Abstract
Underpinned by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic review and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 Statement, this systematic review analyses 58 peer-reviewed articles published during 2008–2021 and retrieved from Scopus and Google Scholar that address the relationship between climate change and UNESCO World Heritage-listed cultural properties. The review reveals a suite of observations that will be important to consider for future research, including: the significant increase in publications since 2008; the prevalence of scholarship focused on the region of Europe and North America; the diversity of research methods and approaches; the instances of climate change hazards; the numerous adaptation measures and barriers. The study also showcases a much greater scholarly concentration on natural sites compared to cultural sites, observing that a reliance on a nature/culture binary does not bode well for the effective safeguarding of cultural World Heritage sites. This article also highlights the need for greater representation from the Global South in terms of both geographic focus and authorship, the lack of collaboration between Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) and Humanities, Arts and Social Science (HASS) disciplines, the capacity for collective action from different stakeholders, the importance of intangible elements, and the effects of both international and national legal frameworks and regulations.
1. Introduction
In September 2022, torrential rains feeding into the Indus River caused a serious flooding event that had devastating impacts throughout much of Pakistan. More than 1300 people were killed and millions lost their houses, with news reports showing people struggling through waist-deep water to reach dry land. In reference to the disaster unfolding in Pakistan, the United Nations (UN) Secretary General Antonio Guterres observed climate change is “supercharging the destruction of our planet”, warning “Today it is Pakistan. Tomorrow it can be anywhere else” [1]. Situated on the bank of the Indus River, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO)-listed World Heritage properties (WHP) of the Archaeological Ruins of Moenjodaro and Historical Monuments at Makli, Thatta were significantly impacted by the rain event. Some outer walls of Moenjodaro were damaged or collapsed, and several larger walls were separated from individual rooms and chambers. Abdul Fatah Shaikh, a heritage specialist working for the provincial government, described how “many parts of the site are now exposed to nature, and we must work extremely hard and very urgently for conservation within the next six months. It cannot be ruled out that if we fail to deliver, the site could be added on the [UNESCO list of World Heritage in] danger” [2]. This major rain and flood event in Pakistan triggered concerns for the integrity of other WHP in the context of climate change intensification [3].
Since 1972, UNESCO has designated heritage properties of global significance based on their “outstanding universal values” under the World Heritage Convention. In the UNESCO World Heritage system, there are 1154 listed properties, of which 897 are inscribed on their cultural values, 218 on natural values and 39 on a combination of cultural and natural qualities. Cultural properties, which represent the legacy of humankind, therefore account for nearly 80% of total World Heritage-listed sites. According to the 1972 Convention, cultural sites are defined as monuments, groups of buildings and sites [4]. Cultural properties are therefore deemed to have played a critically important role in human history, settlement, or civilization, and represent human creativity, values, and cultural traditions [5,6].
Unfortunately, recent years have witnessed many cultural properties worldwide being ravaged by climate change. The shifts in weather patterns and temperatures have influenced the frequency and severity of different hazards that can create serious impacts on cultural heritage, such as droughts, floods, and landslides [3]. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) confirmed that global warming is expected to reach 1.5 °C in the near term (2021–2040) [7]. This figure is much greater than earlier reports, which predicted that global temperature would rise between 0.3 and 0.7 °C before 2035 [8]. Strikingly, the 27th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP 27) of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in Egypt revealed that worldwide temperatures have increased by 1.15 °C since pre-industrial periods, with the most recent eight years on course to be the warmest on record [9]. As the IPCC and UNFCCC observe, such a significant rise in temperature will trigger unavoidable increases in climate-related hazards and pose multiple threats to ecosystems and humans [7].
The global challenges of the climate crisis have fuelled a growing interest in studies on cultural assets and climate change. This growth is reflected in the publication of comprehensive reviews on the topic of heritage and climate change, which seek to capture the state of the field. The first of these reviews, produced by Fatorić and Seekamp [10], assessed the literature from 1900 to 2015, and investigated cultural heritage and climate change in relation to geographic scope, methodologies, type of heritage, timescale, benefits and barriers. A subsequent review published by Orr, Richards and Fatorić [11] produced an updated and comparative study from 2016–2021. Both reviews used data retrieved from Web of Science and offered a general view of the field, the research gaps, and directions. Neither review focused on specific heritage assets. Other reviews have taken a narrower perspective, with publications by Aktürk [12] and Quesada-Ganuza and colleagues [13] paying heed to primary barriers to climate change adaptations and risk assessment methodologies in polar regions and urban areas, respectively. These reviews utilised a smaller number of studies compared to the previous reviews and limited themselves geographically. In terms of climate change’s impacts on cultural heritage, a review by Sesana and colleagues [14] synthesised various effects of climate change on outdoor and indoor heritage and collections, and material degradation. However, this review ignored adaptive measures as well as the importance of cultural heritage in climate action plans. Finally, a review by Maldonado-Erazo and colleagues [15] offered a scientometric analysis of the literature up to 2020, studying cultural, natural, and intangible heritage; however, it primarily paid attention to the evolution of knowledge generation and author productivity. Taken together, these reviews have examined numerous aspects of heritage and climate change, yet none capture scholarship on the relationship between climate change and cultural WHP.
The aim of this article is to assess recent scholarship that has explored the impacts of the climate crisis on UNESCO World Heritage-listed cultural properties. It offers a systematic review of the literature, incorporating peer-reviewed papers published between 2008 and 2021, with data retrieved from Scopus and Google Scholar databases. Before assessing the literature, we first outline how UNESCO has been managing, monitoring, and protecting its properties in the wake of climate change within its own system. The subsequent section focuses on research materials and methods that detail how data were retrieved and analysed. The article then presents the research results extracted from the scholarship, before discussing key observations emerging from the findings, drawing some future directions, and reaching a conclusion.
2. UNESCO’s Efforts against Climate Change
At the 29th session of the World Heritage Committee (WHC) in 2005, climate change was examined by UNESCO for the first time. This was taken to the Committee by a group of non-governmental organisations and individuals from several countries [16]. With the resulting issuance of Decision 29 COM 7B.a, the World Heritage Centre and advisory bodies, including the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS), and the International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property (ICCROM), started to tackle climate change hazards to WHP. The Committee encouraged State Parties to develop management plans for threats, and it requested the World Heritage Centre and stakeholders convene a working group of experts to review the nature and scale of climate change risks and devise proper management strategies [17]. Therefore, several initial preventive and corrective actions and knowledge-sharing steps were proposed to address climate change impacts, and to protect heritage properties [18].
In the 30th session in 2006, UNESCO drafted “Predicting and Managing the effects of climate change on World Heritage” and “Strategy to Assist States Parties to the Convention to Implement Appropriate Management Responses”. These were followed by a compilation of case studies on climate change’s effects on World Heritage, which was then endorsed in 2007 as a policy document on the impacts of climate change on WHP. The document is, effectively, World Heritage climate change policy, and is being updated at the time of writing in response to Committee decisions since 2016 [19]. Those materials have laid the foundation and conditions to handle the effects of climate change on WHP [13].
Regarding heritage management, once a site is inscribed on the World Heritage List, site managers and local authorities must manage, monitor and conserve their properties. States Parties take a responsibility for preparing state-of-conservation reports and different protection measures. The reports have a crucial role in providing valuable information on conservation practices and on factors impacting property conservation [20]. They can be utilised to systematically evaluate patterns related to the identification of threats to heritage properties, management deficiencies, conservation, and development matters [21]. Although the state of conservation report lacks quantitative information, they do contain materials related to impacts on the sites [22]. Based on those reports, the WHC can devise specific measures for identified problems, such as inscribing a property on the List of World Heritage in Danger.
In 2008, the WHC adopted a standard list of 14 primary factors impacting WHP. Climate change and severe weather events are amongst the 14 different factors identified as impacting heritage assets globally [23]. UNESCO utilises a UNFCCC [24] definition of climate change: “a change in climate which is attributed directly or indirectly to human activity that alters the composition of the global atmosphere and which is in addition to natural climate variability observed over comparable time periods” (p. 4). UNESCO has subsequently listed climate change as a general hazard, as well as identifying specific hazards associated with climate change, including flooding, storms, droughts, desertification, changes to oceanic waters, temperature changes and other impacts (severe weather events and natural disasters).
