AI-Enhanced Intrusion Detection for UAV Systems: A Taxonomy and Comparative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- RQ1: Are the results of recent UAV-related IDS studies potentially biased due to outdated or non-UAV-specific datasets and inconsistencies in the evaluation methodology?
- RQ2: What are the primary security threats faced by UAV systems, and what strategies have been proposed to mitigate them in various deployment contexts?
- RQ3: What types of intrusion detection techniques are most suitable for UAV deployment, considering limitations in computational resources, communication bandwidth, and energy consumption? How do centralized, distributed, and hybrid approaches compare in this regard?
- Identify prevailing trends, methodologies, and gaps in UAV-specific IDS research, with a focus on AI-driven approaches.
- Assess the suitability of various machine learning models in light of UAV operational constraints, such as limited compute resources and latency requirements.
- Evaluate the relevance and limitations of existing datasets, especially those that are outdated, synthetic, or not practical to UAV scenarios.
- Investigate the inconsistencies in IDS evaluation practices across studies, including variations in experimental design, preprocessing, and feature selection.
- Guide future research by highlighting promising directions in lightweight model design, data fusion techniques, and deployment strategies tailored to UAV networks.
- First, we present a taxonomy and comparative review of UAV intrusion detection research. To our knowledge, this is one of the most comprehensive and up-to-date reviews in this fast-moving area. Our taxonomy organizes existing IDS approaches based on data type, learning paradigm, and deployment strategy. This makes the landscape clearer and helps identify important trends, such as the dominance of supervised learning and the rise of federated methods.
- Second, we conducted experimental evaluations to highlight generalization issues that were previously assumed but rarely measured. By replicating multiple IDS models and testing them across different datasets, we showed how their performance can change when evaluated under new conditions. These findings serve as an important warning: reported high accuracy may not generalize across various deployment scenarios. We argue that cross-dataset validation should become a standard practice.
- Third, drawing on insights from both the literature review and our experiments, we propose several future research directions. These include improving dataset quality, building more efficient models, exploring collaborative learning, and enhancing robustness.
2. Research Methodology
- Study Identification: We searched six major digital libraries—IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library, Elsevier ScienceDirect, MDPI, Scopus, and SpringerLink—for English-language publications from 1 January 2020 to 31 May 2025. Queries were frozen prior to screening, and results were de-duplicated by DOI/title. To minimize omission risk, we also cross-checked hits via Google Scholar for missing peer-reviewed counterparts. Database-specific query strings were:
- IEEE Xplore (All Metadata): (“UAV” OR “drone” OR “unmanned aerial vehicle” OR “internet of drones”) AND (intrusion OR anomaly) AND (“machine learning” OR “deep learning” OR AI OR “artificial intelligence”) AND (“intrusion detection” OR IDS OR cybersecurity) AND (dataset OR “data set” OR benchmark)
- ACM Digital Library (Anywhere): (“UAV” OR drone OR “unmanned aerial vehicle” OR “internet of drones”) AND (intrusion OR anomaly) AND (“machine learning” OR “deep learning” OR AI OR “artificial intelligence”) AND (“intrusion detection” OR IDS OR cybersecurity) AND (dataset OR “data set” OR benchmark)
- Scopus (TITLE-ABS-KEY): TITLE-ABS-KEY(“UAV” OR drone OR “unmanned aerial vehicle” OR “internet of drones”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(intrusion OR anomaly) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(“machine learning” OR “deep learning” OR AI OR “artificial intelligence”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(“intrusion detection” OR IDS OR cybersecurity) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(dataset OR “data set” OR benchmark) AND PUBYEAR > 2019 AND LANGUAGE(English) AND DOCTYPE(ar OR cp)
- ScienceDirect (All fields; simplified due to Boolean limits): (“UAV” OR drone) AND (intrusion OR anomaly) AND (“machine learning” OR “deep learning” OR AI) AND (“intrusion detection” OR IDS) AND (dataset OR benchmark)
- SpringerLink (Full text): (“UAV” OR “unmanned aerial vehicle” OR drone OR “internet of drones”) AND (“intrusion detection” OR IDS OR intrusion OR anomaly) AND (“machine learning” OR “deep learning” OR AI OR “artificial intelligence”) AND (dataset OR “data set” OR benchmark)
- MDPI (All fields): (“UAV” OR “unmanned aerial vehicle” OR drone OR “internet of drones”) AND (“intrusion detection” OR IDS OR intrusion OR anomaly) AND (“machine learning” OR “deep learning” OR AI OR “artificial intelligence”) AND (dataset OR “data set” OR benchmark)
- Screening and Inclusion Criteria: To ensure relevance and quality, we applied the following criteria:
- Peer-reviewed journal, conference, or early-access articles, written in English.
- Published between 1 January 2020 and 31 May 2025 (inclusive).
- Proposes or evaluates an AI/ML-based intrusion detection system (IDS) for UAV or UAV swarm environments.
- Reports experimental results with performance metrics (for instance, accuracy, F1-score) and dataset details.
- Exclusion Criteria: Studies were excluded if they met any of the following:
- Non-peer-reviewed publications (such as preprints, theses, technical reports, blogs).
- Works focused solely on non-AI security measures (purely cryptographic/firewall solutions without AI/ML).
- No experimental validation (missing performance metrics, dataset description, or implementation details).
- Addressed only hardware vulnerabilities/attack surfaces without proposing or evaluating an IDS.
- Data Extraction and Structuring: For each included paper, we recorded:
- Classifier/model type and AI/ML paradigm (supervised, unsupervised, hybrid, etc.).
- Dataset name, source, structure, and UAV specificity.
- Deployment strategy (centralized, distributed, federated/hybrid).
- Detection timing (online/real-time, offline, hybrid).
- Attack types covered; key findings and limitations.
- Performance metrics (accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, AUC/AUROC; and, when reported, latency, model size, or energy).
Attribute extraction was performed by one author and independently reviewed by a second author; given the largely objective fields (model, dataset, metrics), we did not compute inter-rater statistics such as Cohen’s κ). Any discrepancies would have been resolved by discussion; none occurred as the literature clearly mentions the model, dataset, and metrics they use. - Methodological Quality and Risk of Bias: We did not use a formal risk-of-bias checklist. Instead, we looked for common problems that could skew results: unrealistic or poorly labeled datasets, reusing train/test splits, or leaking information. When we found these issues, we noted them and explained how they might limit generalization.
- Synthesis and Analysis: We synthesized the literature to identify trends, inconsistencies, and research gaps, with emphasis on dataset reuse, attack-type coverage, deployment realism, and cross-dataset generalizability. Reported performance was interpreted in light of dataset relevance and methodological transparency.
Positioning of Our Survey in the Context of Prior Work
| Survey Ref. | Attack Taxonomy | Cross-Dataset Validation | Dataset Critique | Deployment Strategy | Detection Feasibility | AI Paradigm Analysis | Perfor- mance Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [7] | √ | × | Δ | Δ | √ | √ | Δ |
| [8] | √ | × | × | Δ | Δ | Δ | × |
| [9] | √ | × | √ | × | × | √ | √ |
| [10] | √ | × | Δ | × | × | Δ | × |
| [11] | √ | × | × | Δ | × | √ | × |
| [12] | √ | × | × | Δ | Δ | Δ | × |
| [13] | √ | × | Δ | × | √ | √ | × |
| [14] | Δ | × | × | × | × | √ | Δ |
| [15] | Δ | × | Δ | × | × | Δ | Δ |
| [16] | Δ | × | × | Δ | Δ | Δ | × |
| [17] | √ | × | √ | Δ | √ | √ | √ |
| [18] | √ | × | × | × | Δ | √ | Δ |
| [19] | √ | × | Δ | × | √ | √ | × |
| Proposed | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
- Taxonomy of Attacks: Whether the survey categorizes threats using structured taxonomies.
- Cross-Dataset Validation: Whether it evaluates or discusses the generalization of IDS models across multiple datasets.
- Dataset Critique: Whether it critically assesses the suitability and limitations of commonly used datasets.
- Deployment Strategy: Whether it accounts for how IDS systems are implemented (for instance, centralized, distributed, federated).
- Detection Feasibility: Whether it considers latency, compute limits, or practical usability in real-world UAV scenarios.
- AI Paradigm Analysis: Whether the survey organizes and compares works based on learning strategy (for instance, supervised, RL, hybrid).
- Performance Metrics Analysis: Whether it reviews or compares models using standard metrics like accuracy, F1-score, or FAR.
3. Literature
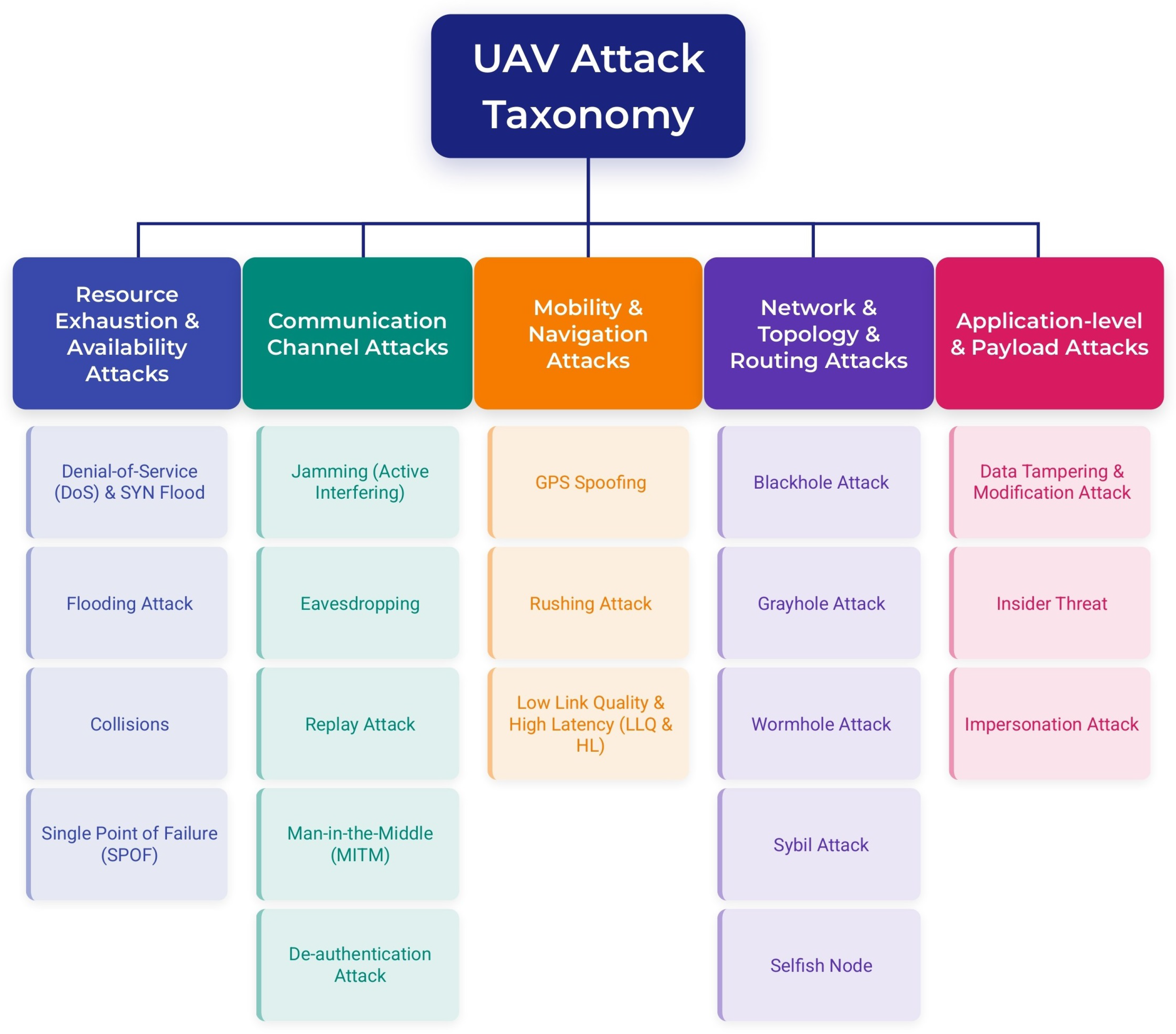
3.1. Taxonomy of UAV Attack Types Based on UAV-Specific Characteristics
3.1.1. Resource Exhaustion and Availability Attacks
- Denial-of-Service (DoS): Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks flood UAV nodes or communication channels with excessive packets, rendering them unresponsive by depleting their limited processing power and bandwidth. SYN Flood, a specific form of DoS, abuses TCP’s handshake process by flooding UAVs with SYN packets, exhausting system resources and causing disruption or crashes [20].
- Flooding Attack: Flooding attacks overwhelm UAVs with excessive data packets, consuming memory buffers and processing capacity, degrading communication reliability, and delaying legitimate data transfers critical for UAV missions [21].
- Collisions: Collisions occur when multiple UAV nodes transmit simultaneously on the same frequency channel, causing packet loss and necessitating retransmissions. High mobility and dynamic topology in FANETs significantly increase collision likelihood [12].
- Single Point of Failure (SPOF): Single Point of Failure arises when a crucial UAV or ground control node fails or is compromised, leading to operational breakdown and disrupting entire UAV missions. This vulnerability is heightened in centralized UAV network architectures.
3.1.2. Communication Channel Attacks
- Jamming (Active Interfering): Jamming involves intentionally transmitting signals to interfere with legitimate UAV communication channels, causing significant disruption of control signals and real-time data exchange crucial for UAV operations [22].
- Eavesdropping: Eavesdropping attacks intercept UAV communication to gather sensitive or classified data, violating confidentiality and potentially enabling further attacks, such as replay or impersonation [12].
