Abstract
Pinellia ternata, a traditional Chinese herb, suffers from soil degradation and nutrient imbalance, which significantly decrease both yield and quality. Here, the application of microbial organic fertilizer (MOF) in the cultivation of P. ternata results in high yields and quality under two soil conditions, whether grown in greenhouse or open-field environments. The application of MOF enhanced seedling emergence rates and photosynthetic efficiency, significantly improving various agronomic traits, and increasing the content of flavonoids and total alkaloids in tubers, with a stronger effect observed at a dosage of 75 g/m2. Moreover, available phosphorus, available potassium, catalase, and urease levels were significantly improved. Further, 16S and ITS sequencing revealed that bacteria diversity was not affected by all treatment, while the fungi unweighted UniFrac index showed significant decline in the MOF treatment. The abundance of bacterial Acidobacteriota and Proteobacteria varied with continuous cropping soil, whereas abundance of fungi Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Mortierellomycota was changed in the first cropping of P. ternata. These findings suggest that applying MOF improves the microbial communities of the rhizosphere soil of P. ternata, enhancing soil enzyme activities and decomposing organic and inorganic matter. This, in turn, contributes to the yield and quality of P. ternata.
1. Introduction
Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Breit, a perennial herb from the Araceae family, holds significant value in traditional Chinese medicine [1,2]. The mature Pinelliae Rhizome is processed from the P. ternata tuber and has been used for thousands of years in traditional Chinese medicine [3,4,5]. Pinelliae Rhizome contains various pharmacological compounds, including alkaloids, flavonoids, amino acids, organic acid, lectins, phenylpropanoids, and volatile oils [6,7,8]. Modern pharmacological studies have demonstrated its antiemetic, antidepressant, antineoplastic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and sedative-hypnotic effects [9,10]. Due to its valuable pharmacological properties, there is an increasing demand for P. ternata.
P. ternata thrives in warm, humid environments below an elevation of 2500 m, favoring gullies and slopes with loose, fertile sandy soil [3]. However, a variety of complex factors such as ecological environment changes, excessive excavation, reproductive capacity limitations, and climate change have led to a reduction of wild P. ternata resources [11]. Artificial cultivation has been suggested as an optimal strategy for sustainable supply of P. ternata. Compared to wild herbal medicines, artificially cultivated ones may have certain differences in efficacy. For example, the levels of flavonoids and chlorogenic acids were higher in wild Artemisa rupestris than in cultivated [12]. This is mainly due to differences in growth environment, soil, climate, and other factors. Additionally, to pursue high yields, some artificial cultivation processes may involve extensive use of chemicals like fertilizers and pesticides, leading to environmental pollution and ecological damage [13]. Moreover, serious obstacles exist for continuous cropping of the same type of Chinese herbal medicine, which can lead to soil degradation and increased pest problems over time, affecting their yields and qualities. It is noted, after just two years of continuous cropping, the yield of P. ternata has significantly decreased by 50% [11]. Meanwhile, the rhizosphere soil pH decreased, nutrients became unbalanced, and enzyme activity decreased as a result of P. ternata continuous cropping [14].
To deal with the problems caused by artificial cultivation, various strategies have been implemented, such as applying microbial agents and organic fertilizer. The application of microbial inoculants can introduce beneficial microorganisms, thereby mitigating soil degradation and enhancing soil fertility [15]. Li et al. demonstrated that the application of Streptomyces jingyangensis T. and Bacillus mucilaginosus A in the cultivation of P. ternata promoted the proliferation of beneficial microorganisms such as Lysobacter, Bacillus, and Trichoderma, thereby improving the soil environment [16]. Wei et al. found that the application of bio-organic fertilizers enhanced soil nitrogen cycling, stimulated starch and sucrose metabolism in plants, and increased the yield of P. ternata [17]. Thus, it is hypothesized that microbial inoculants and organic fertilizers can synergistically improve the structure of the soil microbial community, enhance soil fertility, and promote the growth of P. ternata.
MOF is an innovative eco-friendly blend of organic matter and beneficial microorganisms that results from the fermentation process involving advantageous microbial communities. These fertilizers are rich in beneficial microbes, which facilitate soil nutrient recycling, enhance crop nutrient uptake, and improve soil health and productivity [18,19]. For instance, Li et al. has shown that MOF application can boost wheat yields by modulating nitrogen transformation and utilization processes [20]. Furthermore, incorporating Bacillus subtilis biofertilizer has been observed to reduce ammonia (NH3) emissions, promote ammonia-oxidizing bacteria abundance, maintain high crop yields, and mitigate environmental disturbance [21]. Additionally, MOF have demonstrated their efficacy in enhancing the yield and quality of tea grown in continuously cropped soils and improving sorghum growth in saline conditions [18,22]. In general, MOF applications enhance soil microbial diversity and fertility, supporting sustainable agriculture.
To date, while organic fertilizers and microbial inoculants have been tested for P. ternata cultivation, respectively [16,17], there are no reports on the application of MOF in P. ternata. Therefore, this study systematically investigated the effects of MOF on the growth of P. ternata and the soil environment, revealing that they can effectively improve the soil microbial community, enhance soil fertility, and increase the yield and quality of P. ternata. These findings provide a theoretical basis and technical support for the efficient cultivation of P. ternata.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The original P. ternata were obtained from the specimen room of Huaibei Normal University without any specifically permissive requirement. Tubers with 1.0 to 1.2 cm diameter were cultivated. The MOF applied is a compound microbial fertilizer consisting of Bacillus licheniformis (60%) and Paenibacillus mucilaginosus (40%), effective viable bacteria ≥ 20 million g−1, organic matter ≥ 20%. It is derived from the decomposition of sheep manure and straw at a ratio of 4:1. The total nutrient content (N + P2O5 + K2O) of the microbial fertilizer is 30%, with nitrogen content at 18%, phosphorus content at 7%, and potassium content at 5%. The MOF was purchased from Sinoagri Cargill Chemical Co., Ltd. (Shangqiu, China).
