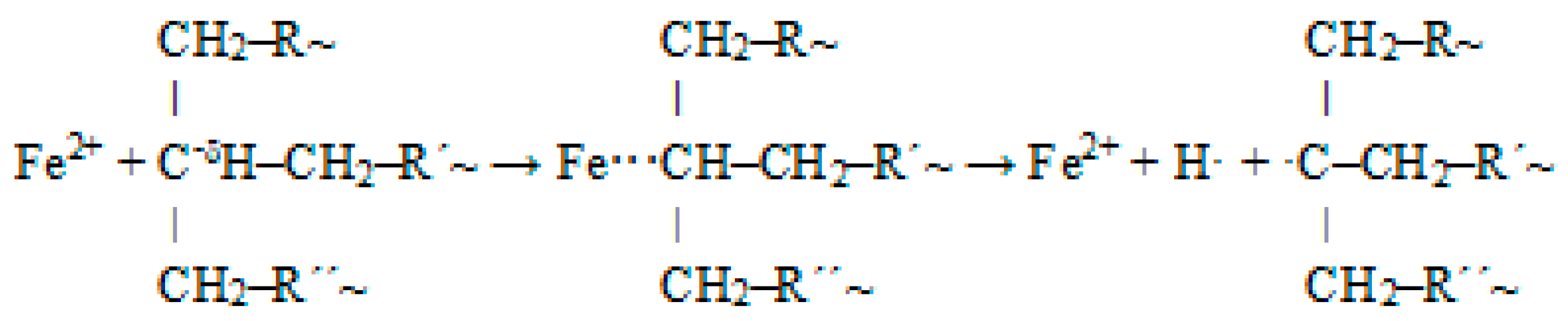Abstract
Crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) is a widely used material which—unlike polyethylene—is very stable both chemically and mechanically. Therefore, waste from this material is difficult to process. A very promising way is slow pyrolysis catalyzed by FeTiO3 (ilmenite), which allows the conversion of this waste into hydrocarbons via degradation of the rigid chemical structure of crosslinked material. High liquid hydrocarbon yields were achieved by slow pyrolysis both without and with a catalyst at a final temperature of 470 °C (65 and 75–76 wt.%, respectively), but with the catalyst significantly changing the composition of the resulting hydrocarbons. To reveal the possibilities of using the FeTiO3 catalyst for processing waste XLPE, the effect of this catalyst on the degradation of the XLPE structure was investigated. The degradation is probably greatly facilitated by the action of the FeTiO3 catalyst at the defect sites of the XLPE structure, i.e., at the tertiary carbons in the main chain where branching into cross-links occurs. In this way, the FeTiO3 catalyst, even in very small amounts (1%), significantly promotes the degradation of the XLPE structure. This leads to the formation of liquid hydrocarbons, up to 92 wt.% of the products obtained. The novelty of this work lies in a technologically feasible method for processing resistant crosslinked waste material using an inexpensive catalyst; the proposed method provides hydrocarbons with high utility value. On the whole, slow pyrolysis of XLPE waste catalyzed by FeTiO3 at a final temperature of 470 °C and carried out under well-defined conditions appears to be a promising method for converting this waste into valuable hydrocarbons and energy gas.
1. Introduction
Thanks to its unique properties and stability, crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) is widely used in the manufacture of pressure pipes for water supply, chlorinated water supply, and steam distribution systems, heating equipment in industrial plants and households, and underfloor heating. It is also used to insulate electrical conductors [1]. The wide range of applications is reflected in the amount of production and installation waste that needs to be removed from the environment. Unfortunately, this waste is currently disposed of mainly by incineration and landfilling, which are neither suitable nor effective methods of disposing of this waste from valuable materials. Therefore, it must be processed [1].
XLPE has a significantly higher heat resistance compared to PE; therefore, XLPE-insulated wires and cables have incomparable advantages over PE-insulated wires and cables: low weight, good heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and high insulation capacity. Furthermore, XLPE is more resistant to thermal deformation, has better mechanical properties at high temperatures, and is significantly more resistant to environmental cracking and thermal aging. It also has enhanced chemical and solvent resistance; its long-term working temperature is up to 125 °C, even up to 150 °C. XLPE can withstand temperatures up to 250 °C in a short time; the current carrying capacity of XLPE is much higher for conductors and cables of the same thickness compared to PE. Under high temperatures, XLPE exhibits a breakdown voltage higher than PE and it is kept practically equal for low temperatures. The main advantages of XLPE are therefore resistance to corrosion, chlorine, and chloramine, use for a wide voltage range from 600 V to 35 kV, thermal stability, and long service life. Given that XLPE is widely used in plumbing, for insulating low-, medium-, and high-voltage electrical cables, in medical implants, transportation, and various consumer products, the volume of waste generated is significant. The development of industries using XLPE is intense (construction and infrastructure, energy sector, renewable energy, eco-friendly materials, and others), and therefore attention must be paid not only to the use of XLPE but also to waste from this material. For clearly organized information, see Supplementary Materials.
As XLPE has exceptional mechanical properties as well as chemical and solvent resistance, its reprocessing, recycling, and modification remain difficult. Moreover, waste XLPE is not of technological nature, which means that it cannot be returned to the production process, because XLPE product quality requirements are too high and could not be met if waste XLPE was used as feedstock. Due to this, it is necessary to find an appropriate method of processing which is not only realistic but also provides useful products [2]. Such a method appears to be slow pyrolysis at a final temperature below 500 °C, possibly catalyzed.
The slow pyrolysis of waste XLPE is rarely addressed in available scientific and professional journals [3,4,5,6]. Recently, high-temperature CO2-assisted gasification of XLPE waste with a focus on the kinetics and syngas yield and properties was investigated [7]. On the other hand, the catalytic function of ilmenite has been intensively studied in recent years.
Ilmenite is a natural iron–titanium oxide mineral. It acts as an effective, inexpensive, and readily available catalyst for various applications, particularly in the decomposition of organic pollutants in water through Fenton-like reactions, which produce highly reactive hydroxyl radicals. It is also used in steam reforming of tars from biomass gasification to improve the quality of the resulting gas. Its catalytic properties result from the action of Fe2+ ions which facilitate decomposition processes. However, its practical use is sometimes limited by a slow induction phase and catalyst deactivation due to coke formation on the catalyst surface. More specifically, ilmenite can be used to degrade various organic pollutants, including dyes and phenols, by generating reactive oxygen species such as hydroxyl radicals (•OH), as the Fe2+ ions in the ilmenite structure facilitate the decomposition of the hydrogen peroxide used, H2O2, into •OH [8,9,10]. Methods of modifying or synthesizing ilmenite are being tested to further improve its catalytic efficiency [11,12,13].