- Replay Attack: Replay attacks involve capturing legitimate packets and retransmitting them fraudulently at later stages to mislead UAV or control stations, enabling unauthorized access or system manipulation [12].
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM): MITM attacks intercept and potentially alter UAV communications in real time, compromising message confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity, significantly affecting UAV mission reliability [23].
- De-authentication Attack: Attackers disrupt UAV network communications by sending falsified de-authentication packets, forcibly disconnecting legitimate UAV nodes or control stations, and creating operational instability [12].
3.1.3. Mobility and Navigation Attacks
- GPS Spoofing: Attackers send false GPS signals to mislead UAV navigation systems, causing incorrect location reporting or complete navigational failure, critically compromising UAV safety and operational effectiveness [24].
- Rushing Attack: Rushing attacks involve rapidly forwarding route discovery packets to establish unauthorized control over network routing, disrupting legitimate navigation paths, and degrading the reliability of UAV network routing protocols [12]
- Low Link Quality and High Latency (LLQ and HL): LLQ and HL occur due to intentional interference or network congestion, causing high communication latency and poor signal quality, critically impacting real-time navigation and coordination among UAVs [12].
| Dataset Name | Ref. | Dataset Characteristics | Attack Types and Applicability |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAVLINK IDS | [25] | Simulated UAV telemetry using MAVLink protocol | GPS spoofing, navigation manipulation, telemetry injection. |
| PX4 IDS | [26] | Flight logs from PX4-based UAVs across diverse missions | Sensor faults, control anomalies, software misbehavior. |
| DJI IDS | [26] | Visual simulation of DJI drone missions with injected faults | Visual inconsistencies, flight path anomalies, spoofed sensor input. |
| UAVCAN IDS | [27] | UAVCAN protocol logs captured from internal UAV buses | Flooding, replay, and fuzzing of internal message traffic. |
| CADIA IDS | [27] | Network traffic from simulated UAV missions under attack | DDoS, spoofing, and packet manipulation |
| ALFA IDS | [9] | Fixed-wing UAV test flights with cyber-attack injections | GPS spoofing, jamming, denial-of-service. |
| WSN-DS | [26] | Simulated UAV swarm behavior with compromised nodes | Blackhole, grayhole, and packet flooding attacks. |
| UAV Attack IDS | [9] | Synthetic UAV telemetry with targeted GPS and RF attacks | GPS spoofing, signal jamming, position falsification. |
3.1.4. Network Topology and Routing Attacks
- Blackhole Attack: Malicious nodes advertise falsely optimal routes to attract network traffic, subsequently dropping all packets, thus disrupting UAV network reliability and operational performance.
- Grayhole Attack: Similar to blackhole attacks, grayhole attackers selectively forward or drop packets unpredictably, complicating detection and causing significant routing instability and uncertainty [28].
- Wormhole Attack: Attackers create a covert communication tunnel between malicious nodes, secretly intercepting and redirecting packets, disrupting UAV network operations, and potentially leading to severe data breaches [29].
- Sybil Attack: In Sybil attacks, an attacker creates multiple fake UAV identities within the network, undermining trust mechanisms, routing decisions, and collaborative mission integrity [30].
- Selfishness (Selfish Node): Selfish nodes intentionally limit their packet forwarding to conserve resources, disrupting network cooperation and decreasing overall UAV network performance [31].
3.1.5. Application-Level and Payload Attacks
- Data Tampering and Modification Attack: Attackers manipulate transmitted payload data or application messages to mislead UAV operations, degrading mission accuracy and reliability [32].
- Insider Threat: Authorized insiders intentionally misuse their legitimate access to leak sensitive information or manipulate UAV operations, posing severe internal security threats [33].
- Impersonation Attack: Attackers disguise their identity as legitimate UAV nodes or ground stations to gain unauthorized access, manipulate data exchanges, or mislead operational decisions [34].
| Dataset Name | Ref. | Dataset Characteristics | Attack Types and Applicability |
|---|---|---|---|
| UNSW-NB15 | [35] | Captured network traffic from hybrid normal/attack scenarios | DoS, brute force, and generic probing attacks (not UAV-specific). |
| DARPA | [36] | Synthetic network traffic for intrusion detection benchmarks | Simulated intrusion patterns from early cybersecurity studies. |
| KDD Cup 99 | [9] | Derived from DARPA dataset with labeled network flows | Traditional attacks: DoS, U2R, R2L (outdated, low UAV relevance). |
| NSL-KDD | [9] | Improved version of KDD with reduced redundancy | Similar to KDD, lacks UAV or modern protocol coverage. |
| Kyoto 2006+ | [36] | Real-world honeypot traffic over multiple years | General anomaly patterns, limited drone protocol representation. |
| CICIDS2017 | [37] | Emulated enterprise traffic with labeled attack flows | Web and DDoS attacks, limited UAV applicability |
| ISCX 2012 | [37] | Simulated user behavior in enterprise networks | Enterprise-focused threats, no UAV-specific telemetry |
| CSE-CIC-IDS2018 | [9] | Labeled enterprise logs for multiple cyber-attacks | Malware, infiltration, botnet attacks in office-like environments. |
| AWID2 | [37] | Wireless network logs from WiFi environments | Deauthentication, injection, and WiFi DoS (not UAV-specific). |
| UKM-IDS20 | [37] | Traffic captured in university network environment | Education network threats; lacks UAV-relevant telemetry. |
| DEFCON-10 | [38] | Capture-the-flag competition data | Artificial competition scenarios, non-representative of UAV use. |
| BoT-IoT | [38] | Simulated IoT botnet behaviors with labeled traffic | IoT-centric botnet/DDoS attacks; limited relevance to aerial systems. |
| ToN-IoT | [9] | Cross-domain IIoT traffic logs with diverse devices | Data poisoning, ransomware, lateral movement (not UAV-focused). |
| Edge-IIoTset | [9] | Edge/cloud IIoT simulation with cyber-physical flows | Industrial attack vectors (data tampering, denial of edge services). |
| MQTT-IoT-IDS2020 | [9] | MQTT protocol logs from IoT smart environments | Broker flooding, message tampering (not applicable to UAV stacks). |
| CICIOT2023 | [25] | IoT topology-based attacks in smart grid simulations | Topology spoofing, DDoS, MQTT manipulation |
3.2. UAV IDS Datasets
- MAVLINK IDS Dataset: The MAVLINK dataset provides detailed simulation data using the PX4 autopilot and Gazebo robotics simulator, specifically focusing on MAVLINK protocol interactions. It contains normal operational parameters alongside GPS spoofing scenarios, capturing critical anomalies relevant to UAV navigation security. This dataset is instrumental in testing anomaly detection systems aimed at identifying navigation-related attacks in UAV networks [25].
- PX4 IDS Dataset: This dataset includes flight logs collected from various UAV platforms equipped with Pixhawk controllers running the open-source PX4 autopilot software. The logs provide sensor data, control commands, and flight statuses from diverse scenarios. The dataset is valuable for assessing IDS performance across various UAV hardware platforms and flight conditions [26].
- DJI IDS Dataset: The DJI dataset consists of simulated visual data derived from models of popular DJI UAV platforms such as Phantom and Mavic. Rendered using computer-generated imagery to emulate realistic UAV flight conditions, this dataset supports the detection of visual and sensor-based anomalies in drone operations, making it suitable for visual IDS implementations [26].
- UAVCAN IDS Dataset: Composed of log files capturing communications within UAVCAN protocol networks, this dataset includes various internal message exchanges, command flows, and sensor communications. It supports training machine learning models and rule-based systems to identify unusual internal communications or cyber-attacks targeting the UAV’s internal network bus systems [27].
- CADIA IDS Dataset: CADIA focuses on intrusion detection for Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) and other network attacks, featuring both normal and attack traffic scenarios. The dataset enables researchers to develop and validate intrusion detection methods that require robust differentiation between benign and malicious network traffic patterns [9].
- ALFA IDS Dataset: ALFA provides data specifically targeting failure and anomaly detection in fixed-wing UAVs, including various sudden engine failures and actuator faults scenarios. It supports both anomaly detection and fault diagnosis systems, crucial for real-time monitoring and response mechanisms in UAV operations [27].
- WSN-DS Dataset: WSN-DS contains simulated network traffic representative of swarm UAV operations under multiple attack scenarios, including blackhole, grayhole, and flooding attacks. This dataset is particularly relevant for studying IDS in swarm UAV environments, capturing unique challenges posed by cooperative UAV networks [26].
- UNSW-NB 15 Dataset: Originally developed for broader network intrusion detection, UNSW-NB15 includes realistic network traffic and various cyber-attack types like DoS and probing attacks. While not UAV-specific, its comprehensive range of network behaviors makes it useful for preliminary training and validation of network-based IDS frameworks that can later be specialized for UAV contexts [35].
- UAV Attack IDS Dataset: This dataset specifically simulates GPS spoofing and jamming attacks across multiple UAV simulation environments. It addresses critical threats to UAV positional integrity and communication reliability, providing targeted scenarios for assessing intrusion detection systems designed to protect UAVs from navigation-related cyber threats [26].
- Class imbalance: We often see UAV datasets where attack samples are few and far between—sometimes making up less than 10% of the total data. This uneven spread can trick IDS models into mostly recognizing normal behavior while missing actual threats. Researchers typically fix this by either balancing the dataset or adjusting how the model weighs different classes. On the flip side, some papers use datasets like CICIDS2017, where attacks are overrepresented through artificial generation. While this makes models look good on paper, they usually fail when faced with real drone networks.
- Attack labeling quality: Most UAV datasets do not label attacks the way security experts would—by carefully examining network packets or system responses. Instead, they rely on automated scripts or simulation triggers that might mark something as an attack when it is not, or miss real intrusions. This labeling problem worsens in virtual test environments like Gazebo, where there is no physical drone to confirm what is happening. When labels are unreliable, it is challenging to trust the detection metrics that models produce.
- Simulation fidelity: Some UAV datasets are just computer simulations that do not capture how drones communicate in the real world. They miss the radio frequency quirks, timing inconsistencies, and hardware feedback (like motor current changes) that occur during actual flights. These simulated datasets might include basic attacks like GPS spoofing, but they completely miss more complex threats that target groups of drones or exploit multiple vulnerabilities in sequence.
