Abstract
In this work, the effect of CNTs content in 3D graphene-PDMS-CNTs electrodes were systematically studied for simultaneous determination of Hg, Pb and Cd by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry. The composites were formed by dip coating CVD graphene on Ni foam in CNTs-dispersed PDMS solution with varying CNTs concentrations. The optimal CNTs content was found to be ~0.5 mg/mL for all analytes. The optimal graphene-PDMS-CNTs electrode showed good analytical performances with sharp well-separated peaks of Pb, Hg and Cd in the concentration range of 100–500 µg/L. Therefore, the graphene-PDMS-CNTs electrode is highly promising for multiple detections of heavy metal pollutants.
1. Introduction
3D graphene foam structure is a highly potential platform for advanced electrochemical sensing applications due to its high electrical conductivity, large effective specific surface area and high electron transfer rate [1,2,3,4]. However, its structural stability must be improved and its sensing performances may enhanced by properly combining with other effective materials such as Polydimethyl-siloxane (PDMS) and carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The combination of graphene and CNTs with PDMS has not been well for electrochemical sensing applications [5]. In this study, innovative graphene/PDMS/CNTs nanocomposites were prepared and optimized for the simultaneous determination of lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd) and mercury (Hg) by varying the CNT contents.
2. Materials and Methods
Firstly, graphene layers was deposited on Ni foam by chemical vapor deposition in H2/CH4 at 10 Torr and 900 °C. PDMS solution dispersed with CNTs (0.1–2 mg/mL) was dip-coated on graphene/Ni foam. Ni template was then removed by wet etching using HCl for 12 h. The composite material was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Raman spectroscopy. Electrochemical measurement was performed in differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry (DPASV) mode using three-electrode configuration, comprising CNTs/PDMS/GP working electrode, Ag/AgCl reference electrode and Pt counter electrode. DPASV measurement of electrodes were investigated in the solution containing Pb, Cd and Hg in a 0.1 M acetate buffer (pH 4.5) with varying concentrations in the range of 100–500 µg/L.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization Results
The SEM image as shown in Figure 1 demonstrates that CNTs are embedded quite uniformly on PDMS/Graphene network. Raman spectra as displayed in Figure 2 further confirms the co-presence of CNTs, graphene and PDMS materials with PDMS characteristic peaks, G peak, 2D peak and D peak. It illustrates that 2D peak becomes lower while D peak is enhanced due to CNTs inclusion.
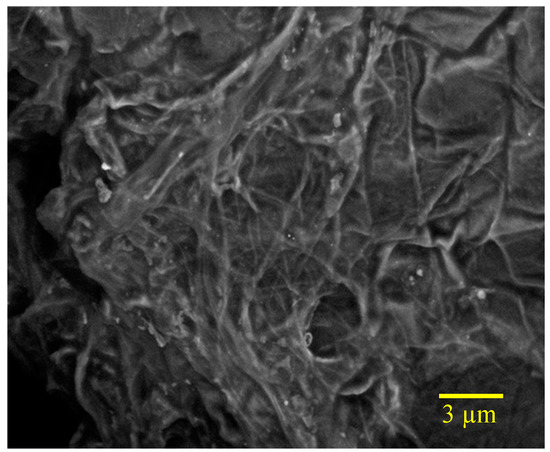
Figure 1.
Typical SEM image of 3D graphene/PDMS with 1 mg/mL CNTs.
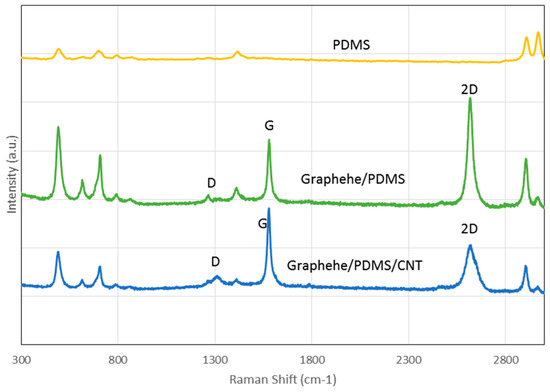
Figure 2.
Raman spectra of PDMS, 3D Graphene/PDMS and 3D graphene/PDMS/CNTs.
3.2. Electrochemical Sensing Results
Figure 3 show DPASV curve of the CNTs/PDMS/GP composite electrodes with different CNTs contents in 200 µg/L Pb solution. It is seen that the electrode with 0.5 mg/mL CNTs gives the sharpest Pb peak at −0.8 V. The corresponding DPSAV peak current vs. CNTs content as demonstrated in Figure 4 confirms that the electrode with 0.5 mg/mL CNTs offers the optimal peak signal. The other results for Cd and Hg in Figure 4 indicates approximately the same optimal CNT content. The optimal electrode were then tested for simultaneous detections of Pb, Hg and Cd with varying analyte concentrations as illustrated in Figure 5. It can be seen that the electrode exhibits three well-defined anodic peaks for Pb, Hg and Cd at −0.79, 0.05 and −1.05 V, respectively, displaying its good selectivity for simultaneous detection of the three analytes. The respective calibration curves for Pb, Cd and Hg (Figure 6) show that the electrode exhibits the highest sensitivity and widest dynamic range (100–500 µg/L) for Pb and the lowest sensitivity and narrowest dynamic range for Cd.