When it comes to biomass gasification, ilmenite has proven to be a promising catalyst, especially in removing tar compounds from producer gas [14]. It can be used both in fixed-bed reactors and fluidized-bed gasifiers [15,16]. For ilmenite’s activity in tar reforming, steam is important because it helps minimize coke formation on the catalyst surface. Ilmenite can improve the quality of producer gas by increasing the concentration of desirable gases like CO and H2, as well as the H2/CO molar ratio [17,18,19].
Ilmenite is known for its structural stability [20], which is important for maintaining catalytic activity over time. It is a great advantage that the ilmenite catalyst is cheap and readily available [8,21]. From the point of view of processing waste polymers, it is significant that it has been successfully tested in the processing of polystyrene [21,22]. Overall, it can be concluded that ilmenite can be used for the thermal decomposition of XLPE, but the pyrolysis conditions must be well defined.
It must be emphasized that there is a big difference between the pyrolysis of polyethylene, whether LDPE, medium density polyethylene, or HDPE, and crosslinked polyethylene. Due to the extraordinary chemical and mechanical stability [1,2,22,23,24,25,26], great attention must be paid to the pyrolysis conditions. Their importance comes to the fore especially when processing waste XLPE on a large scale, as they reduce the temperature of the onset of decomposition, increase the efficiency of the process, and enable deeper degradation of the XLPE structure. Among the catalysts most often used for the decomposition of different types of polyethylene and other plastics [27,28], the following were considered for the decomposition of waste XLPE: amorphous SiO2/Al2O3 [29], mesoporous SiO2/Al2O3 [30], MCM with Al2O3 [31], ZSM-5 zeolite [32,33], FCC [34], activated carbon [35], and faujasite (zeolite Y) [36]. The above catalysts certainly work for various polyethylenes and blends thereof, but often higher amounts of waxy compounds and lower liquid yields are obtained. Therefore, a different approach is required for XLPE waste. The cause can be seen in the undefined impurities and especially in the rigid structure of XLPE. The other problem is that the energy balance of the process/catalyzed process is not evaluated in the above works; the efficiency of the catalyzed process is not evaluated or even considered. However, these items are fundamental in evaluating the catalyst’s efficiency.
