Abstract
Wood polymer composites (WPCs) represent a rapidly growing class of sustainable materials, formed by combining lignocellulosic fibers with thermoplastic or thermoset polymeric matrices. This review summarizes the state of the art in WPC development, emphasizing the use of recyclable (or recycled) and biodegradable polymers as matrix materials. The integration of waste wood particles into the production of WPCs addresses global environmental challenges, including plastic pollution and deforestation, by offering an alternative to conventional wood-based and petroleum-based products. Key topics covered in the review include raw material sources, fiber pre-treatments, compatibilizers, mechanical performance, water absorption behavior, thermal stability and end-use applications.
1. Introduction
Polymers have been present in practically all human-made products since antiquity. Nowadays, most of them are petrochemical industry products, and because of the massive oil output (and consequent immense scale of the petrochemical industry), such goods are highly inexpensive when compared to natural alternatives. The chemical inertness of common thermoplastics (usually named simply plastics), as well as their comparatively simple production procedures, makes them immensely significant and hardly replaceable. Their annual global output surpasses 100 Mtn, which is enormous when compared to the production of other raw materials like glass or paper. Subsequently, grand productions lead to grand wastes, especially in modern lifestyles and developed economies. Over 26 Mtn of plastic garbage are generated in Europe each year. As a result, 87% of Europeans are concerned about the environmental impact of plastic products.
However, most plastics are chemically inert, non-degradable and remain intact for years, resulting in an enormous ecological problem and a difficult waste management issue [1,2]. The very same properties that are regarded as desirable qualities for plastics, and that make them dominant in our modern lives and among all human-made products, are the same properties that stand as obstacles when the issue is the natural extinction (i.e., biodegradation) of polymers. In this sense, it is imperative to substitute conventional plastics with biodegradable and recyclable polymers [3]. In this direction, the European Commission, on the basis of available scientific evidence, has been innovatively following the EU’s plastics strategy [4], as part of the circular economy action plan [5]; the EU has been examining the possibilities of supporting the development of alternative, environmentally friendly raw materials for the manufacture of plastics, and the commission has launched a European campaign commitment to ensure that by the end of this year, 2025, ten million tons of recycled plastic will result in new products on the EU market [2].
There are basically two approaches (the 4 Rs) to reducing the environmental effect of plastics: (a) Replacing plastics with biodegradable polymers and (b) the 3Rs of circular economy: Reduce–Reuse–Recycle. Each approach has its own set of constraints. Biodegradable polymers (approach a), in particular, are challenging to utilize in long-term applications. Non-biodegradable, conventional polymers, on the other hand, are a more viable option for long-term uses (approach b). Although recycling such polymers for long-term applications is an appealing alternative, polymeric characteristics (such as mechanical or thermal strength) decrease.
The depletion of natural wood resources and, at the same time, the global plastic waste crisis have both intensified the interest in wood polymer composites (WPCs), so-called eco-friendly materials. WPCs are typically composed of a thermoplastic polymeric matrix reinforced with natural fibers, such as wood flour, sawdust or agricultural residues. The use of recyclable plastics like polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS) and poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) further enhances their environmental appeal, compared to other polymers that do not burden the environment as much as waste. More recently, the adoption of bio-sourced (and thus biodegradable) polymers, including poly(lactic acid) (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) and starch-based matrices, has broadened the potential applications of WPCs in “green” products’ development.
The final properties of WPCs can be significantly affected by the inherent characteristics of polymers when they are used as impregnating materials. WPC is typically created by infusing wooden matter with a polymer matrix, which eventually fills the voids left by lignin removal. Here is how the inherent characteristics of recycled plastics can affect WPC final properties.
Delignified wood impregnated with recyclable polymers heralds a new era in the area of sustainability. The complex integration of these ingredients not only provides an aesthetically appealing alternative to standard materials, but also demonstrates our dedication to environmental preservation. By reusing abandoned plastics, we breathe new life into these materials that have completed a cycle of use, by converting them into an eco-friendly resource that has the potential to alter the way we approach building, manufacturing and design. This approach is known as “from cradle to cradle” [6]. Several studies report the preparation of composites from lignocellulosic raw materials using, as a matrix, synthetic thermoplastics [7,8,9].
The aim and scope of this review publication is to briefly analyze selected published research papers, regarding the types of polymers used for the impregnation of wood, the production procedures, like delignification and impregnation in wood specimens, along with the final applications of the composites manufactured. A separate brief mention belongs to the innovative “transparent” wood-composite case.
2. Method of Literature Research Executed
The literature of interest for this review was composed of publications in a broad context; thus, the online search was conducted by looking for review papers based on keywords, such as “wood composites”, “recycled polymers”, “mechanical properties”, “delignification”, “solid wood” or “plastics”, as well as combining keywords related to “impregnated wood” and “delignification factors”. The Elsevier Scopus® and Google Scholar databases were chosen for the search for pertinent material. Case studies, book chapters, conference papers, postgraduate and doctoral theses, along with papers written in a language other than English, were all eliminated from the search. Review papers were, therefore, screened by title, keywords and abstract, while keeping in mind the inclusion/exclusion criteria, so that the pertinent publications were added to our list. Each paper’s main body was examined, paying close attention to the abstract, methodology and conclusion sections in particular. The data was extracted from selected studies, including variables such as polymer types, fabrication techniques, optical properties, mechanical properties and delignification methods.
