Abstract
Wild apples and their hybrids are valued as a source of genetic resistance to biotic and abiotic stress. Malus niedzwetzkyana is an endangered ornamental apple species endemic to Southeast Kazakhstan, the center of Malus domestication. To test the fire blight resistance of M. niedzwetzkyana, eight plant genotypes were inoculated with a local strain of Erwinia amylovora. The genotypes possess different genetic backgrounds, which was confirmed via SSR profiling. Four out of eight displayed moderate to severe symptoms of fire blight infection, while the three wild genotypes proved resistant. To search for the source of the resistance, the samples were tested for the presence of FBF7 QTL using SCAR markers, where seven genotypes tested positive for one of the markers (AE10-375) and one for the other (GE80-19). No correlation between resistance phenotype and FBF7 QTL was confirmed, indicating the source lies elsewhere. Developing detailed genetic and phenotypic profiles of wild apple species helps advance both the preservation efforts and marker-assisted selection in apple breeding.
1. Introduction
Southeast Kazakhstan lies in the center of origin and natural habitat of wild apples. The fruit forests of Kazakhstan contain plant material important for botany, geography, and genetics. Wild apples and their hybrids were historically utilized as a source of resistance to biotic and abiotic stress in domestic apple breeding [1,2].
Malus niedzwetzkyana Dieck ex Koehne is an endemic wild apple species featured in the Red Book of Kazakhstan and the International Red List of Endangered Species [3,4]. It naturally grows in Kazakhstan (Karatau and Zailijskei Alatau), Kyrgyzstan (Jalal-Abad region), and western China (Xinjiang region) [1,2,5,6].
Malus niedzwetzkyana is integral to the mixed fruit and nut forests in Central Asia. This species is an important genetic resource for apple breeding and developing new advantageous cultivars [7,8]. The particular value of M. niedzwetzkyana hinges on its genetic predisposition to fire blight resistance [9]. It is also an exquisite ornamental plant due to the pink color of its flowers, fruits, leaves, and trunk, which is attributed to anthocyanins. These compounds have antioxidative, anti-carcinogenic, and anti-inflammatory properties [10].
Improving domestic apple productivity and conserving global biodiversity rely on resistant genotypes whose defense mechanisms have adapted to rapidly evolving local pathogens. Higher plants evolve much slower than their parasites, especially perennial tree plants. Therefore, new sources of resistance for marker-assisted selection (MAS) are ceaselessly sought after. One of the most widespread apple diseases is fire blight, caused by a Gram-negative bacterium Erwinia amylovora. The infection enters through flowers or vegetative parts and leads to leaf and shoot necrosis, ooze droplets, wilting, and trichome development [11,12]. Three major QTLs associated with resistance to the pathogen have been identified: FBF7 on LG7 (linkage group 7) of cultivar “Fiesta”, FB_E on LG12 of “Everest”, and FB_MR5 on LG3 of Malus × robusta 5, which are considered suitable for MAS due to their stability [13,14,15,16,17]. Among them, QTL FBF7 accounted for up to 46% of the observed phenotypic variation in fire blight resistance, and resistant variants are characterized by two SCAR markers, AE10-375 and GE80-19 [14]. This QTL has previously been identified among the local apple lineages, and the positive cultivars for both markers exhibited moderate phenotypic resistance in the field [18].
This work evaluates the resistance of M. niedzwetzkyana genotypes growing in the Republic of Kazakhstan to fire blight both phenotypically via an inoculation test and molecularly using SCAR markers linked to one of the major resistance QTL (FBF7). Each sample was genotyped and introduced into a culture medium to investigate its potential for further selection and to preserve its biodiversity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
A total of eight M. niedzwetzkyana trees were identified according to the botanical description and had leaf samples collected: five samples from four populations across Astana and three specimens from a wild population inside the Tscherkesay Canyon (near Tekeli, Kazakhstan).
A collection of endangered M. niedzwetzkyana was conducted following the decision of the Council of the Eurasian Economic Commission of 26 January 2018 No. 15. “On the approval of Rules of proper practice of cultivation, collection, processing and storage of initial raw materials of plant origin”. The plant material was collected from the Djungar Alatau mountain range (Tscherkesay) by the authors acting with permission from the Forestry and Wildlife Committee and deposited at the Main Botanical Garden (AA) under ID No. 3023/20-3028/20. The specimens collected in the Astana Botanical Garden (NUR) were deposited under ID No. 536/20-552/20.
