Abstract
Biochar has demonstrated effectiveness in environmental remediation. However, the physicochemical properties of biochar change with natural aging, which potentially impacts its efficacy. This study was designed to evaluate the effects of aged biochar (at 1% and 5% rates) on the growth of Chinese cabbage, greenhouse gas emission, and Cd remediation in soils. Canada goldenrod (Solidago canadensis L.) feedstock biochar was subjected to three artificial aging processes (freeze–thaw cycle, dry–wet cycle, and hydrogen peroxide oxidation) to prepare aged biochar. Results showed that aging significantly altered properties and structure of biochar. Biochar addition had no effect on CH4 emissions, but it decreased cumulative N2O emission (all treatments) and increased cumulative CO2 emission (only the pristine biochar at 5% application rate). Aged biochar showed no effect on microbial life strategy and Shannon index. However, PB-5% application shifted the life history strategies of A-strategists (resource acquisition microbe) towards Y-strategists (high-yield microbe) such as Proteobacteria, Gemmatimonadota, Bacteroidota, Firmicutes and Actinobacteriota, which partially attributed to the enhanced soil CO2 emission. Aged biochar reduced plant uptake Cd and soil available Cd concentrations by up to 36.6% and 34.0%, respectively, ascribing to improved soil physicochemical properties and functional bacterial abundance.
1. Introduction
Biochar, a C-rich byproduct, is produced from anoxic thermochemical conversion of organic biomass [1]. Over the last decade, increased interest has been placed on the potential role of biochar as an environmentally functional material due to its unique properties (i.e., relatively large surface areas, highly porous, fused aromatic C structure) [2,3]. Research indicates that negatively charged biochar can act as a strong sorbent to control the lability of contaminants in amended system, thus reducing the persistence of pollutants [4,5]. Particularly, biochar is widely utilized as a multifunctional soil amendment because of its perceived value on climate change mitigation and polluted soil remediation [6].
Although biochar possesses a certain degree of chemical and biological stability, its functionality is inevitably affected by different factors after application in soil, such as precipitation, temperature, oxidation, biodegradation, etc., a phenomenon known as weathering or aging [7,8,9]. Progressive aging can change the physicochemical properties of biochar (i.e., element composition, surface morphology), correspondingly shifting soil microbial structure and affecting its remediation performance [10]. In particular, natural aging could promote biochar physical fragmentation and result in an abundance of oxygen-containing function groups on its surface [11]. Because implementation of long-term aging for biochar is time-consuming and often problematic, artificially approaches were then developed and intended to accelerate and simulate the process [12,13,14,15]. These approaches, such as physical process (i.e., freeze–thaw cycling) and chemical oxidation, were successfully employed [16,17,18]. For instance, Chang et al. (2019) demonstrated that leaching, acidification, and oxidation aging resulted in a decline of cadmium (Cd) adsorption on corn stalk biochar made at 650 °C [11]. Similarly, a meta-study from 22 published works demonstrated that, in comparison with fresh biochar, the artificially aging biochar significantly decreased CO2, N2O, and CH4 emissions by 11%, 15%, and 25%, respectively [19].
Research suggested that biomass feedstock also exserts a crucial influence on the pore structures, surface functional groups, and elemental composition of biochar, which may further determine its efficiency [1]. Currently, the spread of invasion plants is threatening the structure and function of native ecosystems throughout the world. For example, Canada goldenrod (Solidago canadensis L.), a perennial goldenrod weed originating from North America, is expanding into Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and Asia, and it is listed as one of the most destructive invasive plants in China [20]. Biochar production using invasive plants as feedstocks may provide a win–win situation to effectively achieve resource utilization and alleviate associated ecological issues. Some researchers have used invasive plants as raw materials to produce biochar. For instance, Spartina alterniflora biochar prepared under low-temperature pyrolysis conditions (350 and 450 °C) was beneficial to immobilization of Cd in soil, and the available Cd content decreased by up to 26.9% [21].
Cadmium is one the most concerning heavy metals in agricultural soils, with 7% of the arable land exceeding the limiting standard estimated by the Ministry of Environmental Protection of China [22]. The Cd transfer through the soil–plant system is a main exposure path for human bodies, causing a number of disorders such as kidney dysfunction, Itabirites disease, and cancer [23]. As one of the most important vegetables, Chinese cabbage (Brassica chinensis L.) is a main source of Cd for humans via the food chain. Numerous studies have reported that biochar could immobilize Cd in soil, reducing its uptake by vegetable [24,25,26,27].
Despite the vast scientific literature demonstrating a wide range of benefits associated with biochar application, including enhanced crop production, improved microbial function along with immobilization of toxic metals in soil, and carbon sequestration to mitigate climate change [28,29,30,31], limited information currently exists regarding soil greenhouse gas (GHG) emission and Cd remediation responses with aged biochar application. Thus, research is needed to better understand the potential role of aged biochar on soil remediation and agricultural productivity. It was hypothesized that (1) aged biochar can improve soil nutrient status after being applied to soil; (2) aged biochar can reduce Cd accumulation in plant mainly by reducing soil available Cd content; (3) aged biochar can alter GHG emissions while improving soil physical, chemical, and biological properties. Thus, the objectives of the current study were to investigate the effects of aged biochar on soil available Cd content and plant uptake of Cd, and soil GHG emissions on the growth of Chinese cabbage.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Biochar
2.1.1. Preparation of Pristine Biochar
Biochar material was produced in a slow pyrolysis process from Solidago canadensis biomass. Biomass was pyrolyzed in a nitrogen atmosphere (the flow rate of 40 mL m in−1) at a highest temperature of 500 °C and residence time of 120 min in a rotary furnace. The obtained biochar was washed three times by deionized water and ethanol (volume ratio of 1:1) and vacuum dried for 24 h in the oven at 60 °C.
2.1.2. Preparation of Aged Biochar
Aging treatment, including physical and chemical processes, was carried out in the laboratory over one month. For physical aging, we subjected the obtained pristine biochar to 10 freeze–thaw cycles and followed by 10 dry–wet cycles. During the freeze–thaw cycle, biochar samples were frozen at −20 °C for 12 h and then thawed at 25 °C for 12 h. For the alternating dry–wet cycle, biochar samples were moisturized by adding deionized water to maintained the water holding capacity of 100% for 12 h and then dried for another 12 h at 80 °C in an oven.
For chemical aging, the physically aged biochar was oxidized with 30% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) solution in a ratio of 1:20 (w/v) for 24 h [32]. After oxidation, the samples were separated by vacuum filtration, repeatedly washed with deionized water to remove any residual H2O2, and dried at 80 °C. The H2O2 oxidized biochar was reported exhibiting surface properties resembling biochar naturally aged for 10 years [33].