Therefore, this work investigates the effect of the ilmenite catalyst on the degradation of waste XLPE based on the description of the behavior of waste XLPE during slow pyrolysis without and with the catalyst, and the analysis of the pyrolysis products obtained. The advantage of the presented technology is that it can be implemented on existing pyrolysis devices, the catalyst used is available, cheap, and efficient, and the products—liquid hydrocarbons—are in demand and have wide applications as chemicals and solvents, lubricants, and clean liquid fuels. (Note: The presented technology was preliminarily tested with ruthenium as the catalyst, but since ruthenium is expensive, it was modified and adapted for use with FeTiO3).
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Basic Thermal Phenomena of XLPE Decomposition
To describe the effect of the ilmenite catalyst on the decomposition of waste XLPE, the TG/DSC method was firstly used, enabling the determination of melting and decomposition temperatures.
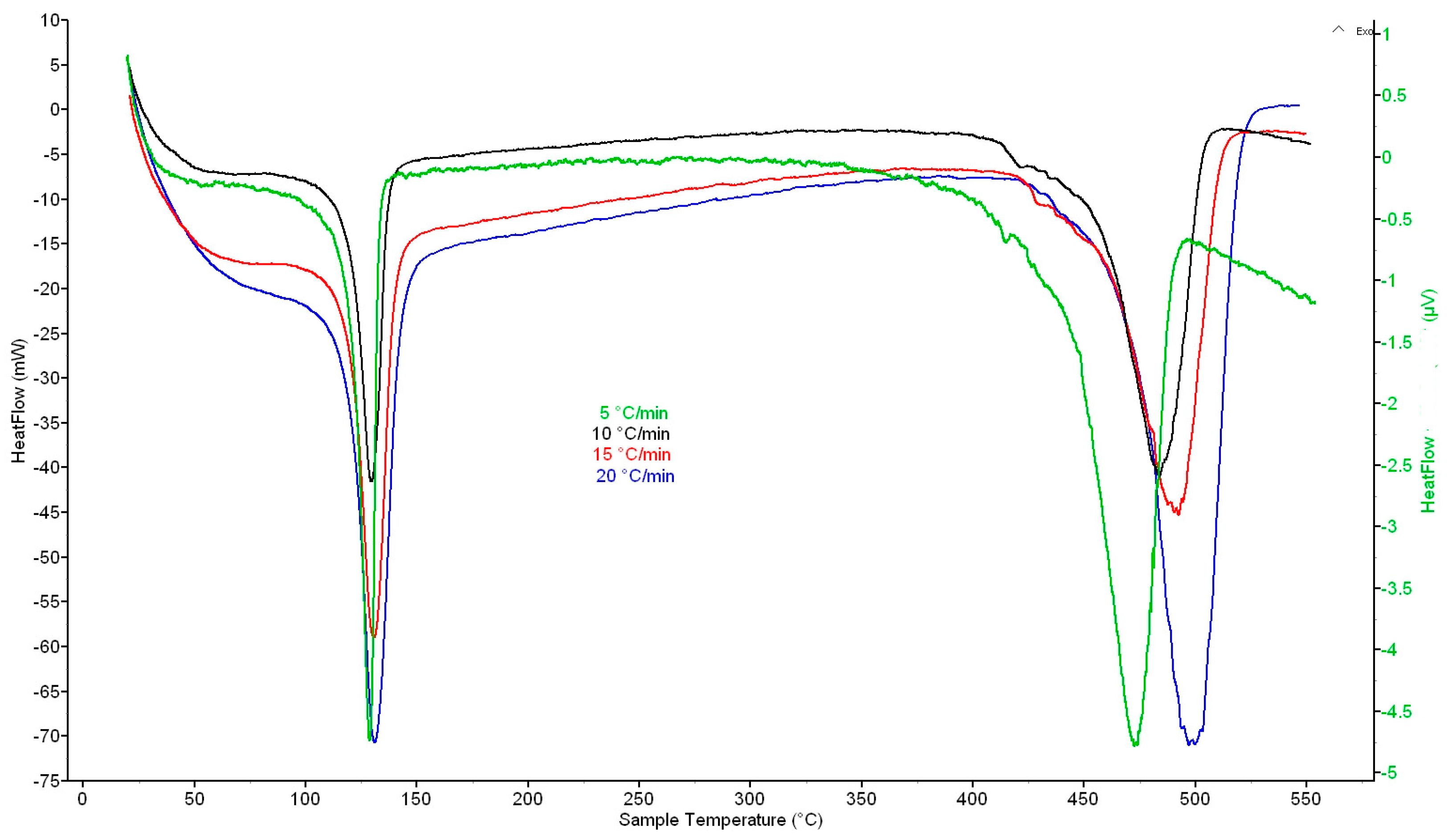
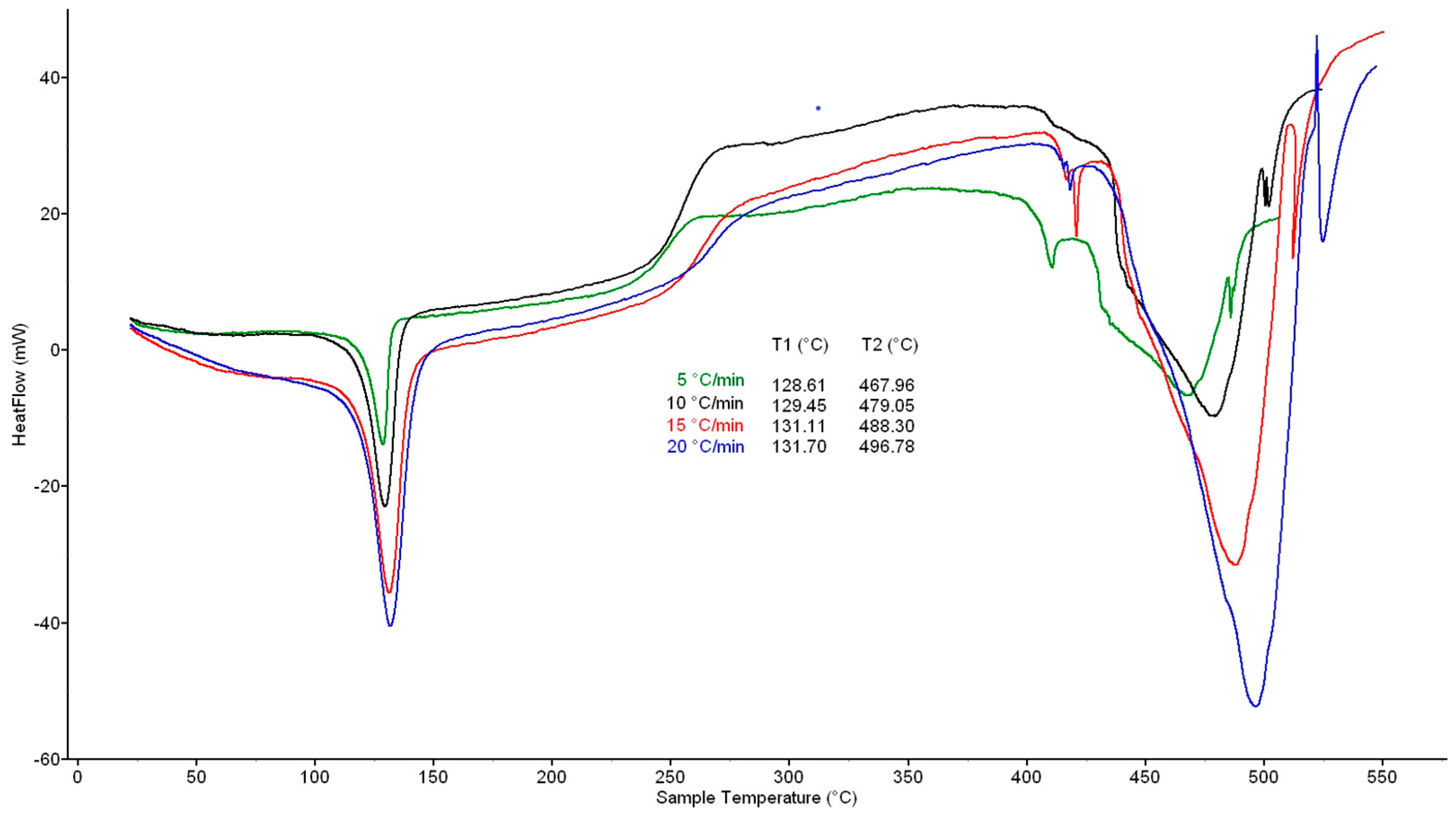
In all cases, two important temperature intervals with significant heat flows were recorded from the DSC curves at heating rates of 5, 10, 15, and 20 K·min−1, where the first one was 100–150 °C with a maximum at 130 °C and the second one was 400–525 °C with a maximum at 470 °C (5 K·min−1), 485 °C (10 K·min−1), 493 °C (15 K·min−1), and 500 °C (20 K·min−1) (Figure 1). In the first interval, melting of material occurs; in the second one, the total decomposition of crosslinked structure is in progress. The above values for DSC with a catalyst were very similar: the first maximum was at ~130 °C and the second maximum at 468 °C (5 K·min−1), 479 °C (10 K·min−1), 488 °C (15 K·min−1) and 497 °C (20 K·min−1) (Figure 2).
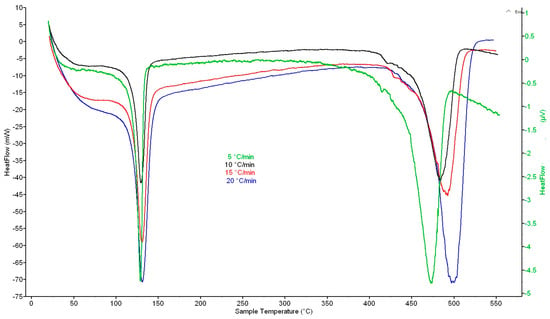
Figure 1.
DSC curves of waste XLPE at heating rates of 5, 10, 15, and 20 K·min−1.
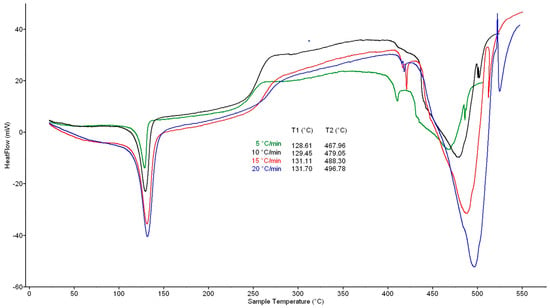
Figure 2.
DSC curves of waste XLPE with catalyst. For heating rates, see Figure 1.
Regarding TG determination, TG curves were obtained for heating rates of 5, 10, 15, and 20 K·min−1 and confirmed the above DSC values (Figure S1 and Table S1, Supplementary Materials). The DSC and TG curves also show that the thermal conversion was completed at temperatures of 500–525 °C.
Previous experience with thermal processing of waste XLPE [37] shows that catalyzed pyrolysis provides oil with a higher content of liquid hydrocarbons compared to that without a catalyst. Pyrolysis must be carried out to final temperatures higher than 460 °C (470 or 480 °C) to produce oil in high yield (over 90 wt.%) at the expense of solid carbonaceous residue. This was demonstrated with the Ru/Al2O3 catalyst, but it is not cheap. Therefore, experiments were performed with the ilmenite catalyst, which is significantly cheaper, and it was tested whether the pyrolysis results were the same or at least comparable to the results achieved with Ru/Al2O3.