Moreover, authentic pieces of research work were identified and selected, regarding specific production techniques and applications of attractive or successfully applied WPCs. Those were evaluated, and later reviewed, under certain perspectives that exemplify the purpose of this document.
3. Treatments and Pre-Treatments of Wood Specimens
According to the literature, the properties of wood composites impregnated with polymers depend on several factors, including (a) the main type of wood, (b) the polymer infused and (c) the filtration technique applied. In general, it has been found that the addition of polymers increases the strength, durability and stiffness of the resulting composites. Even special properties, like the transparency of composite materials, can be improved by using certain impregnation and curing techniques. However, more research is needed to explore the full potential of these steps and address current research gaps in the field.
Among hardwoods, the exotic–invasive hardwood species are mostly underutilized, and are even considered undesirable ones, due to their spreading, which threatens the native plants [10,11]. As fast-growing species, they do not present favorable properties for structural and strength-demanding applications in the wood industry. However, they could be utilized as an abundant and cheap source of wood material for secondary side-production. The potential of using recyclable polymers to impregnate delignified wood has not been thoroughly investigated.
Two of such underutilized invasive hardwood species, which are abundant in Greece, are the black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) and the tree-of-heaven (Ailanthus altissima), whose growth is expected to increase even more in the coming years, due to climate change [12]. Τhe potential of their utilization in the development of alternative wood applications has not been examined so far. Furthermore, both of them are characterized by high extractive contents, with more than 14 flavonoids and condensed tannins that offer biological durability to wood and the composites they participate in [13,14].
Delignification of wood, the first step, involves removing the (light-absorbing) lignin component from wood, while preserving the (translucent) cellulose structure. The process of degreasing involves removing lignin either totally or partially from wood or modifying the lignin to create an advanced, strong and durable material with improved dimensional stability. Delignification may be succeeded by densification or impregnation with polymers in order to enhance the mechanical–optical properties [15]. This technique can be achieved through various methods, such as alkaline or acetic degreasing, as well as reducing catalytic fractionation [16]. An important factor to consider is the degree of degreasing before introducing the polymer into the wood mass. The delignification phase preceding the polymer impregnation of the wood is critical. To ensure adequate amounts of delignification, several combinations of pulping and bleaching chemicals are utilized (Table 1). Curing, also referred to as thermosetting, is the last step, where polymers are cross-linked with the lignin or cellulose remaining in the wood scaffold, for further enhancement. This is a usual final hardening step, although it is not obligatory.

Table 1.
Commonest conditions applied for pulping and bleaching of wood content before delignification.
Consequently, when composites are formed from the usual thermoplastics, they present a more hydrophobic character than natural wood, and at the same time, a more hydrophilic character than neat polymers. Such a balance is affected by the amount of wood in the final material, but even high-wood-content products can be used outdoors and present significantly lower maintenance costs, compared to wood alternatives, and a lower environmental footprint, compared to plastic alternative materials.
However, final WPC products also present some major disadvantages, such as the need to maintain low temperatures during processing (to avoid severe thermal degradation of wood ingredients), higher brittleness caused by the pure dispersion of hydrophilic fibers in hydrophobic matrices, lower values in the ratio of tensile strength to density and higher cost, compared to wood [26]. Strategies to decrease cost include maximizing the amount of wood used in the composite, the production of hollow profiles and the use of recycled plastics, if readily available.
A variety of additives is included in composites, concerning processing aids (lubricants, antioxidants) and property enhancers (biocides, inorganic fillers, fire retardants, UV stabilizers, colorants, etc.) [27]. Also, wood is highly polar and hygroscopic, contrary to the typical hydrophobic nature of most thermoplastic matrices, resulting in poor compatibility. To enhance the compatibility of the filler and the matrix, various coupling agents and compatibilizing routes are used.
Modification of Wood
The inherent characteristics of fillers strongly affect the final wood properties. Therefore, wood of high hygroscopicity, anisotropic dimensional instability and low durability should be modified before impregnation. A way of enhancing the affinity between the wood matrix and the polymer is the physical or chemical treatment of wood. Physical methods (electrical discharge, mercerization, heat treatment, etc.) usually change the structural and surface properties of wood, but not its chemical composition [28]. The shape of the wood to be treated is of physical importance as well: research usually involves square or rectangular specimens of low thickness for successive impregnation of polymers, but industry may provide fibers, flakes, powders and amorphous chops as well. As is known, the mechanical endurance, apart from the components themselves, is based on the geometry of the substrate or specimens, depending on the direction of the force load transferred onto the object of the final application.
Vaccination reactions are perhaps the most important chemical method for modifying lignocellulosic fibers. According to this strategy, cellulose hydroxyl groups react with appropriate chemicals, resulting in various functional groups, which are compatible with the polymeric matrix [29,30]. The most important strategies of this kind are the treatment with acetic anhydride or with maleic anhydride. Anhydrides as compatibilizers, often grafted in polymers, not simply mixed, are used to improve the interfacial adhesion between dissimilar materials, such as polymers, wood and fillers. They achieve this by chemically bonding, producing reactions to unify the matrix with the filler. In that way, the composite functions as one body. Modified polymers with maleic anhydride have been used more than any other method to improve adhesion between polymer and lignocellulosic fibers.
