Impacts of Different Modes of Bariatric Surgery on Plasma Levels of Hepassocin in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Surgical Techniques
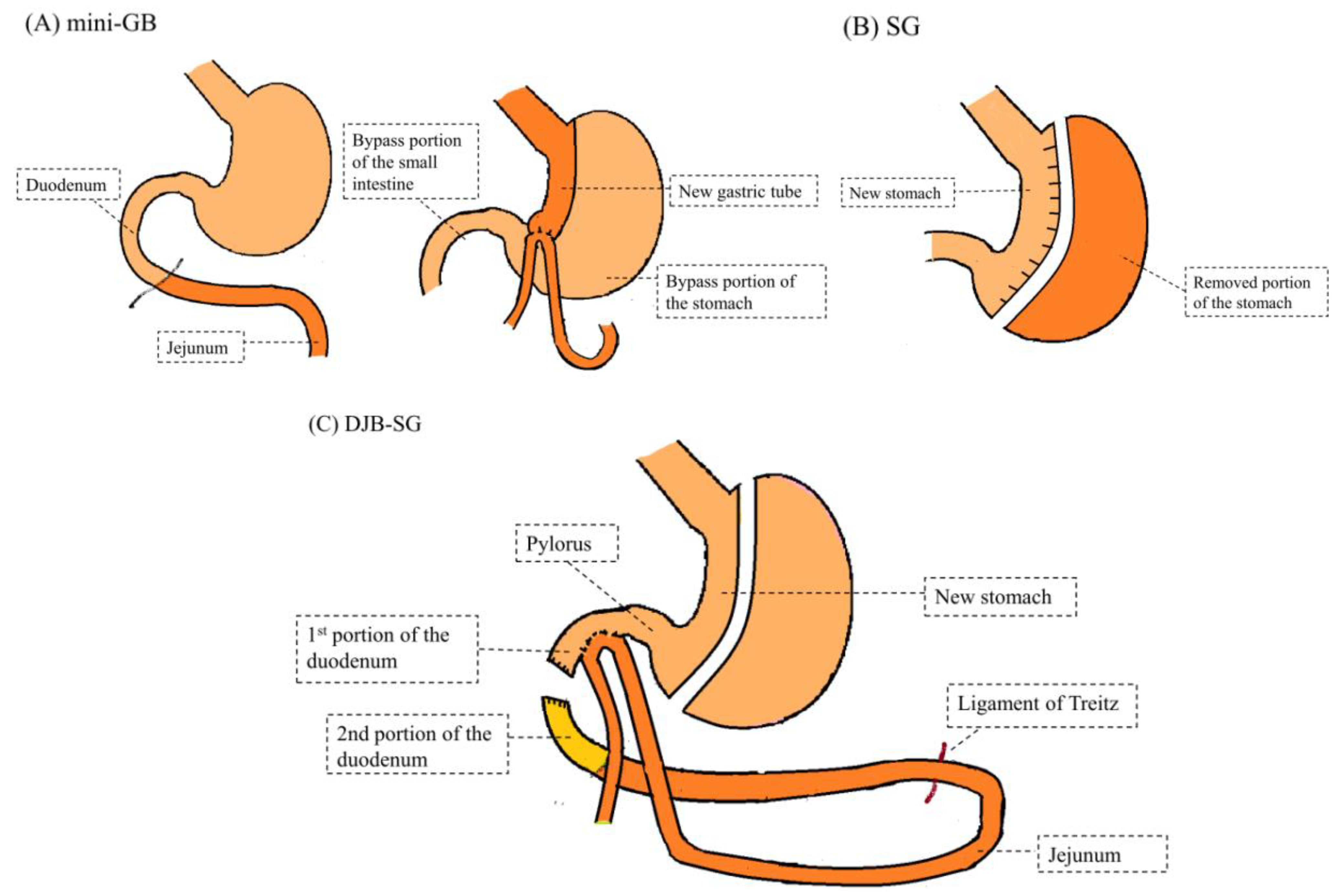
2.2.1. Laparoscopic GB (Mini-GB)
2.2.2. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG)
2.2.3. Laparoscopic Duodeno-Jejunal Bypass with Sleeve Gastrectomy (DJB-SG)
2.3. Blood Sampling
2.4. Assays of Plasma Hepassocin Levels
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
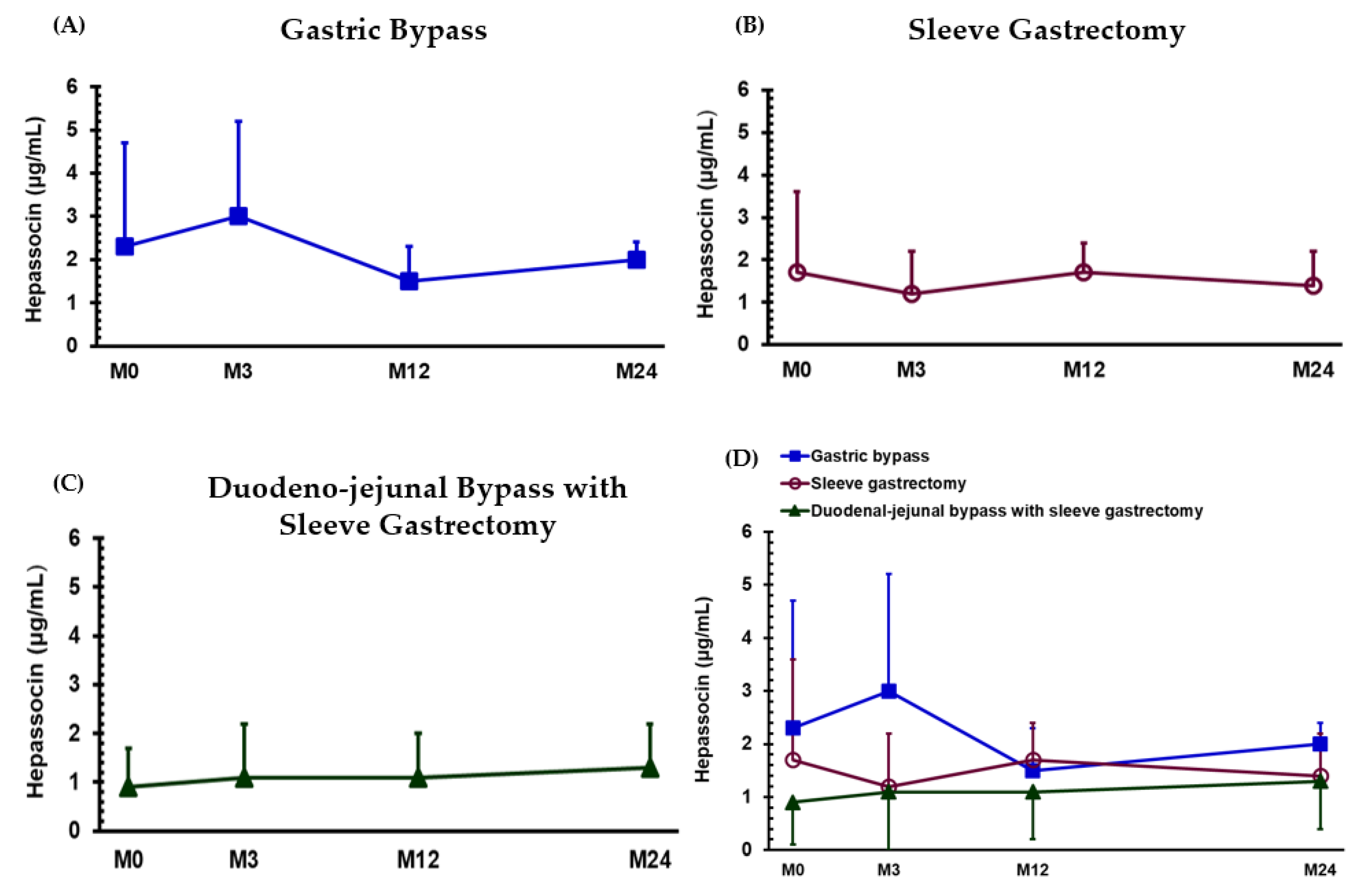
3.1. Effects of the Treatment 24 Months after Bariatric Surgery
3.2. Changes in Hepassocin Levels 12 and 24 Months after Bariatric Surgery
3.3. Relationship between Hepassocin and Clinical Parameters before Surgery and 24 Months after Surgery
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.M.; Rimm, E.B.; Colditz, G.A.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C. Obesity, fatdistribution, and weight gain as risk factors for clinical diabetes in men. Diabetes Care 1994, 17, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colditz, G.A.; Willett, W.C.; Stampfer, M.J.; Manson, J.E.; Hennekens, C.H.; Arky, R.A.; Speizer, F.E. Weight as a risk factor for clinical diabetes in women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1990, 132, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggard-Gibbons, M.; Maglione, M.; Livhits, M.; Ewing, B.; Maher, A.R.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Shekelle, P.G. Bari atric surgery forweight loss and glycemic control in nonmorbidly obese adults with diabetes: Asystematic review. JAMA 2013, 309, 2250–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Almulaifi, A.; Tsou, J.J.; Ser, K.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, S.C. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for type 2 diabetes mellitus: Predicting the success by ABCD score. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2015, 11, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Chong, K.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, S.C.; Lee, S.D. Changes in postprandial gut hormones after metabolic surgery: A comparison of gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2011, 7, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.K.; Tai, C.M.; Chang, P.C.; Malapan, K.; Tsai, C.C.; Yolsuriyan wong, K. Loop duodenojejunal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy: Comparative study with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in type 2 diabetic patients with a BMI <35 kg/m(2), first year results. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 2291–2301. [Google Scholar]
