Abstract
The production of fibre metal laminates (FMLs) is a time consuming and expensive procedure. This paper shows the application of the vacuum assisted resin transfer moulding ((VA)RTM) technique using an injection unit and a rigid mould for the production of FMLs. This processing technique, in combination with a corona discharge activation of the aluminium surface, can lead to enormous reductions to the cycle time. To prove the quality of the produced FML, impact tests were carried out. The influence of the impact energy on the specimen is observed using a deformation scan and ultrasound C-Scan. Furthermore, the peak forces and permanent deflections of the tested specimen were analysed.
1. Introduction
Fibre metal laminates (FMLs), which are part of the hybrid material category, consists of alternating layers of thin metal plies and fibre reinforced plastics (FRPs). They were invented at the Delft University of Technology in Netherlands and have been developed over the past years [,]. FMLs try to combine the material properties of metals and FRPs. This leads to a hybrid material with high impact resistance due to the ductility of the metal and the stiffness of the FRP [,]. As there are a variety of different metals and FRPs usable for FMLs, many different combinations are known. The first generation of FMLs was made out of aramid and aluminium layers and is known as “ARALL”. Due to the surface of the aramid fibres, there is a low interface strength towards the epoxy matrix. Nevertheless the material was used for wing structures and fuselage skins in aircrafts [,,]. Glass fibres (GF) later substituted the aramid fibres to improve the bonding. This material change made the composite cheaper, leading to “GLARE” (Glass Laminate Aluminium Reinforced Epoxy). The first successful application of GLARE was in the cargo floor of the Boeing 777 []. Nowadays, this material is mainly used at fuselage skins and can achieve weight savings between 15% and 25% for the Airbus family compared to standard design []. Depending on the stacking sequence and the sheet thickness, there are various GLARE types numbered from one to six []. The mechanical properties of GLARE and its advantageous properties (e.g., density, impact behaviour, damage tolerance, …) over aluminium have been shown in many different studies []. The main reason for their high damage tolerance is the fibre-bridging effect especially apparent in GLARE types with GF cross-plies in between the aluminium layer, such as GLARE 5 [,]. The [0°/90°/90°/0°] GF orientation of GLARE 5 leads to a flow of forces along these fibre directions in case of an impact. Seyed Yaghoubi et al. [] investigated the impact properties of GLARE 5 at low velocities in detail.
A commonly used technique to produce such FMLs is to use a prepreg material and metal sheets. After the layup, the part is packed into a vacuum bag and transferred into an autoclave [,]. The GLARE grades 2–6 are made out of 2024-T3 aluminium sheets and GF reinforced epoxy sheets. The GLARE 1 type uses a 7475-T16 alloy instead. It has been shown that different processing parameters affect the deformations of FMLs [,]. Furthermore, this conventional prepreg autoclave technique is time consuming and costly []. In order to improve processability in terms of cycle time and cost reduction, researchers have tried to use a special kind of vacuum assisted resin transfer moulding (VARTM) process, which is widely known as vacuum assisted resin infusion (VARI) [,,]. VARI is promising but has two major drawbacks: First, the thickness of the final part cannot be controlled, which results in a variable fibre volume fraction and second, the filling time will increase extremely for larger parts due to the small pressure gradient achievable using only vacuum and ambient pressure as driving force for filling. The VARI process does not allow one to work with higher pressures, because otherwise the vacuum bag will swell with resin. As a result, fibre wash out and shifting of the fibre layer will occur. In order to overcome these limitations and reduce the curing time of the thermoset resin, the next step would be to go towards a pressure driven (VA)RTM process within a rigid mould. The rigid mould of the RTM process enables the use of an injection unit, which injects the resin system with a controllable volume flow. This results in higher injection pressures but also helps to actively control the filling time.