2.2. Experimental Setup
Surface horizon (0–20 cm) of Fluvo-aquic soil (Luvisols consisting of fluviatile deposits with a silt texture) was collected from a crop field located in Zhenjiang, Jiangsu Province, China (32°09′47.0″ N, 119°32′24.4″ E). Soil samples were air-dried, homogenized, and sieved through a 2 mm screen. Selected physicochemical properties of the original soil are shown in Table 1. The uncontaminated soil was mixed with cadmium chloride (CdCl2·2.5H2O) to achieve soil total Cd concentration of 5 mg/kg, which was greater than the value of 0.3 mg/kg (6.5 < soil pH ≤ 7.5) prescribed by the National Environmental Protection Agency of China (GB15618-2018) [34]. Soil moisture content was maintained at 60% of the field capacity and incubated for one month under open conditions.

Table 1.
Basic chemical properties of soil.
Chinese cabbage seeds were germinated in uncontaminated soils in an artificial climate chamber. Once the third true leaf was fully unfolded, healthy seedlings of similar growth were chosen, and three plants of approximately uniform size with equal spacing were transplanted in each pot.
Approximately 1.5 kg of air-dried, Cd-contaminated soils were gently packed into pot (11.5 cm tall, 20.5 cm and 11.2 cm in top and bellow diameter, respectively) to a bulk density of ~1.33 g/cm3 and thoroughly mixed with fertilizer and biochar. Fertilizers were applied at an equivalent rate of 160 kg N/ha and184 kg P/ha. Treatments consisted of a factorial combination of two biochar types (pristine biochar and aged biochar) and two application rates (1% and 5%, by weight basis): PB-1% (pristine biochar applied at 1%), PB-5% (pristine biochar applied at 5%), AB-1% (aged biochar applied at 1%), AB-5% (aged biochar applied at 5%). According to previous studies, the biochar application rates of 1% and 5% were more effective in promoting plant growth and immobilizing soil Cd [35,36]. In addition, control (no biochar, CK) treatment was also evaluated. Each treatment was conducted in quadruplicate for a total of 20 pots.
After eight weeks, Chinese cabbage was harvested. The root and aboveground part of the plant were washed and dried in an oven at 65 °C until a constant weight. Dry plant samples were grounded and sieved through a 100 mm mesh for further analysis. Rhizosphere soil was collected and preserved at −80 °C for microbiological analysis. Subsamples of soil were also taken for chemical analysis.
2.3. Greenhouse Gas Emission Determination
During plant growth, Carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions were measured at 1, 3, 7, 10, 17, 25, and 32 days using the static chamber technique at the same time of a day (8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.), which corresponded to the daily average temperature and mean flux [37]. The chamber was manufactured using a transparent acrylic tube (20 cm height, 4.5 cm diameter, base area:16 cm2) equipped with a flange around the edges. The top of the chamber was equipped with a sampling port fitted with a rubber septum (1 cm diameter) enabled for gas extraction. At each gas collection, the headspace was sampled using a 15 mL syringe at 10 min intervals (0, 10, 20, and 30 min after chamber closure). Gas samples were immediately transferred to evacuated glass vials (10 cm3) and analyzed by gas chromatography (GC 2010, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) with a micro-electron capture detector for N2O, a flame ionization detector for CH4, and a thermal conductivity detector for CO2 detection. Cumulative gas emissions (reported as kg/ha) were calculated by linear interpolation of the average emissions between the measured days.
2.4. Biochar Characterization
Biochar pH and electronic conductivity (EC) were measured using a 1:20 ratio (solid:/deionized water) by a dual channel pH/conductivity meter. The total carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), and nitrogen (N) concentrations of the pristine and aged biochar were determined by dry combustion in an elemental analyzer (Vario macro cube, Elementar, Langenselbold, Germany). Total Cd concentrations of biochar were measured after aqua regia digestion protocol by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, ICPE9820, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The specific surface area, pore volume, and pore size of two biochars were determined using a fulling automatic specific surface and porosity analyzer (JW-BK122F, Gaobo General Instrument, Beijing, China). A Gemeni 300 SEM equipped a Smartedx EDS (ZEISS, Sigma 300, Oberkochen, Germany) was employed to observe the biochar morphology before and after aging.
2.5. Soil Property Characterization
Soil pH was determined using 2.5 g of air-dried soil at a 10:1 (v/w, distilled water/soil) ratio by a pH meter (PHS-25, LeiCi, Shanghai, China). Soil temperature, salinity, and EC were measured using a portable digital senor (Shunda TR-6D kit, Tongde Co., Beijing, China). Total N and C were determined by the combustion method using an elemental analyzer (Vario macro cube, Elementar, Langenselbold, Germany). Soil organic C (SOC) was analyzed by wet oxidation in potassium dichromate solution 1 N and sulfuric acid as described by the Walkley–Black method [38].
Soil extractable NO3-N and NH4-N concentrations were determined by shaking 2.5 g of soil with 25 mL of 2 M KCl solution for 1 h [39]. Extracts were filtered through a Whatman #45 filter paper and analyzed for NO3-N and NH4-N using a UV spectrophotometer (UV2550, Shimadzu). Absorbance was measured at 667 nm and 540 nm for NH4-N and NO3 -N, respectively. Total Cd concentration in soil was determined using the HF-H2SO4-HclO4 solution as described by Alsaleh et al. [40]. The available Cd concentrations in soil were determined according to the diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA) extraction method [41].
To further identify the speciation distribution of Cd in soil (acid-extractable, reducible, oxidizable, and residual fractions), four steps of the Community Bureau of Reference (BCR) sequential extraction method were performed [42]. The detailed procedure is described in Supplementary Information. The Cd concentration in the extractants was analyzed with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, ICPE9820, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) for the soil and plant. The content of microbial biomass C (MBC) was measured using the fumigated extraction method [43]. Soil dissolved organic C (DOC) was measured using the combustion oxidation nondispersive infrared absorption method on a total organic C analyzer (Multi NC 3100, Analytic Jena, Jena, Germany).
2.6. Illumina-Based 16S rRNA Sequencing for Identification of Microbial Species
The bacterial community composition in different treated soils was analyzed using high-throughput sequencing technology. Briefly, bacterial DNA was extracted from soils using the Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit. The quality and purity of the extracted genomic DNA were checked using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. Specific primer pairs 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) were used to selectively amplify the V3-V4 region of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene. DNA was amplified by polymerase chain reaction. Sequence reads processing was performed using QIIME (version 1.9.0). Operational taxonomic unit (OTU) was picked by Vsearch v1.11.1, followed by dereplication, cluster, and detection of chimeras. Generally, the threshold of 97% similarity is set as 1 OTU.