2.2. XLPE Waste Pyrolysis Products
All the above findings indicate that the pyrolysis decomposition of waste XLPE in the presence and absence of a catalyst leads to different compositions of pyrolysis products. In addition, pyrolysis must be carried out under conditions suitable for large-scale processing. Thus, experiments were carried out at an operational heating rate of 5 K·min−1, up to 470 °C, with a 30 min delay at the end temperature, both without and with a catalyst. First, the mass balance of the process was determined. The results are shown in Table 1. This table shows that the dominant product is oil, but attention should also be paid to the by-products, pyrolysis gas for possible energy use and the solid carbonaceous residue for its possible further processing. Due to the importance of mass balance, attention is also paid to it below (see Section 2.3).

Table 1.
Mass balance of pyrolysis of waste XLPE (wt.%) without and with FeTiO3-catalyst (wt.%) at 5 K·min−1, up to 470 °C, with delay at end temperature of 30 min. SCR—solid carbonaceous residue.
The obtained gas, oil, and solid carbon residue (SCR) were immediately analyzed. The results are shown in Table 2 (gas), Table 3, and Table 4 (oil); further, SCR was characterized.

Table 2.
Composition of pyrolysis gas obtained without and with FeTiO3-catalyst (vol.%) at 5 K·min−1, up to 470 °C, with delay at end temperature of 30 min.

Table 3.
Composition of pyrolysis oils obtained without and with FeTiO3-catalyst (wt.%) at 5 K·min−1, up to 470 °C, with delay at end temperature of 30 min.

Table 4.
Elemental analysis of the oils (wt.%) obtained with different catalyst contents, along with their higher heating value (HHV, MJ kg−1) and lower heating value (LHV, MJ kg−1).
Composition of pyrolysis gas. The main components of total pyrolysis gas obtained were light gaseous hydrocarbons; carbon oxides and hydrogen were also identified and determined (Table 2). It is clear from Table 2 that the total gas obtained with the catalyst showed a significant increase in the concentrations of light hydrocarbons C2–C5 compared to the gas obtained without the catalyst. This comparison shows that the catalyst used did significantly promote the cleavage of the XLPE structure, but in a different way than in thermal cleavage without a catalyst, as only 1 vol.% H2 was found with the catalyst versus 17 vol.% H2 without the catalyst. Thanks to the high content of C2–C5 hydrocarbons (70–98 vol.%; Table 2) and relatively higher content of methane (25 vol.%), the obtained gas has high heating values and can therefore be used to heat the operational pyrolysis unit. For heating, it can be used either alone or in a mixture with natural gas. The gas obtained did not contain any undesirable components such as hydrogen sulfide and ammonia, which is advantageous from a practical point of view.
Composition of pyrolysis oil. As expected, both liquid (C10–C17) and dissolved solid (C18–C35) hydrocarbons were found. But low liquid hydrocarbons C6–C9 were found only in oils obtained with the catalyst (15–18 wt.%; Table 3). Thus, the catalyst used promotes the cleavage of XLPE under the above conditions, which is advantageous for the production of highly desirable C6–C9 hydrocarbons. The splitting ability of the ilmenite catalyst results in solid hydrocarbons only up to C24, in contrast to solid hydrocarbons up to C35 obtained by decomposition without the catalyst. While the content of solid hydrocarbons without a catalyst was 30.5 wt.%, with a catalyst, it was only 17–18 wt.%. It can therefore be considered proven that ilmenite promotes the splitting of the XLPE structure in favor of liquid hydrocarbons at the expense of solid hydrocarbons. Solid hydrocarbons are less desirable compared to liquid hydrocarbons, which have wider use as a source of chemicals, solvents, and lubricants. Solid hydrocarbons can be used as, for example, technical paraffin. From a technological point of view, ilmenite is therefore well usable.