3.3. AI-Based Intrusion Detection Approaches
3.3.1. Supervised Learning IDS Approaches for UAV Networks
3.3.2. Unsupervised Learning and Hybrid IDS Approaches for UAV Networks
| Ref. | Model/ Algorithms | Dataset Used | Main Idea/Methodology | Key Findings | Performance Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [2] | LSTM | UAVCAN dataset, UAV attacks dataset, and Kitsune network attack dataset | Proposes E-DIDS, a fully distributed anomaly detection framework for UAV networks. The framework uses LSTM models trained on combined datasets to detect anomalies in real time, facilitating robust, distributed monitoring of UAV operations. | -Distributed IDS (E-DIDS) -Real-time capability -High accuracy demonstrated | Accuracy (Acc): 98.6%, loss of 0.091 |
| [40] | Optimized RF | NSL-KDD | Proposes a hierarchical IDS framework tailored for military UAV operations. It utilizes an optimized Random Forest classifier through Randomized Search Cross-Validation to effectively detect intrusions across multiple operational levels. | -Hierarchical design -Military UAV suitable -Optimized via random search | Multiclass: Acc: 97.24%, F1: 96.38%, Recall: 95.93%, Precision: 96.54% |
| [4] | LSTM-RNN | kDDCup 99, NSL-KDD, UNSW-NB15, Kyoto, CICIDS2017,and TON_IoT. | Introduces a distributed intrusion detection system leveraging LSTM-RNN models. The system emphasizes lightweight computational load, enabling deployment across various UAV platforms while maintaining high detection accuracy. | -Multi-dataset validation -Lightweight implementation -Distributed | Acc: Almost 99% |
| [41] | Random Forest | Framework dataset generated from network traces of FPV drones, IoT cameras, VoIP apps, background traffic, and public Wi-Fi. | Presents a real-time detection framework focused on identifying drone-related threats through WiFi traffic analysis. It employs Random Forest classifiers and a two-phase feature selection process for enhanced performance. | -Real-time detection -High accuracy (WiFi features) | Detection Acc: Upto 99% |
| [5] | Deep Belief Network, Particle Swarm Optimization (DBN-PSO) | KDD Cup 99 | Introduces an intrusion detection system utilizing Deep Belief Networks optimized through Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). The approach enhances DBN performance, demonstrating improved detection rates over traditional methods. | -PSO optimization -Deep learning approach -Moderate performance | Acc: 92.44%, Detection rate: 91.20%, Precision: 99.82%, False alarm rate: 0.68% |
| [42] | XGBoost | Cyber-Physical | Develops an IDS targeted for UAV applications within Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS). Utilizing XGBoost and comparative algorithms, it achieves superior performance and robustness against UAV-specific cyber threats. | -High precision IDS -UAV-focused dataset -Comparative evaluation | Acc: 98% Recall: 98.1% P: 98.1% F1: 98.1% |
| [43] | DT, KNN, RF | CSE-CIC-IDS2018 | Explores the efficacy of various supervised machine learning models, including Decision Trees, KNN, and Random Forests, for detecting intrusions. Highlights the exceptional performance of Decision Trees on specific attacks such as DoS. | -Decision tree best -Diverse ML models -High performance on DoS | Acc: 99.99%, FNR Rate 0% |
| [71] | RF, Suffix Tree and Fourier transformation | Contagio Malware Database | Introduces DNS-based detection mechanisms for Advanced Persistent Threats (APT) and malware within UAV IoT environments. The Random Forest classifier effectively identifies anomalies and malicious DNS behaviors. | -IoT-centric method -DNS anomaly detection -Effective malware detection | Acc: 94.88%, F1-score: 96%, AUC: 94.11% |
| [44] | RF, DT, NB, KNN | NSL-KDD | Proposes a cybersecurity framework integrating multiple classifiers for IoT-enabled UAV networks. The Random Forest classifier emerges as the best model, demonstrating high accuracy in identifying intrusions. | -RF best performer -IoT-enabled IDS | RF Accuracy: 97% |
| [47] | RF, KNN, SVM | CIC-IDS2018 | Presents an IDS simulation testbed specifically designed for UAV scenarios. Evaluates Random Forest Classifier and SVM, demonstrating RFC’s superior accuracy and robustness under diverse cyber-attack conditions. | -RF superior to SVM -UAV simulation testbed | RF, Acc: 96.2%, DR: 98.11% |
| [56] | DNN | UAV Intrusion Detection Dataset | Proposes a hybrid UAV security framework utilizing deep neural networks combined with ICMetric feature extraction for enhanced security of UAV communications. | -ICMetric-based IDS -High accuracy (DL) -Secure UAV applications | Accuracy: 99.99%, False Negative: 1.24%, False Positive: 0% |
| [72] | RF, DNN, CNN | UNSW-NB15 | Proposes a methodology for characterizing IDS performance by benchmarking various classifiers, showing Random Forest as the most effective model for intrusion detection tasks. | -RF highest accuracy -IDS characterization | Acc: upto 81.59%, Weighted Avg F1: 82.83% |
| [48] | Gaussian Processes, Linear Regression, Logistic, Multilayer Perceptron, SGD | Dataset not reported | Evaluates supervised ML classifiers to secure UAV WiFi communications. The study identifies MLP as the most effective in accuracy and response speed. | -MLP highest accuracy -WiFi-based dataset | MLP Accuracy: 72.7% |
| [49] | Optimized RF | CICIDS2017 | Introduces a cyber-edge IDS framework that employs optimized Random Forest for high-performance real-time detection in UAV communications. | -Edge computing IDS -Randomized optimization | Acc: 99.87%, Prec: 99.32%, Recall = 98.81%, F1: 99.06% |
| [62] | Hybrid CNN-LSTM | CICIDS2017 | Evaluates deep learning and machine learning models, demonstrating CNN + LSTM superiority in accuracy, precision, and recall metrics on large datasets. | -CNN + LSTM superior -Large dataset evaluation -High precision and recall | Acc: 99.06%, Precision: 99.07%, Recall 99.06%, F1: 99.065% |
| [50] | RF, LR, KNN, SVM, XGBoost | Generated Dataset | Develops an IDS using side-channel analysis data from UAV testbeds, showing XGBoost’s effectiveness in identifying real-time Hardware Trojan (HT) intrusions. | -Side-channel analysis -XGBoost effectiveness -Real UAV testbed | Yields ROC and Acc: up to 99.5% and 98% |
| [60] | Feedforward convolutional neural network (FFCNN) | UAVIDS Dataset | Proposes UAV-CIDS, a collaborative IDS framework employing convolutional neural networks to effectively identify intrusions in UAV operations. | -Collaborative approach -Convolutional NN -High accuracy and precision | Acc: 98.23%, Detection Rate: 99% |
| [61] | MLP | CSE-CIC-IDS2018 | Demonstrates a proof-of-concept deep learning-based intrusion detection model with MLP, achieving outstanding detection results. | -Proof-of-concept -High F1 scores | Acc: 96.3% |
| Ref. | Model/ Algorithms | Dataset Used | Main Idea/Methodology | Key Findings | Performance Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | One-Class Support Vector Machine, Isolation Forest, Local Outlier Factor, Denoising Autoencoder, Convolutional Autoencoder, LSTM Autoencoder | UAV ATTACK DATASET | Digital-twin-based unsupervised detection architecture for UAV resilience. | Enhanced spoofing detection; high resilience | Conv AE best performing with Acc: 99.75%, Precision: 97.65% Recall: 99.50% F1: 98.51 % AUC: 1.000 |
| [91] | Bi-LSTM, SVM, Observer | Custom UAV datasets | Hybrid IDS with observer mechanism for UAV real-time threats. | Robust; real-time detection | High precision and recall |
| [51] | Stacked AE, OC-SVM, LOF, Isolation Forest | UAV Attack Dataset | Unsupervised one-class classifiers trained on benign UAV flight data detect GPS jamming and spoofing by modeling normal behavior. | Avoids attack labeling, works across hardware, and detects novel threats | Stacked autoencoder scored highest (92.9%), followed by LOF (87.1%), Isolation Forest (83.6%), and OC-SVM (<80%) |
| [92] | Spectral Traffic Analysis | Hybrid UAV network | Spectral IDS for UAV dynamic threat detection. | Real-time UAV traffic analysis | Qualitative only |
| [45] | Decision Tree | CICIDS2017 | Hybrid ML-RL IDS for UAV ad hoc networks. | Adaptive learning; high accuracy | Acc: 100%, FP 0%, FN 0% |
| [57] | Linear Autoencoder | MAVLINK dataset | Unsupervised anomaly detection using reconstruction loss. | DoS and GPS spoofing detection | High Reconstruction Loss During Attack else < 0.05 |
| [93] | One-class Classifier- OC-SVM, LOF, Autoencoder | Generated Flight Log Dataset | Lightweight spoofing IDS for onboard UAV use. | Lightweight and GPS effective | GPS spoofing and jamming macro averaged F1: 90.57% and 94.3% |
| [89] | One-Class Support Vector Machine, Autoencoder Neural Network, and Local Outlier Factor | UAV ATTACK DATASET | Novelty-based UAV IDS for PX4 logs. | PX4 suitability; good detection | AE average F1 score of 94.81%, followed by OC-SVM (81.17%) and LOF (58.93%) |
| [90] | One-Class SVM, Isolation Forest, Local Outlier Factor | Generated via Hardware-in-the-loop simulation | PWM signal anomaly detection using unsupervised learning. | Embedded UAV detection; moderate accuracy | LOF achieved 75.87% accuracy, 88.66% precision, 63.80% recall, and an F1-score of 74.20% |
| [80] | Adversarial GAN, InfoGAN, WGAN | UAV Attack Dataset | GAN-augmented autoencoder IDS for spoofing defense. | Improved robustness via GAN | Detection rate for improved IDS 93.78% and 99.39%, Accuracy of 99.57% against GPS spoofing |
| [51] | FedAvg, FedAvgM, FedAdagrad, FedYogi, FedAdam | UAV Attack Dataset | Federated learning enables UAV swarms to collaboratively train anomaly detection models while preserving data privacy. | Each UAV trains a local stacked autoencoder; only parameters are shared for aggregation. | Best approach Fed Yogi F1: 90.4% |
3.3.3. Reinforcement Learning IDS Approaches for UAV Networks
3.3.4. Bio-Inspired, Other Algorithms, and Mixed IDS Approaches
| Ref. | Category | Model/ Algorithms | Dataset Used | Main Idea/Methodology | Performance Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [85] | Bio-inspired | SUAS-HIS | Simulated from Enviroment | Proposes a bio-inspired IDS (SUAS-HIS) based on the human immune system. | Detection Rate: > 92.93%, Packet Delivery Ratio: > 64.41%, False Positive Rate: < 6.89%, False Negative Rate < 3.95% |
| [86] | Specialized | Model-based observer techniques | Live flight data (position and orientation) generated by 5 Drones and captured by a VICON motion capture system at 50 Hz. | Centralized/decentralized IDS observers for UAV anomaly detection. | Zero Dynamics attack detected from 3.22 s, 5.08 s and Covert Attack at 6.4 s |
| [69] | Hierarchical, Game based | Multilayer cooperative AIS-based UAV IDS | ALFA UAV Network Dataset, NSL-KDD | Combines AIS and game theory for a hierarchical IDS for UAVs. | Acc: 96.13%, Detection Rate: 99.05% in ALFA, NSL-KDD dataset Acc: 95.93% |
| [87] | Cross-Layer Attention | Cross-Layer Convolutional Attention Network (CLCAN) | Tokyo metropolitan drone network communications data | Unified IDS for D2D and D2BS UAV communications using multi-scale CNNs, hierarchical attention, and cross-stream fusion. Real-time, improve scalability, and efficiency. | Acc: 98.4%, Recall: 98.7%, and F1: 98.1%, AUC: 99.1% |
| [82] | Graph Based | Graph Transformer, GraphSAGE, GCNN, GAT | UAVCAN dataset | Graph-learning IDS using modern GNNs, Effective for flooding detection | GraphSAGE reached 99.7% Acc, Graph-Based Transformer achieved 99.9% |
| [81] | Graph Based | Graph Neural Network | Cyber-Physical | GNN-based IDS for swarm communication anomalies. Swarm-focused defense; network-level | Acc: 98.42%, Precision: 98.85%, Recall: 98.97%, F1: 98.91% |
| [84] | Neuro-Fuzzy | ANFIS, Type-2 Fuzzy Logic | UAV ATTACK DATASET | Lightweight fuzzy logic IDS for UAV GPS attacks. High recall; low resource use, Model size only 5kB | Benign F1:0.847, Attack F1:0.899, AUC:0.921, Inference Time: 3024 µs. |
| [83] | Belief Rule Based | EBRB-based model, Evidential Reasoning | UAV intrusion detection Dataset | Interpretable IDS using belief rule-based logic. Accurate and explainable UAV IDS | Acc: 99.95%, Precision: 99.90%, F1: 99.95% |
| [80] | Adversarial GAN, InfoGAN, WGAN | UAV Attack Dataset | GAN-augmented autoencoder IDS for spoofing defense. | Improved robustness via GAN | Detection rate for improved IDS 93.78% and 99.39%, Accuracy of 99.57% against GPS spoofing |
| [79] | Optimal stacked autoencoder | MFSOSAE-ID | UNSW-NB15 | Stacked autoencoders enhanced with Firefly algorithm for hybrid IDS. Effective hybrid; high detection rate | Acc: 99.72%, Precision: 88.32%, Recall: 93.44%, F1: 90.31% |
3.4. Deployment Strategies of UAV Intrusion Detection Systems
3.4.1. Centralized Deployment
3.4.2. Decentralized (Distributed) Deployment
| Deployment Type | References | Technical Analysis (Advantages and Challenges) |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized | [5,41,42,43,44,46,48,50,51,52,56,59,61,62,64,65,66,68,71,72,76,79,80,81,83,84,87,89,90] | Centralized deployment processes all intrusion detection at a single node, usually the ground control station (GCS). This allows for high-performance analysis and the use of powerful models. However, it introduces latency, dependency on communication links, and a single point of failure. Suitable where real-time decisions are not critical. |
| Distributed | [1,2,3,4,40,45,47,49,53,57,60,63,67,73,75,77,78,82,85] | Distributed deployment places IDS modules on individual UAVs, enabling local detection with minimal latency. It is more robust against failure and faster in response, but constrained by limited processing power onboard. Trade-offs include lower model complexity and challenges in synchronized decision-making. |
| Federated | [51,58] | Federated deployment allows each UAV to train locally while sharing only model updates with a global aggregator. It preserves data privacy and enhances collective learning. However, it introduces synchronization delays and communication overhead and requires efficient update mechanisms. Best suited for scalable and privacy-sensitive applications. |
| Hybrid | [69,86,93] | Hybrid deployment combines aspects of centralized and distributed architectures, allowing UAVs to perform preliminary detection locally and escalate uncertain cases to a central unit (for instance, ground control station) for further analysis. This approach balances responsiveness with detection accuracy, enabling real-time mitigation while leveraging more complex analytics when needed. However, it adds architectural complexity, requires robust communication protocols, and may face integration challenges. Best suited for missions with mixed criticality and dynamic threat landscapes. |
3.4.3. Federated Deployment
3.5. Detection Methods in UAV IDS
3.5.1. Real-Time or Online Detection
3.5.2. Offline Detection
3.5.3. Hybrid Detection
3.6. Performance Metrics for UAV Intrusion Detection Systems
3.6.1. Accuracy
- Class Imbalance: UAV datasets frequently comprise over 90% benign instances [1], potentially inflating accuracy scores despite poor attack detection.
- Diverse Attack Patterns: Attacks like GPS spoofing or signal jamming require different detection sensitivities compared to typical network intrusions [2].
3.6.2. Precision
3.6.3. Recall (Detection Rate)
- Performance Trade-offs: Lightweight detection models might deliberately sacrifice some recall (around 5–10%) to achieve faster, real-time inference [49].
3.6.4. F1-Score
3.6.5. UAV-Specific Metrics
- Latency: Real-time detection latency must typically remain within 50–100 ms to ensure flight control responsiveness [49].
- Energy Consumption: Evaluated in joules per prediction to optimize onboard power utilization for extended UAV missions [72].
- Model Size: Crucial due to limited memory availability onboard UAV platforms, typically requiring models below 5 MB [47].
4. Result Analysis
4.1. Replication Protocol
- Preprocessing. We removed identifier/administrative fields and columns with >50% missing values when present; remaining NAs were set to zero. Categorical features were label/ordinal encoded. Numerical features were normalized with either Min–Max scaling or Standardization as specified for each dataset. All transformers (encoders/scalers) were fit on the training split only and applied to the test split. We did not use synthetic resampling or feature engineering unless stated.
- Partitions, seeds, and validation. Unless papers mandated other splits, we used stratified partitions with a fixed seed of value (42). Dataset-specific splits are reported in Table 11.
- Balancing. When class balancing was used (Tokyo–CLCAN; Cyber merged), it was performed after the train/test split, on the training split only, to avoid duplicated samples crossing partitions.
- Author contact. We did not contact the original authors. When preprocessing or partition details were omitted, we followed the conservative practices above and documented all choices.
