Abstract
Pb is a relevant atmospheric pollutant, mainly associated to particulate matter (PM). In this work, an ultrasound probe-assisted microextraction (UAME) pretreatment methodology has been optimized and validated for the extraction of Pb from atmospheric particulate matter samples before determination by ICP-MS. Factors that influence the ultrasonic extraction procedure were evaluated and optimized using a Box-Behnken design in conjunction with a response surface methodology, by assaying a PM certified reference material. The optimum conditions obtained for the Pb extraction are 62.5% of sonication amplitude, 200 s of sonication time, 47.5% v/v HNO3 as extracting medium, and sample/solvent ratio of 35 mg/mL. The US-probe assisted extraction methodology was applied to real PM from active and passive sampling for the extraction of Pb and other relevant elements such As, Cd and Cu. Analytical results demonstrated that ultrasonic microextraction is an efficient tool for the extraction of Pb and Cu from atmospheric samples, faster and greener than standard high temperature acid digestion.
1. Introduction
Atmospheric particulate matter (PM) is a contaminant of great chemical complexity which analysis is of great relevance to estimate health effects and environmental impact. Some elements such as As, Cd, Ni and Pb are recognized toxic components of the atmospheric aerosol. Standards analytical methodologies for the determination of relevant elements of PM, usually include the capture of the PM on filters by high volume samplers, acid digestion of the filters in open vessels or in microwaves and analysis by ICP-OES or ICP-MS, which require highly sophisticated and costly instrumentation. In recent years, research interest is focused on the ultrasonic (US) energy, which has emerged as a simplified and faster pre-treatment activation tool for the extraction of several elements from different kind of environmental and biological matrices, using US baths [1] and probes [2,3] with recoveries comparable to classical techniques. The US probe is standing out as the most efficient technique because provides a higher and more precise US power than other (e.g., US baths) with smaller samples, less power consumption and 100 times faster [4]. Our aim in this work is the optimization of an efficient, miniaturized, fast and low-cost US probe-assisted acid digestion methodology for the extraction of Pb from atmospheric particulate matter samples collected on quartz fiber filters (PM10 fraction), followed by ICP-MS, an analytical approach that has not been previously reported in the literature.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reference Material and Real Samples
Certified Standard Reference Material “SRM 1648a Urban Particulate Matter” was used to optimized and to test the proposed pretreatment methodology. Real samples analyzed were a set of particulate matter samples (PM10) from different monitoring stations to the Air Quality Monitoring Network of Extremadura (REPICA) collected on quartz fiber filter (24 h by high volume Digitel DAH-80 equipments) during 2015. On the other side, we also analyzed atmospheric deposition samples collected by passive sampling at 5 different locations around an industrial area.
2.2. Sample Pretreatment by Ultrasonic Probe
The experiments for optimization of the extraction conditions (sonication time, amplitude, concentration of extraction medium HNO3 and sample/solvent ratio) were carried out on samples of the certified standard reference material (app. 15 mg) mixed with a known quantity of previously pulverized blank quartz fiber filter (app. 135 mg). These solid samples were homogenized previously for 10 s on a vortex mixer and then, were placed in plastic tubes, the extraction solution was added and the US probe (S1-1mm diameter titanium probe in Hielscher UP200S ultrasonic device) was centered in the plastic tube, trying to minimize dead ultrasonic zones (Figure 1). 3, 5 and 15 mL of medium were added to 150 mg sample for three levels of ratio (high, medium and low) and we optimized them. The design of experiment matrix was obtained using UNSCRAMBLE X 10.0 (Camo Software AS, Oslo, Norway). The experimental results were processed using EXCEL 2016 (Microsoft Office 2016, Santa Rosa, CA, USA).
Figure 1.
(a) US probe Hielscher UP200S stand mounted ultrasonic device with a 1 mm diameter titanium probe; (b) US probe with a detail of the vial where the extraction is carried out.
2.3. Determination of Trace Elements by ICP-MS
After extraction, the samples were centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 10 min, and 250 μL of the supernatant fluid with 25 μL of 10 ppm solution of Ge (IV) (internal standard) were taken to 25 mL in HNO3 5% v/v for determination by a validated ICP-MS protocol [3] on a PerkinElmer ELAN 9000 equipment. The technical conditions used were: radiofrequency power, 1000 W; 1 L/min of Ar plasma, time wash 35 s and 3 replicates per sample. Under the optimized conditions we explored the applicability of the method in the real atmospheric samples described in Section 2.1, which were extracted in parallel by standard acid digestion according to a validated protocol [3]. All the pretreated samples were assayed by the validated ICP-MS protocol.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Ultrasonic Probe-Assisted Pretreatment by Experiment Design
The variables to be optimized were extraction time (90, 180, 300 sg), ultrasound amplitude (20, 50, 80%), % v/v of HNO3 (20, 50, 80%) and sample/solvent ratio (10, 30, 50 mg/mL), whose selection is based on previous results [2,3]. To optimize the values of variables, a Box-Behnken design was carried out where all the design variables have exactly three levels: low, central, and high. This design consisted of 27 experiments with three central samples. The ANOVA method was used to determine the regression coefficients (B-coefficients) and p-values of the proposed model. Table 1 shows the regression coefficients of the model.

Table 1.
Regression coefficients (B-coefficients) and p-values obtained with the US probe extraction method. Surface response were based on recovery rates for Pb.
