Malnutrition, Sarcopenia, and Malnutrition Sarcopenia Syndrome in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
Highlights
- The prevalence of malnutrition and sarcopenia in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) patients was assessed using GLIM and EWGSOP2 criteria.
- 77.65% of patients were malnourished, 20% had sarcopenia, and 8.23% presented with the combined malnutrition-sarcopenia syndrome.
- Malnourished patients had significantly lower body weight, height, and muscle mass, as well as poorer health-related quality of life scores.
- Muscle mass was measured using bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), and sarcopenia was screened based on international guidelines.
- The study highlights the need for systematic screening for malnutrition and sarcopenia in IPF to improve comprehensive patient management.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Setting of Study
2.2. Evaluation of Nutritional Status
- Unintentional weight loss: more than 5% of usual body weight lost within the past six months, or more than 10% lost over more than six months.
- Low body mass index (BMI): less than 20 kg/m2 for individuals under 70 years old, and less than 22 kg/m2 for those 70 years or older.
- Low muscle mass (LMM): ASMM (appendicular skeletal muscle mass measured by BIVA) <20 kg for men and <15 kg for women, or ASMI (appendicular skeletal muscle mass index) <7.0 kg/m2 for men and <5.5 kg/m2 for women.
- 4.
- Disease burden/inflammatory condition was identified in all participants diagnosed with IPF.
2.3. Evaluation of Sarcopenia
2.4. Evaluation of Malnutrition-Sarcopenia Syndrome (MSS)
2.5. Respiratory Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
- a.
- General Characterization of the Study Population
- b.
- Malnutrition
- c.
- Sarcopenia
- d.
- Malnutrition-Sarcopenia Syndrome (MSS)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.-F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podolanczuk, A.J.; Thomson, C.C.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Martinez, F.J.; Kolb, M.; Raghu, G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: State of the art for 2023. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuter, M.; Ehlers-Tenenbaum, S.; Palmowski, K.; Bruhwyler, J.; Oltmanns, U.; Muley, T.; Heussel, C.P.; Warth, A.; Kolb, M.; Herth, F.J.F. Impact of comorbidities on mortality in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuka, Y.; Handa, T.; Kokosi, M.; Tanizawa, K.; Puglisi, S.; Jacob, J.; Sokai, A.; Ikezoe, K.; Kanatani, K.T.; Kubo, T.; et al. The clinical significance of body weight loss in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. Respiration 2018, 96, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jang, J.H.; Jang, H.-J.; Kim, S.Y.; Chung, M.P.; Yoo, H.; Jeong, S.H.; Song, J.W.; Lee, H.L.; Choi, S.M.; et al. New prognostic scoring system for mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by modifying the gender, age, and physiology model with desaturation during the six-minute walk test. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1052129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.; Correia, M.; Gonzalez, M.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.-P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society. ATS statement: Guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.W.; Quirk, F.H.; Baveystock, C.M.; Littlejohns, P. A self-complete measure of health status for chronic airflow limitation. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1992, 145, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeeren, M.; Creutzberg, E.; Schols, A.; Postma, D.; Pieters, W.; Roldaan, A.; Wouters, E. Prevalence of nutritional depletion in a large out-patient population of patients with COPD. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosío, B.G.; Hernández, C.; Chiner, E.; Gimeno-Santos, E.; Pleguezuelos, E.; Seijas, N.; Rigau, D.; López-Campos, J.L.; Soler-Cataluña, J.J.; Calle, M.; et al. Spanish COPD guidelines (gesepoc 2021): Non-pharmacological treatment update. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2022, 58, T345–T351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faverio, P.; Fumagalli, A.; Conti, S.; Madotto, F.; Bini, F.; Harari, S.; Mondoni, M.; Oggionni, T.; Barisione, E.; Ceruti, P.; et al. Sarcopenia in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A prospective study exploring prevalence, associated factors and diagnostic approach. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, S.; Gilliland, J.; O’Connor, C.; Seabrook, J.A.; Mura, M.; Madill, J. Fat-free mass index controlled for age and sex and malnutrition are predictors of survival in interstitial lung disease. Respiration 2021, 100, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faverio, P.; Bocchino, M.; Caminati, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Gasbarra, M.; Iovino, P.; Petruzzi, A.; Scalfi, L.; Sebastiani, A.; Stanziola, A.A.; et al. Nutrition in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Critical issues analysis and future research directions. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Zhou, S.; Song, M.; Ouyang, X.; Tan, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Peng, H. Prevalence and prognostic value of malnutrition in patients with IPF using three scoring systems. Respir. Med. 2024, 233, 107774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjrawi, A.A.; Mathers, L.; Webster, S.; Corte, T.J.; Carey, S. Nutritional status and quality of life in interstitial lung disease: A prospective cohort study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Ohkubo, H.; Nakano, A.; Mori, Y.; Fukumitsu, K.; Fukuda, S.