Predictive Biomarkers in the Management of Bladder Cancer: Perspectives in an Evolving Therapeutic Landscape
Abstract
:Introduction
Predictive Tissue Biomarkers
Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
Predictive Urine Biomarkers
Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
Predictive Serum Biomarkers
Unmet Needs in Biomarker Development
Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BC | bladder cancer |
| BCG | Bacillus Calmette-Guérin |
| ctDNA | circulating tumor DNA |
| NAC | neoadjuvant chemotherapy |
| NMIBC | non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer |
| MIBC | muscle-invasive bladder cancer |
| RFS | recurrence-free survival |
| TAM | tumor-associated macrophage |
| TMB | tumor mutational burden |
| TME | tissue microenvironment |
| TURBT | transurethral resection of bladder tumor |
References
- Lacombe, L.; Dalbagni, G.; Zhang, Z.F.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Fair, W.R.; Herr, H.W.; et al. Overexpression of p53 protein in a high-risk population of patients with superficial bladder cancer before and after bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy: Correlation to clinical outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 2646–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pages, F.; Flam, T.A.; Vieillefond, A.; Molinie, V.; Abeille, X.; Lazar, V.; et al. p53 status does not predict initial clinical response to bacillus Calmette-Guerin intravesical therapy in T1 bladder tumors. J. Urol. 1998, 159, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovesen, H.; Horn, T.; Steven, K. Long-term efficacy of intravesical bacillus calmette-guerin for carcinoma in situ: Relationship of progression to histological response and p53 nuclear accumulation. J. Urol. 1997, 157, 1655–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, S.; López-Knowles, E.; Lloreta, J.; Kogevinas, M.; Jaramillo, R.; Amorós, A.; et al. FGFR3 and Tp53 mutations in T1G3 transitional bladder carcinomas: Independent distribution and lack of association with prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5444–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
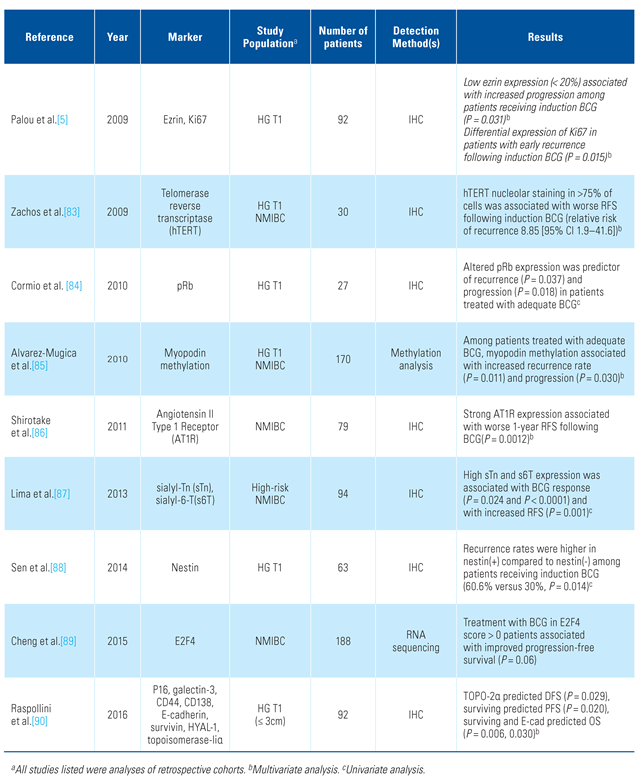
- Palou, J.; Algaba, F.; Vera, I.; Rodriguez, O.; Villavicencio, H.; Sanchez-Carbayo, M. Protein Expression patterns of ezrin are predictors of progression in T1G3 bladder tumours treated with nonmaintenance Bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Eur. Urol. 2009, 56, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Deng, N.; Chen, X.; Chen, L.W.; Qiu, S.P.; Li, X.F.; et al. A novel molecular grading model: Combination of Ki67 and VEGF in predicting tumor recurrence and progression in non-invasive urothelial bladder cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, A.M.; Li, R.; O’Donnell, M.A.; Black, P.C.; Roupret, M.; Catto, J.W.; et al. Predicting response to intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy: Are we there yet? A systematic review. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmström, P.-U.; Hemdan, T.; Segersten, U. Validation of the ezrin, CK20, and Ki-67 as potential predictive markers for BCG instillation therapy of non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 532.e1–532.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Song, C.; Shin, E.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, C.