2.2. SSR Profiling
DNA was extracted from leaves using a modified CTAB protocol [19]. The quantity and quality of extracted DNA were analyzed using a spectrophotometer (NanoDrop1000, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
Twelve SSR markers were used, namely GD12, GD147, CH01h10, CH01h01, CH04c07, Hi02c07, CH01f03b, CH02d08, CH02c11, CH04e05, CH01f02, and CH02c09 [20,21,22,23]. These markers are widely applied in apple genotyping and are suggested by the European Cooperative Programme for Plant Genetic Resources (ECPGR) [24]. CH04e05, CH02c11, CH02c09, CH02d08, CH04c07, CH01h01, Hi02c07, and CH01h10 are highlighted as priority group 1 of the ECPGR marker set, whereas CH01f02, CH01f03b, GD12, and GD147 belong to priority group 2. The primer sequences, fluorescent dye, and multiplex group are described in Table A1 (Appendix A).
Amplification of each SSR marker was conducted in a 15 μL reaction mix containing a 1× DreamTaq buffer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), 0.2 мM dNTPs, 0.2 мM of each of the respective primers for each SSR marker, and 1 unit of DreamTaq polymerase (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The amplification program for each multiplex group was as follows: 94 °C for 3 min, followed by 10 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing for 90 s at 60 °C with a 1 °C decrease in temperature each cycle, and elongation at 72 °C for 60 s. The second step of 30 cycles was denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, followed by annealing at 50 °C for 90 s and further elongation at 72 °C for 60 s. Final elongation continued for 10 min at 72 °C. PCR was performed using a Mastercycler Pro S thermocycler (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). Fragment analysis was conducted using Applied Biosystems 3500 (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). SSR genotyping data were analyzed using GeneMapper™ Software 6 (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The resulting genetic profiles of eight genotypes were analyzed in GenAlEx 6.5 [25].
2.3. In Vitro Cultivation of M. niedzwetzkyana Genotypes
All collected M. niedzwetzkyana genotypes were introduced into a culture medium according to the previously developed protocol for microclonal propagation in the Laboratory of Plant Biotechnology and Selection at the National Center of Biotechnology, Astana [26]. Axillary buds from one-year-old shoots were used as source material. For each genotype, we used no less than 20 buds from different branches. The buds were subjected to aseptic treatment for 4 min using a 12% hydrogen peroxide solution, resulting in up to 80% viable sterile explants for introduction into an in vitro culture. The M. niedzwetzkyana explants were cultivated on the QL medium with the addition of 0.5 mg/L 6-BAP (6-benzylaminopurine) and 1.5 mg/L kinetin; the main shoots formed on day 50. For the multiplication of additional shoots, the explants were cultivated on a QL medium with 0.5 mg/L 6-BAP and 0.01 mg/L IBA (indole butyric acid) for 50 days. The shoots were rooted in a QL medium (half concentration) with the addition of 10 g/L sucrose and 1.5. mg/L IBA. Overall, the number of regenerants varied from 20 to 40 depending on the genotype.
2.4. Screening of a Local E. amylovora Strain
The E. amylovora isolate was obtained from a symptomatic “Golden Delicious” tree from a commercial garden growing cv. Idared, Golden Delicious, and Gala in the Almaty region, where trees of all the grown cultivars were affected by fire blight. The visible symptoms included scorching leaf necrosis, ooze droplets, and blackening of shoots. The culture was plated on a PDA (potato dextrose agar) medium. After 48 h, colonies exhibiting growth patterns similar to E. amylovora were plated onto the selective NSA (nutrient sucrose agar) medium [27,28]. Colonies that were whitish, circular, domed, smooth, and mucoid after 48 h were tested using a peer-reviewed qPCR protocol [29]. Positive samples were carried into the next steps.
To confirm the results of the morphology test and discover related strains, we attempted a whole genome sequencing of the bacterium. A log-phase cell suspension was obtained via 2-day cultivation at 28 °C in LB media and was collected via centrifugation at 5000× g for 2 min, followed by resuspension of the pellet with 2 mL sterilized distilled water [30]. DNA was extracted using the innuPREP Bacteria DNA Kit (Analytik Jena, Jena, Germany).
Library preparation was performed according to the “Ligation sequencing gDNA—whole genome amplification (SQK-LSK109)” legacy protocol from the Nanopore Community tab. DNA libraries were sequenced on a FLO-MIN106D flow cell using MinION (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Oxford, UK). The sequenced reads were subsequently run through “Fastq WIMP” analysis hosted on the Epi2ME platform (Metrichor Ltd., Oxford, UK), confirming the DNA belonging to E. amylovora. Additionally, reads were searched against the NCBI nt database via Blast+ to determine the most closely related strains [31].