The UNESCO World Heritage List indicates there are 34 cultural properties in 26 States Parties and three transboundary regions being impacted by climate change [25]. A review of the listed hazards associated with these properties highlights climate change as a generalised hazard that is the most dominant threat affecting cultural properties (n = 23), while other threats such as drought, sea level rise, severe weather events, temperature changes and storms impact a much smaller number of heritage sites (n = 2–3 for each hazard). Europe and North America are identified as the most climate change-impacted region with 16 States Parties (23 sites), whereas the list makes it appear that the other regions are less vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Asia and the Pacific region has five States Parties (six sites), the African region and Arab States regions have two States Parties (two sites) each, and Latin America and the Caribbean region only have one State Party (one site). The impression is that Cultural WHPs located in the Global North are affected more significantly by climate than those located in the Global South, despite organisations such as the UNFCCC [24] long acknowledging that countries in the Global South are “the most vulnerable to climate change impacts because they have fewer resources to adapt” (p. 5).
3. Research Materials and Methods
Systematic quantitative literature reviews are a valuable tool for analysing the existing literature in a field with the intention to create a structured summary of that field [26]. Collins and Fauser [27] suggest this method can provide a reliable and reproducible evaluation of the existing status of a research field in a way that ameliorates possible biases apparent in more traditional narrative literature reviews. By utilising systematic methods to search and categorise various sources of literature, this article aims to highlight gaps and future directions for researchers examining the relationship between climate change and cultural properties listed by UNESCO. Such a review can also act to inform UNESCO and its advisory bodies of academic materials and evidence for consideration in the management, conservation, and promotion of cultural WHP in the climate change context.
3.1. Material Collection
This study’s research design was informed by previously published systematic reviews on heritage and climate change, taking into consideration data sources, year range, and focus. For example, this study is differentiated from reviews by Fatorić and Seekamp [10] and Orr et al. [11], which focused on Web of Science, instead drawing data from Scopus and Google Scholar. The review has therefore incorporated a crawler-based web search engine and a bibliographic database, each recognised as multidisciplinary and reflecting different retrieval limitations [28]. The start date of the review’s year range of 2008–2021 was purposefully selected to align the assessment of literature with the first year in which the WHC considered climate change as a factor making profound impacts on WHP [23]. Relevant literature was then sourced using search terms drawn from UNESCO’s climate change categories:
- (1)
- “World Heritage Site” or “World Heritage” and “Climate change”;
- (2)
- “World Heritage Site” or “World Heritage” and “Flooding”, or “Storm”, or “Drought”, or “Desertification”, or “Changes to oceanic waters”, or “Temperature change”, or “Severe weather”, or “Natural disasters”.
The search terms were limited to those appearing in the titles, abstracts, and keywords, with acknowledgement that the terms were often used interchangeably within the literature. The publications were then collated and subsequently assessed for inclusion in the review based on a read-through of the abstract and, if needed, the full text (see Figure 1).
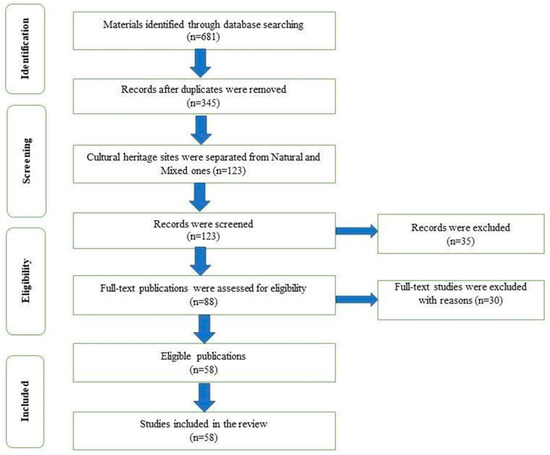
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram of the selection process of publications adapted from Moher et al. [29].
Figure 1 reveals the number of studies being screened, assessed, and excluded at various stages of the systematic review. The literature search from Scopus and Google Scholar for the period 2008–2021 resulted in 681 records. After 336 duplicate references were removed, the next step was separating cultural WHP from natural and mixed heritage sites based on UNESCO’s World Heritage List information. The remaining 123 publications were then screened against the following exclusion criteria: (1) non-English publications, (2) duplicate documents, (3) studies that do not investigate the research scope in the full text, and (4) verification of peer review process. As a result of the final exclusion criteria, 35 sources were removed (namely, book reviews, book chapters, conference proceedings, scientific reports, editorials, research notes). Subsequently, 88 full-text publications were assessed for eligibility against criteria 1–3, resulting in a further 30 studies being excluded including articles from journals such as Journal of Cleaner Production, Building and Environment, Quarterly Science Review, and Journal of Field Archaeology, which lacked a clear focus on cultural WHP and climate change. The process of identification, screening and eligibility assessment resulted in 58 journal articles being included (see Appendix A). This study also considered reports and books on heritage management and climate change produced by UNESCO. Those materials are analysed and critiqued vis-à-vis the 58 articles included in the systematic review.
3.2. Material Analysis
The study’s analytical approach involved entering a summary of basic information from each publication into an Excel spreadsheet. The spreadsheet was built to first capture the “general characteristics” of each article including the author(s), journal title, journal subjects (based on Scopus’s categorisation), year of publication, and author(s) affiliation and discipline. Next, the articles were assessed based on their primary focus such as methodological approaches, research methods, geographic publication, sites and threats, timescale, type of hazards, adaptation contribution and barriers, with this information extracted and recorded in the spreadsheet. A content analysis was then undertaken, which categorised article contributions into various themes. Thematic analysis is a foundational method for identifying, examining, and reporting themes within the data. This method helps provide a flexible approach and research tool for researchers to generate new insights and concepts derived from the literature [30]. Key themes from the articles were added to the spreadsheet with the intention of improving the study’s reliability and reach, as well as underscoring the relevance of the lacunas withdrawn during the literature selection process.
4. Findings
The results of the systematic review are presented in two subsections, which address the 58 articles’ general characteristics and primary focus. Firstly, we highlight the growth of publications, types of journals, authorship, and geographic considerations. We then focus on methodological contributions, research methods, types of hazards, adaptation measures and challenges.
4.1. General Characteristics
4.1.1. Number of Publications
Figure 2 indicates that studies on cultural WHP and climate change remained relatively steady in the years 2008–2017 before experiencing an exponential increase from 2018 onwards. In the last four years of the surveyed period, the number of studies made up approximately 64% (n = 37) of the total reviewed. While there was a drop in the number of articles in 2021 (n = 8) following a peak of publication in 2020 (n = 14), the number of sources remained significantly higher than the rate of publication from 2008 to 2017, where sources per year ranged from one to four. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on scholarly activity, including publication, since the end of 2019 may account for the reduction in articles in 2021, rather than it being indicative of a shift in scholarly interest in the impact of climate change on cultural WHP [31]. This observation reflects that presented in the systematic review conducted by Orr et al. [11], which noted the pandemic created conditions in which some scholars could focus on and speed up their work, while others had difficulty in maintaining their research productivity.
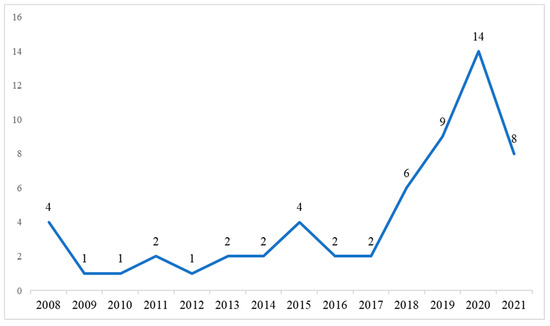
Figure 2.
The number of publications from 2008 to 2021.
4.1.2. Publication Journals
The 58 articles included in the systematic review feature in 40 journals (see Appendix A). While the spread of outlets suggests there are as yet no dominant journals for cultural WHP and climate change research, two titles accounted for 16% of the review’s sources: Sustainability (n = 7), an open access journal from MDPI, and Natural Hazards (n = 4), a hybrid journal from Springer. While the articles in Natural Hazards appeared between 2010 and 2019, those in Sustainability all appeared between 2019 and 2021, which suggests a concentration of articles on climate change and cultural WHP is intensifying in that journal. It is noted that Sustainability is a cross-disciplinary journal encompassing the sciences and humanities. Beyond Sustainability and Natural Hazards, there are only eight other journals listed that feature more than one article on the topic: Journal of Cultural Heritage (n = 3), Climate (n = 2), Climatic Change (n = 2), GMSARN International Journal (n = 2), Heritage Science (n = 2), Historic Environment: Policy and Practice (n = 2), International Journal of Heritage Studies (n = 2) and Landscape Research (n = 2). As such, around 52% of the articles (n = 30) in this review are the sole representative in their targeted journal focusing on the relationship between cultural WHP and climate change, highlighting that the topic has gained attention across various subfields.