-S.; Ahn, H. Do molecular biomarkers have prognostic value in primary T1G3 bladder cancer treated with bacillus Calmette-Guerin intravesical therapy? Urol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguedolce, F.; Cormio, A.; Massenio, P.; Pedicillo, M.C.; Cagiano, S.; Fortunato, F.; et al. Altered expression of HER-2 and the mismatch repair genes MLH1 and MSH2 predicts the outcome of T1 high-grade bladder cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Zhao, H.; Dinney, C.P.; Zhu, Y.; Leibovici, D.; Bermejo, C.E.; et al. Nucleotide excision repair gene polymorphisms and recurrence after treatment for superficial bladder cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeks, J.J.; Carneiro, B.A.; Pai, S.G.; Oberlin, D.T.; Rademaker, A.; Fedorchak, K.; et al. Genomic characterization of high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 75176–75184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietzak, E.J.; Bagrodia, A.; Cha, E.K.; Drill, E.N.; Iyer, G.; Isharwal, S.; et al. Next-generation sequencing of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer reveals potential biomarkers and rational therapeutic targets. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damrauer, J.S.; Roell, K.R.; Smith, M.A.; Sun, X.; Kirk, E.L.; Hoadley, K.A.; et al. Identification of a novel inflamed tumor microenvironment signature as a predictive biomarker of bacillus Calmette-Guerin immunotherapy in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4599–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, R.; Fritz, J.; Zavadil, C.; Schafer, G.; Culig, Z.; Brunner, A. Tumor-infiltrating immune cell subpopulations influence the oncologic outcome after intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy in bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 39916–39930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.J.; Nguyen, P.H.D.; Wasser, M.; Kumar, P.; Lee, Y.H.; Nasir, N.J.M.; et al. Immunological hallmarks for clinical response to BCG in bladder cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 615091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, H.; Nishimura, K.; Tsujimura, A.; Nakai, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Aozasa, K.; et al. Increased infiltration of tumor associated macrophages is associated with poor prognosis of bladder carcinoma in situ after intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin instillation. J. Urol. 2009, 181, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriano, F.; Santini, D.; Perrone, G.; Amato, M.; Vincenzi, B.; Tonini, G.; et al. Tumor associated macrophages polarization dictates the efficacy of BCG instillation in non-muscle invasive urothelial bladder cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 32, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videira, P.A.; Calais, F.M.; Correia, M.; Ligeiro, D.; Crespo, H.J.; Calais, F.; et al. Efficacy of Bacille Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy predicted by expression of antigen-presenting molecules and chemokines. Urology 2009, 74, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayari, C.; LaRue, H.; Hovington, H.; Decobert, M.; Harel, F.; Bergeron, A.; et al. Bladder tumor infiltrating mature dendritic cells and macrophages as predictors of response to Bacillus Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy. Eur. Urol. 2009, 55, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutkin, V.; Pode, D.; Pikarsky, E.; Mandelboim, O. The expression level of ligands for natural killer cell receptors predicts response to bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy: A pilot study. J. Urol. 2007, 178, 2660–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breyer, J.; Wirtz, R.M.; Erben, P.; Rinaldetti, S.; Worst, T.S.; Stoehr, R.; et al. FOXM1 overexpression is associated with adverse outcome and predicts response to intravesical instillation therapy in stage pT1 non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2019, 123, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.K.; Cho, K.S.; Chung, J.; Joung, J.Y.; Park, W.S.; Chung, M.K.; et al. Prognostic value of p53 and Ki-67 expression in intermediate-risk patients with nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer receiving adjuvant intravesical mitomycin C therapy. Urology 2010, 76, 512.e1–512.