First Report of Nigrospora Species Causing Leaf Spot on Olive (Olea europaea L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
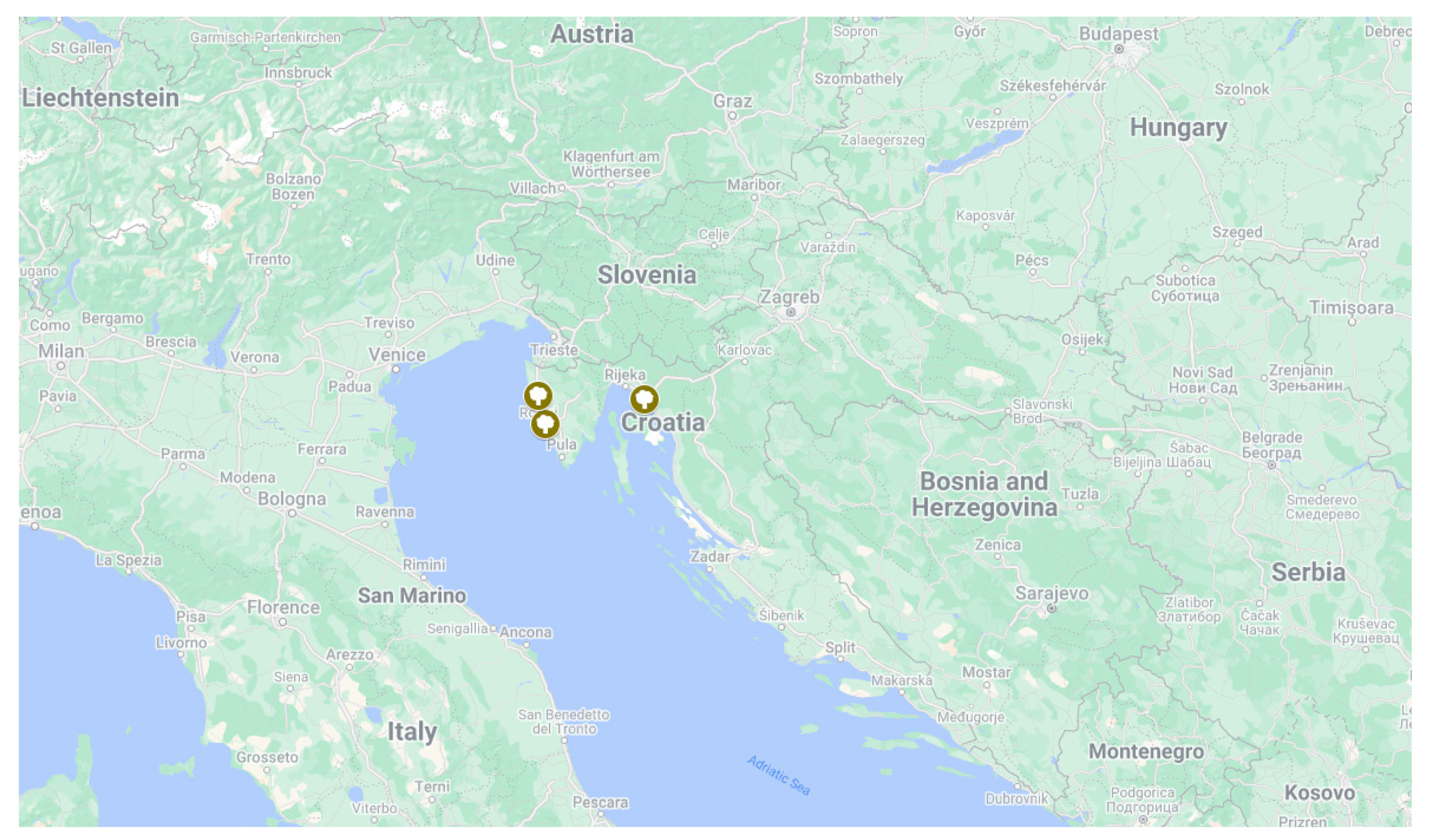
2.1. Collection of Plant Materials and Fungal Isolations
2.2. Morphological Characterization
2.3. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
2.4. DNA Sequence Assembly and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Pathogenicity Test
2.5.1. Pathogenicity Test on Detached Leaves and Scratched Detached Leaves
2.5.2. Pathogenicity Test on Olive Seedlings
3. Results
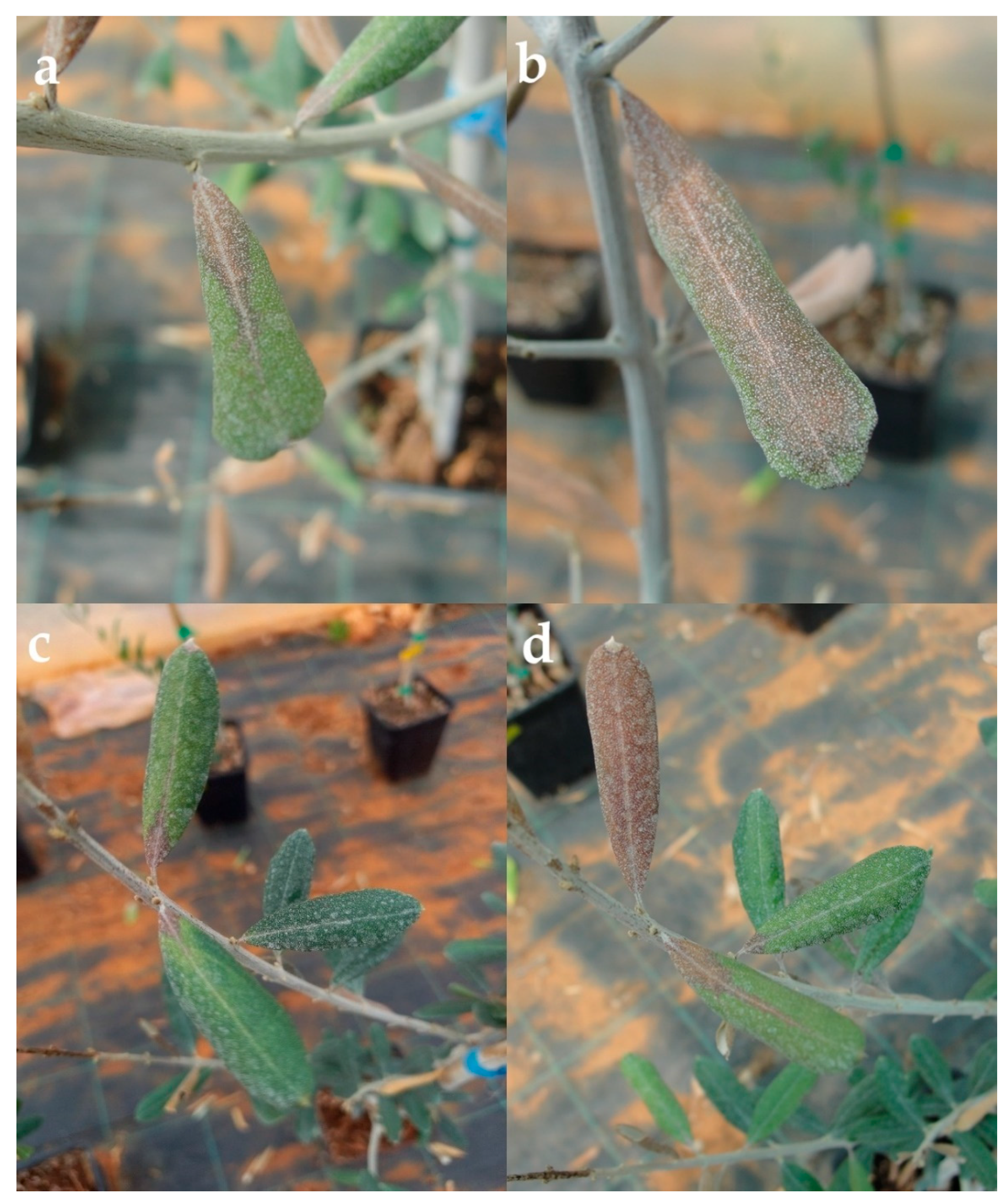
3.1. Field Survey and Disease Symptoms
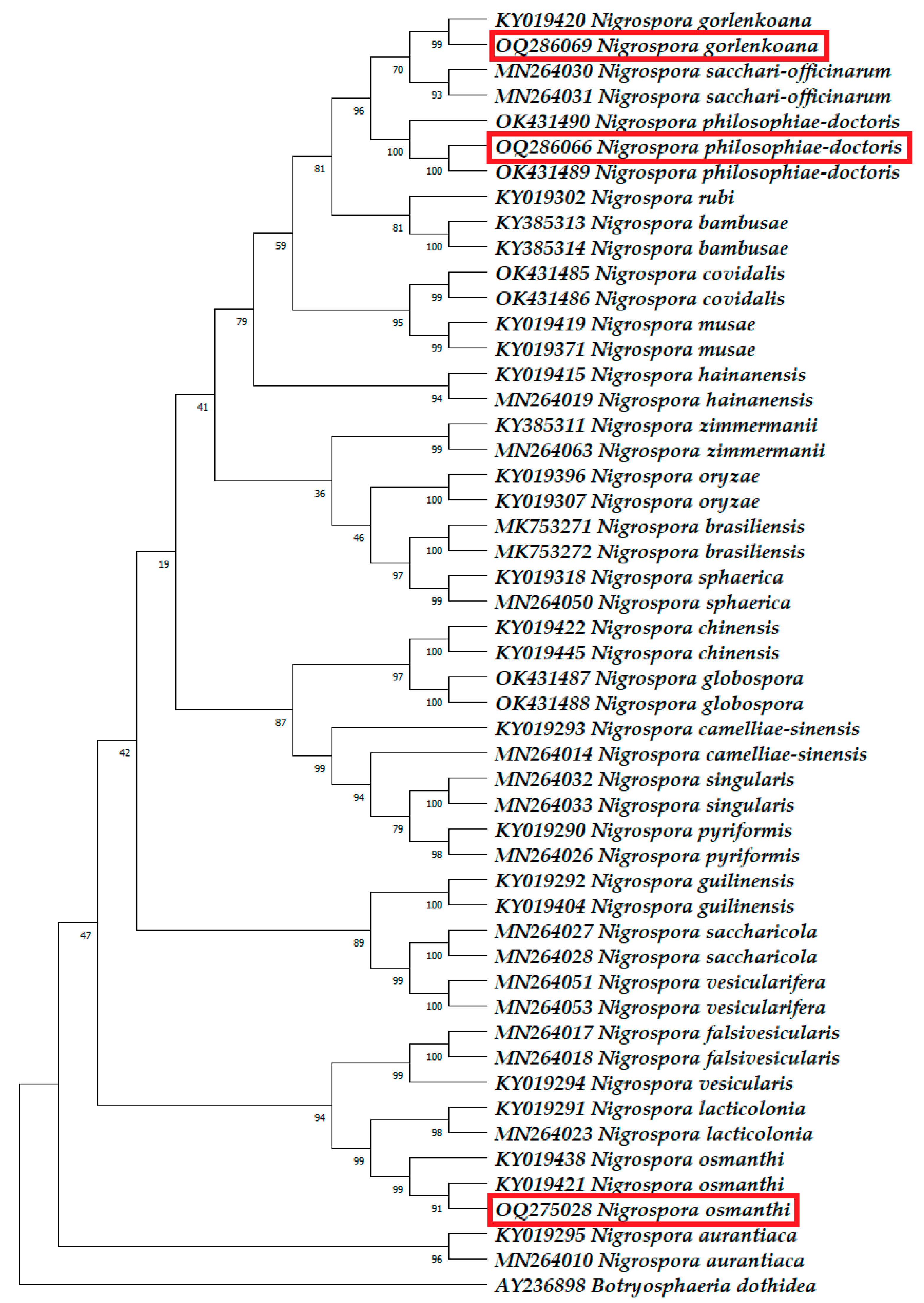
3.2. Molecular Phylogenetic Identification
3.3. Morphological Characterization and Fungal Incidence
3.3.1. Nigrospora gorlenkoana
3.3.2. Nigrospora osmanthi
3.3.3. Nigrospora philosophiae-doctoris
3.4. Pathogenicity Tests
3.4.1. Pathogenicity Test on Detached Leaves
3.4.2. Pathogenicity Test on Olive Seedlings
4. Discussion
| SPECIES | HOST (Common Name) | TAXONOMY ID | DISEASE SYMPTOMS | DISTRIBUTION | REFERENCES |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nigrospora aurantiaca | Chinese chestnut | Castanea mollissima Blume | Leaf spot | China | [62] |
| Pandan rampeh | Pandanus amaryllifolius Roxb. | Leaf spot | Malaysia | [63] | |
| Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum L. | Leaf spot | China | [30] | |
| Tobacco | Nicotiana tabacum L. | Leaf spot | China | [64] | |
| Nigrospora brasiliensis | Cochineal cactus | Nopalea cochenillifera (L.) Salm-Dyck | Brown leaf spot | Brazil | [31] |
| Nigrospora camelliae-sinensis | Black tea | Camellia sinensis L. | Leaf blight | China | [65] |
| Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum L. | Leaf spot | China | [30] | |
| Nigrospora chiensis | Tea-oil plant | Camellia oleifera C. Abel | Leaf blight | China | [66] |
| Nigrospora falsivesicularis | Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum L. | Leaf spot | China | [30] |
| Nigrospora guiliensis | Chinese corktree | Phellodendron chinense C. K. Schneid. | Leaf spot | China | [67] |
| Nigrospora hainanensis | Cochineal cactus | Nopalea cochenillifera (L.) Salm-Dyck | Brown spot | Brazil | [68] |
| Pink wood sorrel | Oxalis corymbosa DC. | Leaf spot | China | [69] | |
| Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum L. | Leaf spot | China | [30] | |
| Nigrospora lacticolonia | Date palm | Phoenix dactylifera L. | Leaf spot | Oman | [70] |
| Dragon fruit | Hylocereus polyrhizus (F.A.C.Weber) Britton & Rose | Reddish-brown spot | Malaysia | [71] | |
| Great Bougainvillea | Bougainvillea spectabilis Raeusch. Willd. | Leaf spot | China | [72] | |
| Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum L. | Leaf spot | China | [30] | |
| Nigrospora oryzae | Aloe-vera | Aloe vera var. chinensis (Haw.) A.Berger | Leaf spot | China | [73] |
| Leaf spot | Pakistan | [74] | |||
| Leaf spot | Bangladesh | [75] | |||
| Asiatic dayflower | Commelina communis L. | Leaf spot | China | [76] | |
| Bayberry | Morella rubra Lour. | Twig blight | China | [53] | |
| Blueberry | Vaccinium corymbosum L. | Leaf spot | China | [77] | |
| Chinese photinia | Photinia serratifolia (Desf.) Kalkman (syn. Photinia serrulata Lindl.) | Leaf spot | China | [78] | |
| Cotton | Gossypium hirsutum L. | Leaf spot | China | [79] | |
| Cotton-rose | Hibiscus mutabilis Mill. | Black leaf spot | China | [80] | |
