Abstract
Up to the present date, according to the official reports of the World Health Organization (WHO), 205,338,159 patients have been confirmed with the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and 4,333,094 have died as a consequence of this infectious disorder. The majority of COVID-19 patients will develop hematological, biochemical, immunological, hormonal and other complex alterations of their laboratory data which may be diagnosed using different biomarkers. In this paper, we review the alterations of the hematology, immunology, biochemistry, hormonal and other laboratory panels discovered in the subjects diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 infection, based on the available data in the literature.
Introduction
Up to the present date, according to the official reports of the World Health Organization (WHO), 205,338,159 patients have been confirmed with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and 4,333,094 have died as a consequence of this infectious disorder [1]. Based on the available laboratory data, the patients who experienced severe COVID-19 forms displayed significant elevation in serum pro-inflammatory cytokine levels via the development of a cytokine storm [2,3,4,5]. In elevated concentrations, pro-inflammatory cytokines can cause shock and tissue damage in the liver, heart, and kidneys, as well as multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) and respiratory failure. Even though the majority of COVID-19 patients had mild to moderate symptoms, almost 15% of them may develop severe pneumonia at some point. Out of these, close to 5% might develop acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), MODS, or septic shock [6].
In COVID-19, the clinical evolution may be divided into three separate stages, based on the severity of the disease, namely "the early infection," "the pulmonary phase," and "the hyper-inflammation phase," each of which being marked by distinct biochemical alterations [7]. During the initial stages, SARS-CoV-2 infects the ciliated bronchial epithelial cells as the virus infiltrates the lung parenchyma and interacts with the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, which is present in large amounts on the surface of pneumocytes [8]. Most patients show several non-specific symptoms at this point, such as fever and dry cough, which are associated with an initial inflammatory response triggered by the innate immunity via the involvement of monocytes and macrophages [9]. The pulmonary phase, marked by viral pneumonia and localized inflammation in the lungs, is when the majority of the patients will require hospitalization. The third and the most severe stage of COVID-19 is marked by systemic inflammation, in particular the so-called "cytokine storm", and it can finally lead to MODS and ARDS. At this point, most of the patients should be transferred to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) [3].
The Clinical Blood Sciences Laboratory (CBSL) plays an important role in the monitoring and treatment of COVID-19. CBSL testing should be performed on a regular basis to ensure that the best medical decisions are made. The majority of COVID-19 patients will develop hematological, biochemical, immunological and other complex alterations of their laboratory data which may be diagnosed using different circulating biomarkers, as pointed out in Figure 1 [10].
Figure 1.
COVID-19 is associated with complex laboratory alterations, namely in the hematological, immunological, biochemical, hormonal and other lab panels. Legend: COVID-19, Coronavirus Disease 2019.
Discussion
Hematological findings and inflammation markers in COVID-19
Patients diagnosed with COVID-19 experience complex hematological changes, as well as elevations in inflammation markers, as reported in Figure 2.
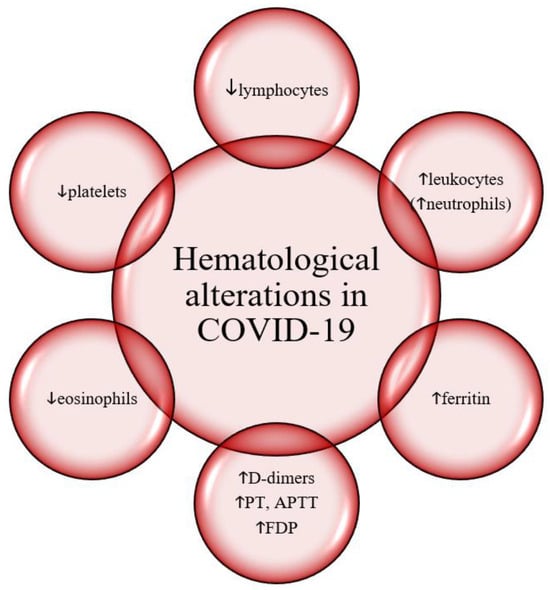
Figure 2.
Hematological alterations in COVID-19. Legend: COVID-19, Coronavirus Disease 2019. PT, prothrombin time. APTT, activated partial thromboplastin time. FDP, fibrin degradation products.
Lymphopenia. A typical observation in patients suffering from COVID-19 is lymphopenia, which indicates a defective immune reaction to the virus [11]. According to a recent meta-analysis, 35% to 75% of the COVID-19 patients experienced lymphopenia which seems a typical finding in the patients admitted to the ICU [12]. The variable frequency of lymphopenia seems to be related to the apparent alterations of the genetics of the virus and the immunological response to SARS-CoV-2, which are changing as the epidemic expands throughout the globe [13]. Lymphopenia is less prevalent in children and it has been reported as low as 3% based on a meta-analysis of the Chinese COVID-19 pediatric cases [14].
Eosinopenia. According to a Chinese study carried out by Zhang et al. (2020) on 140 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, eosinopenia was detected in 52.9% of the cases. The same research confirmed a positive association of eosinophil and lymphocyte counts in the peripheral blood and we may thus hypothesize that these two variables can be employed as markers in the diagnosis of COVID-19 in both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients [15].
Leukocytosis. Leukocytosis has been reported in 11.4% of COVID-19 cases in the settings of bacterial infection or superinfection [11].
Neutrophilia. Neutrophilia can also occur in COVID-19 and it reflects an elevation of cytokines, an exaggerated inflammatory response and/or it can also be a sign of a bacterial illness [4,11]. Neutrophilia seems a more frequent finding in patients admitted to the ICU [16].
Thrombocytopenia. A percentage of 55% of COVID-19 patients displayed thrombocytopenia, which has been linked to a higher risk of hospital death [17]. In particular, 57.7% of the severe and 31.6% of the mild cases were diagnosed with this laboratory abnormality [11]. The evaluation of the number of thrombocytes in conjunction with the degree of hypoxemia are critical examinations in the assessment of severe COVID-19 cases [18].
Hemostasis. Pneumonia, viral sepsis, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and MODS often ensue in individuals with severe COVID-19 [19]. In such instances, the following hemostasis-coagulation abnormalities have been described.
D-dimer levels. Elevated D-dimer levels are a characteristic feature of COVID-19 cases with subsequent coagulopathy [20]. Guan et al. (2020) reported that D-dimer levels in COVID-19 were equal or higher than 0.5 mg/L in 46% of the patients [21]. Huang et al. (2020) also evidenced that in the COVID-19 subjects who were admitted in the ICU, the D-dimer levels were markedly elevated versus non-ICU cases [2]. Similarly, Zhou et al. (2020) estimated that the risk of death increased 18 times when D-dimer levels were >1 mg/L [22].
Prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), and fibrin degradation products (FDP). FDP concentrations were elevated, whereas PT and APTT were prolonged in 138 subjects who died from COVID-19 pneumonia when compared to the counterparts who survived the disease [19]. Similarly, the subjects who died from COVID-19 had significantly lower fibrinogen and antithrombin levels during hospitalization, whereas FDP levels were significantly higher during late hospitalization in all non-survivors. Thus, various pathophysiological mechanisms can be blamed for these laboratory findings: common coagulation activation, dysregulated thrombin generation, impaired natural anticoagulants or hyperfibrinolysis [19]. Moreover, other hematological complications, e.g., acquired coagulopathy, the development of antiphospholipid antibodies and the more frequent occurrence of thrombotic events of both arterial and venous nature, including cerebral infarction, were detected in critically-ill COVID-19 subjects [23].
Serum ferritin. A retrospective study on 191 COVID-19 patients reported a remarkable serum ferritin elevation in non-survivors compared to survivors [23]. In SARS-CoV-2 infected individuals who were hospitalized, an increase in serum ferritin was employed as a predictor of prognosis [17]. C-reactive protein (CRP). A percentage of 93% of COVID-19 subjects displayed increased CRP concentrations, most notably in severe forms of the infection [12].
Procalcitonin. Procalcitonin is a prohormone that regulates calcium homeostasis in the body [24]. Once sepsis in triggered, procalcitonin levels rise, in particular in connection to the development of septic shock and organ failure that require immediate intervention [25]. During the initial examination, most COVID-19 patients display procalcitonin concentrations within the normal limit [19]. However, notably high concentrations of this marker have been linked to a 5-fold increase chance of developing a severe COVID-19 form [2].
Immunological findings in COVID-19
IgA, IgM, IgE and IgD. A study on 87 patients found that IgA against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor-binding domain (RBD) presented the highest diagnostic rate, namely 88.2%, at 4-10 days after the onset of the symptoms, followed by 76.4% for IgM and 64.7% for IgG. In addition, they found that in the severe forms of COVID-19, IgA was significantly higher when compared to mild or moderate cases [26]. IgG and IgM were found to be significantly increased in moderate versus mild cases [26]. Yu et al. (2020) discovered that the first seroconversion for IgA was 2 days and 5 days for IgG and IgM. Moreover, the cumulative seroconversion median was 13 days for IgA and 14 days for IgM and IgG [27]. They reported increased relative levels of IgA and IgG in severe COVID-19 cases, which is a contrasting finding regarding IgG when compared to the study of Ma et al. [27]. Kowitdamrong et al. (2020) revealed that the patients with severe forms presented significantly higher anti-S1 IgA and IgG levels. Males, in particular, displayed a significantly higher SARS-CoV-2 IgG when compared to females [28]. A longitudinal study concluded that IgA response appears early after the onset of the symptoms when compared to IgM, and it also remains persistently higher after 38 days, with a peak at 20-22 days, whereas IgM starts to decline after 18 days with a peak at 10-12 days [29]. A retrospective study revealed that IgA levels were significantly increased versus IgG in severe COVID-19 cases. In addition, they observed elevated anticardiolipin IgA concentrations which could indicate that the antiphospholipid syndrome-linked hypercoagulation state could be mediated by a strong IgA response [30]. Based on the data from 25 patients with severe COVID-19, it was unearthed that subjects who were alive at 28 days post-ICU admission had higher anti-S1 IgA and IgG levels upon admission. Additionally, it was brought to light that serum anti-S1 IgA was a protective factor of day-28 mortality after the adjustment for Sequential Organ Failure Assessment and age [31]. Another study unfolded that IgG, IgM and IgA peaked at 15-21 days after the development of the symptoms and IgG and IgA levels were detected up to 6 months after [32]. Regarding IgD, no paper has evaluated its concentrations in COVID-19.