Soil microbial alpha diversity was expressed using the Shannon index. Microbial life strategies were determined at the phylum level. Considering that biochar applied in soils is likely to create a gradient in resource availability [44,45,46], microbial taxa were categorized into high-yield microbial strategists (Y-strategists, analogous to copiotrophs) and resource-acquisition strategists (A-strategists, analogous to oligotrophs). Proteobacteria, Gemmatimonadota, Bacteroidota, Firmicutes, and Actinobacteriota were categorized as Y-strategists [47,48], while Acidobacteriota, Chloroflexi, Verrucomicrobiota, and Planctomycetota were classified as A-strategists [49,50]. The relative abundance of Y-strategists and A-strategists were summed to calculate oligotrophic/copiotrophic phyla ratio, a reflection of changes in microbial life strategies with biochar addition.
2.7. Statistical Analyses
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s test were employed to assess variations in soil properties and response variables among different treatments at p-value ≤ 0.05 using SAS (Version 9.4, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) [51]. The LSMEANS/PDIFF procedure was used to compare means. Microbial community structures based on the Bray–Curtis distance were subjected to principal coordinates analysis (PcoA) and PERMANOVA analysis (permutations = 999) in R (Version 4.4.1, R Core Team 2022, Vienna, Austria. ‘vegan’ and ‘ggplot2′ packages) [52]. The correlations between soil variables and greenhouse gas emission rate (CO2, N2O, and CH4 emission) were tested by Pearson correlation analyses. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was performed using the ‘vegan’ package to evaluate the changes in cumulative greenhouse gas emission, plant growth, and Cd uptake in relation to soil variables and microbial community traits. Their correlations were also tested by Mantel test in R (‘vegan’ package).
3. Results
3.1. Selected Properties of Biochar
Aging processes influenced the physicochemical properties of biochar (Table 2, Figure 1 and Figure S1). After aging, the pH value decreased from 8.8 (pristine biochar) to 8.1 (aged biochar). Similar decrease was observed in specific surface area (from 24.8 m2/g to 12.5 m2/g). Conversely, an approximate 58.6% increase in pore size was noted in aged biochar. It also had significantly higher electrical conductivity (EC) and C/N ratio (137.1 vs. 124.3) than those of pristine biochar, particularly for EC (4.7 vs. 37.9 μS/cm for pristine biochar and aged biochar, respectively).

Table 2.
Basic physical and chemical properties of biochars.
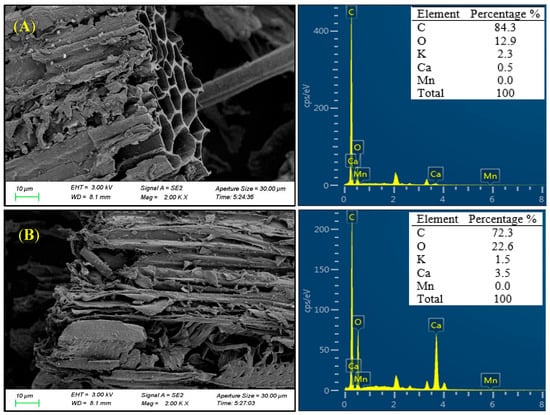
Figure 1.
The SEM image and EDS analysis of biochar before (A) and after (B) aging.
As illustrated in the SEM images (Figure 1), pristine biochar exhibited a smooth tubular structure with numbers of orderly arranged pores; however, after aging, the micromorphology of biochar underwent substantial changes, showing varying degrees of crack, pore wall collapse, and surface roughness. Total C content of biochar surface decreased from 84.3% (pristine biochar) to 72.3% (aged biochar). Conversely, oxygen content in aged biochar was substantially higher than that of pristine biochar (12.9% vs. 22.6%).
3.2. Soil CO2 and NO2 Emissions
Soil CO2 emission flux was affected by biochar treatment × the sampling day interaction (p < 0.0001, Figure 2A). Despite the significant effect, the impact of biochar on soil CO2 emission flux was inconsistent and mainly observed at the 1st and 10th sampling events. At the first day, PB-1% increased CO2 emissions by an average of 46.8% compared to other treatments. However, in subsequent sampling events, biochar either increased or had no effect on CO2 emission. Overall, addition of PB-5% increased cumulative CO2 emission by an average of 37.3% compared to other treatments (p = 0.047, Figure 2B).
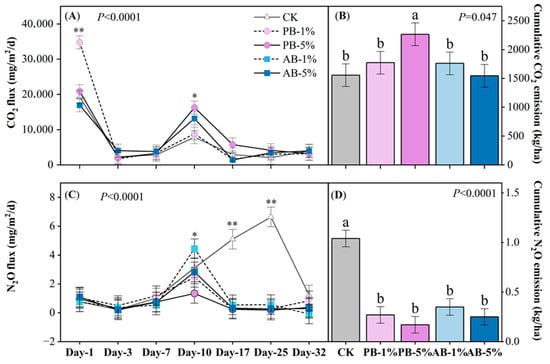
Figure 2.
Soil CO2 and N2O emission rates (A,C) and cumulative CO2 and N2O emission (B,D) during the whole experimentas affected by different treatments. Abbreviations: CK (no biochar application), PB-1% (pristine biochar applied at 1%), PB-5% (pristine biochar applied at 5%), AB-1% (aged biochar applied at 1%), AB-5% (aged biochar applied at 5%). Note: *, **, mean significant at p < 0.05, 0.01, respectively. Bars with the same letters across different treatments are not statistically different (p > 0.05). Data represent the average across four replicates (n = 4). Values are the means ± standard error.
Biochar had no significant effect on soil CH4 emissions, whereas N2O emission fluxes were significantly affected by biochar treatment and the sampling day interaction (p < 0.0001, Figure 2C). The fluxes were low at the first week but then followed a rapid increase at day 10 for all treatments. Overall, greater cumulative N2O emission was associated with CK (1.04 kg/ha) compared to the average across other treatments (0.26 kg/ha) (p < 0.0001, Figure 2D).
3.3. Soil Cd, Plant Cd Uptake, and Plant Biomass
Generally, the Cd speciation in soil showed no significant differences across treatments, except that AB-5% decreased the residual Cd more than other treatments (2.3% vs. 5.4% for AB-5% and other treatments, respectively) (Figure 3A).
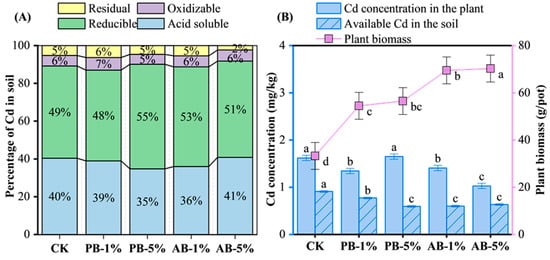
Figure 3.
Effect of aging and rate of biochar application on Cd speciation (A) and concentration (B). Bars with the same letters across treatments are not statistically different (p > 0.05) (n = 4). Abbreviations: CK (no biochar application), PB-1% (pristine biochar applied at 1%), PB-5% (pristine biochar applied at 5%), AB-1% (aged biochar applied at 1%), AB-5% (aged biochar applied at 5%).