A problem that always occurs when two or more materials are bonded together is the interface strength []. Different strategies can be chosen to improve the interface. The surface can be treated mechanically, chemically, or electrically [,,]. The technique used for common GLARE production is chemically anodizing of the aluminium by the use of chromic or phosphoric acid. As this technique is not only time consuming, but also harmful to the environment, other possibilities need to be found []. An alternative method may be the corona treatment []. The corona discharge treatment is advantageous for metal surface activation since it increases the concentration of oxygen groups (“activation”) and effectively reduces the amount of organic impurities on the surface [,,].
This work shows the combination of the corona discharge treatment and the use of the (VA)RTM technique for the production of FMLs consisting of aluminium, GF, and epoxy resin. The main driving force behind this work is to show the possibility to use these techniques for a cost efficient FML production procedure. To prove the quality of the produced parts impact, tests with varying impact energies have been made. The damaged area will be observed by using the ultrasonic C-Scan technique as well as mechanical-sectioning of the specimen showing pictures of the cross-section of the impact area.
2. Experimental Work
2.1. Materials
As mentioned in the introduction, the impact properties of GLARE 5 are well characterized. Therefore, the FML was produced with the same fibre orientation and layup sequence in a 3/2 configuration. The metal ply was an ALCLAD 2024-T3 aluminium with a thickness of 0.5 mm supplied by AMAG Rolling AG (Braunau-Ranshofen, Austria). To produce the glass fibre reinforced plastic (GFRP), a biaxial non-crimped fabric (NCF) made of E-glass was used. The EBX800 consisting of the PPG Roving 2002 (Cheswick, PA, USA), has an aerial weight of 801 g/m2 and is made out of two layers oriented +45°/−45°. To create the preform, the fabric was cut in a 45° direction and stacked in a [0°/90°/90°/0°] sequence as shown in Figure 1.
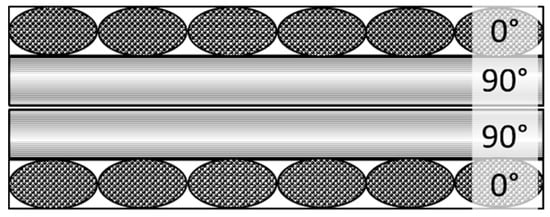
Figure 1.
Schematic of the stack of each GFRP layer.
The epoxy resin EPINAL IR 77.55-A1 and the curing agent EPINAL IH 77.55-B1, both supplied by bto-epoxy GmbH (Amstetten, Austria), with a mixing ratio of 100:32 parts by weight, were used for the resin injection. To ensure easy demoulding the mould was pre-treated with the release agent ACMOScoat 82-1181-71, supplied by Acmos Chemie KG (Bremen, Germany).
2.2. Production Procedure
For the production of the preform, the aluminium sheets, as well as, the GF layers were cut into 265 × 265 mm2 squares. Due to venting positions in the mould, two triangles of 25 × 25 mm2 were cut off at one side of each layer, as shown in Figure 2. In order to achieve good interface strength between the aluminium layers and the GFRP layers the sides of the aluminium sheets which were in contact with the glass fibres, were treated using corona discharges. Before the corona treatment was carried out, the aluminium sheets were cleaned using isopropanol, methyletheretherketone, and acetone to remove any dirt from the surface. The activation with corona discharge was accomplished with corona doses (Cd) of 4444 W min/m2. A benchtop corona instrument from Ahlbrandt GmbH (Lauterbach, Germany) was used. The preform was stacked in a 3/2 order, resulting in a [Al/0°/90°/90°/0°/Al/0°/90°/90°/0°/Al] layup. Afterwards, it was placed in a steel mould, which had a cavity area of 270 × 270 mm2 with 4 mm cavity height and a line distributer for the resin injection. The mould was heated to 100 °C and handled by a Langzauner LZT-OK-80-SO (Lambrechten, Austria) press applying a pressure of 17.5 MPa on the mould to ensure a defined cavity thickness throughout the whole production process. Figure 2 shows the schematics of the mould and the FML preform.
