Abstract
Multi-focus image fusion is an important method for obtaining fully focused information. In this paper, a novel multi-focus image fusion method based on fractal dimension (FD) and parameter adaptive unit-linking dual-channel pulse-coupled neural network (PAUDPCNN) in the curvelet transform (CVT) domain is proposed. The source images are decomposed into low-frequency and high-frequency sub-bands by CVT, respectively. The FD and PAUDPCNN models, along with consistency verification, are employed to fuse the high-frequency sub-bands, the average method is used to fuse the low-frequency sub-band, and the final fused image is generated by inverse CVT. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method shows superior performance in multi-focus image fusion on Lytro, MFFW, and MFI-WHU datasets.
1. Introduction
Multi-focus image fusion (MFIF) is a technique used in image processing to combine multiple images of the same scene, each taken with a different focus setting, into a single image that contains all the focused details from various depths. This method is particularly useful in scenarios where a single image captured with one focus setting cannot provide sufficient clarity for objects at different distances [].
In practical terms, a camera or imaging device typically focuses on one specific plane, leading to blurred details for objects either closer or farther away from the focus point. By using multi-focus image fusion, multiple images taken with different focal distances are merged, resulting in a final image where all parts of the scene are in sharp focus []. This technique has numerous applications in fields such as medical imaging, remote sensing, microscopy, and computer vision, where it is essential to capture fine details at various depths in a single, comprehensive image.
The fusion process often involves various algorithms and techniques, including wavelet transforms, pyramid decompositions, and gradient-based methods, to selectively combine the sharpest details from each input image. These methods aim to preserve the high-frequency details while minimizing artifacts such as ghosting or blurring [,,,,,]. In recent years, deep learning approaches have also been integrated into multi-focus image fusion [,] and remote sensing image fusion [,], further enhancing the quality and efficiency of the fusion process.
In transform domain-based methods, the curvelet [], contourlet [,], and shearlet [,] are commonly used. These algorithms are often applied in fields such as image enhancement [,,], image denoising [,,], and image fusion [,,,,,,]. Vishwakarma et al. [] introduced the multi-sensor image fusion method based on the curvelet transform and Karhunen–Loeve transform, and the algorithm has achieved good results in the fusion of multi-focus images, medical images, and infrared and visible light images, demonstrating strong robustness. Li et al. [] introduced the MFIF method based on fractal dimension and coupled neural P systems in a nonsubsampled contourlet transform (NSCT) domain, and the algorithm was experimentally validated on three multi-focus datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in image fusion and achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) results. Lv et al. [] proposed the MFIF method based on parameter-adaptive pulse-coupled neural network and fractal dimension in nonsubsampled shearlet transform (NSST) domain; in addition to achieving advantages in multi-focus image fusion, the algorithm has also shown significant results in medical, infrared and visible light image fusion.
With the rise in deep learning, several advanced fusion techniques based on neural networks have been proposed [,]. These methods aim to learn optimal fusion strategies from large datasets without requiring manual feature extraction or explicit fusion rules. The convolutional neural networks (CNNs) [], generative adversarial networks (GANs) [], autoencoders [], transformers [], mamba [], and diffusion model [] are widely used in image fusion. CNNs are trained to learn how to fuse images by automatically selecting and combining the most relevant features from multiple inputs []. GANs can be used to generate high-quality fused images by training a generator to combine focus information while using a discriminator to evaluate the quality of the fusion []. Autoencoders can be used to extract and fuse relevant features from images, reconstructing a final output with enhanced focus []. Ouyang et al. [] proposed the MFIF method based on superpixel features generation Graph convolutional neural network and pixel-level feature reconstruction CNN; Zhang et al. [] introduced the unsupervised generative adversarial network with adaptive and gradient joint constraints for multi-focus image fusion; and Shihabudeen et al. [] introduced an autoencoder deep residual network model for multi-focus image fusion. Wang et al. [] proposed the unsupervised universal image fusion approach via a generative diffusion model; the algorithm was simulated for multi-focus image fusion, multi-exposure image fusion, infrared and visible image fusion, and medical image fusion, demonstrating its versatility and broad applicability. These deep learning-based fusion methods can achieve superior performance by learning from data and adapting to complex image characteristics, but they require a large amount of data for training and may be computationally expensive, and they also face challenges such as overfitting, where the model performs well on the training data but poorly on unseen data. To address this, regularization techniques and data augmentation are often employed to improve the generalization of the model. Moreover, the choice of network architecture and hyperparameters can significantly affect the performance of the fusion process. Researchers are continuously exploring novel architectures and optimization strategies to enhance the robustness and efficiency of these fusion techniques.
Pulse-coupled neural networks (PCNNs) have demonstrated significant advantages in the field of image fusion, particularly in multi-source image fusion, where it has garnered widespread attention and in-depth research []. Especially when PCNN and its improved models are combined with multi-scale transforms to fuse the low-frequency or high-frequency components of decomposed images, the fusion performance is significantly enhanced [,]. Deeply inspired by these excellent image fusion algorithms, in this paper, a novel multi-focus image fusion method based on fractal dimension (FD) and parameter adaptive unit-linking dual-channel PCNN (PAUDPCNN) in the curvelet transform domain is proposed to solve the noise and artifact issues. The FD-based expression is utilized to motivate the linking strength while fusing the high-frequency sub-bands. The algorithm is validated for its fusion effectiveness and universality on multi-focus datasets through simulation experiments on three common datasets: Lytro, MFFW, and MFI-WHU.
