Abstract
Laboratory experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of NPK fertilizer, soil type (silty clay and sandy loam) with no history of pesticide application, temperature (28 and 40 °C), and maize residue on the half-life of atrazine herbicide. NPK fertilizer was applied at 375 mg N, 187.5 mg P, and 187.5 mg K per 600 g soil, while maize straw was added at a rate of 12 g per 600 g soil. Atrazine was applied at four concentrations: 0.0678, 1.69, 3.39, and 5.08 mg g−1 soil. The residual concentration of atrazine was measured using gas chromatography over a 150-day period. The results showed that atrazine degradation was highest in Algeraif soil at 40 °C (87%), followed by Algeraif soil at 28 °C (68%) and Gerif soil at 28 °C (54.2%). The addition of NPK and maize straw significantly enhanced atrazine degradation, with degradation reaching 97% at a concentration of 0.0678 mg g−1 soil after 150 days. The lowest half-lives, compared to the control, were 125, 39, 25, 19, and 14 days in Gerif soil (28 °C), Algeraif soil (28 °C), Algeraif soil (40 °C), NPK, and maize straw, respectively, at an atrazine concentration of 5.08 mg g−1 soil. In conclusion, the addition of NPK fertilizer and maize straw significantly enhanced atrazine degradation, reducing both its concentration and half-life in soil.
Keywords:
atrazine; NPK fertilizer; plant residue; half-life; soil type; temperature; degradation; persistence 1. Introduction
Pesticides play a vital role in enhancing agricultural productivity to meet the food demands of a growing global population. By protecting crops from pests, weeds, and diseases, they contribute significantly to the sustainability of food supply systems for both humans and animals. However, the intensive and often indiscriminate application of pesticides in modern agriculture has raised serious concerns regarding their environmental and human health impacts [1,2]. Among these concerns, soil contamination stands out as a critical issue, given that soil serves as an important sink of pesticide residues following agricultural application.
Persistent pesticide residues in soil can negatively affect native microbial communities, which are fundamental for nutrient cycling, organic matter decomposition, and maintaining soil health. Disruption of these microbial communities may interfere with elemental cycles such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon, and may also lead to the bioaccumulation of toxic substances in food chains. Moreover, the horizontal and vertical mobility of certain pesticide compounds in soil profiles increases the risk of surface and groundwater contamination [3,4,5,6].
Given the environmental and health risks associated with the accumulation of pesticide residues in soil, food, and water systems, there is an urgent need to develop effective, safe, and economically viable methods for pesticide remediation. Among these, biodegradation, using soil microorganisms to break down and detoxify organic pollutants, has emerged as one of the most promising strategies [7,8]. Microbial degradation is a natural, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly approach that leverages the metabolic capabilities of native or introduced microbes to transform hazardous pesticide residues into non-toxic compounds.
The efficiency of pesticide biodegradation in soil is influenced by a range of factors, including the physicochemical properties of the pesticide (e.g., solubility, chemical structure) and its application method (e.g., concentration, dosage); soil characteristics (e.g., texture, pH, temperature, moisture, organic matter content, salinity); and the presence and activity of microbial populations capable of degrading the compounds [9,10,11,12,13,14]. Additionally, soil amendments such as organic (e.g., crop residues) and inorganic (e.g., NPK) fertilizers can significantly enhance microbial activity by providing essential nutrients, thereby stimulating enzymes production involved in herbicide degradation [15,16,17,18].