Water-repellent treatment could increase the water repellency and dimensional stability of wood, as well as reduce wood checking, which is increased by outdoor weathering. Paraffin wax is the most often used water-repellent material. It is inexpensive but not ecologically sustainable (as an oil product), and there is an increasing desire for eco-friendly alternatives manufactured from renewable resources such as plant-based waxes and oils.
A novel method for improving the water-repelling qualities of wood has been developed. Linseed oil, a hydrophobic bio-product generated from flax seeds, is used. Linseed oil is a triglyceride, distinctive for its unusually large amount of α-linolenic acid, which oxidizes in air. Through oxidation and polymerization, linseed oil can be converted into a solid. When used in conventional impregnation procedures, it fills the interior structure of the wood, forming a stable coating on its pores. The disadvantage is that oxidative polymerization of linseed oil takes time (it is common knowledge that a simple coat of linseed oil applied on wooden surfaces takes a long time to “dry”). To address this, researchers investigated epoxidized linseed oil. Eventually, it was found that epoxidized linseed oil substantially increases anti-swelling performance, water repellency and durability when used to treat wood.
4. The Case of the Novel “Transparent” Wood Composites
“Transparent” wood composites is a topic that has gained considerable attention in recent years; the first study in this area was conducted by Fink in 1992. From 2001 to 2010, transparent materials, especially films made of lignocellulosic materials (mainly nanocellulose), were the research focus. Some examples of scientific publications on the topic of transparent nanocellulose-based materials are those of [12,24,31,32].
“Transparent” wood composites, according to current research discoveries, hold immense promise in “smart” building materials, solar cells, windows, energy-saving applications and light magnetic switches, as seen in Figure 1. Because all these uses rely on the optical properties of “transparent” wood composites (transmittance, haze, refractive index, surface color), they must be correctly characterized and understood. Nano- and microscale inhomogeneities in surfaces and structures have a substantial influence on light transmission and haze. Although “transparent” wood attributes may be tailored by interface modification, producing optically clear wood requires a thorough understanding of the physics driving the light/transparency wood interaction.
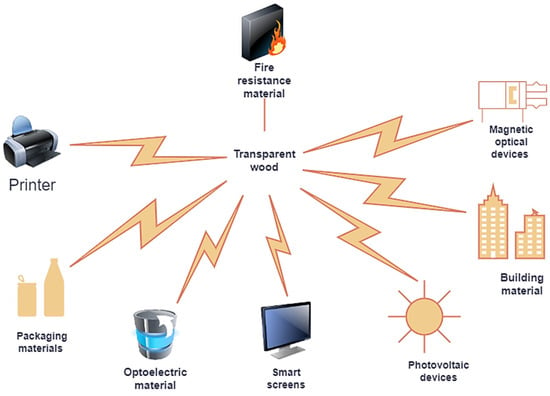
Figure 1.
Broad possible applications of WPCs.
According to the literature, while there is growing interest in “transparent” wood composites as a sustainable building material, the literature on the use of recycled polymers in them is relatively limited. There is a need for more studies investigating the use of different types of recycled polymers and their effects on the properties of the resulting composites. The types of recycled polymers used in “transparent” wood impregnation vary, but common polymers include epoxy resins, polyester resins and polyurethane resins. These polymers have been found to improve the mechanical and thermal properties of “transparent” wood composites. As for the impregnation techniques used in composite transparent wood materials, they vary depending on the desired properties of the final product. Common techniques include vacuum impregnation, pressure impregnation and soluble gel filtration. These techniques have been found to improve the resulting composites’ transparency, mechanical strength and thermal conductivity. An emerging field of application is the creation of cellulose composites with polymeric matrices with very good mechanical properties that were constructed through the densification of wood samples that had previously been delignified [14].
In the impregnation of delignified wood specimens, mainly PMMA and acrylics or epoxy resins are used. Plexiglass and PMMA, which are well-known, serve as excellent replacements for glass, due to their thermoplastic behavior toward heat and shaping, along with their great optical transparency in their amorphous state. However, some other polymers have also been mentioned in the literature for these processes. For example, Rao et al. [33] constructed a “transparent” poplar wood composite using PVA. The “transparent” wood specimens finally obtained were highly flexible, and their optical and mechanical properties were significantly improved by the addition of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) as the plasticizer. Wood/PVA composites laminated with 0.0 wt% and 50 wt% PEG exhibited high rigidity and fragility. The optical transmission of the samples was 65% and 69%, respectively, while the sample turbidity was 80% and 85%, respectively. As the PEG content in PVA increased to 100 wt%, the optical transmission and turbidity increased to 80% and 90%, respectively. Eventually, it was found that the wood/PEG composites are capable of application in diffuse light modulation, decorative lighting, optoelectronics and displays.
The research team Fu et al. created a bio-based, luminescent and hydrophobic film with excellent mechanical properties for use in optical lighting. They incorporated an organic solution of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots after modifying the microstructure of the delignified wood through chemical treatment. They then thickened it and coated it with a thin layer of hydrophobic hexadecyltrimethoxysilane through chemical vapor deposition, creating a material with potential optical applications such as solar panels and laser devices [27].