2.5. E. amylovora Inoculation Test
Syringes bearing cell suspension from the previous step were inserted into locally grown pear fruits in up to 10 different surface patches. Five days later, the pathogenicity of the strain was phenotypically evaluated. The ooze accumulated inside the lesions on the infected pears from the above pathogenicity test was used as an inoculant for the apple regenerants.
Inoculation was conducted through a series of stem incisions via a sterile scalpel dipped into the ooze; the location of the incision was wrapped in paraffin film to create an anoxygenic environment for bacteria growth. Eight 5-month-old apple tree saplings were inoculated on 30 June 2021. Phenotypic fire blight responses of the regenerants were evaluated under glasshouse conditions and scored using a categorical scale of severity of infection (0 to 5) [32,33]:
- 0, no reaction;
- 1, slight trichome development, necrosis of less than 5% of leaf matter;
- 2, moderate trichome development, necrosis of up to 10% of leaf matter localized around the lesion;
- 3, moderate to severe trichome development, necrosis of up to 25% of leaf matter, necrosis progression rootward, severe wilting in adjacent leaves;
- 4, the occurrence of ooze droplets, severe witling of leaves away from the lesion, necrosis both rootward and upward, and up to 35% plant matter affected;
- 5, necrosis affecting up to 50% of leaves, several instances of ooze droplets.
2.6. FBF7 QTL Identification
We used two SCAR markers linked with FBF7 QTL, AE10-375, and GE80-19 [14] (Table 1). For each DNA sample, 60 ng DNA was amplified in a 25 µL reaction mix containing a 1× Taq buffer (750 мM Tris HCl, pH 8.8, 200 мM (NH4)2SO4, 0.1% Tween 20), 2.5 мM MgCl2, 0.2 мM dNTPs, 0.2 мM of each of the respective primers, and 1 unit Taq of polymerase (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The PCR cycling conditions for every marker are described in Table 1. The amplification results were analyzed on 1.5% agarose gel.

Table 1.
Marker, primer (F, forward and R, reverse) sequences, and PCR cycling for the amplification with SCAR markers.
3. Results
3.1. SSR Profiling
To confirm the genetic diversity of M. niedzwetzkyana genotypes, each plant was profiled using SSR markers (Figure 1). It revealed five different amplicons for markers CH01f02 and GD12 and three amplicons for markers CH01h01, CH04c07, CH02d08, and CH04e05. Four amplicons were identified for each of the remaining markers. Of particular interest is the 3-W genotype, which differs significantly in its genetic profile: it amplified unique alleles in eight SSR markers.
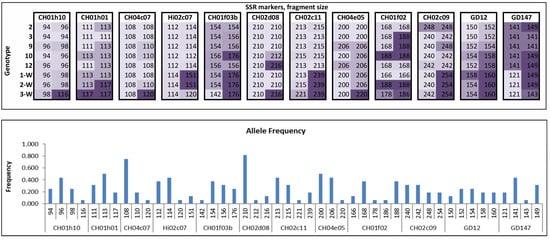
Figure 1.
SSR profiling of in vitro propagated genotypes with resistance to fire blight. Fragment sizes amplified for each marker are non-homogenous, though patterns emerge among samples with similar origins. The color of each fragment corresponds to its length: the longer the fragment, the darker its shade.
M. niedzwetzkyana genotypes were introduced into a culture medium, propagated, and adapted to ex vitro conditions for further screening and preservation (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
In vitro cultivation of M. niedzwetzkyana genotypes for conservation.
3.2. Screening of a Local E. amylovora Strain
Resistance to fire blight in apples was reported to be strain-specific; moreover, artificial inoculation of different accessions, even those belonging to one species, can lead to symptoms of varying severity [16,34]. A local strain of E. amylovora was chosen for the experiment as posing the most consistent threat to apple trees within the region, against which wild forests have evolved.
E. amylovora was isolated from a cultivated apple tree exhibiting leaf necrosis and ooze production and then plated on PDA and NSA mediums. It demonstrated steady growth on the PDA medium characterized by circular whitish colonies coalescing together (Figure 3). The colonies on the NSA medium were less prone to coalescence and appeared as whitish, circular, domed, smooth, and mucoid beads following the EPPO Standard [27].