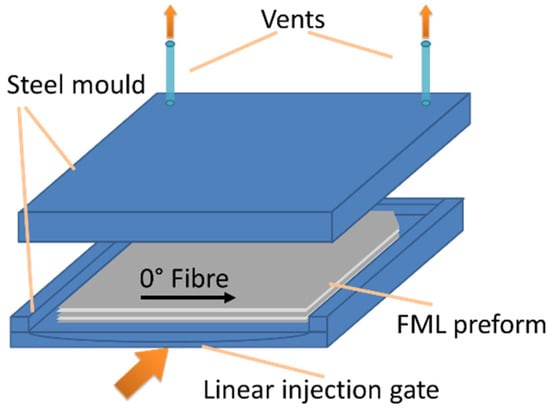
Figure 2.
Steel mould with FML preform.
To reduce the void content of the final part, the mould was evacuated by applying vacuum at the vents after closing the mould. For the preheating, mixing, and injecting of the resin system, a Tartler Nodopur VS-2K (Michelstadt, Germany) injection unit was used. The resin was preheated to 70 °C while the curing agent was kept at room temperature. The injection was made with a constant mass flow of 0.15 kg/min. After filling the mould, the vents were closed to apply a post pressure to the part. After the filling phase, which took around 2 min, the injection was stopped. The curing phase for the used resin system was 25 min. After the curing phase, the part was demoulded and cooled down to ambient temperature due to free convection. Figure 3 shows the production setup while injection of the resin system.
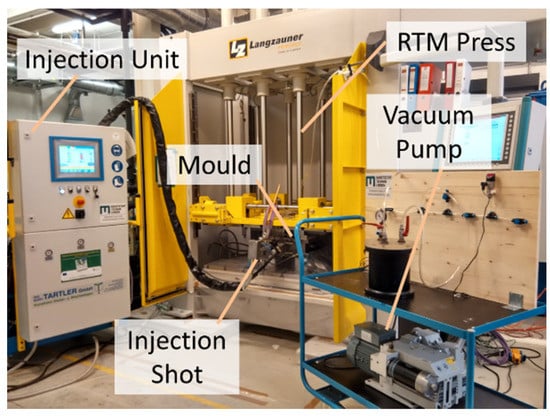
Figure 3.
Production setup while injecting the resin system into the FML preform.
2.3. Specimen and Testing Method
To test the quality of the produced FML plates, impact tests were carried out. Two specimens with dimensions of 100 × 150 × 4 mm³ were cut from each plate using a water jet cutting system. The impact tests were carried out with a Ceast Droptower Impact Systems 9350 from INSTRON CEAST Division (Turin, Italy). A specimen fixture according to ASTM D7136 was used. As a force transducer a 22 kN piezo-electric striker with 20 mm hemispherical tip was used. Impact energies of 20 J, 30 J, 40 J and 60 J were realized by adapting the weight and drop height. To avoid multiple impacts the striker was caught after the first impact using an anti-rebound system. The deformation of the impacted area was measured by means of a laser triangulations sensor scanning a 60 × 60 mm2 matrix in the centre of the specimen.
To define the damage area, C-Scans were carried out using an OmniScan MX test equipment from Olympus (Tokyo, Japan). A 5L64-NW1 5 MHz phased array pulse echo transducer from Olympus (Tokyo, Japan) with a SZ1-0L-IHC5L64 probe/wedge combination from Olympus (Tokyo, Japan) was used for testing. To get a proper coupling between the wedge and the specimen, the specimens were placed in a water bath.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results of the New Processing Technique
The usage of this new production method led to flat plates with a thickness of 4.01 ± 0.01 mm. The average fibre volume fraction at the composite layers was 49.3% with a thickness of 1.25 ± 0.01 mm. The metal volume fraction was calculated to be 37.5%. Figure 4 shows a picture of the cross section of the plate. Visual inspection of the plates did not reveal any macroscopic voids in the composite layers. One of the advantages of the rigid mould can be seen in the uniform thickness distribution of the final part. Compared to the prepreg/autoclave technology the thickness is not a result of the applied pressure in the autoclave. This leads to a defined fibre volume fraction at the whole part. As the mechanical properties of the part are directly linked to the fibre volume fraction, these properties can also be kept constant.