Figure 3 highlights that the 58 articles covered by this review fall under six Scopus subject categories: Arts and Humanities (n = 10), Building and Construction (n = 1), Chemistry (n = 1), Earth and Planetary Sciences (n = 10), Environmental Science (n = 26) and Social Sciences (n = 10). Environmental Science is the most dominant subject, with 44.8% of articles in the review linked to that field. When Environmental Science is combined with articles from the subjects of Building and Construction, Chemistry and Earth and Planetary Sciences, it becomes clear that most of the scholarship (n = 38) on cultural WHP and climate change are in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) disciplines, accounting for 65.5% of publications reviewed.
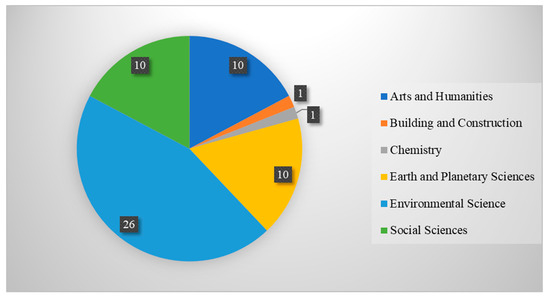
Figure 3.
The number of articles by subject based on Scopus’s categorisation.
4.1.3. Authorship
Based on first author affiliation, 89% of publications were written by scholars from universities and research institutions (n = 52). By contrast, a small percentage of first-named authors were attached to international organisations such as UNESCO and ICOMOS (n = 2), a heritage site (n = 1), or other non-academic organisations (n = 3). Sole-authorship accounts for 19 articles, with the remaining 39 publications being co-authored with teams of between 2 and 25 contributors. Of the 58 publications, only 4 involve collaboration between scholars from the Global North and Global South [31,32,33,34]. No collaboration between STEM and Humanities, Arts and Social Science (HASS) researchers has been found in this review’s analysis of authorship. In terms of the location of first-named authors, researchers from the United Kingdom (n = 8) and Italy (n = 7) dominated the review, followed by those from China (n = 5), Thailand (n = 4), Australia (n = 3) and Germany (n = 3). The majority of authors have only been lead author of one article, with the exception of Howard, who was the first-named author of two studies [35,36].
4.1.4. Geographic Distribution
In terms of the distribution of the geographic focus of the reviewed articles, the largest quantity of publications concerns the UNESCO world heritage region of Europe and North America (n = 28), followed closely by interest in Asia and the Pacific (n = 23). The other regions—Africa (n = 9), Latin America and the Caribbean (n = 7) and Arab States (n = 5)—appear less regularly in the literature. A closer look at Europe and North America reveals that one fourth of those studies relate to the United Kingdom (n = 7), with the second most dominant country of focus being Italy (n = 6). In Asia and the Pacific region, the most common countries of focus are Thailand (n = 4) and China (n = 3). The geographic distribution favouring these two regions reflects trends in authorship locations, where authors from the United Kingdom, Italy, Thailand, and China were dominant.
4.2. Research Focus
4.2.1. Methodological Contribution
Three primary methodological approaches are reflected in the articles reviewed: case study, review, and conceptual studies. Figure 4 illustrates case study-based research to be the most dominant (n = 29), accounting for half the publications reviewed. Case study approaches included articles focused on a single case and those which considered two or more cases. Most analysed risks caused by climate change hazards and the vulnerability of cultural WHP e.g., [33,37,38,39] and sought to advance knowledge about cultural heritage management and conservation e.g., [6,40].
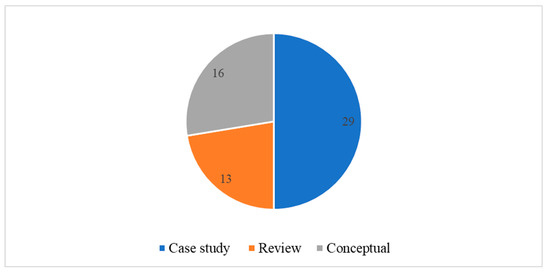
Figure 4.
Methodological contribution in articles reviewed.
Reviews (n = 13) and conceptual approaches (n = 16) accounted for 22% and 28% of methodological contributions, respectively. The conceptual articles drew on theoretical or empirical frameworks for managing and conserving cultural WHP, with a focus on, for example, the long-term monitoring of cultural heritage [40], geo-framework management and the prioritisation of cultural heritage [35], landscape-based conservation and monitoring [41], the vulnerability assessment framework [3], resilience and transformation [42], disaster biography [32], and compatibility in World Heritage climate change policy (18). Review articles, on the other hand, contain unsystematic assessments and documentation with a focus on the application of digital technologies for heritage sites in a climate change context [43], and compassion communities [44]. Reviews also paid attention to legislative aspects, such as challenges in existing heritage policy [45] and the role of the World Heritage Convention [46].
4.2.2. Research Method
Qualitative methods (n = 30) dominated the assessment of cultural WHP and climate change hazards, reflecting 51.7% of the sample (see Figure 5) and encompassing secondary data as the most popular method (n = 24, 41%), followed by observations, interviews, and focus groups (n = 7, 12%). Articles using quantitative methods (n = 21, 36.2%) incorporated surveys and sampling (n = 8, 13.8%), modelling (n = 7, 12.8%), GIS and remote sensing (n = 6, 10.3%) and, with far less representation, questionnaires (n = 4) and simulations (n = 2). Less common were mixed method approaches (n = 7, 12.8%), which involved a combination of interviews and questionnaire surveys e.g., [6,47], surveys, modelling and secondary data [48], archaeological sampling and secondary data [49], and modelling and secondary data [37].
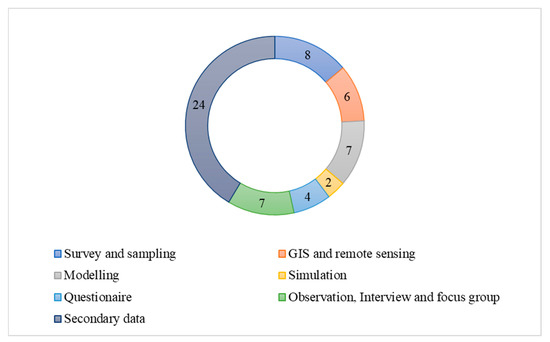
Figure 5.
Research methods used in articles reviewed.
4.2.3. Timescale
Many articles included in the review do not situate their study in a particular time frame (n = 39, 67%), meaning any observations made about cultural WHP and climate change hazards are not in reference to a specified date range. Figure 6 demonstrates that a proportion of articles explicitly refer to the past (n = 14, 24%). These articles considered how climate change hazards affected cultural WHP, and how past knowledge and lessons could be integrated into the adaptation and mitigation plans relating to climate change e.g., [36,37,38]. A smaller number specified a focus on the past to the future (n = 3, 5%), and concentrated on analysing past impacts while also proposing possible scenarios for heritage management and conservation in the future e.g., [5,50,51]. Two articles were solely future-oriented (4%) and focused on scenarios for heritage sites to better prepare for upcoming climate change hazards, such as floods and sea level rises [52,53].
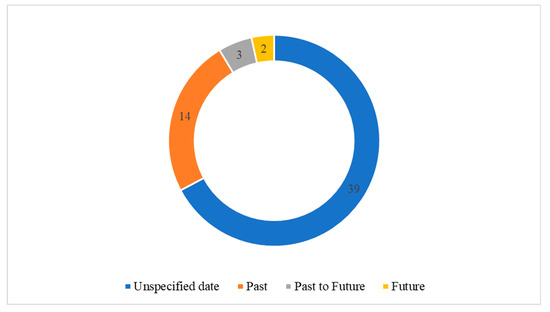
Figure 6.
Time period referenced in articles reviewed.
4.2.4. Type of Hazards
A review of the articles suggests there are 86 cultural WHP from 40 States Parties in five regions being impacted by climate change hazards (see Table 1). Keeping in mind the findings regarding the geographical locations of authors and the country focus of the articles, the data appear to indicate that Europe and North America is the most vulnerable region to climate change, with 50 sites represented in the literature (58%), followed by Asia and the Pacific with 16 sites (18.6%). The resulting perception might be that Africa (n = 10), Latin America and the Caribbean (n = 6) and the Arab States (n = 4) are regions less susceptible to climate change.

