Development of a New Forced Cooling Technology Using a High-Pressure Coolant for Machining Difficult-To-Machine Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Evaluation of the Proposed Forced Cooling Method
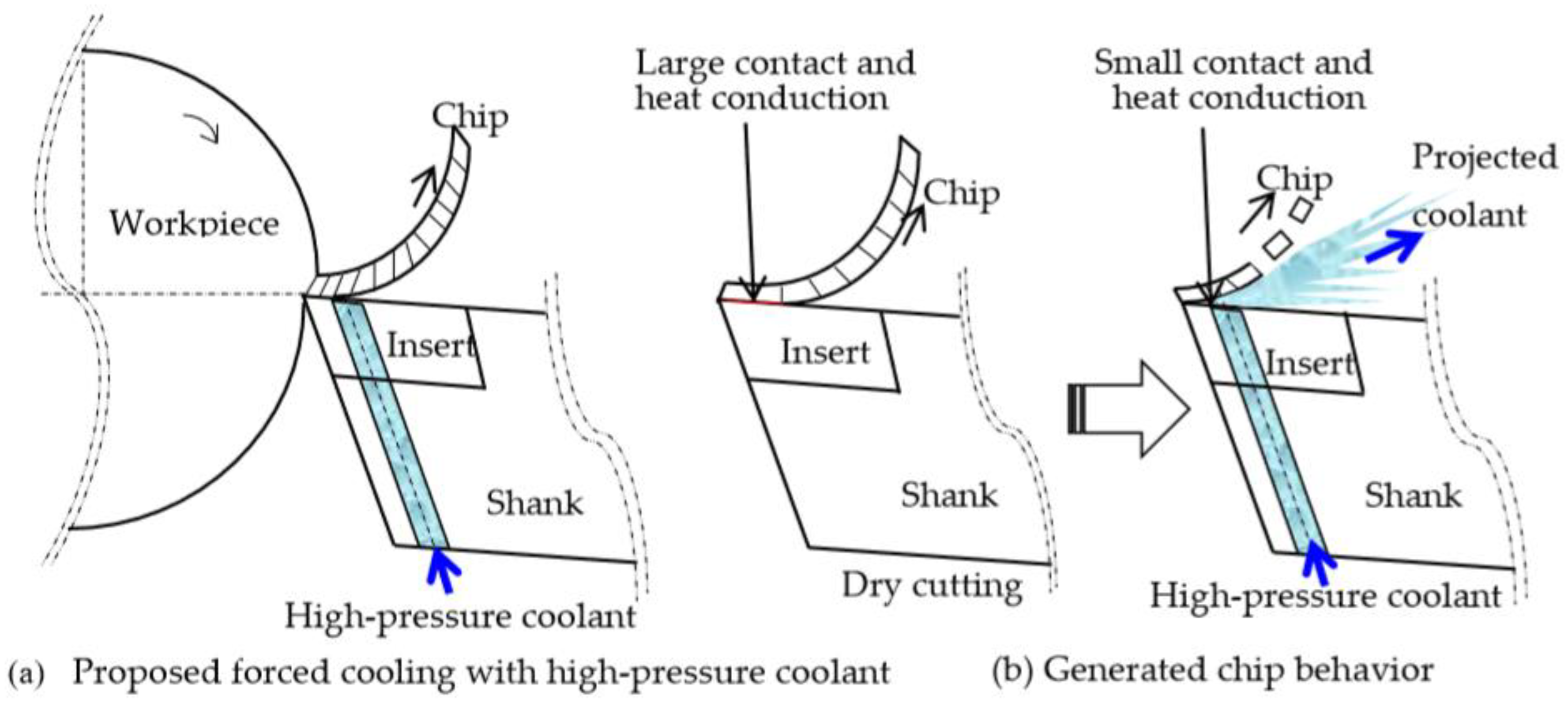