2. Related Work
2.1. Curvelet Transform
Curvelet transform (CVT) [] is a mathematical tool designed to efficiently represent images with discontinuities along curves. Unlike traditional wavelet transforms, which are effective at capturing point singularities, the curvelet transform excels at representing smooth edges and features with more accuracy. It uses multi-scale, multi-directional decompositions that allow for better handling of anisotropic structures in images. This makes it particularly useful in fields like image denoising, compression, edge detection, and image fusion, where preserving fine details and sharp boundaries is crucial.
2.2. PAUDPCNN
The functional diagram of the parameter adaptive unit-linking dual-channel pulse-coupled neural network (PAUDPCNN) model is depicted in Figure 1, and it contains three components: the dendritic tree, pulse generator, and information fusion module. The PAUDPCNN model can be computed by the following []:
where and show the external stimuli of the PAUDPCNN model corresponding to the pixel of the images A and B, respectively. The two symmetric feeding inputs and for the neuron store the external stimuli and , respectively. The shows the linking input at the iteration for the neuron, whereas its 8-neighborhood neurons are represented utilizing the set . The constitutes the internal state of at the neuron acquired after the iteration, which corresponds to the non-linear modulation of feeding and linking inputs. The is the internal activity of the PAUDPCNN model after the iteration corresponding to the neuron, which can be employed to generate the fused image. The external output and dynamic threshold of the neuron after the iteration are represented using and , respectively. The is the linking strength corresponding to , which is computed by the following that uses the sigmoidal membership function.
where . Here, because the other values of either converge to 0 or 1. The value of depends on either or but not both. This ensures different linking strengths for corresponding pixels of the source images, which persist the behavior of HVS. The mechanisms to set the values of are described in Section 3. The and are the exponential decay constants, whereas is the amplitude of the dynamic threshold. The value of for the PAUDPCNN model is computed by the following:
where is the standard deviation of . Always, which prevents the exponential growth of with respect to n. The values of and are estimated using Equations (11) and (12), respectively. Here, and represent the Otsu threshold of and , respectively.
where is the maximum value of .
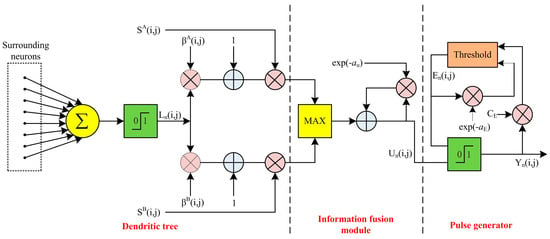
Figure 1.
Parameter adaptive unit-linking dual-channel PCNN.
3. The Proposed Method
In this section, we will provide a detailed introduction to the multi-focus image fusion algorithm proposed in this paper, which can be divided into four parts: image decomposition, high-frequency fusion, low-frequency fusion, and image reconstruction.
3.1. Image Decomposition
The source images A and B are decomposed by CVT into low-frequency sub-bands and high-frequency sub-bands , respectively.
3.2. Fusion of High-Frequency Sub-Bands
The high-frequency part contains most of the noise and detailed information. The fractal and fractional models have extensive applications in fields such as image processing [,,,,,,,,,]. The fused high-frequency sub-bands generated by the PAUDPCNN model combined fractal dimension (FD) [,] and consistency verification []. For , the absolute values of the sub-bands are fed as external inputs, which is defined as follows:
The values of ,, and are initialized using the following:
where ensures the immediate activation of neurons, which prevents unwanted void iterations.
The fractal dimension (FD) is defined as follows []:
where is used to define the linking strength, , for the high-frequency sub-bands. The values of are computed using Equation (9), where can be calculated by the following:
where and are the minimum and maximum values of , respectively. The values of ,, and are estimated utilizing Equations (10)–(12), respectively. The PAUDPCNN model is run up to N iterations, and then the decision map is computed by the following:
where and are the internal activities of and at the iteration, respectively.
Consistency verification (CV), as introduced in [], is a commonly used post-processing step in multi-focus image fusion algorithms to enhance the quality of the fused image. This process involves examining a specific region of the decision map where the central block originates from A, while the majority of surrounding blocks belong to B. In such a case, the central block should also be assigned to B. This can be achieved by applying a majority filter, such as a 3 × 3 averaging filter, as follows:
where the shows the filtered decision map, and the fused high-frequency sub-bands are generated by the following:
3.3. Fusion of Low-Frequency Sub-Bands
The low-frequency part contains the background information of the image; the averaging method is a very common algorithm in image fusion and has wide applications in this field, so we obtain the fused low-frequency sub-band using the averaging method, the corresponding equation is defined as follows:
where denotes the fused low-frequency sub-band.
3.4. Inverse CVT
The fused image F is obtained by using inverse CVT performed on and .