Table 1.
Locations, sites, and climate change hazards captured by articles reviewed.
In terms of identified hazards, climate change as a general category is the most frequent threat cited as impacting cultural WHP (n = 33), followed by floods (n = 23). Other hazards such as sea level rise, earthquake and erosion, coastal flood and erosion and severe weather are less frequent. Storms (n = 2), temperature changes (n = 2) and desertification (n = 1) appear less commonly (n = 2 each).
4.2.5. Adaptation Measures
In the more recent years covered by the review period, articles offering adaptation measures for heritage management and conservation have increased, including those that propose mapping and modelling for hazard and vulnerability assessment (n = 11) e.g., [33,54,55]. The focus on adaptation measures also incorporates studies that emphasise the importance of past knowledge (n = 7) e.g., [37,39,56] as well as the necessity of a more integrated approach (n = 8) e.g., [3,21,47]. Other articles (n = 5) point to the critical role of local communities in addressing the climate crisis and the need to draw on their wisdom in heritage management and conservation e.g., [6,32,33,48]. A focus on plans, policies and regulations is also present (n = 9), with an emphasis on comprehensive, integrated, and timely policies to tackle climate change impacts in a constantly changing context e.g., [57,58,59]. Some articles included adaptation measures specifically focused on the UNESCO World Heritage system, highlighting a need for changes to the monitoring system e.g., [41,60] and the scope of policy e.g., [18].
4.2.6. Adaptation Barriers
The sample indicates the most significant adaptation barriers to be collaboration and cooperation between various stakeholders and institutions (n = 9) e.g., [3,33,42,57,58], methodology (n = 8) e.g., [34,51,54,61] and policy and regulation challenges (n = 6) e.g., [33,48,62]. Barriers relating to management capacity (n = 4), community (n = 3) and finance (n = 2) appear in a smaller number of articles e.g., [3,6,37,63].
5. Discussion
WHP represent a unique class of safeguarded areas; each site (cultural, natural, or mixed) showcases its outstanding universal values and its critical significance to human beings [64]. After the initial search and screening stages of the review removed duplicates, there were a total of 345 articles addressing WHP in the context of climate change (see Figure 1). The subsequent removal of publications focused on natural or mixed properties left only 123 with a focus on cultural sites. This suggests a much greater scholarly concentration on natural sites compared to cultural sites during the period 2008–2021, despite cultural sites comprising roughly four-fifths of the total WHP. The greater focus on natural sites may reflect that the effects of climate change on WHP are more readily observed via natural environments or ecosystems, which are rich in biodiversity and endemism [65]. The vastness of many of the natural sites is quantitatively different to the make-up of cultural WHPs, which tend to be restricted to individual sites or smaller landscapes where traditional buildings, monuments, and structures occur [66]. The findings of the review highlight that there has been an increase in studies of cultural WHP and climate change during 2008–2021; however, this change has not been on par with the increasingly severe and widespread effects of climate change on global heritage properties [21].
Since people are experiencing environmental threats related to anthropogenic activity, both cultural and natural properties are susceptible to climate change [67]. Continued reference to and reliance on a nature/culture binary does not bode well for safeguarding WHP appropriately [68]. Indeed, a study conducted by Lowenthal [69] postulates that the natural environment and the recreations of people co-mingle in such a way that “no aspect of nature is unimpacted by human agency, no artefact devoid of environmental impress” (p. 81). Regarding the World Heritage system, natural properties have been frequently recognised with cultural values, whilst cultural properties aspire to appreciate and respect human–nature exchanges and interactions [70]. Therefore, any damage that happens to human–nature assemblages will rupture other parts of it [67]. One particularly salient example captured in the literature reviewed is the case of Kaifeng city in China, which is categorised by UNESCO as a cultural WHP. A study investigating geo-archaeological materials of Kaifeng city suggests that this site should have been added to the list of mixed UNESCO WHP [39]. If there are inaccuracies in the current listing, it might therefore be posited that the World Heritage Convention would benefit from expanding its role to concentrate on the protection of the already listed WHP, rather than primarily focusing on the continuous inscription of new sites [42]. For instance, the original designation of sites as natural, cultural heritage, or mixed may not adequately account for the complexities of WHP, where relationships between people and nature may mean natural sites are better understood as “cultural landscapes” and managed as such [71]. Indeed, understanding each site as “an organically evolving landscape” rather than as natural, cultural or mixed could potentially better facilitate anticipatory and autonomous adaptation [42] (p. 49).
5.1. Key Observations
A principal observation of this systematic review is that there exist significant commonalities, but also disparities, between the UNESCO World Heritage system and the literature from 2008–2021 focused on cultural WHP and climate change. On the one hand, both UNESCO and the literature align in their assessment of similar regions, sites and climate change hazards facing cultural WHP. What the review demonstrates, however, is that the number of cultural WHPs affected by climate change captured by the literature is approximately 2.5 times greater than those listed by UNESCO. This stems from UNESCO only listing current climate change hazards affecting properties, whereas the literature also considers the impacts of past climate hazards. For example, UNESCO’s considerations may not account for how community knowledge of past climate change-related events is drawn on in the present to address hazards, as highlighted in the work of Sop Lee and Nakai [37] in reference to the flooding impacting Hahoe village’s landscape and structure.
Two further observations emerge from the literature. The UNESCO Convention asserts State Parties’ rights to safeguard their own heritage properties, and thereby does not enforce obligations to mitigate climate change [48]. UNESCO also relies on state of conservation reports from its members to update its statistics on cultural WHP and climate change. However, these systems have not delivered a clear solution or explanation to the threat of climate change. As the article by Dastgerdi et al. [45] noted, around 70% of the state of conservation reports have not regarded change in weather pattern as a type of climate change, with these oversights subsequently reflected in UNESCO’s consideration of climate impact. Moreover, UNESCO is considered a “grindingly slow machinery of national and international governance”, which has been inadequate to tackle the considerably increasing environmental and social obstacles of climate change [48] (p. 8). For example, the UN Scientific Conference (First Earth Summit) held in Stockholm, Sweden, in 1972, raised the issue of climate change for the first time. The conference adopted a declaration that presented principles and action plans for international environmental action, warning governments to pay more attention to climate change activities and to evaluate the possibility and magnitude of climatic impacts [72]. That climate change was not included in UNESCO’s heritage agenda until 2008 highlights its sluggish response to an issue that had been highlighted by both STEM and HASS disciplines for considerably longer, with Scopus and Web of Science databases including literature on World Heritage and climate change published from 1996 onward [10].
5.2. Future Directions
Though the review indicates the literature on cultural WHP and climate change has seen recent growth, there remain gaps, opportunities, and new directions for future studies. Given the greater emphasis on natural WHPs in the literature, there is still significant scope for research on cultural WHPs. Although the reviewed studies on cultural WHP and climate change emerge from various disciplines, there is a clear need for more research to be published from HASS disciplines with a view to foregrounding the social aspects of climate change, as well as encouraging responses from societal governance [73,74]. Collaboration between STEM and HASS disciplines in examining cultural WHP and climate change impacts is advisable. Interdisciplinary, multidisciplinary, crossdisciplinary and transdisciplinary studies all have the capacity to deliver new insights into the impact of climate change hazards while acknowledging there is no “easy fix” [67].
The review also draws attention to the disparity between the geographic focus of scholarship—in which properties in the Europe and North America region dominate—and UNESCO’s listing of cultural WHPs in danger—where 33 out of the 36 designated cultural sites are located in Asia and the Pacific, Arab States, Africa, and Latin America and the Caribbean regions [75]. As Hosseini et al. [76] have indicated, 40% of sites labelled by UNESCO as in danger are situated in developing countries. This disjuncture between the literature and the in-danger listings of cultural WHPs is partially, but not wholly, accounted for by the limitation of the systematic review to scholarship published in the English language [3].
Another contributing factor might be the shortage of Global North/Global South collaboration. Global South scholars face significant structural inequalities that impact many aspects of life, including the capacity to participate in the production and publication of academic knowledge [77]. As reflected in the articles reviewed for this study, knowledge production is a domain that continues to be underscored by Eurocentrism [77,78,79]. The increasing focus on journal metrics and the development of costly publishing models such as Hybrid Open Access further challenge the ability for scholars from the Global South to make their research widely available [80]. Indeed, when considering the existing economic inequalities experienced by scholars in developing countries, it is clear that Article Processing Charges in journals such as Sustainability—which this review notes has recently become a key outlet for research on cultural WHP and climate change—will further contribute to the disparity in knowledge production capacity between researchers from the Global North and Global South [80].