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ABCAM-a, C. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: Update of a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data advanced bladder cancer (ABC) meta-analysis collaboration. Eur. Urol. 2005, 48, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Van Allen, E.M.; Mouw, K.W.; Kim, P.; Iyer, G.; Wagle, N.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; et al. Somatic ERCC2 mutations correlate with cisplatin sensitivity in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1140–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Plimack, E.R.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Garraway, L.A.; Bellmunt, J.; Van Allen, E.; et al. Clinical validation of chemotherapy response biomarker ERCC2 in muscle-invasive urothelial bladder carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1094–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, G.; Balar, A.V.; Milowsky, M.I.; Bochner, B.H.; Dalbagni, G.; Donat, S.M.; et al. Multicenter prospective phase ii trial of neoadjuvant dose-dense gemcitabine plus cisplatin in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimack, E.R.; Dunbrack, R.L.; Brennan, T.A.; Andrake, M.D.; Zhou, Y.; Serebriiskii, I.G.; et al. Defects in DNA repair genes predict response to neoadjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenendijk, F.H.; de Jong, J.; Fransen van de Putte, E.E.; Michaut, M.; Schlicker, A.; Peters, D.; et al. ERBB2 Mutations Characterize a subgroup of muscle-invasive bladder cancers with excellent response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taber, A.; Christensen, E.; Lamy, P.; Nordentoft, I.; Prip, F.; Lindskrog, S.V.; et al. Molecular correlates of cisplatin-based chemotherapy response in muscle invasive bladder cancer by integrated multi-omics analysis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, E.; Birkenkamp-Demtröder, K.; Sethi, H.; Shchegrova, S.; Salari, R.; Nordentoft, I.; et al. Early detection of metastatic relapse and monitoring of therapeutic efficacy by ultra-deep sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA in patients with urothelial bladder carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.; Porten, S.; Kim, S.; Willis, D.; Plimack, E.R.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; et al. Identification of distinct basal and luminal subtypes of muscle-invasive bladder cancer with different sensitivities to frontline chemotherapy. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damrauer, J.S.; Hoadley, K.A.; Chism, D.D.; Fan, C.; Tiganelli, C.J.; Wobker, S.E.; et al. Intrinsic subtypes of high-grade bladder cancer reflect the hallmarks of breast cancer biology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3110–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConkey, D.J.; Choi, W.; Shen, Y.; Lee, I.L.; Porten, S.; Matin, S.F.; et al. A prognostic gene expression signature in the molecular classification of chemotherapy-naïve urothelial cancer is predictive of clinical outcomes from neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A phase 2 trial of dose-dense methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin with bevacizumab in urothelial cancer. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seiler, R.; Ashab, H.A.D.; Erho, N.; van Rhijn, B.W.G.; Winters, B.; Douglas, J.; et al. Impact of Molecular Subtypes in Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer on Predicting Response and Survival after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taber, A.; Christensen, E.; Lamy, P.; Agerbæk, M.; Jensen, J.B.; Dyrskjøt, L. Reply to: Reconciling differences in impact of molecular subtyping on response to cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Necchi, A.; Raggi, D.; Gallina, A.; Ross, J.S.; Farè, E.; Giannatempo, P.; et al. Impact of molecular subtyping and immune infiltration on pathological response and outcome following neoadjuvant pembrolizumab in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariathasan, S.; Turley, S.J.; Nickles, D.; Castiglioni, A.; Yuen, K.; Wang, Y.; et al. TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells. Nature 2018, 554, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.C.; Bondaruk, J.; Yao, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lee, S.; et al. Assessment of luminal and basal phenotypes in bladder cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, T.; Durán, I.; van der Heijden, M.S.; Loriot, Y.; Vogelzang, N.J.; De Giorgi, U.; et al. Atezolizumab versus chemotherapy in patients with platinum-treated locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (IMvigor211): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrylak, D.P.; Powles, T.; Bellmunt, J.; Braiteh, F.; Loriot, Y.; Morales-Barrera, R.; et al. Atezolizumab (MPDL3280A) Monotherapy for patients with metastatic urothelial cancer: Long-term outcomes from a phase 1 study. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, J.E.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Powles, T.; van der Heijden, M.S.; Balar, A.V.; Necchi, A.; et al. Atezolizumab in patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma who have progressed following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy: A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.R.; Ellerton, J.; Infante, J.R.; Agrawal, M.; Gordon, M.; Aljumaily, R.; et al. Avelumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma after platinum failure (JAVELIN Solid Tumor): Pooled results from two expansion cohorts of an open-label, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; O’Donnell, P.H.; Massard, C.; Arkenau, H.T.; Friedlander, T.W.; Hoimes, C.J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of durvalumab in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: Updated results from a phase 1/2 open-label study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, e172411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Retz, M.; Siefker-Radtke, A.; Baron, A.; Necchi, A.; Bedke, J.; et al. Nivolumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma after platinum therapy (CheckMate 275): A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellmunt, J.; de Wit, R.; Vaughn, D.J.; Fradet, Y.; Lee, J.L.; Fong, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab as second-line therapy for advanced urothelial carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necchi, A.; Anichini, A.; Raggi, D.; Briganti, A.; Massa, S.; Lucianò, R.; et al. Pembrolizumab as neoadjuvant therapy before radical cystectomy in Patients With Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Bladder Carcinoma (PURE-01): An open-label, single-arm, phase II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3353–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Kockx, M.; Rodriguez-Vida, A.; Duran, I.; Crabb, S.J.; Van Der Heijden, M.S.; et al. Clinical efficacy and biomarker analysis of neoadjuvant atezolizumab in operable urothelial carcinoma in the ABACUS trial. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1706–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandini, M.; Ross, J.S.; Raggi, D.; Gallina, A.; Colecchia, M.; Lucianò, R.; et al. Predicting the pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant pembrolizumab in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babjuk, M.; Burger, M.; Capoun, O.; Cohen, D.; Compérat, E.M.; Dominguez Escrig, J.L.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (Ta, T1, and Carcinoma in Situ). Eur. Urol. 2022, 81, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, A.M.; Li, R.; O’Donnell, M.A.; Black, P.C.; Roupret, M.; Catto, J.W.; et al. Predicting response to intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy: Are we there yet? a systematic review. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Gilbert, S.M.; Kamat, A.M. Unraveling the mechanism of the antitumor activity of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Eur. Urol. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Thalmann, G.N.; Dewald, B.; Baggiolini, M.; Studer, U.E. Interleukin-8 expression in the urine after bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy: A potential prognostic factor of tumor recurrence and progression. J. Urol. 1997, 158, 1340–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thalmann, G.N.; Sermier, A.; Rentsch, C.; Möhrle, K.; Cecchini, M.G.; Studer, U.E. Urinary Interleukin-8 and 18 predict the response of superficial bladder cancer to intravesical therapy with bacillus Calmette-Guerin. J. Urol. 2000, 164, 2129–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, A.M.; Briggman, J.; Urbauer, D.L.; Svatek, R.; Nogueras González, G.M.; Anderson, R.; et al. Cytokine Panel for Response to Intravesical Therapy (CyPRIT): Nomogram of Changes in Urinary Cytokine Levels Predicts Patient Response to Bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Gu, J.; Ye, Y.; Williams, S.B.; Dinney, C.P.; Wu, X.; et al. High baseline levels of interleukin-8 in leukocytes and urine predict tumor recurrence in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer patients receiving bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy: A long-term survival analysis. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1265719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Kamat, A.M.; Dai, Y.; Pagano, I.; Chen, R.; Sun, Y.; et al. Application of a multiplex urinalysis test for the prediction of intravesical BCG treatment response: A pilot study. Cancer Biomark. 2022, 33, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipp, B.R.; Karnes, R.J.; Brankley, S.M.; Harwood, A.R.; Pankratz, V.S.; Sebo, T.J.; et al. Monitoring intravesical therapy for superficial bladder cancer using fluorescence in situ hybridization. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitson, J.; Berry, A.; Carroll, P.; Konety, B. A multicolour fluorescence in situ hybridization test predicts recurrence in patients with high-risk superficial bladder tumours undergoing intravesical therapy. BJU Int. 2009, 104, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengual, L.; Marín-Aguilera, M.; Ribal, M.J.; Burset, M.; Villavicencio, H.; Oliver, A.; et al. Clinical utility of fluorescent in situ hybridization for the surveillance of bladder cancer patients treated with bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, S.; Zlobec, I.; Thalmann, G.N.; Engeler, D.; Schmauss, M.; Lehmann, K.; et al. The prognostic value of cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridization in the follow-up of nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer after intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy. Int. J. Cancer. 