Abstract
We identified and quantified by LC-MS/MS 11 (quercetin, galangin, pinocembrin, kaempferol, vanillin, chrysin, gallic acid, p-coumaric acid, trans-ferulic acid, caffeic acid, and caffeic acid phenethyl ester) out of the 21 polyphenolic compounds we looked for in ethanolic (25% and 50%) and aqueous propolis extracts by comparison with standards and literature data.
1. Introduction
The purpose of this study is to identify the most common polyphenols found in Romanian propolis and quantify their levels in various hydroalcoholic extracts. In this regard, we have worked to develop an efficient and reliable method of analysis.
LC-MS is the method of choice in various environmental, pharmaceutical, and biochemical laboratories due to its selectivity, sensitivity, and versatility [1].
2. Materials and Methods
The LC-MS/MS analysis was carried out using a Q Trap 5500 Triple Quadrupole Mass spectrometer from Sciex with Electrospray Ionization (ESI)/Turbo Ion Spray mode. In the chromatographic analysis, a Synergi C18 (Fusion-RP 80 Å, 50 × 2 mm, particle size of 4 µm) column (Phenomenex Inc., Torrance, CA, USA) was used with an injection volume of 5 µL. The solvents used were (A) formic acid (0.5%) and (B) methanol. Gradient elution ranged from 2% to 98% B at 30 °C, and elution flow was set at 900 µL/min. The elution time was 20 min. The ionization source temperature of the MS was 500 °C; mass spectra were recorded in the negative ion mode, between 50 m/z and 500 m/z using nitrogen as the collision gas. The pressure of the gas flux to the nebulizer was set at 1000 psi.
ACS standards (quercetin, pinocembrin, galangin, kaempferol, vanillin, chrysin, gallic acid, p−coumaric acid, t-ferulic acid, caffeic acid, and caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE)) were used to prepare individual 500 µg/mL stocks in ethanol. A mixed working standard, 10 µg/mL solution in ethanol, was obtained by appropriate dilution of individual stocks. Ethanol calibration solutions were prepared in a 0.08–5 µg/mL range. Automatic pipettes and class A volumetric glass flasks were used.
All solvents (ethanol, methanol, formic acid) were analytical grade and used without further purification.
Propolis extracts were prepared according to the procedure presented previously [2].
For the analysis of the samples, the type of targeted MS/MS scan was used, in which a selected ion is monitored on Q1 and a chosen fragment of the molecular ion on Q3. The sequence of analysis consisted of the injection from polypropylene filtration plates of the 2 blanks that contain mobile phase A, 7 mix solutions of polyphenols in the order of increasing the concentration 0.08, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 5 µg/mL; 2 blanks, 9 aqueous samples, 2 blanks, 1 calibration solution, 2 blanks, 9 25% ethanolic samples, 2 blanks samples, 1 calibration solution, 2 blanks, 9 50% ethanolic samples, 2 blanks samples, 1 calibration solution, 2 blanks, twice consecutive reinjection of a 25% ethanolic sample, 2 blanks.
3. Results and Discussion
Experimental parameters for each analyte were identified by direct injection in the MS module of individual standards, in the 0.001–0.1 µg/mL concentration range, resulting in the corresponding productions. Individual characteristics are collected in Table 1.

Table 1.
MS experimental characteristics of the investigated compounds.
Selectivity has been investigated in terms of relative standard deviations of the retention times [3]. As data in Table 2 demonstrate, they did not exceed 0.21%.

Table 2.
Method specificity.
Calibration curves were obtained for the 0.08–5 µg/mL concentration range for all analytes of interest. Experiments run at seven concentration levels, using at least two replicate injections for each concentration level, gave linear regressions in terms of peak area, characterized by correlation coefficients larger than 0.9988, except chrysin, with a determination coefficient of 0.9822, as shown in Table 3. The calibration curve for t-ferulic acid is presented in Figure 1.

Table 3.
Calibration parameters.
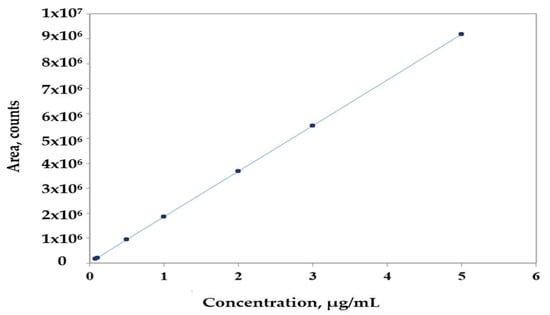
Figure 1.
Calibration curve for t-ferulic acid.
Limit of quantitation, LOQ, and limit of detection, LOD, as shown in Table 4, were evaluated as per International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use Guideline [3,4].