In this case, only the quadratic term of % HNO3 concentration has a p-value < 0.05, indicating that this variable could significantly affect the quantitative extraction of Pb at the 95% confidence level. The recovery of Pb decreased on increasing the concentration of the extraction medium. All variables were optimized. From the analysis of variance (ANOVA), a second-grade quadratic model is assumed, whose p-value is 0.591 at the 95% confidence level. The equation for the fitted model is:
% Recovery (Pb) = 98.000 − 2.862·C2
A coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.508 was obtained, which indicates that our model could explain a 50.8% of the variability of response. Besides, the p-value obtained for the lack of fit (0.000) is less than 0.05, which means that the model does not satisfactorily explain the observed data with a confidence level of 95%. However, very good recoveries are obtained in the extraction of Pb under the conditions in which the extractions are carried out. The response surfaces (contour plots) estimated by the model for each pair of variables are shown in Figure 2.
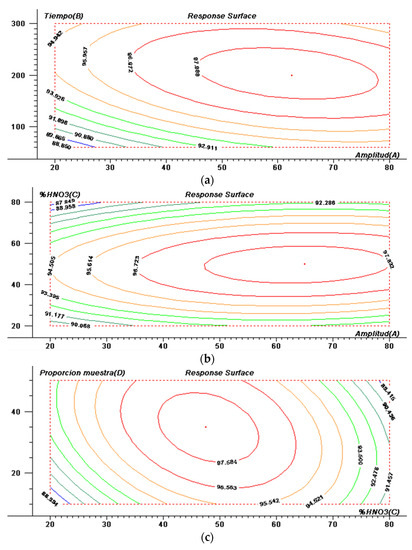
Figure 2.
Response surfaces (contour plots) estimated for (a) Time vs. Amplitude; (b) % HNO3 vs. Amplitude; (c) Sample/solvent ratio vs. % HNO3 after model running.
Figure 2a, shows that the optimal value for the sonication amplitude corresponds to a 62.5% and the optimum value for the sonication time is 200 s. Figure 2b showing that 47.5% is the optimal value for % HNO3. Finally, in Figure 2c, was obtained that the optimal value for the sample/solvent ratio is 35 mg sample per mL of solvent, which corresponds to a 4.3 mL of extraction medium.
3.2. Determination of Pb, Cu, As and Cd in Real Atmospheric Particulate Matter Samples by Ultrasonic Probe Assisted Acid Extraction
The application of optimized probe ultrasound-assisted extraction obtained in the previous sections was carried out to quantify Pb, Cu, As and Cd in a series of samples (see Section 2.1). Regression analysis of the concentrations levels measured by both methods (Figure 3) resulted in satisfactory agreement between standard acid digestion and US probe assisted extraction for Pb (R2 = 0.839) and Cu (R2 = 0.989).
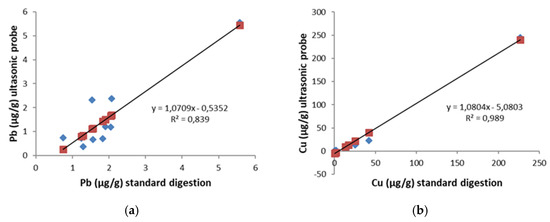
Figure 3.
Regression curves obtained for correlation between standard acid digestion and ultrasonic probe-assisted acid digestion (a) Pb (µg/g); (b) Cu (µg/g).
The Wilcoxon Test confirms that there are no significant differences between for Pb (p-value = 0.083) and Cu (p-value = 0.185) at the 95% confidence level (p-values > 0.05).
4. Conclusions
The microextraction pretreatment by ultrasonic probe has been demonstrated as an efficient tool for the determination of Pb and Cu in atmospheric samples from different environments after optimization by response surface methodology, allowing the fast and quantitative extraction of the selected analytes. The proposed extraction method runs in a total time of less than 4 min, compared with the several hours required for the standard acid digestion, using less sample and less reagent amounts. The method has been successfully applied to atmospheric PM samples.
Author Contributions
M.R.P.-M. and F.R.-H. conceived and designed the experiments; M.R.P.-M. and F.R.-H. performed the experiments; M.R.P.-M., S.C.-P. and E.P.-G. analyzed the data; M.R.P.-M., F.R.-H., E.P.-G. and L.C. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; S.C.-P. and E.P.-G. wrote the paper.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Junta de Extremadura, Spain (projects PRI IB16114 and GR18068), and the Air Quality Surveillance Network of Extremadura (REPICA), all partially financed by European Union Funds for Regional Development (FEDER).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kazi, T.G.; Jamali, M.K.; Arain, M.B.; Afridi, H.I.; Jalbani, N.; Sarfraz, R.A.; Ansari, R. Evaluation of an ultrasonic acid digestion procedure for total heavy metals determination in environmental and biological samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomo, M.R.; Pinilla, E.; Calvo, L.; Capelo-Martínez, J.L. Determination of trace and major elemental profiles in street dust samples by fast miniaturized ultrasonic probe extraction and ICP-MS. Talanta 2011, 84, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyaningsih, W.; Duros, E.; Palma, M.; Barroso, C.G. Optimization of the ultrasound-assisted extraction of melatonin from red rice (Oryza sativa) grains through a response surface methodology. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 103, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picó, Y. Ultrasound-assisted extraction for food and environmental samples. TrAC 2013, 43, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).