Figure 4.
Cross section of the FML plate cut by waterjet.
Figure 5 shows the top view of the composite layer after removing the top aluminium layer of the FML. One can see the nylon sewing threads, which were holding together the NCF layer within a 45° angle towards the 0° and 90° fibre direction. The glass fibres incorporated in the epoxy matrix are transparent and are therefore not visible in the picture. Nevertheless, there are no macroscopic voids visible in the picture, which shows a high-quality impregnation of the preform.
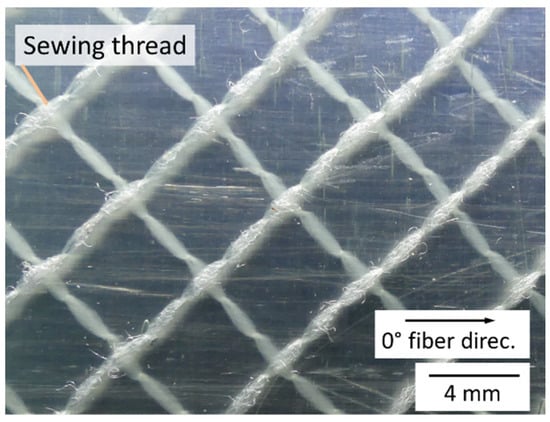
Figure 5.
Top view of the composite after removing the top aluminium layer.
Table 1 shows the potential of (VA)RTM with a rigid mould in saving production time compared to the standard prepreg/autoclave technique. As one can see, the total production time can be reduced from 395 min to 110 min if both methods use the corona treatment as the surface activation technique. This points out that the (VA)RTM process is more than 3.5 times faster than the prepreg/autoclave process. By just comparing the curing time of the described method with the classical prepreg/autoclave method a time reduction of 235 min can be achieved. This means the curing time of the standard processing technique is 1040% higher compared to this method []. The time and cost savings of this method, can clearly be seen. Nevertheless, there are some drawbacks for using the (VA)RTM technique. As there are only thin flow-channels available for the resin flow, areal parts with big dimensions will lead to long filling times. In this case, the time benefit might be reduced. Intelligent injection gate design and filling simulations can reduce the risk of incomplete filling, but the problem of decreasing flow front speed with increasing flow path must be kept in mind. Also, the fibre volume fraction cannot be increased arbitrary, as it is directly linked with the permeability of the preform. A fibre volume fraction that is too high will also result in slow filling.

Table 1.
Comparison of processing times for FML plates at laboratory scale for (VA)RTM and prepreg/autoclave technique considering corona surface treatment method [].
Another feature of this production method is that an epoxy film that is a few micrometre thin could be applied on the outer aluminium surface to prevent corrosion. Nevertheless, the outer surface was not treated by the corona discharge technique, leading to a weak bonding of the epoxy on the surface and partial chipping off during the impact tests. This can be seen at the optical view figure of the 20 J impact test in Figure 6. The epoxy film can either be prevented by using a sealing or be bonded stronger to the aluminium surface by using the corona treatment on both sides of the outer aluminium sheets.
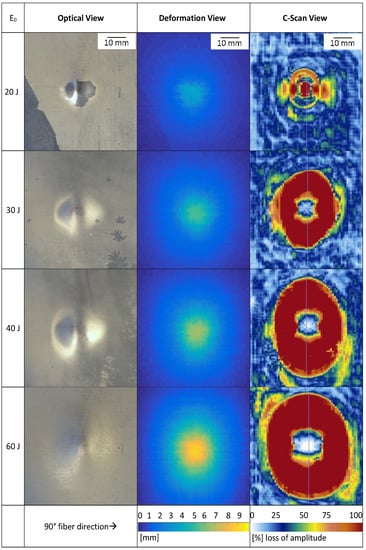
Figure 6.
Optical (left), deformation (centre) and C-Scan (right) views of the opposite sides of impacted FML plates.