5. Types of Polymers Applied in WPCs: Plastics and Resin Examples
The process of polymer impregnation involves two steps: penetration of the reactant mixture (monomer, cross-linking agent, initiator) into the to-be-reinforced material, and its subsequent in situ polymerization. A third subsequent step, post-polymerization, may occur, known as setting or hardening, for further cross-linking among the matrices, in case the polymers’ chemistry allows it.
5.1. Polystyrene for Impregnation of Wood
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic thermoplastic polymer that is the world’s third most common after PE and PP. Its annual global output is approximately 14.6 Mtn, with a 6% yearly rise. It is produced by addition polymerization, and because of its linear macromolecular structure, it is considered a thermoplastic, and even a great thermoplastic (proven by the majority of objects manufactured by PS), with a Tg around 90 °C and a Tm around 240 °C in its high crystallinity. The majority of this quantity is utilized in construction (with expanded PS being the most often used material for building thermal insulation), 31% in packaging, and the remaining 4% in other uses [34]. As a result, the amount of polystyrene waste is rising, and recycling is now getting a lot of attention [34,35]. As 31% of PS produced (almost 4.5·106 tn) is used for single-use packaging applications, reducing its content in such porous composite materials would have a substantial environmental impact. Only a few literature studies investigate the use of PS for impregnation of delignified wood, and there is no study on using recycled PS.
Recycled PS has the potential to be a polymer matrix in the production of wood composites. Moreover, recycled PS is frequently less expensive than other transparent polymers, making it an appealing alternative for some applications. PS is rather easy to recycle, since the polymer is diluted in solvents and even in the monomer itself, which is rare in repolymerization. PS is a lightweight polymer, which might be useful in situations where weight is an issue. It is critical that the recycled PS structure is compatible with the delignified wood structure. Proper impregnation and adhesion are critical for the strength and optical clarity of the final product. PS, however, may not have the same mechanical strength as other polymers, such as epoxy resins. A careful balance of transparency and mechanical characteristics should be explored. Although employing recovered PS is a sustainable alternative, it is critical to address any potential environmental problems associated with PS, such as long-term durability and recycling possibilities for the final wood product. To obtain the appropriate level of mechanical performance, the processing conditions and procedures utilized to impregnate the wood with recycled PS must be tuned. The quality and purity of recycled PS should be carefully monitored to ensure consistent results and minimize impurities that could affect final qualities. Expanded PS (ePS) or extruded PS (xPS) are both in foam form for insulating uses, which means that when in waste, they occupy great volumes in landfills. Those types are the first to be recycled and assimilated into secondary applications.
5.2. Polyurethane for Impregnation of Wood
Polyurethanes (PUs) contribute to over 8% of all plastics manufactured, making them the world’s sixth most commonly used polymer [10]. PUs are formed as resins, because of the polycondensation reactions gradually occurring and extending, or, to some degree, cross-linking. They are broadly categorized into two types: foams and CASEs (coatings, adhesives, sealants, elastomers) [11]. Furthermore, foams are classified into two types: flexible (used in beds and automobile seats) and stiff (used in building insulation and commercial freezers). CASEs are commonly seen in sports shoes, sporting tracks, electrical devices and ship constructions. The final polyurethane products market in the EMEA region (Europe, the Middle East and Africa) are almost evenly divided between flexible foams (36%), rigid foams (32%) and CASEs. However, due to the depletion of world supplies of fossil fuels such as petroleum and the diminishing availability of landfill space, polyurethane waste processing has gained relevance all over the world in recent years.
Legislative reforms, such as the European Commission’s revision of Directive 1999/31/EC on landfilling, are also significant. Following the implementation of updated legislation on 1 January 2015, only 25% of municipal garbage can be placed in landfills, and this percentage will not exceed 5% beginning on 1 January 2030. Furthermore, the percentage of recycling and incineration should be increased greatly [10].
Recycled polyurethane (PU) is another polymer that can be considered for use as filler material in the development of wood composites. First of all, one advantage of using PU as filler is that it can be engineered to be transparent, which makes it suitable for maintaining the optical properties in wood composites. Moreover, PU comes in various foam forms, including rigid and flexible types, allowing for versatility in tailoring the properties of the final wood product. In addition, the use of recycled PU aligns with sustainability goals involving the reuse and repurposing of solid waste materials. Again, the foam type of the polymer occupies great volumes in landfills when in waste; thus, its further processing through recycling is a priority when it is consumed. PU can be engineered to have excellent mechanical properties, offering good strength, and it is known for its durability and resistance to moisture and environmental factors, which can enhance the long-term performance of wood composites. On the other hand, there are some considerations and challenges. It is essential to ensure that recycled PU is compatible with the delignified wood structure. Proper impregnation and adhesion are crucial for the final product’s strength and optical clarity. Moreover, the processing conditions and techniques used to impregnate the wood with recycled PU need to be optimized to achieve the desired level of transparency and mechanical performance. While using recycled polyurethane is a sustainable choice, it is important to address any potential environmental concerns related to polyurethane, such as its long-term durability and recycling options for the final transparent wood product. The quality and purity of recycled polyurethane should be monitored to ensure consistent results and minimize impurities that could affect transparency. The choice to use recycled PU in wood composite should be based on the specific requirements of the intended application. The readers may find the main parameters affecting WPC manufacturing in Table 2.