2.2. Experimenal Site and Design
To investigate the effect of microbial organic fertilizer on the yield and quality in P. ternata, we grew them in pots and fields under two soil conditions with different doses of MOF, respectively. Continuous cropping soils and first cropping P. ternata soils were chosen for this study due to the significant 50% reduction in yield observed in continuous cropping of two years compared to first cropping soils [11]. The experiments were conducted from April 2024 to August 2024 at the experimental field of Huaibei Normal University in Huaibei City, Anhui Province, China, as well as at the Laboratory for Efficient Utilization of Characteristic Resource Plants in Anhui Province. The coordinates for the field experiment are 116.23° E and 33.16° N, at an altitude of 40 m. The average annual temperature is 14.8 °C, with an average annual sunshine duration of 4430.2 h and an annual precipitation of 944.6 mm. Manual weeding is conducted once per week. The experimental design employs a randomized block design, with a plot size of 1 m × 1 m = 1 m2. The preceding crop for the continuous cropping soil was P. ternata, while no crops were planted in the previous season for the non-continuous cropping soil. In the potted experiment, P. ternata was planted in a blue rectangular pot measuring 45 cm in length, 33.5 cm in width, and 12.5 cm in height, with 20 tubers of P. ternata placed in each pot. The soil used in the pots was sourced from the field. Under controlled conditions, the temperature was maintained at 22 °C, with a light cycle of 16:8 h, relative humidity at 70%, and watering every five days until the soil surface was moist. Three different dosages of MOF and two soil types were used in the experiment (Table 1). Each treatment was repeated three times. This specific MOF was applied as a base fertilizer in a single application at a depth of 0–20 cm. The method involved evenly spreading the fertilizer over the soil surface, followed by thorough mixing to ensure homogeneous integration of the MOF within the 0–20 cm soil layer.
2.3. Quantification of P. ternata Agronomic Traits, Yield, and Quality
The agronomic traits of P. ternata were assessed at the flowering stage around 60 days after planting. Twenty-one to twenty-seven randomly selected plants from each pot were used for the measurement of tuber and bulbil weight, plant height, plant and root fresh weight, and root length. At the same time, the germination rate of P. ternata was calculated as the number of seedlings divided by the number of planted seeds, multiplied by 100%. The yield of P. ternata tubers was harvested and weighed from each plot after the above-ground parts of the plants had wilted in the summer. Then, tubers were washed with tap and sterile water, rapidly frozen in liquid nitrogen, and subsequently kept at −80 °C until metabolites analysis.
The total flavonoid content of P. ternata was determined using the aluminum chloride colorimetric method [23]. Quercetin was used as the standard substance to prepare solutions of quercetin at concentrations of (10, 25, 50, 75, and 100 μg/mL). For each concentration, 100 μL of the quercetin dilution was taken, followed sequentially by the addition of 500 μL of water, 100 μL of 5% sodium nitrite (allowed to stand for 6 min), 150 μL of 10% aluminum chloride (allowed to stand for 5 min), and 200 μL of 1 M sodium hydroxide. The absorbance was measured at 510 nm using a (METASH, UV-5500, Shanghai, China) spectrophotometer. We repeated the same process for the ethanol extract of P. ternata. The total flavonoid content was determined from the linear equation of the standard curve prepared with quercetin and expressed as mg/g quercetin equivalent in the dry extract.
The total phenolic content of P. ternata was determined using the Folin–Ciocalteu method with slight modifications according to Ainsworth and Gillespie [24]. Using gallic acid as a standard, we prepared a series of concentration solutions (10, 20, 40, 80, 120 μg/mL). We began with 0.5 mL of the standard or sample, added 2 mL of diluted Folin-Ciocalteu reagent (1:10) and 4 mL of sodium carbonate solution (7.5%), mixed well, and allowed the solution to react at room temperature for 30 min. We then measured the absorbance at 765 nm using a spectrophotometer (METASH, UV-5500). The total phenolic content was determined using the linear equation of the standard curve prepared from gallic acid, expressed as mg/g gallic acid equivalent of the dry extract.
Total alkaloids content of P. ternata was measured with analytical kits (Grace Biotechnology, Suzhou, China), following the instructions provided by the manufacturer. Each experiment was performed in three technological replicates.
2.4. Determination of Photosynthetic Parameters and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters
The photosynthetic rate (Pn), stomatal conductance (Gs), intercellular carbon dioxide concentration (Ci) and transpiration rate (Tr) of P. ternata leaves were measured using LI-6400 photosynthesis system (LI-6400 Inc., Lincoln, NE, USA) between 9:00 and 11:00 a.m. during flowering stage.
The quantum yield of PSII (ΦPSII) and the maximum chemical efficiency (Fv/Fm) in leaves of P. ternata were determined using a PAM-2500 portable chlorophyll fluorescence spectrometer (PAM-2500, Walz, Nuremberg, Germany). The minimal fluorescence (Fo) was obtained with modulated light, while the maximal fluorescence (Fm) was determined after applying saturating light to a leaf that had been dark-adapted for 20 min. The steady-state fluorescence (First cropping soil of P. ternata) was recorded when the leaf reached a stable state of photosynthesis, and the maximal fluorescence in the light-adapted state (Fm’) was also noted. Fv/Fm and ΦPSII were then calculated using the formulas:
Fv/Fm = (Fm − Fo)/Fm and ΦPSII = (Fm’—First cropping soil of P. ternata)/Fm’, respectively [25].
The middle leaflet of trifoliate leaves of P. ternata was consistently used for measuring all leaf indicators, and six randomly chosen plants per pot were employed for assessing photosynthetic and chlorophyll-related parameters.
The photosynthetic pigment level in fresh P. ternata leaves was quantified using a modified method from Wang et al. (2021) [26]. Briefly, 1 g of fresh P. ternata leaves was placed into a 20 mL tube, followed by the addition of 10 mL of 80% acetone. The mixture was then extracted in the dark for 48 h, with shaking every 8 h to ensure thorough extraction. The extract solution was collected and diluted to a final volume of 25 mL with 80% acetone. The absorbance of the solution was measured at wavelengths of 665 nm, 649 nm, and 470 nm.
The above indicators are all sampled from the flowering period of P. ternata, with each treatment replicated three times.
2.5. Soil Physicochemical Analysis
Soil physicochemical analysis was conducted during the flowering period of P. ternata. Soil pH and conductivity were measured using a pH meter and an electrode method, respectively [27]. Organic matter and carbon content were determined via the potassium dichromate heating method [28]. Total nitrogen (TN) was assessed through acid digestion–Kjeldahl analysis [29]. Total phosphorus (TP) was measured using the sulfate-perchloric acid digestion method [30]. The levels of available potassium (AK) and available phosphorus (AP) were analyzed using flame photometry and sodium bicarbonate extraction-molybdenum antimony colorimetric method, respectively [31,32].
2.6. Determination of Soil Enzyme Activities
The determination of soil enzyme activity is similarly carried out during the flowering period of P. ternata. The activities of soil catalase (CAT), soil urease (UE), acid phosphatase (ACP), and sucrase (SC) were individually determined using assay kits supplied by Zhihui Biotechnology (Nanjing, China), following the instructions provided by the manufacturer.