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Uemura, T.; Tajiri, T.; Maeno, K.; et al. Frequency and impact on clinical outcomes of sarcopenia in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2022, 19, 14799731221117298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandewoude, M.F.; Alish, C.J.; Sauer, A.C.; Hegazi, R.A. Malnutrition-sarcopenia syndrome: Is this the future of nutrition screening and assessment for older adults? J. Aging. Res. 2012, 2012, 651570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, A.T.; Santos, C.; Cravo, M.; Vinhas, M.D.C.; Morais, C.; Carolino, E.; Mendes, L.; Vieira, J.R.; Fonseca, J. Handgrip dynamometry and Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment in patients with nonresectable lung cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccialanza, R.; Cereda, E.; Klersy, C.; Bonardi, C.; Cappello, S.; Quarleri, L.; Turri, A.; Montagna, E.; Iacona, I.; Valentino, F.; et al. Phase angle and handgrip strength are sensitive early markers of energy intake in hypophagic, non-surgical patients at nutritional risk, with contraindications to enteral nutrition. Nutrients 2015, 7, 1828–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Jiménez, R.; Dalla-Rovere, L.; García-Olivares, M.; Abuín-Fernández, J.; Sánchez-Torralvo, F.J.; Doulatram-Gamgaram, V.K.; Hernández-Sanchez, A.M.; García-Almeida, J.M. Phase angle and handgrip strength as a predictor of disease-related malnutrition in admitted patients: 12-month mortality. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávalos-Yerovi, V.; Marco, E.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, D.; Guillen-Solà, A.; Duran, X.; Pascual, E.M.; Muniesa, J.M.; Escalada, F.; Duarte, E. Sarcopenia according to the revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis (EWGSOP2) criteria predicts hospitalizations and long-term mortality in rehabilitation patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 20, 1047–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadrous, H.F.; Collazo-Clavell, M.; Ryu, J.H. Body mass index and mortality in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2007, 131, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Vestbo, J.; Prescott, E.; Almdal, T.; Dahl, M.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Andersen, T.; Sørensen, T.I.A.; Lange, P. Body mass, fat-free body mass, and prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease from a random population sample: Findings from the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouneau, S.; Rousseau, C.; Lederlin, M.; Lescoat, A.; Kerjouan, M.; Chauvin, P.; Luque-Paz, D.; Guillot, S.; Oger, E.; Vernhet, L.; et al. Malnutrition and decreased food intake at diagnosis are associated with hospitalization and mortality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Jiménez, R.; Cesar, E.C.; García, A.S.; Hernández, F.E.; Vegas-Aguilar, I.M.; Amaya-Campos, M.d.M.; Cornejo-Pareja, I.; Guirado-Peláez, P.; Simón-Frapolli, V.; Murri, M.; et al. Rectus Femoris Cross-Sectional Area and Phase Angle as Predictors of 12-Month Mortality in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Patients. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuka, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Kono, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Hashimoto, D.; Yokomura, K.; Inoue, Y.; Yasui, H.; Hozumi, H.; Karayama, M.; et al. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index is a predictor of tolerability of antifibrotic therapy and mortality risk in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2023, 28, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