| Crepe-ginger | Hellenia speciosa (J.Koenig) Govaerts (syn. Costus speciosus (J.Koenig) Sm.) | Leaf spot | China | [36] | |
| Dendrobium (Shi Hu) | Dendrobium candidum Wall. ex Lindl. | Leaf spot | China | [81] | |
| Dove tree | Davidia involucrata Baill. | Leaf blight | China | [82] | |
| Dryland winter wheat | Triticum L. | Crown and rot root | Azerbaijan | [83] | |
| Giant red | Arundo donax L. | Foliar and cane rot | Europe | [84] | |
| Ginger | Zingiber officinale Roscoe | Leaf spot | China | [85] | |
| Indian lotus | Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. | Leaf spot | China | [86] | |
| Indian mustard | Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. | Stem blight | India | [87] | |
| Kentucky bluegrass | Poa pratensis L. | Leaf spot | Ontario | [88] | |
| Kidney bean | Phaseolus vulgaris L. | Leaf spot | China | [89] | |
| Kiwifruit | Actinidia deliciosa (A.Chev.) C.F.Liang & A.R.Ferguson | Brown/black spot | China | [90] | |
| Million bells | Calibrachoa hybrid cultivar | Leaf spot | Argentina | [91] | |
| Pearl millet | Cenchrus americanus (L.) Morrone (syn. Pennisetum americanum (L.) Leeke) | Leaf spot | Iran | [92] | |
| Peppermint | Mentha spicata L. | Brown leaf spot | Iran | [93] | |
| Poplar | Populus alba L. × P. berolinensis Dipp. (hybrid poplar) | Leaf blight | China | [94] | |
| Rice | Oryza sativa L. | Sheaths and grains of sheath rot | Bangladesh | [95] | |
| Tobacco | Nicotiana tabacum L. | Leaf spot | China | [96] | |
| Watermelon | Citrullus lanatus (Thunb.) Matsum. & Nakai | Leaf spot | China | [97] | |
| Wheat | Triticum aestivum Vill. | Dark brown to black lesions | Kazahstan | [98] | |
| Crown and root rot | Kazahstan | [99] | |||
| Wild rice | Oryza rufipogon Griff. | Leaf spot | China | [100] | |
| Zebra leaf aloe | Aloe zebrina Baker | Flower malformation | Namibia | [101] | |
| Nigrospora osmanthi | Fiddle-leaf fig | Ficus pandurata Hance | Leaf blight | China | [102] |
| Java tea | Orthosiphon stamineus Benth. | Leaf blight | Malaysia | [103] | |
| St. Augustine grass | Stenotaphrum secundatum (Walter) Kuntze | Leaf blight | China | [104] | |
| Tartary buckwheat | Fagopyrum tataricum (L.) Gaertn. | Leaf spot | China | [105] | |
| Nigrospora panici | Big marigold | Tagetes erecta L. | Leaf blight | Bangladesh | [106] |
| French marigold | Tagetes patula L. | Leaf blight | Bangladesh | [106] | |
| Nigrospora pyriformis | Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum L. | Leaf spot | China | [30] |
| White goosefoot | Chenopodium album L. | Leaf spot | China | [107] | |
| Nigrospora sacchari-officinarum | Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum L. | Leaf spot | China | [30] |
| Nigrospora saccharicola | Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum L. | Leaf spot | China | [30] |
| Nigrospora singularis | Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum L. | Leaf spot | China | [30] |
| Nigrospora sp. | Black tea | Camellia sinensis L. | Blister blight lesions | India | [108] |
| Cochineal cactus | Nopalea cochenillifera (L.) Salm-Dyck | Brown spot | Brazil | [68] | |
| Maize | Zea mays L. | Weight/discoloration/necrosis of grains | Brazil | [109] | |
| Nigrospora sphaerica | Balloon flower | Platycodon grandiflorus (Jacq.) A. DC. | Necrosis | China | [28] |
| Black tea | Camellia sinensis L. | Leaf blight | India | [110] | |
| China | [111] | ||||
| Blueberry | Vaccinium corymbosum L. | Leaf spot, twig and shoot blight | Argentina | [112] | |