Previous studies have provided valuable insights into atrazine degradation, but they have mostly examined single factors, such as soil type, temperature, or fertilizer application, in isolation. In reality, these factors interact under field conditions and jointly determine the persistence of atrazine. The lack of integrated studies that simultaneously consider soil type, temperature variation, and different amendments represents a critical gap in understanding the environmental fate of atrazine. To address this gap, the present study investigated the effects of NPK fertilizer, plant residue, soil type, and temperature on the half-life of atrazine.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
Three soil samples were collected from the Al Geraif area (Blue Nile bank), East Khartoum, Sudan (15°34′0.46″ N; 32°35′33.21″ E), where there is no history of pesticide application. Samples were randomly collected with an auger from the top 15 cm of different parts of the selected site. Large clods were crushed to a uniform size, thoroughly mixed to make a composite sample, and air-dried at room temperature. The chemical and physical characteristics of the Al Geraif soil were as follows: pH = 7.8, ECe = 0.69 dS/m, N = 0.18%, P2O5 = 0.0034%, K2O = 0.03%, clay = 52.0%, silt = 47.3%, sand = 0.7%, organic matter = 0.62%. Al Geraif soil was classified as silty clay, fine, montmorillonitic, superactive, isohyperthermic, Vertic Haplocambids. Soils were then divided into five 600 g lots and transferred into 1000 mL beakers. Four sets of atrazine concentrations (0.0678, 1.69, 3.39, and 5.08 mg g−1 soil) were prepared, each with two fertilizer additives, and mixed thoroughly.
Inorganic NPK fertilizers were added as urea, P2O5, and KCl at rates of 375, 187.5, and 187.5 mg per 600 g of atrazine-amended soil, respectively. Maize straw was added at a rate of 12 g per 600 g of atrazine-amended soil. Soils were then wetted with water to 60% of field capacity, mixed thoroughly, and incubated in the dark at 28 °C for 150 days. At time zero and after 15, 30, 60, 90, 120, and 150 days, soil samples were taken to determine atrazine residues. Atrazine residues were determined according to the method described by AOAC [19].
To study the effect of soil type on the half-life of Herbicide atrazine similar experiment (Control without addition fertilizers) was repeated using Shambat Gerif (River Nile Bank), north of Khartoum, Sudan, between latitude 15°40′22.21′′ N and longitude 32°31′7.34′′ E. The chemical and physical characteristics of the Gerif soil were as follows: pH = 7.3, ECe = 0.58 dS/m, N = 0.11%, P as P2O5 = 0.43%, K as K2O = 0.13%, Clay = 31.7%, Silt =53.6%, Sand =14.7%, total organic carbon = 0.36%, organic matter = 0.31%. Gerif soil was classified as sandy loam, Fine, mixed, Isohyperthermic, Typic Haplustepts.
Determination of atrazine half –life in soil residues of atrazine in soil after 150 days incubation were used to calculate the half-life of the herbicides using the following equation suggested by Müller et al. [20]:
where
T½ = the half—life.
K = the degradation rate constant.
The degradation rate constant can be calculated with the following equation:
where
C0 = the initial concentration (ppm)
Ct = concentration at time t (ppm).
2.2. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using Statistica software (version 14.0.1.25). A one-way ANOVA was performed separately for each soil treatment to evaluate the effect of atrazine concentrations (0.678–5.80 mg g−1 soil). When significant differences were detected (p < 0.05), Tukey’s HSD test was applied, and means were labeled with different letters to indicate statistically significant differences among the treatments.
3. Results
3.1. Factors Affecting Atrazine Persistence in Soil: Influence of Temperature, Fertilization, and Soil Type
Atrazine degradation in the soils was affected by temperature, NPK fertilization, and soil type. The half-life of atrazine was longer at lower temperatures than at higher temperatures. For instance, in non-fertilized Al Geraif soil incubated at 28 °C, the half-life ranged from 90 to 39 days, whereas at 40 °C it decreased significantly, ranging from 36 to 25 days. Fertilization also had a strong influence on atrazine persistence. In Al Geraif soil incubated at 28 °C, the half-life ranged from 90 to 39 days in non-fertilized samples, but it decreased to 19–25 days with NPK amendment and to 14–22 days with plant residue amendment. Moreover, soil type played a significant role in the persistence of atrazine. The half-life in Al Geraif soil ranged from 39 to 90 days, while in Gerif soil it was longer, ranging from 70 to 125 days. These results indicate that higher temperatures, NPK fertilization, and soil characteristics significantly accelerate the degradation of atrazine in soil (Table 1).

Table 1.
Half-life (days) of various concentrations of atrazine in soils after 150 days of incubation.