2009, 124, 2899–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liem, E.; Baard, J.; Cauberg, E.C.C.; Bus, M.T.J.; de Bruin, D.M.; Laguna Pes, M.P.; et al. Fluorescence in situ hybridization as prognostic predictor of tumor recurrence during treatment with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy for intermediate- and high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, A.M.; Dickstein, R.J.; Messetti, F.; Anderson, R.; Pretzsch, S.M.; Gonzalez, G.N.; et al. Use of fluorescence in situ hybridization to predict response to bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy for bladder cancer: Results of a prospective trial. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, Y.; Inman, B.A.; Davis, L.G.; Kassouf, W.; Messing, E.; Daneshmand, S.; et al. Evaluation of the fluorescence in situ hybridization test to predict recurrence and/or progression of disease after bacillus Calmette-Guérin for primary high grade nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer: Results from a prospective multicenter trial. J. Urol. 2019, 202, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, A.M.; Willis, D.L.; Dickstein, R.J.; Anderson, R.; Nogueras-González, G.; Katz, R.L.; et al. Novel fluorescence in situ hybridization-based definition of bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) failure for use in enhancing recruitment into clinical trials of intravesical therapies. BJU Int. 2016, 117, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eich, M.L.; Rodriguez Pena, M.D.C.; Springer, S.U.; Taheri, D.; Tregnago, A.C.; Salles, D.C.; et al. Incidence and distribution of UroSEEK gene panel in a multi-institutional cohort of bladder urothelial carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msaouel, P.; Koutsilieris, M. Diagnostic value of circulating tumor cell detection in bladder and urothelial cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2011, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, W.; Deng, Q.; Tang, S.; Wang, P.; Xu, P.; et al. The prognostic and diagnostic value of circulating tumor cells in bladder cancer and upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A meta-analysis of 30 published studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59527–59538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rink, M.; Chun, F.K.; Dahlem, R.; Soave, A.; Minner, S.; Hansen, J.; et al. Prognostic role and HER2 expression of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood of patients prior to radical cystectomy: A prospective study. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Du, L.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhan, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Evaluation of serum exosomal LncRNA-based biomarker panel for diagnosis and recurrence prediction of bladder cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Gu, L.; Gao, Y.; et al. MicroRNAs with prognostic significance in bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkenkamp-Demtröder, K.; Nordentoft, I.; Christensen, E.; Høyer, S.; Reinert, T.; Vang, S.; et al. Genomic alterations in liquid biopsies from patients with bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Assaf, Z.J.; Davarpanah, N.; Banchereau, R.; Szabados, B.E.; Yuen, K.C.; et al. ctDNA guiding adjuvant immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma. Nature 2021, 595, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindskrog, S.V.; Prip, F.; Lamy, P.; Taber, A.; Groeneveld, C.S.; Birkenkamp-Demtröder, K.; et