| Calabash | Lagenaria siceraria (Molina) Standl. | Leaf spot | Georgia | [113] | |
| China fir | Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook. | Leaf blight | China | [114] | |
| Chinese Wisteria | Wisteria sinensis (Sims) DC., 1825 | Leaf spot | Turkey | [115] | |
| Cochineal cactus | Nopalea cochenillifera (L.) Salm-Dyck | Brown spot | Brazil | [68] | |
| Corn mint | Mentha canadensis L. | Leaf blight | China | [116] | |
| Cowpea | Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. | Leaf spot | India | [117] | |
| Curcuma | Curcuma wenyujin Y.H.Chen & C.Ling | Leaf blight | China | [118] | |
| Date palm | Phoenix dactylifera L. | Not applicable | Iraq | [119] | |
| Root disease | Oman | [120] | |||
| Leaf spot | Pakistan | [121] | |||
| Devilpepper | Rauvolfia serpentina (L.) Benth. ex Kurz | Leaf spot and antracnose | Bangladesh | [122] | |
| Dragon fruit | Selenicereus monacanthus (hort. ex Lem.) D.R.Hunt (syn. Hylocereus polyrhizus (F.A.C.Weber) Britton & Rose) | Reddish-brown spot | Malaysia | [71] | |
| Dragon fruit (pitaya) | Selenicereus undatus (Haw.) D.R.Hunt (syn. Hylocereus undatus (Haw.) Britton & Rose) | Reddish-brown spot | Philippines | [123] | |
| Reddish-brown spot | China | [124] | |||
| Elephant grass | Cenchrus purpureus (Schumach.) Morrone | Leaf blight | China | [125] | |
| European nettle tree | Celtis australis L., 1753 | Leaf spot | India | [126] | |
| False Daisy | Eclipta prostrata (L.) L. | Leaf spot | China | [127] | |
| Kinnow mandarin | hybrid: Citrus nobilis Lour. × Citrus deliciosa Ten. | Leaf spot | Pakistan | [128] | |
| Kiwifruit | Actinidia deliciosa (A. Chev.) C.F.Liang & A.R.Ferguson | Leaf spot | China | [129] | |
| Liqourice | Glycyrrhiza glabra L. | Leaf spot | India | [130] | |
| Mango | Mangifera indica L. | Leaf spot | India | [131] | |
| Twig dieback and leaf spot | Egypt | [132] | |||
| Moonlight cactus | Selenicereus monacanthus (hort. ex Lem.) D.R.Hunt (syn. Hylocereus monacanthus (hort. ex Lem.) Britton & Rose) | Reddish-brown spot | Philippines | [123] | |
| Mulberry | Morus alba Hort. ex Loudon L | Shot hole | China | [133] | |
| India | [134] | ||||
| Passion fruit | Passiflora edulis Sims | Leaf blight | China | [135] | |
| Peanut | Arachis hypogaea L. | Leaf blight | China | [136] | |
| Pitaya | Selenicereus megalanthus (K.Schum. ex Vaupel) Moran (syn. Hylocereus megalanthus (K.Schum. ex Vaupel) Ralf Bauer) | Reddish-brown spot | Philippines | [123] | |
| Purging nut | Jatropha curcas L. | Necrosis, chlorosis | India | [137] | |
| Qing qian liu | Cyclocarya paliurus (Batalin) Iljinsk. | Leaf blight | China | [138] | |
| Sesame | Sesamum indicum L. | Leaf blight | China | [139] | |
| Leaf blight | Pakistan | [140] | |||
| Sugarcane | Saccharum spp. | Leaf blight | China | [141] | |
| Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum L. | Leaf spot | China | [30] | |
| Three-leaf Akebia | Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. | Dried-shrink fruit | China | [142] | |
| Tea-oil plant | Camellia oleifera C. Abel | Leaf blight | China | [143] | |
| Watermelon (wild melon) | Citrullus lanatus (Thunb.) Matsum. & Nakai | Leaf spot | Malaysia | [144] | |
| White moho | Heliocarpus americanus L. | Leaf spot | Brazil | [145] | |
| Nigrospora vesicularifera | Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum L. | Leaf spot | China | [30] |