The main steps of the proposed method can be summarized in Algorithm 1, and the flowchart of the proposed fusion method is depicted in Figure 2.
| Algorithm 1: The proposed fusion method |
| Input: the source images: A and B Parameters: the number of CVT decomposition levels: L, the number of PAUDPCNN iterations: N Main step: Step 1: CVT decomposition For each source image Perform CVT on to generate ; End Step 2: High-frequency sub-bands’ fusion For each level For each direction For each source image Initialize the PAUDPCNN model: ; Estimate the PAUDPCNN parameters , , and via Equations (10)–(12); Compute the value of using Equations (9), (16)–(17); For each iterations Compute the PAUDPCNN model using Equations (3)–(8); End Get the decision map based on Equation (18); Perform the majority filtering on decision map to guarantee the consistency using Equation (19); Compute the fused high-frequency sub-bands according to Equation (20); End End End Step 3: Low-frequency sub-bands’ fusion For each source image Merge and using Equation (21) to generate End Step 4: Inverse CVT Perform inverse CVT on to obtain ; Output: the fused image . |
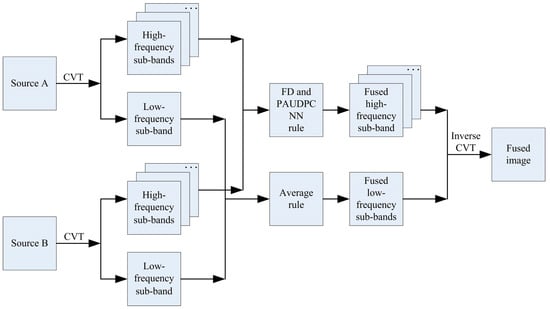
Figure 2.
The flowchart of the proposed fusion method.
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
In this section, we utilize the classical Lytro [], MFFW [], and MFI-WHU [] datasets for experimentation, with examples from each of the three datasets illustrated in Figure 3. The Lytro dataset contains 20 pairs of multi-focus data, the MFFW dataset contains 13 pairs of data, and the MFI-WHU dataset contains 120 pairs of data, and we randomly selected 30 pairs from the MFI-WHU dataset for testing. Additionally, we can refer to the dataset summary in the field of fusion compiled by authors from Wuhan University, which can be found at the following link: https://github.com/Linfeng-Tang/Image-Fusion, accessed on 30 November 2024. Our algorithm does not require training data and directly conducts simulation experiments on the test dataset.

Figure 3.
Examples of the multi-focus datasets: (a) Lytro, (b) MFFW, and (c) MFI-WHU.
The eight image fusion methods, GD [], MFFGAN [], LEGFF [], U2Fusion [], EBFSD [], UUDFusion [], EgeFusion [], and MMAE [], are used for comparison. The parameters for each method are configured as described in the original published papers to ensure a fair comparison. The metrics such as the edge-based similarity measurement [], the Chen–Blum metric [], the Chen–Varshney metric [], the structural-similarity-based metric proposed by Piella [], the feature mutual information metric [], the mutual information metric [], mean square error [], the nonlinear correlation information entropy [], the normalized mutual information [], and peak signal-to-noise ratio [] are used to evaluate the fusion results. Except for indicators and , the larger the values of the other indicators, the better the fusion performance. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations ensure consistency and accuracy in the comparison. In our method, N is set to 200.
The number of CVT decomposition levels has a significant impact on the fusion results, and we will now focus on analyzing these effects in detail. We tested seven different decomposition levels on the Lytro dataset and analyzed the impact of decomposition levels on fusion results using both subjective and objective evaluations, as shown in Figure 4 and Table 1. From Figure 4, it can be observed that when the decomposition level is 1, the fusion result appears blurry. When the decomposition level is 2, artifacts emerge in the fusion result. When the decomposition level is 7, noise is introduced into the fusion result, along with darker regions. For decomposition levels 3, 4, 5, and 6, no significant differences are visible in the fusion results, and the outcomes are relatively favorable. To further evaluate the fusion performance, we compared the average metrics for levels 3–6 on the Lytro dataset. As indicated in Table 1, when the decomposition level is 4, six out of ten metrics achieve optimal values. Their values are 0.7285 for , 0.7213 for , 0.8773 for , 6.7296 for , 0.8279 for , and 0.8964 for , respectively. Based on a comprehensive analysis, we set the CVT decomposition level to 4.
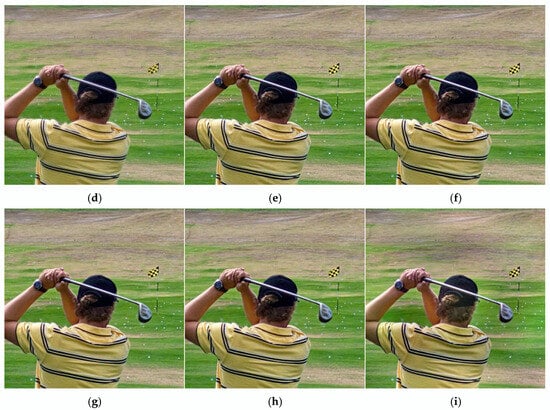


Figure 4.
Fusion results of the proposed algorithm with varying CVT decomposition levels on Lytro-01: (a) Source A, (b) Source B, (c) Level 1, (d) Level 2, (e) Level 3, (f) Level 4, (g) Level 5, (h) Level 6, and (i) Level 7.

Table 1.
The average quantitative comparison of different CVT decomposition levels evaluated on the Lytro dataset.