- Zachariah, P.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, W.J.; Chen, S.C.; Ser, K.H.; Chen, J.C.; Lee, Y.C. Compared to sleeve gastrectomy, duodenal-jejunal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy gives better glycemic control in T2DM patients, with a lower β-cell response and similar appetite sensations:mixed-meal study. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 2862–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroz, A.; Couty, J.P.; Postic, C. Hepatokines: Unlocking the multi-organ network in metabolic diseases. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.H.; Ou, H.Y.; Wu, H.T.; Hung, H.C.; Yang, Y.C.; Chang, C.J. Serum hepassocin concentrations in diabeticpatients with or without nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Manag. 2014, 4, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.T.; Ou, H.Y.; Hung, H.C.; Su, Y.C.; Lu, F.H.; Wu, J.S.; Yang, Y.C.; Wu, C.L.; Chang, C.J. Anovelhepatokine, HFREP1, plays a crucial role in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1732–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, H.Y.; Wu, H.T.; Lin, C.H.; Du, Y.F.; Hu, C.Y.; Hung, H.C.; Wu, P.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Chang, C.J. The hepatic protection effects of hepassocinin hyperglycemic crisis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, V.; Jambrina, C.; Casana, E.; Sacristan, V.; Muñoz, S.; Darriba, S.; Rodó, J.; Mallol, C.; Garcia, M.; León, X.; et al. FGF21 gene therapy as treatment forobesity and insulin resistance. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Hur, K.Y.; Lakadawala, M.; Kasama, K.; Wong, S.K.; Chen, S.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Ser, K.H. Predicting success of metabolic surgery: Age, body mass index, C-peptide, and duration score. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2013, 9, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.H.; Yeh, C.; Chen, J.C.; Lee, T.H.; Chen, S.C.; Lee, W.J.; Chen, C.Y. Does bariatric surgery influence plasma levels of fetuin-A and leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus? PeerJ 2018, 6, e4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Lee, K.T.; Kasama, K.; Seiki, Y.; Ser, K.H.; Chun, S.C.; Chen, J.C.; Lee, Y.C. Laparoscopic single- anastomosis duodenal-jejunal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy (SADJB-SG): Short-term result and comparison with gastric bypass. Obes. Surg. 2014, 24, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoli, S.; Leone, A.