2.7. DNA Extraction and Microbial Analysis
Rhizosphere soil of P. ternata was collected during its flowering stage, approximately 60 days post-planting. DNA extracted from frozen samples was amplified, sequenced, and processed by GIS Huiyuan Biological Co., Ltd. in Nanjing, China. Bacterial 16S rRNA genes targeting the V3–V4 regions were amplified using primers 341F (5′-CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) via PCR [33]. The target-specific primers ITS1F (5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′) and ITS1R (5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′) were used to amplify the ITS1 variable region of the fungi [34]. Amplification was conducted on a Geneamp 9700 thermal cycling system (ABI, Natick, MA, USA). QIIME 2 2021.11 was used for microbiome analyzing on the Illumina Miseq platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) [35].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
To evaluate the role of microbial organic fertilizer, plant performance, soil physicochemical properties, and microbial abundance levels were compared under different MOF dosage treatments in both continuous cropping and non-continuous cropping soils of P. ternata. Two sets of data were evaluated by the two-sided Student’s t-test, and multiple data were evaluated by Tukey HSD post-hoc test after one-way ANOVA. All statistical analysis was performed with JMP pro 17 software (version 17.0).
Microbial analyses, including amplicon sequence variants (ASV) analysis, alpha diversity analysis, and beta diversity analysis, were conducted using QIIME2 software version 2021.11. Based on the relative abundance of ASV and PCA, a Mantal test was performed using R (version 3.6.2) [36]. The Mantel test was used to explore the correlation between the soil’s physical and chemical properties and bacterial and fungi abundance.
3. Result
3.1. The Application of MOF Improved the Yield and Quality of P. ternata
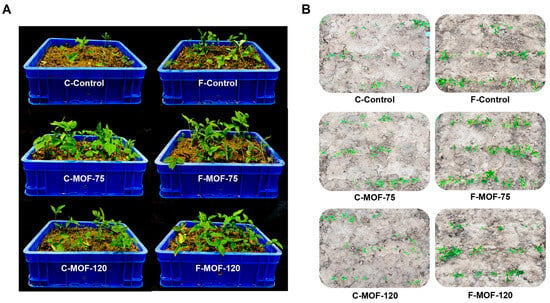
After a two-month treatment, P. ternata grown in both greenhouse and field conditions at 75 and 120 g/m2 MOF displayed a significantly higher germination rate and vigor in comparison to controls, with a stronger effect when 75 g/m2 MOF was used (Figure 1A,B).
Figure 1.
Effect of microbial organic fertilizer application on growth and yield in P. ternata. (A) Phenotype of pot experiments under different treatments after two months. (B) Phenotype of field experiments under different treatments after two months.
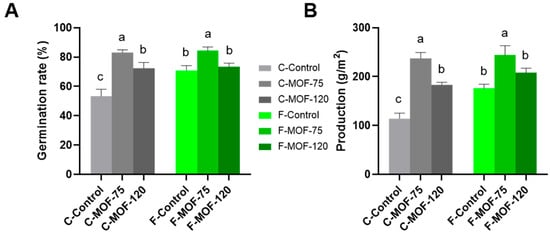
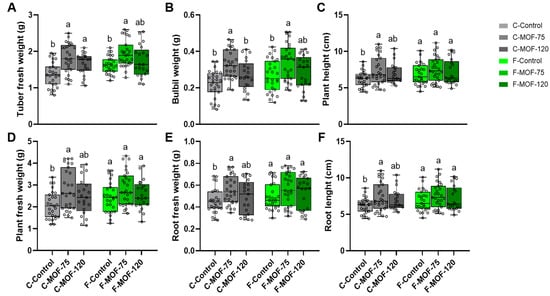
Moreover, MOF-treated at 75 g/m2 caused a significant increase in germination rate and yield (Figure 2). In particular, the application of MOF at 75 g/m2 in continuous cropping soils resulted in a 2-fold increase in yield, reaching to 237 g/m2, with a comparable effect to that observed when the same MOF was applied to first cropping soil of P. ternata, where the yield was 244 g/m2. This suggests that it has great potential as an effective strategy for alleviating the negative impacts of continuous cropping on soil productivity and plant performance. This effect was also detected in other agronomic traits in continuous cropping soils after MOF supply, including tuber and bulbil weight, plant height, plant fresh weight, root fresh weight, and root length (Figure 3). The most significant increase was observed in the weight of bulbils. In the continuous cropping soils, the weight of the bulbils ranged from 0.08 g to 0.34 g, while after treatment with 75 g/m2 MOF, the range increased to 0.19–0.47 g. For the first cropping soil, the weight of the bulbils was 0.12–0.43 g, and with MOF treatment, it ranged from 0.19–0.51 g (Figure 3B). However, MOF application had a minor effect on the P. ternata agronomic traits in first cropping soils, with an increase of up to 1.2-fold and 1.3-fold in tuber and bulbil weights mainly due to 75 g/m2 treatment (Figure 3A,B).
Figure 2.
Effect of MOF application on germination rate and production of P. ternata in field experiments. (A) Germination rate of P. ternata under different treatments. (B) Yield of P. ternata under different treatments. Data are given as mean ± SE (n = 3). Lowercase letters represent significant differences among samples in each soil condition using one-way ANOVA (p < 0.05) followed by a Tukey HSD post-hoc test (p < 0.05).
Figure 3.
Effect of microbial organic fertilizer application on agronomic traits of P. ternata in field experiments. Tuber fresh weight (A), bulbil weight (B), plant height (C), Plant fresh weight (D), Root fresh weight (E), Root length (F), after a three-month treatment with different doses of MOF are presented. Data are given as mean ± SE (n = 21~27). Lowercase letters represent significant differences among samples in each soil condition using one-way ANOVA (p < 0.05) followed by a Tukey HSD post-hoc test (p < 0.05).
3.2. The Application of MOF Improved the Quality of P. ternata
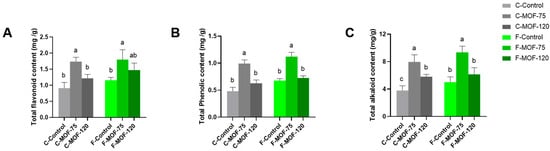
The metabolite content in medicinal plants is crucial due to its direct impact on their therapeutic efficacy compared to other plants. As indicators of quality, the secondary metabolites of tuber, including total phenols, flavonoids, and total alkaloid were determined. All of them significantly increased at 75 g/m2 MOF under both soil conditions; while 120 g/m2 MOF had no such effect, only total alkaloid content was slightly increased after 120 g/m2 MOF applied in continuous cropping soils condition. Total phenols, flavonoids, and total alkaloids increased by 2.1-fold, 1.91-fold, and 2.09-fold in continuous cropping soils, respectively, and by 1.65-fold, 1.57-fold, and 1.87-fold in first cropping soil (Figure 4). These results indicated that the optimal rate of MOF was 75 g/m2, as both yield and quality were enhanced when this dose was applied to P. ternata.