3.2. Atrazine Degradation in Gerif Soil at 28 °C
The study revealed that atrazine degradation rates were inversely proportional to its initial concentration. In Gerif soil, degradation of all atrazine concentrations started early during the incubation period. However, only 5% degradation was recorded for the maximum concentration after 15 days, increasing to 54.2% after 150 days. At the same time interval, degradation at the minimum concentration was 12.2% and 7%, respectively (Figure 1).
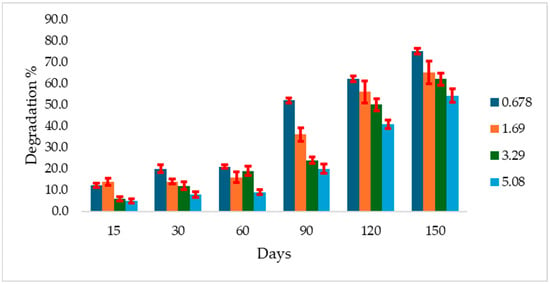
Figure 1.
Atrazine degradation rate (%) in Greif soil incubated at 28 °C over 150 days at different initial concentrations (mg g−1 soil). Error bars indicate the standard deviation of replicate measurements.
3.3. Atrazine Degradation in Algeraif Soil at 28 °C
In Al Geraif soil incubated at 28 °C, atrazine degradation was generally low at all tested concentrations. After 15 days of incubation, the degradation percentages were 8%, 9.4%, 10.4%, and 14% for concentrations of 5.08, 3.39, 1.69, and 0.0678 mg g−1 soil, respectively. By 150 days, the degradation had increased to 72.0, 70.0, 69.3, and 68% for the same respective concentrations (Figure 2).
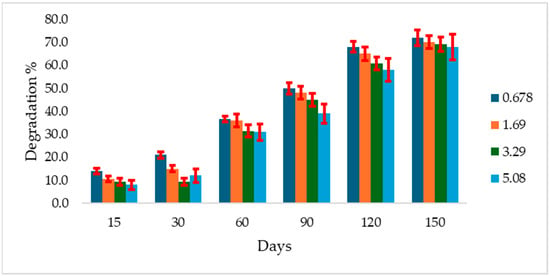
Figure 2.
Atrazine degradation rate (%) in Algeraif soil incubated at 28 °C over 150 days at different initial concentrations (mg g−1 soil). Error bars indicate the standard deviation of replicate measurements.
3.4. Atrazine Degradation in Algeraif Soil at 40 °C
In Al Geraif soil incubated at 40 °C, degradation started earlier at the lower concentrations. After 15 days, 62.5% degradation was recorded at 1.69 mg g−1 soil, while 28% and 42% degradation were recorded at 0.0678 and 3.39 mg g−1 soil, respectively. After 150 days, a degradation range of 55.2% to 87.0% was observed across all concentrations (Figure 3).
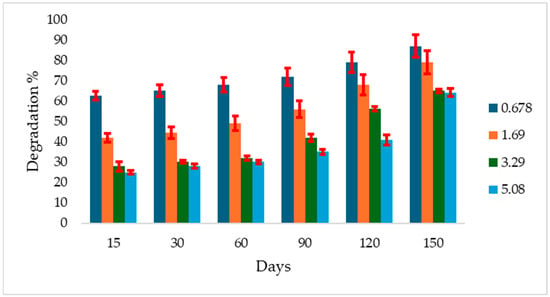
Figure 3.
Atrazine degradation rate (%) in Algeraif soil incubated at 40 °C over 150 days at different initial concentrations (mg g−1 soil). Error bars indicate the standard deviation of replicate measurements.