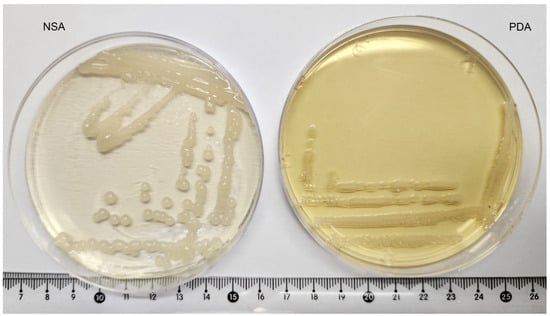
Figure 3.
Colony morphology on NSA medium (left) and PDA medium (right) after incubation at 28 °C for 48 h. Off-white, bead-like formations on NSA medium are characteristic of E. amylovora.
To confirm the results of the first positive screening and investigate the bacterium’s genetic makeup, we attempted Nanopore-based whole-genome sequencing. Over the course of sequencing, 33,285,592 bases were generated. Coverage of the chromosome was approximately 8.09 and of the plasmid 19.8; both were calculated via Samtools [35]. According to Blast+, the most frequent matches for contigs were the FN434113.1 CFBP 1430 strain [36], FN666575.1 ATCC 49,946 strain (chromosome), and HF560649.1 MR1 strain (plasmid).
3.3. E. amylovora Inoculation Test
Because ooze exuded from infected plant tissue is the primary method of dispersal for E. amylovora in vivo [37], it was chosen as the inoculant. To obtain the ooze, five pear fruits of a local susceptible cultivar, “Lesnaya krasavitsa”, were injected with the same E. amylovora cell suspension, with one pear left out as a negative control (LB medium) (Figure 4). Six days after inoculation, points of injection started excreting opaque ooze, which was then used for the inoculation of apple plantlets.
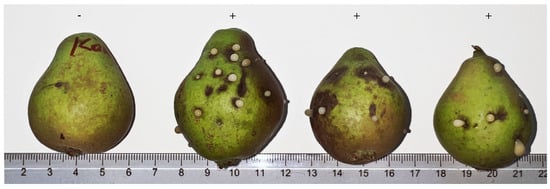
Figure 4.
Local pears 6 days after inoculation with an E. amylovora cell suspension. “-” indicates negative control (LB medium), “+”—replications of inoculation with the same strain. Whitish ooze droplets forming inside the lesions are characteristic of fire blight infection and were used for inoculation of M. niedzwetzkyana genotypes.
Results were recorded and photographed after 5 and 39 days after inoculation (dai), which can be seen in Table 2. All five apple genotypes sampled from a cultured environment exhibited mild to severe symptoms of fire blight infection, while all three wild genotypes appeared to resist the pathogen. This phenomenon is exemplified by genotypes 12 and 2-W (Figure 5). The inoculated regenerant of genotype 2-W bears no signs of infection aside from slight trichome development, and even young leaves present at the moment of inoculation were able to mature over the course of observation. On the contrary, genotype 12 was characterized by a classic fire blight infection profile, complete with the occurrence of ooze and wilting of five top leaves on the shoot.

Table 2.
Symptoms of fire blight detected in genotypes bearing resistance markers.

Figure 5.
Phenotypic response to fire blight at 0, 5, and 39 days after inoculation (dai) with E. amylovora of all collected M. niedzwetzkyana genotypes. The representative resistant genotype 2-W displays no visible signs of infection at day 5. Slight trichome development around the lesion on day 39. The representative susceptible genotype 12 has an open lesion-producing ooze by day 5. Note the white trichome visible on the shoot around the lesion. By day 39, six of the top leaves had dried out and wilted.
3.4. FBF7 QTL Identification
To search for the source of the resistance, the plants were tested for the presence of FBF7 QTL using SCAR markers AE10-375 and GE80-19 [13,14,38]. This QTL has previously been identified among the local apple lineages and the cultivars, a few of which originated from wild apple species [18].
The resistant alleles of markers AE10-375 and GE80-19 are characterized by amplicons of 375 bp and 397 bp, respectively [13,14]. Seven genotypes tested positive for AE10-375 (Table 2), and only the 3-W genotype from the wild forest in the Tscherkesay Canyon amplified GE80-19 (Figure 6). The plants amplifying both markers had been previously characterized with higher resistance to the pathogen compared with the genotypes bearing only the resistance allele for one of the two markers [14].
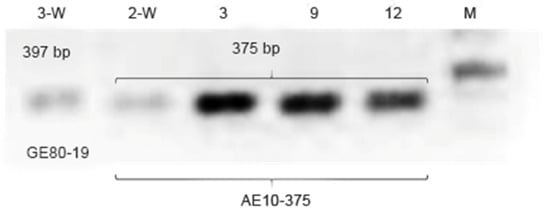
Figure 6.