In terms of plant available Cd in soil (Figure 3B), lower concentration was associated with aged biochar and PB-5% treatments compared to CK and PB-1%. Similarly, compared to CK, the Cd concentration in plants was significantly reduced with biochar application (except of PB-5%). Particularly for AB, average across its application rate, plant Cd uptake was reduced by as much as 36.6%. Conversely, biochar application increased plant biomass (p = 0.001), with a promotion of 63.9% to 111.3% compared to that of CK (Figure 3B).
3.4. Changes in Soil Microbial Communities and Their Life Strategies
The Venn diagram (Figure S3) reveals that, irrespective of biochar type, CK and 1% of biochar application rate share slightly greater operational taxonomic unit compared to that in soils treated with 5% rate biochar (5.8% vs. 5.3%). Differences in microbial community structure were found with biochar application based on Bray–Curtis distance through PcoA analyses (Figure 4A), with CK, PB-1%, and AB-1% being different from PB-5%; however, there was also a certain distance among AB-1%, PB-1%, and PB-5% soils, implying their difference in varying microbial community structure.
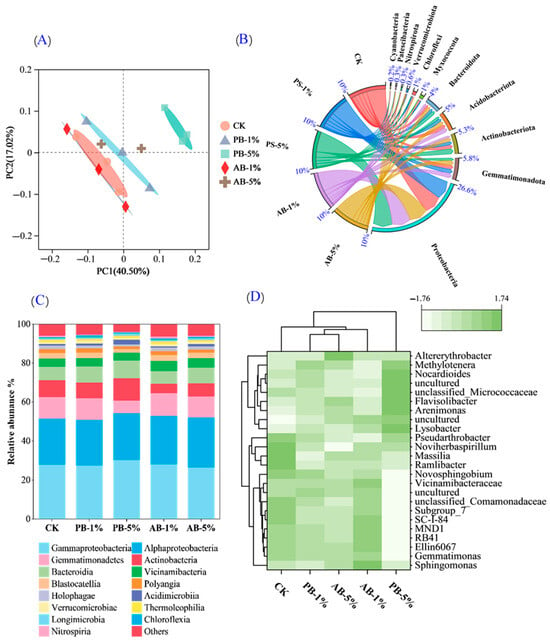
Figure 4.
The PcoA (A) and structure of microbial community at phylum (B), class (C), and genus (D) level in soils of control (CK) or treated by pristine biochar (PB-1% and PB-5%) and aged biochar (AB-1% and AB-5%).
The relative abundance of soil microbial communities of different treatments varied in terms of phylum, class, and genus levels (Figure 4B–D). Proteobacteria, Gemmatimonadota, Actinobacteria, Acidobacteria, and Bacteroidota were the top five microbes at the phylum level for all treatments, and their sum was greater in PB-5%-treated soil (94.1%) than other soils (averaged of 91.6%) (Figure 4B). Similarly, at the class level, the top five soil microbes were Gammaproteobacteria, Alphaproteobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, Actinobacteria, and Bacteroidia, the sum of which were greater in PB-5%-treated soil (81.5%) relative to other soils (averaged of 77.6%) (Figure 4C). Most of the dominant genera at the genus level were Sphingomonas and Gemmatimonas in all treatments (accounted for 30.7–37.6%) (Figure 4D).
Compared to CK, the relative abundance of total copiotrophs increased by 6.2% while that of oligotrophs decreased by 25.0% with PB-5% addition. Therefore, the oligotroph/copiotroph ratio of PB-5% decreased dramatically by 30.1% (Figure S2A). Concurrently, the Shannon index was slightly decreased with PB-5% addition, but no difference was found across other treatments (Figure S2B).
3.5. Relationship Between Soil Factors and Plant Biomass, Plant Cd, and Greenhouse Gas Emission
Although there was generally a significant correlation between soil variables and GHG emission rate, the relatively low coefficients (0.03–0.37) suggested that other factors involved in determining the variation of GHG emissions (Figure 5A). Soil temperature explained 25% of the variation in CO2 emissions (coefficient of 0.25) and a positive correlation was found. Similarly, there were positive correlations between soil moisture, EC, salinity, and CH4 and N2O emissions (coefficient of correlation ranging from 0.17 to 0.37).
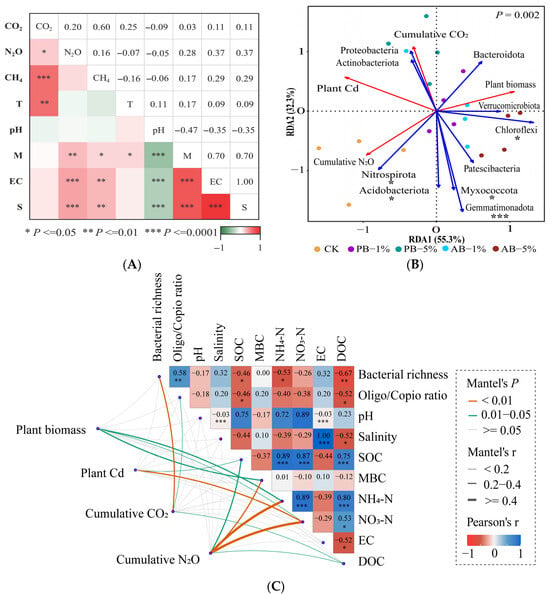
Figure 5.
(A) Correlation between soil variables and GHG emission rate (mg/m2/d). Note: The colors in the panels represent Pearson’s correlation coefficients, with red and green indicating positive and negative correlations, respectively. *** indicates p < 0.001; ** indicates p < 0.01; * indicates p < 0.05. (B) RDA analysis, including the top 10 bacterial communities at phylum level in different treatments as explanatory variables and cumulative GHG emissions, plant growth and Cd uptake as response variables. Abbreviations: CK (no biochar application), PB-1% (pristine biochar applied at 1%), PB-5% (pristine biochar applied at 5%), AB-1% (aged biochar applied at 1%), AB-5% (aged biochar applied at 5%). (C) Cumulative GHG emissions, plant growth and Cd uptake are related to each soil variable by Mantel test. Abbreviation: T = soil temperature, M = soil moisture, S = soil salinity, EC = soil electrical conductivity, MBC = soil microbial biomass carbon, DOC = dissolved organic carbon, SOC = soil organic carbon.
The redundancy analysis results (Figure 5B) indicated that the first two principal components explained 55.3% and 32.3% of the overall variance, respectively (p = 0.002). Plant biomass was significantly and positively correlated with Chloroflexi while negatively correlated with Nitrospirota and Acidobacteriota (p < 0.05). Plant Cd uptake was positively correlated with Nitrospirota (p < 0.05), while plant Cd and cumulative CO2 emission were both negatively correlated with Gemmatimonadota, Chloroflexi, Myxococcota, and Acidobacteriota (p < 0.05). Cumulative N2O emission was positively correlated with Nitrospirota, Gemmatimonadota, Acidobacteriota, Myxococcota and negatively correlated with Chloroflexi (p < 0.05).