4.2. Fusion Results and Discussion
Figure 5 shows the image fusion results with different methods on Lytro-01 data. From the results, we can denote that the GD method generated a blurry fused image and introduced more noise, such as a ghosting artifact in the left arm of the person. The fused image generated by the MFFGAN algorithm causes the color of the person’s hat region to darken. The LEGFF algorithm produces relatively good fusion results, but the colors of the hat and watch areas on the person in the fused image are too dark, which makes it difficult to observe the fine details. The U2Fusion algorithm causes some areas of the fused image to become brighter, while others become darker; for example, the brightness of the lawn has been enhanced, but the hat area becomes severely darkened, leading to a significant loss of information. The EBFSD algorithm did not produce a focused fused image, resulting in significant information loss and poor fusion quality. The UUDFusion algorithm introduced artifacts in the fused image, such as in the areas of the left arm, hat, and golf club; additionally, some regions, such as the shirt on the left arm, have excessively high brightness, leading to significant information loss; as a result, the overall fusion quality is poor. The EgeFusion algorithm has improved the extraction and preservation of texture and color information in the fused image; however, the overall fused image appears somewhat distorted, making it difficult to realistically observe the objects themselves; additionally, some areas, such as the left arm, have excessively high brightness, leading to significant information loss. The MMAE algorithm produced relatively good fusion results, achieving a full-focus image; however, the brightness of the left arm of the person is too high, resulting in some information loss. Through comparison, the fused image obtained by our algorithm achieved the best results; it not only provides a full-focus image but also ensures that the fused information is fully complementary, with balanced brightness and clarity.
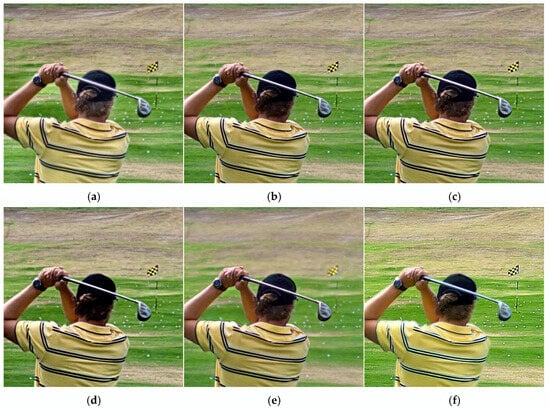


Figure 5.
Results of Lytro-01: (a) GD, (b) MFFGAN, (c) LEGFF, (d) U2Fusion, (e) EBFSD, (f) UUDFusion, (g) EgeFusion, (h) MMAE, and (i) Proposed.
Figure 6 is a line chart of the performance metrics obtained from simulation experiments on 20 data sets from the Lytro dataset using different fusion algorithms. The average performance metrics of the different algorithms are shown in Figure 6 and Table 2. Considering that a lower value of indicates better performance, we take its negative value (i.e., ) to illustrate the sub-figure of . The horizontal axis represents the number of image pairs in the dataset, and the vertical axis represents the metric value. From Figure 6 and Table 2, we can observe that our algorithm achieves the optimal values in terms of the average of 10 evaluation metrics. Their values are 0.7285 for , 0.7213 for , 20.8957 for , 0.8773 for , 0.8988 for , 6.7296 for , 22.2336 for , 0.8279 for , 0.8964 for , and 35.0684 for , respectively. These quantitative results are consistent with the conclusions of the qualitative analysis, providing strong evidence of the fusion advantages of our algorithm on the Lytro dataset.
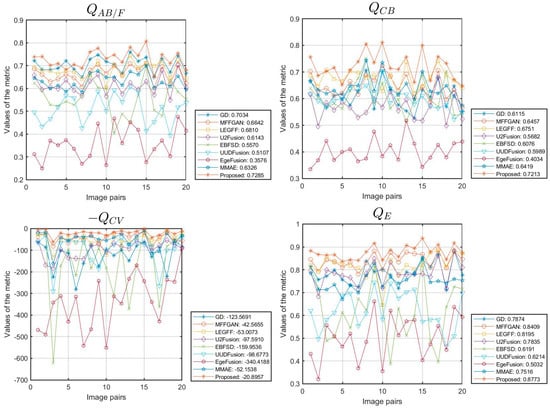
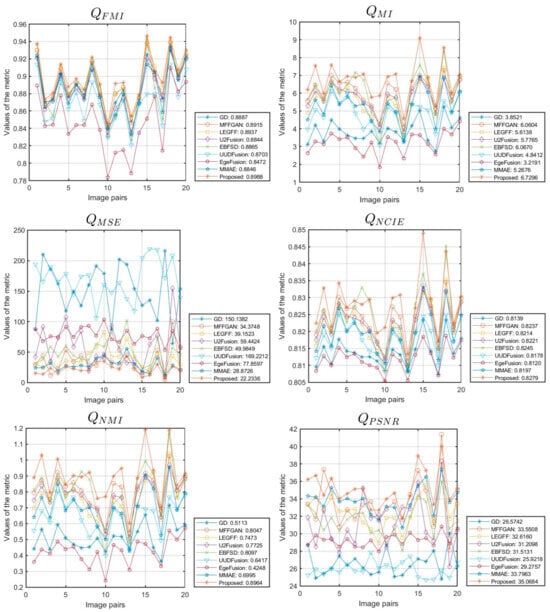
Figure 6.
The line chart illustrates the metrics of various data in the Lytro dataset.

Table 2.
Quantitative average comparative analysis of different methods on the Lytro dataset.
Figure 7 shows the image fusion results with different methods on MFFW-01 data. From the results, we can denote that the GD and MFFGAN algorithms generate artifacts in the fused images. Although LEGFF achieves full-focus results, some information is lost in the stone areas due to excessive brightness. The image produced by U2Fusion exhibits blurring. The EBFSD algorithm produces distortion and exhibits block artifacts. The fused image produced by UUDFusion is of poor quality, with information loss in the stone areas due to excessive brightness. Additionally, stripe patterns appear in the sea areas, and a significant amount of noise is introduced. The fused image produced by the EgeFusion algorithm suffers from severe information loss due to excessive sharpening. In the fused image produced by MMAE, the brightness of the stone area on the left is too dark, making it difficult to accurately capture the corresponding information. Through comparison, our algorithm produces the best fusion results, with both brightness and detailed information well preserved.