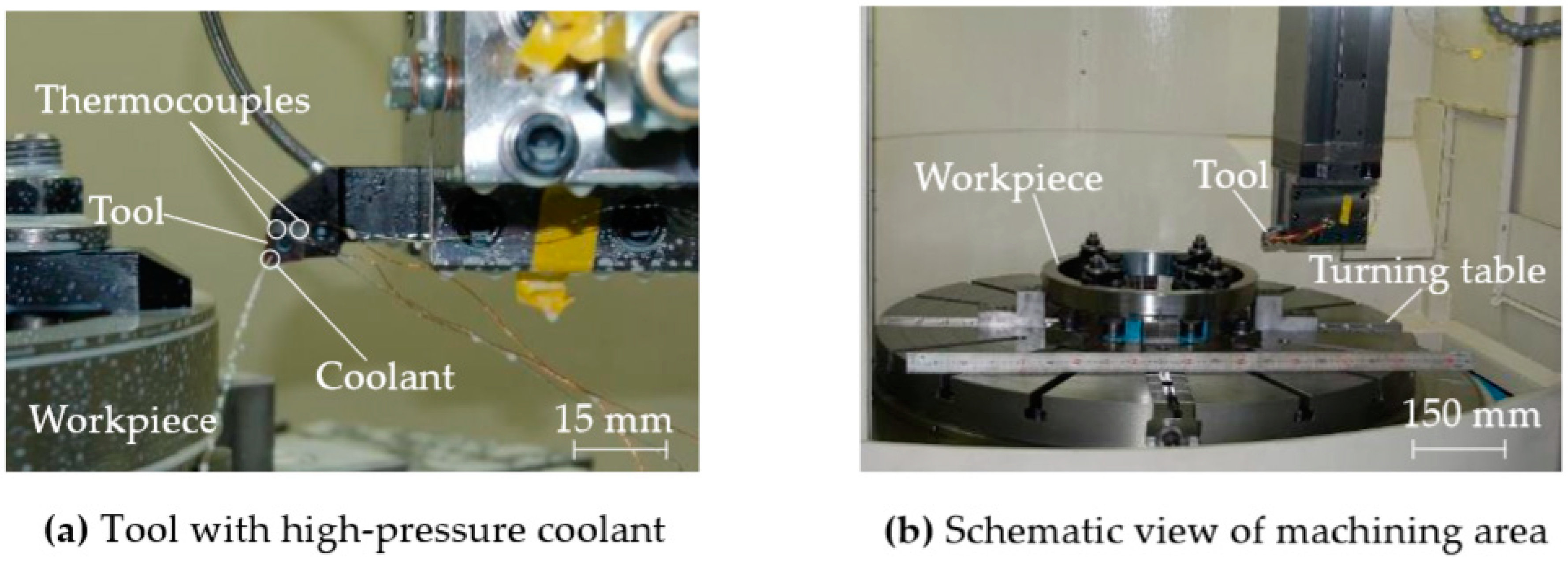
2.1. Proposed Forced Cooling Method in a Vertical Lathe
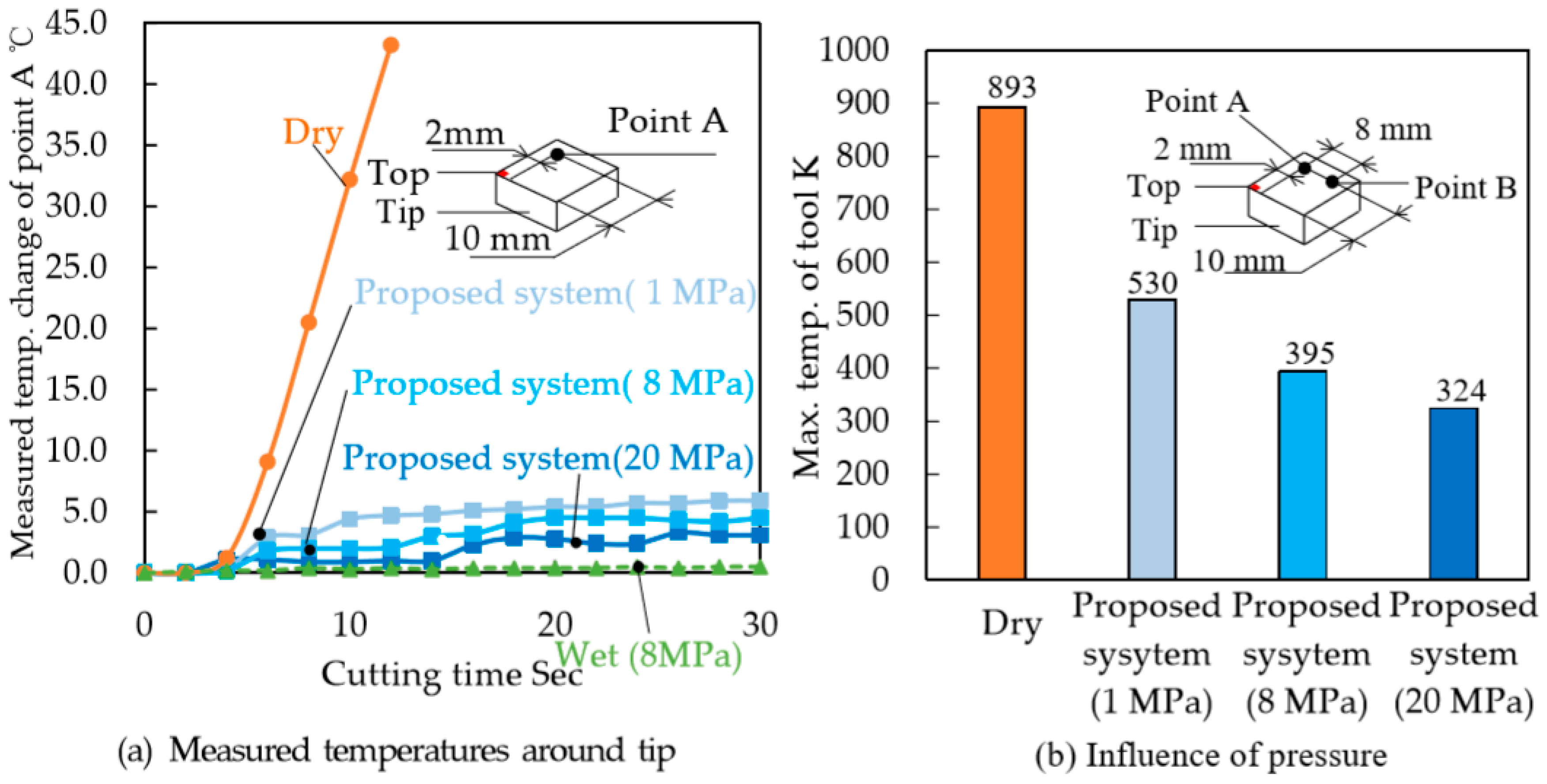
2.2. Tool Temperature Evaluation
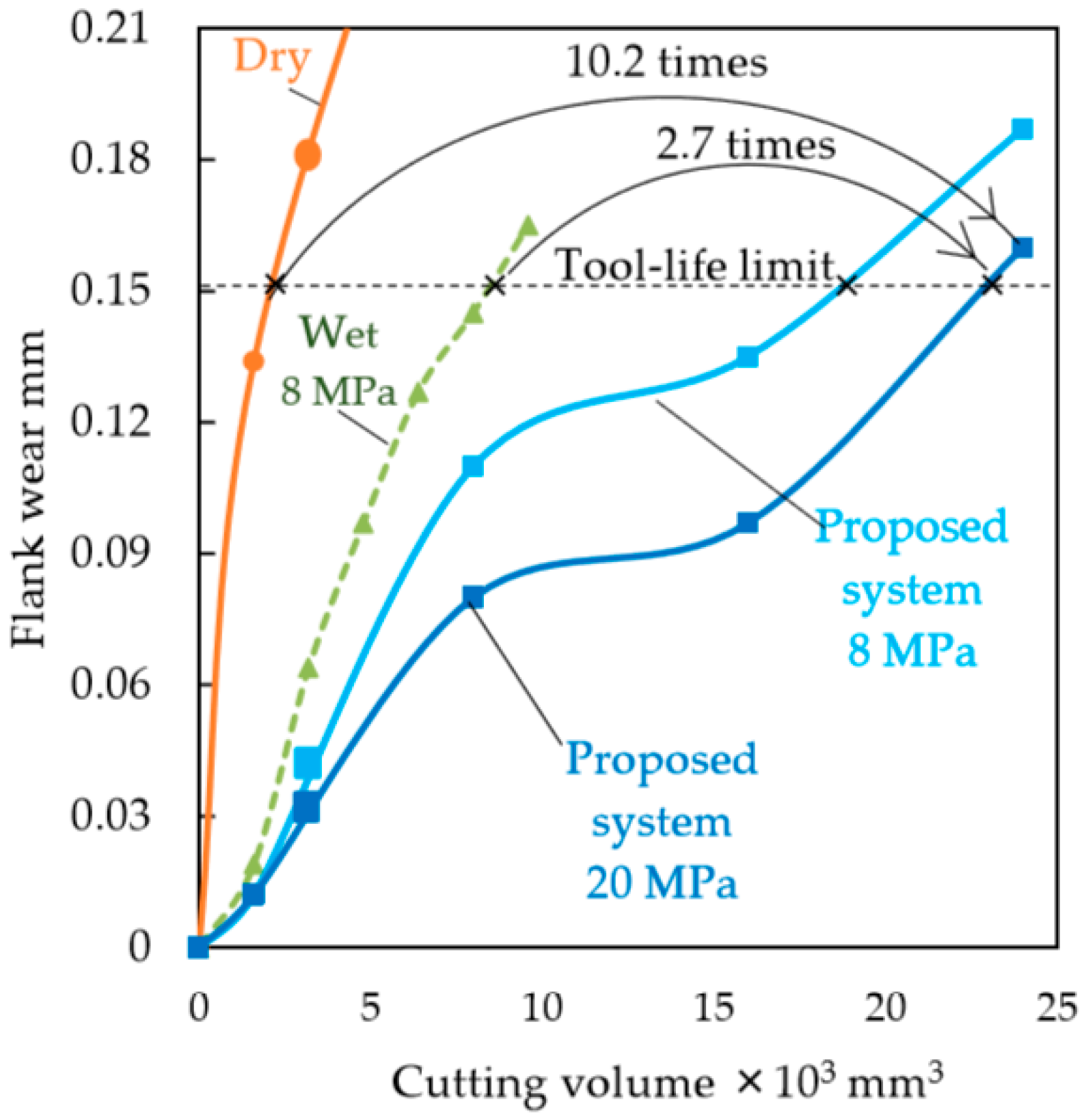
2.3. Tool-Life Evaluation
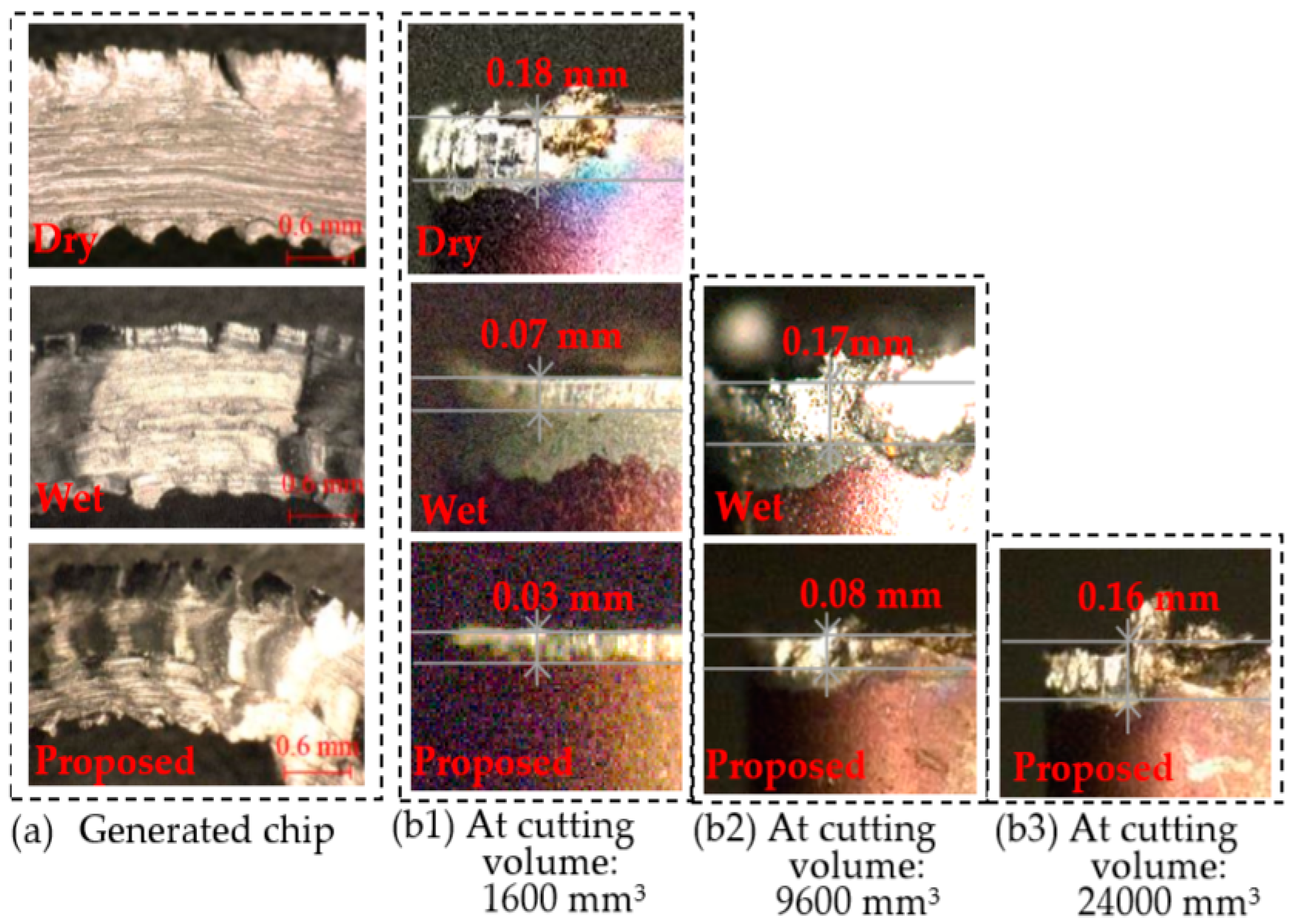
3. Conclusions
- (1)
- It was concluded that a coolant delivery method that consists of machining a hole at the tool tip from which high-pressure coolant is supplied achieves an improved tool-life. Here, given that coolant was directly supplied between the tool rake face and the workpiece, heat generation during the machining of difficult-to-machine materials can be suppressed to a certain extend.
- (2)
- From intermittent bended sections found in the generated chip it was concluded that the high-pressure coolant pushes the chip from the bottom and effectively reduces the frictional heat generation over the rake face.
- (3)
- Coolant can be supplied between the tool rake face and the workpiece by devising a high-pressure coolant delivery method as observed in (1) and, (2) while maintaining the tool hardness and integrity.