Analysis of M. niedzwetzkyana genotypes using SCAR markers AE10-375 and GE80-19. For fire blight resistance, the key alleles are 397 bp (GE80-19) and 375 bp (AE10-375) long. See also Supplementary File S1 for the original full-size images.
4. Discussion
Wild plants are an important source of genetic material for marker-assisted selection (MAS), aiming to improve crops’ resistance to pathogens [39]. One of the ways to prevent infection is the introgression of strong resistance factors originating from wild species [40]. For example, involving wild apple trees in the breeding of Golden Delicious made it possible to intensify the world’s apple production more than twofold over 25 years [41]. Therefore, conservation and rational use of wild plants are integral for germplasm biodiversity and thriving agroindustry [42].
Wild apple, apricot, and walnut forests are indigenous to Central Asia [41]. The species forming these communities are classified as endangered and require protection [3]. However, up to 70% of apple forests have suffered habitat degradation over the past 40 years. Wild apple forest recultivation is the main priority of the country’s wild flora conservation program, which requires fundamental research of their genomics. To date, no wide-scale studies of M. niedzwetzkyana genomics have been conducted, neither in Kazakhstan nor elsewhere.
In the present study, four out of eight plant genotypes showed moderate to severe susceptibility to fire blight infection, while the three wild genotypes 1-W, 2-W, and 3-W proved to be resistant. Phenotypic expression was evaluated based on an inoculation test, which revealed that the presence of any of the two markers of FBF7 does not correlate with a tangible resistance profile. The fact that all the domesticated genotypes displayed varied levels of susceptibility, while the wild population was characterized by a lack of symptoms, suggests that the wild M. niedzwetzkyana population from the Tscherkesay Canyon possesses resistance traits not covered by FBF7. Indeed, major QTLs associated with resistance to fire blight originating from wild species have been described in linkage groups LG3 [16,34], LG10 [43,44], and LG12 [15]. However, only FBF7 has been found among the local Kazakhstani apple varieties, many of which are derived from various wild apples growing in the vicinity, such as M. sieversii and M. niedzwetzkyana [18]. On the contrary, when the same cultivars were tested for FB_E and FB_MR5 via SNP-genotyping, all markers appeared monomorphic [45].
In the case of 3-W, it tested positive for the GE80-19 marker and lacked AE10-375, which others shared. We could not detect any measurable difference in its infection response from the other wild regenerants. However, the origin of GE80-19-SCAR and AE10-375-SCAR as markers for commercial apples [13] may explain the reduced specificity when applied to a wild Malus species.
SSR analysis confirmed the genetic individuality of the specimens bearing fire blight resistance markers. Previously, three genotypes of M. niedzwetzkyana from the Krutoye tract (Kazakhstan) were fingerprinted using 16 microsatellite markers and clustered together with M. sieversii [46]. Previously, investigations of fire blight resistance in M. sieversii revealed accessions with a high degree of resistance, although the overall percentage of resistant individuals was low [47,48]. In this study, for the first time, three M. niedzwetzkyana specimens proved the resistance phenotypically in the inoculation test.
Tscherkesay Canyon genotypes represent a prospective genetic pool for the breeding of new cultivars bearing loci associated with resistance to fire blight. The results of the work would help to preserve the important genetic material of endangered M. niedzwetzkyana species and would assist its further use in apple breeding, conservation, and revival of wild apple populations.
5. Conclusions
In the present work, the fire blight resistance of the eight genotypes of M. niedzwetzkyana from different populations was investigated using genetic SCAR markers and an inoculation test. While all of the specimens bore either AE10-375 or GE80-19, their phenotypic reaction to E. amylovora differed dramatically, suggesting a new avenue should be pursued in search of the origin of its resistance, such as a cross with a known susceptible background, generating a population to investigate the genetic control of the resistant accessions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae9101066/s1. Supplementary File S1: The original image of the electrophoretic gel featured in Figure 6.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: D.G.; methodology—A.N. and D.D.; formal analysis—A.K. (Anastasiya Kapytina); investigation: G.N. and A.T.; writing—original draft preparation: A.N. and M.K. (Mariya Kolchenko); writing—review and editing: M.K. (Mariya Kolchenko) and D.G.; resources: A.K. (Almagul Kakimzhanova); software: A.P.; data curation: M.K. (Marina Knusnitdinova); funding acquisition: D.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan, AP14871004 “Investigation of phytopathological and botanical aspects of wild apple populations growing in the Northern Tien Shan” 2022–2024 and 0.0809 “Creation of a biobank of microorganisms, cell cultures, genomic, and genetically engineered materials to preserve biodiversity and provide a resource base for biotechnology”.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is available in the Open Science Foundation repository: https://osf.io/dz5gf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Astana Botanical Garden and the Forestry and Wildlife Committee of the Ministry of Ecology, Geology, and Natural Resources of the Republic of Kazakhstan for supporting the collection of plant materials for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Sequences of primers (F—forward, R—reverse), fluorescent dye type, linkage group (LG), and multiplex group numbers for SSR genotyping [24].