ANCA. According to a case presentation, a false positive SARS-CoV-2 IgM test was detected in an 82-year-old female later diagnosed with granulomatosis with polyangiitis, positive for anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA). The authors suggested that a cross-reaction may occur in patients with autoimmune diseases [33]. Another case report of a 12-year-old girl reported the onset of ANCA vasculitis after asymptomatic COVID-19 infection. The authors hypothesized that the disease could have been triggered by the SARS-CoV-2 immune response [34]. Another case report of two males with COVID-19 delineated that glomerulonephritis (GN), a common kidney disorder observed in SARS-CoV-2 infection, was due to the development of ANCA associated autoimmune disease [35]. Another case presentation of a 25-year-old male diagnosed with COVID-19, with no history of autoimmune disease, outlined the development of ANCA-associated with GN [36]. A study on 33 patients with pneumonia induced by COVID-19 found no reactivity for ANCA [37]. Contrastingly, another research on 29 severe COVID-19 cases revealed that 6.9% of the cases were positive for p-ANCA and 2.9% for c-ANCA [38]. In addition, based on the data from 40 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Sacchi et al. (2021) announced a prevalence of 25% positivity for ANCA in their study group [39].
ANA. Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) were identified in 35.6% of the 45 patients admitted to the hospital with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in the study by Gazzaruso et al. (2020), suggesting an involvement of autoimmunity in SARS-CoV-2 infection [40]. In the case of an 18-year-old SARS-CoV-2 infected girl, the development of ARDS coincided with the onset of systemic lupus erythematosus and ANA positivity [41]. A clinical study on 33 patients out of whom 31 with interstitial pneumonia induced by COVID-19 found that 33% of the patients were tested positive for ANA [37]. A study with severe and critical cases of COVID-19 on 21 patients found that 50% of them were tested positive for ANA [42]. According to a study on 40 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 out of whom 57.5% tested positive for ANA, ANA positivity was correlated with hospitalization in the ICU [39]. Another research delineated a positive correlation between ANA levels and cardiovascular symptoms/disease in moderate and severe COVID-19 patients [43]. Out of the 9 children with COVID-19 who presented pernio-like cutaneous manifestations, 3 of them were tested positive for ANA [44]. A prospective study found that ANA detection was associated with the occurrence of severe complications and necessity for ICU admission in COVID-19 cases [45].
ENA. Voljdani and Kharrazian (2020) communicated a positivity for Extractable Nuclear Antigens (ENA) in 3 out of the 5 samples analyzed, suggesting that cross-reactivity between SARS-CoV-2 proteins and human tissues might exist and might induce autoimmune phenomena in COVID-19 [46]. Similarly, a 19-year-old female with COVID-19 who developed severe thrombocytopenia was also tested positive for ENA [47]. In a pediatric COVID-19 cohort with pernio-like cutaneous manifestations, ENA-positivity was detected in one patient who was later diagnosed with connective tissue damage [44]. A prospective study found that half of the COVID-19 patients who developed ARDS were positive for ENA [45].
β2-microglobulin. In the case of a 60-year-old patient with COVID-19 who developed steroid-responsive encephalitis, increased β2-microglobulin (b2M) concentrations were found in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) at the time of presentation with akinetic mutism [48]. A case series of 6 patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 and neurological symptoms demonstrated elevated b2M concentrations in the serum and the CSF of the subjects [49]. A cohort of 34 COVID-19 subjects discovered a linear trend between b2M levels and disease severity, suggesting that higher b2M in the serum could be an early predictor of COVID-19 outcomes [50].
β2-glycoprotein 1 (b2GP1) and cardiolipin. A small number of subjects of the 92 COVID-19 cases assessed displayed positivity for b2GP1, i.e., one in the early infection and one in the late infection group, respectively [51]. Karahan et al. (2020) communicated no significant differences in the positivity for anti-b2GP1 IgG, IgM and IgA between patients with/without COVID-19 [52]. A single-center study on 74 critically-ill patients discovered that 12% of the individuals had elevated anticardiolipin/anti-b2GP1 levels [53]. Devreese et al. (2020) also announced a low positivity for anticardiolipin/anti-b2GP1, namely 3 out of the 31 critically-ill COVID-19 patients evaluated [54]. Contrastingly, a research paper on 29 severe COVID-19 cases disclosed that 34% and 24.1% of the individuals were tested positive for anti-b2GP1 and anticardiolipin antibodies, respectively [38]. A multi-center study on 122 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection depicted a prevalence of 13.4% and 2.7% for IgG and IgM anticardiolipin antibodies, and of 6.3% and 7.1% IgG and IgM antibodies for anti-b2GP1, respectively, however no association between thrombotic events and the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies was proven [55]. In a cohort of 122 patients, Borghi et al. (2020) depicted a prevalence of 15.6%, 6.6% and 9%, respectively, for IgG, IgA and IgM anti-b2GP1, and of 15.7% and 6.6% for IgG and IgM anticardiolipin antibodies. Similarly, no association was communicated between the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies and the occurrence of thrombotic events [56]. In critical COVID-19 patients, Xiao et al. (2021) concluded that the prevalence of IgA and IgG anti-b2GP1 was 28.8% and 18.2%, whereas that for IgA anticardiolipin antibodies was 25.8% [57]. In 172 patients hospitalized for COVID-19, there was a prevalence of 2.9%, 5.2% and 4.1% for IgG, IgM and IgA anti-b2GP1. In addition, the prevalence of IgG, IgM and IgA anticardiolipin antibodies was 4.7%, 23% and 3.5% [58]. In the peripheral blood of 276 COVID-19 patients, increased levels of c3, c4 and c5 were detected. When stratified by symptom severity, the individuals with mild and moderate symptoms had increased c3 and c4 levels [59].
Complement. Tammaro et al. (2021) reported that a 15-year-old male with COVID-19 and cutaneous acral lesions displayed c4d depositions at an endothelial level [60]. The analysis of clotted plasma adsorber from COVID-19 patients found that c3 was the main component with a sequence coverage of 53% [61]. The same study found depositions of c3 cleavage products, e.g., c3c and c3d in renal arteries and glomerular capillaries. The majority of c5b-9 was found in the peritubular capillaries, renal arterioles, and tubular basement membrane [61]. The assessment of granulocytes and monocytes in COVID-19 patients detected elevated cr3 (Complement Receptor 3) levels in patients with respiratory failure, with cr3 being suggested as a potential biomarker for disease severity [62]. A prospective longitudinal study with 197 COVID-19 subjects detected higher c3a, c3c and TCC concentrations versus healthy controls. Moreover, c3a and TCC levels were elevated in ICU versus non-ICU admitted individuals [63]. C3a and TCC were elevated in subjects who developed thromboembolic events. Persistent C3a levels were recorded in COVID-19 who succumbed to the infection [63]. Other researchers depicted elevated Complement Factor H, I and c5 levels in the sera of COVID-19 patients [64]. Increased levels of sc5b-9, c5a, c3bc, c3bBbP and c4d, consistent with an activation of the whole complement system, were found in 39 COVID-19 subjects. Increased concentrations of complement system markers were seen in patients with respiratory failure. Sc5B-9 and c4d were significantly associated with markers of inflammation, namely ferritin and CRP [65]. In a 61-year-old female with COVID-19 and punctiform purpura on the legs, the cutaneous biopsy displayed fibrin-hematic thrombi with c3 deposition in the wall of the superficial dermal capillary plexus [66].
dsDNA antibodies and CPP. In 29 severe COVID-19 subjects, no reactivity for dsDNA antibodies was detected. Only one individual was positive for CCP [38]. However, dsDNA titers were positive in an 18-year-old female infected with SARS-CoV-2 and a new onset of lupus was tested [41].
Hormonal changes in COVID-19
The thyroid: T3, T4 and TSH. When compared to healthy counterparts, 19.56% of the COVID-19 patients had lower TSH and T3 levels, with lower concentrations of these hormones being associated with severe forms of the infection [67]. Similarly, decreased TSH and T3 concentrations were recorded in patients who succumbed to COVID-19 versus those who recovered after the infection [68]. Brancatella et al. (2020) presented the case of an 18-year-old female who was diagnosed with COVID-19 and had T3, T4 and thyroglobulin antibody levels above the upper normal limit and very low TSH levels. Thus, the diagnosis of subacute thyroiditis was also established [69]. Gao et al. (2020) depicted that severe/critical COVID-19 cases displayed lower concentrations of TSH and T3 when compared to non-severe patients. Moreover, reduced T3 levels were associated with and were said to be predictors of all-cause mortality in the aforementioned group [70]. A single center study on 287 patients hospitalized for COVID-19 delineated that 20.2% of the patients had low TSH levels and were diagnosed with thyrotoxicosis, which was also linked with increased IL-6 levels [71]. Of 191 COVID-19 patients, the thyroid function was abnormal in 13.1% of the cases and 7.3% were diagnosed with thyrotoxicosis. T3 displayed a decreasing trend based on disease severity [72]. Zhang et al. (2021) found that SARS-CoV-2-positive individuals who were diagnosed with thyroid dysfunction (TD) had increased values for CPR, PCT, LDH, creatinine, AST and APTT when compared to patients without TD. TD patients were more likely to become critically-ill and experienced an elevated mortality rate [73]. Another study on 334 patients with COVID-19 discovered no cases of thyrotoxicosis, namely 86.6% of the subjects displayed normal thyroid function, whereas lower levels of TSH were reported in the subgroup admitted to the ICU [74]. Güven and Gültekin (2021) found no difference in the TSH levels of mild and critical COVID-19 pneumonia patients. However, critically-ill individuals had significantly lower levels of T3 and T4, with T3 levels being negatively associated with CRP values [75]. Malik et al. (2021) communicated that 75% of the patients with COVID-19 pneumonia had TD and that significantly lower levels of TSH and T3 were measured in the severe forms of the infection. The thyroid function returned to normal after recovery in non-critical subjects [76]. In 84 COVID-19 hospitalized patients versus healthy subjects, decreased levels of T3 and TSH were registered. A percentage of 61.9% of the COVID-19 subjects had TD which was also linked with elevated CRP values [77]. Sen et al. (2020) evaluated 60 COVID-19 cases and diagnosed 35% of them with TD, but concluded that there was no association between the thyroid function and the disease severity [78].