Figure 4.
Effects of microbial organic fertilizer application on the contents of total flavonoids (A), total phenols (B), and total alkaloids (C) of P. ternata tubers in field experiments. Data are given as mean ± SE. Lowercase letters represent significant differences among samples in each soil condition using one-way ANOVA (p < 0.05) followed by a Tukey HSD post-hoc test (p < 0.05).
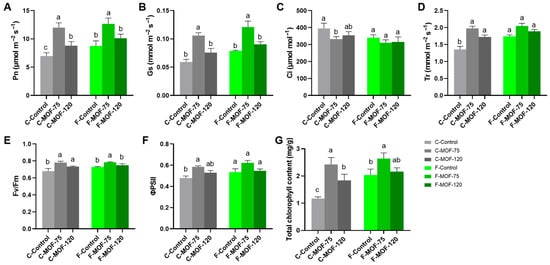
3.3. The Application of MOF Elevated Photosynthetic Parameters and Chlorophyll Content
Under both soil conditions, P. ternata leaves treated with MOF exhibited a significant increase in Pn and Gs (Figure 5A,B). Similar to the growth changes observed in P. ternata, a more substantial effect was identified at 75 g/m2 MOF application (Figure 1). Specifically, in continuous cropping soil, Pn and Gs increased by 72.91% and 79.66%, respectively, while in first cropping soils, they increased by 44.36% and 53.85%, respectively. Transpiration rate (Tr) was elevated only under continuous cropping soil conditions following MOF treatment, increasing by 46.05% and 27.41% at 75 and 120 g/m2 MOF treatments, respectively (Figure 5D). Regarding Ci, there were no significant differences among the various treatments, but it decreased to some extent after applying 75 g/m2 MOF in continuous cropping soils (Figure 5C).
Figure 5.
Effect of microbial organic fertilizer application on photosynthetic indexes, photochemical efficiency, and chlorophyll content of P. ternata in field experiments (A): Pn, net photosynthetic rate, (B): Gs, stomatal conductance, (C): Ci, intercellular CO2 concentration, (D): Tr, transpiration rate, (E): Fv/Fm, maximum photochemical efficiency of PSII, (F): ΦPSII, quantum yield, (G): total chlorophyll content. Data are given as mean ± SE (n = 3). Lowercase letters represent significant difference among samples in each soil condition using one-way ANOVA (p < 0.05) followed by a Tukey HSD post-hoc test (p < 0.05).
When MOF was used, the potential quantum efficiency of PSII (Fv/Fm) and quantum yield (ΦPSII) were elevated by 15% and 23%, respectively, under continuous cropping soils conditions, and by 8% and 17%, respectively, under first cropping soil conditions (Figure 5E,F). In turn, the contents of total chlorophyll were higher when P. ternata was treated with 75 g/m2 MOF in comparison to controls (Figure 5G). Applying 120 g/m2 MOF only led to higher contents of total chlorophyll in continuous cropping soils conditions (Figure 5G). Similar to agronomic traits, photosynthetic and chlorophyll-related parameters showed higher values in first cropping soils compared to continuous cropping soils. After treatment with MOF at 75 g/m2, almost all parameters were similar, suggesting that MOF effectively improved continuous cropping soils. Therefore, the best effect, 75 g/m2 MOF, was chosen to test the changes in microbial communities and soil properties.
3.4. The Application of MOF Elevated Soil Fertility and Enzyme Activities
Planting P. ternata significantly affected soil properties, including pH, OM, OC, AP, AK. At our experimental sites, the levels of OM and OC showed decreased trend in continuous cropping soils in comparison to those in first cropping soils. Surprisingly, the continuous cropping soils accumulated higher AP and AK in comparison to those in first cropping soils. This could be due to the functional bacteria, which could dissolve the insoluble phosphorus and potassium differently between continuous cropping soils and first cropping soil. When both continuous cropping soils and first cropping soils were treated with MOF, pH level was decreased while AP and AK contents significantly increased, accompanied by slight increases of OM, OC, TN, TP (Table 2).
Table 2.
Soil physicochemical properties and enzyme activities under different treatments in field experiments. *, ** and *** indicate significant differences at p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively, ns indicate not significant.. OM: Organic Matter. OC: Organic Carbon. TN: Total Nitrogen. TP: Total Phosphorus. AP: Available Phosphorus. AK: Available Potassium. CAT: Catalase. UE: Urease. ACP: Acid Phosphatase. SC: Sucrase.
The application of MOF improved soil enzyme activities under both soil conditions; continuous cropping soils increased to a much greater extent. Further, the activity of CAT was significantly increased by 22.75% in continuous cropping soils and 19.05% in first cropping soils, while the activity of UE was significantly elevated by 84.95% in continuous cropping soils and 55.08% in first cropping soils (Table 2).
3.5. The Application of MOF Changed Soil Microbial Communities
Good’s coverage index for the observed bacterial and fungi ASV was 99%, this indicating the entirety of the microbial diversity present in our samples. The soil conditions at the two selected experimental sites showed similar bacterial and fungi alpha diversity, but exhibited distinct differences in fungi beta diversity, while maintaining comparable bacterial beta diversity (Tables S1 and S2). This could be due to variations in soil pH, OM, OC, AP, and AK that fungi are more sensitive to than bacteria. Upon the application of MOF, there was a slight increase in bacterial and fungi Shannon, ACE, and Chao1 indexes under both conditions (Table S1). While no significant differences were observed in bacterial weighted UniFrac, unweighted UniFrac, and Bray–Curtis, the fungi unweighted UniFrac index showed a significant decrease after MOF application (Table S2). PCoA analyses demonstrated Beta diversity, where samples from the same treatment clustered together and samples from all four treatments were distinguishable (Figure S1). Regarding bacteria, the first and second principal coordinates together explained 33.05% of the variation in community structure. To fungi, the first and second principal coordinates together explained 61.88% of the variation in community structure.