Whilst the climate crisis has primarily been a product of the Global North, it is undoubtedly and seriously felt by those in the Global South [81,82]. At COP 27, “wealthy nations” were encouraged “to come good on their promises of finance to help the developing world tackle climate change” [83]. Our call for collaboration between Global North and Global South researchers is aligned with this statement, with a view that there is significant scope for Global North scholars to partner with Global South scholars in ways that will override some of the inequalities currently being experienced. Partnerships between scholars from the Global North and Global South could work to address the paucity of studies published in English that assess climate change impacts on cultural WHP in regions beyond Europe and North America and, in particular, on cultural WHPs in countries in the Global South which are as yet absent from the recent literature, including, for example, the Marshall Islands, Fiji, India, Pakistan, Ethiopia, Jordan and Uruguay. Overall, what is needed is research cooperation and comparative studies which promote knowledge exchanges or transfers concerning heritage management and conservation in a climate change context, between scholars in developed and developing countries, between Global North and Global South, and just as importantly between STEM and HASS.
Throughout the review, various kinds of hazards have been identified as having had impacts on cultural WHP in the last 14 years. Most articles consider climate change as the most frequent threat, followed by flooding. However, other serious hazards such as temperature changes, storms and desertification are rarely present in the existing literature. Given that many cultural WHPs have had a long history of adaptation to climate issues, the literature points to a need to investigate how climate change, cultural heritage sites and people have evolved and interacted over a long time. This is represented in the study conducted by Gomez-Heras and McCabe [84], which asserts that built heritage might be a recorder of past climate change effects that can be utilised to justify social and ecological interactions. While some articles examined climate change adaptations at different heritage sites, most paid heed to technical measures for hazard vulnerability and assessment. The collective actions from locals, private companies, non-governmental organisations, civil society and others towards heritage management and conservation have not been comprehensively studied. Notably, the intangible elements of cultural WHP such as lived experience, identity, belonging, and sense of place, along with traditions, values and cultural practices, need to be taken into account to understand the local community’s participation in tackling climate change impacts [85]. Concerning the legislative framework, most studies analysed how either international or domestic frameworks impact the management of cultural properties. There is therefore an opportunity to investigate how the combination of international and national legislative frameworks influences cultural WHP management, and what barriers are attached. Finally, it emerged in the more recent literature that some policies are quick-fix, profit-oriented but ultimately short-sighted urban planning responses in the wake of growing urbanization [86], thus making heritage sites more vulnerable to climate change. What the field now requires are studies that seek to better understand how such policies have affected heritage management and the conservation of cultural WHPs, and what changes should be made to ensure more appropriate policy frameworks moving forward.
6. Conclusions
This systematic review provides new insights into the state of knowledge about cultural WHP and climate change. By examining 58 peer reviewed articles from 2008 to 2021, this study identified primary research themes and the directions and lacunas for scholarship on cultural WHP and the climate crisis. The review has its limitations, particularly in that it is limited to secondary sources published in peer-reviewed, English language journals indexed in Scopus and Google Scholar. There is a plethora of studies that the inclusion criteria exclude, such as work in languages other than English, as well as publications in English that appear in places other than peer-reviewed journals, including grey literature. We recognize, for example, the vast number of resources produced by organisations such as the Association for Preservation and Training International that have not been captured due to the search engine and database used, or the specified inclusion criteria e.g., [87]. To address such limitations, future studies could screen and analyse the literature with a focus on alternative sources, languages other than English, and the application of a larger period for publication. However, despite these limitations—limitations that are common to SQLRs [12,13]—the review revealed a suite of observations that will be important to consider for future research, including, for example, the prevalence of scholarship focused on the region of Europe and North America reflecting a need for greater representation from the Global South in terms of both geographic focus and authorship, and the role of Global North scholars in partnering with Global South scholars to address current inequalities in knowledge production. Such collaboration is reflected in the co-authorship of this systematic review. The review further noted the lack of collaboration between STEM and HASS disciplines, the focus on collective action from different stakeholders, the importance of intangible elements and weakness of the culture/nature binary, and the effects of both international and national legal frameworks and regulations. Given that cultural WHPs are the legacy of all people [6], it is the responsibility of both scholars and heritage practitioners to help understand, protect, and conserve these sites in the wake of the severe climate change impacts being experienced globally. The key observations and suggested directions for future research that have been highlighted in this article provide a way forward for new scholarship that tackles challenges to cultural heritage conservation and management in the wake of the climate emergency.
Author Contributions
K.N.N. contributed to the conception, design, acquisition and analysis of data, as well as drafting and revising the work to critically guide intellectual contribution. S.B. contributed to supporting the conception and design of the work, auditing the analysis and interpretation of data, and revising the draft critically for intellectual content. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data were gathered from Scopus and Google Scholar.
Acknowledgments
The authors express gratitude to Associate Professor Kerrie Foxwell-Norton (Griffith University) and Associate Professor Robert Mason (Griffith University) for their resourceful feedback. This research was supported by a Griffith University International Postgraduate Research Scholarship and Postgraduate Research Scholarship.
Conflicts of Interest
There is no competing interest to declare.
Appendix A. Publications Included in the Systematic Review (2008–2021)
| Authors | Date | Title | Source | DOI |
| Khaing, T. W., Tantanee, S., Pratoomchai, W., Mahavik, N | 2021 | Coupling Flood Hazard with Vulnerability Map for Flood Risk Assessment: A Case Study of Nyaung-U Township in Myanmar | GMSARN International Journal | |
| Hemeda, S | 2021 | Geo-environmental monitoring and 3D finite elements stability analysis for site investigation of underground monuments. Horemheb tomb (KV57), Luxor, Egypt | Heritage Science | 10.1186/s40494-021-00487-3 |
| D’alpaos, C., D’alpaos, A | 2021 | The Valuation of Ecosystem Services in the Venice Lagoon: A Multicriteria Approach | Sustainability | 10.3390/su13179485 |
| Megarry, W., Hadick, K | 2021 | Lessons from the Edge: Assessing the impact and efficacy of digital technologies to stress urgency about climate change and cultural heritage globally | Historic Environment: Policy and Practice | 10.1080/17567505.2021.1944571 |
| Hemeda, S | 2021 | Geotechnical modelling of the climate change impact on world heritage properties in Alexandria, Egypt | Heritage Science | 10.1186/s40494-021-00547-8 |
| Kern, K., Irmisch, J., Odermatt, C., Haupt, W., Kissling-Näf, I | 2021 | Cultural Heritage, Sustainable Development, and Climate Policy: Comparing the UNESCO World Heritage Cities of Potsdam and Bern | Sustainability | 10.3390/su13169131 |