The elemental composition of the oils is shown in Table 4. The high carbon content also results in very favorable lower heating values (LHVs) and higher heating values (HHVs). High carbon and hydrogen contents and very low nitrogen and oxygen contents were recorded. The oils obtained were sulfur-free and ash-free. Such a composition also results in very favorable LHVs and HHVs. Oils obtained using the catalyst are therefore usable as high-quality liquid fuel.
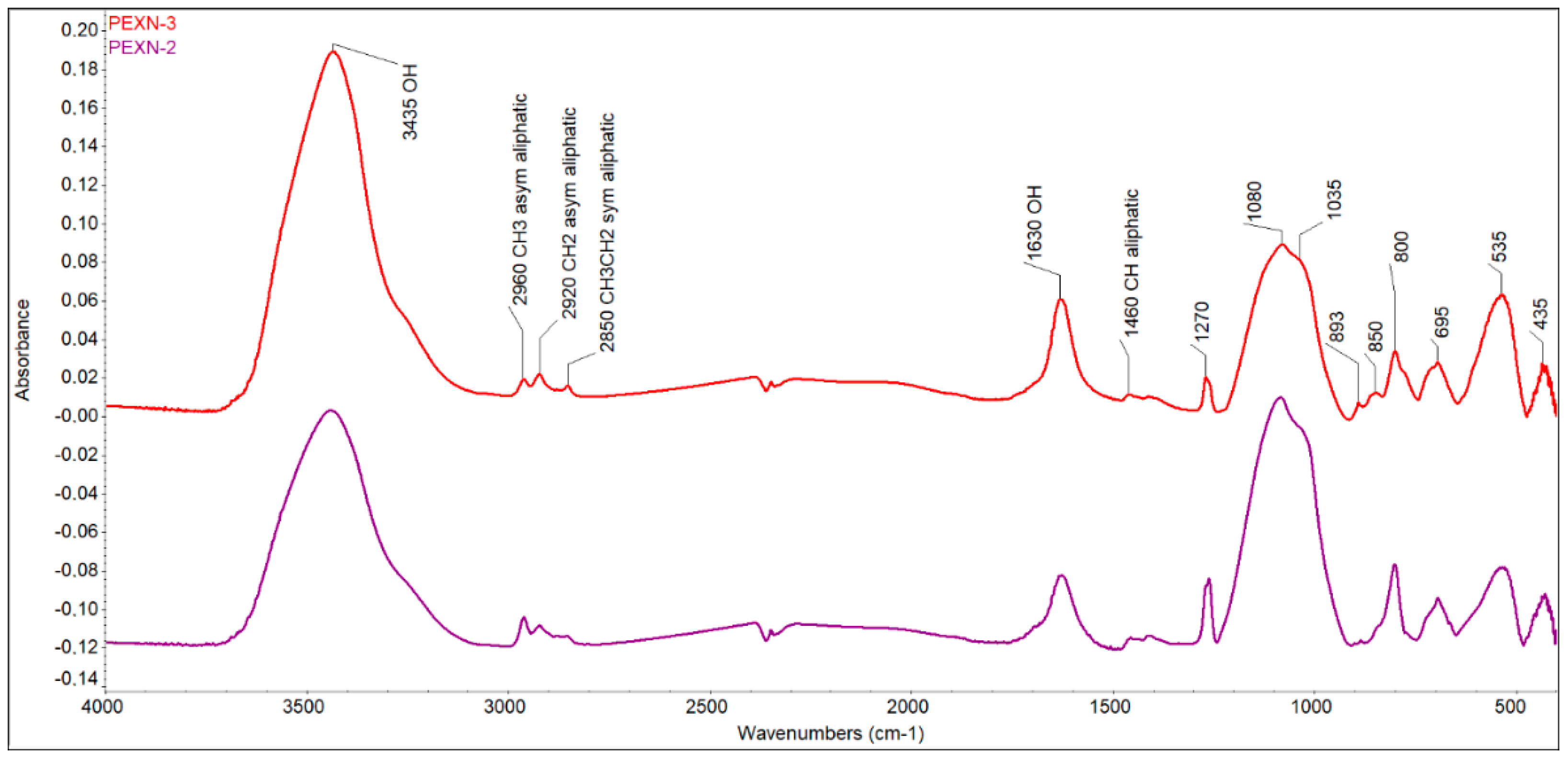
Characterization of solid carbonaceous residue (SCR). No coke formations were found in the SCRs either in the case without a catalyst or in the case with a catalyst. The habitus of SCR clearly shows that SCR is an asphalt-like solid without a porous texture (Figure 3). Further, in the FTIR spectrum, no polyaromatics or aromatics, typical for coke, were proved because no =C–H stretch in aromatics at 3100–3000 cm−1, no overtones at 2000–1665 cm−1, and no C–C in-ring stretch at 1600–1585 and 1500–1400 cm−1 were observed (Figure 4). Bands corresponding to moisture from pellets (3435 cm−1 and 1630 cm−1) and aliphatic (2960 cm−1—aliphatic CH3; 2920 cm−1—aliphatic CH2; 2850—aliphatic CH3CH2; 1460 cm−1—aliphatic CH) and inorganic components (1270, 1080, 1035, 800, 695, 535, and 435 cm−1) were found in the FTIR spectrum. (Note: Two samples were evaluated for possible heterogeneity of SCR. The lower purple line is the spectrum of the control sample, which is not different from the upper spectrum in red).
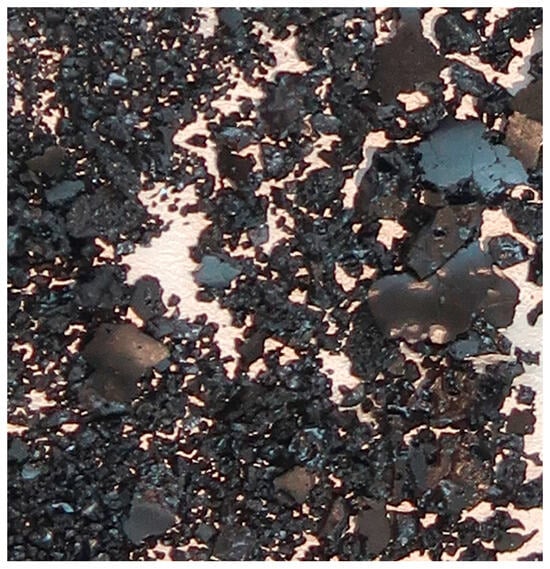

Figure 3.
Asphalt-like solid carbonaceous residue.
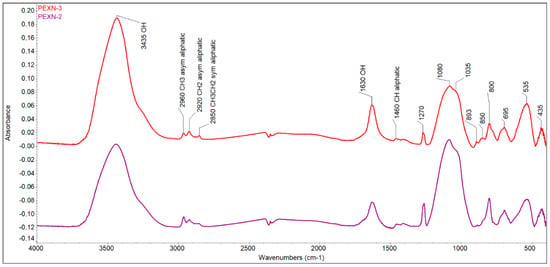
Figure 4.
FTIR spectrum of SCR obtained from pyrolysis with 1 wt.% catalyst (KBr pellet technique, red curve); the purple curve is the control FTIR spectrum.
Under the given pyrolysis conditions, the amount of SCR was only 1% of the amount of the products obtained (see below). After the pyrolysis was completed, it remained in the reactor together with the ilmenite. In this case, SCR was disposed by oxidation with air at a higher temperature. This separated it from ilmenite, the reuse of which was not tested. Ilmenite does not have a clearly defined melting point, as it varies depending on the composition. The literature often reports high melting points for ilmenite or claims that the exact melting point of ilmenite can vary but is generally high. However, it can be estimated that due to the low price of ilmenite, its reuse is not worthwhile.
2.3. Mass Balance of the Process
The mass balance of waste XLPE pyrolysis was evaluated as a key insight both for assessing the catalyst efficiency in the production and composition of the main product, oil, and for implementing large-scale thermochemical processing of waste XLPE [38]. The results are summarized in Table 5. The presented data show that the amount of gas obtained in the presence of catalyst is 7–8 wt.%. Given the high calorific value resulting from its composition (Table 2), this amount is sufficient to heat the process pyrolysis unit. If operating conditions require more gas, the obtained gas can be mixed with natural gas. As for oil production, its liquid fraction obtained with catalyst was by 10–11 wt.% higher than without it. On the contrary, the production of solid hydrocarbons dissolved in oil was by 12–13 wt.% lower compared to the production without a catalyst. This is a favorable result, since the need for liquid hydrocarbons is always significantly higher than that for solids. It is also advantageous that the amount of SCR was very low, only 1 wt.%, which indicates the high efficiency of the process. However, it will be appropriate to express the efficiency of the process numerically after a large-scale experiment.

Table 5.
Mass balance of pyrolysis of waste XLPE (wt.%) without and with FeTiO3-catalyst (wt.%) at 5 K·min−1, up to 470 °C, with delay at end temperature of 30 min. HCs—hydrocarbons, SCR—solid carbonaceous residue.
Another question addressed by the mass balance is the comparison of the efficiency of the tested catalyst with a partially used FCC catalyst [34]. The comparison is shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Mass balance and oil composition from slow pyrolysis of waste XLPE (wt.%) without and with catalysts at 5 K·min−1, at an end temperature of 470 °C, with a delay at the end temperature of 30 min. SCR—solid carbonaceous residue.