al. An integrated multi-omics analysis identifies prognostic molecular subtypes of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boorjian, S.A.; Alemozaffar, M.; Konety, B.R.; Shore, N.D.; Gomella, L.G.; Kamat, A.M.; et al. Intravesical nadofaragene firadenovec gene therapy for BCG-unresponsive non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A single-arm, open-label, repeat-dose clinical trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.P.N.V.; Boorjian, S.A.; Alemozaffar, M.; Konety, B.R.; Shore, N.D.; et al. Anti-Adenoviral Antibody Levels Predict Nadofaragene Firadenovec Response in BCG-Unresponsive NMIBC: Results from a Phase 3 Trial; AUA Annual Meeting: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
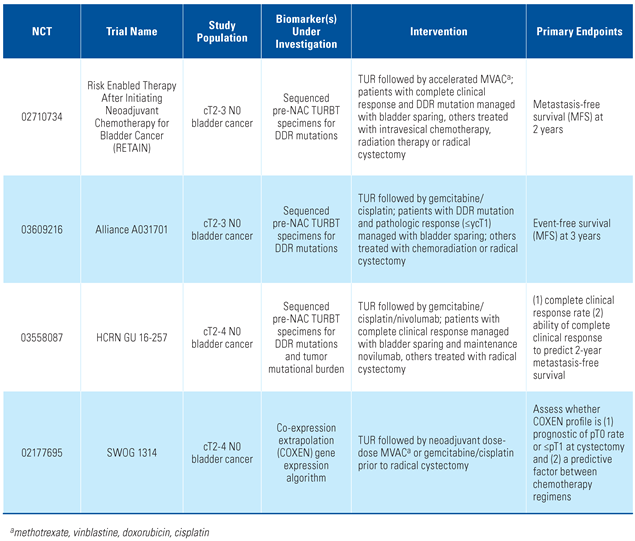
- Culp, S.H.; Dickstein, R.J.; Grossman, H.B.; Pretzsch, S.M.; Porten, S.; Daneshmand, S.; et al. Refining patient selection for neoadjuvant chemotherapy before radical cystectomy. J. Urol. 2014, 191, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, P.J.; Bree, K.K.; Campbell, M.T.; Alhalabi, O.; Kokorovic, A.; Miest, T.; et al. Progression of disease after BCG therapy: Refining patient selection for neoadjuvant chemotherapy before radical cystectomy. J. Urol. 2021, 206, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxley, P.; Plets, M.; Flaig, T.W. Review of SWOG S1314: Lessons from a randomized phase II study of Co-Expression Extrapolation (COXEN) with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Localized, Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Bladder Cancer. 2020, 6, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukhtina, E.; Pradere, B.; Mori, K.; Schuettfort, V.M.; Quhal, F.; Mostafaei, H.; et al. Catalog of prognostic tissue-based biomarkers in patients treated with neoadjuvant systemic therapy for urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: A systematic review. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley, P.J.; Kyprianou, N.; Purdom, M.S.; He, D.; DiCarlo, V.; Wang, C.; et al. Predictive value of phenotypic signatures of bladder cancer response to cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 572.e1–572.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, P.; Moran, G.W.; Li, G.; Robins, D.J.; Matulay, J.T.; Herr, H.W.; et al. Conservative management following complete clinical response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy of muscle invasive bladder cancer: Contemporary outcomes of a multi-institutional cohort study. J. Urol. 2018, 200, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachos, I.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Vandoros, G.P.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Papatsoris, A.G.; Podimatas, T.; et al. Predictive value of telomerase reverse transcriptase expression in patients with high risk superficial bladder cancer treated with adjuvant BCG immunotherapy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 135, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormio, L.; Tolve, I.; Annese, P.; Saracino, A.; Zamparese, R.; Sanguedolce, F.; et al. Altered p53 and pRb expression is predictive of response to BCG treatment in T1G3 bladder cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 4201–4204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Múgica, M.; Cebrian, V.; Fernández-Gómez, J.M.; Fresno, F.; Escaf, S.; Sánchez-Carbayo, M. Myopodin methylation is associated with clinical outcome in patients with T1G3 bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2010, 184, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirotake, S.; Miyajima, A.; Kosaka, T.; Tanaka, N.; Maeda, T.; Kikuchi, E.; et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression and microvessel density in human bladder cancer. Urology 2011, 77, 1009.e19–1009.