| Armenat, M., Malek, K | 2021 | The underground world heritage site in the Harz Mining Region | Zeitschrift fur Geomorphologie (Journal of Geomorphology) | 10.1127/zfg-suppl/2021/0698 |
| Kittipongvises, S., Phetrak, A., Rattanapun, P., Brundiers, K., Buizer, J. L., Melnick, R | 2020 | AHP-GIS analysis for flood hazard assessment of the communities nearby the world heritage site on Ayutthaya Island, Thailand | International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction | 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.101612 |
| Srijuntrapun, P | 2020 | Vulnerability and Integrated Adaptation Guidelines for Flood Risks in the World Heritage Site: The Historic City of Ayutthaya | GMSARN International Journal | |
| Zhang, Y | 2020 | How Did the Lost Shangri-La Get Lost? The Tragedy of the Groundwater Commons in Lijiang, China | Water | 10.3390/w12113131 |
| Sesana, E., Gagnon, A. S., Bonazza, A., & Hughes, J. J. | 2020 | An integrated approach for assessing the vulnerability of World Heritage Sites to climate change impacts | Journal of Cultural Heritage | 10.1016/j.culher.2019.06.013 |
| Samuels, K. L., Platts, E. J | 2020 | An Ecolabel for the World Heritage Brand? Developing a Climate Communication Recognition Scheme for Heritage Sites | Climate | 10.3390/cli8030038 |
| Seekamp, E., Jo, E. | 2020 | Resilience and transformation of heritage sites to accommodate for loss and learning in a changing climate | Climatic Change | 10.1007/s10584-020-02812-4 |
| Guzman, P., Fatorić, S., Ishizawa, M | 2020 | Monitoring Climate Change in World Heritage Properties: Evaluating Landscape-Based Approach in the State of Conservation System | Climate | 10.3390/cli8030039 |
| Khalaf, R. W | 2020 | A Proposal to Operationalise the Concept of Compatibility in World Heritage Climate Change Policy | Historic Environment: Policy and Practice | 10.1080/17567505.2020.1782697 |
| Di Napoli, M., Carotenuto, F., Cevasco, A., Confuorto, P., Di Martire, D., Firpo, M., Pepe, G., Raso, E., Calcaterra, D | 2020 | Machine learning ensemble modelling as a tool to improve landslide susceptibility mapping reliability | Landslides | 10.1007/s10346-020-01392-9 |
| LemÉE, C., Navarro, O., Restrepo-Ochoa, D., Mercier, D., Fleury-Bahi, G | 2020 | Protective behaviors regarding coastal flooding risk in a context of climate change | Advances in Climate Change Research | 10.1016/j.accre.2020.12.001 |
| Li, K., Zhang, Y., Liao, M., Ni, J., Chen, Y | 2020 | Late-Holocene vegetation change reveals the environment of ancient people and the origin of Huashan cliff paintings in Guangxi, southwestern China | Holocene | 10.1177/0959683620919980 |
| Ndour, A., Ba, K., Almar, A., Almeida, P., Sall, M., Diedhiou, P. M., Floc’h, F., Daly, C., Grandjean, P., Boivin, J. P., Castelle, B., Marieu, V., Biausque, M., Detandt, G., Folly, S. T., Bonou, F., Capet, X., Garlan, T., Marchesiello, P., Benshila, R., Diaz, H., Bergsma, E., Sadio, M., Sakho, I., Sy, B | 2020 | On the Natural and Anthropogenic Drivers of the Senegalese (West Africa) Low Coast Evolution: Saint Louis Beach 2016 COASTVAR Experiment and 3D Modeling of Short Term Coastal Protection Measures | Journal of Coastal Research | 10.2112/SI95-114.1 |
| Ballard, C., Wilson, M., Nojima, Y., Matanik, R., Shing, R | 2020 | Disaster as Opportunity? Cyclone Pam and the Transmission of Cultural Heritage | Anthropological Forum | 10.1080/00664677.2019.1647825 |
| De Luca, G., Dastgerdi, A. S., Francini, C., Liberatore, G | 2020 | Sustainable cultural heritage planning and management of over tourism in art cities: Lessons from atlas world heritage | Sustainability | 10.3390/su12093929 |
| Fumagalli, M | 2020 | Luang Prabang: Climate change and rapid development | Cities | 10.1016/j.cities.2019.102549 |
| Liu, J., Xu, Z., Chen, F., Chen, F., Zhang, L | 2019 | Flood hazard mapping and assessment on the Angkor World Heritage Site, Cambodia | Remote Sensing | 10.3390/rs11010098 |
| Thanvisitthpon, N | 2019 | Impact of land use transformation and anti-flood infrastructure on flooding in world heritage site and peri-urban area: A case study of Thailand’s Ayutthaya province | Journal of Environmental Management | 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.06.094 |
| Wu, P., Liu, D., Ma, J. Miao, C., Chen, L., Gu, L., Tong, J | 2019 | A geoarchaeological reading of the city-overlap- city phenomenon in the lower Yellow River floodplain: A case study of Kaifeng city, China | Sustainability | 10.3390/su11041029 |
| Chim, K., Tunnicliffe, J., Shamseldin, A., Ota, T | 2019 | Land Use Change Detection and Prediction in Upper Siem Reap River, Cambodia | Hydrology | 10.3390/hydrology6030064 |
| Ducusin, R. J. C., Espaldon, M. V. O., Rebancos, C. M., De Guzman, L. E. P | 2019 | Vulnerability assessment of climate change impacts on a Globally Important Agricultural Heritage System (GIAHS) in the Philippines: the case of Batad Rice Terraces, Banaue, Ifugao, Philippines | Climatic change | 10.1007/s10584-019-02397-7 |
| Miranda, F. N., Ferreira, T. M | 2019 | A simplified approach for flood vulnerability assessment of historic sites | Natural Hazards | 10.1007/s11069-018-03565-1 |
| Dastgerdi, A. S., Francini, C., Liberatore, G | 2019 | Climate Change Challenges to Existing Cultural Heritage Policy | Sustainability | 10.3390/su12093929 |
| Porȩbska, A., Godyń, I., Radzicki, K., Nachlik, E., Rizzi, P | 2019 | Built Heritage, Sustainable Development, and Natural Hazards: Flood Protection and UNESCO World Heritage Site Protection Strategies in Krakow, Poland | Sustainability | 10.3390/su11184886 |
| Eppich, R., Grinda, J. L. G | 2019 | Sustainable financial management of tangible cultural heritage sites | Journal of Cultural Heritage Management and Sustainable Development | 10.1108/JCHMSD-11-2018-0081 |
| Reimann, L., Vafeidis, A. T., Brown, S., Hinkel, J., Tol, R. S. J | 2018 | Mediterranean UNESCO World Heritage at risk from coastal flooding and erosion due to sea-level rise | Nature Communications | 10.1038/s41467-018-06645-9 |
| Hategekimana, Y., Yu, L., Nie, Y., Zhu, J., Liu, F., Guo, F | 2018 | Integration of multi-parametric fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and GIS along the UNESCO World Heritage: a flood hazard index, Mombasa County, Kenya | Natural Hazards | 10.1007/s11069-018-3244-9 |
| Jamaludin, I. S., Sulaiman, N | 2018 | Malaysia resilient initiatives: case study of Melaka into resilient city | Planning Malaysia | |
| D’Onofrio, R., Trusiani, E | 2018 | Strategies and Actions to Recover the Landscape after Flooding: The Case of Vernazza in the Cinque Terre National Park (Italy) | Sustainability | 10.3390/su10030742 |
| Haugen, A., Bertolin, C., Leijonhufvud, G., Olstad, T., Broström, T | 2018 | A Methodology for Long-Term Monitoring of Climate Change Impacts on Historic Buildings | Geosciences | 10.3390/geosciences8100370 |
| Génova, M., Díez-Herrero, A., Moreno-Asenjo, M. A., Rodríguez-Pascua, M. A | 2018 | Natural disasters written in historical woods: Floods, a thunderbolt fire and an earthquake | Journal of Cultural Heritage | 10.1016/j.culher.2017.12.011 |
| Rinalduzzi, S., Farroni, L., Billi, A., De Filippis, L., Faccenna, C., Poncia, P. P., Spadafora, G | 2017 | Geocultural landscaping: Guidelines and conceptual framework to design future scenarios of exploited lands | Land Use Policy | 10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.02.033 |
| Saul, H., Waterton, E | 2017 | Heritage and communities of compassion in the aftermath of the great earthquake, Nepal: A photographic reflection | Journal of Community Archaeology and Heritage | 10.1080/20518196.2017.1299328 |
| Vojinovic, Z., Hammond, M., Golub, D., Hirunsalee, S., Weesakul, S., Meesuk, V., Medina, N., Sanchez, A., Kumara, S., Abbott, M | 2016 | Holistic approach to flood risk assessment in areas with cultural heritage: a practical application in Ayutthaya, Thailand | Natural Hazards | 10.1007/s11069-015-2098-7 |
| Howard, A. J., Knight, D., Coulthard, T., Hudson-Edwards, K., Kossoff, D., Malone, S | 2016 | Assessing riverine threats to heritage assets posed by future climate change through a geomorphological approach and predictive modelling in the Derwent Valley Mills WHS, UK | Journal of Cultural Heritage | 10.1016/j.culher.2015.11.007 |
| Sop Lee, H., Nakai, Y | 2015 | Effect of Floods on Village Spatial Structure and Hierarchy—Hahoe Village, Korea | Landscape Research | 10.1080/01426397.2014.918093 |