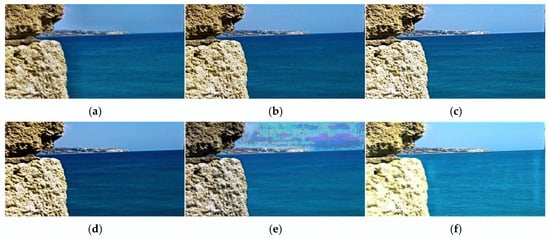

Figure 7.
Results of MFFW-01: (a) GD, (b) MFFGAN, (c) LEGFF, (d) U2Fusion, (e) EBFSD, (f) UUDFusion, (g) EgeFusion, (h) MMAE, and (i) Proposed.
Figure 8 is a line chart of the performance metrics obtained from simulation experiments on 13 data sets from the MFFW dataset using different fusion algorithms. The average performance metrics of the different algorithms are shown in Figure 8 and Table 3. From Figure 8 and Table 3, we can see that our algorithm achieves the optimal values for 9 out of the 10 evaluation metrics in terms of the average value, except for metric . The LEGFF algorithm achieved the optimal value on metric , reaching 0.6294; our algorithm achieved a value of 0.6290 on metric , ranking second among all the algorithms we used. The values of our proposed algorithm on the other nine metrics are as follows: 0.6276 for , 123.8589 for , 0.8021 for , 0.8796 for , 5.1029 for , 43.0355 for , 0.8181 for , 0.7199 for , and 32.5370 for . These quantitative results are consistent with the conclusions of the qualitative analysis, providing strong evidence of the fusion advantages of our algorithm on the MFFW dataset.
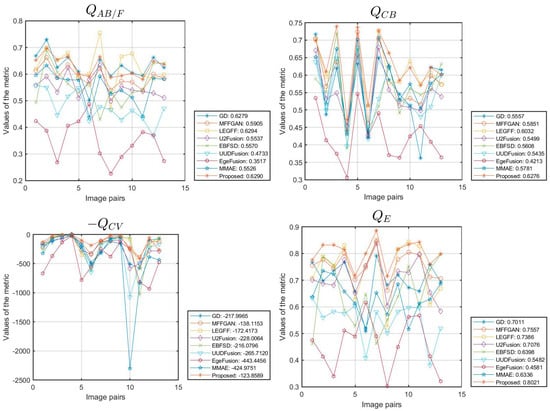
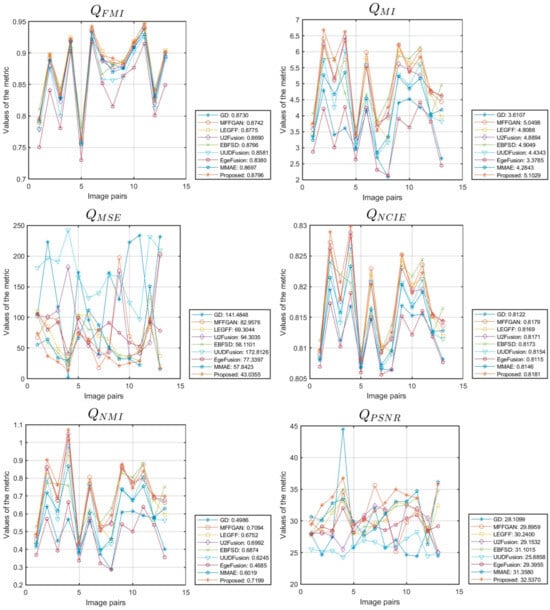
Figure 8.
The line chart illustrates the metrics of various data in the MFFW dataset.

Table 3.
Quantitative average comparative analysis of different methods on the MFFW dataset.
Figure 9 shows the image fusion results with different methods on MFI-WHU-01 data. From the results, we can see that the image fused using the GD algorithm is blurry, and the noise has increased, especially in areas like the wooden door; additionally, the marble region has become darker, resulting in information loss. The fusion image generated by the MFFGAN algorithm results in reduced brightness at the door and window areas, making it darker and unable to accurately capture interior details. The LEGFF algorithm produces a fully focused image, but the brightness in the window and marble areas is reduced, resulting in a darker appearance and causing some information to be lost. The U2Fusion method causes certain areas of the fused image to become darker, resulting in poor fusion quality. The EBFSD algorithm does not produce a fully focused image, and the image is blurry and distorted, leading to a significant loss of information. The UUDFusion algorithm results in a fused image with a yellowish tint, causing severe color distortion. The EgeFusion algorithm enhances and sharpens the details of the fused image, but it also introduces some degree of distortion, making it difficult to observe the true information in the image. The MMAE algorithm generates a fully focused fused image, and while it enhances the image’s texture and details, it also leads to some loss of real information. Through comparison, our algorithm achieves the optimal fusion result, preserving all the information from the two source images in the fused image and achieving the best complementary effect.


Figure 9.
Results of MFI-WHU-01: (a) GD, (b) MFFGAN, (c) LEGFF, (d) U2Fusion, (e) EBFSD, (f) UUDFusion, (g) EgeFusion, (h) MMAE, and (i) Proposed.