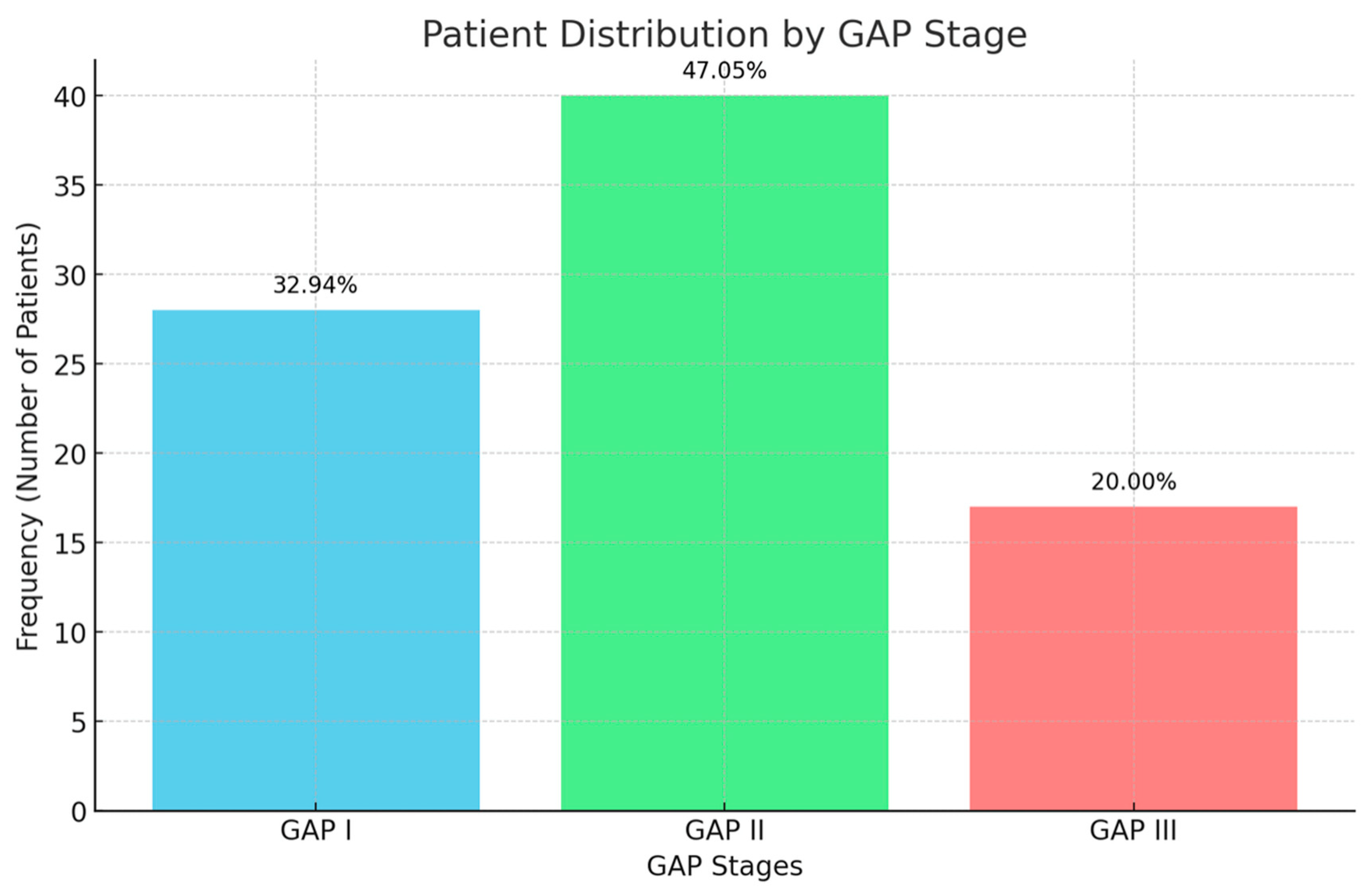
| Variable | Malnutrition (n = 66) | Non-Malnutrition (n = 19) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 71.08 ± 7.13 | 70.90 ± 7.72 | 0.924 |
| Weight (kg) | 76.86 ± 12.29 | 86.73 ± 10.29 | 0.002 |
| Height (cm) | 168.02 ± 8.27 | 172.21 ± 6.33 | 0.044 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.16 ± 3.33 | 29.30 ± 3.52 | 0.017 |
| ASMM (kg) | 19.61 ± 3.13 | 23.18 ± 2.30 | <0.001 |
| ASMI_Sarc | 6.91 ± 0.71 | 7.81 ± 0.53 | <0.001 |
| HGS (kg) | 31.66 ± 10.15 | 37.21 ± 7.99 | 0.031 |
| TUG (s) | 7.87 ± 2.28 | 7.08 ± 1.40 | 0.105 |
| 6 MWT (m) | 410.68 ± 72.22 | 411.25 ± 36.06 | 0.602 |
| GAP I | 26.8% | 5.6% | 0.198 |
| GAP II | 33.8% | 14.1% | |
| GAP III | 18.3% | 1.4% | |
| DLCO (%) | 49.06 ± 18.01 | 51.64 ± 15.20 | 0.628 |
| KCO (%) | 77.04 ± 21.55 | 85.92 ± 19.22 | 0.124 |
| FVC (%) | 2539.76 ± 775.36 | 2884.44 ± 744.48 | 0.100 |
| CRSG tot | 48.55 ± 25.37 | 28.27 ± 19.10 | 0.006 |
| CRSG symptoms | 37.66 ± 20.00 | 25.75 ± 15.21 | 0.038 |
| CRSG act | 74.81 ± 30.85 | 54.61 ± 43.04 | 0.049 |
| CRSG imp | 36.85 ± 28.94 | 14.03 ± 12.55 | 0.004 |
| SF-12 Physical | 35.54 ± 10.72 | 42.44 ± 8.76 | 0.027 |
| SF-12 Mental | 45.72 ± 13.96 | 42.06 ± 13.25 | 0.372 |
| Variable | Sarcopenic (n = 17) | Non-Sarcopenic (n = 67) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 73.90 ± 7.19 | 70.21 ± 7.07 | 0.049 |
| Weight (kg) | 72.83 ± 9.87 | 80.86 ± 12.69 | 0.013 |
| Height (cm) | 162.26 ± 7.30 | 170.88 ± 7.20 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.71 ± 3.71 | 27.61 ± 3.43 | 0.919 |
| ASMM (kg) | 16.96 ± 1.75 | 21.40 ± 2.98 | <0.001 |
| ASMI_Sarc | 6.44 ± 0.46 | 7.31 ± 0.73 | <0.001 |
| HGS (kg) | 20.19 ± 4.39 | 36.56 ± 7.84 | <0.001 |
| TUG (s) | 9.27 ± 2.68 | 7.23 ± 1.71 | <0.001 |
| 6 MWT (m) | 384.60 ± 78.77 | 417.05 ± 61.16 | 0.160 |
| GAP I | 12.7% | 19.7% | 0.068 |
| GAP II | 7.0% | 40.8% | |
| GAP III | 2.8% | 16.9% | |
| DLCO (%) | 54.07 ± 24.46 | 48.23 ± 14.41 | 0.260 |
| KCO (%) | 78.93 ± 26.36 | 79.02 ± 19.53 | 0.989 |
| FVC (%) | 2185.00 ± 796.61 | 2753.15 ± 727.41 | 0.006 |
| CRSG tot | 57.37 ± 22.58 | 39.45 ± 24.94 | 0.016 |
| CRSG symptoms | 41.35 ± 16.69 | 32.79 ± 20.07 | 0.140 |
| CRSG act | 83.08 ± 19.88 | 65.91 ± 37.59 | 0.096 |
| CRSG imp | 47.36 ± 30.07 | 26.44 ± 25.20 | 0.009 |
| SF-12 Physical | 31.84 ± 9.93 | 38.85 ± 10.39 | 0.025 |
| SF-12 Mental | 49.58 ± 14.69 | 43.37 ± 13.29 | 0.129 |
| Variable | MSS (n = 7) | Non-MSS (n = 78) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 76.86 ± 5.18 | 70.51 ± 7.17 | 0.022 |
| Weight (kg) | 65.03 ± 7.57 | 80.32 ± 12.13 | 0.002 |