Table 2.
Parameters affecting the efficiency of the WPC.
The term “recycling” does not belong to only to the scientific community today, but is banalized and common for state authorities, industry and commerce, citizens and local organizations. This is why recycling processes may be perceived differently from case to case. The recycling processes may describe simpler or more drastic processes, such as for certain feedstocks, e.g., the reuse of an object after its life cycle under the same terms, the shredding of the object and the reuse of its raw material in a different form/condition, the decomposition of the material to produce the raw ingredients and attempts to remanufacture the same one, or its degradation to other secondary materials, etc. Moreover, scrap materials (the mal-manufactured products or useless shreds in industry) are non-contaminated matter, since they have not been in contact with consumers. Thus, in that concept, readers may see the variations, the broad options and the restrictions, at the same time, for the routes of “recycling” processes. This is why PE, PP, PS, PMMA and polyesters, as thermoplastics, may be reshaped and reformed easily and purified easily without losing their macromolecular skeletons, if chosen. On the contrary, resins—all kind of resins (PU and epoxy among them)—cannot be purified, reformed thermally and be reused, since they are cross-linked. Resins undergo chemical decomposition or chemical treatments, such as hydrolysis, solvolysis, swelling or pyrolysis. Thus, resins are recycled by chemical reactions depending on the degree of cross-linking and their groups. Recycling is harder for resinous polymers. This is true for elastomers that are partially cross-linked as well. This is why the literature does not include very much research on resins’ or elastomers’ actual recycling; usually, plastic recycling is studied and promoted as being more efficient and doable.
Rigid PUs owe their high density to the extensive degree of cross-linking between the polyols and the isocyanates that form the stiff network that provides mechanical tolerance. Flexible PU does not promote all possible reactions among the functional groups, so some amendment of the final properties is possible through reactants. In the case of CASE PU adhesives, sealants and coatings (which are currently the most durable coatings), they are harder to reuse, due to their blending with other substrate materials when removed.
Regarding the WPCs that have already been manufactured and studied in certain research studies, they are presented analytically in Table 3, in terms of wood type, polymers, treatment conditions and final applications. Readers may find technical information in that list.

Table 3.
Applications of WPC in the literature: details that were extracted from the publications.
6. Discussion
Based on the recommendations of the European Council Directive concerning the plastics strategy, this project suggests the production of innovative material made of significantly smaller amounts of non-biodegradable thermoplastics (i.e., PS) primarily, and then made of fully biodegradable wood-based matrices [10]. It is crucial to assess the environmental sustainability of the proposed composite material through life cycle analysis (LCA). A particular challenge of these projects is to optimize the properties of wood composites when converting them into new, environmentally friendly, high-added value and low-cost materials (better with invasive hardwood species of countries’ flora as a cellulose matrix), so that they can meet the market requirements and substitute for conventional plastic materials in various applications. Furthermore, we suggest the exploration of potential applications and commercialization prospects of the developed materials in high-added-valued commercial products in the construction industry.
6.1. Scientific Impact of WPC Manufacturing
The state-of-the-art aspects of the studies referring to the manufacture of WPCs and their potential include the following:
- The reduction of used synthetic polymers in waste through the development of WPCs using hardwood species, from low-value and low-cost (considered to be waste) invasive fast-growing species.
- Addressing the problem of the deterioration of various properties of recycled polymers during recycling processes through the development of WPCs using novel modification routes.
- The development of novel impregnation routes and compatibilization strategies for increasing the hydrophobicity of wood, apart from reagents, using supercritical CO2, tall oil and tannins.
- The development of fully biodegradable solid materials with enhanced properties due to reinforcement by recycled polymers.
- The evaluation of the recycling potential of the developed materials.
The studies aim toward the development of novel strategies for increasing the hydrophobicity of wood, which is a scientific issue that attracts significant research efforts, but it is also a very demanding task. Novel and not well-studied routes will be used, such as the impregnation of fully delignified wood using recyclable polymers. Such goals will allow new approaches for the development of “transparent” wood composites and new routes for addressing the problem of the deterioration of various properties of plastics during recycling.
Thus, the suggested research should aim to elucidate and provide answers regarding the potential of successfully mixing the suggested raw materials, the recycling potential of recovered polymers such as PS, PMMA and epoxy resins, the utilization potential of natural resources, such as the wood of invasive underutilized species, for single-use packaging materials, the impact of bio-based additives, compatibilizers and reinforcing substances, as well as the effect of novel fiber modification strategies on the properties of solid transparent wood.
The studies should aim to provide new knowledge that can be utilized in the implementation of, as well as triggering of, future research projects and the cooperation between the fields of natural resource management, biomass utilization, bio-based biodegradable materials, bio-sourced plastic production, packaging materials engineering, the reuse and recycling of materials, the circular economy, etc.
The main restrictions that make well-established practices difficult to develop are(a) the variations in the feedstock of the recycling raw materials, depending on the consumers’ habits and the municipalities’ regulations, (b) the contaminations that prevent easy and “green” treatments for purification and, certainly, (c) the mechanical abasement of the final materials, depending on the cycles of treatments. Thus, the viability of the final composites, to demonstrate actual uses in societies, demands mechanical reinforcement on one hand, hopefully with eco-friendly fillers, and physicochemical treatments on the other hand, like melting, purification and reforming, or degradation and reactions to create new polymers, with hardeners and additives. Additives may alter the final properties of the polymers, in terms of cross-linking, color shades, the UV-stabilizing and antioxidative profile, coupling possibilities with the rest of the ingredients, etc.