Table 6 shows that the cleavage of the XLPE structure by slow pyrolysis proceeds differently without a catalyst, in the presence of FeTiO3, and in the presence of FCC. Pyrolysis without a catalyst gave a relatively high yield of liquid hydrocarbons C10–C17 (65 wt.%), but without a significant C6–C9 fraction, and a higher yield of solid hydrocarbons C18–C35 (29 wt.%). In the presence of 1% FeTiO3, a significant amount of C6–C9 fraction (13 wt.%) was obtained as well as a high yield of liquid hydrocarbons C10–C17 (62 wt.%) and a relatively lower yield of solid hydrocarbons C18–C24 (17 wt.%). In the case of FCC, it was different. To achieve an acceptable oil yield on a laboratory scale (above 80 wt.%), 10% FCC was needed. Under this condition, practically equal amounts of C6–C9 and C10–C17 fractions (32 wt.%) and a small amount of C18–C35 solid hydrocarbons (5 wt.%) were obtained. However, the use of FCC resulted in a high proportion of solid hydrocarbons >C35 (17 wt.%) at the expense of liquid hydrocarbons. This is not a favorable feature of the use of FCC.
2.4. Approach to the Catalytic Effect of FeTiO3
From the above, it follows that the used catalyst significantly promotes the cleavage of XLPE. It is likely that during the thermal degradation of XPLE, reactions similar to those that occur during the degradation of different types of polyethylene occur [39,40,41], but they are promoted by the action of Fe2+ incorporated in the ilmenite structure. The catalytic mechanism can simplistically be described as follows. The +I inductive effect of CH2 groups in the vicinity of tertiary carbons increases the electron density on the tertiary carbons; thus, the tertiary carbons are more reactive compared to secondary ones. In the branched structure of XLPE, the tertiary carbons are hydrogen-bonded and surrounded by CH2 groups. These groups tend to give electrons, leading to the induction effect. They are less electron-withdrawing than hydrogen, and so, they are electron-releasing (electron-donating). This electron-releasing function (indicated by the +I effect) leads to an increase in electron density on the tertiary carbon. This increased electron density on the tertiary carbon allows interaction with the Fe2+ ion. A highly unstable complex is formed, which decomposes into radicals that react further (Figure 5). This promotes the concentration of radicals. Thus, the action of the ilmenite catalyst can be characterized as promoting the formation of radicals, the concentration of which is a key factor in the cleavage of the rigid crosslinked structure of XLPE.
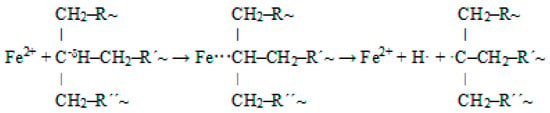
Figure 5.
Interaction of Fe2+ ion with tertiary carbon and resulting radicals.
2.5. XLPE Waste Processing Strategy
From a practical point of view, it is important that the FeTiO3 catalyst is inexpensive and readily available, as mentioned. Moreover, only 1% catalyst is needed for the successful decomposition of XLPE. Therefore, the reusability of the catalyst was not tested. The following strategy can be considered for XLPE waste processing.
- XLPE waste can be successfully processed without a catalyst if oil with a lower liquid hydrocarbon content (e.g., 65%) and a higher dissolved solid hydrocarbon content (e.g., 30%) is acceptable.
- If oil with a high content of liquid hydrocarbons (e.g., 75%) is required, especially with a content of low C6–C9 hydrocarbons, it is advantageous to use an ilmenite catalyst, even at an amount of 1%.
- In principle, the well-known FCC catalyst can also be used. However, a lower yield of liquid hydrocarbons (around 60%) and a relatively high proportion of solid hydrocarbons (around 20%) must be taken into account. It is also necessary to use a fairly large amount of that catalyst (10%).
2.6. Catalyst Regeneration and Possibility for Its Reuse
The separation of ilmenite from the solid carbonaceous residue (SCR) is facilitated by the fact that SCR is not coke, as it does not contain aromatic structures typical of coke, but is an asphalt-like substance that is considerably more reactive than coke. Therefore, the separation was carried out by gasifying the SCR with carbon dioxide at 800 °C (the CO2 flow rate in a laboratory-scale experiment was 16 dm3/h). The high melting point of ilmenite (1550–1850 °C) and its chemical stability then allow its regeneration and reuse. Regeneration through gasification seems to be much easier than the patented method “Process for separating ilmenite” [42]. However, it should be emphasized that our findings were obtained only on a laboratory scale. The findings on a large scale will be decisive. In principle, the regeneration of ilmenite and its subsequent use are possible. However, it must be carefully considered that ilmenite is cheap and whether its regeneration is worthwhile.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
The waste used was XLPE flakes of a few mm up to 1 cm in size, resulting mainly from the production of XLPE pressure tubes, hot water pipes, and cable insulation. This waste was obtained from Central and South Bohemian producers, Czech Republic, in quantities of several tens of kg. It was homogenized and then samples of 20 g, 50 g, and 100 g were taken for analyses and pyrolysis experiments. The waste used contained little water (0.09 wt.%) and ash (0.66 wt.%), and a high percentage of combustible matter (99.25 wt.%). The degree of crosslink of the XLPE used was 65% according to DIN 16892 [43].
Ilmenite with a grain size 0.2–0.5 mm was used as the catalyst. The catalyst contained ilmenite (85 wt.%), rutile (5 wt.%), quartz (7 wt.%), and hematite (3 wt.%) (determined by X-ray diffraction on a powder diffractometer Bruker D-8 Discover (Karlsruhe, Germany); see Supplementary Materials, Figure S2). For elemental concentrations, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy was used on a Quanta 450 scanning electron microscope (FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA) equipped with a Si(Li) Apollo XL Silicon Drift Detector with a FET preamplifier (EDAX Inc., Mahwah, NJ, USA). Data acquisition was performed on EDAX TSL OIM software, v.7.0, with ZAF corrections (see Supplementary Materials, Figure S3). For selected characteristics of ilmenite supporting its function as a catalyst, see Note 1 [22,24], Supplementary Materials.
3.2. Methods
The waste XLPE was pyrolyzed on a laboratory pyrolysis unit for the thermal treatment of organic waste. The unit consists of a vertical electric resistance furnace with programmable heating, a quartz reactor with the removal of volatile products (raw gas), a primary air cooling of the volatile products, two coolers in a series cooled by ethylene glycol at −10 °C for secondary cooling, a liquid-product receiving flask, and a gasholder with a capacity of 130 dm3. The unit is equipped with continuously operating analyzers (an infrared CH4, CO, and CO2 analyzer and an electrochemical hydrogen analyzer), continuous temperature sensing of the reactor wall, reactor interior, and released volatile products, continuous sensing of the volume and pressure of the developed gas, and a cooling control. The heating is controlled by a programmable module; all sensed data are recorded by the control PC. Its design makes it possible to reduce losses in the pyrolysis of charges up to 100 g to a maximum of 5 wt.%, most commonly to 2–4 wt.%. Pyrolysis was performed with waste XLPE, both with and without a catalyst. Feedstock weight was 100 g, and catalyst weights were 1, 5, and 10 g. Dry mixing was applied to them. The heating rate was 5 K·min−1, the end temperature was 470 °C, and the delay at the end temperature was 30 min. Each pyrolysis run was carried out three times. The relative standard deviation of oil yield was 1–2%, the solid carbon residue yield was 4–5%, and the pyrolysis gas yield was 1–2%.
