Abstract
Textile wastewaters are characterized by high chemical oxygen demand (COD) concentration, strong color, high pH and temperature, and low biodegradability. Conventional treatment methods are considered to be inefficient to comply with the discharge limits. Recently, nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) technology has received increasing attention of the scientific community as an emerging technology for treatment of polluted streams. Due to smaller particle size, larger surface area and higher surface reactivity of iron nanoparticles, the removal of pollutants occur very rapidly. In this work, we synthesized nZVI employing green chemistry principles in a chemical reduction reaction. Iron precursor solution (FeSO4) was reduced by plant extracts that contain polyphenols. Plant polyphenols are known to possess strong reducing agent properties and act as effective metal chelators. The objective of this study was to characterize the green synthesized iron nanoparticles in terms of size and zeta potential parameters under various synthesis conditions (pH, precursor concentration and precursor/extract volume ratio) and compare the reactivity of the engineered nanoparticles for textile wastewater treatment. Green tea leaves-GT and Rose leaves-R were selected as the plant sources. Plant extracts were examined in terms of their Total Phenolic Content (TPC) expressed as Gallic Acid Equivalent (GAE). Rose leaves were found to possess 2062 mg/L TPC whereas, Green Tea leaves were found to have 1882 mg/L in grinded powder form. Results showed that 74% color removal along with 18% TOC removal could be achieved with 5 ppm of GT-ZVI nanoparticles synthesized at a 2/1 ratio (v/v) of precursor to extract. With the same concentration of R-ZVI nanoparticles, 78% color removal and 40% of TOC removal were observed.
1. Introduction
Textile industry is one of the most polluting industries. Due to continuous improvement in textile industry, management and control of water pollution has become more crucial issue for the countries. Pollutants released by textile industry are continuously harmful for the environment. It includes high concentration of organic and inorganic chemicals which have strong color, BOD and residual COD. The resistance of textile dyes to biodegradation makes it more difficult to remove organic matter from textile wastewaters. These wastewaters are dangerous for the environment if they do not disposed properly. Conventional treatment methods are considered to be inefficient to comply with the discharge limits. Nanotechnology (NT) is a recently emerged and rapidly progressing science field. It is now evident that nanotechnologies are becoming a substantial part of society and indeed there are already a multitude of nanotechnology products, or at least products with a nano-based claim, are commercially available [1]. Nanotechnology has been considered as an effective way in solving water treatment problems related to quality and quantity and it proposes efficient, economic, and environmentally friendly technologies to decrease pollutant in wastewater to acceptable levels [2]. Various nanomaterials have been used for removal of many pollutants present in water source or industrial water [3]. One of these nanomaterials is nZVI (nano zero-valent iron), which is one of the most capable reactants along with its efficiency, low cost and high reactive nature [4,5]. nZVI can be synthesized by 2 different methods. First method is based on the chemical reaction of the iron precursor and reducing agent and the second method is based on the content of the plant polyphenols. In the first method; during the chemical reaction process, H2 is released and this method is toxic because of using strong compound as a reducing agent. The second method; nZVI is synthesized which employs green chemistry principles in a chemical reduction reaction. This method is based on the polyphenol obtained by plant extract. Plant polyphenols are known to possess strong reducing properties and they are effective metal chelators, forming stable complexes with iron [6]. Production of nZVI nanoparticles to use various plants or different synthesis conditions affects nanoparticles’ properties because of the reactivity [7].
The objective of this study is to characterize the green synthesized iron nanoparticles in terms of size and zeta potential parameters under various synthesis conditions (pH, precursor concentration, precursor/extract ratio (v/v)) and compare the reactivity of the engineered nanoparticles for textile wastewater treatment. Green tea leaves-GT and Rose leaves-R were selected as the plant sources. Although, reactivity of green synthesized iron nanoparticles has been assessed with several pollutants such as Cr(VI) or synthetic dye solutions, a comparative evaluation with plant extracts for real textile wastewater has not been addressed yet, to the best of our knowledge.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Dry & powder leaves of green tea and rose were used as source of polyphenols for extract and supplied from a local market in a package. Analytical reagent grade FeSO4.7H2O (>99.0%) was used for preparing the iron precursor. Folin–Ciocalteu’s phenol reagent, anhydrous sodium carbonate and gallic acid were used for the determination of total polyphenol content in solution. All chemicals were supplied from Merck, Darmstadt, Germany. pH and ORP (3 M KCl; reference electrode) were measured with a Tethys online monitoring system. Textile wastewater was supplied from a local industry in Turkey.