Table 4.
Limit of quantitation (LOD) and limit of detection (LOQ) calculated for analytes of interest.
The method was applied for the analysis of Romanian propolis extracts. Figure 2 and Figure 3 show typical LC-MS/MS chromatograms. The quantified levels of polyphenolics are collected in Table 5.
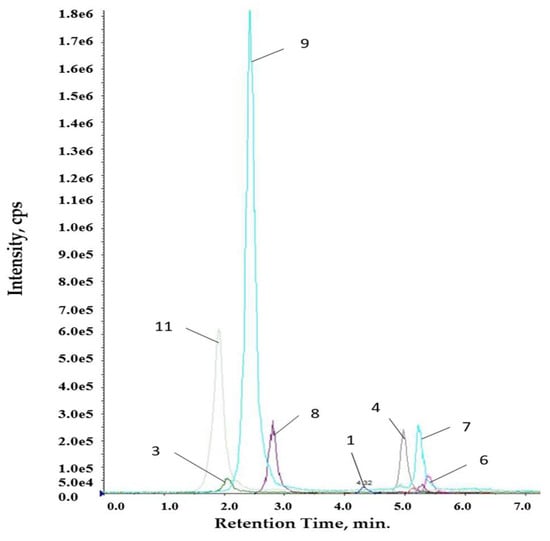
Figure 2.
Chromatogram for ethanolic extract.
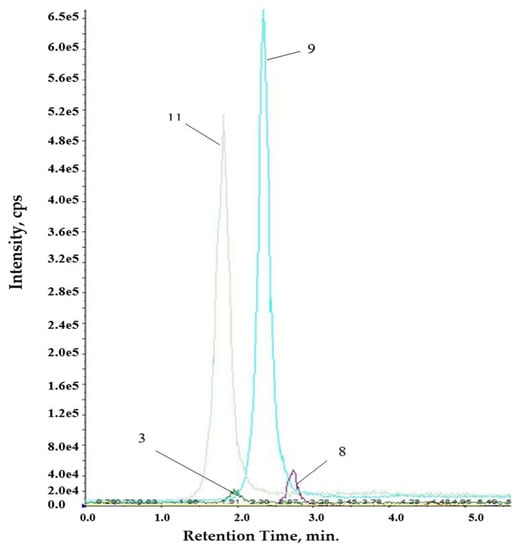
Figure 3.
Chromatogram for aqueous extract.

Table 5.
Polyphenolics in ethanolic and aqueous extracts.
The polyphenols identified in the propolis under study fall into two categories: compounds that are not extracted in water (quercetin, chrysin, pinocembrin, kaempferol, galangin, CAPE) and compounds that are extracted both in water and ethanolic solutions (p-coumaric acid, trans-ferulic acid, caffeic acid, vanillin).
4. Conclusions
The system used for the analysis of phenolic compounds in propolis extracts consisted of an Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatograph coupled with a 5500 Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer and the mass spectra were recorded in the negative ion mode.
Calibration curves were obtained by injecting mixtures of exactly known concentrations (0.08; 0.1; 0.5; 1; 2; 3; 5 μg/mL), resulting in correlation coefficients larger than 0.9988, except for chrysin.
Relative standard deviations of the retention times were below 0.2%. The values corresponding to the detection limits were between 0.01 and 0.23 µg/mL and limits of quantitation had values in the range 0.03 µg/mL (for t-ferulic acid)—0.69 µg/mL (chrysin).
The use of the LC-MS analysis method proposed proved effective in quantifying 11 polyphenolics in aqueous and ethanolic extracts of propolis.
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Center for Instrumental Analysis SCIENT, 1E Petre Ispirescu Street, 077167 Tâncăbești, Ilfov, Romania. Also, the authors would like to thank project Work-based entrepreneurial learning systems for Ph.D. and postdoctoral students (SIMBA), MySMIS 124705, co-financed by the European Social Fund (ESF), through the Human Capital Operational Program (POCU)/ 51668/09.07.2019.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hokkanen, J. Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry of bioactive secondary metabolites- in vivo and in vitro studies. Acta Universitatis Ouluensis a Scientiae Rerum Naturalium 606 University of Oulu Repository, Finland. 2013. Available online: http://jultika.oulu.fi/files/isbn9789526200897.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Nichitoi, M.M.; Josceanu, A.M.; Isopescu, R.D.; Isopencu, G.; Lavric, V. Romanian propolis extracts: Characterization and statistical analysis and modelling. UPB. Sci. Bull. Series B 2019, 81, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Josceanu, A.M.; Postelnicescu, P.; Dumitrescu, A.M. Validation of an Ion Chromatographic Method for Lead and Cooper Quantification. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference of Slovak Society of Chemical Engineering, Tatranske Matliare, Slovakia, 24–28 May 2010; p. 471, ISBN 978-80-227-3290-1. [Google Scholar]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), Q2 (R1)—Validation of analytical procedures text and methodology. Available online: https://www.ich.org/ (accessed on 8 July 2020).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).