Table A1.
Sequences of primers (F—forward, R—reverse), fluorescent dye type, linkage group (LG), and multiplex group numbers for SSR genotyping [24].
| Marker | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Fluorescent Dye | Linkage Group | Multiplex Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GD12 | F-TTGAGGTGTTTCTCCCATTGGA R-CTAACGAAGCCGCCATTTCTTT | TAMRA | 3 | III |
| GD147 | F-TCCCGCCATTTCTCTGC R-GTTTAAACCGCTGCTGCTGAAC | ATTO565 | 13 | III |
| CH01h10 | F-TGCAAAGATAGGTAGATATATGCCA R-AGGAGGGATTGTTTGTGCAC | HEX | 8 | II |
| CH01h01 | F-GAAAGACTTGCAGTGGGAGC R-GGAGTGGGTTTGAGAAGGTT | TAMRA | 17 | II |
| CH04c07 | F-GGCCTTCCATGTCTCAGAAG R-CCTCATGCCCTCCACTAACA | 6-FAM | 14 | II |
| Hi02c07 | F-AGAGCTACGGGGATCCAAAT R-GTTTAAGCATCCCGATTGAAAGG | ATTO565 | 1 | II |
| CH01f03b | F-GAGAAGCAAATGCAAAAC CC R-CTCCCCGGCTCCTATTCTAC | HEX | 9 | III |
| CH02d08 | F-TCCAAAATGGCGTACCTCTC R-GCAGACACTCACTCACTATCTCTC | HEX | 11 | I |
| CH02c11 | F-TGAAGGCAATCACTCTGTGC R-TTCCGAGAATCCTCTTCGAC | TAMRA | 10 | I |
| CH04e05 | F-AGGCTAACAGAAATGTGGTTTG R-ATGGCTCCTATTGCCATCAT | 6-FAM | 7 | I |
| CH01f02 | F-ACCACATTAGAGCAGTTGAGG R-CTGGTTTGTTTTCCTCCAGC | 6-FAM | 12 | III |
| CH02c09 | F-TTATGTACCAACTTTGCTAACCTC R-AGAAGCAGCAGAGGAGGATG | ATTO565 | 15 | I |
References
- Janick, J. Wild Apple and Fruit Trees of Central Asia. In Horticultural Reviews; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 29, p. 416. ISBN 978-0-47065-086-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, B.; Mills, M.; Kulikov, M.; Clubbe, C. The Future of Walnut–Fruit Forests in Kyrgyzstan and the Status of the Iconic Endangered Apple Malus niedzwetzkyana. Oryx 2019, 53, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, A.; Lazkov, G.; Newton, A.C. The Red List of Trees of Central Asia; Fauna and Flora International: Cambridge, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-1-90370-327-4. [Google Scholar]
- The Red Data Book of the Republic of Kazakhstan, 4th ed.; DPS: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 2010; Volume 2, ISBN 9-96-532738-6.