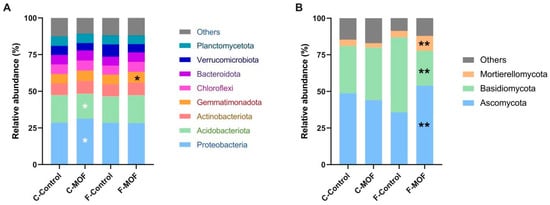
At the phylum level, species with a relative abundance greater than 3% were identified as dominant bacteria and fungi. The dominant bacterial phyla in the soil were Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, Actinobacteriota, Gemmatimonadota, Chloroflexi, Bacteroidota, Verrucomicrobiota, and Planctomycetota, accounting for >89% of the ASVs. When MOF was used in continuous cropping soils, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria increased by 8.4%, while that of Acidobacteriota decreased by 8.9%. Additionally, the application of MOF in first cropping soil of P. ternata resulted in a significant increase of 13.3% in the relative abundance of Gemmatimonadota (Figure 6A). The dominant fungi phyla in the soil were Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Mortierellomycota. Interestingly, only the first cropping soils treatment with MOF led to significant changes in their abundance, whereas no alterations were observed in the continuous cropping soils treatment following MOF application. The relative abundance of Ascomycota and Mortierellomycota increased by 34% and 57%, while Basidiomycota decreased by 53% (Figure 6B).
Figure 6.
Effect of microbial organic fertilizer application on the relative abundance of bacteria and fungi in the rhizosphere soil of P. ternata at the phylum level. (A) bacterial phyla, (B) fungi phyla. Statistical significance was analyzed by Student’s t-test. Black asterisks of * and ** indicate significant differences at p < 0.05 and p < 0.01 in relative abundance between F-Control and F-MOF, white asterisks represent significant difference at p < 0.05 in relative abundance between C-Control and C-MOF. C-Control: Planting in continuous 2-year cropping soils of P. ternata. C-MOF: Application of microbial organic fertilizer in continuous 2-year cropping soils with a concentration of 75 g/m2. F-Control: Planted in the soil of the first planting of P. ternata. F-MOF: Application of microbial organic fertilizer in first planting soils with a concentration of 75 g/m2.
Similar changes were also observed in the relative abundance of both bacterial and fungi communities at the family and genus levels. Specifically, the most significant alterations in bacterial abundance were noted within the continuous cropping soils condition, while the changes in fungi abundance were seen in the first cropping soil condition (Figure S2).
3.6. Relationships Between Soil Microbial Community and Soil Biochemical Properties
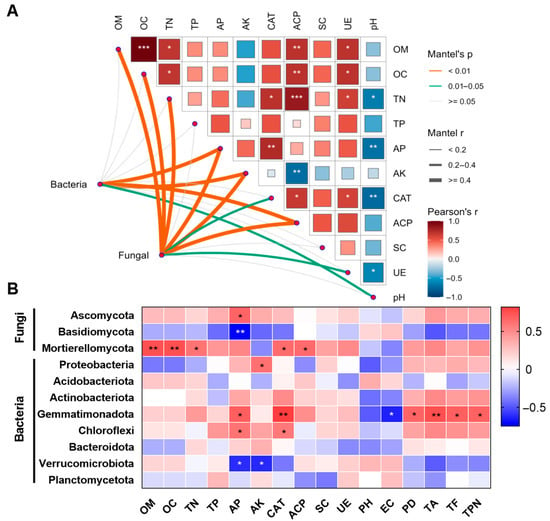
The Mantel test was used to explore the correlation between soil physical and chemical properties and bacterial and fungi abundance. The Mantel test revealed a positive correlation between the observed fungi abundance and OM, OC, TN, AP, AK, and ACP. Additionally, the ASV abundance of bacterial was positively correlated with AP, AK, and ACP (Figure 7A). This suggested MOF application mainly affected the levels of AP, AK, and ACP activity. These changes, in turn, affected the abundance of both bacterial and fungi communities.
Figure 7.
Relationship between soil properties and microbial abundance. (A) The relationships of the physicochemical factors with bacteria and fungi were obtained by the Mantel test. The color gradient and the squares represent the Pearson correlation coefficient. The relationships of the physicochemical factors with bacteria and fungi were obtained by Mantel test. The width of the curve represents Mantel’s r statistic for the correlation coefficient (R), and the color represents the type of association. (B) The Pearson correlation between various microbial and soil properties. *, ** and *** indicate significant differences at p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively.
Furthermore, Pearson correlation analysis was performed to investigate the precise relationship between each dominant bacterial and fungi phylum and soil biochemical characteristics. The analysis revealed that Ascomycota, Mortierellomycota, Gemmatimonadota, and Chloroflexi showed significant correction with various soil biochemical properties. Specifically, Mortierellomycota exhibited strong positive correlations with OM, OC, TN, and activities of CAT and ACP. Additionally, Gemmatimonadota demonstrated positive relationships with AP and CAT activity (Figure 7B). These findings suggested that specific microbial phyla play crucial roles in influencing soil biochemical properties, highlighting the intricate interactions within soil ecosystems.
4. Discussion
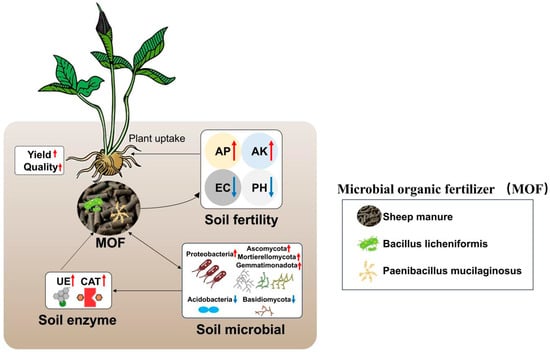
MOF are composed of natural ingredients and live microorganisms [37]. Previous studies have shown that MOF can enhance crop yield and quality by improving soil ecosystems, with these effects demonstrated in crops such as potato [38], tea [22], rice [39], and wheat [40]. In our case, application of MOF at a dosage of 75 g/m2 resulted in a significant increase in both yield and quality of P. ternata (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3). This improvement could be due to the live microorganisms in MOF affecting microbial communities, regulating nutrient cycling, and influencing soil properties, which in turn enhanced the growth and development of P. ternata (Figure 8).
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of the changes of soil after application of microbial organic fertilizer in P. ternata. The red and blue arrows represent an increase and decrease, respectively.
4.1. Effect of MOF Application on Soil Quality
Soil physicochemical properties serve as indicators of soil quality, reflecting the ability of soil to maintain environmental quality and promote plant productivity [41]. Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus mucilaginosus, known for their safety, are used in commercial probiotics and have been widely applied in many plants, including tomato, rice, and wheat [39,40,42]. Here, we selected one commonly used MOF containing Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus mucilaginosus to test its effect on P. ternata growth and soil quality. Our results demonstrated that applying appropriate MOF significantly increased the content of AP and AK while reducing soil pH and EC in both soil types (Table 2), and one possible reason for these improvements is that MOF contain active Bacillus spores. It was noted that the experimental site was located in the north of Anhui providence, China, which is a typical saline–alkali type land. Our results showed that applying MOF led to a decrease in pH value. This reduction occurred because the bacteria produced pyruvate, which was then converted into organic acids such as lactic acid and acetic acid, thereby decreasing soil acidity [18].