3.2. Results of the Performed Impact Tests
Figure 6 shows three different representative views of the specimen tested with different impact energies. While the optical image and the deformation view show the specimen from the opposite side of the impact, the C-Scan was performed at the impacted side of the specimen. As can be seen no fracture of the top aluminium layer is visible at any impact energy. Comparing the 60 J impact test results with the results presented by Seyed Yaghoubi et al. for their (5/4) and (6/5) configuration, which had a similar thickness as the presented material, the deformed area seems to be bigger []. The C-Scan results focus on the delamination between the lowest aluminium ply and the GFRP layer. It seems that the damage is propagating more into the 0° fibre direction when higher impact energies are applied. This is linked to the deformation and built up stresses in the interface. The damage area after a 20 J impact is directly linked to the dimension of the impactor tip. There is almost no visible damage outside this area. As expected, the damaged area is increasing with the impact energy. The area in the middle of the 30–60 J C-Scans showing no loss of amplitude, is due to reflections at the surface aluminium layer.
The highest tested impact energy was 60 J. This energy also leads to the highest maximum permanent out-of-plane deflection and largest damage area, as expected. The deformation of the specimen increases from 4 mm at 20 J up to 9 mm at 60 J. Figure 7 shows the permanent maximum deflection of the specimen after the impact at different impact energies. The maximum deflection is increasing linearly with the impact energy. It has to be noted that the deflection was measured at the opposite side of the impact, where the aluminium shows a permanent deflection after the maximum displacement of the impact.
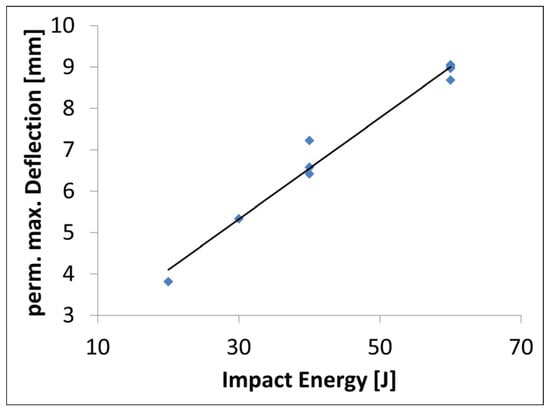
Figure 7.
Maximum deflection over impact force of the tested FML.
Figure 8 shows the impact force and the impact energy plotted against time for the tested impact energies.
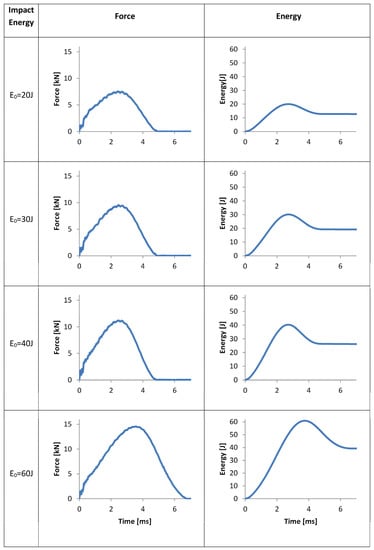
Figure 8.
Impact force and transferred energy over time during impact tests of the FML at defined impact energies.
The curves look rather smooth but there is an unstable phase between 0.05 ms and 0.25 ms. This is lined out in Figure 9. There are two peaks visible during this time period followed by a significant increase of the force. Similar observations were reported by Seyed Yaghoubi et al. but between 0.53 ms and 0.83 ms []. They explained it with a debonding of the 0° and 90° prepreg layers. Due to the different production procedure, this is different in this case. Since there are no prepreg layers, which are bonded together, the effect can be explained by a delamination between aluminium and GFRP layers. As the dry fibres move more easily, more nesting effects occur during the preform compaction in the RTM mould. Furthermore, there are no entrapped air bubbles in between the two fibre layers as the resin filled them completely. In turn, the layup of two prepreg layers may result in voids in the interface between them, which leads to crack initiation points due to stress concentrations. The shift to shorter times might be linked to a lower interface strength between the aluminium and GF layer. Therefore, a smaller bending induced shear stress is needed to induce an interface failure compared to conventional GLARE. Another explanation could be the inertia effect occurring at impact tests. The impact energy does not reach more than 1 J until this point, which seems to be insufficient to create a delamination in the FML material. Figure 9 shows this phenomenon for a 60 J impact, however this effect was observed at similar times and forces at the lower levels of impact energy as well.