Figure 10 presents a line chart displaying the performance metrics obtained from simulation experiments on 30 datasets from the MFI-WHU dataset using various fusion algorithms. The average performance metrics for each algorithm are summarized in both Figure 10 and Table 4. As shown in these figures, our algorithm achieves the best overall performance across 10 evaluation metrics. Their values are 0.7199 for , 0.7875 for , 23.7432 for , 0.8429 for , 0.8772 for , 7.5215 for , 20.5981 for , 0.8350 for , 1.0270 for , and 35.3640 for , respectively. These quantitative results align with the findings of the qualitative analysis, providing robust evidence of the superior fusion capabilities of our algorithm on the MFI-WHU dataset.
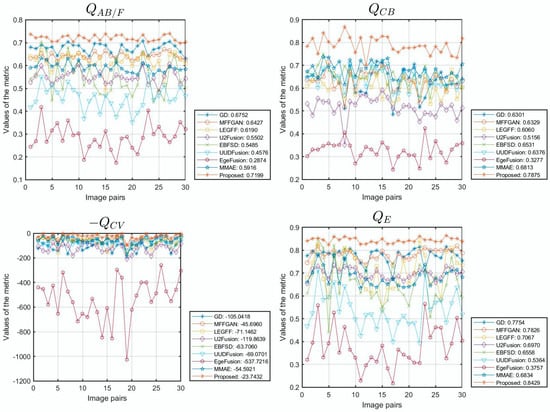
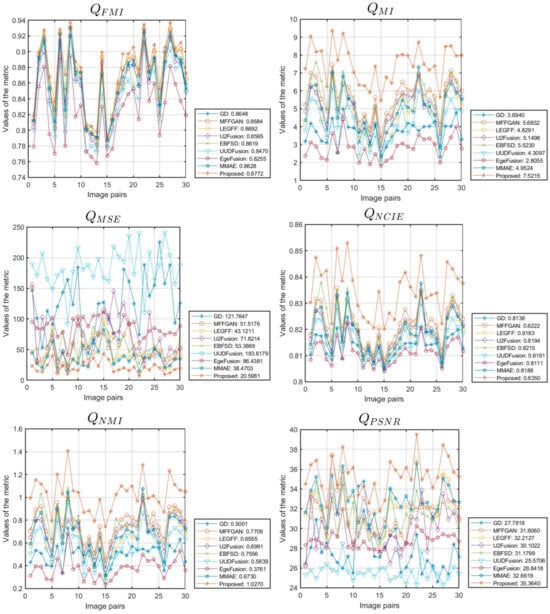
Figure 10.
The line chart illustrates the metrics of various data in the MFI-WHU dataset.

Table 4.
Quantitative average comparative analysis of different methods on the MFI-WHU dataset.
4.3. Application Extension
In this section, we extend the application of the proposed algorithm to the fusion of triple series images within the Lytro dataset [] and multi-exposure image fusion []. The Lytro dataset comprises four groups of triple-series image data. If the data include three images, we need to first fuse two of them and then fuse the resulting image with the third one to obtain the final fused image. The fusion results of our proposed algorithm are illustrated in Figure 11. Specifically, Figure 11a–c represent the input images, while Figure 11d demonstrates the fusion outcome achieved by our algorithm. The results demonstrate that our algorithm is capable of producing fully focused fused images even when multiple source images are input, which further validates the versatility and robustness of our algorithm in the field of multi-focus image fusion.

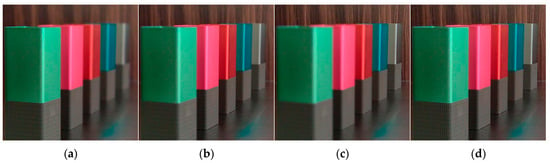
Figure 11.
Triple-series image fusion results: (a) Source A, (b) Source B, (c) Source C, and (d) Proposed.
Multi-exposure image fusion is a sophisticated technique designed to address the limitations of single-exposure imaging, particularly in scenes with high dynamic range (HDR) or complex lighting conditions []. By combining multiple images captured at different exposure levels, this method aims to produce a single, high-quality image that retains optimal detail in both bright and dark regions. The process leverages the strengths of each individual exposure, integrating them to enhance overall image quality, improve detail representation, and achieve a more balanced and visually appealing result. With applications spanning photography and beyond, multi-exposure image fusion has become an essential tool for overcoming the challenges posed by varying illumination and expanding the capabilities of digital imaging systems. We applied the proposed algorithm to the multi-exposure image dataset collected by Zhang [] for simulation validation, and some of the results are shown in Figure 12. Figure 12a,b represent the underexposed and overexposed images, respectively, while Figure 12c illustrates the fusion result obtained by our algorithm. As can be seen from the results, the proposed algorithm demonstrates significant effectiveness in multi-exposure image fusion, producing a more detailed and vivid fused image.

Figure 12.
Multi-exposure image fusion results: (a) under-exposure image, (b) over-exposure image, and (c) proposed.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, a novel multi-focus image fusion algorithm using FD and parameter adaptive unit-linking dual-channel pulse-coupled neural network (PAUDPCNN) in the CVT domain is proposed. The high-frequency sub-bands of decomposition are fused by FD and PAUDPCNN models, along with consistency verification; and the low-frequency sub-bands are fused by the average method. The public Lytro, MFFW, and MFI-WHU datasets are used to test, through subjective and objective evaluation analysis, the experimental results and show that our proposed multi-focus image fusion algorithm has robustness and better fusion performance compared with state-of-the-art algorithms. Additionally, it has a clear advantage in these 10 image fusion indicators: , , , , , , , , , and . The proposed method demonstrates its superiority in preserving the details and textures of the original images while effectively eliminating artifacts and enhancing the overall quality of the fused images. The algorithm’s adaptability to various imaging conditions and its ability to handle images with different focus points make it a promising solution for applications requiring high-resolution and clear images from multiple sources. The algorithm proposed in this paper requires selecting the decomposition level of CVT based on experimental results or prior experience. In future work, we plan to further investigate and optimize this selection process to enhance its adaptability and accuracy. Additionally, we will explore the extended applications of this algorithm in various domains, including change detection [,,] and remote sensing image fusion [], to assess its effectiveness and potential improvements.