The total gas obtained was analyzed on two Agilent Technologies 6890N (Buffalo, NY, USA) gas chromatographs with three 30 m × 0.32 mm capillary columns while the analysis of O2, N2, and CO was performed on an HP-MOLSIV (40 °C) with carrier gas He (5 cm3 min−1) using TCD; CH4 and C2–C5 hydrocarbons on a GS-Gaspro (60 °C) with carrier gas N2 (20 cm3 min−1) using FID; CO2 on a GS-Gaspro (40 °C) with carrier gas He (5 cm3 min−1) using TCD; H2 on an HP-5 (40 °C) with carrier gas N2 (7 cm3 min−1) using TCD. The relative standard deviations of individual gas component determinations were 1–3% (n = 6).
Oil components were identified and determined on an Agilent Technologies 6890 (Buffalo, NY, USA) chromatograph with an MSD 5975 mass spectrometer and a DB XLB capillary column (30 m × 0.25 mm). The column was maintained at 50 °C for the first min and then the temperature was increased from 50 to 300 °C at a heating rate of 10 K·min−1; the column was then maintained at 300 °C for 6 min. The carrier gas was helium. The calibration curve method using the digital response of the instrument was used to determine the oil components. (Note: Together with liquid hydrocarbons, the solid hydrocarbons were determined in this way as hydrocarbons C18–C35 or C18–C24 were dissolved in liquid oil.)
4. Conclusions
Overall, the amount of XLPE waste is still growing and needs to be processed. The FeTiO3-catalyzed slow pyrolysis of waste XLPE up to 470 °C seems to be a promising way to convert this waste into valuable hydrocarbons and energy gas. Pyrolysis must be carried out under well-defined conditions either without or with a catalyst. However, pyrolysis with a catalyst significantly affects the quality and amount of the main product, the oil. It has been shown that the effect of the FeTiO3 catalyst on XLPE degradation is favorable, even in very small amounts (1%), as it allows for deep cleavage of the rigid XLPE structure and, as a result, a high yield of hydrocarbons. This is evidenced by the high content of liquid hydrocarbons in the pyrolysis oil (82–83 wt.%). The FeTiO3 catalyst is cheap and readily available. The proposed technology provides a viable solution for the processing of chemically and mechanically resistant material, with the obtained products having wide practical applications. Slow pyrolysis is well feasible on a large scale, as technical knowledge from thermochemical processes can be used and the process parameters (heating rate, final temperature, final temperature delay, and residence time) obtained from laboratory measurements are realistically transferable to larger scales. The presented technology thus becomes part of the effort to utilize waste XLPE and the indisputable benefits that these efforts bring [44,45].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/recycling10060202/s1, Figure S1: TG curves of XLPE decomposition at different heating rates. Green line—5 K·min−1; black line—10 K·min−1; red line—15 K·min−1; blue line—20 K·min−1; Figure S2: X-ray diffractogram of the catalyst used. The crystalline phase of ilmenite is marked in red (85 wt.%), rutile in green (5 wt.%). Quartz (7 wt.%) and hematite (3 wt.%) were also found; Figure S3: Concentrations of elements of the catalyst used as found by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (K lines, wt.%). C 0.37; O 35.35; Mg 0.31; Al 1.35; Si 4.98; P 0.24; S 0.59; Ru 0.22; Ca 0.18; Ti 31.41; Mn 0.41; Fe 24.59; Table S1: Additional data for Figure S1. Heating rate (w); Tinf—temperature at the inflection point. Note 1.
Author Contributions
P.S.: Investigation, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, and Writing—Review and Editing. O.B.: Methodology and Formal Analysis. J.C.: Methodology and Formal Analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Long-Term Project for the Conceptual Development of the Research Organization No. RVO 67985891; Project No. TP01010055, Technology Agency of the Czech Republic, GAMA 2 program, Part 2-06; and the Strategy AV21 Research Program of the Czech Academy of Sciences: Sustainable Energy (VP27).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Selvin, M.; Shah, S.; Maria, H.J.; Thomas, S.; Tuladhar, R.; Jacob, M. Review on recycling of cross-linked polyethylene. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 1200–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Rodrigue, D. Crosslinked polyethylene: A review on the crosslinking techniques, manufacturing methods, applications, and recycling. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 2376–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Celik, M.B. Modeling the effect of plastic oil obtained from XLPE cable waste on diesel engine performance and emision parameters with the response surface method. Sci. Technol. Energy Transit. 2024, 79, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Jun, Z.; Dong, L.; Chen, H. Study on pyrolysis characteristics of cross-linked polyethylene material cable. Procedia Eng. 2013, 52, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcilla, A.; Ruiz-Femenia, R.; Hernández, J.; García-Quesada, J.C. Thermal and catalytic pyrolysis of crosslinked polyethylene. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2006, 76, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamboli, S.M.; Mhaske, S.T.; Kale, D.D. Crosslinked polyethylene. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2004, 11, 853–864. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Déparrois, N.; Burra, K.R.G.; Gupta, A.K. Energy recovery from cross-linked polyethylene wastes using pyrolysis and CO2 assisted gasification. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Muñoz, P.; Pliego, G.; Zazo, J.A.; Bahamonde, A.; Casas, J.A. Ilmenite (FeTiO3) as low-cost catalyst for advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Huang, R.; Yuan, J.; Chen, R.; Chen, F. Efficient removal of aromatic pollutants via catalytic wet peroxide oxidation over synthetic anisotropic ilmenite/carbon nanocomposites. Clean Water 2023, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malato, S.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Maldonado, M.I.; Blanco, J.; Gernjak, W. Decontamination and disinfection of water by solar photocatalysis: Recent overview and trends. Catal. Today 2009, 147, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzenda, C.; Nkwachukwu, O.V.; Arotiba, O.A. Synthetic Ilmenite (FeTiO3) Nanoparticles as a Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Catalyst for the Degradation of Tetracycline in Wastewater. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 11417–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, L.; Gong, X.; Liu, Y.; Tian, J. Defect-enriched ilmenite-type catalyst derived from titanium dioxide slag for peroxymonosulfate activation in efficient tetracycline removal. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 280, 119068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; He, H.; Chen, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhai, J.; Sun, W. Surface modification of ilmenite with sodium persulfate and its effect on flotation performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 680, 161354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Z.; Asadullah, M.; Yimsiri, P.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Li, C.-Z. Catalytic reforming of tar during gasification. Part I. Steam reforming of biomass tar using ilmenite as a catalyst. Fuel 2011, 90, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pio, D.T.