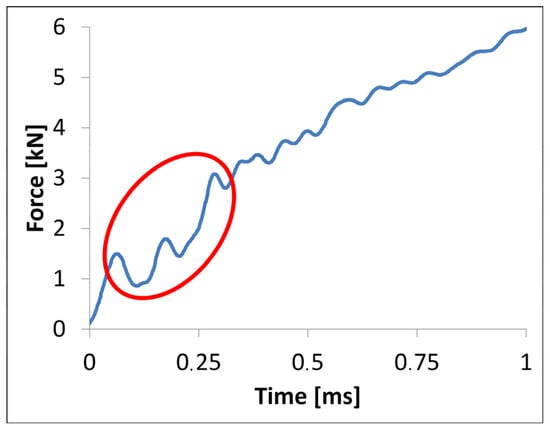
Figure 9.
Impact force characteristics from 0 ms to 1 ms at 60 J impact energy at the FML.
To show the post-impact condition of the specimen, Figure 10 shows the cross-sectional view of the cut specimen at different impact energies. It is visible that the lowest aluminium layer is debonded while the other layers are still in contact to each other. Due to the elastic behaviour of the GFRP layers, the material showed a spring back after the impact. Because the interface towards the lowest aluminium layer already failed at the maximum deflection during the impact, there was no adhesive force restoring it and hence it stayed at the position of maximum deflection.
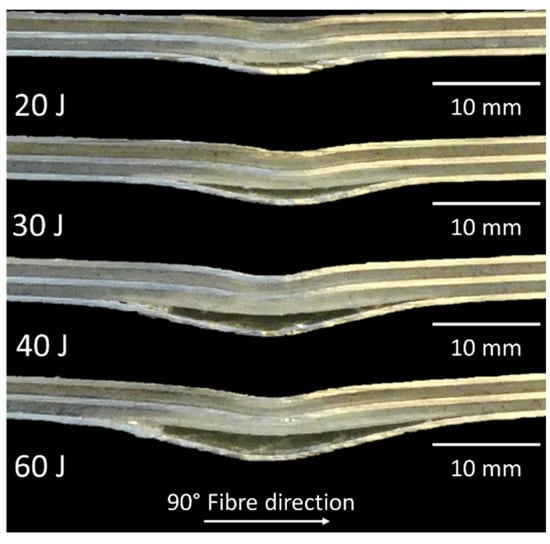
Figure 10.
Cross-sectional view of the impacted area of the FML at different impact energies.
To focus more on the damaged area, Figure 11 shows a 60 J impacted specimen at three different magnifications. The brighter areas in the GFRP which are spreading from the impact point towards the lower side, indicate damaged fibres. As this area is spreading towards the lower side, one can conclude that the failure mechanism is bending induced. Furthermore, one can see the cohesive failure towards the lowest aluminium layer, as there are still parts of the resin bonded towards it. Due to the anisotropic mechanical properties of the different fibre orientations in the GFRP, delamination occurred between the 0° and 90° fibre layers. This again occurred at the lower part of the FML, where higher bending induced strains existed.

Figure 11.
Microscopic cross-sectional view of the 60 J impacted specimen at three different magnifications.
As Figure 12 shows, there is a linear increase of peak force in respect of impact energy. This proves that none of the layers were totally broken at the tested levels of impact energies. Otherwise, a significant nonlinearity beyond certain impact energies should be observable.