Plants mainly get phosphorus and potassium from the soil, but most of them are in an insoluble form that plants cannot use. Our study showed a significant increase in soil’s available phosphorus and potassium levels after application of microbial fertilizers (Table 2), and Mantel’s test showed that the bacterial and fungi communities were significantly correlated with soil AP and AK (Figure 7A). This suggested the bacteria and fungi in the MOF dissolved insoluble phosphorus and potassium, enhancing their bioavailability. For example, the abundance of Proteobacteria was reported to be positively related to the content of AP and AK [43]. As expected, after MOF application, its abundance was increased in the continuous cropping soils (Figure 6A). Collectively, our results indicated that MOF could improve soil nutrient status and fertility compared to using only chemical fertilizers or no fertilizer at all.
4.2. Effect of MOF Application on Soil Enzyme Activities
Soil enzymes serve as crucial indicators of soil quality, mirroring the biological activity and health of soil ecosystems [44]. Soil enzyme activities, excreted by both microorganisms and plant roots, serve as indicators of microbial growth and activity and overall soil quality [39,45,46]. Our findings showed that MOF notably enhanced the activity of specific soil enzymes, particularly CAT and UE. CAT serves as an important redox enzyme system for soil humus synthesis and preventing hydrogen peroxide toxicity to soil enzymes [47]. UE is the only enzyme that significantly impacts urea conversion, the enzymatic product of UE, ammonia, is a vital nitrogen source for plants. The enhanced activity of these two enzymes contributed to the observed increase in plant growth in our study, underscoring the importance of enzymatic processes in promoting soil health and plant development. Therefore, our results indicate that Bacillus type MOF has significant benefits for the alleviation of continuous cropping obstacle and improve the yield and quality of P. ternata.
4.3. Effect of MOF Application on Bacterial and Fungi Communities in the Rhizosphere of P. ternata
Soil microbiomes play a pivotal role in agroecosystems, governing soil fertility, crop productivity, and stress tolerance [48]. Zhao et al. had reported that CC changed the composition of the microbial community, causing an increase in the relative abundance of pathogenic microorganisms in the P. ternata rhizosphere [14]. Similarly in this study, the alteration of soil microbial communities was different in the first cropping and continuous cropping soils. In the continuous cropping soils, the abundance of Proteobacteria was significantly increased, while the abundance of Acidobacteriota was decreased (Figure 6A). Proteobacteria is a common type of Gram-negative bacteria, divided into five major classes [43]. These classes participate in symbiotic relationships with root nodules, nitrogen cycling, soil nutrient transformation, and other ecological processes, as well as regulate soil microbial diversity and the degradation of organic matter [49,50]. This result indicated that continuous cropping obstacles could be alleviated by MOF application.
However, unlike continuous cropping soils, changes in the microbial community in the rhizosphere of P. ternata in first cropping soil were mainly observed among fungi. A recent study reported that Ascomycota and Mortierellomycota thrived, while the abundance of Basidiomycota showed significantly decrease in healthy soil [51], and our study revealed a similar pattern (Figure 6). As a key species of the fungi community, Ascomycetes is considered to be composed of eutrophic fungi [52]. Fertilizer application has been found to boost the relative abundance of ascomycetes with increasing soil nutrient levels. Furthermore, a mutualistic relationship may exist between Bacillus strains and Ascomycota, where Bacillus metabolic byproducts or environmental conditions favor the growth and reproduction of Ascomycota.
Additionally, previous research indicates that Mortierellomycota can solubilize mineral phosphorus and enhance soil nutrients by producing oxalic acid [53,54]. Therefore, our results suggest that Bacillus-based MOF significantly improves soil quality and enhances the yield and quality of P. ternata.
4.4. Effect of MOF Application on P. ternata Quality Mainly Through the Action of Microbial Communities
To our knowledge, only bacterial inoculants have been found to impact the quality of P. ternata, with no such effect for chemical or organic fertilizers. For instance, organic fertilizer application in P. ternata increased the yield by 42.35% while maintaining the alkaloid content [17]. In contrast, exogenous microbial inoculum treatments, such as Streptomyces jingyangensis T. and Bacillus mucilaginosus, not only increased the yield of P. ternata by 60% and 48%, respectively, but also enhanced the alkaloid content by 3% and 3.6% [16]. In this study, the bioactive compounds and yield of P. ternata were simultaneous increased following MOF application, particularly in continuous cropping soil. This is important for medicinal plants like P. ternata, where the bioactive compounds are crucial for their therapeutic value. It was speculated that this effect may be due to the products of 2,3-butanediol and acetoin from Bacillus strains, which could regulate the synthesis of abscisic acid and gibberellin. Another contribution may be the interaction between P. ternata and soil microorganisms after MOF application. MOF promote plant growing, in turn, plants secrete some specific substances, recruit specific soil microorganisms, and form complex reciprocal relationships, ultimately improving the viability of plants.
This study investigated the effects of MOF on the quality and yield of P. ternata in both continuous-cropping and non-continuous-cropping soils, providing scientifically significant insights for P. ternata cultivation. However, the geographical constraints of the study area may limit the generalizability of findings to P. ternata growth regulation in diverse habitats. Thereby, future research should examine how MOF influence P. ternata growth across different regions and throughout developmental stages, subsequently verifying functional contributions of candidate microbial communities.
5. Conclusions
With the increasing prominence of field soil deterioration and nutrient imbalance, the yield and quality of cultivated P. ternata have been consistently challenged. The present study demonstrated that the application of MOF significantly enhanced the yield and quality of P. ternata under both continuous cropping soils and first cropping soil conditions. This improvement was attributed to increased photosynthetic efficiency, and various agronomic traits, as well as elevated the levels of flavonoids and total alkaloids in tubers, particularly at a dosage of 75 g/m2. Additionally, soil biochemical properties such as AP, AK, CAT, and UE were improved. The abundance of specific bacterial and fungal also varied after MOF application.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae11091103/s1, Figure S1: Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of rhizosphere microorganisms under different treatments of Pinellia ternata in field experiments. distance algorithm; Figure S2: Effect of microbial organic fertilizer application on the relative abundance of bacteria and fungi in the rhizosphere soil of Pinellia ternata at the genus level. Table S1: Microbial community Alpha and Beta diversity of bacteria; Table S2: Microbial community Alpha and Beta diversity of fungi.