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Bedogni, G.; Vanzulli, A.; Redaelli, V.I.; DeAmicis, R.; Vignati, L.; Krakauer, J.C.; Battezzati, A. Association of body shape index (ABSI) with cardio-metabolic risk factors: A cross-sectional study of 6081 Caucasian adults. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautt, W.W. The HISS story overview: A novel hepatic neurohumoral regulationof peripheral insulin sensitivity in health and diabetes. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1999, 77, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.F.; Tygstrup, N. A liver factor increasing glucose uptake in rathindquarters. J. Hepatol. 1994, 20, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Stein, D.T.; Barzilai, N.; Cui, M.H.; Tonelli, J.; Kishore, P.; Hawkins, M. Increased intrahepatic triglyceride is associated with peripheral insulin resistance: In vivo MR imaging and spectroscopy studies. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E1663–E1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.T.; Lu, F.H.; Ou, H.Y.; Su, Y.C.; Hung, H.C.; Wu, J.S.; Yang, Y.C.; Wu, C.L.; Chang, C.J. The role of hepassocin in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Krakauer, J.C. A new body shape index predicts mortality hazard independently of body mass index. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.H.; Lee, W.J.; Chen, S.C.; Chen, T.F.; Lee, S.D.; Chen, C.Y. Bile acid and fibroblast growth factor 19 regulation in obese diabetics, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease after sleeve gastrectomy. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, E815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condello, G.; Chen, C.Y. Fostering the acupuncture practice for health outcomes research: The perspective from Taiwan. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2019, 82, 603–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, P.R.; Kashyap, S.R.; Wolski, K.; Brethauer, S.A.; Kirwan, J.P.; Pothier, C.E.; Thomas, S.; Abood, B.; Nissen, S.E.; Bhatt, D.L. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in obese patients with diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, D.A. Mechanisms for the metabolic success of bariatric surgery. J.Neuroendocr. 2019, 31, e12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.B.; Zimmet, P.; Alberti, K.G.; Rubino, F. International diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention. Bariatric surgery: An IDF statement for obese type 2 diabetes. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2011, 7, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| mGB (n =12) | SG (n =10) | DJB-SG (n =11) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | M24 | M0 | M24 | M0 | M24 | |