| Height (cm) | 162.71 ± 7.41 | 169.51 ± 7.89 | 0.031 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.59 ± 2.63 | 27.91 ± 3.42 | 0.015 |
| ASMM (kg) | 16.74 ± 2.15 | 20.73 ± 3.21 | 0.002 |
| ASMI_Sarc | 6.30 ± 0.48 | 7.19 ± 0.75 | 0.003 |
| HGS (kg) | 23.71 ± 2.98 | 33.72 ± 9.94 | 0.005 |
| TUG (s) | 8.17 ± 1.72 | 7.65 ± 2.17 | 0.386 |
| 6 MWT (m) | 423.75 ± 49.56 | 409.73 ± 66.78 | 0.891 |
| GAP I | 4.2 % | 28.2 % | 0.302 |
| GAP II | 2.8 % | 45.1 % | |
| GAP III | 0.0 % | 19.7 % | |
| DLCO (%) | 68.00 ± 22.73 | 48.04 ± 16.05 | 0.049 |
| KCO (%) | 93.20 ± 25.29 | 77.68 ± 20.59 | 0.072 |
| FVC (%) | 2663.33 ± 894.44 | 2616.70 ± 773.83 | 0.842 |
| CRSG tot | 60.22 ± 21.14 | 41.66 ± 25.30 | 0.071 |
| CRSG symptoms | 43.45 ± 19.51 | 33.75 ± 19.44 | 0.255 |
| CRSG act | 79.97 ± 20.49 | 68.75 ± 36.19 | 0.764 |
| CRSG imp | 53.38 ± 25.24 | 28.67 ± 26.93 | 0.022 |
| SF-12 Physical | 30.54 ± 9.38 | 38.02 ± 10.57 | 0.044 |
| SF-12 Mental | 52.78 ± 14.28 | 43.86 ± 13.52 | 0.123 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Polish Respiratory Society. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabrera-César, E.; Fernández-Jiménez, R.; Lopez-Garcia, J.; Sanmartín-Sánchez, A.; Benítez Cano-Gamonoso, M.; Asschert Agüero, I.; Espíldora-Hernández, F.; Fernandez de Rota Garcia, L.; Vega-Aguilar, I.; Amaya-Campos, M.d.M.; et al. Malnutrition, Sarcopenia, and Malnutrition Sarcopenia Syndrome in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Adv. Respir. Med. 2025, 93, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93030011
Cabrera-César E, Fernández-Jiménez R, Lopez-Garcia J, Sanmartín-Sánchez A, Benítez Cano-Gamonoso M, Asschert Agüero I, Espíldora-Hernández F, Fernandez de Rota Garcia L, Vega-Aguilar I, Amaya-Campos MdM, et al. Malnutrition, Sarcopenia, and Malnutrition Sarcopenia Syndrome in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Advances in Respiratory Medicine. 2025; 93(3):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93030011
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabrera-César, Eva, Rocío Fernández-Jiménez, Javier Lopez-Garcia, Alicia Sanmartín-Sánchez, Miguel Benítez Cano-Gamonoso, Isabel Asschert Agüero, Francisco Espíldora-Hernández, Luis Fernandez de Rota Garcia, Isabel Vega-Aguilar, Maria del Mar Amaya-Campos, and et al. 2025. "Malnutrition, Sarcopenia, and Malnutrition Sarcopenia Syndrome in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis" Advances in Respiratory Medicine 93, no. 3: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93030011
APA StyleCabrera-César, E., Fernández-Jiménez, R., Lopez-Garcia, J., Sanmartín-Sánchez, A., Benítez Cano-Gamonoso, M., Asschert Agüero, I., Espíldora-Hernández, F., Fernandez de Rota Garcia, L., Vega-Aguilar, I., Amaya-Campos, M. d. M., Tinahones, F. J., Garcia-Almeida, J. M., & Velasco-Garrido, J. L. (2025). Malnutrition, Sarcopenia, and Malnutrition Sarcopenia Syndrome in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Advances in Respiratory Medicine, 93(3), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93030011