The adrenals: aldosterone, cortisol and epinephrine. A retrospective study demonstrated that critically-ill COVID-19 patients had decreased cortisol levels when compared to non-COVID-19 critically-ill patients, with six out of nine COVID-19 patients having very low concentrations of cortisol and meeting the criteria for the diagnosis of critical illness-related corticosteroid insufficiency (CIRCI). These differences occurred despite the use of antifungals and glucocorticoids [79]. Alzahrani et al. (2021) recorded a positive correlation between higher disease severity and low cortisol levels [80]. Tan et al. (2020) found that COVID-19 patients had an increased cortisol stress response and that elevated cortisol levels were linked to a decreased probability of survival [81]. On admission, cortisol concentrations and the Anxiety and Depression Scale scores were significantly higher in patients who succumbed to COVID-19 [82]. Rieder et al. (2020) found no difference in serum aldosterone levels on admission in COVID-19 cases versus controls [83]. Contrastingly, Villard et al. (2020) recorded elevated aldosterone levels upon admission in COVID-19 cases who developed severe forms of the infection versus mild/moderate forms [84].
The Hypophysis: ACTH, GH, LH, FSH and prolactin. COVID-19 subjects displayed higher levels of prolactin and ACTH when compared to healthy controls. Critical cases, however, registered decreased ACTH levels versus non-critical ones, whereas no difference was observed in GH, FSH, LH, or TSH concentrations [85]. In females hospitalized for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Ding et al. (2021) observed increased levels of prolactin on admission versus healthy controls, yet LH or FSH concentrations were similar [86]. Male subjects with COVID-19 and non-COVID respiratory infections registered increased LH and prolactin levels versus healthy controls [87]. Okçelik et al. (2021) reported no differences in LH and FSH between SARS-CoV-2-positive and negative patients [88]. Increased LH levels were also detected in male COVID-19 subjects who required ICU admission and succumbed to the disease [89]. Ma et al. (2020) detected elevated LH levels in COVID-19 versus healthy subjects, but FSH levels were similar [90]. Li et al. (2020) found significant decreased concentrations of the growth hormone in non-severe COVID patients versus healthy counterparts [91].
Biochemical findings in COVID-19
Liver involvement in COVID-19
COVID-19 patients and, in particular, those who experienced severe forms of the illness were reported to have had underlying chronic liver disease as well as advanced hepatic dysfunction. According to the literature, 12% of the COVID-19 patients had pre-existing liver illness, and 14-53% of them had increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) values. Liver dysfunction was more pronounced in severe COVID-19 cases, with liver enzymes peaking at 1,445 U/L and 7,590 U/L, respectively. Moreover, 1.8% of the hospitalized individuals exhibited elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels. However, liver dysfunction might have arisen either from the infection and/or it might have been drug-induced [92,93,94]. In severe cases, liver damage can also be caused by the inflammatory cytokine storm [95]. In the individuals diagnosed with COVID-19, alterations in liver enzymes, e.g., AST and ALT, albumin and bilirubin can occur. Although ACE2 receptors are expressed by hepatocytes and bile duct epithelial cells, no substantial changes in the histopathological features of cells have been detected in COVID-19 [3,96]. An elevation in ALT and AST signals the destruction of hepatocytes. Considering that bilirubin, prothrombin and fibrinogen are produced by the liver, their alterations, together with D-dimer levels and the platelet count are indicators of the disease severity [10]. Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) is a biomarker for the detection of cholangiocyte damage. In some COVID-19 subjects, GGT values were elevated, probably because ACE2 receptors are also expressed on cholangiocytes. This indicates that SARS-CoV-2 might be able to bind them directly and cause their destruction [96]. COVID-19-induced liver failure might also be the result of subsequent direct hepatocyte destruction produced by hepatotoxic medications, systemic inflammatory response, respiratory distress syndrome-induced hypoxia or MODS [97]. Severity and poor outcomes were linked to elevated levels of liver dysfunction markers [11]. The SARS-CoV-2 virus itself might be a direct cause of hepatocyte destruction. About 2% to 10% of the individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 exhibited diarrhea, with viral ARN being detected in their blood and stool samples [98]. More research is needed to clarify whether COVID-19 exacerbates cholestasis in individuals with primary sclerosing cholangitis and primary biliary cholangitis [99]. Hepatic impairment is more likely generated by the cytokine storm rather than by the direct cytotoxic effects of SARS-CoV-2, but further research is needed to establish the precise pattern and the severity of liver injury in affected individuals [100]. Acute liver injury in COVID-19 patients has also been documented and linked to a greater death rate. ACE2 receptors are expressed in higher amounts by type 2 alveolar cells and are thought to be the site of viral entrance, but they are also present on the endothelium of blood vessels, the lining of the gastrointestinal tract and on cholangiocytes [100].
Kidney involvement in COVID-19
The human kidney is a vulnerable and potential target for the infection with SARS-CoV-2. Severe disturbances in renal function are regarded as key complications of COVID-19 and a substantial risk factor of elevated mortality. Several studies have investigated the correlation between impaired kidney function and death in hospitalized COVID-19 patients [2,101,102].
In COVID-19 subjects suffering from pre-existing renal disorders, elevated serum creatinine, tubular damage, endothelial dysfunction and microcirculatory alterations might occur due to the presence of viral-induced circulating mediators interacting with kidney cells. As ACE2 receptors are also found on the surface of tubular cells, SARS-CoV-2 might be able to infect them directly [103]. The presence of ACE2 receptors has been reported on glomerular epithelial and parietal cells, distal tubular cells, smooth muscle cells and the endothelium of kidney interlobular arteries [104].
Acute kidney injury (AKI) was previously thought to be less common in people infected with COVID-19 (3-9%), however it has emerged as one of the fatal consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection [105,106]. AKI is characterized by a fast decline in the renal excretory function, as well as an accumulation of nitrogen metabolism products, e.g., urea and other clinically undetectable waste products. Serum Cystatin-C detection may be beneficial in estimating the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), particularly in detecting minor changes, and therefore in the early diagnosis of renal failure in a range of renal illnesses for which the early treatment is vital [107]. In the critical care context, cystatin C has been employed to investigate the renal function and it has been found to be associated with mortality. Higher Cystatin-C levels have been shown to be independent predictors of death in COVID-19 and markers of poor prognosis [106].
Urea. The estimation of the blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level is an important diagnostic marker for the progression of kidney damage. The elevation of urea in the serum helps evaluate the Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) [108]. According to the results of the prospective study based on Cheng et al. (2020)’s COVID-19 cohort (N=701 subjects) from Wuhan, China, with typical clinical features of SARS-CoV-2 infection, a high prevalence of kidney dysfunction in hospitalized patients was detected, with more than 40% of the patients displaying typical signs of renal dysfunction with elevated blood urea nitrogen values in 13.1% of the cases. The presence of kidney injury was associated with a higher percentage of in-hospital mortality and it is considered a high-risk factor for regression [101]. Liu et al. (2020) conducted another study on 12,413 patients with COVID-19 out of whom 764 (6.29%) demonstrated remarkable elevations of blood urea nitrogen on admission [109]. The metabolic pathway involved in the elevation of BUN following the infection with SARS-CoV-2 has not been clearly understood. The ACE2 receptor is also present on the epithelial cells located in the kidney, thus the virus can interact directly with its renal receptor to decrease the expression of ACE2, leading to the irregular activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) that significantly increases the absorption of water and the resorption of urea by renal tubules, resulting in increased BUN concentrations [110,111,112]. Moreover, BUN elevation can also signal inflammation, catabolism, hypovolemia-induced renal hypoperfusion, sepsis or decreased cardiac performance, all of which have been associated with adverse outcomes in COVID-19 [109,112,113,114].
Creatinine. Chu et al. (2020) conducted a Kaplan-Meier analysis on hospitalized COVID-19 individuals and revealed that the death rate was significantly higher when kidney dysfunction was present, especially manifested by elevated baseline serum creatinine. During hospitalization, patients with higher serum creatinine levels were more likely to develop AKI (11.9%) versus subjects with normal baseline values (4%). The mortality rate was significantly higher in the individuals with elevated (33.7%) versus normal baseline serum creatinine (13.2%). Thus, it is necessary to understand the relationship between elevated serum creatinine and AKI in hospitalized COVID-19 subjects [115]. Liu et al. (2020) evaluated 12,413 COVID-19 subjects and reported that the frequency of elevated serum creatinine on admission was 5.22%. High serum creatinine and elevated BUN are viewed as risk factors for mortality in COVID-19 individuals who require hospitalization. On the contrary, COVID-19 survivors showed minimum variations in the standard ranges of BUN and serum creatinine [109].
Portolés et al. (2020) conducted the first large prospective cohort study in Europe in a tertiary hospital to evaluate the burden of kidney dysfunction during the outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 infection. On admission, 21% of the patients showed an elevated level of serum creatinine, out of whom 43.5% had been previously diagnosed with chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage 3 or higher. Subjects with normal serum creatinine who developed AKI during hospitalization represented 11.4% of the study group. Elevated mortality during hospitalization was noted in individuals with elevated serum creatinine (32.4%) and in those previously diagnosed with CKD (41.1%). The mortality rate was lower in patients with AKI on hospital admission (15.9%) and even lower in individuals with normal serum creatinine (5.8%). Thus, based on their results, CKD and elevated serum creatinine on admission were correlated with a greater risk of hospital death [116]. Cheng et al. (2020) also reported that the presence of kidney diseases was associated with greater in-hospital mortality [101].
Uric Acid. Uric acid is considered an important kidney function marker. Under normal conditions, uric acid reabsorption and excretion by renal tubules are maintained in a controlled state [117]. Liu et al. (2020) conducted a study on 12,413 COVID-19 cases out of whom 1,422 (11.66%) had decreased uric acid levels on admission. The study reported for the first time that uric acid was significantly lower in COVID-19 subjects with more severe symptoms and was associated with a higher risk of death [109]. This alteration might result from an abnormal rise in uric acid excretion due to renal dysfunction via inflammation or hypoxemia or due to an intensive uricolysis resulting from enteric dysbiosis [117]. In COVID-19, lower uric acid levels have also been correlated with the development of a cytokine storm [109,118,119].
β2-microglobulin (β2M) and β-trace protein (TP) are some of the new glomerular filtration markers whose levels seems to be linked more to the outcomes of COVID-19 versus creatinine. Unfortunately, the lack of thoroughly developed GFR estimation algorithms for these new biomarkers limits their comparisons to cystatin C and creatinine [120]. Patients with increased urinary β2M and α1-microglobulin (α1MG) levels were less likely to be discharged from the hospital versus individuals with values within the normal limits [121].