| Age | 43.5 ± 8.9 | 37.6 ± 9.1 | 44.8 ± 8.0 | |||
| Body weight (kg) | 86.4 ± 14.0 | 64.6 ± 7.2 *** | 98.0 ± 14.9 | 77.6 ± 19.3 *** | 91.5 ± 13.1 | 71.7 ± 8.7 *** |
| Weight loss (kg) | 18.3 ± 6.4 | 21.9 ± 5.3 | 19.9 ± 7.1 | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 33.0 ± 4.2 | 26.2 ± 3.2 *** | 34.9 ± 2.5 | 27.0 ± 4.0 *** | 34.2 ± 5.0 | 26.9 ± 3.6 *** |
| Waist-hip ratio | 0.96 ± 0.04 | 0.88 ± 0.06 *** | 0.94 ± 0.07 | 0.86 ± 0.06 ** | 0.90 ± 0.07 | 0.86 ± 0.05 * |
| ABSI | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.08 ± 0.01 *** | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.00 ** | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.00 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 190.3 ± 44.2 | 169.7 ± 23.8 | 182.3 ± 49.7 | 184.9 ± 35.3 | 190.0 ± 36.3 | 184.3 ± 41.9 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 171.3 ± 62.6 | 91.3 ± 31.7 ** | 189.6 ± 132.7 | 96.6 ± 51.2 ** | 211.7 ± 111.9 | 132.7 ± 66.5 ** |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 43.0 ± 5.8 | 47.6 ± 7.7 | 39.2 ± 6.8 | 50.5 ± 12.6 ** | 46.6 ± 10.0 | 49.5 ± 12.4 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 122.5 ± 34.1 | 111.3 ± 26.5 | 112.6 ± 35.9 | 115.1 ± 25.6 | 113.9 ± 38.1 | 110.7 ± 33.1 |
| FBS (mg/dL) | 164.1 ± 44.7 | 116.9 ± 6.5 * | 127.4 ± 43.7 | 88.8 ± 7.1 * | 158.0 ± 46.4 | 122.7 ± 33.1 * |
| HbA1c (%) | 9.0 ± 1.6 | 6.7 ± 1.6 ** | 8.0 ± 1.5 | 5.6 ± 0.3 ** | 8.9 ± 1.6 | 6.6 ± 1.4 ** |
| Insulin (μU/mL) | 15.1 ± 8.7 | 4.5 ± 2.3 *** | 11.9 ± 5.7 | 6.4 ± 2.8 * | 19.1 ± 20.0 | 11.9 ± 23.1 |
| C-peptide (ng/mL) | 3.0 ± 1.4 | 1.3 ± 0.7 *** | 3.3 ± 1.6 | 1.9 ± 0.7 * | 2.2 ± 0.8 | 1.4 ± 0.4 ** |
| HOMA-IR | 5.9 ± 3.4 | 1.8 ± 1.8 *** | 3.7 ± 1.8 | 1.4 ± 0.6 ** | 6.7 ± 5.5 | 4.5 ± 10.3 |
| mGB (n = 12) | SG (n = 10) | DJB-SG (n = 11) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rho | p | Rho | p | rho | p | |
| Body weight | −0.0699 | 0.817 | −0.176 | 0.607 | −0.355 | 0.270 |
| BMI | 0.0769 | 0.800 | −0.200 | 0.559 | −0.591 | 0.0510 |
| Waist-hip ratio | −0.287 | 0.352 | −0.590 | 0.0665 | −0.0545 | 0.860 |
| ABSI | −0.0839 | 0.783 | 0.0545 | 0.865 | 0.236 | 0.467 |
| TC | 0.112 | 0.716 | −0.491 | 0.137 | −0.382 | 0.233 |
| TG | 0.0420 | 0.886 | −0.292 | 0.384 | −0.436 | 0.168 |
| HDL-C | 0.00353 | 0.974 | −0.632 | 0.0427 | −0.369 | 0.245 |