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamane, Y.; Amano, N.; Hayashi, K.; Narutaki, N. High speed machining of Inconel 718 with ceramic tools—Suppression of notch wear. J. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng. 1993, 59, 1815–1820. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, T.; Kubo, A.; Maekawa, K. Temperature and wear of cutting tools in high-speed machining of Inconel 718 and Ti-6Al-6V-2Sn. Wear 1997, 202, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuki, H.; Sato, K.; Furuya, S. High speed dry end milling of titanium alloys with coated carbide tool. J. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng. 2005, 71, 491–495. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P. Metal Cutting Technologies: Progress and Current Trends; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 60–74. ISBN 978-3-11-044942-6. [Google Scholar]
- López de Lacalle, L.N.; Pérez-Bilbatua, J. Using High Pressure Coolant in the Drilling and Turning of Low Machinability Alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2000, 16, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N. Effects of high-pressure cooling on the wear patterns on turning inserts used on alloy IN718. J. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 32, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.; Rodríguez, A. Nozzle design for combined use of MQL and cryogenic gas in machining. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2017, 4, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynak, Y.; Gharibi, A. Progressive Tool Wear in Cryogenic Machining: The Effect of Liquid Nitrogen and Carbon Dioxide. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2018, 2, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V. Advanced Modeling and Optimization of Manufacturing Processes: International Research and Development; Springer: London, UK, 2011; pp. 339–357. ISBN 978-0-85729-014-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, Y.; Matsumura, T. Theory and Practice in Machining Systems; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 71–89. ISBN 978-3-319-53900-3. [Google Scholar]
- Horn GmbH. Internally Cooled Inserts for Grooving and Parting Off; Horn GmbH: Flensburg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Takeyama, H. Cutting Process; Maruzen Inc.: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1980; pp. 15–25, 30, 35–42, 64. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe, I.; Junior, D.C.; Ye, H.S.; Tomioka, K.; Takahashi, S. Drilling technology using strong alkaline water with micro-bubble. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. Ser. C 2013, 79, 748–758. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High Concentration of Micro Bubble Generator Type A-01 Specification. Available online: http://www.idea-techno.com/pd/micro-bubble/naturan/kaatuyoukai-kounoudo.html (accessed on 1 June 2015). (In Japanese).
- UNI-BTACH Catalog; E plan Inc.: Irvine, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–2. (In Japanese)
- Shimohira, S. Material Science for Corrosion and Its Protection; AGNE Gijutsu Center: Tokyo, Japan, 1995; pp. 30–32, 255–257, 287–288. [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe, I.; Ye, H.S.; Iyama, T.; Shibuya, M. Development of cutting technology in strong alkaline water. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. Ser. C 2012, 78, 262–271. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakao, K.; Fujiwara, J.; Miyamoto, T. Cutting temperature and tool wear progress in turning of cemented carbid. In Proceedings of the JSPE Semestrial Meeting 2009, Hyogo, Japan, 21 September 2009; pp. 119–120. (In Japanese). [Google Scholar]
| Specifications of vertical lathe | Table diameter | 1100 mm |
| Max. turning diameter | 1250 mm | |
| Max. mass of workpiece | 3000 kg | |
| Max. cutting torque | 10,000 N·m | |
| Vertical travel of ram | 800 mm | |
| Max. feed speed | 500 mm/rev | |
| Main motor | 30 kW | |
| Max. height of machine | 3790 mm | |
| Floor space | 3955 × 3840 mm | |
| Cutting conditions | Workpiece material | Ti-6Al-4V |
| Insert type | Tungsten Carbide | |
| Depth of cut | 1.0 mm | |
| Feed speed | 0.8 mm/rev | |
| Cutting speed | 60 m/min | |
| Cooling fluid | JIS A1 cutting fluid emulsion | |
| Fluid pressure | 1, 8, 20 MPa | |
| Quantity of flow | 0.5 ℓ/min |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanabe, I.; Hoshino, H. Development of a New Forced Cooling Technology Using a High-Pressure Coolant for Machining Difficult-To-Machine Materials. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2018, 2, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp2020039
Tanabe I, Hoshino H. Development of a New Forced Cooling Technology Using a High-Pressure Coolant for Machining Difficult-To-Machine Materials. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2018; 2(2):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp2020039
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanabe, Ikuo, and Hideo Hoshino. 2018. "Development of a New Forced Cooling Technology Using a High-Pressure Coolant for Machining Difficult-To-Machine Materials" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 2, no. 2: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp2020039
APA StyleTanabe, I., & Hoshino, H. (2018). Development of a New Forced Cooling Technology Using a High-Pressure Coolant for Machining Difficult-To-Machine Materials. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 2(2), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp2020039