Author Contributions
R.W., T.X. and J.X. conceptualized the study. Y.C., Y.W., P.L., Z.L., Q.C. and R.Y. performed the experiments. Y.C. and Y.W. analyzed the data with advice from Y.D., J.X., R.W. and T.X.; R.W. wrote the manuscript with the input from Y.C., D.W., J.X., V.K., T.X., T.X. and J.X. revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82274048 and 82373993), the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (2408085QH288), the Project of Natural Science Research of Universities in Anhui Province (2024AH051697), and Excellent Scientific Research and Innovation Team of University in Anhui Province (2022AH010029).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
C: continuous cropping two years soil of P. ternata. F: first planting P. ternata soil. C-Control: No fertilizer was applied in the soil of P. ternata continuous cropping. C-MOF: Applying 75 g/m2 MOF in the continuous cropping soil of P. ternata. F-Control: No fertilizer was applied in the soil of P. ternata first cropping. F-MOF: Applying 75 g/m2 MOF in the soil of P. ternata first cropping. MOF: Microbial organic fertilizer. OM: Organic Matter. OC: Organic Carbon. TN: Total Nitrogen. TP: Total Phosphorus. AP: Available Phosphorus. AK: Available Potassium. CAT: Catalase. UE: Urease. ACP: Acid Phosphatase. SC: Sucras. Pn: The photosynthetic rate. Gs: stomatal conductance. Ci: intercellular carbon dioxide Concentration. Tr: transpiration rate. ΦPSII: The quantum yield of PSII. Fv/Fm: the maximum chemical efficiency.
References
- Zhang, J.Y.; Luo, M.; Miao, Y.H.; Xu, R.; Wang, M.X.; Xu, J.W.; Liu, D.H. Germplasm resources, genetic diversity, functional genes, genetic breeding, and prospects of Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Breit: A review. Med. Plant Biol. 2023, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.F.; Liu, M.M.; Zheng, X.Y.; Xiao, C.N.; Ji, Y.C.; Duan, Y.B.; Zhu, Y.F.; Xue, J.P.; Bo, C.; Xue, T. Pinellia ternata HD-Zip6 gene positively regulates heat stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis by increasing ROS scavenging and NAC019 expression. Plant Stress 2025, 16, 100806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.J.; He, Z.H. Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Breit: A review of its germplasm resources, genetic diversity and active components. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 113252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Cui, W.N.; Bo, C.; Wang, R.; Zhu, Y.F.; Duan, Y.B.; Wang, D.X.; Xue, J.P.; Xue, T. PtWRKY2, a WRKY transcription factor from Pinellia ternata confers heat tolerance in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Singh, B.; Chauhan, R.S.; Duan, Y.B.; Xue, J.P.; Kumar, V.; Xue, T. A novel transcription factor PtMYB77 from Pinellia ternata enhances heat tolerance in Arabidopsis by inducing early expression of heat shock factor genes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 227, 120791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Xiong, Y.J.; Shi, J.; Chao, Q.J.; Zhu, Y.F.; Duan, Y.B.; Sheng, W.; Teng, J.T.; Xue, J.P. UHPLC-MS-based metabolomic approach for the quality evaluation of Pinellia ternata tubers grown in shaded environments. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Jia, H.F.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.T.; Liu, X.; Chao, Q.J.; Zhao, F.L.; Meng, Z.; Xue, J.P.; Lin, J.S.; et al. A chromosome-level Pinellia ternata genome assembly provides insight into the evolutionary origin of ephedrine and acrid raphide formation. Med. Plant Biol. 2024, 3, e013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahagi, T.; Atsumi, T.; Mano, S.; Kikuchi, Y.; Hara, Y.; Furukawa, M.; Yang, Z.G.; Matsuzaki, K. Quality evaluation of Pinellia tuber by LC-TOF/MS targeted to ephedrine. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sun, Y.T.; Wang, Z.J.; Huang, Z.H.; Zou, Y.Q.; Yang, F.F.; Hu, J.; Cheng, H.J.; Shen, C.J.; Wang, S.L. Pinellia genus: A systematic review of active ingredients, pharmacological effects and action mechanism, toxicological evaluation, and multi-omics application. Gene 2023, 870, 147426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Qi, J.B.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.T.; Wang, R.; Shi, Y.H. A comprehensive review on ethnopharmacological, phytochemical, pharmacological and toxicological evaluation, and quality control of Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Breit. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.G.; Mao, R.J.; Dong, J.E.; Liang, Z.S.; Zhang, H.H.; Liu, L. Remediation of deterioration in microbial structure in continuous Pinellia ternata cropping soil by crop rotation. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xie, B.; He, B.S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Abliz, Z. Multidimensional molecular differences between artificial cultivated and wild Artemisia rupestris L. based on metabolomics–transcriptomics integration strategy. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Zhao, C.L.; Song, W. Review of the evolution of cultivated land protection policies in the period following China’s reform and liberalization. Land Use Policy 2017, 67, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qin, X.M.; Tian, X.P.; Yang, T.; Deng, R.; Huang, J. Effects of continuous cropping of Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Breit. on soil physicochemical properties, enzyme activities, microbial communities and functional genes. Chem. Biol Technol. Agric. 2021, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, M.; Zhao, X. Brassica juncea seed meal particle size influences chemistry but not soil biology-based suppression of individual agents inciting apple replant disease. Plant Soil 2010, 337, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.T.; Alami, M.M.; Tang, H.M.; Zhai, J.S.; Nie, Z.N.; Hu, J.L.; Shu, S.H.; Zhu, D.W.; Yang, T.W. Applications of Streptomyces jingyangensis T. and Bacillus mucilaginosus A. improve soil health and mitigate the continuous cropping obstacles for Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Breit. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 180, 114691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, J.X.; Qu, K.L.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.X.; Xia, S.J.; Cai, H.X.; Long, X.E.; Miao, Y.H.; Liu, D.H. Organic fertilizer application promotes the soil nitrogen cycle and plant starch and sucrose metabolism to improve the yield of Pinellia ternata. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.C.; Chen, Y.; Dou, X.H.; Liao, D.X.; Li, K.Y.; An, C.C.; Li, G.H.; Dong, Z. Microbial fertilizers improve soil quality and crop yield in coastal saline soils by regulating soil bacterial and fungal community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, K.; Maheshwari, D.K. Bacillus megaterium strain CDK25, a novel plant growth promoting bacterium enhances proximate chemical and nutritional composition of Capsicum annuum L. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, J.L.; Ma, L.; Wu, X.B.; Zheng, F.L.; Cui, R.Z.; Tan, D.S. Enhancing wheat yield through microbial organic fertilizer substitution for partial chemical fertilization: Regulation of nitrogen conversion and utilization. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Bai, Z.H.; Bao, L.J.; Xue, L.X.; Zhng, S.W.; Wei, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhuang, G.Q.; Zhuang, X.L. Bacillus subtilis biofertilizer mitigating agricultural ammonia emission and shifting soil nitrogen cycling microbiomes. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 105989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.B.; Cui, S.Y.; Wu, L.T.; Qi, W.L.; Chen, J.H.; Ye, Z.Q.; Ma, J.W.; Liu, D. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on soil fertility, yield, and quality of tea. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 5109–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shraim, A.M.; Ahmed, T.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Hijji, Y.M. Determination of total flavonoid content by aluminum chloride assay: A critical evaluation. LWT 2021, 150, 111932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, E.A.; Gillespie, K.M. Estimation of total phenolic content and other oxidation substrates in plant tissues using Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnaggar, A.; Tsombou, M.F.; Hussain, I.M.; Almehdi, A.M.; Abideen, Z.; Yong, J.W.H.; El-Keblawy, A. Citrullus colocynthis regulates photosynthetic and biochemical processes to develop stress resilience and sustain growth under sub-optimal temperatures. Plant Stress 2024, 12, 100502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Fang, H.; Xie, J.M.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Z.Q.; Liu, Z.C.; Lv, J.; Yu, J.H. Physiological responses of cucumber seedlings to different supplemental light duration of red and blue LED. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 709313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.B.; DeSutter, T.; Prunty, L.; Hopkins, D.; Jia, X.H.; Wysocki, D.A. Evaluation of 1:5 soil to water extract electrical conductivity methods. Geoderma 2012, 185–186, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. Methods for Soil Agro-Chemistry Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Segura, C.; Horrocks, C.; Lopez-Aizpun, M.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Darch, T.; Hood, J.; Le Cocq, K.; McAuliffe, G.A.; Lee, M.R.F.; Cardenas, L. Response of soil health indicators to dung, urine and mineral fertilizer application in temperate pastures. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tian, J.; Wu, X. Correlation between plant diversity and the physicochemical properties of soil microbes. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 10371–10388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.J.; Lai, S.S.; Luo, X.S.; Lu, J.W.; Huang, Q.Y.; Chen, W.L. Effects of long term rice straw application on the microbial communities of rapeseed rhizosphere in a paddy-upland rotation system. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 575–558, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Duan, Y.S.; Huo, W.G.; Xu, M.G.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, B.R.; Blackwel, M.S.A.; Feng, G. Soil microbial biomass phosphorus can serve as an index to reflect soil phosphorus fertility. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 57, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begmatov, S.; Dorofeev, A.G.; Kadnikov, V.V.; Beletsky, A.V.; Pimenov, N.V.; Ravin, N.V.; Mardanov, A.V. The structure of microbial communities of activated sludge of large-scale wastewater treatment plants in the city of Moscow. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.I.; Miletto, M.; Taylor, J.W.; Bruns, T.D. Dispersal in microbes: Fungi in indoor air are dominated by outdoor air and show dispersal limitation at short distances. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knigh, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, T.Y.; Hu, Q.F.; Mao, W.J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; Sun, L.N.; Zhai, M.Z. Metagenomics insights into the functional profiles of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles in a walnut orchard under various regimes of long-term fertilisation. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 148, 126887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Cota, F.I.; Peña-Cabriales, J.J.; Santos-Villalobos, S.D.L.; Santos-Villalobos, N.A.; Délano-Frier, J.P. Burkholderia ambifaria and B. caribensis promote growth and increase yield in grain amaranth (Amaranthus cruentus and A. hypochondriacus) by improving plant nitrogen uptake. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.X.; Zhang, F.Y.; Cui, G.H.; Wang, Y.N.; Yang, J.G.; Cheng, H.C.; Liu, H.W.; Zhang, L.P. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on soil fertility, microbial community composition, and potato growth. ScienceAsia 2021, 47, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, W.; Sun, T.; Ma, Y.Y.; Chen, C.; Ma, Q.X.; Wu, L.H.; Wu, Q.C.; Xu, Q. Higher yield sustainability and soil quality by manure amendment than straw returning under a single-rice cropping system. Field Crops Res. 2023, 292, 108805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.L.; Gong, T.; Wang, J.W.; Li, G.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhen, J.; Ning, M.; Yue, D.; Du, Z.M.; Chen, G.C. Effects of compound microbial fertilizer on soil characteristics and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, S.; Abraham, J.S.; Somasundaram, S.; Toteja, R.; Gupta, R.; Makhija, S. Indicators for assessment of soil quality: A mini-review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de O Nunes, P.S.; de Medeiros, F.H.V.; de Oliveira, T.S.; de Almeida Zago, J.R.; Bettiol, W. Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis promote tomato growth. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuña, J.J.; Marileo, L.G.; Araya, M.A.; Rilling, J.I.; Larama, G.A.; Mora, M.L.; Epstein, S.; Jorquera, M.A. In situ cultivation approach to increase the culturable bacterial diversity in the rhizobiome of plants. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 1411–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yu, L. Effects of Cd or/and Pb on soil enzyme activities and microbial community structure. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Wei, T.X.; Sha, G.L.; Zhu, Q.K.; Liu, Z.; Ren, K.; Yang, C. Soil enzyme activities of typical plant communities after vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 170, 104292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daunoras, J.; Kačergius, A.; Gudiukaitė, R. Role of soil microbiota enzymes in soil health and activity changes depending on climate change and the type of soil ecosystem. Biology 2024, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowiak, A.; Lemanowicz, J.; Breza-Boruta, B. Evaluation of the content of Zn, Cu, Ni and Pb as well as the enzymatic activity of forest soils exposed to the effect of road traffic pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 23893–23902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Six, J. Soil structure and microbiome functions in agroecosystems. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.H. Identifying the dominant soil bacterial taxa in libraries of 16S rRNA and 16S rRNA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spain, A.M.; Krumholz, L.R.; Elshahed, M.S. Abundance, composition, diversity and novelty of soil Proteobacteria. ISME J. 2009, 3, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.J.; Ge, C.; Zhou, J.F.; Li, J. Diversity of soil fungi in the vineyards of Changli region in China. Can. J. Microbiol. 2022, 68, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.A.; Mahboubi, A.; Lennartsson, P.R.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Waste biorefineries using filamentous ascomycetes fungi: Present status and future prospects. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Jin, L.; Zhu, R.; Yu, X.-Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, B.-T.; Ruan, H.-H.; Jin, F.-J.; Lee, H.-G. Phosphorus-solubilizing capacity of Mortierella species isolated from rhizosphere soil of a Poplar Plantation. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatafora, J.W.; Chang, Y.; Benny, G.L.; Lazarus, K.; Smith, M.E.; Berbee, M.L.; Bonito, G.; Corradi, N.; Grigoriev, I.; Gryganskyi, A.; et al. A phylum-level phylogenetic classification of zygomycete fungi based on genome-scale data. Mycologia 2016, 108, 1028–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).