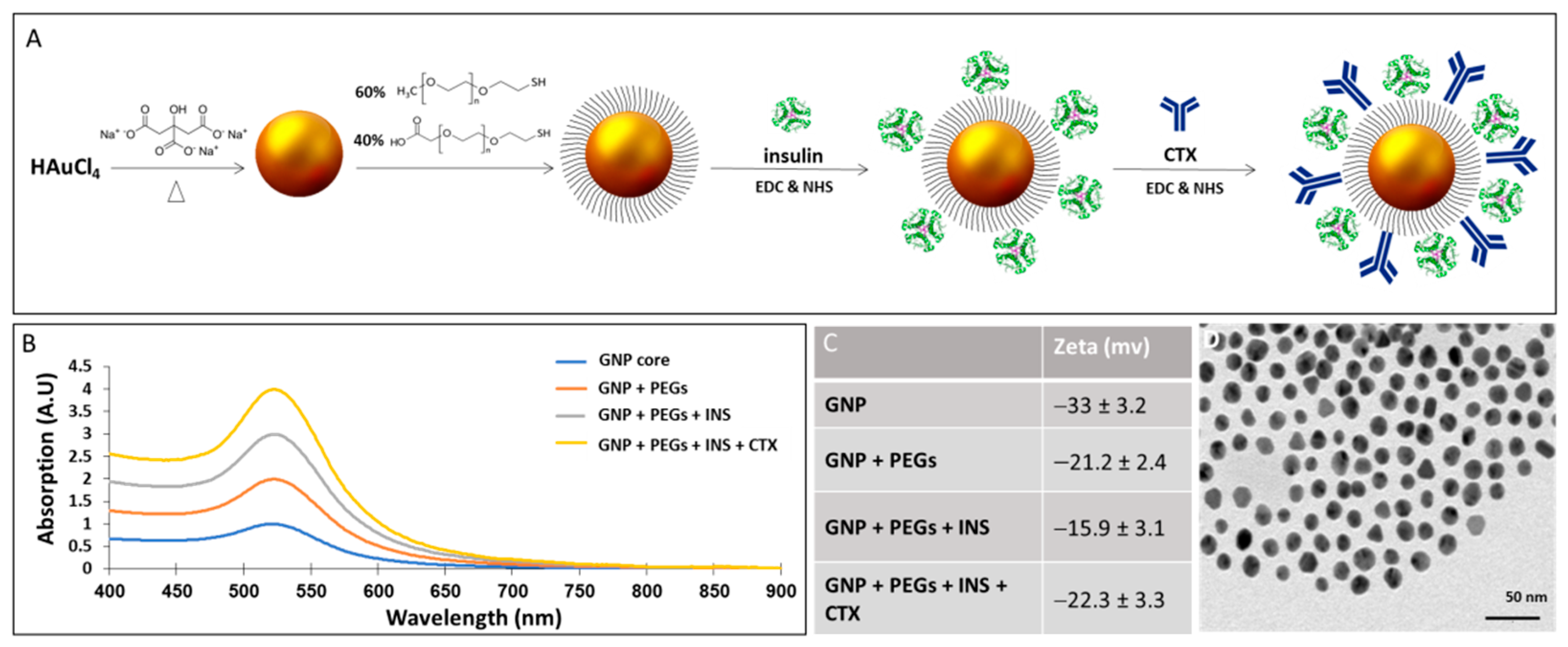
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of CTX-INS-GNPs
2.2. Animal Experiments
2.3. Orthotopic Glioblastoma Xenografts
2.4. Treatment of Mice
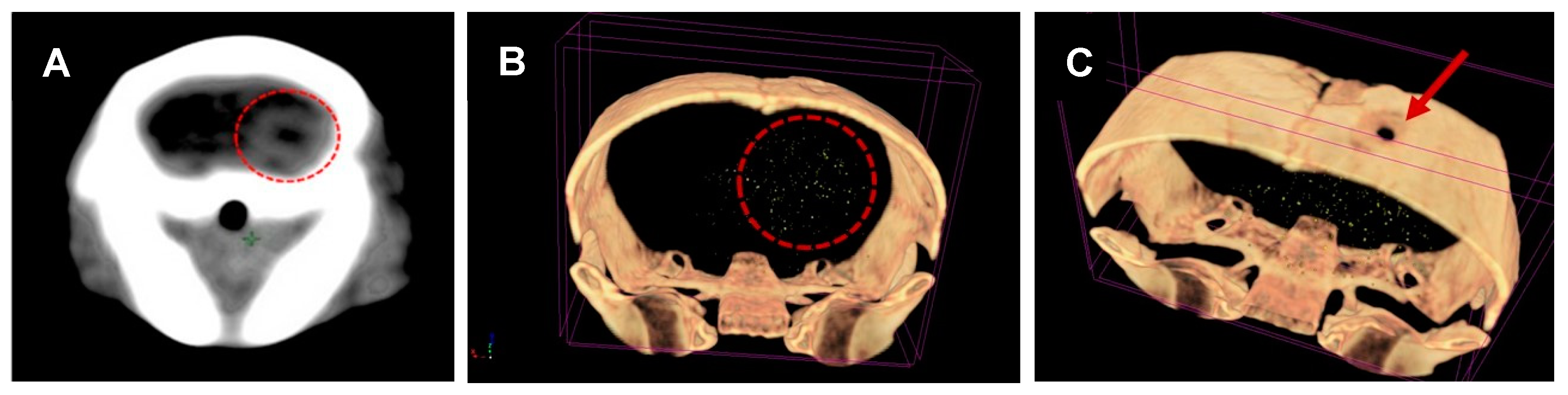
2.5. Micro-CT Scans
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Inductively Coupled Plasma–Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. GNP Characterization
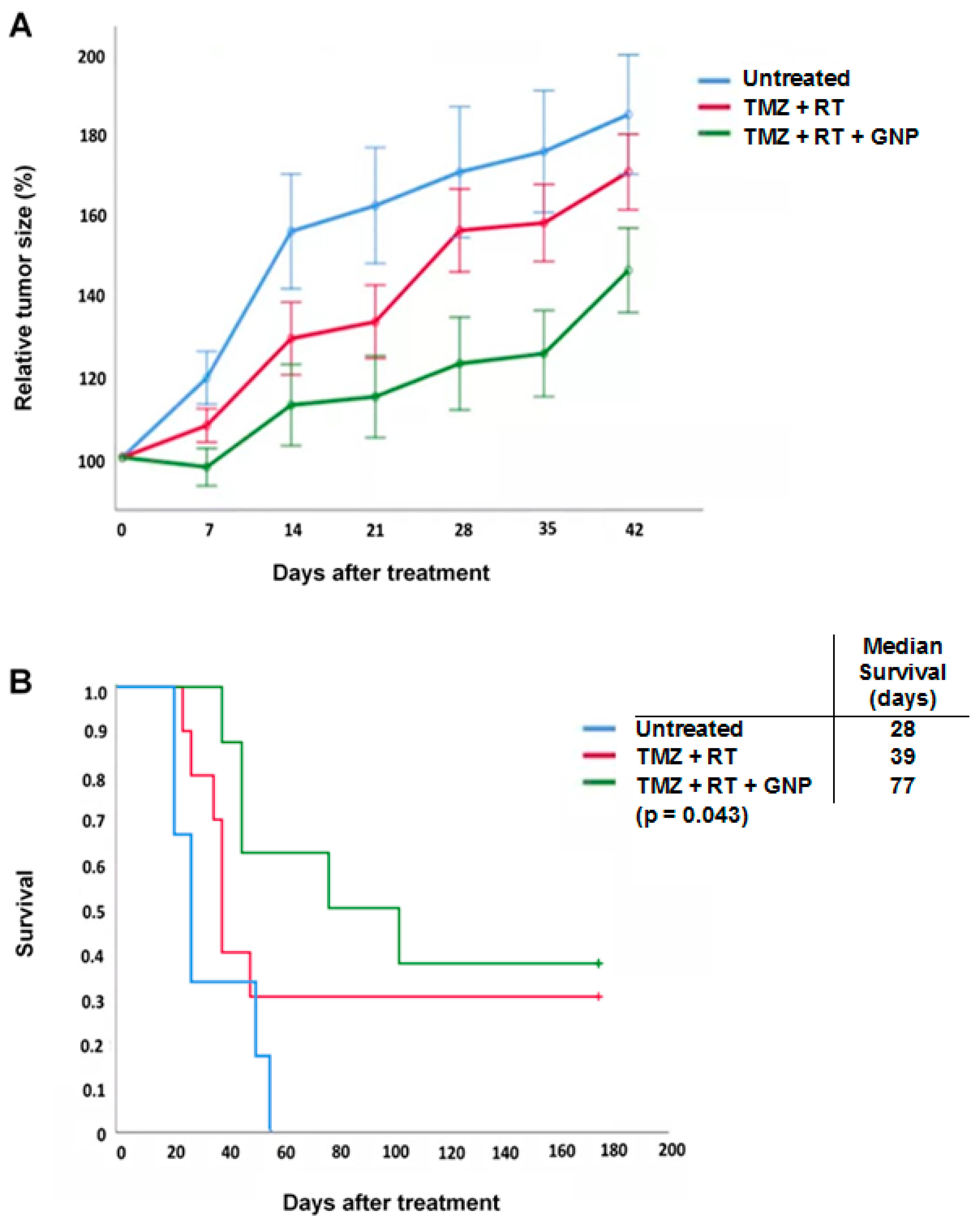
3.2. CTX-INS-GNPs Combined with Standard Therapy Inhibits Tumor Progression and Prolongs Survival
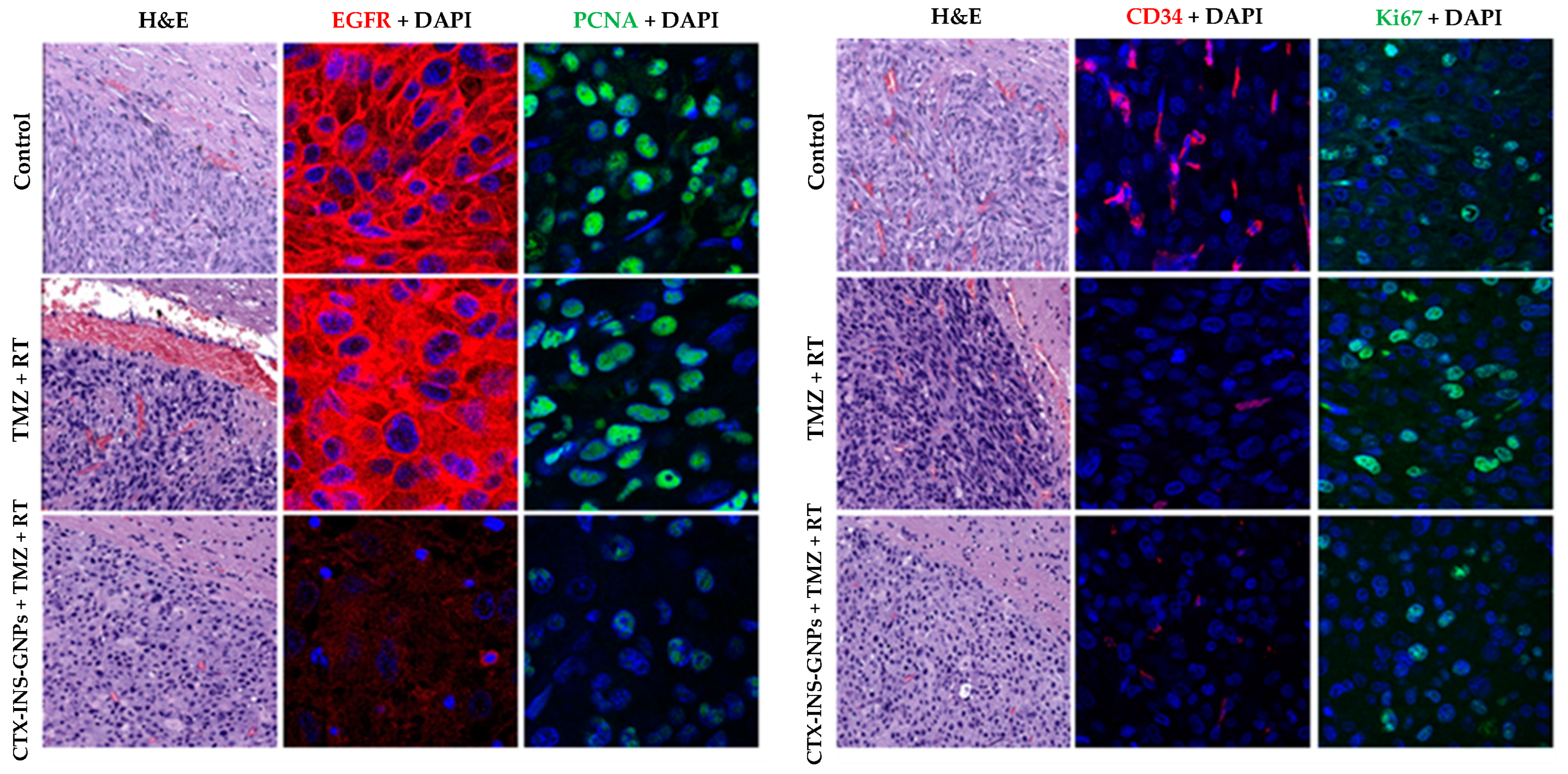
3.3. Combined Treatment with CTX-INS-GNPs Eradicates Tumor Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Liao, P.; Vecchione-Koval, T.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2010–2014. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 19, v1–v88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, K.; Knisely, J.; Symons, M.; Ruggieri, R. Radioresistance of Brain Tumors. Cancers 2016, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.Y.; Oliva, C.R.; Noman, A.S.M.; Allen, B.G.; Goswami, P.C.; Zakharia, Y.; Monga, V.; Spitz, D.R.; Buatti, J.M.; Griguer, C.E. Radioresistance in Glioblastoma and the Development of Radiosensitizers. Cancers 2020, 12, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.F.; Diener-West, M.; Horton, J.; Chang, C.H.; Schoenfeld, D.; Nelson, J.S. Combined modality approach to treatment of malignant gliomas--re-evaluation of RTOG 7401/ECOG 1374 with long-term follow-up: A joint study of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group and the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. NCI Monogr. 1988, 279–284, 3281031. [Google Scholar]
- Prados, M.D.; Wara, W.M.; Sneed, P.K.; McDermott, M.; Chang, S.M.; Rabbitt, J.; Page, M.; Malec, M.; Davis, R.L.; Gutin, P.H.; et al. Phase III trial of accelerated hyperfractionation with or without difluromethylornithine (DFMO) versus standard fractionated radiotherapy with or without DFMO for newly diagnosed patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 49, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souhami, L.; Seiferheld, W.; Brachman, D.; Podgorsak, E.B.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Lustig, R.; Schultz, C.J.; Sause, W.; Okunieff, P.; Buckner, J.; et al. Randomized comparison of stereotactic radiosurgery followed by conventional radiotherapy with carmustine to conventional radiotherapy with carmustine for patients with glioblastoma multiforme: Report of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 93-05 protocol. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 60, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butowski, N.; Prados, M.D.; Lamborn, K.R.; Larson, D.A.; Sneed, P.K.; Wara, W.M.; Malec, M.; Rabbitt, J.; Page, M.; Chang, S.M. A phase II study of concurrent temozolomide and cis-retinoic acid with radiation for adult patients with newly diagnosed supratentorial glioblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 61, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Krishnan, S.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Wu, W.; Jaeckle, K.A.; Uhm, J.H.; Geoffroy, F.J.; Arusell, R.; Kitange, G.; Jenkins, R.B.; et al. Phase I/II Trial of Erlotinib and Temozolomide With Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma Multiforme: North Central Cancer Treatment Group Study N0177. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5603–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butowski, N.; Chang, S.M.; Lamborn, K.R.; Polley, M.Y.; Pieper, R.; Costello, J.F.; Vandenberg, S.; Parvataneni, R.; Nicole, A.; Sneed, P.K.; et al. Phase II and pharmacogenomics study of enzastaurin plus temozolomide during and following radiation therapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme and gliosarcoma. Neuro-Oncology 2011, 13, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.Q.; Kaley, T.J.; Duda, D.G.; Schiff, D.; Lassman, A.B.; Wong, E.T.; Mikkelsen, T.; Purow, B.W.; Muzikansky, A.; Ancukiewicz, M.; et al. A Multicenter, Phase II, Randomized, Noncomparative Clinical Trial of Radiation and Temozolomide with or without Vandetanib in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3610–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnaiyan, P.; Won, M.; Wen, P.Y.; Rojiani, A.M.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Shih, H.A.; Ashby, L.S.; Yu, H.H.M.; Stieber, V.W.; Malone, S.C.; et al. A randomized phase II study of everolimus in combination with chemoradiation in newly diagnosed glioblastoma: Results of NRG Oncology RTOG 0913. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanis, E.; Anderson, S.K.; Miller, C.R.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Jaeckle, K.; Buckner, J.C.; Ligon, K.L.; Ballman, K.V.; Moore, D.F., Jr.; Nebozhyn, M.; et al. Phase I/II trial of vorinostat combined with temozolomide and radiation therapy for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: Results of Alliance N0874/ABTC 02. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.