6.2. Social Impact, Industrial and Environmental Impact
The social impact of the research studies is obvious, since they are totally aligned with the main EU strategic policies and directives for the Reducing, Recycling and Reusing of plastics, as well as for the replacement of traditional plastics with biopolymers or bio-based polymers [65,66,67]. In more detail, the recycling of polymers for the production of WPCs could support an additional market for recycled plastics channeling and generally support the bio-based sector, creating new cross-sector interconnections in the bio-based economy. This interconnection could provide many business opportunities and create new jobs and additional economic growth, particularly in urban areas. Additionally, the production of the suggested bio-based plastics or recycled polymer-based composites would address the consumers’ awareness of and concerns about environmental and health problems arising from the use of traditional plastics and could fulfill their expectations for the use of efficient bio-based materials, consistent with the principles of the circular economy. Finally, municipal or central government authorities who are responsible for supervising and limiting the growth of invasive species in urban or natural environments could find a potential solution for the management of the resulting biomass wastes.
The industrial impact has been proven to be equally significant. The studies explore engineering solutions in the areas of biomass use, bio-based, biodegradable materials, bio-sourced plastics manufacturing, packaging materials and plastic reuse and recycling. The findings of the studies could aid industries in the sector, since they are keen on raw materials that are readily available, inexpensive in cost and environmentally friendly.
The studies aim to address the enormous ecological problem and difficult waste management problem connected to the use of conventional petroleum-based polymers [1,2]. This is accomplished by the Reuse of Recycled polymers and the Reduction of such polymers through the development of WPCs. In more detail, recycling a widely applied polymer, such as PS, PMMA or epoxy resin (with the physicochemical and mechanical restrictions each polymer shows), and its reinforcement with bio-based substances can substantially reduce the demand for the virgin polymer. Additional environmental positive impacts arise from using low-value biomass, which is actually regarded as waste, as a reinforcement agent. Finally, these practices are in alignment with EU directions [65,66,67] for the cessation of single-use plastics. This research addresses pressing environmental concerns by offering a sustainable alternative to conventional construction materials. By utilizing fully delignified wood and recycled polymers/biopolymers, this study seeks to reduce the carbon footprint of the construction industry while enhancing material performance. The findings of these studies can potentially revolutionize the construction sector, leading to “greener” and more livable manufacturing practices. These practices constitute what ordinary sustainability means, and they are applicable in many communities.
7. Conclusions
The reduction of the wasted synthetic polymers in materials through the development of WPCs from low-value, low-cost, invasive fast-growing species will eventually address numerous challenges of modern life. The natural flora of each country plays a key role in the choices of the wood type (as industrial residues). The incorporation of polymers (thermoplastics or resins) provides an opportunity to include recycled polymers as well, through the impregnation routes and compatibilization strategies for increasing the hydrophobicity of wood. Finally, the evaluation of the recycling potential of the developed materials is a matter of question. This review seems to spotlight the most crucial aspects of manufacturing WPCs, which is a good start for the field experts who are interested in researching the topic. After all, scientific research in the chemical, mechanical and applied treatments reviewed is directed in the service of developing doable, and at the same time sustainable, processes for the creation of WPCs that will address both industry needs and environmental needs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.T.; methodology, P.T. and E.C.V.; investigation, P.T.; data curation, P.T. and E.C.V.; writing—original draft preparation, P.T. and E.C.V.; writing—review and editing, D.S.A.; supervision, D.S.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CASE | Coatings, adhesives, Sealants, Elastomers |
| EC | European Commission |
| EU | European Union |
| EMEA | Europe, the Middle East and Africa |
| HDPE | High-density Polyethylene |
| LCA | Life cycle assessment |
| LDPE | Low-density Polyethylene |
| PA-6 | Polyamide-6 (or nylon-6) |
| PE & rPE | Polyethylene and recycled Polyethylene |
| PEG | Poly(ethylene glycol) |
| PHA | Polyhydroxyalkanoates |
| PLA & rPLA | Poly(lactic acid) and recycled Poly(lactic acid) |
| PMMA | Poly(methyl methacrylate) |
| PP & rPP | Polypropylene and recycled Polypropylene |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PVA | Poly(vinyl acetate) |