Figure 3.
DPASV for analysis of 200 µg/L Pb using Graphene/PDMS with different CNT contents.
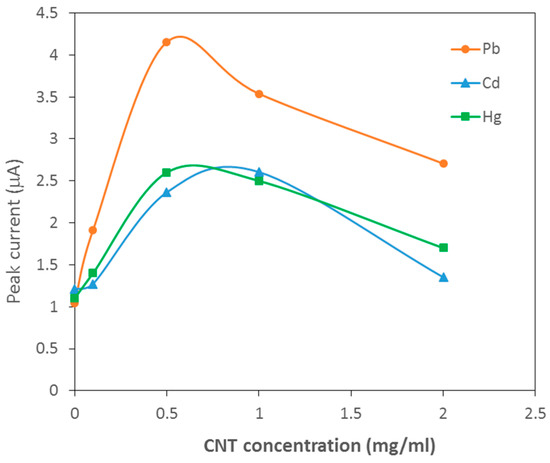
Figure 4.
Peak DPSAV current vs. CNT content towards 200 µg/L Pb, 400 µg/L Cd and 400 µg/L Hg.
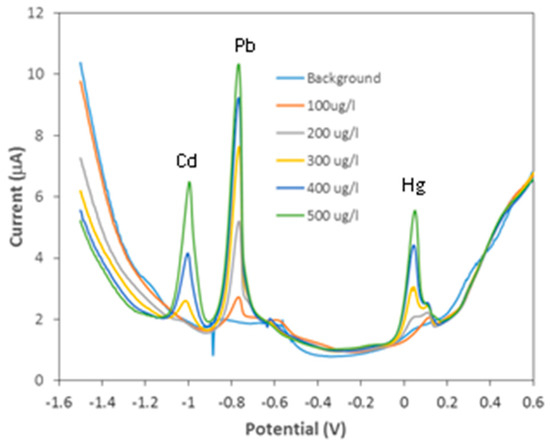
Figure 5.
DPASV for analysis of Pb, Cd and Hg using Graphene/PDMS with 0.5 mg/mL CNTs.
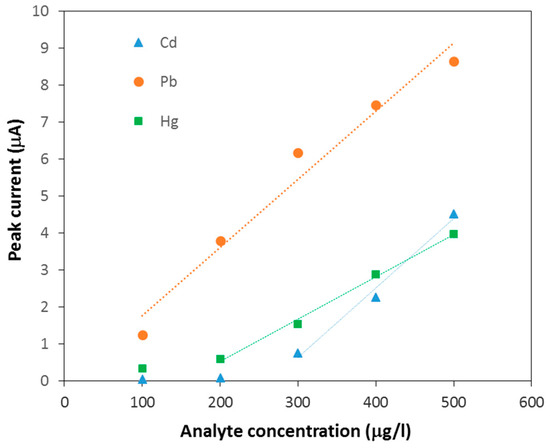
Figure 6.
Peak DPASV current for analysis of Pb, Cd and Hg using Graphene/PDMS with 0.5 mg/mL CNTs with different analyte concentrations.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, the effect of CNTs content in 3D graphene-PDMS-CNTs electrodes were systematically studied for simultaneous determination of Hg, Pb and Cd by DPSAV methods. The composites were formed by dip coating CVD graphene on Ni foam in CNT-dispersed PDMS solution followed by Ni wet etching. The optimal CNTs content was found to be ~0.5 mg/mL for all heavy metal analytes. The optimal graphene-PDMS-CNTs electrode showed good analytical performances with sharp well-separated peaks of Pb, Hg and Cd in the concentration range of 100–500 µg/L. The graphene-PDMS-CNTs electrode is thus highly potential for multiple detections of heavy metal pollutants.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dong, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Song, H.; Zhang, H.; Huang, W.; Chen, P. 3D graphene foam as a monolithic and macroporous carbon electrode for electrochemical sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3129–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Huang, X.; Wu, Y.; Luo, L.; Jin, Y.; Li, Q. Differential Pulse Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Detection of Cadmium with Nafion-Graphene Modified Bismuth Film Electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 8255–8262. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Yan, X. Three-dimensional nitrogen-doped graphene as an ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor for the detection of dopamine. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2427–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Jin, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Ag Nanoparticles-Modified 3D Graphene Foam for Binder-Free Electrodes of Electrochemical Sensors. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Shang, J.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, X. Performance Investigation of Multilayer MoS2 Thin-Film Transistors Fabricated via Mask-free Optically Induced Electrodeposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6255–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).