Author Contributions
The experimental measurements and data collection were carried out by L.L., S.S., M.L., Z.J. and H.M. The manuscript was written by L.L. with the assistance of S.S., M.L., Z.J. and H.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant No. 2024M752692; the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region under Grant No. 2024D01C240; the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 62261053; the Tianshan Talent Training Project-Xinjiang Science and Technology Innovation Team Program (2023TSYCTD0012).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhai, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Luo, N. MSI-DTrans: A multi-focus image fusion using multilayer semantic interaction and dynamic transformer. Displays 2024, 85, 102837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Peng, H. Multi-focus image fusion with parameter adaptive dual channel dynamic threshold neural P systems. Neural Netw. 2024, 179, 106603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Deng, L.; Vivone, G. A general image fusion framework using multi-task semi-supervised learning. Inf. Fusion 2024, 108, 102414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X. Injected infrared and visible image fusion via L1 decomposition model and guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2022, 8, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, H.; Zhang, J. Multi-focus image fusion based on fractional order differentiation and closed image matting. ISA Trans. 2022, 129, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, H. Medical image fusion and noise suppression with fractional-order total variation and multi-scale decomposition. IET Image Process. 2021, 15, 1688–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, X. Adaptive fractional multi-scale edge-preserving decomposition and saliency detection fusion algorithm. ISA Trans. 2020, 107, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, H.; He, H. Multi-focus image fusion based on fractional-order derivative and intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2020, 21, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Generation and recombination for multifocus image fusion with free number of inputs. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 6009–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shen, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Song, X. EDMF: A new benchmark for multi-focus images with the challenge of exposure difference. Sensors 2024, 24, 7287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteo, C.; Giuseppe, G.; Gemine, V. Hyperspectral pansharpening: Critical review, tools, and future perspectives. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2024. early access. [Google Scholar]
- Vivone, G.; Deng, L. Deep learning in remote sensing image fusion: Methods, protocols, data, and future perspectives. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2024. early access. [Google Scholar]
- Candes, E.; Demanet, L. Fast discrete curvelet transforms. Multiscale Model. Simul. 2006, 5, 861–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, M.N.; Vetterli, M. The contourlet transform: An efficient directional multiresolution image representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2005, 14, 2091–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, A.; Zhou, J.; Do, M. The nonsubsampled contourlet transform: Theory, design, and applications. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 3089–3101. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, K.; Labate, D. Optimally sparse multidimensional representation using shearlets. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 2007, 39, 298–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easley, G.; Labate, D.; Lim, W.Q. Sparse directional image representations using the discrete shearlet transform. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2008, 25, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannoth, S.; Kumar, H.; Raja, K. Low light image enhancement using curvelet transform and iterative back projection. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Si, Y.; Jia, Z. A novel brain image enhancement method based on nonsubsampled contourlet transform. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2018, 28, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Si, Y. Enhancement of hyperspectral remote sensing images based on improved fuzzy contrast in nonsubsampled shearlet transform domain. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 18077–18094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Liu, S. Multiscale reweighted smoothing regularization in curvelet domain for hyperspectral image denoising. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 45, 3937–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Diwakar, M. Total variation-based ultrasound image despeckling using method noise thresholding in non-subsampled contourlet transform. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2023, 33, 1073–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Chen, J.; Tang, P.; Gan, J.; Zhang, H. A multi-scale fusion strategy for side scan sonar image correction to improve low contrast and noise interference. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jin, S.; Bian, G.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, B. A curvelet-transform-based image fusion method incorporating side-scan sonar image features. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Luo, J.; Liu, H.; Zheng, X.; Zan, G. Feature-level image fusion scheme for X-ray multi-contrast imaging. Electronics 2025, 14, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, H.; Jia, Z. Multiscale geometric analysis fusion-based unsupervised change detection in remote sensing images via FLICM model. Entropy 2022, 24, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, H.; Jia, Z.; Si, Y. A novel multiscale transform decomposition based multi-focus image fusion framework. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 12389–12409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Si, Y.; Wang, L.; Jia, Z.; Ma, H. A novel approach for multi-focus image fusion based on SF-PAPCNN and ISML in NSST domain. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 24303–24328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.; Goyal, N. Dual-channel Rybak neural network based medical image fusion. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 181, 112018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lv, M.; Jia, Z.; Ma, H. Sparse representation-based multi-focus image fusion method via local energy in shearlet domain. Sensors 2023, 23, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, A.; Bhuyan, M. A curvelet-based multi-sensor image denoising for KLT-based image fusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 4991–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, X.; Hou, H.; Zhang, X.; Lv, M.; Jia, Z.; Ma, H. Fractal dimension-based multi-focus image fusion via coupled neural P systems in NSCT domain. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Jia, Z. Multi-focus image fusion via PAPCNN and fractal dimension in NSST domain. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Deep learning-based multi-focus image fusion: A survey and a comparative study. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 4819–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Zhao, B. A review on multi-focus image fusion using deep learning. Neurocomputing 2025, 618, 129125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. IFCNN: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Ma, J. Deep learning-based image fusion: A survey. J. Image Graph. 2023, 28, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xu, T.; Wu, X. FusionBooster: A unified image fusion boosting paradigm. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2024. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Yang, B. An infrared and visible image fusion network based on Res2Net and multiscale transformer. Sensors 2025, 25, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Cui, Y.; Tan, T. FusionMamba: Dynamic feature enhancement for multimodal image fusion with Mamba. Vis. Intell. 2024, 2, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Z.J.; Chen, X. VDMUFusion: A versatile diffusion model-based unsupervised framework for image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2025, 34, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Zhai, H.; Hu, H. FusionGCN: Multi-focus image fusion using superpixel features generation GCN and pixel-level feature reconstruction CNN. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 262, 125665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Le, Z. MFF-GAN: An unsupervised generative adversarial network with adaptive and gradient joint constraints for multi-focus image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2021, 66, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihabudeen, H.; Rajeesh, J. An autoencoder deep residual network model for multi focus image fusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 34773–34794. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Fang, L.; Zhao, J. UUD-Fusion: An unsupervised universal image fusion approach via generative diffusion model. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2024, 249, 104218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yan, X.; Xie, W.; Wang, Y. Image fusion method based on snake visual imaging mechanism and PCNN. Sensors 2024, 24, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Liu, X. Medical image fusion with parameter-adaptive pulse coupled neural network in nonsubsampled shearlet transform domain. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinmaya, P.; Ayan, S.; Nihar, K.M. Parameter adaptive unit-linking dual-channel PCNN based infrared and visible image fusion. Neurocomputing 2022, 514, 21–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, R.; Ren, J. Adaptive fractional image enhancement algorithm based on rough set and particle swarm optimization. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, L. Image enhancement based on rough set and fractional order differentiator. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Boutat, D.; Liu, D. Applications of fractional operator in image processing and stability of control systems. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Boutat, D.; Liu, D. Fractional-order complex systems: Advanced control, intelligent estimation and reinforcement learning image-processing algorithms. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X. Supplemental stability criteria with new formulation for linear time-invariant fractional-order systems. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Pedrycz, W.; Yang, S.; Boutat, D. Consensus of T-S fuzzy fractional-order, singular perturbation, multi-agent systems. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. Admissibility and robust stabilization of continuous linear singular fractional order systems with the fractional order α: The 0<α<1 case. ISA Trans. 2018, 82, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, J.; Chai, T. Fault-tolerant prescribed performance control of wheeled mobile robots: A mixed-gain adaption approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2024, 69, 5500–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, K.; Wang, Q. Prescribed performance tracking control of time-delay nonlinear systems with output constraints. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2024, 11, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Qin, Z.; Hong, Y.; Jiang, Z. Distributed optimization of nonlinear multiagent systems: A small-gain approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 67, 676–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Pardis, R.; Ali, A. Multi-focus image fusion using singular value decomposition in DCT domain. In Proceedings of the 10th Iranian Conference on Machine Vision and Image Processing (MVIP), Isfahan, Iran, 22–23 November 2017; pp. 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Nejati, M.; Samavi, S.; Shirani, S. Multi-focus image fusion using dictionary-based sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 25, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wei, X.; Zhang, C. MFFW: A newdataset for multi-focus image fusion. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.04780. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, S.; Sevcenco, I.; Agathoklis, P. Multi-exposure and multi-focus image fusion in gradient domain. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2016, 25, 1650123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiang, W. Local extreme map guided multi-modal brain image fusion. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1055451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Han, D.; Wang, X.; Yi, P.; Yan, L.; Li, X. Multi-sensor medical-image fusion technique based on embedding bilateral filter in least squares and salient detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liu, G.; Qian, Y. EgeFusion: Towards edge gradient enhancement in infrared and visible image fusion with multi-scale transform. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2024, 10, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, L.; Zhao, J.; Pan, Z.; Li, H.; Li, Y. MMAE: A universal image fusion method via mask attention mechanism. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 158, 111041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Yan, J.; Xiao, H. Image fusion algorithm based on spatial frequency-motivated pulse coupled neural networks in nonsubsampled contourlet transform domain. Acta Autom. Sin. 2008, 34, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Blasch, E.; Xue, Z. Objective assessment of multiresolution image fusion algorithms for context enhancement in night vision: A comparative study. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, M.; Razian, M. Fast-FMI: Non-reference image fusion metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE 8th International Conference on Application of Information and Communication Technologies, Astana, Kazakhstan, 15–17 October 2014; pp. 424–426. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ward, R.K.; Chen, X. Multi-focus image fusion with complex sparse representation. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 34744–34755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Ren, X.; Yin, H.; Jiang, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. SFDA-MEF: An unsupervised spacecraft feature deformable alignment network for multi-exposure image fusion. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wu, K.; Zhang, G.; Yan, W.; Wang, X.; Tao, C. MEFSR-GAN: A multi-exposure feedback and super-resolution multitask network via generative adversarial networks. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Benchmarking and comparing multi-exposure image fusion algorithms. Inf. Fusion 2021, 74, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, A.; You, T. A global patch similarity-based graph for unsupervised SAR image change detection. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 15, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Lv, M.; Jia, Z. Synthetic aperture radar image change detection based on principal component analysis and two-level clustering. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, H.; Jia, Z. Change detection from SAR images based on convolutional neural networks guided by saliency enhancement. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cao, Z.; Huang, T.; Deng, L.; Chanussot, J.; Vivone, G. Fully-connected transformer for multi-source image fusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 2071–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).