| PVC & rPVC | Poly(vinyl chloride) and recycled Poly(vinyl chloride) |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| WPC | Wood/Polymer Composites |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Stevens, E. Green Plastics: An Introduction to the New Science of Biodegradable Plastics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 83–134. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Press Release. 2018. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/IP_18_3927 (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Álvarez-Chávez, C.R.; Edwards, S.; Moure-Eraso, R.; Geiser, K. Sustainability of bio-based plastics: General comparative analysis and recommendations for improvement. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 23, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/strategy/plastics-strategy_en (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/strategy/circular-economy-action-plan_en (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- El-Haggar, S.M.; Kamel, M.A. Wood Plastic Composites. In Advances in Composite Materials—Analysis of Natural and Man-Made Materials; Pavla, T., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Mireja, S.; Khandelwal, V.; Arun, B.; Manik, G. Light-weight high-strength hollow glass microspheres and bamboo fiber based hybrid polypropylene composite: A strength analysis and morphological study. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 109, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh Vu, N.; Thi Tran, H.; Duy Nguyen, T. Characterization of polypropylene green composites reinforced by cellulose fibers extracted from rice straw. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 1, 1813847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, P.; Fei, B.; Yu, Y.; Xiong, H.; Tan, J. Thermal properties and crystallization behavior of bamboo fiber/high-density polyethylene composites: Nano-TiO2effects. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 39846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastics Europe Association of Plastics Manufacturers Plastics—The Facts 2019 An analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data. 2019. Available online: https://www.plasticseurope.org/en/resources/market-data (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Magnin, A.; Pollet, E.; Phalip, V.; Avérous, L. Evaluation of biological degradation of polyurethanes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 39, 107457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abral, H.; Ariksa, J.; Mahardika, M.; Handayani, D.; Aminah, I.; Sandrawati, N.; Pratama, A.B.; Fajri, N.; Sapuan, S.; Ilyas, R. Transparent and antimicrobial cellulose film from ginger nanofiber. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Li, T.; Su, H.; Ni, Y.; Yan, L. Transparent wood film incorporating carbon dots as encapsulating material for whitelight-emitting diodes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, M.; Widner, D.; Segmehl, J.S.; Casdorff, K.; Keplinger, T.; Burgert, I. Delignified and Densified Cellulose Bulk Materials with Excellent Tensile Properties for Sustainable Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5030–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, M.; Widner, D.; Segmehl, J.S.; Casdorff, K.; Keplinger, T.; Burgert, I. A highly transparent compressed wood prepared by cell wall densification. Wood Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oriez, V.; Peydecastaing, J.; Pontalier, P.Y. Lignocellulosic biomass mild alkaline fractionation and resulting extract purification processes: Conditions, yields, and purities. Clean Technol. 2020, 2, 91–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, S. Transparent Wood—A New Approach in the Functional Study of Wood Structure. Holzforschung 1992, 46, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, H. Potential strength for resin-impregnated compressed wood. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2001, 20, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, Q.; Yu, S.; Yan, M.; Berglund, L. Optically Transparent Wood from a Nanoporous Cellulosic Template: Combining Functional and Structural Performance. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Xu, L.; Jia, C.; Dai, J.; Song, J.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Anisotropic, Transparent Films with Aligned Cellulose Nanofibers. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, C.A.; Ragauskas, A.J. Effect of acid-chlorite delignification on cellulose degree of polymerization. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7410–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Kong, Z.; Yao, X.; Gan, J.; Zhan, X.; Wu, Y. Transparent wood with self-cleaning properties for next-generation smart photovoltaic panels. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 613, 155927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, H.L.; Cho, S.-W.; Kwon, G.; Lee, D.-Y.; Ma, S.-Y.; Bandi, R.; Kim, J.K.; Han, S.-Y.; Dadigala, R.; Lee, S.-H. Fabrication of eco-friendly transparent wood for UV-shielding functionality. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 201, 116918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Song, J.; Li, T.; Gong, A.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Yao, Y.; Luo, W.; Henderson, D.; Hu, L. Highly Anisotropic, Highly Transparent Wood Composites. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5181–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; O’dWyer, J.P.; Chang, V.S.; Granda, C.B.; Holtzapple, M.T. Structural features affecting biomass enzymatic digestibility. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3817–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, W.T.; Gao, L.K.; Xiao, S.L.; Zhang, W.B.; Zhan, X.X.; Li, J. Transparent magnetic wood composites based on immobilizing Fe3O4 nanoparticles into a delignified wood template. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Tu, K.; Goldhahn, C.; Keplinger, T.; Adobes-Vidal, M.; Sorieul, M.; Burgert, I. Luminescent and hydrophobic woodfilms as optical lighting materials. ACSNano 2020, 14, 13775–13783. [Google Scholar]
- Fryer, J. Field Guide for Mapping Post-Fire Soil Burn Severity; U.S. US Depart Agric, Forest Service, Fire Scie Lab: FortCollins, CO, USA, 2010.