| Sugio, K | 2015 | Large-scale Disasters on World Heritage and Cultural Heritage in Japan: Significant Impacts and Sustainable Management Cases | Landscape Research | 10.1080/01426397.2015.1057806 |
| Phillips, H | 2015 | The capacity to adapt to climate change at heritage sites—The development of a conceptual framework | Environmental Science and Policy | 10.1016/j.envsci.2014.11.003 |
| Utaka, Y | 2015 | Managing “buffer”: A special focus on the Itsukushima Shinto Shrine World Heritage site, Japan | International Review for Spatial Planning and Sustainable Development | 10.14246/irspsd.3.2_79 |
| Amador, J. A., Alfaro, E. J | 2014 | Weather and climate socio-economic impacts in Central America for the management and protection of world heritage sites and the Diquis Delta culture in Costa Rica (a case study) | Advances in Geosciences | 10.5194/adgeo-35-157-2014 |
| Marzeion, B., Levermann, A | 2014 | Loss of cultural world heritage and currently inhabited places to sea-level rise | Environmental Research Letters | 10.1088/1748-9326/9/3/034001 |
| Knight, J., Harrison, S | 2013 | ‘A land history of men’: The intersection of geomorphology, culture and heritage in Cornwall, southwest England | Applied Geography | 10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.03.020 |
| Howard, A. J | 2013 | Managing global heritage in the face of future climate change: the importance of understanding geological and geomorphological processes and hazards | International Journal of Heritage Studies | 10.1080/13527258.2012.681680 |
| Kocabas, A | 2012 | Urban conservation in Istanbul’s Historic Peninsula: Progress and challenges | WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment | 10.2495/SC120281 |
| Pucci, S., Pantosti, D., De Martini, P. M., Smedile, A., Munzi, M., Cirelli, E., Pentiricci, M., Musso, L | 2011 | Environment-human relationships in historical times: The balance between urban development and natural forces at Leptis Magna (Libya) | Quaternary International | 10.1016/j.quaint.2011.03.050 |
| Daly, C | 2011 | Climate change and the conservation of archaeological sites: A review of impacts theory | Conservation and Management of Archaeological Sites | 0.1179/175355212X13315728646058 |
| Grunert, J., Hess, S. | 2010 | The Upper Middle Rhine Valley as a risk area | Natural Hazards | 10.1007/s11069-010-9661-z |
| Burns, William CG | 2009 | Belt and Suspenders? The World Heritage Convention’s Role in Confronting Climate Change | Review of European Community & International Environmental Law | |
| Terrill, G | 2008 | Climate change: How should the world heritage convention respond? | International Journal of Heritage Studies | 10.1080/13527250802284388 |
| Beniston, M | 2008 | Sustainability of the landscape of a UNESCO World Heritage site in the Lake Geneva region (Switzerland) in a greenhouse climate | International Journal of Climatology | 10.1002/joc.1644 |
| Fallahi, A | 2008 | Bam earthquake reconstruction assessment: An interdisciplinary analytical study on the risk preparedness of Bam and its cultural landscape: A World Heritage property in danger | Structural Survey | 10.1108/02630800810922739 |
| Shearing, Susan | 2008 | Here today, gone tomorrow?: climate change and world heritage | Australasian Journal of Natural Resources Law and Policy |
References
- Munir, A. In Flood-Stricken Pakistan, Rains Damage Archaeological Site. 2022. Available online: https://apnews.com/article/floods-pakistan-asia-south-dating-e3ee9f66c3a8e338e5037744e1f1cfa5 (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Abid, H. Record Rains in Pakistan Damage Mohenjo Daro Archaeological Site. 2022. Available online: https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2022/9/8/record-rains-in-pakistan-damage-mohenjo-daro-archeological-site (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.S.; Bonazza, A.; Hughes, J.J. An integrated approach for assessing the vulnerability of World Heritage Sites to climate change impacts. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 41, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage. In UNESCO World Heritage Centre—Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage; 1972; Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/archive/convention-en.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Reimann, L.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Brown, S.; Hinkel, J.; Tol, R.S.J. Mediterranean UNESCO World Heritage at risk from coastal flooding and erosion due to sea-level rise. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srijuntrapun, P. Vulnerability and Integrated Adaptation Guidelines for Flood Risks in the World Heritage Site: The Historic City of Ayutthaya. GMSARN Int. J. 2020, 14, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. 2022. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg2/ (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report; Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Available online: https://epic.awi.de/id/eprint/37530/1/IPCC_AR5_SYR_Final.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Esme, S. COP27: ‘Climate Chaos’ Warning as UN Summit Begins. 2022. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-63517078 (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Fatorić, S.; Seekamp, E. Are cultural heritage and resources threatened by climate change? A systematic literature review. Clim. Chang. 2017, 142, 227–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, S.A.; Richards, J.; Fatorić, S. Climate Change and Cultural Heritage: A Systematic Literature Review (2016–2020). Hist. Environ. Policy Pr. 2021, 12, 434–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktürk, G. A systematic overview of the barriers to building climate adaptation of cultural and natural heritage sites in polar regions. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 136, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Ganuza, L.; Garmendia, L.; Roji, E.; Gandini, A. Do we know how urban heritage is being endangered by climate change? A systematic and critical review. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 65, 102551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.S.; Ciantelli, C.; Cassar, J.; Hughes, J.J. Climate change impacts on cultural heritage: A literature review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Erazo, C.P.; Álvarez-García, J.; Río-Rama, M.D.L.C.D.; Durán-Sánchez, A. Scientific Mapping on the Impact of Climate Change on Cultural and Natural Heritage: A Systematic Scientometric Analysis. Land 2021, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chechi, A. The Cultural Dimension of Climate Change: Some Remarks on the Interface between Cultural Heritage and Climate Change Law. In Climate Change as a Threat to Peace: Impacts on Cultural Heritage and Cultural Diversity; von Schorlemer, S., Maus, S., Eds.; Peter Lang Academic Research: Frankfurt, Germany, 2014; pp. 161–197. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. World Heritage Committee Decision 29COM 7B.a (9 September 2005) WHC-05/29.COM/22. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/archive/2005/whc05-29com-07BReve.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Khalaf, R.W. A Proposal to Operationalise the Concept of Compatibility in World Heritage Climate Change Policy. Hist. Environ. Policy Pract. 2021, 12, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Decision 40 COM 7 State of Conservation of World Heritage Properties. 2016. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/decisions/6817 (accessed on 16 October 2022).
- Guzman, P.; Pereira Roders, A.R.; Colenbrander, B. Impacts of Common Urban Development Factors on Cultural Conservation in World Heritage Cities: An Indicators-Based Analysis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducusin, R.J.C.; Espaldon, M.V.O.; Rebancos, C.M.; De Guzman, L.E.P. Vulnerability assessment of climate change impacts on a Globally Important Agricultural Heritage System (GIAHS) in the Philippines: The case of Batad Rice Terraces, Banaue, Ifugao, Philippines. Clim. Chang. 2019, 153, 395–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Operational Guidelines for the Implementation of the World Heritage Convention; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. List of Factors Affecting the Properties. 2008. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/factors/ (accessed on 17 October 2022).