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Pinto, R.G.; Matos, M.A.A.; Frade, J.R.; Yaremchenko, A.; Mishra, G.S.; Pinto, P.C.R. Low-cost catalysts for in-situ improvement of producer gas quality during direct gasification of biomass. Energy 2018, 165, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.A.; Tsuda, H.; Wu, S.; Sasaoka, E. Catalytic decomposition of biomass tars with iron oxide catalysts. Fuel 2008, 87, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, F.; Seemann, M.; Thunman, H. Continuous catalytic tar reforming of biomass derived raw gas with simultaneous catalyst regeneration. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.N.T.; Berguerand, N.; Schwebel, G.L.; Thunman, H. Importance of Decomposition Reactions for Catalytic Conversion of Tar and Light Hydrocarbons: An Application with an Ilmenite Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 11900–11909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.N.T.; Berguerand, N.; Thunman, H. Mechanism and Kinetic Modeling of Catalytic Upgrading of a Biomass-Derived Raw Gas: An Application with Ilmenite as Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 5843–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, C.; Liang, Y.; Peng, Q.; Hess, P. The stability and major element partitioning of ilmenite and armalcolite during lunar cumulate mantle overturn. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 820–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royuela, D.; Martínez, J.D.; Callén, M.S.; López, J.M.; García, T.; Murillo, R.; Veses, A. Pyrolysis of polystyrene using low-cost natural catalysts: Production and characterisation of styrene-rich pyro-oils. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2024, 182, 106690. [Google Scholar]
- Zazo, J.A.; Bedia, J.; Fierro, C.M.; Pliego, G.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Highly stable Fe on activated carbon catalysts for CWPO upon FeCl3 activation of lignin from black liquors. Catalysis Today 2012, 187, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.N.; Willms, R.B.; Gray, G.T.; Rae, P.J.; Cady, C.M.; Vecchio, K.S.; Flowers, J.; Flowers, M.Y. Influence of Molecular Conformation on the Constitutive Response of Polyethylene: A Comparison of HDPE, UHMWPE, and PEX. Exp. Mech. 2007, 47, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Kullmann, S.; Keller, H. Wastewater treatment with heterogeneous Fenton-type catalysts based on porous materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9002–9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikri, M.; Abdul-Malek, Z. Partial discharge diagnosis and remaining useful lifetime in XLPE extruded power cables under DC voltage: A review. Electr. Eng. 2023, 105, 4195–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Hu, W.; Liu, B. Recent Overview and Future Research Prospects of Cross-linked Polyethylene Materials: Cross-linking Methods and Applications. preprints 2024, 2024091601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, L.O.; Cendejas, M.C.; Hermans, I. The use of heterogeneous catalysis in the chemical valorization of plastic waste. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 5808–5836. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miandad, R.; Barakat, M.A.; Aburiazaiza, A.S.; Rehan, M.; Nizami, A.S. Catalytic pyrolysis of plastic waste: A review. Process Saf. Environ. 2016, 102, 822–838. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkita, H.; Nishiyama, R.; Tochihara, Y.; Mizushima, T.; Kakuta, N.; Morioka, Y.; Ueno, A.; Tanifuji, S.; Katoh, H.; Sunazuka, H.; et al. Acid Properties of Silica–Alumina Catalysts and Catalytic Degradation of Polyethylene. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, 32, 3112–3116. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.A.; Koizumi, K.; Murata, K.; Sakata, Y. Thermal and catalytic degradation of structurally different types of polyethylene into fuel oil. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1997, 56, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, C.; Wei, R.; Wang, J. Experimental study of polyethylene pyrolysis and combustion over HZSM- 5, HUSY, and MCM-41. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 333, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, N.; Afonso, D.; Santos, E.; Fonseca, I.; Lemos, F.; Lemos, M.A.N.D.A. Coprocessing of Waste Plastic and Hydrocarbons over MFI (HZSM-5). Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2016, 48, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.L.; Araujo, A.S.; Linares, M.; Peral, A.; Garcia, R.A.; Serrano, D.P.; Fernandes, V.J. Catalytic cracking of LDPE over nanocrystalline HZSM-5 zeolite prepared by seed-assisted synthesis from an organic-template- free system. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2016, 117, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Palos, R.; Gutierrez, A.; Vela, F.J.; Arandes, J.M.; Bilbao, J. Effect of the FCC Equilibrium Catalyst Properties and of the Cracking Temperature on the Production of Fuel from HDPE Pyrolysis Waxes. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 5191–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, D.; Lei, H.; Villota, E.; Ruan, R. Jet fuel production from waste plastics via catalytic pyrolysis with activated carbons. Appl. Energy 2019, 251, 113337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colantonio, S.; Cafiero, L.; De Angelis, D.; Ippolito, N.M.; Tuffi, R.; Ciprioti, S.V. Thermal and catalytic pyrolysis of a synthetic mixture representative of packaging plastics residue. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, P.; Bičáková, O.; Cihlář, J. Slow low-temperature pyrolysis of waste cross-linked polyethylene with a ruthenium catalyst. preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, P.; Bičáková, O.; Cihlář, J. Low-temperature treatment of waste crosslinked polyethylene with ruthenium catalyst. Paliva 2023, 15, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mahadas, N.A.; Zhang, M.; DePodesta, J.; Stefik, M.; Tang, C. Sustainable high-density polyethylene via chemical recycling: From modification to polymerization methods. Polymer 2024, 295, 126698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Panda, A.K.; Singh, R.K. A review on tertiary recycling of high-density polyethylene to fuel. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 893–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.K.; Singh, R.K.; Mishra, D.K. Thermolysis of waste plastics to liquid fuel. A suitable method for plastic waste management and manufacture of value added products—A world prospective. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walpole, E.A. Process for Separating Ilmenite. Patent Application No. WO1992004121A1, 28 August 1991. [Google Scholar]
- DIN 16892:219-10; Crosslinked Polyethylene (PE-X) Pipes—General Quality Requirements, Testing. Normservis: Hamry nad Sázavou, Czech Republic, 2019.
- Shamsaei, M.; Aghayan, I.; Kazemi, K.A. Experimental investigation of using cross-linked polyethylene waste as aggregate in roller compacted concrete pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.J.; Brigandi, P.J.; Moubarak, M.; Sengupta, S.S.; Epps, T.H., III. Cross-Linked Polyolefins: Opportunities for Fostering Circularity Throughout the Materials Lifecycle. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 11859–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).