- Data-loss control and leakage checks. We de-duplicated records before splitting where applicable, fit all transformers on training only, and verified that session-like identifiers (when available) did not cross partitions. These controls guard against label or distribution leakage.
| Dataset | Pipeline | Dropped/Selected Columns | Split/Seed = 42 | Scaling | Encoding/Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNSW-NB15 | DCA (CNN + Attn) | Drop id, srcip, sport, dstip, dsport, attack_cat, proto, service, state | 80/20 (strat.) | Min–Max (fit on train; apply to test) | Label-encode; target = label (binary) |
| Tokyo Drone Comm. | DCA (CNN + Attn) | Drop Timestamp, GPS Coordinates | 70/30 (strat.) | Min–Max (fit on train; apply to test) | Label-encode; multi-class |
| Tokyo Drone Comm. | LSTM/1D-CNN | Drop Timestamp, GPS Coordinates | 75/25 (strat.) | Min–Max (fit on train; apply to test) | Label-encode; multi-class |
| Tokyo Drone Comm. | ConvLSTM2D | Drop Timestamp, GPS Coordinates | 70/30 (strat.) | Min–Max (fit on train; apply to test) | Label-encode; multi-class |
| Tokyo Drone Comm. | AE + classical (DT/RF/KNN/ MLP/SVM) | Drop frame.number, wlan.bssid, timestamp_c | 75/25 (strat.) | Min–Max (fit on train; apply to test) | Label-encode; AE bottleneck = {8,4}; binary (benign vs. attack) |
| Tokyo Drone Comm. | CLCAN (15 features) | Packet Size, Transmission Rate, Battery Level, Signal Strength etc. | 70/30 (strat.) | StandardScaler | Upsample 8k/class on train only; one-hot |
| Cyber Merged | LSTM/1D-CNN (balanced) | Drop cols > 50% NA; remove remaining NA rows | 75/25 (strat.) | Min–Max (fit on train; apply to test) | Label-encode; upsample 3500/class on train only; 5-class |
| Cyber Merged | CLCAN (balanced) | Drop cols > 50% NA; remove remaining NA rows | 70/30 (strat.) | StandardScaler | Upsample 8000/class on train only; one-hot |
| Cyber Merged (aligned) | AE + classical (DT/RF/KNN/ MLP/SVM) | Align across {benign, dos, replay, eviltwin, fdi}; drop frame.number, wlan.bssid, timestamp_c; fill NA = 0 | 75/25 (strat.) | Min–Max (fit on train; apply to test) | Label-encode; 5-class and a binary view (benign vs. attack) |