Cardiac involvement in COVID-19
Subjects with risk factors for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD) and those with long-lasting coronary artery disease are more likely to develop infections and acute coronary syndromes during the influenza season [122,123,124]. Heart failure, acute myocardial infarction (AMI), impaired renal function (which leads to troponin accumulation), myocarditis, cardiac arrest, arrhythmias, sepsis, septic shock, and pulmonary embolism can also be associated with COVID-19 [9]. Furthermore, SARS-CoV-2 infected patients with pre-existing CVD were more likely to succumb to the infection [125].
Myocardial injury is indicated by elevated cardiac troponin levels. When compared to patients with no cardiac damage, Shi et al. discovered that a higher proportion of CVD subjects with COVID-19 required non-invasive or invasive mechanical breathing. Based on the particular SARS-CoV-2 affinity for the host ACE2 receptors, direct viral infection of the vascular epithelium and heart tissue can occur [126]. As a result, regardless of the pre-existing or newly diagnosed CVD, certain individuals with COVID-19 are more likely to develop myocarditis [127,128]. Guo et al. (2020) discovered that cardiac troponin concentrations are substantially connected to C-reactive protein (CRP) and B-type natriuretic peptide values, connecting myocardial injury to inflammation intensity during hospitalization in patients with a deteriorating clinical course leading to death [129]. Increased cardiac troponin and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)/NT-proBNP levels have been linked to a poor prognosis and a greater risk of death [22,125,127,130,131,132]. Elevated leukocyte counts, creatinine phosphokinase (CPK), CRP and procalcitonin levels have been associated with myocardial injury [10]. Although the exact underlying processes are unknown, some of the several hypotheses proposed are: cardiac stress caused by respiratory failure and hypoxia, direct SARS-CoV2 infection of myocardial cells (via the ACE2 receptor) and indirect alterations induced by the systemic inflammatory response [9]. Thus, the evaluation of the heart damage biomarkers on hospital admission and their continuous monitoring during hospital stay may emerge as a useful technique in the early diagnosis of heart damage in COVID-19 patients [130].
Dyselectrolytemia in COVID-19
Lippi et al. (2020) performed a pooled analysis and confirmed that COVID-19 severity is associated with lower calcium, potassium and sodium serum concentrations. They concluded that the electrolyte levels should be monitored during hospitalization to provide timely and effective interventions [133]. Regarding the chloride levels, Lippi et al. (2020) reported that there were no statistical differences between COVID-19 individuals with severe and non-severe forms [133]. Regarding the phosphorus levels, Zazzo et al. (2020) indicated that the rate of hypophosphatemia in critically-ill COVID-19 cases reached 44.8% [134]. Hypophosphatemia is also considered an independent risk factor for mortality in critically-ill patients [135].
Potassium. Potassium levels were significantly decreased in COVID-19 patients (up to 62%) [133,136]. It is known that hypokalemia aggravates ARDS and acute cardiac injury, a common complication of COVID-19, in particular in individuals suffering from lung or heart diseases. The mechanism of hypokalemia in COVID-19 patients could be attributed to the binding of SARS-CoV-2 to the ACE2 receptors which leads to a reduction in ACE2 expression. Subsequently, there is an elevation of angiotensin II levels and aldosterone secretion leading to an increase in potassium kidney excretion [133,136,137]. Another contributor to electrolyte imbalance and hypokalemia in COVID-19 is the gastrointestinal loss as many individuals present to the hospital with diarrhea and/or nausea in 34.0% and 3.9% of the cases, respectively [136,138]
Sodium (mmol/L). Hyponatremia was reported in patients with severe COVID-19 and up to 12% of the COVID-19 individuals exhibited decreased sodium levels [115,133,139]. In COVID-19, IL-6 might be responsible for electrolyte imbalances by promoting the vasopressin non-osmotic release. IL-6 and Na levels are reversely correlated and associated with the PaO2/FiO2 ratio. This ratio and sodium levels were significantly diminished in COVID-19 subjects, whereas IL-6 concentrations were elevated [140]. Hyponatremia was viewed as a risk factor for severe forms of COVID-19 and sodium concentrations were lower in patients who developed pneumonia versus those who did not [141,142,143].
Muscle involvement in COVID-19
COVID-19 patients usually have higher levels of muscle injury biomarkers, e.g. myoglobin and creatine kinase. These alterations might arise from the direct influence of SARS-CoV-2 which may enter myocytes due to their expression of ACE2 receptors [94].
Vitamin D: 25(OH)D
Vitamin D deficiency/insufficiency is a threat to global public health and it affects primarily inpatients and nursing home residents who are more susceptible to develop COVID-19 [2,22,144]. The S1 domain of the spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 has recently been discovered to interact with the human dipeptidyl peptidase-4 receptor (DPP-4/CD26), suggesting that it might be a critical virulence component in COVID-19 [145]. DPP-4/CD26 receptor expression has been shown to be considerably decreased in vivo when vitamin D insufficiency has been corrected, therefore indicating a reason for vitamin D supplementation in COVID-19 patients [146,147].
Figure 3 depicts the main biochemical alterations in COVID-19.
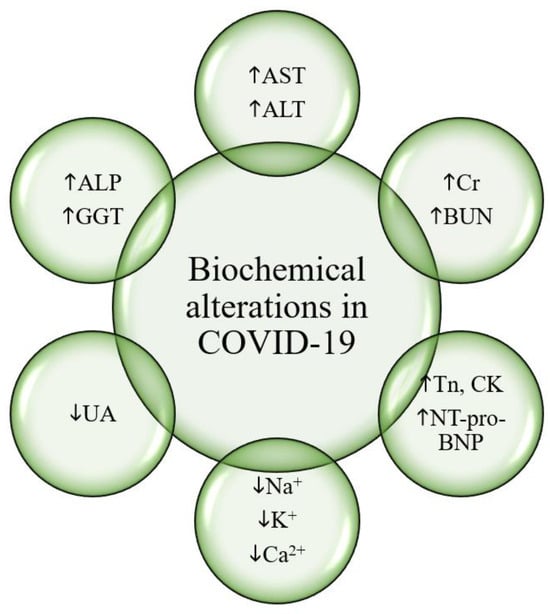
Figure 3.
Biochemical alterations in COVID-19. Legend: COVID-19, Coronavirus Disease 2019. AST, aspartate aminotransferase. ALT, alanine aminotransferase. ALP, alkaline phosphatase. GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase. UA, uric acid. Na+, sodium. K+, potassium. Ca2+, calcium. Tn, troponins. CK, creatine kinase. NT-proBNP, N-terminal (NT)-pro hormone BNP. Cr, creatinine. BUN, blood urea nitrogen.
Overall, the main lab panel changes in COVID-19 are depicted in Figure 4.
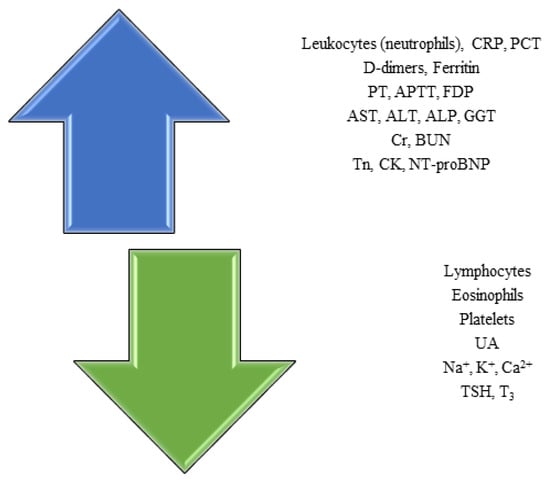
Figure 4.
The main changes in lab panels identified in COVID-19. Legend: COVID-19, Coronavirus Disease 2019. PT, prothrombin time. APTT, activated partial thromboplastin time. FDP, fibrin degradation products. AST, aspartate aminotransferase. ALT, alanine aminotransferase. ALP, alkaline phosphatase. GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase. UA, uric acid. Na+, sodium. K+, potassium. Ca2+, calcium. Tn, troponins. CK, creatine kinase. NT-proBNP, N-terminal (NT)-pro hormone BNP. Cr, creatinine. BUN, blood urea nitrogen. PCT, procalcitonin. TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone. T3, triiodothyronine.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we have briefly summarized the main laboratory features of COVID-19 based on the current available evidence. Future and preferably prospective studies conducted on large cohorts of subjects diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 infection are needed to clarify and confirm the alterations in the hematological, immunological, biochemical, hormonal and other lab panels discovered in this infectious disease.
COVID-19 remains a multifaceted disease, with atypical presentations depending on the age of the patient and the different viral variants circulating in nature, whereas its evolution might sometimes be marked by the development of cardiovascular and/or neurological complications to name a few, and thromboembolism at different sites in the body in particular [148,149,150,151,152]. Moreover, seeking additional risk factors for thrombosis, e.g., active solid or blood cancers, the history of thrombotic complications or use of drugs which favor the development of such complications, in addition to applying prediction scores dedicated to COVID-19, is of paramount importance in the management of the individuals diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 infection [153,154,155]. The investigation of the best available therapy to treat COVID-19, including the evaluation of the potential benefits of natural products, in addition to mass vaccination, are current strategies to counteract and manage the management of this infection [156,157]. In addition, the pandemic has forced us to revisit relatively neglected topics in the near past, such as the mental health of both healthcare workers and patients alike which should be evaluated periodically to reduce the risk of burnout, as well as the future of online versus on-site medical education [158,159].
Conflict of interest disclosure
There are no known conflicts of interest in the publication of this article. The manuscript was read and approved by all authors.
Compliance with ethical standards
Any aspect of the work covered in this manuscript has been conducted with the ethical approval of all relevant bodies and that such approvals are acknowledged within the manuscript.
