- Article
Long-Term Patient-Reported Outcomes of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Haematuria Due to Radiation Cystitis Secondary to External Beam Radiotherapy for Pelvic Malignancy
- Thomas Milton,
- Darcy Noll and
- Peter Stapleton
- + 7 authors
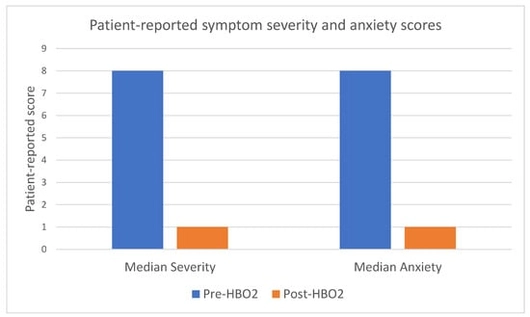
Background/Objectives: To determine long-term patient-reported outcomes for patients undergoing hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO2) following external beam radiotherapy. Methods: A retrospective cohort study of all consecutive patients who underwent HBO2 for radiation cystitis in South Australia from September 2017 to March 2023 was performed. Patient-reported symptom severity, anxiety, healthcare use and transfusion requirements pre- and post-treatment were collected through telephone interview. Readmission data and procedural data was collected through both telephone interview and a state-wide electronic medical record. Jamovi was used to perform paired sample t-tests for statistical analysis. Results: There were 89 patients who underwent HBO2 for radiation cystitis with 54 completing the questionnaire. There were 85% of patients alive at the time of follow-up, with 61% of the total cohort and 74% of survivors completing the questionnaire. For those completing the questionnaire, 96% were male with all of them having prostate cancer. Median age was 74 (interquartile range [IQR] 69–78). The mean reduction in patients’ perceived symptom severity after HBO2 on a scale out of 10 was 7.9 to 2 with a difference of 5.9 (95% confidence interval [CI] 5.1–6.7, p < 0.001) and the mean reduction in perceived anxiety was 6.9 to 2.1 with a difference of 4.7 (95% CI 3.6–5.8 p < 0.001). Patients reported a reduction in family doctor visits from 2.7 to 0.76 with a mean reduction of 2 (95% CI 0.8 to 3.2, p = 0.003), emergency department presentations from 3.3 to 0.57 with a mean reduction of 2.7 (95% CI 1.4–4.1, p ≤ 0.001) and blood transfusions from 0.67 to 0.31 with a mean reduction of 0.34 (95% CI −0.44 to 1.1, p = 0.017). Ongoing haematuria was reported in 21 of the 54 patients (39%). Further treatment was required for 20 patients (25%). No patients reported any severe or ongoing adverse effects from HBO2 via the questionnaire. Conclusions: HBO2 is a safe option for recurrent haematuria due to radiation cystitis with high patient satisfaction and reduction in patient-perceived symptom severity, anxiety and healthcare utilisation. Level of evidence: 4.
21 October 2025