2.2. Preparation of Plant Extracts
This experimental study is divided into 3 parts. First part is preparing the extracts of leaves, second part is get ready to iron precursor and the last part is synthesizing nanoparticle. For preparing the extracts, leaves of plant were washed with deionized water (DI) and dried in the oven at 103 °C over night. After cooling in desiccator, dried leaves are grinded with the help of a shredder. Powder form of the plant’s extract was prepared by brewing 20 g/L of the green tea or rose leaves at 80 °C for 20 min. For the extraction process, cold brew method [8] was applied to leaves and using DI water as the extraction solvent. The plant extract was then cooled down was filtered through by 0.7 µm and 0.45 µm filter papers, respectively, to obtain an aqueous solution.
Amount of plants’ total phenolic content is expressed antioxidant capacity and determined by Folin-Ciolcalteu Method (ISO 14502-1). For determination of total phenolic content, UV/Vis spectrophotometer (Shimadzu 2450) was used. Before the measurements of TPC, calibration curve was prepared from the Gallic acid standard for device calibration at 765 nm (R = 0.9989). TPC value was calculated as µg/L of gallic acid equivalents (GAE).
2.3. Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts
For nanoparticle synthesis optimization, iron precursor solution was prepared in different molarities (0.1 & 0.01 M FeSO4·7H2O) in a 100 mL volumetric flask followed by the adjustment to different pH values (3, 4, 5). For the same reason, the iron precursor and the extract was mixed with a magnetic mixer at 250 rpm mixing rate for 20 min at different volumetric ratios (1/1, 2/1, 1/2, 1/3) in the glove box at room temperature (Table 1).

Table 1.
Experimental matrix for synthesis optimization of iron nanoparticles.
2.4. Removal Study
The prepared GT-ZVI and R-ZVI nanoparticles were used for the removal study of the industrial wastewater supplied from a local textile industry. In addition, the characterization of the wastewater was determined. TOC, UV, pH and conductivity measurements were investigated. By changing the pH of the wastewater (3, 4, 5) removal study was performed using various GT-ZVI/R-ZVI nanoparticle concentrations in 500 mL beakers. In the process samples were taken at different time intervals (5, 15, 30, 45, 60 and 90 min). The pH and ORP values were monitored when the samples were taken. The samples were filtered through 0.22 µm PES filters. The color of the filtered samples was measured at 465 nm as Pt-Co and DOC (Dissolved Organic Carbon) measurements and TPC (Total phenolic content) were performed.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Extraction Procedure
The objective of this procedure was to identify the plant type and effect of the filtration on the extract analyses. Therefore, for each plant extract the most appropriate form and filtered type were identified. Figure 1 showed the results obtained in this optimization.
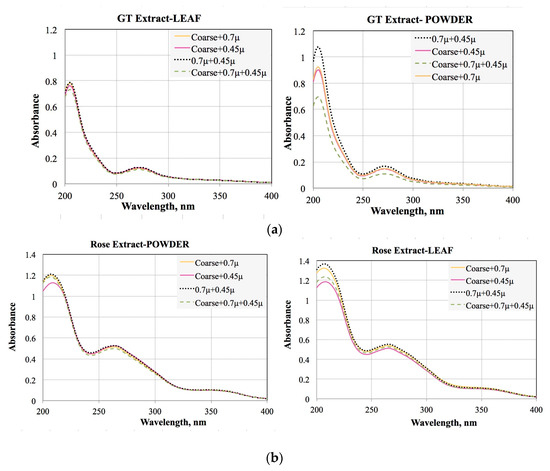
Figure 1.
Comparison of the powder and leaf forms for (a) Green Tea leaves and (b) Rose leaves.
Comparing these results, Table 2 showed that the best extract type and filtration method from their absorbance value. This result indicated that extract type and also filtration method has a significant role on the concentration of the plant extract.

Table 2.
Best extract type and filtration method according to UV/Vis spectrum of the extracts.