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.; Severino, P.F.; Silva, M.; Miranda, A.; Tavares, A.; Pereira, S.; et al. Response of high-risk of recurrence/progression bladder tumours expressing sialyl-Tn and sialyl-6-T to BCG immunotherapy. Br. J. Cancer. 2013, 109, 2106–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, V.; Bozkurt, O.; Demir, O.; Tuna, B.; Yorukoglu, K.; Ellidokuz, H.; et al. Prognostic significance of Nestin expression in pT1 high-grade bladder urothelial carcinoma patients treated with intravesical BCG. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 10813–10817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Varn, F.S.; Marsit, C.J. E2F4 program is predictive of progression and intravesical immunotherapy efficacy in bladder cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raspollini, M.R.; Luque, R.J.; Menendez, C.L.; Bollito, E.; Brunelli, M.; Martignoni, G.; et al. T1 high-grade bladder carcinoma outcome: The role of p16, topoisomerase-IIα, survivin, and E-cadherin. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 57, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, R.; Zilber, S.; Di Natale, R.G.; Kedar, D.; Lifshitz, D.A.; Yossepowitch, O.; et al. Heat shock proteins 60 and 70 are associated with longterm outcome of T1-stage high-grade urothelial tumors of the bladder treated with intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy. Urol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 531.e9–531.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Hu, X.; Yang, Z.; Lia, T.; Yang, W.; Wu, K.; et al. Prognostic factors of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: A study based on next-generation sequencing. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
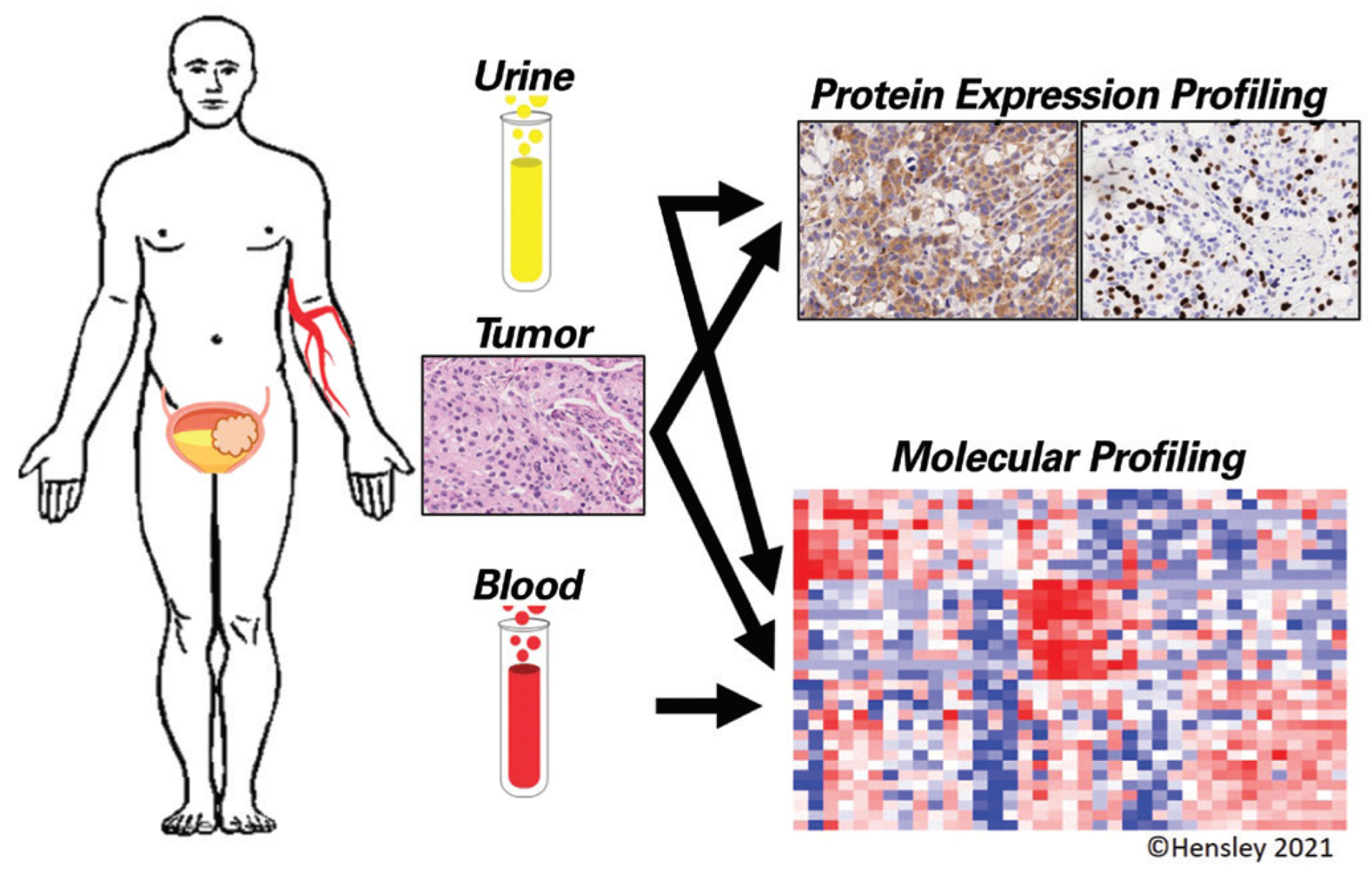

This is an open access article under the terms of a license that permits non-commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. © 2022 The Authors. Société Internationale d'Urologie Journal, published by the Société Internationale d'Urologie, Canada.
Share and Cite
Hensley, P.J.; Lobo, N.; Bree, K.K.; Tan, W.S.; Gontero, P.; Williams, S.B.; Guo, C.C.; Giannarini, G.; Dyrskjøt, L.; Kamat, A.M. Predictive Biomarkers in the Management of Bladder Cancer: Perspectives in an Evolving Therapeutic Landscape. Soc. Int. Urol. J. 2022, 3, 245-257. https://doi.org/10.48083/RVZV1144
Hensley PJ, Lobo N, Bree KK, Tan WS, Gontero P, Williams SB, Guo CC, Giannarini G, Dyrskjøt L, Kamat AM. Predictive Biomarkers in the Management of Bladder Cancer: Perspectives in an Evolving Therapeutic Landscape. Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal. 2022; 3(4):245-257. https://doi.org/10.48083/RVZV1144
Chicago/Turabian StyleHensley, Patrick J., Niyati Lobo, Kelly K. Bree, Wei Shen Tan, Paolo Gontero, Stephen B. Williams, Charles C. Guo, Gianluca Giannarini, Lars Dyrskjøt, and Ashish M. Kamat. 2022. "Predictive Biomarkers in the Management of Bladder Cancer: Perspectives in an Evolving Therapeutic Landscape" Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal 3, no. 4: 245-257. https://doi.org/10.48083/RVZV1144
APA StyleHensley, P. J., Lobo, N., Bree, K. K., Tan, W. S., Gontero, P., Williams, S. B., Guo, C. C., Giannarini, G., Dyrskjøt, L., & Kamat, A. M. (2022). Predictive Biomarkers in the Management of Bladder Cancer: Perspectives in an Evolving Therapeutic Landscape. Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal, 3(4), 245-257. https://doi.org/10.48083/RVZV1144