| LDL-C | 0.186 | 0.542 | −0.491 | 0.137 | −0.136 | 0.673 |
| FBS | −0.126 | 0.683 | −0.515 | 0.116 | 0.345 | 0.283 |
| HbA1c | −0.295 | 0.340 | −0.103 | 0.759 | −0.330 | 0.310 |
| Insulin | −0.0140 | 0.956 | 0.345 | 0.309 | 0.200 | 0.538 |
| C-peptide | 0.0350 | 0.904 | −0.297 | 0.384 | −0.0364 | 0.903 |
| HOMA-IR | −0.0140 | 0.956 | −0.0424 | 0.892 | 0.218 | 0.502 |
| mGB (n = 12) | SG (n = 10) | DJB-SG (n = 11) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rho | p | Rho | p | rho | p | |
| Body weight | −0.460 | 0.123 | 0.347 | 0.309 | −0.200 | 0.538 |
| BMI | −0.309 | 0.317 | 0.158 | 0.631 | −0.400 | 0.210 |
| Waist-hip ratio | 0.108 | 0.733 | 0.552 | 0.0892 | 0.178 | 0.575 |
| ABSI | 0.0877 | 0.766 | 0.924 | 0.000 | 0.500 | 0.109 |
| TC | 0.0989 | 0.749 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.210 | 0.520 |
| TG | 0.561 | 0.0547 | 0.256 | 0.446 | 0.355 | 0.270 |
| HDL-C | 0.164 | 0.603 | 0.0547 | 0.865 | 0.0729 | 0.818 |
| LDL-C | 0.00879 | 0.974 | 0.0518 | 0.865 | −0.0909 | 0.776 |
| FBS | 0.540 | 0.0663 | −0.105 | 0.759 | 0.282 | 0.384 |
| HbA1c | 0.337 | 0.273 | 0.0686 | 0.838 | 0.164 | 0.614 |
| Insulin | −0.0756 | 0.800 | 0.261 | 0.446 | 0.0320 | 0.903 |
| C-peptide | −0.382 | 0.206 | 0.332 | 0.327 | 0.0364 | 0.903 |
| HOMA-IR | −0.0599 | 0.834 | 0.152 | 0.656 | 0.291 | 0.369 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.-C.; Lee, W.-J.; Yeh, C.; Chen, S.-C.; Chen, C.-Y. Impacts of Different Modes of Bariatric Surgery on Plasma Levels of Hepassocin in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Reports 2019, 2, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports2040024
Wu W-C, Lee W-J, Yeh C, Chen S-C, Chen C-Y. Impacts of Different Modes of Bariatric Surgery on Plasma Levels of Hepassocin in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Reports. 2019; 2(4):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports2040024
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wen-Chi, Wei-Jei Lee, Chun Yeh, Shu-Chun Chen, and Chih-Yen Chen. 2019. "Impacts of Different Modes of Bariatric Surgery on Plasma Levels of Hepassocin in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus" Reports 2, no. 4: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports2040024
APA StyleWu, W.-C., Lee, W.-J., Yeh, C., Chen, S.-C., & Chen, C.-Y. (2019). Impacts of Different Modes of Bariatric Surgery on Plasma Levels of Hepassocin in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Reports, 2(4), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports2040024