To compare the total phenolic content (TPC) of Green Tea and Rose leaves, Figure 2 presents the results obtained in this optimization. Obtaining extracts’ TPC values are approximately the same.
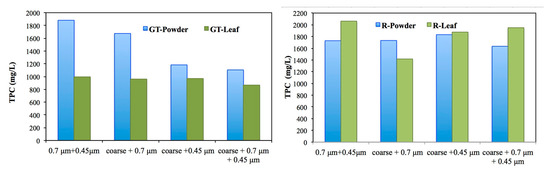
Figure 2.
Comparison of the powder and leaf form of the two extract’s TPC with different filtration types.
According to the result, although the same filter type was applied to the plants’ leaves, Green tea TPC concentration was more affected than the Rose TPC concentration (Table 3). It is emphasized that the biomolecules were trapped on different pore diameter filters. This is important for the synthesis of nZVI which enables the reduction of Fe+2. Moreover these biomolecules are dispersive and capping agent and also help to minimize oxidation and agglomeration of nZVI [9].

Table 3.
Best extract type and filtration method according to TPC results.
3.2. Synthesis and Size Determination of GT- ZVI and R-ZVI Nanoparticles
FeSO4 precursor ratio is a reducing agent and it is an important factor in the synthesis of nZVI. In this study, it can be observed that as the ratio of the amount of extract to Fe2SO4 decreases, the particle size also decreases. On the other hand, it is not a limiting factor of the size. Because the size and shape of nZVIs could be influenced not only by the concentrations of the extract and the Fe precursor but also by the complex chemical composition of the extract [10]. The increasing molar ratio of reducing agent to iron precursor is affected by the growing of particle size. The effect of pH, molality of precursor and the ratio of reducing agent onto size of Fe precursor was also investigated. Figure 3 shows how the precursor concentration and synthesis pH value affects the size and zeta potential of the nanoparticles for GT-ZVI nps. Similary, Figure 4 demonstrates the change in size and zeta potential for R-ZVI nps.
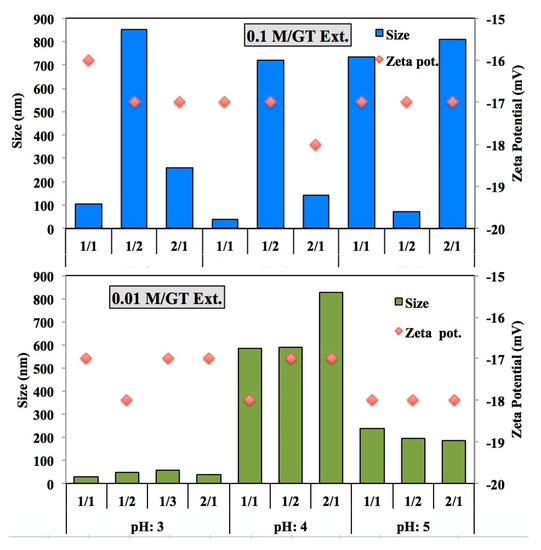
Figure 3.
Comparison of the precursor/extract ratio, molarity and pH effect on the GT-ZVI nanoparticles.
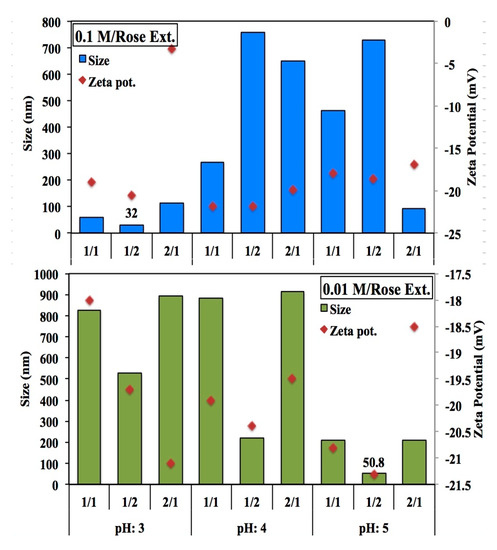
Figure 4.
Comparison of the precursor/extract ratio, molarity and pH effect on the R-ZVI nanoparticles.