In addition, the Mantel test (Figure 5C) and correlation analysis (Figure S4) revealed that plant biomass was positively correlated with microbial biomass carbon, NH4-N, and NO3-N, while plant Cd was negatively correlated with soil organic carbon and NO3-N; cumulative N2O emission was negatively correlated with soil organic carbon, microbial biomass carbon, dissolved organic carbon, NH4-N, and NO3-N; cumulative CO2 emission was negatively correlated with bacterial richness and the oligotroph/copiotroph ratio while positively correlated with dissolved organic carbon.
4. Discussion
4.1. Greenhouse Gas Emissions as Affected by Biochar Application
Soil CO2 emissions, which involve both heterotrophic (macro- and microorganism decomposition of organic matter) and autotrophic component (plant root respiration), are regulated by numbers of biotic and abiotic factors such as environmental conditions, substrate availability (C/N ratio), soil microbial composition, and activity [53]. In the current study, the emission pattern of CO2 over time was coincident with changes in soil temperature, with greater fluxes occurring on days 1 (27.4 °C) and 10 (28 °C) when soil temperatures were relatively higher (averaged 22.9 °C of other sampling days). Also corroborating our correlation data, previous studies have shown that higher soil temperature is often associated with greater microbial activity, thereby favoring CO2 production [54].
Our data showed no significant effects of biochar application on CO2 fluxes during most sampling events; however, pristine biochar (PB-1%) promoted CO2 emission on the first day, and a similar situation was observed on day 10 (PB-5% and AB-1% resulted in CO2 spikes). Although labile C from biochar was expected to have a positive priming effect (a stimulus facilitates the decomposition of native soil organic carbon) and promote microbial activity, these data implied that biochar effects on soil CO2 are likely short-lived and dependent on biochar characteristics and soil variables [55].
The observed increase in CO2 emission in PB-5% was not surprising, as previous research has confirmed similar phenomena under exogenous organic amendments such as organic fertilizers and biochar [56]. One possible reason is that pristine biochar inherently contained less resistant C molecules, which directly induced the priming effect on soil organic matter through biochar-derived C, thereby becoming a direct source of CO2 [57]. Another possible reason is that pristine biochar (5% rate) indirectly affected microbial diversity by regulating soil bacterial community composition, plant litter, and root exudates. Conversely, most of aged biochar-C was an aromatic form that can be more recalcitrant to microbial decomposition since labile C in pristine biochar was likely degraded in the aging process [58].
In contrast with many studies conducted under controlled laboratory and field conditions that demonstrated significant decrease in CH4 with biochar addition [59], both aged and pristine biochars showed no effect on CH4 emission. Lack of biochar response herein was likely attributed to the aerobic conditions because CH4 is predominantly produced under anaerobic conditions [60]. Differences in biochar types and application rate, soil conditions, and environmental factors co-affect treatment manifestations. However, soil N2O emissions were significantly reduced with biochar addition compared to unamended control. The reduction in N2O emissions was likely caused by direct absorption of N on biochar surface and followed by indirect inhibition of N mineralization [61]. The exact mechanisms by which biochar influences N availability in soils are not fully understood. Earlier studies proposed that both biotic (mineralization/immobilization, nitrification/denitrification) and abiotic (sorption of ammonium and nitrate N onto biochar) processes affected N dynamics in biochar-amended soils [55]. In addition, over the course of Chinese cabbage growth, plants could directly absorb the inorganic N in soil and reduce the available N for N2O production. The negative correlation between cumulative N2O emission and plant biomass supports this hypothesis.
4.2. Soil Cd Content and Plant Cd Uptake as Affected by Biochar Application
Regardless of biochar type and application rate, we observed a reduction in available Cd concentration in soil when biochar was applied. This response was likely due to the contribution of enhanced SOC content in biochar treatments, which aids in the adsorption and fixation of Cd [62]. Moreover, as depicted in Figure 3B, biochar application significantly reduced plant Cd uptake (except for PB-5%) and simultaneously promoted plant biomass in Cd-contaminated soils, which was also in agreement with other studies [63]. Biochar addition in soil alleviated Cd toxicity that should inhibit Chinese cabbage growth, therefore favoring plant biomass accumulation. In addition, compared to CK, aged biochar (1% and 5%) and pristine biochar (only 1%) application reduced Cd accumulation in plants. One likely explanation is that biochar application may have affected nutrient status in soil, possibly resulting in varied Cd uptake by plants [64]. The relationship between plant Cd uptake with SOC and soil NO3-N further supported this hypothesis.
Plant Cd assimilation and remediation effect of Cd contamination in soil depend on both total Cd content and its speciation distribution. The acid soluble and reducible fractions of Cd are bioavailable for plants, while the oxidizable and residual fractions are recalcitrant (e.g., bound to organic matter and sulfides) [65]. In the current study, except for AB-5% decreasing the residual Cd more than other treatments, no significant differences in Cd speciation in soil were observed for biochar treatments. A similar situation was observed in a previous study [66]. Prolonging the duration of the experiment may show significant differences in the future.
4.3. Linking Microbial Communities with Greenhouse Gas Emission in Biochar-Treated Soils
Earlier studies have reported that biochar application to soil can influence nitrification and denitrification processes regulated by microorganisms [15,67,68]. The higher relative abundance of key soil bacteria such as Proteobacteria and Verrucomicrobiota in biochar-treated soils was reported, involving in the cycling of N2O. For example, according to Yan et al. (2023), Proteobacteria could contribute to N stabilization and subsequently suppress N2O emissions [69]. Similarly, recent research identified Verrucomicrobiota as the key bacterial species in the inhibition on N2O emission [70]. The authors explained that Verrucomicrobia may inhibit the nitrification process by an antagonistic relationship with bacteria carrying the ammonia-oxidizing archaea and nirS genes.
Although N2O emission was significantly reduced with biochar application, CO2 emission was promoted in PB-5% amended soils. According to the microbial sequencing result, PB-5% application stimulated the members of bacterial phyla Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria. At the genus level, several bacterial taxa alternately dominated, including Lysobacter, Arenimonas, and unclassified_Micrococcaceae, likely due to their high heat resistance ability [71,72]. Compared to aged biochar, pristine biochar addition resulted in higher SOC and labile C fraction, which likely promoted microbial growth and metabolism, thereby accelerating the decomposition of soil organic matter [73]. Moreover, pristine biochar may have led to growth and metabolic activity stimulations for microorganisms involved in nutrient cycling. Our data of varying bacterial diversity in different treatments further verified the hypothesis, with PB-5% application shifting the bacterial community from A- to Y-strategists, as supported by decreased oligotroph/copiotroph ratio. Abrupt resources availability in soils are expected to favor the fast-growing microbial proliferation and the dominance of copiotrophs [74]. Soils dominated by Y-strategists, such as Proteobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, and Actinobacteria, are expected to survive in copiotroph soils with higher SOC mineralization, which is also consistent with our CO2 emission data. Similar results have been reported in a field study, where biochars (47.1–67.5 tons totally) applied in rice paddy soils (pH = 7.07) increased labile C availability to microbes and shifted bacterial communities, favoring the soil life-history strategies of copiotroph bacteria [73].