- UNFCCC. Climate Change: Impacts, Vulnerabilities and Adaptation in Developing Countries. 2007. Available online: https://unfccc.int/resource/docs/publications/impacts.pdf (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- UNESCO. World Heritage List. 2022. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/?type=cultural&danger=1 (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Pickering, C.; Byrne, J. The benefits of publishing systematic quantitative literature reviews for PhD candidates and other early-career researchers. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2014, 33, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.A.; Fauser, B.C. Balancing the strengths of systematic and narrative reviews. Hum. Reprod. Update 2005, 11, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusenbauer, M.; Haddaway, N.R. Which academic search systems are suitable for systematic reviews or meta-analyses? Evaluating retrieval qualities of Google Scholar, PubMed, and 26 other resources. Res. Synth. Methods 2019, 11, 181–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramo, G.; D’Angelo, C.A.; Mele, I. Impact of Covid-19 on research output by gender across countries. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 6811–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, C.; Wilson, M.; Nojima, Y.; Matanik, R.; Shing, R. Disaster as Opportunity? Cyclone Pam and the Transmission of Cultural Heritage. Anthr. Forum 2020, 30, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittipongvises, S.; Phetrak, A.; Rattanapun, P.; Brundiers, K.; Buizer, J.L.; Melnick, R. AHP-GIS analysis for flood hazard assessment of the communities nearby the world heritage site on Ayutthaya Island, Thailand. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 48, 101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndour, A.; Ba, K.; Almar, A.; Almeida, P.; Sall, M.; Diedhiou, P.; Floc’H, F.; Daly, C.; Grandjean, P.; Boivin, J.-P.; et al. On the Natural and Anthropogenic Drivers of the Senegalese (West Africa) Low Coast Evolution: Saint Louis Beach 2016 COASTVAR Experiment and 3D Modeling of Short Term Coastal Protection Measures. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 95, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.J. Managing global heritage in the face of future climate change: The importance of understanding geological and geomorphological processes and hazards. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2013, 19, 632–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.J.; Knight, D.; Coulthard, T.; Hudson-Edwards, K.; Kossoff, D.; Malone, S. Assessing riverine threats to heritage assets posed by future climate change through a geomorphological approach and predictive modelling in the Derwent Valley Mills WHS, UK. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 19, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Nakai, Y. Effect of Floods on Village Spatial Structure and Hierarchy – Hahoe Village, Korea. Landsc. Res. 2014, 40, 411–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanvisitthpon, N. Impact of land use transformation and anti-flood infrastructure on flooding in world heritage site and peri-urban area: A case study of Thailand’s Ayutthaya province. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Liu, D.; Ma, J.; Miao, C.; Chen, L.; Gu, L.; Tong, J. A Geoarchaeological Reading of the City-Overlap-City Phenomenon in the Lower Yellow River Floodplain: A Case Study of Kaifeng City, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alpaos, C.; D’Alpaos, A. The Valuation of Ecosystem Services in the Venice Lagoon: A Multicriteria Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, P.; Fatorić, S.; Ishizawa, M. Monitoring Climate Change in World Heritage Properties: Evaluating Landscape-Based Approach in the State of Conservation System. Climate 2020, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seekamp, E.; Jo, E. Resilience and transformation of heritage sites to accommodate for loss and learning in a changing climate. Clim. Chang. 2020, 162, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megarry, W.; Hadick, K. Lessons from the Edge: Assessing the impact and efficacy of digital technologies to stress urgency about climate change and cultural heritage globally. Hist. Environ. Policy Pract. 2021, 12, 336–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saul, H.; Waterton, E. Heritage and communities of compassion in the aftermath of the great earthquake, Nepal: A photographic reflection. J. Community Archaeol. Herit. 2017, 4, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgerdi, A.S.; Sargolini, M.; Pierantoni, I. Climate Change Challenges to Existing Cultural Heritage Policy. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrill, G. Climate Change: How Should the World Heritage Convention Respond? Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2008, 14, 388–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojinovic, Z.; Hammond, M.; Golub, D.; Sianee, H.; Weesakul, S.; Meesuk, V.; Media, N.; Sanchez, A.; Kummara, S.; Abbott, M. Holistic approach to flood risk assessment in areas with cultural heritage: A practical application in Ayutthaya, Thailand. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 589–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, K.L.; Platts, E.J. An Ecolabel for the World Heritage Brand? Developing a Climate Communication Recognition Scheme for Heritage Sites. Climate 2020, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Génova, M.; Díez-Herrero, A.; Moreno-Asenjo, M.A.; Rodríguez-Pascua, M.A. Natural disasters written in historical woods: Floods, a thunderbolt fire and an earthquake. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 32, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniston, M. Sustainability of the landscape of a UNESCO World Heritage site in the Lake Geneva region (Switzerland) in a greenhouse climate. Int. J. Clim. 2008, 28, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chim, K.; Tunnicliffe, J.; Shamseldin, A.; Ota, T. Land Use Change Detection and Prediction in Upper Siem Reap River, Cambodia. Hydrology 2019, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemeda, S. Geo-environmental monitoring and 3D finite elements stability analysis for site investigation of underground monuments. Horemheb tomb (KV57), Luxor, Egypt. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzeion, B.; Levermann, A. Loss of cultural world heritage and currently inhabited places to sea-level rise. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Napoli, M.; Carotenuto, F.; Cevasco, A.; Confuorto, P.; Di Martire, D.; Firpo, M.; Pepe, G.; Raso, E.; Calcaterra, D. Machine learning ensemble modelling as a tool to improve landslide susceptibility mapping reliability. Landslides 2020, 17, 1897–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, F.; Chen, F.; Zhang, L. Flood Hazard Mapping and Assessment on the Angkor World Heritage Site, Cambodia. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, M.; Ni, J.; Chen, Y. Late-Holocene vegetation change reveals the environment of ancient people and the origin of Huashan cliff paintings in Guangxi, southwestern China. Holocene 2020, 30, 1296–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, A. Bam earthquake reconstruction assessment: An interdisciplinary analytical study on the risk preparedness of Bam and its cultural landscape: A World Heritage property in danger. Struct. Surv. 2008, 26, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, K.; Irmisch, J.; Odermatt, C.; Haupt, W.; Kissling-Näf, I. Cultural Heritage, Sustainable Development, and Climate Policy: Comparing the UNESCO World Heritage Cities of Potsdam and Bern. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utaka, Y. Managing ‘buffer’: A special focus on the Itsukushima Shinto Shrine World Heritage site, Japan. Int. Rev. Spat. Plan. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 3, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, W.C. Belt and Suspenders? The World Heritage Convention’s Role in Confronting Climate Change. Rev. Eur. Community Int. Environ. Law 2009, 18, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, A.; Bertolin, C.; Leijonhufvud, G.; Olstad, T.; Broström, T. A Methodology for Long-Term Monitoring of Climate Change Impacts on Historic Buildings. Geosciences 2018, 8, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaludin, I.S.; Sulaiman, N. Malaysia resilient initiatives: Case study of Melaka into resilient city. Plan. Malays. 2018, 16, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Eppich, R.; Grinda, J.L.G. Sustainable financial management of tangible cultural heritage sites. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 282–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K. A new paradigm for the identification, nomination and inscription of properties on the World Heritage List. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2010, 16, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, H. Adaptation to Climate Change at UK World Heritage Sites: Progress and Challenges. Hist. Environ. Policy Pract. 2014, 5, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, M. Climate change and its impacts on Australia’s cultural heritage. Hist. Environ. 2008, 21, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R. Beyond “natural” and “cultural” heritage: Toward an ontological politics of heritage in the age of Anthropocene. Herit. Soc. 2015, 8, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, E.; Gillespie, J. Separating natural and cultural heritage: An outdated approach? Aust. Geogr. 2022, 53, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenthal, D. Natural and cultural heritage. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2005, 11, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, S. Governing the Anthropocene: Novel Ecosystems, Transformation and Environmental Policy; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rössler, M. World Heritage cultural landscapes: A UNESCO flagship programme 1992–2006. Landsc. Res. 2006, 31, 333–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfang, G. Environmental mega-conferences—from Stockholm to Johannesburg and beyond. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2003, 13, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blue, G. Framing Climate Change for Public Deliberation: What Role for Interpretive Social Sciences and Humanities? J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2015, 18, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adger, W.N.; Jon Barnett, F.; Stuart, C., III; Ellemor, H. This must be the place: Underrepresentation of identity and meaning in climate change decision-making. Glob. Environ. Politics 2011, 11, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. World Heritage List of Cultural Properties Impacted by Climate Change. 2022. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/?search=climate+change&order=country&type=cultural (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Hosseini, K.; Stefaniec, A.; Hosseini, S.P. World Heritage Sites in developing countries: Assessing impacts and handling complexities toward sustainable tourism. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2021, 20, 100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collyer, F.M. Global patterns in the publishing of academic knowledge: Global North, global South. Curr. Sociol. 2016, 66, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.F.C.; Alburez-Gutierrez, D. North and South: Naming practices and the hidden dimension of global disparities in knowledge production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119373119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztig, L.I. The Global North/South inequalities in the IR discipline: Some reflections and insights. Alternatives 2022, 47, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeter, M.; Istratii, R. Scrutinising what Open Access Journals Mean for Global Inequalities. Publ. Res. Q. 2020, 36, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnwell, G.; Wood, N. Climate justice is central to addressing the climate emergency’s psychological consequences in the Global South: A narrative review. S. Afr. J. Psychol. 2022, 52, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.S. Linking Gender to Climate Change Impacts in the Global South; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justin, R. COP27: Why the Latest UN Climate Conference Matters. 2022. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-63502762 (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Gomez-Heras, M.; McCabe, S. Weathering of stone-built heritage: A lens through which to read the Anthropocene. Anthropocene 2015, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.S.; Bertolin, C.; Hughes, J. Adapting Cultural Heritage to Climate Change Risks: Perspectives of Cultural Heritage Experts in Europe. Geosciences 2018, 8, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Spina, L. Adaptive Sustainable Reuse for Cultural Heritage: A Multiple Criteria Decision Aiding Approach Supporting Urban Development Processes. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APT International. Climate change and cultural heritage conservation: A literature review. 2016. Available online: https://www.apti.org/assets/docs/APT%20TC-SP%20Literature%20Review%20Climate%20Change%20%20Cultural%20Heritage%20Conservation%202016June30.pdf (accessed on 13 February 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).