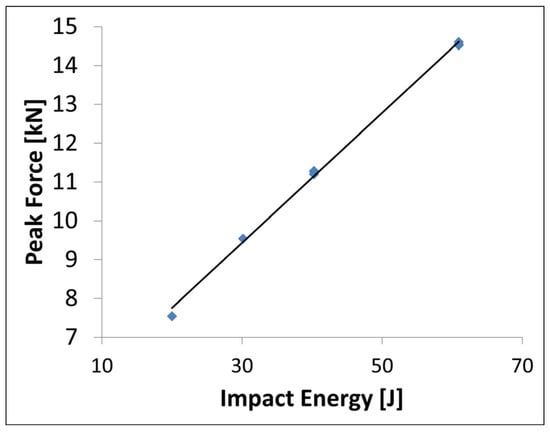
Figure 12.
Peak forces over impact energies of the tested specimen.
4. Summary and Conclusions
This study shows a new way of producing FMLs by using a RTM two-component injection unit and a rigid mould. The applied vacuum helped to reduce the void content during the filling phase while the corona treatment of the aluminium plies increased the bonding force between the GFRP layers and the aluminium layers. The epoxy resin system, which was especially designed for hybrid material structures, was able to provide a good adhesion between the two materials.
To test the quality of the produced parts, impact tests were carried out and ultrasonic C-Scan images were made to define the area of delamination between the GFRP and the aluminium layers. The results showed that the damage area increased with higher impact energies. It was observed that the delamination between the aluminium layer and the GFRP layer propagated more along the 0° fibre direction with increasing impact energies. Pictures of the cross-section of the impacted area showed the delamination of the lowest aluminium layer as well as the damaged GFRP.
The unsteady behaviour in the force versus time curves in the time between 0.05 ms and 0.25 ms may be described by two effects: Either a debonding of the aluminium layer and the GFRP layer or an effect of inertia occurring at the impact test itself. However, a similar effect was observed by Seyed Yaghoubi et al. []. In this case, the reason for the effect was different. It seems that the interface between the GFRP layers was much stronger compared to the interface between the GFRP and aluminium layer. This led to a failure between the aluminium and the GFRP. The weaker interface strength might be explained by the corona treatment of the aluminium layers in contrast to anodizing via chromic acid for standard GLARE.
The maximum deflection of the specimen reached 9 mm at 60 J, but there was still no detectable fracture of the aluminium layer. This can be proven by the linear increase of the peak force in respect to the impact energy. By comparing the force versus time and also the energy versus time characteristics of the tests shown in literature [], one can conclude that impact strength of the produced FML was on a similar level with FMLs produced with the standard procedure. The steepness as well as the height of these curves are comparable. Nevertheless, it has to be mentioned that the thicknesses and layup of the compared material was slightly divergent.
Using this production method can help to improve the production efficiency compared to the traditional prepreg/autoclave method used at FML production these days. Furthermore, the shown production technique is also suitable to produce more complex parts, which have double curved shapes. The rigid mould enables one to produce parts with defined thicknesses and fibre volume fractions. Nevertheless, a drawback for bigger parts is the decreasing flow front speed when using a single injection gate, which can lead to increasing injection times.
Furthermore, the corona treatment method seems to be a promising approach. Nevertheless, further investigations comparing the impact of this technique with that of the standard procedure need to be carried out in future.