- Wechsler, A.; Hiziroglu, S. Some of the properties of wood–plastic composites. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2637–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Bandyopadhyay, J.; Bousmina, M. Thermal and thermomechanical properties of poly[(butylene succinate)-co-adipate] nanocomposite. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, R.J.; Martini, A.; Nairn, J.; Simonsen, J.; Youngblood, J. Cellulose nanomaterials review: Structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogi, M.; Yano, H. Transparent Nanocomposites Based on Cellulose Produced by Bacteria Offer Potential Innovation in the Electronics Device Industry. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 1849–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.N.S.; Nagarajappa, G.B.; Nair, S.; Chathoth, A.M.; Pandey, K.K. Flexible transparent wood prepared from poplar veneer and polyvinyl alcohol. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 182, 107719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhong, H.; Xu, C. Fabrication and mechanism analysis of wood polymer composites with improved hydrophobicity, dimensional stability and mechanical strength. Cellulose 2023, 30, 3099–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.; Fu, G.; Jin, Z. Transparent wood prepared by polymer impregnation of rubber wood (Heveabrasiliensis Muell. Arg). BioResouces 2021, 16, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, N.M.; Rowlands, R.E. Effects of wood fiber characteristics on mechanical properties of wood/polypropylene composites. Wood Fiber Sci. 2003, 35, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Clemons, C.M. Wood–plastic composites in the United States: The interfacing of two industries. For. Prod. J. 2002, 52, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Faruk, O. Wood fibre reinforced polypropylene composites: Effects of fibre treatment and matrix modification. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 558–568. [Google Scholar]
- Mwaikambo, L.Y.; Ansell, M.P. Chemical modification of hemp, sisal, jute, and kapok fibers by alkalization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 84, 2222–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, N.M.; Matuana, L.M. Characterization of weathered wood–plastic composite surfaces using FTIR spectroscopy, contactangle, and XPS. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiyi, J.S.; McDonald, A.G.; Morrell, J.J.; Freitag, C. Effects of wood species on durability and chemical changes ofwood–plastic composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Butylina, S.; Martikka, O.; Kärki, T. Properties of wood–plastic composites made of milled birch wood and polylactic acid. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 618–624. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, G. Developments in the use of wood flour and fib resin thermoplastics. Plast. RubberCompos. 2004, 33, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Klyosov, A.A. Wood–Plastic Composites; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Clemons, C.M. Wood–plastic composites in the United States. For. Prod. J. 2010, 60, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ondiek, W.; Kondo, M.; Adachi, M.; Macadre, A.; Goda, K. Effect of surface coating and plasma treatment on mechanical properties of wood plastic composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Črešnar, K.P.; Bek, M.; Luxbacher, T.; Brunčko, M.; Zemljič, L.F. Insightintothesurfacepropertiesofwoodfiber–polymercomposites. Polymers 2021, 13, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, A.; Papadopoulos, A.N.; Policardi, F. Wood composites and their polymer binders. Polymers 2020, 12, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiyi, J.S.; McDonald, A.G. Effect of wood species on property and weathering performance of wood plastic composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukala, S.G.; Kong, I.; Kakarla, A.B.; Tshai, K.Y.; Kong, W. Preparation and characterization of wood polymer composites using sustainable raw materials. Polymers 2022, 14, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorova, A.; Hrabalova, M.; Kovalcik, R.; Wimmer, R. Surface modification of spruce wood flour and effects on the dynamic fragility of PLA/wood composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winandy, J.E.; Stark, N.M.; Clemons, C.M. Considerations in recycling of wood–plastic composites. In Proceedings of the 5th Global Wood and Natural Fibre Composites Symposium 2004, Kassel, Germany, 27–28 April 2004; pp. 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Morrell, J.J.; Stark, N.M.; Pendleton, D.E.; Mcdonald, A.G. Durabilityofwood–plasticcomposites. Wood Des. Focus 2006, 16, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ayrilmis, N.; Jarusombuti, S.; Fueangvivat, V.; Bauchongkol, P. Effect of thermal-treatment of wood fibres on properties offlat-pressed wood plastic composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirp, A.; Wolcott, M.P. Influence of fungal decay and moisture absorption on mechanical properties of extrudedwood–plastic composites. Wood Fiber Sci. 2005, 37, 643–652. [Google Scholar]
- Durmaz, S.; Erdil, Y.Z.; Avci, E. Improvement of technological properties of wood plastic composites reinforced with glass and carbon fibre fabric. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2021, 29 (Suppl. 9), S1457–S1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Yan, F.; Ma, C. Manufacturing Technologies of Polymer Composites—A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercher, J.; Fombuena, V.; Diaz, A.; Soriano, M. Influence of fibre and matrix characteristics on properties and durability of wood–plastic composites in outdoor applications. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2018, 33, 477–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellah, A.; Ali, S.F.; Althobaiti, I.O.; El-Rafey, E.; Gad, E.S. Wooden polymer composites of poly(vinylchloride), olive pits flour, and precipitated bio-calcium carbonate. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 23924–23933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukala, S.G.; Kong, I.; Kakarla, A.B.; Kong, W.; Kong, W. Development of Wood Polymer Composites from Recycled Wood and Plastic Waste: Thermal and Mechanical Properties. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashori, A. Wood–plastic composites as promising green-composites for automotive industries. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4661–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Fan, M.; Chen, L. Interface and bonding mechanisms of plant fibre composites: An overview. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 101, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; He, Z.; Lu, S.; Guo, D.; Yu, J. Enhanced thermal and mechanical properties of lignin/polypropylene wood-plastic composite by using flexible segment-containing reactive compatibilizer. Macromol. Res. 2014, 22, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.K.; Lim, E.; Song, Y. S. Synergistic effect of lignin/polypropylene as a compatibilizer in multiphase eco-composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 118, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives. Available online: https://www.eumonitor.eu/9353000/1/j4nvk6yhcbpeywk_j9vvik7m1c3gyxp/vitgbgip5dwf (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Directive (EU) 2015/720 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 2015 on Amending Directive 94/62/EC as Regards Reducing the Consumption of Lightweight Plastic Carrier Bags. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/plastics/plastic-bags_en (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Directive (EU) 2019/904 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 2019 on the Reduction of the Impact of Certain Plastic Products on the Environment. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/plastics/single-use-plastics_en (accessed on 25 June 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).