| WSN-DS | CNN–LSTM; ConvLSTM2D | Drop cols > 50% NA; fill NA = 0 | 70/30 (strat.) | Min–Max (fit on train; apply to test) | Label-encode; multi-class |
| UAVCAN CAN logs | RF/DT; LSTM | Features = can_id, dlc, data_0.12; exclude timestamp | 70/30 (strat.) | Min–Max (fit on train; apply to test) | Labels = {benign, replay, fuzzy, flood, spoof} (5-class) |
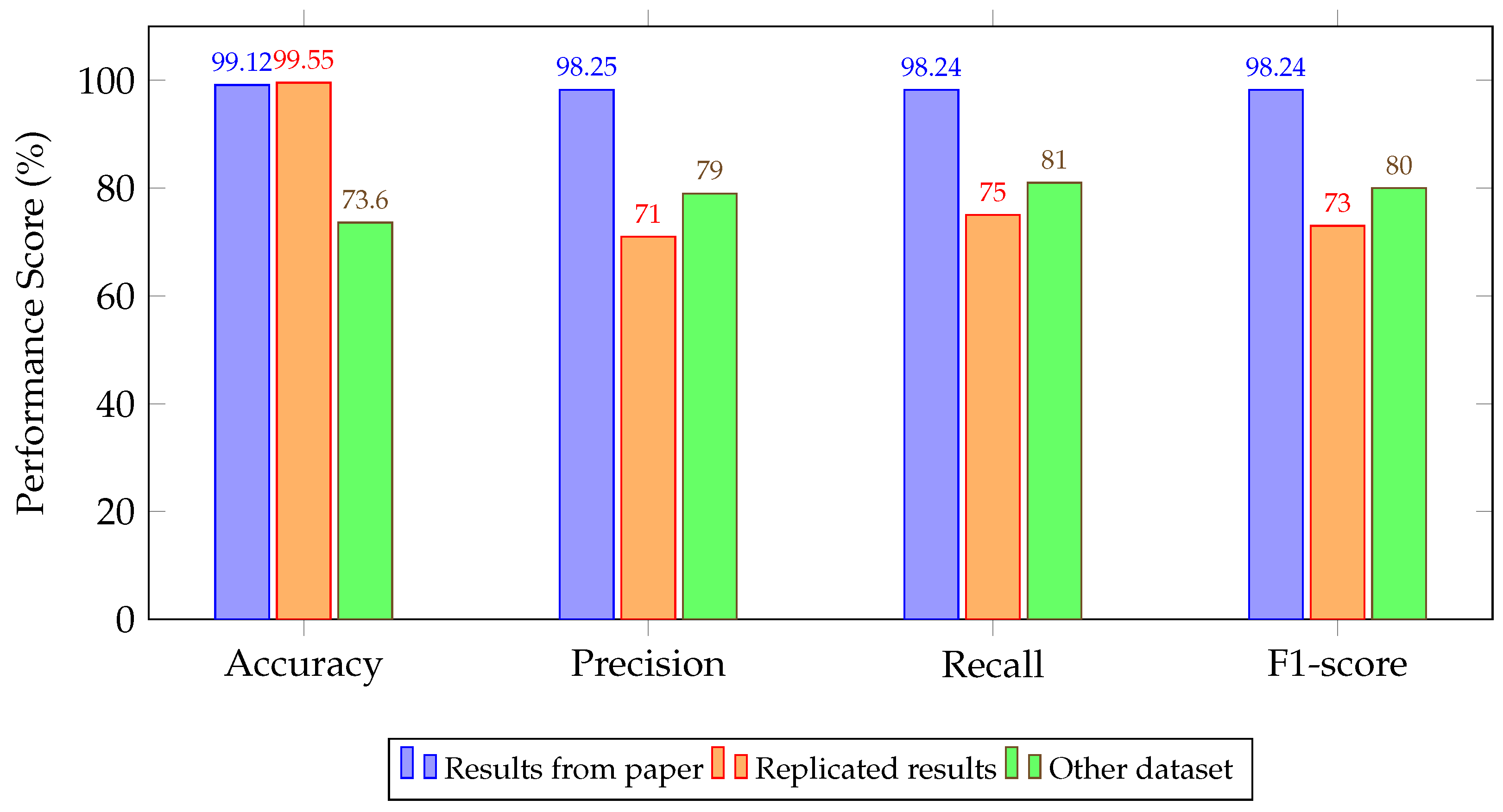
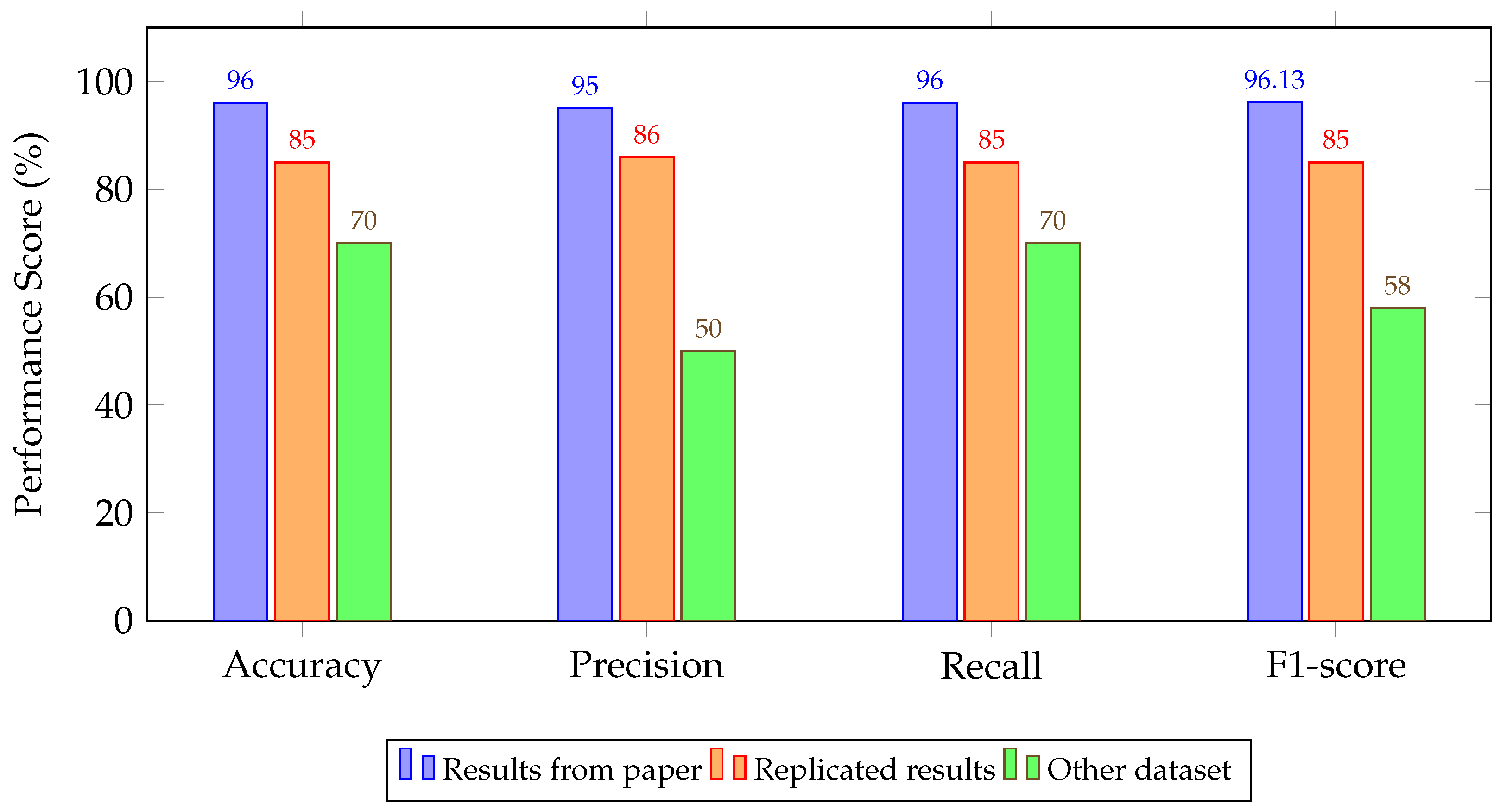
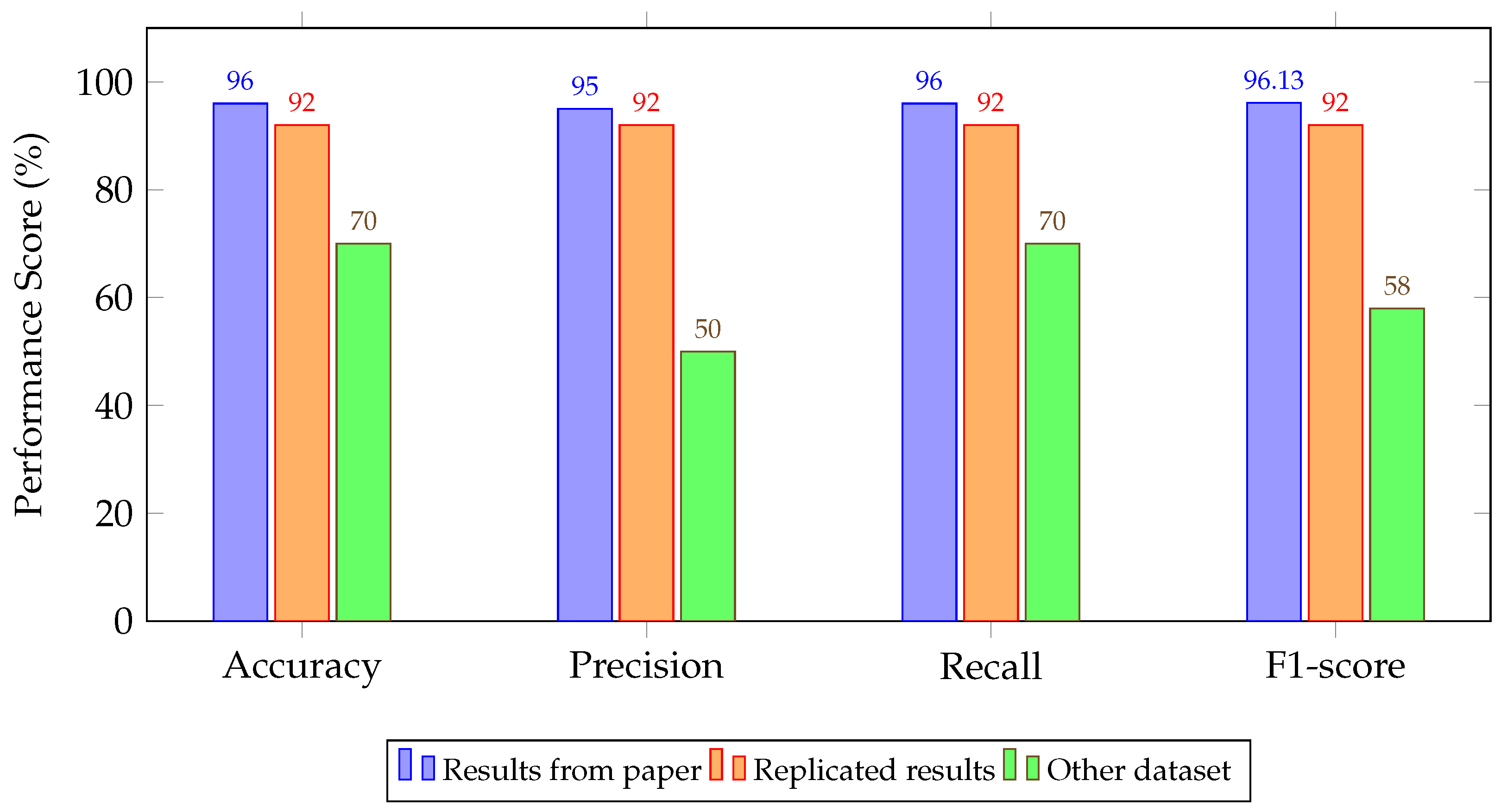
4.2. Experimental Results
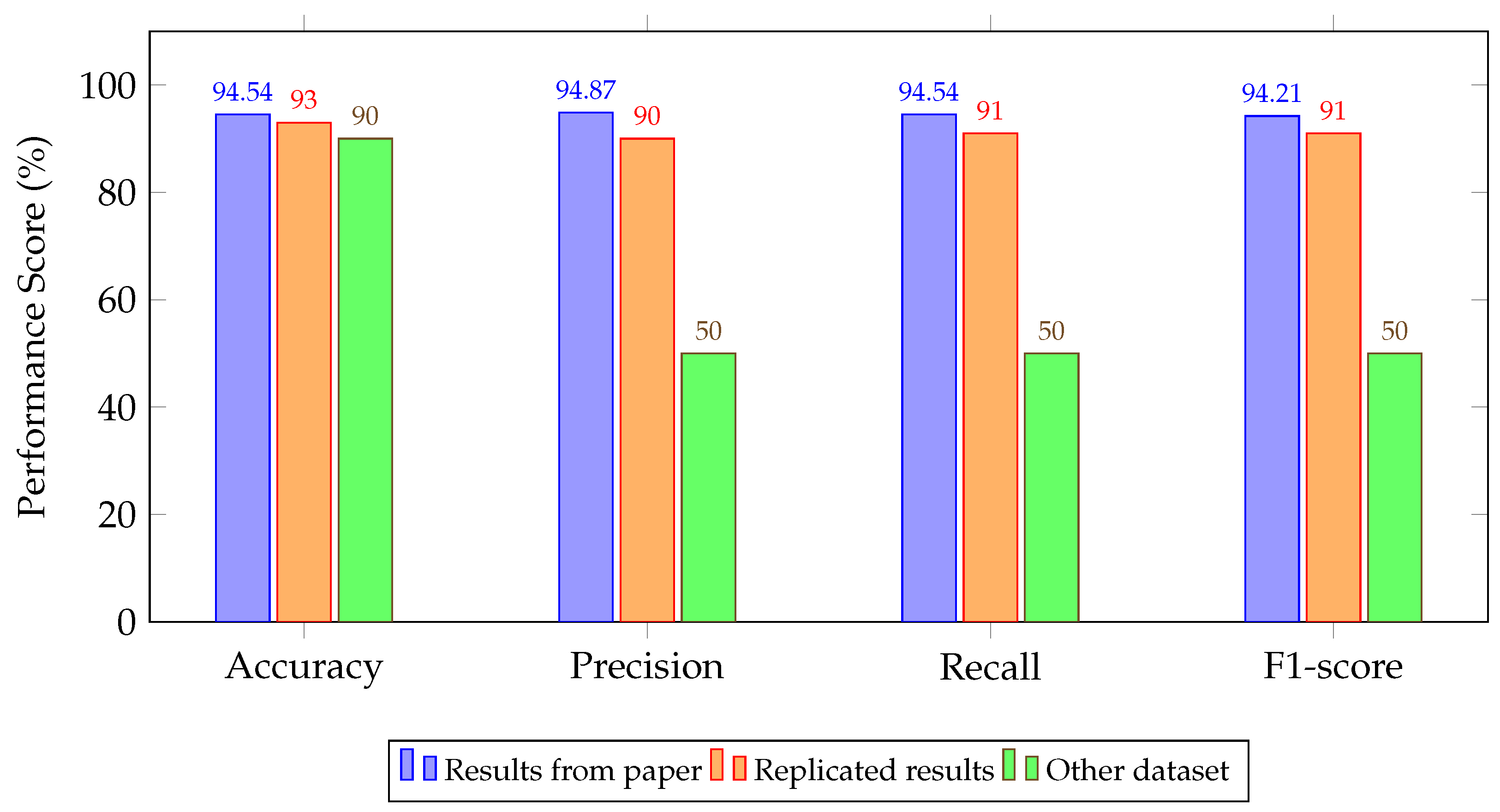

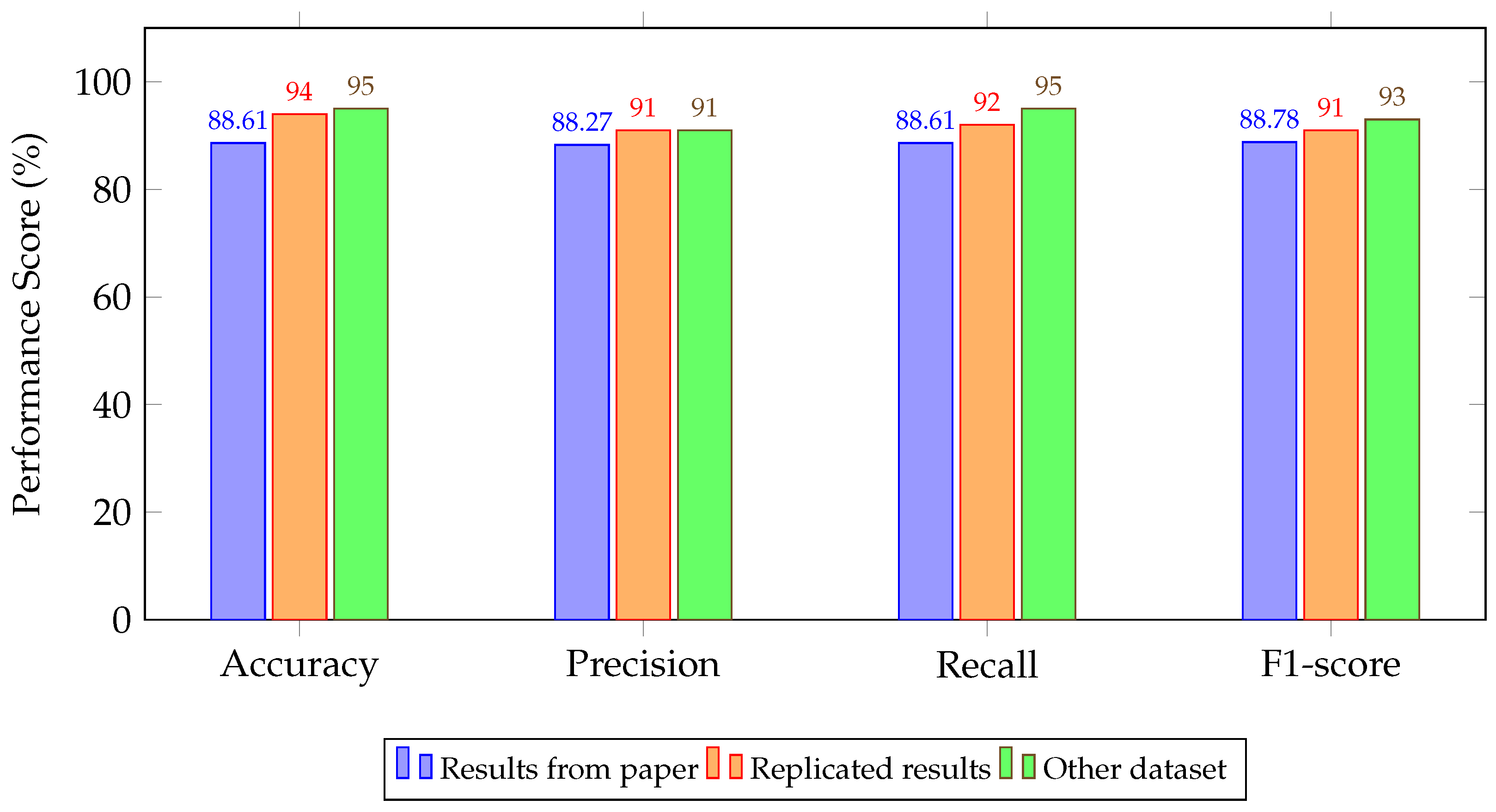



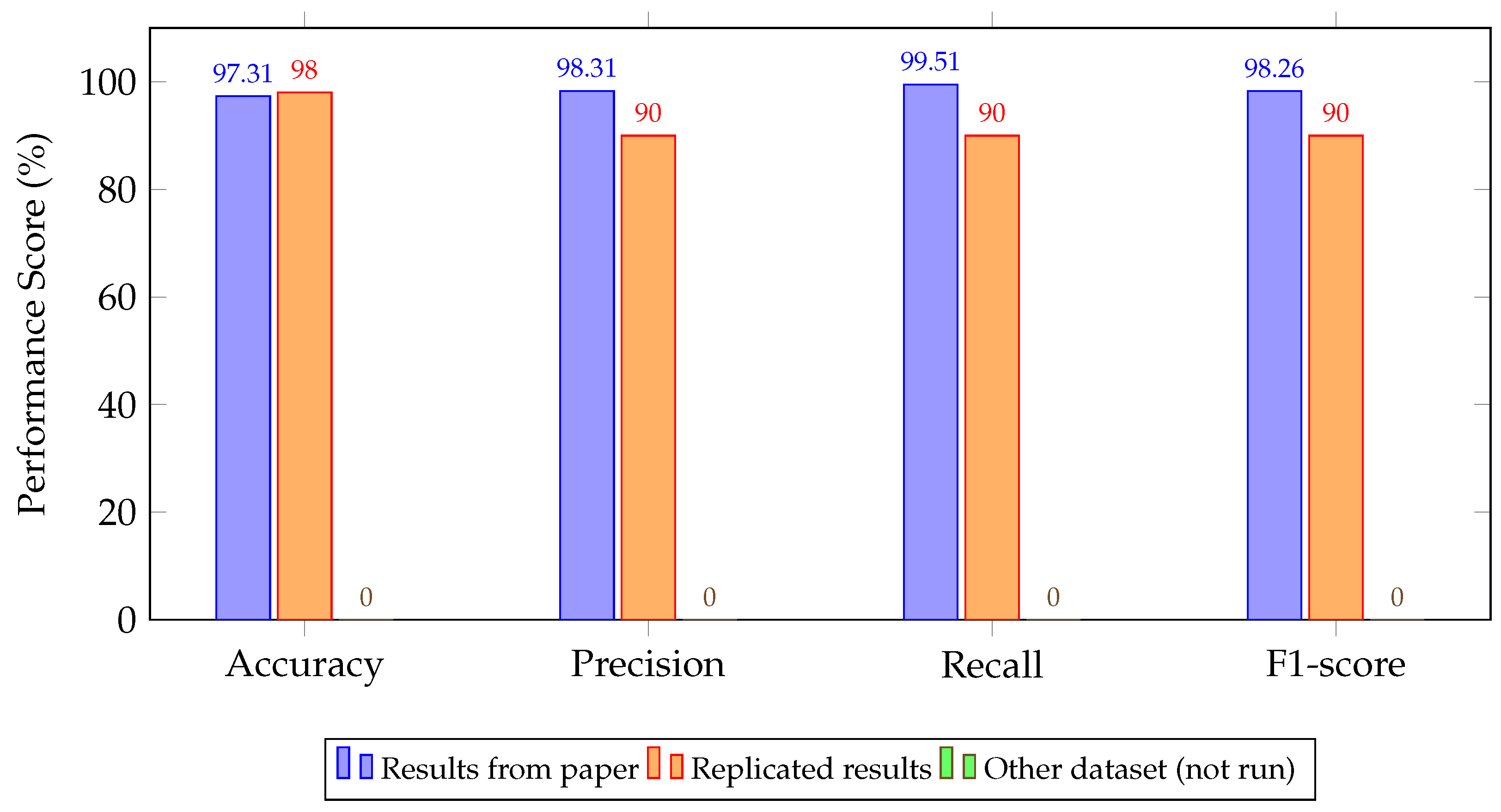
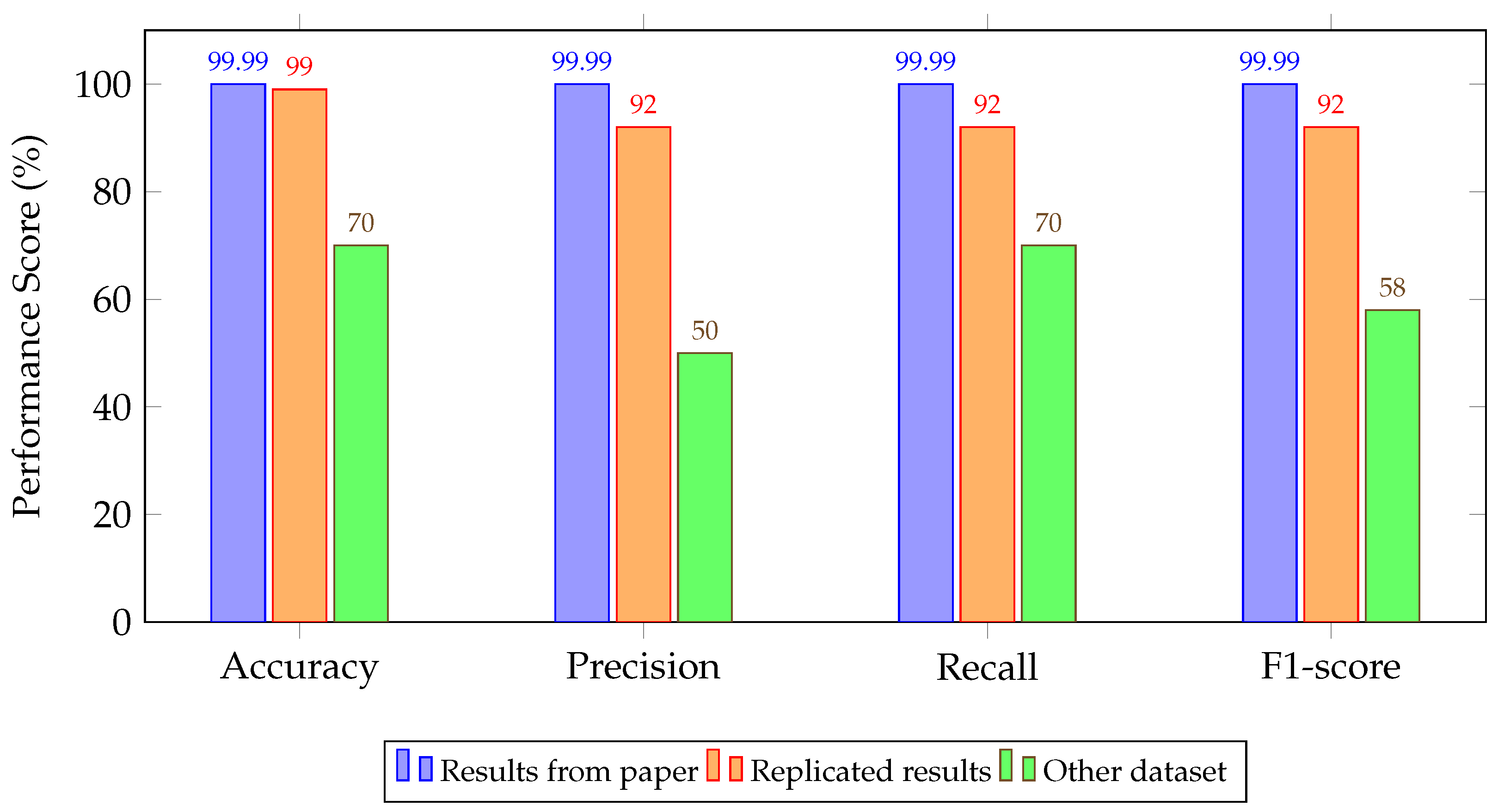
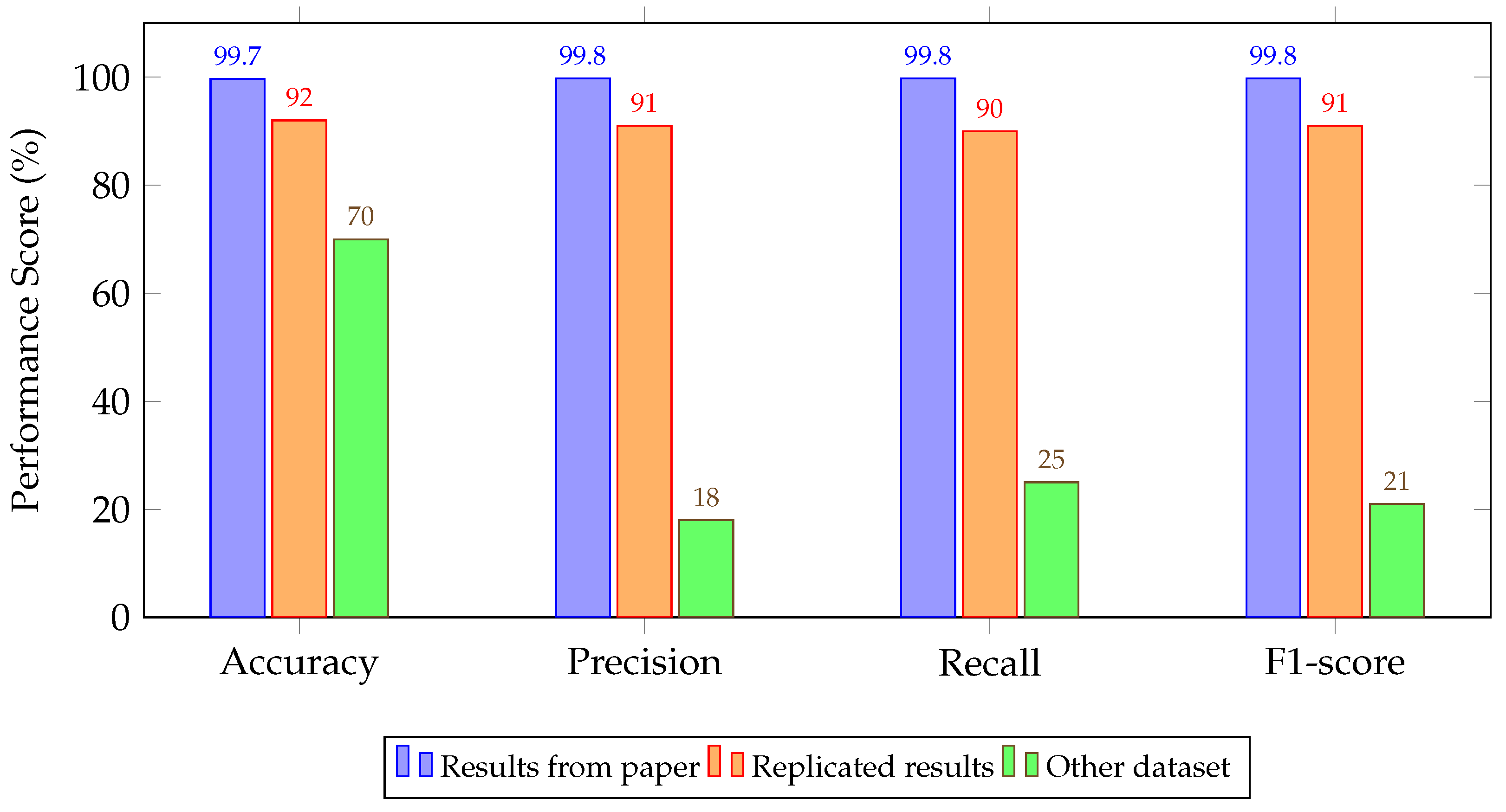
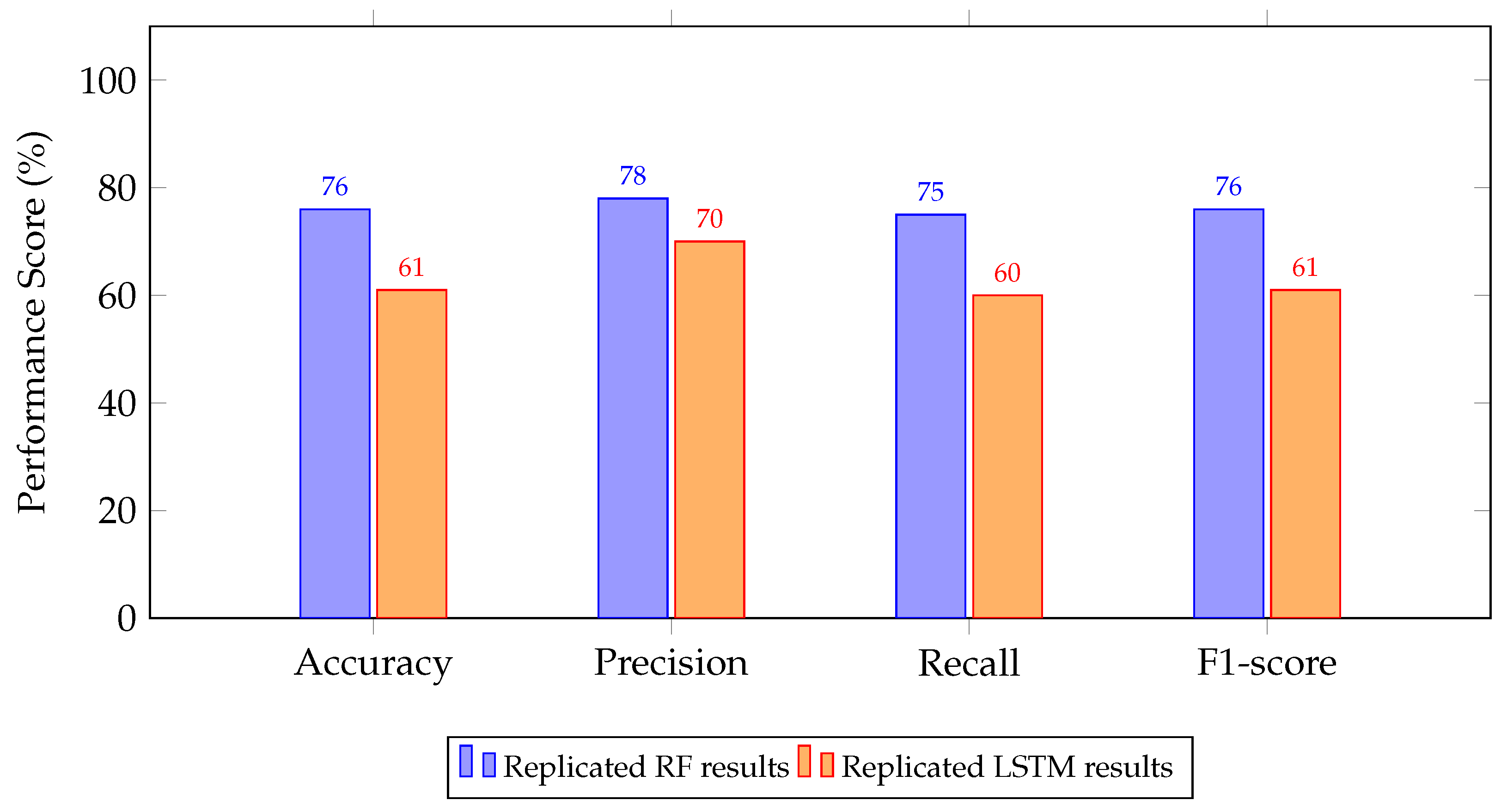
5. Discussion and Key Findings
5.1. RQ1—Dataset Relevance and Model Generalizability
- Inconsistent data preprocessing and train-test splits obstruct proper comparisons.
- Feature selection and normalization choices significantly affect reported accuracy.
- Data augmentation methods (oversampling, synthetic attacks) may distort true performance.