4.4. Linking Microbial Communities with Cd Remediation in Biochar-Treated Soils
Although biochar addition led to changes in microbial structure and abundance in soil, Proteobacteria had the highest relative abundance of 51.0–54.5% for all treatments. In line with our results, Xu et al. (2023) proved that Proteobacteria are more easily adapted to heavy metal-rich environment than other microorganisms [75]. Among these treatments, application of PB-5% in soil exhibited no effect in reducing plant Cd uptake relative to CK, probably related to the reduced abundance of Acidobacteria, because Acidobacteria favor plant Cd uptake as indicated by Bandara et al. (2022) [76]. Niu et al. (2021) also reported that Acidobacteria were able to secrete organic acids that can release heavy metals from soil binding sites, thereby enhancing plant uptake [77,78]. Additionally, our data suggested the addition of pristine biochar at the 5% rate decreased the diversity of soil microbial communities compared to other treatments, as seen from the reduced Shannon index, because a high rate of biochar application may exert more pressure on some microbes, leaving the most resistant species to remain, thus minimizing their diversity [79,80].
As mentioned above, although decreased available Cd concentration was observed in all biochar-treated soils, only three treatments (PB-1%, AB-1%, and AB-5%) significantly reduced the Cd concentration in plant. Despite the complexity and multiple mechanisms involved in fixation and speciation transformation of Cd in the soil–plant system, data reported here and in previous studies suggest that both biotic and abiotic factors, including soil microbes, soil property, and biochar characteristics [81,82,83], might result in the inconsistent effects across biochar treatments. Further research is especially necessary to explore microbial mechanisms and quantify transformation pathways using such as isotope labeling techniques to refine our conclusions.
5. Conclusions
Our data highlighted the importance of both biochar type and the application rate in affecting biochar performance. This is particularly evident for the remediation of Cd-contaminated soil and GHG emission during Chinese cabbage growth. Although biochar-treated soil exhibited significantly reduced cumulative N2O emission, PB-5% treatment increased soil cumulative CO2 emission by 45.7%, likely ascribing to the increased labile C components and stimulated microbial activity. Data also demonstrated that higher application rate of pristine biochar shifted the soil bacterial life history strategy towards copiotrophs, characterized by a lower oligotroph/copiotroph ratio. Despite the fact that biochar application showed no effect in total Cd concentration in soil, aged biochar promoted plant biomass and simultaneously decreased plant Cd uptake and available Cd concentration. These responses were attributed to a combination of biotic (i.e., functional bacteria) and abiotic factors (i.e., reduced Cd toxicity, improved nutrient status) that provided favorable conditions for plant growth.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae11070800/s1, Table S1. Selected soil chemical property as affected by biochar application. Figure S1. FTIR spectra of pristine biochar (blue) and aged biochar (orange). Figure S2. Changes in life strategies and Shannon index as affected by biochar treatments. Figure S3. Venn diagram represents the unique OTUs among treatments. Figure S4. Pearson correlation between soil factors and plant biomass, plant Cd uptake, and GHG emission.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, Y.L. (Yanyan Lu); Funding acquisition, Y.L. (Yanyan Lu), J.L. and D.D.; Literature searching and Data curation, X.Z. and Y.L. (Yuxuan Li); Investigation and Proofreading, G.L. and G.W.; Writing—reviews and editing, Q.W. and J.L.; Supervision, D.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number: 32301429], the Start-up Fund for Introduced Scholar of Jiangsu University [grant number: 5501370018], and Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality Technology Innovation Special Foundation of Jiangsu Province [grant number: BK20220030].
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Qianwu Wang was employed by the companies National Engineering Laboratory for Site Remediation Technologies (NEL-SRT) and Beijing Construction Engineering Group Environmental Remediation Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management: An Introduction. In Biochar for Environmental Management: Science, Technology and Implementation; Lehmann, J., Joseph, S., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2015; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Ma, S.; Ma, Y.; Xu, S.; Li, G.; Fu, H.; Wu, X.; Du, J.; Zhao, P. Efficient inactivation of antibiotic resistant bacteria by iron-modified biochar and persulfate system: Potential for controlling antimicrobial resistance spread and mechanism insights. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 492, 138182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Jiang, M.; He, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gustave, W.; Vithanage, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Challenges in safe environmental applications of biochar: Identifying risks and unintended consequence. Biochar 2025, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Dai, Z.; Ge, C.; Yu, H.; Bolan, N.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Song, H.; Hou, D.; Shaheen, S.M.; Wang, H.; et al. Multiple-functionalized biochar affects rice yield and quality via regulating arsenic and lead redistribution and bacterial community structure in soils under different hydrological conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, W.; Ding, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.C.; Gao, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.Z. Biochar-supported zero-valent iron enhanced arsenic immobilization in a paddy soil: The role of soil organic matter. Biochar 2024, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeewani, P.H.; Brown, R.W.; Evans, C.D.; Cook, J.; Roberts, B.P.; Fraser, M.D.; Chadwick, D.R.; Jones, D.L. Rewetting alongside biochar and sulphate addition mitigates greenhouse gas emissions and retain carbon in degraded upland peatlands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 207, 109814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, M.; Hu, Y.; Sun, X.; Yan, H.; Yu, G.; Tang, G.; Chen, S.; Xu, W.; Jia, H. Long-term effects of biochar application on the growth and physiological characteristics of maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1172425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, X. Does biochar field aging reduce the kinetic retention for weakly hydrophobic antibiotics in purple soil? Biochar 2025, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Cao, W.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, J. Aging influence and long-term stable mechanism of biofuel ash immobilizing cadmium in alkaline soil combining artificial aging simulation. Environ. Res. 2025, 277, 121570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Xing, D.; Twagirayezu, G.; Lin, S.; Gu, S.; Tu, C.; Hill, P.W.; Chadwick, D.R.; Jones, D.L. Effects of field-aging on the impact of biochar on herbicide fate and microbial community structure in the soil environment. Chemosphere 2024, 348, 140682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.H.; Sohi, S.P.; Jing, F.Q.; Liu, Y.Y.; Chen, J.W. A comparative study on biochar properties and Cd adsorption behavior under effects of ageing processes of leaching, acidification and oxidation. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ye, X.; Geng, Z.; Zhou, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G. The influence of biochar type on long-term stabilization for Cd and Cu in contaminated paddy soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 304, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, B.S.Q.; Fernandes, L.A.; Southard, R.J. Biochar-cadmium retention and its effects after aging with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Heliyon 2021, 7, e08476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Zhao, L.; Rui, X.; Hu, J.; Zhu, N. A review of pristine and modified biochar immobilizing typical heavy metals in soil: Applications and challenges. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, P.; Lu, Y.; Cui, X.; Peng, F. Hydrogen peroxide-aged biochar mitigating greenhouse gas emissions during co-composting of swine manure with rice bran. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 374, 126255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; He, Q.; Dai, W. Aging alters the physicochemical properties of biochar, enhances its adsorption performance for tris-(1-chloro-2-propyl) phosphate, and changes the adsorption mechanism. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 104053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Ye, R.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X. Enhanced stabilization of lead in soil using novel biochar composites under simulated accelerated aging conditions. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, S.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Singh, B. Chapter One—Long-Term Aging of Biochar: A molecular understanding with agricultural and environmental implications. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 141, pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; Hou, P.; Poinern, G.; Jiang, Z.; Fawcett, D.; Xue, L.; Lam, S.S.; et al. How does biochar aging affect NH3 volatilization and GHGs emissions from agricultural soils? Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Gu, R.; Yang, Y.; Yan, J.; Ma, Y.; Shen, Y. Recent distribution changes of invasive Asteraceae species in China: A five-year analysis (2016–2020). J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.-F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.-X.; Li, H.-L.; Xia, H.-J.; Kong, W.-J.; Yu, F.-H. Remediation of cadmium-contaminated coastal saline-alkaline soil by Spartina alterniflora derived biochar. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Song, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Z.; Wu, W. Cadmium threshold for acidic and multi-metal contaminated soil according to Oryza sativa L. Cadmium accumulation: Influential factors and prediction model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Rinklebe, J.; Tack, F.M.G.; Ok, Y.S. A critical review on effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of cadmium in vegetables. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubair, M.; Ramzani, P.M.A.; Rasool, B.; Khan, M.A.; Rahman, M.; Akhtar, I.; Turan, V.; Tauqeer, H.M.; Farhad, M.; Khan, S.A.; et al. Efficacy of chitosan-coated textile waste biochar applied to Cd-polluted soil for reducing Cd mobility in soil and its distribution in moringa (Moringa oleifera L.). J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 284, 112047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aborisade, M.A.; Geng, H.; Oba, B.T.; Kumar, A.; Ndudi, E.A.; Battamo, A.Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Okimiji, O.P.; Ojekunle, O.Z.; et al. Remediation of soil polluted with Pb and Cd and alleviation of oxidative stress in Brassica rapa plant using nanoscale zerovalent iron supported with coconut-husk biochar. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 287, 154023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghani, M.I.; Ahanger, M.A.; Sial, T.A.; Haider, S.; Siddique, J.A.; Fan, R.; Liu, Y.; Ali, E.F.; Kumar, M.; Yang, X.; et al. Almond shell-derived biochar decreased toxic metals bioavailability and uptake by tomato and enhanced the antioxidant system and microbial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.U.; Ain, N.; Khan, I.; Farooq, M.; Cai, H.L.; Li, Y. Co-application of biochar and plant growth regulators improves maize growth and decreases Cd accumulation in cadmium-contaminated soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 440, 140515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Tong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Tao, Y.; Dai, X.; et al. Applications of functionalized magnetic biochar in environmental remediation: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Liu, L.; Ling, Q.; Cai, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, S.; Fu, D.; Hu, B.; Wang, X. Biochar for the removal of contaminants from soil and water: A review. Biochar 2022, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, S.; Kumar, R.; Sahoo, P.K.; Nadda, A.K. Recent advances in biochar amendments for immobilization of heavy metals in an agricultural ecosystem: A systematic review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 319, 120937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xie, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, X.; Ren, J.; Shi, Y.; Liu, D.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J. Biochar co-pyrolyzed from peanut shells and maize straw improved soil biochemical properties, rice yield, and reduced cadmium mobilization and accumulation by rice: Biogeochemical investigations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, A.; Sohi, S.P. A method for screening the relative long-term stability of biochar. Glob. Change Biol. Bioenergy 2013, 5, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Yu, P.; Spanu, L.; Hinojosa, J.; Zhang, S.; Long, M.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Masiello, C.A. Rapid simulation of decade-scale charcoal aging in soil: Changes in physicochemical properties and their environmental implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality: Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Lu, Y.; Silveira, M.L.; Vendramini, J.M.B.; Erickson, J.E.; Li, Y. Biosolids and biochar application effects on bahiagrass herbage accumulation and nutritive value. J. Agron. 2020, 112, 1330–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Abbas, T.; Adrees, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Abbas, F.; Farooq Qayyum, M.; Nawaz, R. Residual effects of biochar on growth, photosynthesis and cadmium uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Cd stress with different water conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, B.J.R.; Smith, K.A.; Flores, R.A.; Cardoso, A.S.; Oliveira, W.R.D.; Jantali, C.P.; Boddey, R.M. Selection of the most suitable sampling time for static chambers for the estimation of daily mean N2O flux from soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 46, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.J.; Black, I.A. Estimation of soil organic carbon by the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, R.L. Nitrogen-Inorganic Forms. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3, Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpoor, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, C.T., Sumner, M.E., Eds.; SSSA Book Series No. 5; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 1123–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Alsaleh, K.A.M.; Meuser, H.; Usman, A.R.A.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Al-Farraj, A.S. A comparison of two digestion methods for assessing heavy metals level in urban soils influenced by mining and industrial activities. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.X.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; et al. Microplastics promoted cadmium accumulation in maize plants by improving active cadmium and amino acid synthesis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ure, A.M.; Quevauviller, P.; Muntau, H.; Griepink, B. Speciation of heavy metals in soils and sediments. An account of the improvement and harmonization of extraction techniques undertaken under the auspices of the BCR of the commission of the European communities. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1993, 51, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Landman, A.; Pruden, G.; Jenkinson, D.S. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.; Di Lonardo, D.P.; Bodelier, P.L. Revisiting life strategy concepts in environmental microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parasar, B.J.; Agarwala, N. Unravelling the role of biochar-microbe-soil tripartite interaction in regulating soil carbon and nitrogen budget: A panacea to soil sustainability. Biochar 2025, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Lauber, C.L.; Ramirez, K.S.; Zaneveld, J.; Bradford, M.A.; Knight, R. Comparative metagenomic, phylogenetic and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrisey, E.M.; Mau, R.L.; Schwartz, E.; Caporaso, J.G.; Dijkstra, P.; van Gestel, N.; Koch, B.J.; Liu, C.M.; Hayer, M.; McHugh, T.A.; et al. Phylogenetic organization of bacterial activity. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2336–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, K.S.; Craine, J.M.; Fierer, N. Consistent effects of nitrogen amendments on soil microbial communities and processes across biomes. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe-Ranney, C.; Campbell, A.N.; Koechll, C.N.; Berthrong, S.; Buckley, D.H. Unearthing the ecology of soil microorganisms using a high resolution DNASIP approach to explore cellulose and xylose metabolism in soil. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, e703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS/STAT 9.2 User’s Guide; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Silveira, M.L.; Cavigelli, M.; O’Connor, G.A.; Vendramini, J.M.B.; Erickson, J.E.; Li, Y.C. Biochar impacts on nutrient dynamics in a subtropical grassland soil: 2. Greenhouse gas emissions. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, W.; Chi, M.; Sun, Y.; An, J.; Yu, N.; Zou, H. Simulating the effects of soil temperature and soil moisture on CO2 and CH4 emissions in rice straw-enriched paddy soil. Catena 2020, 194, 104677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Silveira, M.L.; Vendramini, J.M.B.; Li, Y.C. Biochar impacts on soil nitrogen and carbon dynamics in a Spodosol amended with biosolids and inorganic fertilizer. J. Environ. Qual. 2023, 52, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Silveira, M.L.; O’Connor, G.A.; Vendramini, J.M.B.; Erickson, J.E.; Li, Y.C. Assessing the impacts of biochar and fertilizer management strategies on N and P balances in subtropical pastures. Geoderma 2021, 394, 115038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto, T.; Nhamo, N.; Chikoye, D.; Mukumbuta, I.; Uchida, Y. Responses of CO2 emissions and soil microbial community structures to organic amendment in two contrasting soils in Zambia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; O’Connor, D.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Shen, Z.; Hou, D. Biochar aging: Mechanisms, physicochemical changes, assessment, and implications for field applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14797–14814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.; Xu, X.; Xiong, Z. Microbial explanations for field-aged biochar mitigating greenhouse gas emissions during a rice-growing season. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31307–31317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Mer, J.; Roge, P. Production, oxidation, emission and consumption of methane by soils: A review. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2001, 37, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, J. Pathways and mechanisms by which biochar application reduces nitrogen and phosphorus runoff losses from a rice agroecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Duan, T.; Wu, X.; Liao, M.; Sun, J. Can the aging process necessarily weaken the effect of biochar on cadmium-contaminated soil remediation: Considering biochar at different pyrolysis temperatures and aging treatment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, S.; Prit, H.; Maturi, K.C.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Amendment of nutrient-deficient alluvial soil by municipal solid waste char and compost for the remediation of contaminants and enhancement of plant growth. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Rengel, Z.; Chang, H.; Meney, K.; Pantelic, L.; Tomanovic, R. Bioremediation potential of Juncus subsecundus in soils contaminated with cadmium and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Geoderma 2012, 175–176, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Bai, L.; Liu, X.; Zhu, P.; Liu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Geng, J.; Liu, Q.; Huang, L.; Jiang, H. Cadmium speciation distribution responses to soil properties and soil microbes of plow layer and plow pan soils in cadmium-contaminated paddy fields. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 774301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Cheng, H.; Ning, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lin, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Hill, P.; Chadwick, D.; Jones, D.L. Field aging declines the regulatory effects of biochar on cadmium uptake by pepper in the soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ge, C.; Chapman, S.J.; Yao, H. Can aged biochar offset soil greenhouse gas emissions from crop residue amendments in saline and non-saline soils under laboratory conditions? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Chen, Y.; Hi, J.; Zhang, C.; Mao, S.; Ruan, H.; Malghani, S. Effects of fresh and aged biochar on N2O emission from a poplar plantation soil. Pedosphere 2025, 35, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Wu, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, C.; Lyu, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Liu, T.; Li, R.; Yao, Y. Soil decreases N2O emission and increases TN content during combined composting of wheat straw and cow manure by inhibiting denitrification. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Liang, F.; Tu, L.; Xu, Z.; Li, R.; Ma, R.; Huang, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Mineral fertilizer substitution and application of Bacillus velezensis SQR9 reduced nitrogen-oxide emissions in tropical vegetable fields. Agricu. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 384, 109554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, F. Separation of heat-stable antifungal factor from Lysobacter enzymogenes fermentation broth via photodegradation and macroporous resin adsorption. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 13, 663065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, D.; Song, M.; Guan, G.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. The positive role of root decomposition on the bioremediation of organic pollutants contaminated soil: A case study using PCB-9 as a model compound. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 171, 108726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, W.; Fan, X.; Gao, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, C.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Drosos, M.; Shan, S. The molecular composition of soil organic matter is regulated by bacterial community under biochar application. Geoderma 2025, 457, 117308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, G.; Robinson, D.; Yang, Z.; Guo, J.; Xie, J.; Fu, S.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Y. Large amounts of easily decomposable carbon stored in subtropical forest subsoil are associated with r-strategy-dominated soil microbes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 95, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Mao, K.; Zhang, H. Health risk assessments and microbial community analyses of groundwater from a heavy metal-contaminated site in Hezhou city, Southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, T.; Krohn, C.; Jin, J.; Chathurika, J.B.A.J.; Franks, A.; Xu, J.; Potter, I.D.; Tang, C. The effects of biochar aging on rhizosphere microbial communities in cadmium-contaminated acid soil. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Leng, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, Q.; Wu, H.; Gong, J.; Li, H.; Chen, K. Behaviors of cadmium in rhizosphere soils and its interaction with microbiome communities in phytoremediation. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankar, A.; Nagaraja, G. Chapter 18—recent trends in biosorption of heavy metals by Actinobacteria. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Singh, B.P., Gupta, V.K., Passari, A.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Cong, M.; Hu, Y.; Qiu, C.; Yang, Z.; Tang, G.; Xu, W.; Zhu, X.; Sun, X.; Jia, H. Biochar-mediated changes in the microbial communities of rhizosphere soil alter the architecture of maize roots. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 4, 1023444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Chai, Y.; Ai, C.; Hussain, Q.; Drosos, M.; Shan, S. Effects of rice straw biochar application rates on soil aggregate biogeochemistry and linkages to microbial community structure and enzyme activities. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 252, 106589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.T.; Hao, X.; Jing, R.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Gu, C.; Wang, Y.; Lin, R.; Zheng, X. Pig bedding biochar enhances the Cd extraction capacity of Perilla frutescens by mitigating the toxicity of Cd-contaminated soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 156, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Huang, D.; Zhou, W.; Xiao, R.; Chen, H.; Huang, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, G.; Li, R. Higher remediation efficiency of Cd and lower CO2 emissions in phytoremediation systems with biochar application. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 376, 126345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Sun, J.; Pan, G.; Qi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, J.; Gao, Y. Ball-milling-modified biochar with additives enhances soil Cd passivation, increases plant growth and restrains Cd uptake by Chinese cabbage. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).