- Ji, X.-H.; Wang, Y.-T.; Zhang, R.; Wu, S.-J.; An, M.-M.; Li, M.; Wang, C.-Z.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Chen, X.-S. Effect of Auxin, Cytokinin and Nitrogen on Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Callus Cultures of Red-Fleshed Apple (Malus sieversii f. niedzwetzkyana). Plant Cell Tiss. Organ. Cult. 2015, 120, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Long, H.; Song, W.; Chen, R. Genetic Polymorphism of Malus sieversii Populations in Xinjiang, China. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2008, 55, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.A.; Robinson, J.P.; Juniper, B.E. Genetic Clues to the Origin of the Apple. Trends Genet. 2002, 18, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omasheva, M.E.; Chekalin, S.V.; Galiakparov, N.N. Evaluation of Molecular Genetic Diversity of Wild Apple Malus sieversii Populations from Zailiysky Alatau by Microsatellite Markers. Russ. J. Genet. 2015, 51, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Che, S.; Zhang, Y.; Song, W.; Yan, G.; Yu, W. Malus niedzwetzkyana (Dieck) Langenf Transcriptome Comparison and Phylogenetic Analysis with Malus sieversii (Ledeb) Roem. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2020, 67, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Malus sieversii: The Origin, Flavonoid Synthesis Mechanism, and Breeding of Red-Skinned and Red-Fleshed Apples. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flachowsky, H.; Szankowski, I.; Fischer, T.C.; Richter, K.; Peil, A.; Höfer, M.; Dörschel, C.; Schmoock, S.; Gau, A.E.; Halbwirth, H.; et al. Transgenic Apple Plants Overexpressing the Lc Gene of Maize Show an Altered Growth Habit and Increased Resistance to Apple Scab and Fire Blight. Planta 2010, 231, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.-S.; Beer, S.V. Molecular Genetics of Erwinia amylovora Involved in the Development of Fire Blight. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 253, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calenge, F.; Drouet, D.; Denancé, C.; Van de Weg, W.E.; Brisset, M.-N.; Paulin, J.-P.; Durel, C.-E. Identification of a Major QTL Together with Several Minor Additive or Epistatic QTLs for Resistance to Fire Blight in Apple in Two Related Progenies. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Durel, C.-E.; Duffy, B.; Drouet, D.; Kellerhals, M.; Gessler, C.; Patocchi, A. Development of Molecular Markers Linked to the ‘Fiesta’ Linkage Group 7 Major QTL for Fire Blight Resistance and Their Application for Marker-Assisted Selection. Genome 2007, 50, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durel, C.-E.; Denancé, C.; Brisset, M.-N. Two Distinct Major QTL for Resistance to Fire Blight Co-Localize on Linkage Group 12 in Apple Genotypes “Evereste” and Malus Floribunda Clone 821. Genome 2009, 52, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peil, A.; Emeriewen, O.F.; Khan, A.; Kostick, S.; Malnoy, M. Status of Fire Blight Resistance Breeding in Malus. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 103, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, D.; Békefi, Z.; Balotai, B.; Tóth, M. Identification of Marker Alleles Linked to Fire Blight Resistance QTLs in Apple Genotypes. Plant Breed. 2015, 134, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omasheva, M.Y.; Pozharskiy, A.S.; Maulenbay, A.D.; Ryabushkina, N.A.; Galiakparov, N.N. SSR Genotyping of Kazakhstani Apple Varieties: Identification of Alleles Associated with Resistance to Highly Destructive Pathogens. Eurasian J. Appl. Biotechnol. 2016, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amraee, L.; Rahmani, F. Modified CTAB Protocol for RNA Extraction from Lemon Balm (Melissa officinalis L.). Acta Agric. Slov. 2020, 115, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmat, M.; Weeden, N.F.; Brown, S.K. Mapping and Evaluation of Malus × domestica Microsatellites in Apple and Pear. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2003, 128, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokanson, S.C.; Szewc-McFadden, A.K.; Lamboy, W.F.; McFerson, J.R. Microsatellite (SSR) Markers Reveal Genetic Identities, Genetic Diversity and Relationships in a Malus × domestica Borkh. Core Subset Collection. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1998, 97, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebhard, R.; Gianfranceschi, L.; Koller, B.; Ryder, C.D.; Tarchini, R.; Van De Weg, E.; Gessler, C. Development and Characterisation of 140 New Microsatellites in Apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Mol. Breed. 2002, 10, 217–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, C.M.; Volk, G.M.; Reilley, A.A.; Henk, A.D.; Lockwood, D.R.; Reeves, P.A.; Forsline, P.L. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure in Malus sieversii, a Wild Progenitor Species of Domesticated Apple. Tree Genet. Genomes 2009, 5, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, F. Common Set of ECPGR SSR Markers for Malus Characterization; Bioversity International: Weggis, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic Analysis in Excel. Population Genetic Software for Teaching and Research—An Update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurtaza, A.; Magzumova, G.; Yessimseitova, A.; Karimova, V.; Shevtsov, A.; Silayev, D.; Lutsay, V.; Ramankulov, Y.; Kakimzhanova, A. Micropropagation of the Endangered Species Malus niedzwetzkyana for Conservation Biodiversity in Kazakhstan. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2021, 57, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PM 7/20 (3) Erwinia amylovora. EPPO Bull. 2022, 52, 198–224. [CrossRef]