- Domain-specific datasets provide better UAV threat detection
- Multi-dataset validation provides stronger generalizability evidence
- Standardized UAV IDS benchmarks are urgently needed for reliable model assessment
5.2. RQ2—Trade-Offs Between Real-Time and Offline Detection
5.3. RQ3—Suitability of Centralized, Distributed, and Federated Deployment
5.4. Evaluation of Different AI Paradigms
6. Recommendations and Future Work
6.1. Improve Dataset Quality and Standardization
6.2. Lightweight, Real-Time Models
6.3. Privacy-Preserving and Federated Learning Approaches
6.4. Energy-Efficient and Resource-Aware IDS Architecture
6.5. Addressing Model Robustness and Explainability
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fraser, B.; Al-Rubaye, S.; Aslam, S.; Tsourdos, A. Enhancing the Security of Unmanned Aerial Systems using Digital-Twin Technology and Intrusion Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/AIAA 40th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), IEEE, San Antonio, TX, USA, 3–7 October 2021; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tlili, F.; Ayed, S.; Chaari Fourati, L. Exhaustive distributed intrusion detection system for UAVs attacks detection and security enforcement (E-DIDS). Comput. Secur. 2024, 142, 103878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Abdulghani, A.; M. Abdulghani, M.; L. Walters, W.; H. Abed, K. Improving Intrusion Detection in UAV Communication Using an LSTM-SMOTE Classification Method. J. Cyber Secur. 2022, 4, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, R.A.; Emara, A.H.; Al-Sarem, M.; Elhamahmy, M. Internet of Drones Intrusion Detection Using Deep Learning. Electronics 2021, 10, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Su, S.; Zuo, Z.; Guo, X.; Sun, X. Intrusion Detection of UAVs Based on the Deep Belief Network Optimized by PSO. Sensors 2019, 19, 5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceviz, O.; Sen, S.; Sadioglu, P. A Survey of Security in UAVs and FANETs:Issues, Threats, Analysis of Attacks, and Solutions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Kumar, N.; Alsamhi, S.H.; Barb, G.; Zywiołek, J.; Ullah, I.; Noor, F.; Shah, J.A.; Almuhaideb, A.M. Security and Privacy Issues and Solutions for UAVs in B5G Networks: A Review. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2025, 22, 892–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.B.; Fourati, L.C. Investigation on datasets toward intelligent intrusion detection systems for Intra and inter-UAVs communication systems. Comput. Secur. 2025, 150, 104215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, E.; Waheed, T.; Calabrò, A. Cybersecurity Testing in Drones Domain: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 171166–171184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostis, I.; Kotzanikolaou, P.; Douligeris, C. Understanding and Securing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Services: A Comprehensive Tutorial. TechRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, K.Y.; Girdler, T.; Vassilakis, V.G. A survey of cyber security threats and solutions for UAV communications and flying ad-hoc networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2022, 133, 102894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıkaya, B.S.; Bahtiyar, Ş. A survey on security of UAV and deep reinforcement learning. Ad Hoc Netw. 2024, 164, 103642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimon, O.; Götthans, T. A Survey on the Use of Deep Learning Techniques for UAV Jamming and Deception. Electronics 2022, 11, 3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.M.; Ferrao, I.G.; Branco, K.R.L.J.C. A Systematic Mapping Study in Intrusion Detection System for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Security. In Proceedings of the 2022 Latin American Robotics Symposium (LARS), 2022 Brazilian Symposium on Robotics (SBR), and 2022 Workshop on Robotics in Education (WRE), IEEE, São Bernardo do Campo, Brazil, 18–21 October 2022; pp. 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar Jagatheesaperumal, S.; Rahouti, M.; Chehri, A.; Xiong, K.; Bieniek, J. Blockchain-Based Security Architecture for Uncrewed Aerial Systems in B5G/6G Services and Beyond: A Comprehensive Approach. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2025, 6, 1042–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.B.; Fourati, L.C.; Fakhrudeen, A.M. Comprehensive systematic review of intelligent approaches in UAV-based intrusion detection, blockchain, and network security. Comput. Netw. 2024, 239, 110140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadi, R.; Ghazzai, H.; Massoud, Y. Reinforcement Learning Based Intrusion Detection Systems for Drones: A Brief Survey. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Smart Mobility (SM), IEEE, Thuwal, Saudi Arabia, 19–21 March 2023; pp. 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Adil, M.; Song, H.; Mastorakis, S.; Abulkasim, H.; Farouk, A.; Jin, Z. UAV-Assisted IoT Applications, Cybersecurity Threats, AI-Enabled Solutions, Open Challenges with Future Research Directions. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 9, 4583–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljehani, M.; Inoue, M.; Watanbe, A.; Yokemura, T.; Ogyu, F.; Iida, H. UAV communication system integrated into network traversal with mobility. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chriki, A.; Touati, H.; Snoussi, H.; Kamoun, F. FANET: Communication, mobility models and security issues. Comput. Netw. 2019, 163, 106877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekmezci, İ.; Sahingoz, O.K.; Temel, Ş. Flying Ad-Hoc Networks (FANETs): A survey. Ad Hoc Netw. 2013, 11, 1254–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altawy, R.; Youssef, A.M. Security, privacy, and safety aspects of civilian drones: A survey. ACM Trans. Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2016, 1, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekmezci, İ.; Şentürk, E.; Türker, T. Security issues in flying ad-hoc networks (FANETS). J. Aeronaut. Space Technol. 2016, 9, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ghurab, M.; Gaphari, G.; Alshami, F.; Alshamy, R.; Othman, S. A Detailed Analysis of Benchmark Datasets for Network Intrusion Detection System. Asian J. Res. Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorcia-Gutierrez, J.; Gamarra, M.; Leal, E.; Madera, N.; Soto, C.; Mansour, R.F.; Alharbi, M.; Alkhayyat, A.; Gupta, D. Sea turtle foraging algorithm with hybrid deep learning-based intrusion detection for the internet of drones environment. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 108, 108704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, F.; Ayed, S.; Chaari Fourati, L. Dynamic intrusion detection framework for UAVCAN protocol using AI. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security (ARES), ACM, Benevento, Italy, 9 August–1 September 2023; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bujari, A.; Palazzi, C.E.; Ronzani, D. FANET Application Scenarios and Mobility Models. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Micro Aerial Vehicle Networks, Systems, and Applications (MobiSys), ACM, Niagara Falls, NY, USA, 23 June 2017; pp. 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Giordan, D.; Adams, M.S.; Aicardi, I.; Alicandro, M.; Allasia, P.; Baldo, M.; De Berardinis, P.; Dominici, D.; Godone, D.; Hobbs, P.; et al. The use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for engineering geology applications. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 3437–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, T.F.; Salimi, F.; Morton, K.; Morawska, L.; Gonzalez, F. Development and validation of a UAV based system for air pollution measurements. Sensors 2016, 16, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahuza, M.; Idris, M.Y.I.; Ahmedy, I.B.; Wahab, A.W.A.; Nandy, T.; Noor, N.M.; Bala, A. Internet of Drones Security and Privacy Issues: Taxonomy and Open Challenges. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 57243–57270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, L.; Jain, R.; Vaszkun, G. Survey of Important Issues in UAV Communication Networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 1123–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezwan, S.; Choi, W. A survey on applications of reinforcement learning in flying ad-hoc networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoub, J.P.; Noura, H.; Salman, O.; Chehab, A. Security analysis of drones systems: Attacks, limitations, and recommendations. Internet Things 2020, 11, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, M.; Layeghy, S.; Moustafa, N.; Portmann, M. NetFlow Datasets for Machine Learning-Based Network Intrusion Detection Systems. In Big Data Technologies and Applications (BDTA 2020); Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 117–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hassija, V.; Chamola, V.; Agrawal, A.; Goyal, A.; Luong, N.C.; Niyato, D.; Yu, F.R.; Guizani, M. Fast, Reliable, and Secure Drone Communication: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 2802–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halisdemir, M.E.; Karacan, H.; Pihelgas, M.; Lepik, T.; Cho, S. Data quality problem in AI-based network intrusion detection systems studies and a solution proposal. In Proceedings of the 2022 14th International Conference on Cyber Conflict: Keep Moving! (CyCon), IEEE, Tallinn, Estonia, 31 May–3 June 2022; Volume 700, pp. 367–383. [Google Scholar]
- Gargalakos, M. The role of unmanned aerial vehicles in military communications: Application scenarios, current trends, and beyond. J. Def. Model. Simul. 2024, 21, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Syouf, R.A.; Bani-Hani, R.M.; AL-Jarrah, O.Y. Machine learning approaches to intrusion detection in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 18009–18041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihekoronye, V.U.; Ajakwe, S.O.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, J.M. Hierarchical Intrusion Detection System for Secured Military Drone Network: A Perspicacious Approach. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2022—2022 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), IEEE, Rockville, MD, USA, 28 November–2 December 2022; pp. 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Alsoliman, A.; Rigoni, G.; Callegaro, D.; Levorato, M.; Pinotti, C.M.; Conti, M. Intrusion Detection Framework for Invasive FPV Drones Using Video Streaming Characteristics. ACM Trans. Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 7, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, T.A.O.D.; Ferrão, R.C.; Cugnasca, P.S. Machine Learning Models for Intrusion Detection in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: An Approach to Cybersecurity and Operational Safety. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 27th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), IEEE, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 24–27 September 2024; pp. 4236–4241. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, R.; Omidkar, A.; Roudi, S.A.; Abbas, R.; Kim, S. Machine-Learning-Enabled Intrusion Detection System for Cellular Connected UAV Networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Mishra, S. ML-based Intrusion Detection for Drone IoT Security. J. Cybersecur. Inf. Manag. 2024, 14, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouiazzane, S.; BarramoU, F.; Addou, M. Towards a multi-agent based network intrusion detection system for a fleet of drones. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2020, 11, 315–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, N.; Jolfaei, A. Autonomous detection of malicious events using machine learning models in drone networks. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM MobiCom Workshop on Drone Assisted Wireless Communications for 5G and Beyond (MobiCom), ACM, London, UK, 25 September 2020; pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, R.T.; Ahmed, G.; Siddiqui, S. Simulating ML-Based Intrusion Detection System for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) using COOJA Simulator. In Proceedings of the 2022 16th International Conference on Open Source Systems and Technologies (ICOSST), IEEE, Lahore, Pakistan, 14–15 December 2022; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sivachandran, M.; Krishnakumar, T. Classification approaches in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) intrusion detection data set by using big data analysis. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 51, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihekoronye, V.U.; Ajakwe, S.O.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, J.M. Cyber Edge Intelligent Intrusion Detection Framework For UAV Network Based on Random Forest Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2022 13th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), IEEE, Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 19–21 October 2022; pp. 1242–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, A.; Asif, M.; Rahman, M.T.; Rahman, M.A. Side-Channel-Driven Intrusion Detection System for Mission Critical Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2024 25th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ISQED), IEEE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–5 April 2024; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, L.M.; Ferrão, I.G.; Dezan, C.; Espes, D.; Branco, K.R.L.J.C. Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection System for In-Flight and Network Security in UAV Swarm. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), IEEE, Warsaw, Poland, 6–9 June 2023; pp. 812–819. [Google Scholar]
- Akbar, M.R.; Nuha, H.H.; Mugitama, S.A. Intrusion Detection on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) using Binary Decision Tree. In Proceedings of the 2023 11th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology (ICoICT), IEEE, Melaka, Malaysia, 23–24 August 2023; pp. 633–638. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.T.; Kisacikoglu, M.; Akkaya, K. Intrusion detection systems-enabled power electronics for unmanned aerial vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE CyberPELS (CyberPELS), IEEE, Miami, FL, USA, 13 October 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sarikaya, B.S.; Bahtiyar, Ş. Generative Adversarial Networks for Synthetic Jamming Attacks on UAVs. In Proceedings of the 2024 9th International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering (UBMK), IEEE, Antalya, Turkiye, 26–28 October 2024; pp. 760–765. [Google Scholar]
- Vuong, T.C.; Nguyen, C.C.; Pham, V.C.; Le, T.T.H.; Tran, X.N.; Van Luong, T. Effective Intrusion Detection for UAV Communications using Autoencoder-based Feature Extraction and Machine Learning Approach. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.02827. [Google Scholar]
- Alheeti, K.M.A.; Khaled Alarfaj, F.; Alreshoodi, M.; Almusallam, N.; Al Dosary, D. A hybrid security system for drones based on ICMetric technology. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Park, E.; Kim, H.K. Unsupervised intrusion detection system for unmanned aerial vehicle with less labeling effort. In Proceedings of the Information Security Applications: 21st International Conference, (WISA), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 26–28 August 2020; pp. 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ntizikira, E.; Lei, W.; Alblehai, F.; Saleem, K.; Lodhi, M.A. Secure and Privacy-Preserving Intrusion Detection and Prevention in the Internet of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Sensors 2023, 23, 8077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulalan, V.; Balamurugan, G.; Premanand, V. A Deep CNN Framework for UAV Intrusion Detection in Intelligent Systems. Int. J. Recent Innov. Trends Comput. Commun. 2023, 11, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil Hadi, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Real-Time Collaborative Intrusion Detection System in UAV Networks Using Deep Learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 33371–33391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schermann, R.; Ammerer, T.; Stelzer, P.; Macher, G.; Steger, C. Risk-Aware Intrusion Detection and Prevention System for Automated UAS. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 34th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops (ISSREW), IEEE, Florence, Italy, 9–12 October 2023; pp. 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Niyonsaba, S.; Konate, K.; Soidridine, M.M. Deep Learning Based Intrusion Detection for Cybersecurity in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Network. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Energy Technologies (ICECET), IEEE, Chengdu, China, 12–14 April 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, S.N.; Manickam, S.; Zia, S.S.; Abro, A.A.; Obaidat, M.; Uddin, M.; Abdelhaq, M.; Alsaqour, R. IoT empowered smart cybersecurity framework for intrusion detection in internet of drones. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, A. Novel Approach for Intrusion Detection Attacks on Small Drones Using ConvLSTM Model. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 149238–149253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javeed, D.; Gao, T.; Kumar, P.; Shoukat, S.; Ahmad, I.; Kumar, R. An Intelligent and Interpretable Intrusion Detection System for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. In Proceedings of the ICC 2024—IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), IEEE, Denver, CO, USA, 9–13 June 2024; pp. 1951–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, L.; Ding, S.; Wu, T.; Dong, W.; Yin, Y. An Intrusion Detection Model for Drone Communication Network in SDN Environment. Drones 2022, 6, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Arora, A. A Novel Distributed Anomaly Intrusion Detection Model for Drone Swarm Network in Smart Nations. In Proceedings of the 2023 Second International Conference On Smart Technologies For Smart Nation (SmartTechCon), IEEE, Singapore, 18–19 August 2023; pp. 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, S.; Pan, Q.; Zheng, D.; Mohi-ud din, G. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Intrusion Detection: Deep-Meta-Heuristic System. Veh. Commun. 