-T.; Nguyen, N.T.; Choi, Y.J.; Zhang, G.; Nguyen, H.N.; Filka, E.; Green, S.; Yong, W.H.; Liau, L.M.; Green, R.M.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Bortezomib Combined with Temozolomide and Regional Radiation Therapy for Upfront Treatment of Patients with Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma Multiforme: Safety and Efficacy Assessment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 100, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskilsson, E.; Røsland, G.V.; Solecki, G.; Wang, Q.; Harter, P.N.; Graziani, G.; Verhaak, R.G.W.; Winkler, F.; Bjerkvig, R.; Miletic, H. EGFR heterogeneity and implications for therapeutic intervention in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shergalis, A.; Bankhead, A.; Luesakul, U.; Muangsin, N.; Neamati, N.; Barker, E.L. Current Challenges and Opportunities in Treating Glioblastoma. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 412–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, A.R.; Saadatzadeh, M.R.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A.; Pollok, K.E.; Bijangi-Vishehsaraei, K. Emerging targets for glioblastoma stem cell therapy. J. Biomed. Res. 2016, 30, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Belykh, E.; Shaffer, K.V.; Lin, C.; Byvaltsev, V.A.; Preul, M.C.; Chen, L. Blood-Brain Barrier, Blood-Brain Tumor Barrier, and Fluorescence-Guided Neurosurgical Oncology: Delivering Optical Labels to Brain Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolburg, H.; Noell, S.; Fallier-Becker, P.; Mack, A.F.; Wolburg-Buchholz, K. The disturbed blood–brain barrier in human glioblastoma. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tellingen, O.; Yetkin-Arik, B.; de Gooijer, M.C.; Wesseling, P.; Wurdinger, T.; de Vries, H.E. Overcoming the blood–brain tumor barrier for effective glioblastoma treatment. Drug Resist. Updat. 2015, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; Slatkin, D.N.; Smilowitz, H.M. The use of gold nanoparticles to enhance radiotherapy in mice. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, N309–N315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.J.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, S.T.; Chen, H.H.; Leng, W.H.; Chien, C.C.; Wang, C.L.; Kempson, I.M.; Hwu, Y.; Lai, T.C.; et al. Enhancement of cell radiation sensitivity by pegylated gold nanoparticles. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovtzer, A.; Mizrachi, A.; Motiei, M.; Bragilovski, D.; Lubimov, L.; Levi, M.; Hilly, O.; Ben-Aharon, I.; Popovtzer, R. Actively targeted gold nanoparticles as novel radiosensitizer agents: An in vivo head and neck cancer model. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2678–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.D.; Huang, L. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuemann, J.; Bagley, A.F.; Berbeco, R.; Bromma, K.; Butterworth, K.T.; Byrne, H.L.; Chithrani, B.D.; Cho, S.H.; Cook, J.R.; Favaudon, V.; et al. Roadmap for metal nanoparticles in radiation therapy: Current status, translational challenges, and future directions. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 21RM02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzer, O.; Barnoy, E.; Sadan, T.; Elbaz, I.; Braverman, C.; Liu, Z.; Popovtzer, R. Advances in imaging strategies for in vivo tracking of exosomes. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 12, e1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, H.K.; Tsvirkun, D.; Ben-Nun, Y.; Merquiol, E.; Popovtzer, R.; Blum, G. Molecular Imaging of Cancer Using X-ray Computed Tomography with Protease Targeted Iodinated Activity-Based Probes. Nano Letters 2018, 18, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilo, M.; Berenstein, P.; Dreifuss, T.; Nash, Y.; Goldsmith, G.; Kazimirsky, G.; Motiei, M.; Frenkel, D.; Brodie, C.; Popovtzer, R. Insulin-coated gold nanoparticles as a new concept for personalized and adjustable glucose regulation. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 20489–20496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithrani, D.B.; Jelveh, S.; Jalali, F.; van Prooijen, M.; Allen, C.; Bristow, R.G.; Hill, R.P.; Jaffray, D.A. Gold nanoparticles as radiation sensitizers in cancer therapy. Radiat. Res. 2010, 173, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; Dilmanian, F.A.; Slatkin, D.N.; Smilowitz, H.M. Radiotherapy enhancement with gold nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazkani, I.; Motiei, M.; Betzer, O.; Sadan, T.; Bragilovski, D.; Lubimov, L.; Mizrachi, A.; Hadar, T.; Levi, M.; Ben-Aharon, I.; et al. Can molecular profiling enhance radiotherapy? Impact of personalized targeted gold nanoparticles on radiosensitivity and imaging of adenoid cystic carcinoma. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3962–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betzer, O.; Shilo, M.; Motiei, M.; Popovtzer, R. Insulin-coated gold nanoparticles as an effective approach for bypassing the blood-brain barrier. In Proceedings of the Nanoscale Imaging Sensing, and Actuation for Biomedical Applications XVI (SPIE BiOS 2019.), San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–4 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Betzer, O.; Shilo, M.; Opochinsky, R.; Barnoy, E.; Motiei, M.; Okun, E.; Yadid, G.; Popovtzer, R. The effect of nanoparticle size on the ability to cross the blood–brain barrier: An in vivo study. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enustun, B.V.; Turkevich, J. Coagulation of Colloidal Gold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 85, 3317–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyns, B.; Sadones, J.; Joosens, E.; Bouttens, F.; Verbeke, L.; Baurain, J.F.; D’Hondt, L.; Strauven, T.; Chaskis, C.; In’t Veld, P.; et al. Stratified phase II trial of cetuximab in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, S.E.; Heeger, S.; Haselmann, R.; Edler, L.; Debus, J.; Schulz-Ertner, D. Treatment of primary glioblastoma multiforme with cetuximab, radiotherapy and temozolomide (GERT)—Phase I/II trial: Study protocol. BMC Cancer 2006, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A. Developing drugs that can cross the blood-brain barrier: Applications to Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Neuroscience 2008, 9, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, G.; Hatcher, J.; Hearn, A.; Paterson, J.; Rodrigo, N.; Beljean, A.; Gurrell, I.; Webster, C. Isolation of blood-brain barrier-crossing antibodies from a phage display library by competitive elution and their ability to penetrate the central nervous system. mAbs 2017, 10, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindra, R.S.; Chalmers, A.J.; Evans, S.; Dewhirst, M. GBM radiosensitizers: Dead in the water…or just the beginning? J. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 134, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rosenblum, D.; Joshi, N.; Tao, W.; Karp, J.M.; Peer, D. Progress and challenges towards targeted delivery of cancer therapeutics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; McVeigh, P.Z.; O’Reilly, M.A.; Burrell, K.; Bebenek, M.; Smith, C.; Etame, A.B.; Zadeh, G.; Hynynen, K.; Wilson, B.C.; et al. Focused ultrasound delivery of Raman nanoparticles across the blood-brain barrier: Potential for targeting experimental brain tumors. Nanomed. NBM 2014, 10, e1075–e1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A.; Yndart, A.; Atluri, V.; Tiwari, S.; Tomitaka, A.; Gupta, P.; Jayant, R.D.; Alvarez-Carbonell, D.; Khalili, K.; Nair, M. Magnetically guided non-invasive CRISPR-Cas9/gRNA delivery across blood-brain barrier to eradicate latent HIV-1 infection. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, N.