| Nigrospora zimmermani | Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum L. | Leaf spot | China | [30] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Crop and Livestock Products. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Land & Water. Available online: https://www.fao.org/land-water/databases-and-software/crop-information/olive/en/ (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Varanda, C.M.R.; Materatski, P.; Landum, M.; Campos, M.D.; Rosário Fėlix, M.D. Fungal communities associated with peacock and cercospora leaf spots in olive. Plants 2019, 8, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueres, G. Repilos del Olivo: Ataque en Fruto; Phytoma España: Valencia, Spain, 1991; pp. 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Civantes, M. Olive Pest and Disease Management; IOCC: Towson, MD, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Benitez, Y.; Botella, M.A.; Trapero, A.; Alsalimiya, M.; Caballero, J.L.; Dorado, G.; Muñoz-Blanco, J. Molecular analysis of the interaction between Olea europaea and the biographic fungus Spilocaea oleagina. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2005, 6, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obanor, F.; Jaspers, M.; Jones, E.E.; Walter, M. Greenhouse and field evaluation of fungicides for control of olive leaf spot in New Zealand. Crop Prot. 2008, 27, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei, S.; Razav, S. Survey of Spilocaea oleagina, causal agent of olive leaf spot, in North of Iran. J. Yeast Fungal Res. 2011, 2, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basim, E.; Basim, H.; Abdulai, M.; Baki, D.; Ozturk, N. Identification and characterization of Alternaria alternata causing leaf spot of olive tree (Olea europaea) in Turkey. Crop Prot. 2017, 92, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeeva, V.; Spooner-Hart, R.; Nair, N.G. First report of Colletotrichum acutatum and C. gloeosporioides causing leaf spots of olives (Olea europaea) in Australia. Australas. Plant Dis. Notes 2008, 3, 143–144. [Google Scholar]
- Trouillas, F.P.; Nouri, M.T.; Lawrence, D.P.; Moral, J.; Travadon, R.; Aegerter, B.J.; Lightle, D. Identification and Characterization of Neofabraea kienholzii and Phlyctema vagabunda Causing Leaf and Shoot Lesions of Olive in California. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 3018–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A. Ueber einige an tropischen Kulturpfianzen beobachtete Pilze III. Zentralblatt Bakteriol. Parasitenkd. 1992, 8, 216–221. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, H.L.; Hunter, B.B. Illustrated Genera of Imperfect Fungi, 4th ed.; APS Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, P.M.; Cannon, P.F.; Minter, D.W.; Stalpers, J.A. Dictionary of the Fungi. Mycol. Res. 2008, 113, 908–910. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, F.; Crous, P.W.; Cai, L. Phylogenetic reassessment of Nigrospora: Ubiquitous endophytes, plant and human pathogens. Persoonia 2017, 39, 118–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, K.D.; Norphanphoun, C.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Bhat, D.J.; Jones, E.B.G.; Bundhun, D.; Chen, Y.J.; Bao, D.F.; Boonmee, S.; Calabon, M.S.; et al. Refiend families of Sordariomycetes. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 305–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MycoBank Database. Available online: https://www.mycobank.org/Basic%20names%20search (accessed on 18 September 2023).