2024, 46, 100726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, J.; Li, W.; Fang, W.; Lan, X.; Ma, W.; Li, T. A Hierarchical Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Network Intrusion Detection and Response Approach Based on Immune Vaccine Distribution. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 33312–33325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menssouri, S.; Delamou, M.; Ibrahimi, K.; Amhoud, E.M. Enhanced Intrusion Detection System for Multiclass Classification in UAV Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 35th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), IEEE, Valencia, Spain, 2–5 September 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, W.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Du, X.; Huang, X.; Guizani, M. Malware on Internet of UAVs Detection Combining String Matching and Fourier Transformation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 9905–9919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, C.; Morge-Rollet, L.; Lemarchand, L.; Le Roy, F.; Espes, D.; Boukhobza, J. Characterizing Intrusion Detection Systems On Heterogeneous Embedded Platforms. In Proceedings of the 2023 26th Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD), IEEE, Golem, Albania, 6–8 September 2023; pp. 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Mughal, U.A.; Hassler, S.C.; Ismail, M. Machine Learning-Based Intrusion Detection for Swarm of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS), IEEE, Orlando, FL, USA, 2–5 October 2023; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.W.; Yoo, D.Y. Multiple Intrusion Detection Using Shapley Additive Explanations and a Heterogeneous Ensemble Model in an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle’s Controller Area Network. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhamed, O.; Bouachir, O.; Aloqaily, M.; Al Ridhawi, I. Lightweight ids for uav networks: A periodic deep reinforcement learning-based approach. In Proceedings of the 2021 IFIP/IEEE International Symposium on Integrated Network Management (IM), IEEE, Bordeaux, France, 17–21 May 2021; pp. 1032–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Praveena, V.; Vijayaraj, A.; Chinnasamy, P.; Ali, I.; Alroobaea, R.; Yahya Alyahyan, S.; Ahsan Raza, M. Optimal Deep Reinforcement Learning for Intrusion Detection in UAVs. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 70, 2639–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Han, T.; Li, R. Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Based Intrusion Detection in Aerial Computing Networks. IEEE Netw. 2021, 35, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhu, Z.; Xia, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhu, X.; Ye, N. A Q-Learning-Based Two-Layer Cooperative Intrusion Detection for Internet of Drones System. Drones 2023, 7, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. Mohamed, H.; S. Alotaibi, S.; M. Eltahir, M.; Mohsen, H.; Ahmed Hamza, M.; Sarwar Zamani, A.; Yaseen, I.; Motwakel, A. Feature Selection with Stacked Autoencoder Based Intrusion Detection in Drones Environment. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 73, 5441–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Akkaya, K.; Shahriar, H.; Cuzzocrea, A. Adversarial Data-Augmented Resilient Intrusion Detection System for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData), IEEE, Sorrento, Italy, 15–18 December 2023; pp. 5428–5437. [Google Scholar]
- Mughal, U.A.; Atat, R.; Ismail, M. Graph Neural Network-Based Intrusion Detection System for a Swarm of UAVs. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2024—2024 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), IEEE, Washington, DC, USA, 6 December 2024; pp. 578–583. [Google Scholar]
- Majumder, R.; Comert, G.; Werth, D.; Gale, A.; Chowdhury, M.; Salek, M.S. Graph-Powered Defense: Controller Area Network Intrusion Detection for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.02539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; He, W.; Zhu, H.; Yang, R.; Mu, Q. A new unmanned aerial vehicle intrusion detection method based on belief rule base with evidential reasoning. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.A.; Rahman, M.A. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System-based Lightweight Intrusion Detection System for UAVs. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 48th Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN), IEEE, Daytona Beach, FL, USA, 2–5 October 2023; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fotohi, R. Securing of Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) against security threats using human immune system. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 193, 106675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, M.; Jafarnejadsani, H. Detection of stealthy adversaries for networked unmanned aerial vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), IEEE, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 1111–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Aldossary, M.; Alzamil, I.; Almutairi, J. Enhanced Intrusion Detection in Drone Networks: A Cross-Layer Convolutional Attention Approach for Drone-to-Drone and Drone-to-Base Station Communications. Drones 2025, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsumayt, A.; Nagy, N.; Alsharyofi, S.; Al Ibrahim, N.; Al-Rabie, R.; Alahmadi, R.; Alesse, R.A.; Alahmadi, A.A. Detecting Denial of Service Attacks (DoS) over the Internet of Drones (IoD) Based on Machine Learning. Sci 2024, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, J.; Sangarapillai, T.; Minawi, O.; Almehmadi, A.; El-Khatib, K. Novelty-based Intrusion Detection of Sensor Attacks on Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM Symposium on QoS and Security for Wireless and Mobile Networks (MSWiM), ACM, Alicante, Spain, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Alva, A.; Moreno, L.M.; Asif, M.; Khalil, A.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Cuzzocrea, A.; Hossain, S. Secured UAV Navigation: A Novel Intrusion Detection System Based on PWM Signal Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2024 11th IEEE Swiss Conference on Data Science (SDS), IEEE, Zurich, Switzerland, 30–31 May 2024; pp. 174–180. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R. Intrusion Detection System in a Fleet of Drones. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut Supérieur de l’Aéronautique et de l’Espace, Toulouse, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Condomines, J.P.; Zhang, R.; Larrieu, N. Network intrusion detection system for UAV ad-hoc communication: From methodology design to real test validation. Ad Hoc Netw. 2019, 90, 101759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, J.; Almehmadi, A.; El-Khatib, K. Artificial intelligence for intrusion detection systems in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 99, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, I.M.; Mase, J.M.; Rengasamy, D.; Rothwell, B.; Figueredo, G.P. Anomaly Detection for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Sensor Data Using a Stacked Recurrent Autoencoder Method with Dynamic Thresholding. SAE Int. J. Aerosp. 2022, 15, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmila, B.S.; Nagapadma, R. Quantized autoencoder (QAE) intrusion detection system for anomaly detection in resource-constrained IoT devices using RT-IoT2022 dataset. Cybersecurity 2023, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotohi, R.; Abdan, M. A Self-Adaptive Intrusion Detection System for Securing UAV-to-UAV Communications Based on the Human Immune System in UAV Networks. J. Grid Comput. 2022, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarayalu, V.; Vensuslaus, M.A. An Intrusion Detection System for Drone Swarming Utilizing Timed Probabilistic Automata. Drones 2023, 7, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.; Bouk, S.H. Intrusion Detection Systems for Flying Ad-hoc Networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.05589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, L.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q. Intrusion Detection of UAVs in Cell-Free Networks with Clock Asynchronism. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems (ICUS), IEEE, Nanjing, China, 18–20 October 2024; pp. 1492–1497. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W.; Almaiah, M.A.; Ali, A.; Al-Shareeda, M.A. Deep Learning Based Network intrusion detection for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). In Proceedings of the 2024 7th World Conference on Computing and Communication Technologies (WCCCT), IEEE, Chengdu, China, 12–14 April 2024; pp. 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ceviz, O.; Sadioglu, P.; Sen, S.; Vassilakis, V.G. A novel federated learning-based IDS for enhancing UAVs privacy and security. Internet Things 2025, 31, 101592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alissa, K.A.; Alotaibi, S.S.; Alrayes, F.S.; Aljebreen, M.; Alazwari, S.; Alshahrani, H.; Ahmed Elfaki, M.; Othman, M.; Motwakel, A. Crystal Structure Optimization with Deep-Autoencoder-Based Intrusion Detection for Secure Internet of Drones Environment. Drones 2022, 6, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, S.C.; Mughal, U.A.; Ismail, M. Cyber-Physical Intrusion Detection System for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 6106–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, R. Enhancing unmanned aerial vehicle and smart grid communication security using a ConvLSTM model for intrusion detection. Front. Energy Res. 2024, 12, 1491332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Yusupov, K.; Muminov, I.; Sahlabadi, M.; Yim, K. Cybersecurity in UAVs: An Intrusion Detection System Using UAVCAN and Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Advances on Broad-Band Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Riyami, S.; Lisitsa, A.; Coenen, F. Cross-Datasets Evaluation of Machine Learning Models for Intrusion Detection Systems. In Proceedings of Sixth International Congress on Information and Communication Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 815–828. [Google Scholar]
- Layeghy, S.; Baktashmotlagh, M.; Portmann, M. DI-NIDS: Domain invariant network intrusion detection system. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 273, 110626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Mi, W.; Wang, Y. EDGS-YOLOv8: An Improved YOLOv8 Lightweight UAV Detection Model. Drones 2024, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhi, J.; Liu, R.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X. A lightweight and efficient intrusion detection system (IDS) for unmanned aerial vehicles. Neural Comput. Appl. 2025, 37, 15819–15836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrak, S. Unveiling intrusions: Explainable SVM approaches for addressing encrypted Wi-Fi traffic in UAV networks. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2024, 66, 6675–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, P.; Berríos, S.; Allende-Cid, H. Explainable AI for Forensic Analysis: A Comparative Study of SHAP and LIME in Intrusion Detection Models. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | References | Description (Key Characteristics) |
|---|---|---|
| ML-based Approaches | [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55] | Classical machine learning models such as Decision Trees, Random Forests, SVMs, Logistic Regression, Naïve Bayes, Gradient Boosting (XGBoost, LightGBM), and Ensembles. These approaches are computationally efficient, interpretable, and well-suited for tabular UAV traffic data, but they often fail to capture temporal or spatial dependencies. |
| DL-based Approaches | [2,3,4,5,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70] | Includes deep neural models such as CNNs, LSTMs, RNNs, ConvLSTMs, DBNs, and hybrid deep frameworks. These capture complex temporal and spatial dependencies in UAV telemetry and network data. They achieve high accuracy and robustness but require more computation and are harder to deploy on resource-limited UAV platforms. |
| Mixed ML + DL Approaches | [71,72,73,74] | Papers that combine both classical ML and DL models. Examples include RF+CNN+DNN, SVM+FNN+LSTM, and LSTM+DT. Such approaches aim to leverage the interpretability of ML and the representational power of DL, balancing efficiency and accuracy. |
| RL-based Approaches | [75,76,77,78] | Includes Reinforcement Learning methods such as Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG), DQN, DRL-BWO, and cooperative Q-learning. These are adaptive and dynamic, suitable for evolving UAV environments, but computationally intensive and mostly validated in simulation. |
| Specialized / Other Approaches | [69,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87] | Encompasses approaches outside standard ML/DL/RL categories. These include model-based observers, graph neural networks, cross-layer attention frameworks, fuzzy/neuro-fuzzy systems (ANFIS), evolutionary rule-based systems (EBRB), bio-inspired immune-system IDS, autoencoders in unsupervised mode, and GAN-based anomaly detection. These often target UAV-specific constraints or novel attack scenarios. |
| Ref. | Category | Model/ Algorithms | Dataset Used | Main Idea/Methodology | Performance Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [75] | Reinforcement Learning | Deep Q-Network (DQN) | CICIDS2017 | Proposes a lightweight RL-based intrusion detection and Prevention System (IDPS) framework for UAV networks. | Acc: 99.70%, Precision: 95%, Recall: 97%, F1: 96% |
| [76] | Reinforcement Learning | DRL with Deep Belief Network | NSL-KDD | Uses Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) combined with Deep Belief Networks to enhance UAV intrusion detection. | Precision: 98.5%, Recall: 99.3%, F-measure: 98.8%, Acc: 98.9% |
| [77] | Reinforcement Learning | Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient | Simulated from Environment | Introduces a DRL-based IDS for UAV aerial computing networks, focusing on continuous control and real-time defense. | More than 90% detection ratio over 1000 time slot |
| [78] | Reinforcement Learning | Q-learning-based two-layer cooperative IDS (Q-TCID) | Simulated IoD environment | Implements cooperative intrusion detection using a layered Q-learning model tailored for UAV swarm environments. | Accuracy: 90%+ under varying attack intensities |
| Detection Type | References | Technical Analysis (Strengths and Limitations) |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time | [1,2,3,4,40,41,44,45,46,49,53,58,59,60,63,67,71,75,77,84,85,86,87,89,90,93] | Strengths: Real-time detection enables immediate reaction to threats during flight. These systems are critical for mission-critical UAV operations, enabling on-the-fly inference of GPS spoofing, jamming, or network intrusion. Lightweight models such as LSTM, decision trees for fast inference on constrained UAV hardware. Limitations: Sacrifices complexity and precision for speed. Also susceptible to communication loss or latency in swarm-based or distributed UAV environments. |
| Offline | [5,42,43,47,48,50,51,52,54,55,57,62,64,65,66,68,70,72,73,74,76,78,79,80,81,82,83] | Strengths: Allows application of heavy deep learning models (for instance, DNN, CNNs) for in-depth post-flight forensics. Can leverage stored logs for higher detection accuracy, anomaly analysis, or model retraining. Useful in secure settings or early-stage research environments. Limitations: Cannot respond to live threats, which limits use in autonomous or high-risk UAV missions requiring real-time intervention. |
| Hybrid | [56,61,69] | Strengths: Combines in-flight anomaly detection with post-flight training and evaluation. Many frameworks adopt this implicitly, using lightweight onboard classifiers and offline retraining for robustness. Offers better coverage and adaptability across missions. Limitations: Increases architectural and operational complexity. Requires proper synchronization between online inference and offline updates. Vulnerable to inconsistency or model drift if not carefully managed. |
| Model Architecture | Reported | Replicated | Cross-Dataset Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stacked Autoencoder + FC [102] | 99.12/98.25/98.24/98.24 | 99.55/71.00/75.00/73.00 | 73.60/79.00/81.00/80.00 |
| LSTM [103] | 96.00/95.00/96.00/96.13 | 85.00/86.00/85.00/85.00 | 70.00/50.00/70.00/58.00 |
| 1D-CNN [103] | 96.00/95.00/96.00/96.13 | 92.00/92.00/92.00/92.00 | 70.00/50.00/70.00/58.00 |
| Autoencoder + DT [42,55] | 94.54/94.87/94.54/94.21 | 93.00/90.00/91.00/91.00 | 90.00/50.00/50.00/50.00 |
| Autoencoder + RF [42,55] | 91.45/92.31/91.45/91.23 | 95.00/91.00/93.00/92.00 | 95.00/91.00/95.00/93.00 |
| Autoencoder + KNN [42,55] | 88.61/88.27/88.61/88.78 | 94.00/91.00/92.00/91.00 | 95.00/91.00/95.00/93.00 |
| Autoencoder + MLP [42,55] | 91.19/93.22/91.19/92.54 | 92.00/87.00/89.00/88.00 | 95.00/91.00/95.00/93.00 |
| CLCAN [87] | 99.10/97.30/98.70/98.10 | 65.77/59.00/59.00/59.00 | 99.00/99.00/99.00/99.00 |
| Autoencoder + SVM [42,55] | 84.19/83.48/84.19/84.33 | 90.00/85.00/91.00/87.00 | 95.00/91.00/95.00/93.00 |
| ConvLSTM [104] | 99.99/99.99/99.99/99.99 | 99.00/92.00/92.00/92.00 | 70.00/50.00/70.00/58.00 |
| DCA [66] | 99.70/99.80/99.80/99.80 | 92.00/91.00/90.00/91.00 | 70.00/18.00/25.00/21.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.S.; Mahmoud, A.S.; Sheltami, T.R. AI-Enhanced Intrusion Detection for UAV Systems: A Taxonomy and Comparative Review. Drones 2025, 9, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9100682
Islam MS, Mahmoud AS, Sheltami TR. AI-Enhanced Intrusion Detection for UAV Systems: A Taxonomy and Comparative Review. Drones. 2025; 9(10):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9100682
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, MD Sakibul, Ashraf Sharif Mahmoud, and Tarek Rahil Sheltami. 2025. "AI-Enhanced Intrusion Detection for UAV Systems: A Taxonomy and Comparative Review" Drones 9, no. 10: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9100682
APA StyleIslam, M. S., Mahmoud, A. S., & Sheltami, T. R. (2025). AI-Enhanced Intrusion Detection for UAV Systems: A Taxonomy and Comparative Review. Drones, 9(10), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9100682