Author Contributions
P.H. conceived of the presented idea. P.H., L.Z. and Y.L. manufactured the specimen. B.K. had the idea to use corona treatment for better bonding and applied it. F.A. carried out the impact tests. E.F. and R.S. contributed to the interpretation of the results. P.H. took lead in writing the manuscript. All authors provided critical feedback and helped shape the research, analysis and manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The work presented in this paper has been elaborated within the context of project “HybridRTM” [848666], financed through the Austrian Ministry for Transport, Innovation and Technology in the frame of the program “Produktion der Zukunft”, which is greatly acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gunnink, J.W.; Vlot, A.; de Vries, T.J.; van der Hoeven, W. Glare technology development 1997–2000. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2002, 9, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibre Metal Laminates. An Introduction; Vlot, A., Gunnink, J.W., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Yang, J.-M.; Hahn, H.T. The impact properties and damage tolerance and of bi-directionally reinforced fiber metal laminates. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yang, J.-M. The mechanical behavior of GLARE laminates for aircraft structures. JOM 2005, 57, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asundi, A.; Choi, A.Y.N. Fiber metal laminates: An advanced material for future aircraft. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1997, 63, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marissen, R. Fatigue Crack Growth in ARALL. A Hybrid Aluminium-Aramid Composite Material: Crack Growth Mechanisms and Quantitative Predictions of the Crack Growth Rates. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Delft, Delft, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Botelho, E.C.; Silva, R.A.; Pardini, L.C.; Rezende, M.C. A review on the development and properties of continuous fiber/epoxy/aluminum hybrid composites for aircraft structures. Mater. Res. 2006, 9, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderliesten, R.; Homan, J. Fatigue and damage tolerance issues of Glare in aircraft structures. Int. J. Fatigue 2006, 28, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyed Yaghoubi, A.; Liu, Y.; Liaw, B. Low-velocity impact on GLARE 5 fiber-metal laminates: Influences of specimen thickness and impactor mass. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2012, 25, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Choi, W.J.; Choi, H.S. A comparative study on the properties of GLARE laminates cured by autoclave and autoclave consolidation followed by oven postcuring. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 49, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinke, J. Manufacturing of GLARE parts and structures. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2003, 10, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhamzeh, M.; Sinke, J.; Benedictus, R. On the prediction of cure-process shape deviations in fibre metal laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 49, 1705–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhamzeh, M.; Sinke, J.; Benedictus, R. Investigation of curing effects on distortion of fibre metal laminates. Compos. Struct. 2015, 122, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, F.; Davé, R.S. Processing of Composites; Hanser: Munich, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- De Mendibil, I.O.; Aretxabaleta, L.; Sarrionandia, M.; Mateos, M.; Aurrekoetxea, J. Impact behaviour of glass fibre-reinforced epoxy/aluminium fibre metal laminate manufactured by Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Moulding. Compos. Struct. 2016, 140, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumert, E.K.; Johnson, W.S.; Cano, R.J.; Jensen, B.J.; Weiser, E.S. Fatigue damage development in new fibre metal laminates made by the VARTM process. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2011, 34, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, B.J.; Cano, R.J.; Hales, S.J.; Alexa, J.A. Fiber metal laminates made by the VARTM process. In Proceedings of the ICCM-17 17th International Conference on Composite Materials, Edinburgh, UK, 27–31 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ostapiuk, M.; Surowska, B.; Bieniaś, J. Interface analysis of fiber metal laminates. Compos. Interfaces 2014, 21, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Abliz, D.; Jiang, B.; Ziegmann, G.; Meiners, D. A novel process for cost effective manufacturing of fiber metal laminate with textile reinforced pCBT composites and aluminum alloy. Compos. Struct. 2014, 108, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bobbert, M.; Dammann, C.; Zinn, C.; Lauter, C.; Mahnken, R.; Meschut, G.; Schaper, M.; Troester, T. Influences of interface and surface pretreatment on the mechanical properties of metal-CFRP hybrid structures manufactured by resin transfer moulding. IJAUTOC 2016, 2, 272–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.M. Review: Replacements for Chromium Pretreatments on Aluminum. Corrosion 1995, 51, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendero, C.; Tixier, C.; Tristant, P.; Desmaison, J.; Leprince, P. Atmospheric pressure plasmas: A review. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2006, 61, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynak, B.; Alpan, C.; Kratzer, M.; Ganser, C.; Teichert, C.; Kern, W. Anti-adhesive layers on stainless steel using thermally stable dipodal perfluoroalkyl silanes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 416, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Lu, N.; Myung, S.-W.; Choi, H.-S. Enhancement of adhesion strength between two AISI 316 L stainless steel plates through atmospheric pressure plasma treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 5220–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Newsome, J.R.; Ensor, D.S. Modification of surface energy, dry etching, and organic film removal using atmospheric-pressure pulsed-corona plasma. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1995, 31, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).