- Schaad, N.W.; Jones, J.B.; Chun, W. Laboratory Guide for the Identification of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria, 3rd ed.; American Phytopathological Society (APS Press): St Paul, MI, USA, 2001; ISBN 0-89-054263-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gottsberger, R.A. Development and Evaluation of a Real-time PCR Assay Targeting Chromosomal DNA of Erwinia amylovora. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lima, J.E.O.; Miranda, V.S.; Hartung, J.S.; Brlansky, R.H.; Coutinho, A.; Roberto, S.R.; Carlos, E.F. Coffee Leaf Scorch Bacterium: Axenic Culture, Pathogenicity, and Comparison with Xylella fastidiosa of Citrus. Plant Dis. 1998, 82, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cock, P.J.A.; Chilton, J.M.; Grüning, B.; Johnson, J.E.; Soranzo, N. NCBI BLAST+ Integrated into Galaxy. GigaScience 2015, 4, s13742-015-0080-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrefiga, J.; Montesinos, E. Lysozyme Enhances the Bactericidal Effect of BP100 Peptide against Erwinia amylovora, the Causal Agent of Fire Blight of Rosaceous Plants. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.J.; Sario, S.; Luz, J.P.; Tassi, N.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, P.; Tavares, F.; Santos, C. Evaluation of Three Antimicrobial Peptides Mixtures to Control the Phytopathogen Responsible for Fire Blight Disease. Plants 2021, 10, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peil, A.; Bus, V.G.M.; Geider, K.; Richter, K.; Flachowsky, H.; Hanke, M.-V. Improvement of Fire Blight Resistance in Apple and Pear. Int. J. Plant Breed. 2009, 3, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M. Twelve Years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, T.H.M.; Rezzonico, F.; Kamber, T.; Blom, J.; Goesmann, A.; Frey, J.E.; Duffy, B. Complete Genome Sequence of the Fire Blight Pathogen Erwinia Amylovora CFBP 1430 and Comparison to Other Erwinia Spp. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2010, 23, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slack, S.M.; Zeng, Q.; Outwater, C.A.; Sundin, G.W. Microbiological Examination of Erwinia amylovora Exopolysaccharide Ooze. Phytopathology 2017, 107, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Duffy, B.; Gessler, C.; Patocchi, A. QTL Mapping of Fire Blight Resistance in Apple. Mol. Breed. 2006, 17, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauzin, E. The Role of Wild Fruit Species in the Development of Modern Horticulture and the Experience of Preserving Their Gene Pool; DPS: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bus, V.; Brewer, L.; Morgan, C. Observations on Scab Resistance in Interspecific Pear Seedling Families. Acta Hortic. 2013, 976, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksanyan, S.; Ponomarenko, V.; Burmistrov, L.; Smekalova, T.; Sorokin, A. Modern Methods and International Experience of Preserving the Gene Pool of Wild Plants (on the Example of Wild Fruits); United Nations Development Program in Kazakhstan: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 2011; ISBN 978-6-01703-220-3. [Google Scholar]
- Vitkovsky, V. Fruit Plants of the World; Lan’: Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Emeriewen, O.; Richter, K.; Kilian, A.; Zini, E.; Hanke, M.-V.; Malnoy, M.; Peil, A. Identification of a Major Quantitative Trait Locus for Resistance to Fire Blight in the Wild Apple Species Malusfusca. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeriewen, O.F.; Richter, K.; Berner, T.; Keilwagen, J.; Schnable, P.S.; Malnoy, M.; Peil, A. Construction of a Dense Genetic Map of the Malus Fusca Fire Blight Resistant Accession MAL0045 Using Tunable Genotyping-by-Sequencing SNPs and Microsatellites. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairova, G.; Daulet, N.; Solomadin, M.; Sandybayev, N.; Orkara, S.; Beloussov, V.; Kerimbek, N.; Gritsenko, D.; Sapakhova, Z. Identification of Apple Varieties Resistant to Fire Blight (Erwinia amylovora) Using Molecular Markers. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omasheva, M.Y.; Flachowsky, H.; Ryabushkina, N.A.; Pozharskiy, A.S.; Galiakparov, N.N.; Hanke, M.-V. To what extent do wild apples in Kazakhstan retain their genetic integrity? Tree Genet. Genomes 2017, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, I.O.; Patocchi, A.; Franck, L.; Kellerhals, M.; Broggini, G.A.L. Fire Blight Resistance from “Evereste” and Malus sieversii Used in Breeding for New High Quality Apple Cultivars: Strategies and Results. Acta Hortic. 2011, 896, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshman, J.M.; Evans, K.M.; Allen, H.; Potts, R.; Flamenco, J.; Aldwinckle, H.S.; Wisniewski, M.E.; Norelli, J.L. Fire Blight Resistance in Wild Accessions of Malus sieversii. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).