References
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Yu, T.; Xia, J.; Wei, Y.; Wu, W.; Xie, X.; Yin, W.; Li, H.; Liu, M.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, H.; Guo, L.; Xie, J.; Wang, G.; Jiang, R.; Gao, Z.; Jin, Q.; Wang, J.; Cao, B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; Tai, Y.; Bai, C.; Gao, T.; Song, J.; Xia, P.; Dong, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, F.S. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Zhou, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Tao, Y.; Xie, C.; Ma, K.; Shang, K.; Wang, W.; Tian, D.S. Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020, 71, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, R.; Deng, X.; Li, F.; Liang, K.; Shi, Y. Immunopathological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 cases in Guangzhou, China. Immunology. 2020, 160, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X. COVID-19: immunopathology and its implications for therapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020, 20, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, H.K.; Mehra, M.R. COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: A clinical-therapeutic staging proposal. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020, 39, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cao, Q.; Qin, L.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Pan, A.; Dai, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, F.; Qu, J.; Yan, F. Clinical characteristics and imaging manifestations of the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19):A multi-center study in Wenzhou city, Zhejiang, China. J Infect. 2020, 80, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmerov, A.; Marbán, E. COVID-19 and the Heart. Circ Res. 2020, 126, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Shea, P.M.; Lee, G.R.; Griffin, T.P.; Tormey, V.; Hayat, A.; Costelloe, S.J.; Griffin, D.G.; Srinivasan, S.; O'Kane, M.; Burke, C.M.; Faul, J.; Thompson, C.J.; Curley, G.; Tormey, W.P. COVID-19 in adults: test menu for hospital blood science laboratories. Ir J Med Sci. 2020, 189, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Plebani, M. The critical role of laboratory medicine during coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and other viral outbreaks. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020, 58, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Plebani, M. Laboratory abnormalities in patients with COVID-2019 infection. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020, 58, 1131–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornelas-Ricardo, D.; Jaloma-Cruz, A.R. Coronavirus Disease 2019: Hematological Anomalies and Antithrombotic Therapy. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2020, 251, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, B.M.; Lippi, G.; Plebani, M. Laboratory abnormalities in children with novel coronavirus disease 2019. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020, 58, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Dong, X.; Cao, Y.Y.; Yuan, Y.D.; Yang, Y.B.; Yan, Y.Q.; Akdis, C.A.; Gao, Y.D. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy. 2020, 75, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.E.; Chong, V.C.L.; Chan, S.S.W.; Lim, G.H.; Lim, K.G.E.; Tan, G.B.; Mucheli, S.S.; Kuperan, P.; Ong, K.H. Hematologic parameters in patients with COVID-19 infection. Am J Hematol. 2020, 95, E131–E134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.M.; de Oliveira, M.H.S.; Benoit, S.; Plebani, M.; Lippi, G. Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020, 58, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Xin, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X.; Mao, Y.; Hu, L.; Liu, D.; Chang, B.; Chang, W.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Prognostic factors for severe acute respiratory syndrome: a clinical analysis of 165 cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2004, 38, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; Thachil, J.; Iba, T.; Levy, J.H. Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e438–e440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; Du, B.; Li, L.J.; Zeng, G.; Yuen, K.Y.; Chen, R.C.; Tang, C.L.; Wang, T.; Chen, P.Y.; Xiang, J.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Liang, Z.J.; Peng, Y.X.; Wei, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Peng, P.; Wang, J.M.; Liu, J.Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, G.; Zheng, Z.J.; Qiu, S.Q.; Luo, J.; Ye, C.J.; Zhu, S.Y.; Zhong, N.S. China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; Guan, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Tu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Cao, B. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, S.; Xia, P.; Cao, W.; Jiang, W.; Chen, H.; Ding, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X.; Tian, R.; Wu, W.; Wu, D.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xie, J.; Yan, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Du, B.; Qin, Y.; Gao, P.; Qin, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. Coagulopathy and Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020, 382, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frater, J.L.; Zini, G.; d'Onofrio, G.; Rogers, H.J. COVID-19 and the clinical hematology laboratory. Int J Lab Hematol. 2020, 42 (Suppl. 1), 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Plebani, M. Procalcitonin in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 2020, 505, 190–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zeng, W.; He, H.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, P.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Jin, T. Serum IgA, IgM, and IgG responses in COVID-19. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020, 17, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.Q.; Sun, B.Q.; Fang, Z.F.; Zhao, J.C.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, Y.M.; Sun, X.Z.; Liang, H.F.; Zhong, B.; Huang, Z.F.; Zheng, P.Y.; Tian, L.F.; Qu, H.Q.; Liu, D.C.; Wang, E.Y.; Xiao, X.J.; Li, S.Y.; Ye, F.; Guan, L.; Hu, D.S.; Hakonarson, H.; Liu, Z.G.; Zhong, N.S. Distinct features of SARS-CoV-2-specific IgA response in COVID-19 patients. Eur Respir J. 2020, 56, 2001526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowitdamrong, E.; Puthanakit, T.; Jantarabenjakul, W.; Prompetchara, E.; Suchartlikitwong, P.; Putcharoen, O.; Hirankarn, N. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with differing severities of coronavirus disease 2019. PLoS One. 2020, 15, e0240502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoan, A.; Sciacovelli, L.; Basso, D.; Negrini, D.; Zuin, S.; Cosma, C.; Faggian, D.; Matricardi, P.; Plebani, M. IgA-Ab response to spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19: A longitudinal study. Clin Chim Acta. 2020, 507, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan Ali, O.; Bomze, D.; Risch, L.; Brugger, S.D.; Paprotny, M.; Weber, M.; Thiel, S.; Kern, L.; Albrich, W.C.; Kohler, P.; Kahlert, C.R.; Vernazza, P.; Bühler, P.K.; Schüpbach, R.A.; Gómez-Mejia, A.; Popa, A.M.; Bergthaler, A.; Penninger, J.M.; Flatz, L. Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) is Associated With Elevated Serum Immunoglobulin (Ig) A and Antiphospholipid IgA Antibodies. Clin Infect Dis. 2021, 73, e2869–e2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourati, S.; Hue, S.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Mekontso-Dessap, A.; de Prost, N. SARS-CoV-2 viral loads and serum IgA/IgG immune responses in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1781–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo-Campos, P.; Blankenhaus, B.; Mota, C.; Gomes, A.; Serrano, M.; Ariotti, S.; Costa, C.; Nunes-Cabaço, H.; Mendes, A.M.; Gaspar, P.; Pereira-Santos, M.C.; Rodrigues, F.; Condeço, J.; Escoval, M.A.; Santos, M.; Ramirez, M.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Simas, J.P.; Vasconcelos, E.; Afonso, Â.; Veldhoen, M. Seroprevalence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in COVID-19 patients and healthy volunteers up to 6 months post disease onset. Eur J Immunol. 2020, 50, 2025–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Han, X.; Jiang, N.; Cao, Y.; Alwalid, O.; Gu, J.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, C. Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020, 20, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, W.T.; Campbell, J.A.; Ross, F.; Peña Jiménez, P.; Rudzinski, E.R.; Dickerson, J.A. Acute ANCA Vasculitis and Asymptomatic COVID-19. Pediatrics. 2021, 147, e2020033092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, N.N.; Kello, N.; Shah, H.H.; Khanin, Y.; De Oleo, I.R.; Epstein, E.; Sharma, P.; Larsen, C.P.; Bijol, V.; Jhaveri, K.D. De Novo ANCA-Associated Vasculitis With Glomerulonephritis in COVID-19. Kidney Int Rep. 2020, 5, 2079–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeinzadeh, F.; Dezfouli, M.; Naimi, A.; Shahidi, S.; Moradi, H. Newly Diagnosed Glomerulonephritis During COVID-19 Infection Undergoing Immunosuppression Therapy, a Case Report. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2020, 14, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Pascolini, S.; Vannini, A.; Deleonardi, G.; Ciordinik, M.; Sensoli, A.; Carletti, I.; Veronesi, L.; Ricci, C.; Pronesti, A.; Mazzanti, L.; Grondona, A.; Silvestri, T.; Zanuso, S.; Mazzolini, M.; Lalanne, C.; Quarneti, C.; Fusconi, M.; Giostra, F.; Granito, A.; Muratori, L.; Lenzi, M.; Muratori, P. COVID-19 and Immunological Dysregulation: Can Autoantibodies be Useful? Clin Transl Sci. 2021, 14, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.G.; Magira, E.; Alexopoulos, H.; Jahaj, E.; Theophilopoulou, K.; Kotanidou, A.; Tzioufas, A.G. Autoantibodies related to systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases in severely ill patients with COVID-19. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020, 79, 1661–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, M.C.; Tamiazzo, S.; Stobbione, P.; Agatea, L.; De Gaspari, P.; Stecca, A.; Lauritano, E.C.; Roveta, A.; Tozzoli, R.; Guaschino, R.; Bonometti, R. SARS-CoV-2 infection as a trigger of autoimmune response. Clin Transl Sci. 2021, 14, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaruso, C.; Carlo Stella, N.; Mariani, G.; Nai, C.; Coppola, A.; Naldani, D.; Gallotti, P. High prevalence of antinuclear antibodies and lupus anticoagulant in patients hospitalized for SARS-CoV2 pneumonia. Clin Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2095–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani Cardoso, E.; Hundal, J.; Feterman, D.; Magaldi, J. Concomitant new diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus and COVID-19 with possible antiphospholipid syndrome. Just a coincidence? A case report and review of intertwining pathophysiology. Clin Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2811–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Han, T.; Chen, J.; Hou, C.; Hua, L.; He, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Q.; Zuo, X.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Cao, Q.; Jia, E. Clinical and Autoimmune Characteristics of Severe and Critical Cases of COVID-19. Clin Transl Sci. 2020, 13, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagova, O.; Varionchik, N.; Zaidenov, V.; Savina, P.; Sarkisova, N. Anti-heart antibodies levels and their correlation with clinical symptoms and outcomes in patients with confirmed or suspected diagnosis COVID-19. Eur J Immunol. 