According to the results it was decided that the best synthesis conditions were pH 3, 2/1, 0.01 M for GT-ZVI and pH 3, 1/2, 0.1 M for R-ZVI nanoparticles. Although there is no significant difference between the polyphenol contents of the extract, the smallest particle size was observed in different molarity and different precursor to extract ratio. It shows that, each plant have unique characterization and composition, so each plant should be evaluated independently.
3.3. Color and Organic Matter Removal from Textile Wastewater with GT-ZVI and R-ZVI Nanoparticles
Textile wastewater was subjected to treatment with 5 ppm of GT-ZVI and R-ZVI nanoparticles (Figure 5). Both of the nanoparticles showed almost 80% color removal at the end of 90 min. reaction period. It was noticed that even in the first 5 min the reaction was almost complete in terms of color removal. This is an important point to consider as the process can be scaled up with smaller volume requirement. TOC removal was lower with GT-ZVI nanoparticles when compared with R-ZVI nanoparticles. Although, the size of the nanoparticles are close, it is likely that the active biomolecules in R-ZVI nps played a significant role in terms of organic matter removal.
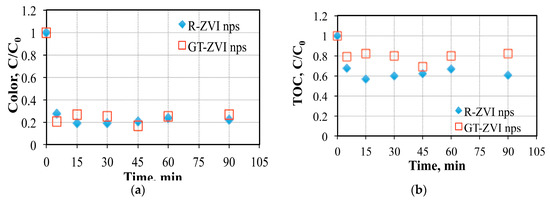
Figure 5.
Color and TOC removal with (a) GT-ZVI nps (0.01 M, pH: 3, 2/1) and (b) R-ZVI nps (0.1 M, pH: 3, ½).
4. Conclusions
The conclusions and contributions of this study can be summarized as follows:
- Laboratory synthesized iron nanoparticle (nZVI) particles were considered as a medium for the removal of color and organic matter from wastewater streams.
- Two different plants were prepared and their physical and chemical properties were determined. These are: TPC, UV-Vis Spectra and form of plant were observed.
- GZVI particles demonstrated better size performances than RZVI particles.
- Results obtained in this study would be.
Nanoparticles which have small surface area by its nature, has high reactivity and this leads to high removal rate.
Author Contributions
Funda Sağırkaya and Melis Terzi carried out the experiments. Zeynep Yücesoy-Özkan and Mohib Rezayee assisted the experiments and characterization of the nanoparticles. Zeynep Yücesoy-Özkan wrote the manuscript with input from all authors. Esra Erdim supervised the project.
Funding
The authors wish to thank Marmara University, Scientific Research Projects Committee (FEN-E-120314-0066) for their financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- The Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies. 2005. Available online: www.nanotechproject.org (accessed on 8 May 2018).
- Bottero, J.-Y.; Rose, J.; Wiesner, M.R. Nanotechnologies: Tools for sustainability in a new wave of water treatment processes. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2006, 2, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.T.; Alazba, A.A.; Manzoor, U. A Review of Removal of Pollutants from Water/Wastewater Using Different Types of Nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 825910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noubactep, C. A Critical review on the process of contaminant removal in FE0–H2O systems. Environ. Technol. 2008, 29, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mystrioti, C.; Sparis, D.; Papasiopi, N.; Xenidis, A.; Dermatas, D.; Chrysochoou, M. Assessment of Polyphenol Coated Nano Zero Valent Iron for Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Contaminated Waters. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 94, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perron, N.R.; Brumaghim, J.L. A review of the antioxidant mechanisms of polyphenol compounds related to iron binding. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 53, 75–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, S.; Pacheco, J.-G.; Nouws, H.P.; Albergaria, J.T.; Delerue-Matos, C. Characterization of green zero-valent iron nanoparticles produced with tree leaf extracts. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkan, Z.Y.; Cakirgoz, M.; Kaymak, E.S.; Erdim, E. Rapid Decolorization of Textile Wastewater by Green Synthesized Iron Nanoparticles. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumelac, V.; Varma, R.; Sikdar, S.; Bhattacharyya, D. Green Synthesis of Fe and Fe/Pd bimetallic nanoparticles in membranes for reductive degradation of cholorinated organics. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, S.; Grosso, J.P.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Albergaria, J.T.; Delerue-Matos, C. Utilization of food industry wastes for the production of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).