- Fisher, P.J.; Petrini, O.; Petrini, L.E.; Descals, E. A preliminary study of fungi inhabiting xylem and whole stems of Olea europaea. Sydowia 1992, 44, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Landum, M.C.; Félix, M.d.R.; Alho, J.; Garcia, R.; Cabrita, M.J.; Rei, F.; Varanda, C.M. Antagonistic activity of fungi of Olea europaea L. against Colletotrichum acutatum. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 183, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.-Y.; Qi, Y.-L.; Cai, L. Induction of sporulation in plant pathogenic fungi. Mycology 2012, 3, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Kindo, A.J.; Tupaki-Sreepurna, A.; Yuvaraj, M. Banana peel culture as an indigenous medium for easy identification of late-sporulation human fungal pathogens. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 34, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.D.; Lee, S.B.; Taylor, J.W. 38—Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA Genes for phylogenetics. In PCR—Protocols and Applications—A Laboratory Manual; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- EPPO. European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization. PM 7/129 (1) DNA barcoding as an identification tool for a number of regulated pests. Bull. OEPP 2016, 46, 501–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woudenberg, J.H.C.; Aveskamp, M.M.; de Grutyer, J.; Spiers, A.G.; Crous, P.W. Multiple Didymella teleomorphs are linked to the Phoma clematidina morphotype. Persoonia 2009, 22, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A Method for Designing Primer Sets for Speciation Studies in Filamentous Ascomycetes. Mycologia 1995, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Aluthmuhandiram, J.V.S.; Chethana, K.W.T.; Manawasinghe, I.S.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Hyde, D.K.; Phillips, A.J.L.; Zhang, W. Nigrospora Species Associated with Various Hosts from Shandong Peninsula, China. Mycobiology 2020, 48, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Bakhshi, M.; Balci, Y.; Broders, K.D.; Cheewangkoon, R.; Chen, S.F.; Fan, X.L.; Gramaje, D.; Halleen, F.; Jung, M.H.; et al. Genera of phytopathogenic fungi: GOPHY 4. Stud. Mycol. 2022, 101, 417–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slippers, B.; Crous, P.W.; Denman, S.; Coutinho, T.A.; Wingfield, B.D.; Wingfield, M. Combined multiple gene genealogies and phenotypic characters differentiate several species previously identified as Botryosphaeria dothidea. Mycologia 2004, 96, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, M.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Hyde, K.D.; Diao, Y.-Z.; Cai, L. Culturable plant pathogenic fungi associated with sugarcane in southern China. Fungal Diver 2019, 99, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous, P.W.; Carnegie, A.J.; Wingfield, M.J.; Sharma, R.; Mughini, G.; Noordeloos, M.E.; Santini, A.; Shouche, Y.S.; Bezerra, J.D.P.; Dima, B.; et al. Fungal Planet description sheets: 868–950. Persoonia 2019, 42, 291–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11030–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA 11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashmi, M.; Kushveerm, J.; Sarma, V. A worldwide list of endophytic fungi with notes on ecology and diversity. Mycosphere 2019, 10, 798–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Cai, X.L.; Pang, Q.Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.S.; Bian, Q. First record of leaf spot disease on Costus speciosus caused by Nigrospora oryzae in Hainan, China. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoko, Z.; Marasas, W.F.O.; Rheeder, J.P.; Shephard, G.S.; Wingfield, M.J.; Cardwell, K.F. Fungal infection and mycotoxin contamination of maize in the humid forest and the western highlands of Cameroon. Phytoparasitica 2001, 29, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkat, E.H.; Hardy, G.E.S.J.; Ren, Y.; Calver, M.; Bayliss, K.L. Fungal contaminants of stored wheat vary between Australian states. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2016, 45, 621–628. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, S.I.; Dutra, D.; Rodrigues, A.; de Oliveira, J.; Dhingra, O.; Pereira, O. Fungi and bacteria associated with post-harvest rot of ginger rhizomes in Espírito Santo, Brazil. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2013, 38, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.; Kim, M.; Kwack, Y.-B.; Kwak, Y.-S. First report of Nigrospora sp. causing kiwifruit postharvest black rot. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2016, 45, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Pan, H.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhong, C.H. First report of Nigrospora oryzae causing brown/black spot disease of kiwifruit in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, S.; Ghaffar, A. New records of soilborne root infecting fungi in Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 1995, 27, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Lucca, A.J.D.; Mich, M.; Boue, S.; Cleveland, T.E.; Sien, T.; Walsh, T.J. Fungicidal activity of plant saponin CAY-i for fungi isolated from diseased vitis fruit and stems. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2008, 59, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, K.R.; Etten, J. Physiology and biochemistry of fungal sporulation. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1982, 20, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, R.W. Permanent stained mycological preparations obtained by slide culture. Mycologia 1950, 42, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masangkay, R.F.; Paulitz, T.C.; Hallett, S.G.; Watson, A.K. Characterization of sporulation of Alternaria alternata f. sp. sphenocleae. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2000, 10, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-C.; Tsai, J.-C.; Li, F.-C.; Lung, S.-C.; Su, H.-J. Increased levels of ambient fungal spore in Taiwan are associated with dust events from China. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4879–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J. Spore projection in hyphomycete Nigrospora sphaerica. New Phytol. 1952, 51, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savulescu, T.; Rayss, T. Contribution a la connaissance de la hiologie de Nigrospora oryzae (B. et Br.) Petch Parasite du mats. Rec. Trav. Cryptogam. dédiés à Louis Mangin. Muséum Nat. d’Hist. Nat. Paris 1931, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaro, A. El Ácara Pediculopsis graminum Reut. y el hongo Nigrospora oryzae (Berk, et Br.). Petch en associación parasitaria sobre Tigos arogeneses. Bol. Pathol. Veg. Entomol. Agric. 1946, 16, 321. [Google Scholar]
- Njokuocha, R.C.; Agwu, C.O.C.; Okezie, C.E.A. Effects of weather conditions on selected airborne fungal spores in the southern part of the state of Enugu, Nigeria. Grana 2017, 56, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Girisham, S.; Reddym, S.M. Influence of temperature and relative humidity on the development of post-harvest rot of banana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. 2011, 81, 285–287. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.J.; Hu, M.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Lu, G.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J. Five fungal pathogens are responsible for bayberry twig blight and fungicides were screened for disease control. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.U.; Ashraf, M.; Choudary, M.I.; Rehman, H.U.; Kazmi, M.H. Antifungal aryltetralin lignans from leaves of Podophyllum-hexandrum. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Ramirez, A.; Escudero-Abarca, B.I.; Aguilar-Uscanga, G.; Hayward-Jones, P.M.; Barboza-Corona, J.E. Antifungal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis chitinase and its potential for the biocontrol of phytopathogenic fungi in soybean seeds. J. Food Sci. 2020, 69, M131–M134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd-Baseri, N.; Anuar, M.S.K.; Shamsuhazli, N.A.S.; Zulkifli, M.A.F.; Wasoh, H.; Yusof, M.T. Antagonistic activity of wild growing mushrooms against various fungal rice pathogen. Int. Microbiol. 2023, 26, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornakili, A.; Thankappan, S.; Sridharan, A.P.; Nithya, P.; Uthandi, S. Antagonistic fungal endophytes and their metabolite-mediated interactions against phytopathogens in rice. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 112, 101525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Hyde, K.D.; Suwannarach, N.; Elgorban, A.M.; Stephenson, S.L.; Al-Rejaie, S.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Tibpromma, S. Endophytic fungi associated with coffee leaves in China exhibited in vitro antagonism against fungal and bacterial pathogens. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesha, K.P.; Mohana, N.C.; Nuthan, B.R.; Rakshith, D.; Satish, S. Antimicrobial metabolite profiling of Nigrospora sphaerica from Adiantum philippense L. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2020, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-C.; Choi, G.J.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, H.T.; Cho, K.Y. Activity against plant pathogenic fungi of phomalactone isolated from Nigrospora sphaerica. Pest Manag. Sci. 2001, 57, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, D.; Lee, C.C.; Yenn, T.W.; Zakaria, L.; Sheh-Hong, L. Effect of the extract of endophytic fungus, Nigrospora sphaerica CL-OP 30, against the growth of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Klebsiella pneumonia cells. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 14, 2091–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Li, W.; Zhu, T.; Han, S.; Qiao, T.; Li, S. First report of Nigrospora aurantiaca causing leaf spot disease of Castanea mollissima in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, Y.W.; Tan, H.T.; Khaw, Y.S.; Li, S.-F.; Chong, K.P. First report of Nigrospora aurantiaca causing leaf spot on Pandanus amaryllifolius in Malaysia. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 104, 1205–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.-C.; Chen, Q.; Li, W.H. First report of leaf spot caused by Nigrospora aurantiaca in tobacco in China. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manawasinghe, I.S.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Li, H.L.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.; Phillips, A.J.L.; Wanasinghe, D.N.; Dissanayake, A.J.; Li, X.H.; Li, Y.H.; et al. Microfungi associated with Camellia sinensis: A case study of leaf and shoot necrosis on Tea in Fuijan, China. Mycosphere 2021, 12, 430–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, J.; Baccelli, I.; Cernava, T. First report of Camellia oleifera leaf blight caused by Nigrospora chiensis. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 103, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, L.; Zhu, T.; Han, S.; Li, S. First report of brown leaf spot disease caused by Nigrospora guiliensis on Phellodendron chinense in China. Plant Disease 2020, 104, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforto, C.; Lima, N.B.; Silva, F.J.A.; Câmara, M.P.S.; Macharachchikumbura, S.; Michereeff, S.J. Characterization of fungal species associated with cladode brown spot on Nopalea cochenillifera in Brazil. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 155, 1179–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Zhao, L.; Huang, M.-G.; Deng, J.-X.; Wang, Y.-H. First report of leaf spot caused by Nigrospora hainanensis on Oxalis corymbose—China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nadabi, H.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Al-Gahaffi, Z.S.; Al-Hasani, A.S.; Velazhahan, R.; Al-Sadi, A.M. Molecular identification of fungal pathogens associated with leaf spot disease of date palms (Phoenix dactylifera). All Life 2020, 13, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, Y.J.; Hafifi, A.B.M.; Huda-Shakirah, A.R.; Wong, K.L.; Jin, X.L.; Nordahliawate, M.S.S.; Zakaria, L.; Mohd, M.H. First report of reddish brown spot disease of red-fleshed dragon fruit (Hypocereus polyrhizus) caused by Nigrospora lacticolonia and Nigrospora sphaerica in Malaysia. Crop Prot. 2019, 122, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Gong, D.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, M. First report of Nigrospora lacticolonia causing leaf spot of Bougainvillea spectabilis in China. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 44, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.X.; Hong, N.; Wang, G.P.; Wang, L.P. The first report of leaf spot in Aloe vera caused by Nigrospora oryzae in China. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.W.; Rehman, A.; Saira, M.; Khan, N.A.; Aslam, S.; Fiaz, M.; Muhammad, S. First report of leaf spots in Aloe vera caused by Nigrospora oryzae in Pakistan. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, M.; Hamza, A.; Tanny, T.; Das, K.C.; Mahmud, M.T.; Salimullah, M.; Alam, I. First report of leaf spot disease in Aloe vera caused by Nigrospora oryzae in Bangladesh. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Zhu, W.; Niu, T.; Liu, Z. Nigrospora oryzae causing leaf spot on asiatic dayflower on Chongqing, China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Q.; Jiang, S.; Meng, J.J.; An, H.S.; Zhang, X.Y. First report of leaf spot caused by Nigrospora oryzae on blueberry in Shangai, China. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.Y.; Cernava, T.; He, H.D.; Li, H.X.; Chen, X.Y.L.; Yang, H. First report of leaf spon on Photinia serrulata caused by Nigrospora oryzae in China. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Li, S.S.; Tan, G.J.; Shen, J.T.; He, T. First report of Nigrospora oryzae causing leaf spot on cotton in China. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Yu, S.T.; Zhu, T.; Li, S.; Qiao, T.; Liu, Y.; Lin, T.; Yang, C. Nigrospora oryzae causing black leaf spot disease of Hibiscus mutabilis in China. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.B.; Zhang, C.L.; Mao, P.P.; Qian, Y.S.; Wang, H.Z. First report of leaf spot caused by Nigrospora oryzae on Dendrobium candidum in China. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.L.; Du, C.M.; Liang, L.Y.; Qin, Q.Y.; Wang, C.; Cui, D.X.; Wu, Q.G.; Zou, L. First report of Davida involucrata leaf blight caused by Nigrospora oryzae in Sichuan, China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özer, G.; Paulitz, T.C.; Imren, M.; Alkan, M.; Muminjanov, H.; Dababat, A.A. Identity and pathogenicity of fungi associated with crown and root rot of dryland winter wheat in Azerbaijan. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, T.; Kirk, A.; Kirk, G.; Guermache, F. Foliar and cane rot of Arundo donax caused by Nigrospora oryzae in Europe. Plant Dis. 2006, 90, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Qi, L.; Wang, X.; Song, J.; Li, D.; Chen, T.; Wang, Q. First report of Nigrospora oryzae causing leaf spot on ginger in China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Huang, L.L.; Liu, Y.J.; Ai, Y.; Pend, D.H. First report of leaf spot of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) caused by Nigrospora oryzae in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Meena, P.D.; Chauhan, J.S. First report of Nigrospora oryzae (Berk. & Broome) petch causing stem blight on Brassica juncea in India. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 161, 439–441. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Shi, F.; Kelly, D.; Hsiang, T. First report of leaf spot of Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis) caused by Nigrospora oryzae in Ontario. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-L. First report of leaf spot on kidney bean caused by Nigrospora oryzae in China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Pan, H.; Liu, Y.F.; Li, D.W.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, L.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhong, C.H. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing kiwifruit postharvest rot disease in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, N.P.; Stancanelli, S.; Papone, M.L.; Moreno, M.V.; Stenglein, S.; Wright, E.R.; Hagiwara, J.C.; Rivera, M.C. Leaf spots on calibrachoa caused by Nigrospora oryzae. Ornam. Hortic. 2020, 26, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalati, T.H.; Jahani, M.; Zare, R.; Mirzaee, M. First report of Nigrospora leaf spot on Pennisetum americanum in Iran. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 96, 606. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, K.; Zafari, D.; Soleimani, M.J.; Bagherabadi, S. First report of Nigrospora oryzae causing brown leaf spot on Mentha spicata. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 102, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kong, N.; Ji, S.; Liu, B.; Tian, Z.; Qi, J.; Liu, Z. First report of leaf blight caused by Nigrospora oryzae on Poplar in China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, S.; Khan, A.; Shahjahan, A.K.M.; Miah, S.A. Fungal species associated with sheaths and grains of sheath rot affected rice varietes from Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2003, 32, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Sun, G.; Ai, Y.F.; Wang, F.; Wang, X. First report of leaf spot disease caused by Nigrospora oryzae on Nicotiana tabacum in China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, N.; Yang, M.F.; Li, H.-X. First report of Nigrospora leaf spot caused by Nigrospora oryzae on watermelon in China. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eken, C.; Spanbayev, A.; Tulegenova, Z.; Yechshzhanov, T. First report of Nigrospora oryzae on wheat iz Kazahstan. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozoğlu, T.; Dervis, S.; Imren, M.; Amer, M.; Özdemir, F.; Paulitz, T.C.; Morgounov, A.; Dababat, A.A.; Özer, G. Fungal pathogens associated with crown and root rot of wheat in Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Kazahstan. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.L.; Tang, J.R.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.K. First report of leaf spot caused by Nigrospora oryzae in wild rice in China. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kido, L.R.; Uzabakirihno, J.D.; Chimwamourombe, P.M. Isolation and identification of pathogenic fungi associated with Aloe zebrina flower malformation—First report. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 6, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Miao, P.; Wu, D.; Cai, G.; Li, X.; Lu, J. First report of leaf blight on Ficus pinduara caused by Nigrospora osmanthi in China. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.I.; Norzaki, N.A.M.; Ya’acob, M.E.; Jamian, S. First report of Nigrospora osmanthi causing leaf blight on Orthosiphon stamineus in Malaysia. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, S.S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; Rong, W. First report of leaf blight on Stenotaphrum secundatum caused by Nigrospora osmanthi in China. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Peng, X.; He, F.; Li, S.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Zhou, M. First report of Nigrospora osmanthi causing leaf spot on Tartary buckwheat in China. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktar, M.; Shamsi, S. Mycloflora associated with infected plant parts of Tagetes erecta L. and Tagetes patula L. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2021, 50, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Y.-L.; Zhang, C.; Yang, H.; Yang, M.-F.; Cernava, T. First report of leaf spot on Chenopodium album caused by Nigrospora pyriformis in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, A.; Nath, A.; Thakur, D. Identification and characterization of fungi associated with blister blight lesion of tea (Camellia sinensis L. Kuntze) isolated from Meghalaya, India. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 240, 126561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szilagyi-Zecchin, V.J.; Adamoski, D.; Rodrigues Gomes, R.; Hungria, M.; Ikeda, A.C.; Kava-Cordeiro, V.; Glienke, C.; Galli-Terasawa, L.V. Composition of endophytics fungal community associated with leaves of maize cultivated in south Brazilian field. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2016, 63, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, J.; Gupta, S.; Thakur, D.; Handique, P.J. First report of Nigrospora leaf blight on tea caused by Nigrospora sphaerica in India. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Tang, Q.; Fang, L. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing leaf blight on Camellia sinensis in China. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.R.; Folgado, M.; Rivera, M.C.; Crelier, A.; Vasquez, P.; Lopez, S.E. Nigrospora sphaerica causing leaf spot and twig and shoot blight on blueberry: A new host of the pathogen. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Huang, M.H.; Sun, L.P.; Ji, P. Occurence of leaf spot on calabash caused by Nigrospora sphaerica in Georgia. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1506. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.M.; Liu, Y.J. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing leaf bligh on Cunninghamia lanceolata—China. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu, S.; Dervis, S.; Soylu, E.M. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing leaf spots on Chinese Wisteria: A new host of the pathogen. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Cai, X.L.; Pang, Q.Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.S.; Bian, Q. First report of leaf blight on Mentha canadensis caused by Nigrospora sphaerica in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, Y.S.; Mahadevakumar, S.; Amruthesh, K.N.; Lakshmidevi, N. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica associated with leaf spot disease of Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) from India. Plant Dis. 2020, 105, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Song, J.H.; Tan, G.J.; Li, S.S. First report of leaf blight caused by Nigrospora sphaerica on Curcuma in China. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, M.H.; Hameed, M.A.; Ahmed, A.N. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica (Sacc.) Mason as potential pathogen on date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 35, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, A.M.; Al-Jabri, A.H.; Al-Mazroui, S.S.; Al-Mahmooli, I.H. Characterization and pathogenicity of fungi and oomycetes associated with root disease of date palm in Oman. Crop Prot. 2012, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.W.; Rehman, A.; Ahmad, S.; Sarwar, M.; Nawaz, A.; Khan, S.M.; Ali, S.; Aslam, S.; Mannan, A. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing leaf spot of date palm in Pakistan. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 102, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, Z.; Shamsi, S. Mycoflora associated with symptomatic leaves of Rauvolfia serpentina (L.) Benth. Ex. Kurz. in Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon. 2020, 27, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguiam, J.D.; Evallo, E.; Bengoa, J.; Maghirang, R.; Balendres, M.A. Detection of Nigrospora sphaerica in the Philippines and the suscpetibility of three Hylocereus species to reddish-brown spot disease. J. Prof. Assoc. Cactus Dev. 2020, 22, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wu, J.B.; Zhan, R.L.; Ou, X.C. First report of reddish brown spot disease on pitaya caused by Nigrospora sphaerica in China. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.Z.; Fan, Z.W.; Wu, C.F.; Li, M.Y.; Zhou, D.D. First report of Nigrospora leaf blight on elephant grass caused by Nigrospora sphaerica in China. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.K. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing leaf spot on Celtis australis from Himachal Pradesh, India. Int. Lett. Nat. Sci. 2015, 40, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Liu, C.; Niu, T.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Z. Nigrospora sphaerica causing leaf spot in a new host, Eclipta prostrata (False Daisy), in China. J. Phytopathol. 2022, 170, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.W.; Rehman, A.; Gleason, M.L.; Riaz, K.; Saira, M.; Aslam, S.; Rosli, H.; Muhammad, S. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing leaf spot on Kinnow mandarin in Pakistan. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 99, 295. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, A.F.; Zhang, H.Y.; Gu, C.Y.; Hameed, U.; Qi, Y.J.; Xu, Y.L. First report of leaf spot caused by Nigrospora sphaerica on kiwifruit in China. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, O.P.; Gupta, R.B.L. A new host for Nigrospora sphaerica causing leaf spots on Glycyrrhiza glabra. Plant Pathol. 2008, 57, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Pandey, S.; Awasthi, A.K. A new host record of Nigrospora sphaerica on Mangifera indica from Jabalpur, India. J. Mycol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 43, 255–256. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, K.; Mosa, M.A.; Kamhawy, M.A. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing twig dieback and leaf spot of mango in Egypt. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 104, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xiang, T.T.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, W.H.; Zhang, B.L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, W.; Wan, Y.J.; Chen, G.; Zhu, H.S. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing shot hole disease on mulberry in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunakumar, G.S.; Gnanesh, B.N.; Supriya, M.; Sivaprasad, V. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing shot hole disease on mulberry in India. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cernava, T.; Zhou, X.; Yang, L.; Baccelli, I.; Wang, J.; Gou, Y.; Sang, W.; Chen, X. First report of passion fruit leaf blight caused by Nigrospora sphaerica in China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, F.; Fu, D.; Yang, W. First report of leaf blight on peanut caused by Nigrospora sphaerica in China. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 102, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Cubero, L.C.; Ampofo, P.; Montes, J.M.; Voegele, R.T. Identification of pathogenic fungi and preliminary screening for resistance in Jatropha curcas L. germplasm. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 149, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M.; Shang, X.; Fang, S.; Chen, F. First report of leaf blight of Cyclocarya paliurus caused by Nigrospora sphaerica in China. Crop Prot. 2021, 140, 105453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, H.Y.; Yang, X.S.; Liu, Y.X.; Ni, Y.X.; Wang, F.; Tang, L. First report of Nigrospora leaf blight on sesame caused by Nigrospora sphaerica in China. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Alam, M.W.; Saira, M.; Naz, S.; Mushtaq, R.; Chohan, T.A.; Din, S.U.; Noureen, A.; Gilani, K.; Hussain, D. Nigrospora sphaerica causing leaf blight disease on sesame in Palkistan. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.P.; Wu, B.; Peng, A.T.; Li, Z.L.; Lin, J.F.; Song, X.B. First report of Nigrospora leaf blight on sugarcane caused by Nigrospora sphaerica in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Liu, Y.S.; Huang, S. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing fruit dried-shrink disease in Akebia trifolitata from China. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Hu, F.; Chen, L.S.; Xu, S.W. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing leaf blight on oil tea (Camellia oleifera) in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.I.; Razak, N.F.A. First report of Nigrospora sphaerica causing leaf spot on watermelon (Citrullus lanatus L.) in Malaysia. Plant Dis. 2020, 105, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, C.; Busso, C.; Borin, R.C.; Mazaro, S.M.; Saburo, R.S.S. The first report of Nigrospora sphaerica associated with Helicarpus americanus seeds in Brazil. Floresta Ambiente 2021, 28, e20190103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Locus | Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) | ITS1 | 5′ TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG 3′ |
| ITS4 | 5′ TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC 3′ | |
| ITS5 | 5′ GGAAGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG 3′ | |
| Beta-tubulin | Btub2Fd | 5′ AACATGCGTGAGATTGTAAGT 3′ |
| Btub4Rd | 5′ TAGTGACCCTTGGCCCAGTTG 3′ | |
| Translation elongation factor 1-alpha | EF1-728F | 5′ CATCGAGAAGTTCGAGAAGG 3′ |
| EF1-986R | 5′ TACTTGAAGGAACCCTTACC 3′ |
| ITS1/ITS4 and EF-728F/EF-986R | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOT START 95 °C | Start Cycle 34 times | Denaturation 95 °C | Annealing 58 °C | Elongation 72 °C | End Cycle | Elongation 72 °C |
| 3 min | 30 s | 30 s | 1 min | 10 min | ||
| ITS5/ITS4, and Btub2Fd/Btub4Rd | ||||||
| HOT START 95 °C | Start Cycle 34 times | Denaturation 95 °C | Annealing 58 °C | Elongation 72 °C | End Cycle | Elongation 72 °C |
| 3 min | 30 s | 30 s | 1 min | 10 min | ||
| Species | GenBank Accession Number | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | TUB | TEF1α | ||
| Botryosphaeria dothidea | AY236949 | AY236927 | AY236898 | [29] |
| Nigrospora aurantiaca | KX986064 | KY019465 | KY019295 | [15] |
| MN215771 | MN329935 | MN264010 | [30] | |
| N. bambusae | KY385307 | KY385319 | KY385313 | [15] |
| KY385306 | KY385320 | KY385314 | [15] | |
| N. brasiliensis | KY569629 | MK720816 | MK753271 | [31] |
| KY569630 | MK720817 | MK753272 | [31] | |
| N. cameliae-sinensis | KX985986 | KY019460 | KY019293 | [15] |
| MN215775 | MN329939 | MN264014 | [30] | |
| N. chinensis | KX986023 | KY019462 | KY019422 | [15] |
| KX986026 | KY019548 | KY019445 | [15] | |
| N. covidalis | OK335209 | OK431479 | OK431485 | [28] |
| OK335210 | OK431480 | OK431486 | [28] | |
| N. falsivesicularis | MN215778 | MN329942 | MN264017 | [30] |
| MN215779 | MN329943 | MN264018 | [30] | |
| N. globospora | OK335211 | OK431481 | OK431487 | [28] |
| OK335212 | OK431482 | OK431488 | [28] | |
| N. gorlenkoana | KX986048 | KY019456 | KY019420 | [15] |
| N. guilinensis | KX985983 | KY019459 | KY019292 | [15] |
| KX986063 | KY019608 | KY019404 | [15] | |
| N. hainanensis | KX986091 | / | KY019415 | [15] |
| MN215780 | MN329944 | MN264019 | [30] | |
| N. lacticolonia | KX985978 | KY019458 | KY019291 | [15] |
| / | MN329948 | MN264023 | [30] | |
| N. musae | KX986076 | KY019455 | KY019419 | [15] |
| KX986042 | KY019567 | KY019371 | [15] | |
| N. oryzae | KX985931 | KY019601 | KY019396 | [15] |
| KX985954 | KY019481 | KY019307 | [15] | |
| N. osmanthi | KX986010 | KY019461 | KY019421 | [15] |
| KX986017 | KY019540 | KY019438 | [15] | |
| N. philosophiae-doctoris | OK335213 | OK431483 | OK431489 | [28] |
| OK335214 | OK431484 | OK431490 | [28] | |
| N. pyriformis | KX985940 | KY019457 | KY019290 | [15] |
| MN215787 | MN329988 | MN264026 | [30] | |
| N. rubi | KX985948 | KY019475 | KY019302 | [15] |
| N. sacchari-officinarum | MN215791 | MN329954 | MN264030 | [30] |
| MN215792 | MN329955 | MN264031 | [30] | |
| N. saccharicola | MN21578 | / | MN264027 | [30] |
| MN215789 | MN329952 | MN264028 | [30] | |
| N. singularis | MN215793 | MN329956 | MN264032 | [30] |
| MN215794 | MN329957 | MN264033 | [30] | |
| N. sphaerica | KX985965 | KY019492 | KY019318 | [15] |
| MN215811 | MN329974 | MN264050 | [30] | |
| N. vesicularifera | MN215812 | MN329975 | MN264051 | [30] |
| MN215814 | MN329977 | MN264053 | [30] | |
| N. vesicularis | KX986088 | KY019463 | KY019294 | [15] |
| KX985939 | KY019467 | / | [15] | |
| N. zimmermanii | KY385309 | KY385317 | KY385311 | [15] |
| MN215824 | MN329987 | MN264063 | [30] | |
| SPECIES | ISOLATE | COLLECTION DATE | Varieties | Genbank Accession Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | TUB | Ef1α | ||||
| Nigrospora gorlenkoana | P13 LECIII | 24 September 2021 | Leccino | OP999642 | OQ286068 | OQ286069 |
| Nigrospora osmanthi | JA20 NP | 31 October 2021 | Unknown | OP999639 | OQ275027 | OQ275028 |
| Nigrospora philosophiae-doctoris | R18 BI | 14 October 2021 | Buža | OP999644 | OQ286067 | OQ286066 |
| TECHNIQUES | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDA Temperatures: 22 °C, 25 °C, 28 °C, 30 °C | 1/2 strength PDA medium | WA Temperatures: 22 °C, 25 °C, 28 °C, 30 °C | Pine needle extracts + WA | MEA Temperatures: 22 °C, 25 °C, 28 °C, 30 °C | Host tissue | Slide culture | Exposure to near-ultraviolet light (12 h day/12 h night) | Banana peel | PDA + banana medium |
| x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrović, E.; Vrandečić, K.; Ćosić, J.; Đermić, E.; Godena, S. First Report of Nigrospora Species Causing Leaf Spot on Olive (Olea europaea L.). Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9101067
Petrović E, Vrandečić K, Ćosić J, Đermić E, Godena S. First Report of Nigrospora Species Causing Leaf Spot on Olive (Olea europaea L.). Horticulturae. 2023; 9(10):1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9101067
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrović, Elena, Karolina Vrandečić, Jasenka Ćosić, Edyta Đermić, and Sara Godena. 2023. "First Report of Nigrospora Species Causing Leaf Spot on Olive (Olea europaea L.)" Horticulturae 9, no. 10: 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9101067
APA StylePetrović, E., Vrandečić, K., Ćosić, J., Đermić, E., & Godena, S. (2023). First Report of Nigrospora Species Causing Leaf Spot on Olive (Olea europaea L.). Horticulturae, 9(10), 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9101067