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, Y. Gene Therapy for Drug-Resistant Glioblastoma via Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles Combined with Focused Ultrasound. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retif, P.; Pinel, S.; Toussaint, M.; Frochot, C.; Chouikrat, R.; Bastogne, T.; Barberi-Heyob, M. Nanoparticles for Radiation Therapy Enhancement: The Key Parameters. Theranostics 2015, 5, 1030–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulla, D.F.; Hieber, L.B.; Seidenbusch, M. Physical and biological interface dose effects in tissue due to X-ray-induced release of secondary radiation from metallic gold surfaces. Rad. Res. 1998, 150, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmani, L.; Labar, D.; Valembois, V.; Bouchat, V.; Nagaswaran, P.G.; Bol, A.; Gillart, J.; Levêque, P.; Bouzin, C.; Bonifazi, D.; et al. Antibody-functionalized nanoparticles for imaging cancer: Influence of conjugation to gold nanoparticles on the biodistribution of 89Zr-labeled cetuximab in mice. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2013, 8, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Bouchy, S.; Penninckx, S.; Marega, R.; Fichera, O.; Gallez, B.; Feron, O.; Martinive, P.; Heuskin, A.C.; Michiels, C.; et al. Antibody-functionalized gold nanoparticles as tumor-targeting radiosensitizers for proton therapy. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daems, N.; Verlinden, B.; Van Hoecke, K.; Cardinaels, T.; Baatout, S.; Michiels, C.; Lucas, S.; Aerts, A. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics, Biodistribution and Toxicity of Antibody-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles in Healthy Mice. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2020, 16, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuveni, T.; Popovtzer, A.; Romman, Z.; Popovtzer, A.; Popovtzer, R. Targeted gold nanoparticles enable molecular CT imaging of cancer: An in vivo study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2859–2864. [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss, T.; Betzer, O.; Shilo, M.; Popovtzer, A.; Motiei, M.; Popovtzer, R. A challenge for theranostics: Is the optimal particle for therapy also optimal for diagnostics? Nanoscale 2015, 7, 15175–15184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobyk, L.; Edouard, M.; Deman, P.; Vautrin, M.; Pernet-Gallay, K.; Delaroche, J.; Adam, J.F.; Estève, F.; Ravanat, J.L.; Elleaume, H. Photoactivation of gold nanoparticles for glioma treatment. Nanomed. NBM 2013, 9, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joh, D.Y.; Sun, L.; Al Zaki, A.; Murty, S.; Santoiemma, P.P.; Davis, J.J.; Baumann, B.C.