3.5. Effect of NPK and Plant Residue on Atrazine Degradation
Soil amendment with NPK and plant residue significantly enhanced atrazine degradation compared with the control. At a concentration of 0.0678 mg g−1 soil, 79% degradation was recorded at 120 days with NPK addition, while 91% degradation occurred earlier in soils amended with plant residue. At 1.69 mg g−1 soil, NPK induced 82% degradation at 150 days, while plant residue led to faster degradation. At 3.39 mg g−1 soil, NPK resulted in 60% degradation at 120 days, with degradation occurring earlier with plant residue. At the highest concentration (5.08 mg g−1), both NPK fertilizer and plant residue application promoted rapid degradation as early as 30 days. The maximum degradation recorded was 97% at 150 days for both NPK- and plant residue–amended soils (Figure 4A,B).
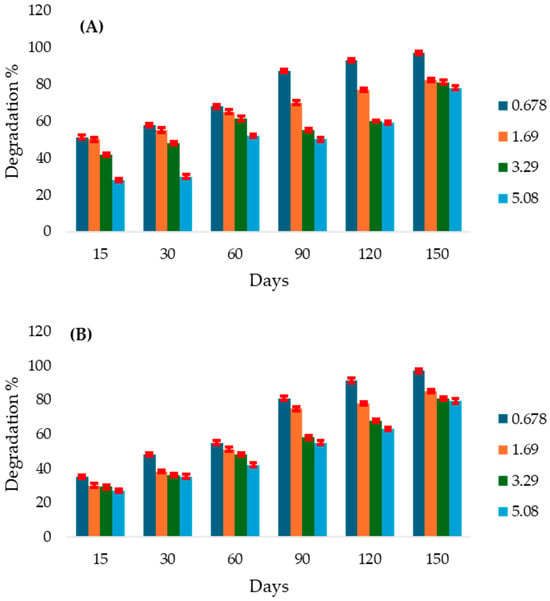
Figure 4.
Atrazine degradation rates (%) in Algeraif: (A): Soil amended with NPK, incubated at 28 °C, and (B): Soil amended with plant residue, incubated at 28 °C over 150 days at different initial concentrations (mg g−1 soil). Error bars indicate the standard deviation of replicate measurements.
4. Discussion
The present study demonstrates that the half-life of atrazine was longer at low temperature compared to higher temperature. Temperature is a key climatic factor, and the increased temperature significantly increased both the biological metabolic processes and the rate of chemical reactions. In this context, Singh and Kulshrestha [21] and Pan [22] stated that a 10 °C increase in temperature reduced the apparent half-life of pesticides by 2–3 times. Similarly, Dong et al. [23] found that the half-life of atrazine decreased by 3–4 times as the temperature increased from 5 °C to 35 °C, with degradation reaching 95.6% at 35 °C after 60 days. Similarly, Cessna et al. [24] observed that the half-life of several herbicides were markedly shorter at 20 °C compared to lower temperatures. Elevated temperatures not only accelerate microbial activity but also enhance both the biological and chemical processes responsible for pesticide dissipation [25,26,27,28]. Rapid degradation of pesticides at a higher level of temperatures may also result from increased volatility and photodecomposition of the molecules. These findings align with those of Osman [29] who observed that the fungicide azoxystrobin degraded slowly and persisted in the soil for up to five months under incubation. He also reported that the biodegradation rate of the fungicide Amistar in soil incubated at 40 °C was higher than in soil incubated at 18 °C. Moreover, Mohamed et al. [30] indicated that biodegradation of oxyfluorfen in soil incubated at 40 °C after 45 days of incubation ranged from (55.2–78.3%) than in soil incubated at 28 °C (17.5–36.6). Lee et al. [31] and Xuan and Gergon [32] reported that half- life Benomyl–MBC was found to decrease with increased temperature from 23 to 33 °C. Working on oxyfluorfen [33,34] reported lower half- life values, at higher temperature.
The data further revealed that the application of organic and inorganic fertilizers enhanced early degradation of atrazine and reduced half-life of this herbicide. Organic fertilizers, especially those derived from plant residues enhanced degradation and improved soil fertility. This could possibly be due to the available carbon in organic material, which is important for the pesticide-degrading microorganisms as sources of nutrients, carbon and energy [35,36,37].