2021, 51, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallizzi, R.; Sutera, D.; Spagnolo, A.; Bagnato, A.M.; Cannavò, S.P.; Grasso, L.; Guarneri, C.; Nunnari, G.; Mazza, F.; Pajno, G.B. Management of pernio-like cutaneous manifestations in children during the outbreak of COVID-19. Dermatol Ther. 2020, 33, e14312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagiannis, D.; Steinestel, J.; Hackenbroch, C.; Schreiner, B.; Hannemann, M.; Bloch, W.; Umathum, V.G.; Gebauer, N.; Rother, C.; Stahl, M.; Witte, H.M.; Steinestel, K. Clinical, Serological, and Histopathological Similarities Between Severe COVID-19 and Acute Exacerbation of Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD). Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 587517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojdani, A.; Kharrazian, D. Potential antigenic cross-reactivity between SARS-CoV-2 and human tissue with a possible link to an increase in autoimmune diseases. Clin Immunol. 2020, 217, 108480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaro, E.; Novara, E.; Bonometti, R.; Sacchi, M.C.; Stobbione, P.; Lauritano, E.C.; Boverio, R. Isolated immune thrombocytopenic purpura in a young adult Covid-19 patient. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020, 24, 10850–10852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotto, A.; Odolini, S.; Masciocchi, S.; Comelli, A.; Volonghi, I.; Gazzina, S.; Nocivelli, S.; Pezzini, A.; Focà, E.; Caruso, A.; Leonardi, M.; Pasolini, M.P.; Gasparotti, R.; Castelli, F.; Ashton, N.J.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Padovani, A. Steroid-Responsive Encephalitis in Coronavirus Disease 2019. Ann Neurol. 2020, 88, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edén, A.; Kanberg, N.; Gostner, J.; Fuchs, D.; Hagberg, L.; Andersson, L.M.; Lindh, M.; Price, R.W.; Zetterberg, H.; Gisslén, M. CSF Biomarkers in Patients With COVID-19 and Neurologic Symptoms: A Case Series. Neurology. 2021, 96, e294–e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conca, W.; Alabdely, M.; Albaiz, F.; Foster, M.W.; Alamri, M.; Alkaff, M.; Al-Mohanna, F.; Nagelkerke, N.; Almaghrabi, R.S. Serum β2-microglobulin levels in Coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19): Another prognosticator of disease severity? PLoS One. 2021, 16, e0247758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, A.; Fortunati, V.; Cherubini, F.; Bernardini, S.; Nuccetelli, M. Anti-phospholipids antibodies and immune complexes in COVID-19 patients: a putative role in disease course for anti-annexin-V antibodies. Clin Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 2939–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, S.; Erol, K.; Yuksel, R.C.; et al. Antiphospholipid antibodies in COVID-19-associated pneumonia patients in intensive care unit. Mod Rheumatol. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siguret, V.; Voicu, S.; Neuwirth, M.; Delrue, M.; Gayat, E.; Stépanian, A.; Mégarbane, B. Are antiphospholipid antibodies associated with thrombotic complications in critically ill COVID-19 patients? Thromb Res. 2020, 195, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devreese, K.M.J.; Linskens, E.A.; Benoit, D.; Peperstraete, H. Antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with COVID-19: A relevant observation? J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 2191–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatto, M.; Perricone, C.; Tonello, M.; Bistoni, O.; Cattelan, A.M.; Bursi, R.; Cafaro, G.; De Robertis, E.; Mencacci, A.; Bozza, S.; Vianello, A.; Iaccarino, L.; Gerli, R.; Doria, A.; Bartoloni, E. Frequency and clinical correlates of antiphospholipid antibodies arising in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: findings from a multicentre study on 122 cases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 754–759. [Google Scholar]
- Borghi, M.O.; Beltagy, A.; Garrafa, E.; Curreli, D.; Cecchini, G.; Bodio, C.; Grossi, C.; Blengino, S.; Tincani, A.; Franceschini, F.; Andreoli, L.; Lazzaroni, M.G.; Piantoni, S.; Masneri, S.; Crisafulli, F.; Brugnoni, D.; Muiesan, M.L.; Salvetti, M.; Parati, G.; Torresani, E.; Mahler, M.; Heilbron, F.; Pregnolato, F.; Pengo, M.; Tedesco, F.; Pozzi, N.; Meroni, P.L. Anti-Phospholipid Antibodies in COVID-19 Are Different From Those Detectable in the Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 584241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Estes, S.K.; Ali, R.A.; Gandhi, A.A.; Yalavarthi, S.; Shi, H.; Sule, G.; Gockman, K.; Madison, J.A.; Zuo, M.; Yadav, V.; Wang, J.; Woodard, W.; Lezak, S.P.; Lugogo, N.L.; Smith, S.A.; Morrissey, J.H.; Kanthi, Y.; Knight, J.S. Prothrombotic autoantibodies in serum from patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Sci Transl Med. 2020, 12, eabd3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qin, X.; Xia, P.; Cao, W.; Jiang, W.; Chen, H.; Ding, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X.; Tian, R.; Wu, W.; Wu, D.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xie, J.; Yan, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Du, B.; Qin, Y.; Gao, P.; Lu, M.; Hou, X.; Wu, X.; Zhu, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Jiménez, A.; Sánchez-Alonso, S.; Alcaraz-Serna, A.; Esparcia, L.; López-Sanz, C.; Sampedro-Núñez, M.; Mateu-Albero, T.; Sánchez-Cerrillo, I.; Martínez-Fleta, P.; Gabrie, L.; Del Campo Guerola, L.; Rodríguez-Frade, J.M.; Casasnovas, J.M.; Reyburn, H.T.; Valés-Gómez, M.; López-Trascasa, M.; Martín-Gayo, E.; Calzada, M.J.; Castañeda, S.; de la Fuente, H.; González-Álvaro, I.; Sánchez-Madrid, F.; Muñoz-Calleja, C.; Alfranca, A. Deregulated cellular circuits driving immunoglobulins and complement consumption associate with the severity of COVID-19 patients. Eur J Immunol. 2021, 51, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammaro, A.; Adebanjo, G.A.R.; Del Nonno, F.; Pezzuto, A.; Ramirez-Estrada, S.; Parisella, F.R.; Rello, J.; Scarabello, A. Cutaneous Endothelial Dysfunction and Complement Deposition in COVID-19. Am J Dermatopathol. 2021, 43, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, F.; Vonbrunn, E.; Ries, T.; Jäck, H.M.; Überla, K.; Lochnit, G.; Sheriff, A.; Herrmann, M.; Büttner-Herold, M.; Amann, K.; Daniel, C. Complement Activation in Kidneys of Patients With COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2021, 11, 594849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Gant, V.A.; Williams, B.; Enver, T. Increased Complement Receptor-3 levels in monocytes and granulocytes distinguish COVID-19 patients with pneumonia from those with mild symptoms. Int J Infect Dis. 2020, 99, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Nooijer, A.H.; Grondman, I.; Janssen, N.A.F.; Netea, M.G.; Willems, L.; van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Toonen, E.J.M.; Joosten, L.A.B. RCI-COVID-19 study group. Complement Activation in the Disease Course of Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Its Effects on Clinical Outcomes. J Infect Dis. 2021, 223, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Alessandro, A.; Thomas, T.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Hill, R.C.; Francis, R.O.; Hudson, K.E.; Zimring, J.C.; Hod, E.A.; Spitalnik, S.L.; Hansen, K.C. Serum Proteomics in COVID-19 Patients: Altered Coagulation and Complement Status as a Function of IL-6 Level. J Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 4417–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holter, J.C.; Pischke, S.E.; de Boer, E.; Lind, A.; Jenum, S.; Holten, A.R.; Tonby, K.; Barratt-Due, A.; Sokolova, M.; Schjalm, C.; Chaban, V.; Kolderup, A.; Tran, T.; Tollefsrud Gjølberg, T.; Skeie, L.G.; Hesstvedt, L.; Ormåsen, V.; Fevang, B.; Austad, C.; Müller, K.E.; Fladeby, C.; Holberg-Petersen, M.; Halvorsen, B.; Müller, F.; Aukrust, P.; Dudman, S.; Ueland, T.; Andersen, J.T.; Lund-Johansen, F.; Heggelund, L.; Dyrhol-Riise, A.M.; Mollnes, T.E. Systemic complement activation is associated with respiratory failure in COVID-19 hospitalized patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020, 117, 25018–25025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea Polak, A.; Romero Madrid, B.; García Ocaña, P.P.; Lomeña Alvarez, G.; Martínez Pilar, L.; Gómez-Moyano, E. Complement-mediated thrombogenic vasculopathy in COVID-19. Int J Dermatol. 2021, 60, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, W.; Xu, W. Thyroid Function Analysis in 50 Patients with COVID-19: A Retrospective Study. Thyroid. 2021, 31, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wu, D.; Chen, H.; Yan, W.; Yang, D.; Chen, G.; Ma, K.; Xu, D.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Guo, W.; Chen, J.; Ding, C.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Han, M.; Li, S.; Luo, X.; Zhao, J.; Ning, Q. Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study. BMJ. 2020, 368, m1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancatella, A.; Ricci, D.; Viola, N.; Sgrò, D.; Santini, F.; Latrofa, F. Subacute Thyroiditis After Sars-COV-2 Infection. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020, 105, dgaa276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Guo, W.; Guo, Y.; Shi, M.; Dong, G.; Wang, G.; Ge, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, X. Thyroid hormone concentrations in severely or critically ill patients with COVID-19. J Endocrinol Invest. 2021, 44, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lania, A.; Sandri, M.T.; Cellini, M.; Mirani, M.; Lavezzi, E.; Mazziotti, G. Thyrotoxicosis in patients with COVID-19: the THYRCOV study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020, 183, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, D.T.W.; Lee, C.H.; Chow, W.S.; Lee, A.C.H.; Tam, A.R.; Fong, C.H.Y.; Law, C.Y.; Leung, E.K.H.; To, K.K.W.; Tan, K.C.B.; Woo, Y.C.; Lam, C.W.; Hung, I.F.N.; Lam, K.S.L. Thyroid Dysfunction in Relation to Immune Profile, Disease Status, and Outcome in 191 Patients with COVID-19. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021, 106, e926–e935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, F.; Tu, W.; Zhang, J.; Choudhry, A.A.; Ahmed, O.; Cheng, J.; Cui, Y.; Liu, B.; Dai, M.; Chen, L.; Han, D.; Fan, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Shen, M.; Pan, P. Thyroid dysfunction may be associated with poor outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021, 521, 111097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, B.; Tan, T.; Clarke, S.A.; Mills, E.G.; Patel, B.; Modi, M.; Phylactou, M.; Eng, P.C.; Thurston, L.; Alexander, E.C.; Meeran, K.; Comninos, A.N.; Abbara, A.; Dhillo, W.S. Thyroid Function Before, During, and After COVID-19. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021, 106, e803–e811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güven, M.; Gültekin, H. The prognostic impact of thyroid disorders on the clinical severity of COVID-19: Results of single-centre pandemic hospital. Int J Clin Pract. 2021, 75, e14129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, J.; Malik, A.; Javaid, M.; Zahid, T.; Ishaq, U.; Shoaib, M. Thyroid function analysis in COVID-19: A retrospective study from a single center. PLoS One. 2021, 16, e0249421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Su, X.; Ding, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhou, W.; Su, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, H.; Xu, K.; Ni, Q.; Xu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Teng, L. Thyroid Function Abnormalities in COVID-19 Patients. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021, 11, 623792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, K.; Sinha, A.; Sen, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Alam, M.S. Thyroid Function Test in COVID-19 Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2020, 24, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Xu, B.; Guan, W.; Xu, D.; Li, F.; Ren, R.; Zhu, X.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, L. The Adrenal Cortex, an Underestimated Site of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021, 11, 593179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.S.; Mukhtar, N.; Aljomaiah, A.; Aljamei, H.; Bakhsh, A.; Alsudani, N.; Elsayed, T.; Alrashidi, N.; Fadel, R.; Alqahtani, E.; Raef, H.; Butt, M.I.; Sulaiman, O. The Impact of COVID-19 Viral Infection on the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. Endocr Pract. 2021, 27, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Khoo, B.; Mills, E.G.; Phylactou, M.; Patel, B.; Eng, P.C.; Thurston, L.; Muzi, B.; Meeran, K.; Prevost, A.T.; Comninos, A.N.; Abbara, A.; Dhillo, W.S. Association between high serum total cortisol concentrations and mortality from COVID-19. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 659–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Simani, L.; Karimialavijeh, E.; Rezaei, O.; Hajiesmaeili, M.; Pakdaman, H. The Role of Anxiety and Cortisol in Outcomes of Patients With Covid-19. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2020, 11, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, M.; Wirth, L.; Pollmeier, L.; Jeserich, M.; Goller, I.; Baldus, N.; Schmid, B.; Busch, H.J.; Hofmann, M.; Kern, W.; Bode, C.; Duerschmied, D.; Lother, A. Serum ACE2, Angiotensin II, and Aldosterone Levels Are Unchanged in Patients With COVID-19. Am J Hypertens. 2021, 34, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villard, O.; Morquin, D.; Molinari, N.; Raingeard, I.; Nagot, N.; Cristol, J.P.; Jung, B.; Roubille, C.; Foulongne, V.; Fesler, P.; Lamure, S.; Taourel, P.; Konate, A.; Maria, A.T.J.; Makinson, A.; Bertchansky, I.; Larcher, R.; Klouche, K.; Le Moing, V.; Renard, E.; Guilpain, P. The Plasmatic Aldosterone and C-Reactive Protein Levels, and the Severity of Covid-19: The Dyhor-19 Study. J Clin Med. 2020, 9, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.T.; Zhou, F.; Xie, W.Q.; Wang, S.; Yao, H.; Liu, Y.T.; Gao, L.; Wu, Z.B. A potential impact of SARS-CoV-2 on pituitary glands and pituitary neuroendocrine tumors. Endocrine. 2021, 72, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Cui, P.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, S.; Yuan, S.; Ma, W.; Zhang, M.; Rong, Y.; Chang, J.; Miao, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, S. Analysis of Ovarian Injury Associated With COVID-19 Disease in Reproductive-Aged Women in Wuhan, China: An Observational Study. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021, 8, 635255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadihasanoglu, M.; Aktas, S.; Yardimci, E.; Aral, H.; Kadioglu, A. SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Affects Male Reproductive Hormone Levels: A Prospective, Cohort Study. J Sex Med. 2021, 18, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okçelik, S. COVID-19 pneumonia causes lower testosterone levels. Andrologia. 2021, 53, e13909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastrelli, G.; Di Stasi, V.; Inglese, F.; Beccaria, M.; Garuti, M.; Di Costanzo, D.; Spreafico, F.; Greco, G.F.; Cervi, G.; Pecoriello, A.; Magini, A.; Todisco, T.; Cipriani, S.; Maseroli, E.; Corona, G.; Salonia, A.; Lenzi, A.; Maggi, M.; De Donno, G.; Vignozzi, L. Low testosterone levels predict clinical adverse outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia patients. Andrology. 2021, 9, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xie, W.; Li, D.; Shi, L.; Ye, G.; Mao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, H.; Zheng, F.; Chen, Z.; Qin, J.; Lyu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M. Evaluation of sex-related hormones and semen characteristics in reproductive-aged male COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol. 2021, 93, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wei, W. Characteristics of laboratory indexes in COVID-19 patients with non-severe symptoms in Hefei City, China: diagnostic value in organ injuries. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020, 39, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, F.S. Liver injury in COVID-19: management and challenges. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020, 5, 428–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, A.; Karslioglu, B. Did Covid-19 pandemic narrow the spectrum of surgical indications? J Clin Invest Surg. 2021, 6, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Yang, J.; Tian, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, J. Clinical Features of COVID-19-Related Liver Functional Abnormality. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, S.A.; Schattenberg, J.M. Liver injury in COVID-19: The current evidence. United European Gastroenterol J. 2020, 8, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Lu, Z.; Ke, A.; et al. Specific ACE2 expression in cholangiocytes may cause liver damage after 2019-nCoV infection [Internet]. bioRxiv. 2020. Available online: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.03.9 31766v1 (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- Feng, G.; Zheng, K.I.; Yan, Q.Q.; Rios, R.S.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Poucke, S.V.; Liu, W.Y.; Zheng, M.H. COVID-19 and Liver Dysfunction: Current Insights and Emergent Therapeutic Strategies. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2020, 8, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, C.; Kaushal, S.; Yeo, D. Enteric involvement of coronaviruses: is faecal-oral transmission of SARS-CoV-2 possible? Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020, 5, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Clinical insights for hepatology and liver transplant providers during the covid-19 pandemic [Internet]. 2020. Available online: www.aasld.org (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- Jothimani, D.; Venugopal, R.; Abedin, M.F.; Kaliamoorthy, I.; Rela, M. COVID-19 and the liver. J Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Ge, S.; Xu, G. Kidney disease is associated with in-hospital death of patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, B.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Yuan, Z.; Hou, X.; Ren, L.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y. Human kidney is a target for novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. Nat Commun. 2021, 12, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joannidis, M.; Forni, L.G.; Klein, S.J.; Honore, P.M.; Kashani, K.; Ostermann, M.; Prowle, J.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Cantaluppi, V.; Darmon, M.; Ding, X.; Fuhrmann, V.; Hoste, E.; Husain-Syed, F.; Lubnow, M.; Maggiorini, M.; Meersch, M.; Murray, P.T.; Ricci, Z.; Singbartl, K.; Staudinger, T.; Welte, T.; Ronco, C.; Kellum, J.A. Lung-kidney interactions in critically ill patients: consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 21 Workgroup. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 654–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharpour, M.; Zare, E.; Mubarak, M.; Alirezaei, A. COVID-19 and Kidney Disease: Update on Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, Pathophysiology and Management. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2020, 30, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleebrahim-Dehkordi, E.; Reyhanian, A.; Saberianpour, S.; Hasanpour-Dehkordi, A. Acute kidney injury in COVID-19; a review on current knowledge. J Nephropathol. 2020, 9, e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, I.; Patella, G.; Michael, A.; Serra, R.; Provenzano, M.; Andreucci, M. COVID-19 and the Kidney: From Epidemiology to Clinical Practice. J Clin Med. 2020, 9, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, E.; Botey, A.; Alvarez, L.; Poch, E.; Quintó, L.; Saurina, A.; Vera, M.; Piera, C.; Darnell, A. Serum cystatin C as a new marker for noninvasive estimation of glomerular filtration rate and as a marker for early renal impairment. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000, 36, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisha, R.; Srinivasa Kannan, S.R.; Thanga Mariappan, K.; Jagatha, P. Biochemical evaluation of creatinine and urea in patients with renal failure undergoing hemodialysis. J Clin Path Lab Med. 2017, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.M.; Xie, J.; Chen, M.M.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, F.; Qin, J.J.; Lei, F.; Chen, Z.; Lin, L.; Yang, C.; Mao, W.; Chen, G.; Lu, H.; Xia, X.; Wang, D.; Liao, X.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, B.H.; Yuan, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; She, Z.G.; Li, H. Kidney Function Indicators Predict Adverse Outcomes of COVID-19. Med (N Y). 2021, 2, 38–48.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, M. Acute Kidney Injury in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Direct Effect of Virus on Kidney Proximal Tubule Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21, 3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, B.; Doinița, O.I.; Balalau, C.; Scaunasu, V.; et al. Fibroscopic examination on ENT patients in COVID-19 era. J Clin Invest Surg. 2020, 5, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, E. Blood urea nitrogen beyond estimation of renal function. Crit Care Med. 2011, 39, 405–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, C.; Reis, T.; Husain-Syed, F. Management of acute kidney injury in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Respir Med. 2020, 8, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thum, T. SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 expression in the human heart: cause of a post-pandemic wave of heart failure? Eur Heart J. 2020, 41, 1807–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.H.; Tsang, W.K.; Tang, C.S.; Lam, M.F.; Lai, F.M.; To, K.F.; Fung, K.S.; Tang, H.L.; Yan, W.W.; Chan, H.W.; Lai, T.S.; Tong, K.L.; Lai, K.N. Acute renal impairment in coronavirus-associated severe acute respiratory syndrome. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portolés, J.; Marques, M.; López-Sánchez, P.; de Valdenebro, M.; Muñez, E.; Serrano, M.L.; Malo, R.; García, E.; Cuervas, V. Chronic kidney disease and acute kidney injury in the COVID-19 Spanish outbreak. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020, 35, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, J.; Oppedisano, F.; Gratteri, S.; Muscoli, C.; Mollace, V. Regulation of uric acid metabolism and excretion. Int J Cardiol. 2016, 213, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werion, A.; Belkhir, L.; Perrot, M.; Schmit, G.; Aydin, S.; Chen, Z.; Penaloza, A.; De Greef, J.; Yildiz, H.; Pothen, L.; Yombi, J.C.; Dewulf, J.; Scohy, A.; Gérard, L.; Wittebole, X.; Laterre, P.F.; Miller, S.E.; Devuyst, O.; Jadoul, M.; Morelle, J. Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc (CUSL) COVID-19 Research Group. SARS-CoV-2 causes a specific dysfunction of the kidney proximal tubule. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, V.C.; Huang, J.W.; Hsueh, P.R.; Yang, Y.F.; Tsai, H.B.; Kan, W.C.; Chang, H.W.; Wu, K.D. SARS Research Group of National Taiwan University College of Medicine and National Taiwan University Hospital. Renal hypouricemia is an ominous sign in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005, 45, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inker, L.A.; Tighiouart, H.; Coresh, J.; Foster, M.C.; Anderson, A.H.; Beck, G.J.; Contreras, G.; Greene, T.; Karger, A.B.; Kusek, J.W.; Lash, J.; Lewis, J.; Schelling, J.R.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Sondheimer, J.; Shafi, T.; Levey, A.S. GFR Estimation Using β-Trace Protein and β2-Microglobulin in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.Q.; Wang, T.Y.; Zheng, K.I.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Chen, Y.P.; Zheng, M.H. Subclinical Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nephron. 2020, 144, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeeth, L.; Thomas, S.L.; Hall, A.J.; Hubbard, R.; Farrington, P.; Vallance, P. Risk of myocardial infarction and stroke after acute infection or vaccination. N Engl J Med. 2004, 351, 2611–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, J.C.; Schwartz, K.L.; Campitelli, M.A.; Chung, H.; Crowcroft, N.S.; Karnauchow, T.; Katz, K.; Ko, D.T.; McGeer, A.J.; McNally, D.; Richardson, D.C.; Rosella, L.C.; Simor, A.; Smieja, M.; Zahariadis, G.; Gubbay, J.B. Acute Myocardial Infarction after Laboratory-Confirmed Influenza Infection. N Engl J Med. 2018, 378, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.L.; Yang, W.; Ito, K.; Matte, T.D.; Shaman, J.; Kinney, P.L. Seasonal Influenza Infections and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality. JAMA Cardiol. 2016, 1, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Q.; Yang, K.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L.; Song, J. Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheblawi, M.; Wang, K.; Viveiros, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Zhong, J.C.; Turner, A.J.; Raizada, M.K.; Grant, M.B.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the Discovery of ACE2. Circ Res. 2020, 126, 1456–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Qin, M.; Shen, B.; Cai, Y.; Liu, T.; Yang, F.; Gong, W.; Liu, X.; Liang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, H.; Yang, B.; Huang, C. Association of Cardiac Injury With Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inciardi, R.M.; Lupi, L.; Zaccone, G.; Italia, L.; Raffo, M.; Tomasoni, D.; Cani, D.S.; Cerini, M.; Farina, D.; Gavazzi, E.; Maroldi, R.; Adamo, M.; Ammirati, E.; Sinagra, G.; Lombardi, C.M.; Metra, M. Cardiac Involvement in a Patient With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Fan, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; He, T.; Wang, H.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z. Cardiovascular Implications of Fatal Outcomes of Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Lavie, C.J.; Sanchis-Gomar, F. Cardiac troponin I in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Evidence from a meta-analysis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020, 63, 390–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, Z. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arentz, M.; Yim, E.; Klaff, L.; Lokhandwala, S.; Riedo, F.X.; Chong, M.; Lee, M. Characteristics and Outcomes of 21 Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 in Washington State. JAMA. 2020, 323, 1612–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; South, A.M.; Henry, B.M. Electrolyte imbalances in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Ann Clin Biochem. 2020, 57, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazzo, J.F.; Troché, G.; Ruel, P.; Maintenant, J. High incidence of hypophosphatemia in surgical intensive care patients: efficacy of phosphorus therapy on myocardial function. Intensive Care Med. 1995, 21, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, D.G.; Lindner, G.; Wolzt, M.; Ahmad, S.S.; Sauter, T.; Leichtle, A.B.; Fiedler, G.M.; Fuhrmann, V.; Exadaktylos, A.K. Hyperphosphatemia Is an Independent Risk Factor for Mortality in Critically Ill Patients: Results from a Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0133426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hu, C.; Su, F.; Dai, J. Hypokalemia and clinical implications in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). MedRxiv. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, F.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Feng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Peng, L.; Chen, L.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, D.; Tan, S.; Yin, L.; Xu, J.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, C.; Liu, L. Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury. Sci China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Mu, M.; Yang, P.; Sun, Y.; Wang, R.; Yan, J.; Li, P.; Hu, B.; Wang, J.; Hu, C.; Jin, Y.; Niu, X.; Ping, R.; Du, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, G.; Hu, Q.; Tu, L. Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients With Digestive Symptoms in Hubei, China: A Descriptive, Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, I.; Sawlani, V.; Geberhiwot, T. Prolonged confusional state as first manifestation of COVID-19. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020, 7, 1450–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni, A.; Malandrino, D.; Parenti, G.; Maggi, M.; Poggesi, L.; Peri, A. Hyponatremia, IL-6, and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection: may all fit together? J Endocrinol Invest. 2020, 43, 1137–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, A.; Dullaart, R.P.F.; Bakker, S.J.L. Is low sodium intake a risk factor for severe and fatal COVID-19 infection? Eur J Intern Med. 2020, 75, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, A.; Dullaart, R.F.; Bakker, S.L. Sodium status and kidney involvement during COVID-19 infection. Virus Res 2020, 286, 198034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, H.; Hu, J.; Lian, J.; Gu, J.; Zhang, S.; Ye, C.; Lu, Y.; Jin, C.; Yu, G.; Jia, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, J.; Li, L.; Yang, Y. Epidemiological, clinical characteristics of cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection with abnormal imaging findings. Int J Infect Dis. 2020, 94, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, T.P.; Wall, D.; Blake, L.; Griffin, D.G.; Robinson, S.M.; Bell, M.; Mulkerrin, E.C.; O'Shea, P.M. Vitamin D Status of Adults in the Community, in Outpatient Clinics, in Hospital, and in Nursing Homes in the West of Ireland. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020, 75, 2418–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vankadari, N.; Wilce, J.A. Emerging WuHan (COVID-19) coronavirus: glycan shield and structure prediction of spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komolmit, P.; Charoensuk, K.; Thanapirom, K.; Suksawatamnuay, S.; Thaimai, P.; Chirathaworn, C.; Poovorawan, Y. Correction of vitamin D deficiency facilitated suppression of IP-10 and DPP IV levels in patients with chronic hepatitis C: A randomised double-blinded, placebo-control trial. PLoS One. 2017, 12, e0174608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, D.M.; Byrne, D.G. Optimisation of Vitamin D Status for Enhanced Immuno-protection Against Covid-19. Ir Med J. 2020, 113, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Dara, N.; Hosseini, A.; Sayyari, A.; et al. Gastrointestinal Manifestations and Dynamics of Liver Enzymes in Children and Adolescents with COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Iran J Pediatr. 2020, 30, e106935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifonova, K.Z.; Slaveykov, K.S.; Dochev, I.S.; Parusheva, P.O.; Pekova, L.M. COVID-19 presenting with central retinal vein occlusion: a case report. Arch Balk Med Union. 2021, 56, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, C. Thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19. Arch Balk Med Union. 2021, 56, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vural, A.; Kahraman Ahmet, N. D-dimer levels and acute pulmonary embolism development in COVID-19 patients. J Mind Med Sci. 2021, 8, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, C. Cardiovascular complications of COVID-19. Arch Balk Med Union. 2021, 56, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Kuderer, N.M.; Hsu, C.Y.; Shyr, Y.; Warner, J.L.; Shah, D.P.; Kumar, V.; Shah, S.; Kulkarni, A.A.; Fu, J.; Gulati, S.; Zon, R.L.; Li, M.; Desai, A.; Egan, P.C.; Bakouny, Z.; Kc, D.; Hwang, C.; Akpan, I.J.; McKay, R.R.; Girard, J.; Schmidt, A.L.; Halmos, B.; Thompson, M.A.; Patel, J.M.; Pennell, N.A.; Peters, S.; Elshoury, A.; de Lima Lopes, G.; Stover, D.G.; Grivas, P.; Rini, B.I.; Painter, C.A.; Mishra, S.; Connors, J.M.; Lyman, G.H.; Rosovsky, R.P. CCC19 consortium. The CoVID-TE risk assessment model for venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with cancer and COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost. 2021, 19, 2522–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisa, C.; Gaman, M.A.; Diaconu, C.C.; et al. Oxidative Stress Levels, JAK2V617F Mutational Status and Thrombotic Complications in Patients with Essential Thrombocythemia. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 2822–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaman, A.M.; Moisa, C.; Diaconu, C.C.; et al. Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress, Chronic Inflammation and Disease Progression in Essential Thrombocythemia. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 3486–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.K.; Pradeep, S.; Shimavallu, C.; Kollur, S.P.; Syed, A.; Marraiki, N.; Egbuna, C.; Gaman, M.A.; Kosakowska, O.; Cho, W.C.; Patrick-Iwuanyanwu, K.C.; Ortega Castro, J.; Frau, J.; Flores-Holguín, N.; Glossman-Mitnik, D. Evaluation of Annona muricata Acetogenins as Potential Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agents Through Computational Approaches. Front Chem. 2021, 8, 624716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibensteiner, F.; Ritschl, V.; Nawaz, F.A.; Fazel, S.S.; Tsagkaris, C.; Kulnik, S.T.; Crutzen, R.; Klager, E.; Völkl-Kernstock, S.; Schaden, E.; Kletecka-Pulker, M.; Willschke, H.; Atanasov, A.G. People's Willingness to Vaccinate Against COVID-19 Despite Their Safety Concerns: Twitter Poll Analysis. J Med Internet Res. 2021, 23, e28973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Găman, M.A.; Ryan, P.M.; Bonilla-Escobar, F.J. To Stay at Port or to Go to Sea: Are Clinical Clerkships a Double-Edged Sword During the COVID-19 Pandemic? Where Do We Go From Here? Int J Med Students. 2020, 8, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakka, S.; Nikopoulou, V.; Bonti, E.; et al. Assessing test anxiety and resilience among Greek adolescents during COVID-19 pandemic. J Mind Med Sci. 2020, 7, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2022 by the author. 2022 Yousef Rasmi, Lucas Paulo Jacinto Saavedra, Matei-Alexandru Cozma, Heba A.S. El-Nashar, Shaza H. Aly, Nouran M. Fahmy, Omayma A. Eldahshan, Mohamed El-Shazly, Elena-Codruța Dobrică, Hamed Kord-Varkaneh, Camelia Cristina Diaconu, Mihnea-Alexandru Găman