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Bhang, D.; Kao, G.D.; et al. Selective Targeting of Brain Tumors with Gold Nanoparticle-Induced Radiosensitization. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kefayat, A.; Ghahremani, F.; Motaghi, H.; Amouheidari, A. Ultra-small but ultra-effective: Folic acid-targeted gold nanoclusters for enhancement of intracranial glioma tumors’ radiation therapy efficacy. Nanomed. NBM 2019, 16, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; Smilowitz, H.M.; O’Connor, M.J.; Dilmanian, F.A.; Slatkin, D.N. Gold nanoparticle imaging and radiotherapy of brain tumors in mice. Nanomed. NBM 2013, 8, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perets, N.; Betzer, O.; Shapira, R.; Brenstein, S.; Angel, A.; Sadan, T.; Ashery, U.; Popovtzer, R.; Offen, D. Golden Exosomes Selectively Target Brain Pathologies in Neurodegenerative and Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 3422–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gal, O.; Betzer, O.; Rousso-Noori, L.; Sadan, T.; Motiei, M.; Nikitin, M.; Friedmann-Morvinski, D.; Popovtzer, R.; Popovtzer, A. Antibody Delivery into the Brain by Radiosensitizer Nanoparticles for Targeted Glioblastoma Therapy. J. Nanotheranostics 2022, 3, 177-188. https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt3040012
Gal O, Betzer O, Rousso-Noori L, Sadan T, Motiei M, Nikitin M, Friedmann-Morvinski D, Popovtzer R, Popovtzer A. Antibody Delivery into the Brain by Radiosensitizer Nanoparticles for Targeted Glioblastoma Therapy. Journal of Nanotheranostics. 2022; 3(4):177-188. https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt3040012
Chicago/Turabian StyleGal, Omer, Oshra Betzer, Liat Rousso-Noori, Tamar Sadan, Menachem Motiei, Maxim Nikitin, Dinorah Friedmann-Morvinski, Rachela Popovtzer, and Aron Popovtzer. 2022. "Antibody Delivery into the Brain by Radiosensitizer Nanoparticles for Targeted Glioblastoma Therapy" Journal of Nanotheranostics 3, no. 4: 177-188. https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt3040012
APA StyleGal, O., Betzer, O., Rousso-Noori, L., Sadan, T., Motiei, M., Nikitin, M., Friedmann-Morvinski, D., Popovtzer, R., & Popovtzer, A. (2022). Antibody Delivery into the Brain by Radiosensitizer Nanoparticles for Targeted Glioblastoma Therapy. Journal of Nanotheranostics, 3(4), 177-188. https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt3040012