Generally, mineral fertilization of arable land positively affects and increases the biological productivity of various ecosystems as well as the microbial activity in soil [38,39,40,41]. This study found that the half-life of atrazine was shorter in Algeraif soil compared to Gerif soil. This could be attributed to the higher clay content, organic matter and other nutrient content [30,42,43]. This is because organic materials enhance microbial growth and activities [44,45,46,47]. Additionally, clayey soils generally exhibit greater adsorption capacity than light (sandy) soils [48,49,50].
Finally, the results indicated that degradation rates of atrazine were inversely proportional to concentrations. Shirkot and Gupta [51], Sherif et al. [52] and Reddy et al. [53] reported similar findings, concluding that the degradation of Thiram fungicide in soil is inversely proportional to its concentration. One of the crucial factors affecting pesticide degradation is the organic matter content of the soil, which increases the biomass of the active microbial population and the degradation as well [49,54,55].
5. Conclusions
This study underscores the pivotal role of some abiotic factors studied in this experiment namely NPK fertilization, soil type, temperature and residue in reducing the half-life of atrazine and promoting its degradation across different soil types. Results demonstrate that higher temperatures and the application of plant residue or NPK fertilizers significantly accelerated atrazine degradation, underscoring the synergistic influence of biological and environmental factors in mitigating pesticide persistence. Additionally, soil composition played a vital role, with Algeraif soil’s higher clay and organic matter content leading to shorter atrazine half-lives compared to Gerif soil. These findings highlight the importance of tailored soil management to optimize atrazine degradation and reduce environmental contamination. Future studies should validate these results under field conditions and explore interactions between microbial communities and amendments. Farmers can apply NPK fertilizer and plant residues according to soil type and temperature to enhance degradation and minimize environmental risks. Further research should also investigate long-term field effects, microbial roles, amendment interactions across soils and climates, and the broader ecological impacts of atrazine degradation.
Author Contributions
A.K.A.E.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review and Editing. E.H.E.Y.: Formal Analysis, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review and Editing. M.M. and A.M.Z.: Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review and Editing. K.C.: Supervision, Writing—Review and Editing. A.G.O.: Supervision, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review and Editing. E.A.E.E.: Supervision, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review and Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge funding from the Sudanese Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the first author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Department of Soil and Environment Science, University of Khartoum, for lab support; the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research for funding; and the Institute of Geomatics and Civil Engineering, University of Sopron, for academic collaboration.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Abdulrahman, N.M.; Hamasalim, H.J.; Mohammed, H.N.; Arkwazee, H.A. Effects of pesticide residues in animal by-products relating to public health. J. Appl. Vet. Sci. 2023, 8, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, A. Pesticide Pressure on Insect and Human Population: A Review. Arch. Curr. Res. Int. 2024, 24, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Qiao, C.L. Novel approaches for remediation of pesticide pollutants. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 18, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudh, S.; Singh, J.S. Pesticide contamination: Environmental problems and remediation strategies. In Emerging and Eco-Friendly Approaches for Waste Management; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, V.M.; Verma, V.K.; Rawat, B.S.; Kaur, B.; Babu, N.; Sharma, A.; Dewali, S.; Yadav, M.; Kumari, R.; Singh, S.; et al. Current status of pesticide effects on environment, human health and its eco-friendly management as bioremediation: A comprehensive review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovac, A.; Petrović, S. Pesticide use and degradation strategies: Food safety, challenges and perspectives. Foods 2023, 12, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoefs, O.; Perrier, M.; Samson, R. Estimation of contaminant depletion in unsaturated soils using a reduced-order biodegradation model and carbon dioxide measurement. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Meng, F. Efficiency, mechanism, influencing factors, and integrated technology of biodegradation for aromatic compounds by microalgae: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 335, 122248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Pradhan, S.; Saha, M.; Sanyal, N. Impact of pesticides on soil microbiological parameters and possible bioremediation strategies. Indian. J. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaid, O.G.; Abdelbagi, A.O.; Elsheikh, E.A.E. Effects of fertilizers (activators) in enhancing microbial degradation of endosulfan in soil. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2009, 3, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shahgholi, H.; Ahangar, A.G. Factors controlling degradation of pesticides in the soil environment: A review. Agric. Sci. Dev. 2014, 3, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Bosu, S.; Rajamohan, N.; Al Salti, S.; Rajasimman, M.; Das, P. Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos pollution from contaminated environment—A review on operating variables and mechanism. Environ. Res. 2024, 248, 118212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.S.; Parihar, K.; Goyal, N.; Mahapatra, D.M. Synergistic insights into pesticide persistence and microbial dynamics for bioremediation. Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, A.; Walia, Y.; Kumar, R.; Umar, A.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Akhtar, M.S.; Alkhanjaf, A.A.M.; Baskoutas, S. A review on ecology implications and pesticide degradation using nitrogen fixing bacteria under biotic and abiotic stress conditions. Chem. Ecol. 2023, 39, 753–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanissery, R.G.; Sims, G.K. Biostimulation for the enhanced degradation of herbicides in soil. Appl. Environ. Soil. Sci. 2011, 2011, 843450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H. The application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as microbial biostimulant, sustainable approaches in modern agriculture. Plants 2023, 12, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhlifi, Z.; Iftikhar, J.; Sarraf, M.; Ali, B.; Saleem, M.H.; Ibranshahib, I.; Bispo, M.D.; Meili, L.; Ercisli, S.; Torun Kayabasi, E.; et al. Potential role of biochar on capturing soil nutrients, carbon sequestration and managing environmental challenges: A review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Khan, M.S.; Singh, U.B. Pesticide-tolerant microbial consortia: Potential candidates for remediation/clean-up of pesticide-contaminated agricultural soil. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC): Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, K.; Magesan, G.N.; Bolan, N.S. A critical review of the influence of effluent irrigation on the fate of pesticides in soil Agric. Ecosys. Environ. 2007, 120, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Kulshrestha, G. Degradation of fluchloralin in soil under predominating anaerobic conditions. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part. B 1995, 30, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W. Review on the Effects of Temperature on Toxicity of Insecticides. J. Hebei Agric. Sci. 2010, 14, 12–18. Available online: https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HBKO201008005.htm (accessed on 3 June 2023).
- Dong, X.; Sun, H. Effect of temperature and moisture on degradation of herbicide atrazine in agricultural soil. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Res. 2016, 2, 150–157. [Google Scholar]
- Cessna, A.J.; Knight, J.D.; Ngombe, D.; Wolf, T.M. Effect of temperature on the dissipation of seven herbicides in a biobed matrix. Can. J. Soil. Sci. 2017, 97, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, R.G.; Miller, J.R.; Fontaine, D.D.; Laskowski, D.A.; Hunter, J.H.; Cordes, R.C. Degradation of a sulfonamide herbicide as a function of soil sorption. Weed Res. 1992, 32, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reedich, L.M.; Millican, M.D.; Koch, P.L. Temperature impacts on soil microbial communities and potential implications for the biodegradation of turfgrass pesticides. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukhurebor, K.E.; Aigbe, U.O.; Onyancha, R.B.; Adetunji, C.O. Climate change and pesticides: Their consequence on microorganisms. Microb. Rejuvenation Pollut. Environ. 2021, 3, 83–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, M.M.; Reehana, N.; Imran, M.M. Microbial Degradation of Pesticides in Agricultural Environments: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanisms, Factors and Biodiversity. Mol. Sci. Appl. 2024, 4, 65–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.G. Degradation of the fungicide azoxystrobin by soil microorganisms. UK J. Agric. Sci. 2006, 14, 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.T.; Elhussein, A.A.; Elsiddig, M.A.; Osman, A.G. Degradation of Oxyfluorfen herbicide by soil microorganisms biodegradation of herbicides. Biotechnology 2011, 10, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Chang, H.H.; Jang, Y.S.; Hyung, S.W.; Chung, H.Y. Partial reduction of dinitroaniline herbicide pendimethalin by Bacillus sp. MS202. Korean J. Environ. Agric. 2004, 23, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, T.H.; Gergon, E.B. Strategies for the management of rice pathogenic fungi. In Fungi; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 396–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.H.; Sheu, W.S.; Wang, Y.S. Dissipation of the herbicide oxyfluorfen in subtropical soils and its potential to contaminate groundwater. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2003, 54, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnar, D.J. The Fate and Risk of Oxyfluorfen Under Simulated California Rice Field Conditions; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Duah-Yentumi, S.; Kuwatsuka, S. Effect of organic matter and chemical fertilizers on the degradation of benthiocarb and MCPA herbicides in the soil. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 1980, 26, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, H.; Solanki, P.; Narayan, M.; Tewari, L.; Rai, J.P.N.; Khatoon, H.C. Role of microbes in organic carbon decomposition and maintenance of soil ecosystem. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2017, 5, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, T.; Kole, S.C. Soil organic matter and microbial role in plant productivity and soil fertility. In Advances in Soil Microbiology: Recent Trends and Future Prospects, Volume 2: Soil-Microbe-Plant Interaction; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabasz, W.; Albinska, D.; Jaskowska, M.; Lipiec, J. Biological effects of mineral nitrogen fertilization on soil microorganisms. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2002, 11, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Koskinen, W.; Banks, P. Soil movement and persistence of triazine herbicides. In The Triazine Herbicides: 50 Years Revolutionizing Agriculture; LeBaron, H., McFarland, J., Burnside, O., Eds.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 355–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisseler, D.; Scow, K.M. Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincă, L.C.; Grenni, P.; Onet, C.; Onet, A. Fertilization and soil microbial community: A review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, K.K. Sorption and degradation of imidacloprid in soil and water. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part. B 2006, 41, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudhoo, A.; Garg, V.K. Sorption, transport and transformation of atrazine in soils, minerals and composts: A review. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.C.; Debnath, A.; Mukherjee, D. Effect of the herbicides oxadiazon and oxyfluorfen on phosphates solubilizing microorganisms and their persistence in rice fields. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R.; Chakrabarti, K.; Chakraborty, A.; Chowdhury, A. Pencycuron application to soils: Degradation and effect on microbiological parameters. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Senbayram, M.; Blagodatsky, S.; Myachina, O.; Dittert, K.; Kuzyakov, Y. Decomposition of biogas residues in soil and their effects on microbial growth kinetics and enzyme activities. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 45, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Sánchez, A.; Soares, M.; Rousk, J. Testing the dependence of microbial growth and carbon use efficiency on nitrogen availability, pH, and organic matter quality. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceló, D.; Hennion, M.C. Trace Determination of Pesticides and Their Degradation Products in Water; Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003; p. 539. [Google Scholar]
- Rasool, S.; Rasool, T.; Gani, K.M. A review of interactions of pesticides within various interfaces of intrinsic and organic residue amended soil environment. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 11, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aswad, A.F.; Fouad, M.R.; Aly, M.I. Experimental and modeling study of the fate and behavior of thiobencarb in clay and sandy clay loam soils. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 4405–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirkot, C.K.; Gupta, K.G. Accelerated tetramethylthiuram disulfide (TMTD) degradation in soil by incubation with TMT-utilizing bacteria. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1985, 35, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, A.M.; Elhussein, A.A.; Osman, A.G. Biodegradation of fungicide thiram (TMTD) in soil under laboratory conditions. Am. J. Biotechnol. Mol. Sci. 2011, 1, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.; Jose, S.; Fayaz, T.; Renuka, N.; Ratha, S.K.; Kumari, S.; Bux, F. Microbe-Assisted Bioremediation of Pesticides from Contaminated Habitats. In Bioremediation for Sustainable Environmental Cleanup; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; p. 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandin-España, P.; Loureiro, I.; Escorial, C. Herbicides: Theory and Applications; Soloneski, S., Larramendy, M.L., Eds.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2011; p. 610. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, S.; Arora, S.; Sahni, D.; Sehgal, M.; Srivastava, D.S.; Singh, A. Pesticides use and its effect on soil bacteria and fungal populations, microbial biomass carbon and enzymatic activity. Curr. Sci. 2019, 116, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).