Abstract
The Dalbergia genus, a morphologically diverse group within the Fabaceae family, encompasses species of significant value in furniture production and medicinal and aromatic applications. The taxonomy of Dalbergia has relied on morphological traits, chloroplast (cp) DNA fragments, and cp genomic data. However, genomic resources for tropical liana species within this genus remain scarce. In this study, we assembled and analyzed the cp genomes of 3 liana species—Dalbergia peishaensis, D. pinnata, and D. tsoi—and compared them with those of 26 other Dalbergia species to explore their cp genome characteristics and evolutionary patterns. We employed a combination of traditional cp genome analysis and methods adapted from plant whole-genome sequencing. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that D. peishaensis has a close relationship with D. cultrata, forming a recently diverged clade, whereas D. tsoi and D. pinnata are positioned within a basal clade of the Dalbergia genus, suggesting an earlier divergence. The Dalbergia cp genomes exhibit considerable variation in size, with evidence of pseudogenization, gene loss, and duplication observed in the three liana species. Notably, the infA gene, previously reported as absent in the chloroplast genomes of Dalbergia species, was identified in the cp genomes of these three liana Dalbergia species. A total of 4533 simple sequence repeats (SSRs) were identified, providing valuable insights into cp genome evolution and facilitating future population genetics studies, particularly when combined with the high structural variation observed in the genus through whole-genome analysis methods. Additionally, seven highly divergent regions were identified as potential DNA barcode hotspots. This study enhances the genomic characterization of liana Dalbergia species and offers a robust framework for future plant cp genome analyses by integrating methodologies originally developed for whole-genome studies.
1. Introduction
Dalbergia L.f., a genus within the Fabaceae (Papilionaceae) family, comprises trees, shrubs, and lianas. This genus includes approximately 269 species globally, predominantly found in tropical and subtropical areas [1]. In China, there are 29 species, 14 of which are endemic, primarily distributed from the southwestern to the central southern regions [2]. The heartwood of Dalbergia, either naturally formed or induced by wounding, is highly valued for its resin content, which imparts exquisite color and texture, as well as superior mechanical properties such as hardness and strength [3]. Additionally, this wood offers various pharmacological benefits, including analgesic, angiogenic, antidiarrheal, antioxidant, and diuretic effects [4,5,6,7]. The genus also contributes to the production of dyes [8,9] and plays a role in nitrogen fixation [10,11]. Due to the depletion of wild populations and escalating market demands, all Dalbergia species have been listed under the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) to control their trade and ensure sustainability.
Based on their growth forms, Dalbergia species can be categorized into two different ecotypes, namely of trees and lianas/climbing shrubs [12]. The tree types of the Dalbergia species, such as D. odorifera T.C. Chen, D. cochinchinensis Pierre ex Laness, and D. tonkinensis Prain, are renowned for their high-quality timber that is usually used for furniture manufacturing [13,14]. The various types of lianas and climbing shrubs are also widely distributed, with over 50 species only found in Asia, including large lianas like D. borneensis Prain and D. confertiflora Benth., and climbing shrubs such as D. reticulata Merr. [1,15,16]. In China, about 16 liana species represent approximately 55% of the total prevalence of the 29 species, including D. benthamii Prain, D. pinnata (Lour.) Prain, D. tsoi Merr. & Chun, D. hancei Benth., D. peishaensis Chun & T.C. Chen, and D. yunnanensis Franch [17,18].
Historically, Dalbergia species have garnered significant attention for their ability to produce premium wood products [3,19]. Conversely, relatively little attention has been devoted to lianas or climbing shrubs in either the literature or in scientific research more generally. Nevertheless, these species’ resinous wood has been utilized in traditional Chinese medicine and for its aromatic properties since ancient times. Recently, as market interest has increased, the term ‘Jiangzhenxiang’ has been revisited. This name, originating from Taoism in China, encapsulates several meanings: ‘Jiang’ implies descent, ‘Zhen’ denotes the true god, and ‘Xiang’ suggests burning with fragrance. Thus, ‘Jiangzhenxiang’ refers to a substance that, when burned, emits a fragrance believed to attract a divine presence [20]. It is also known by several local names, including Zongguanteng, Tengzongguan (in Hainan), and Meilongteng (in Hainan and Fujian). It is prized as an excellent material for rattan moxibustion, a distinctive external therapy practiced by the Hainan Li ethnic group [21]. Scholarly consensus identifies the primary botanical sources of ‘Jiangzhenxiang’ as various lianas or climbing shrubs within the Dalbergia genus, including D. benthamii, D. peishaensis (Figure 1A–C), D. tsoi (Figure 1D–F), D. pinnata (Figure 1G–I), D. parviflora (potentially the primary source of ‘Jiangzhenxiang’ abroad), D. rimosa, D. hancei, and D. yunnanensis, among others [22,23,24,25]. The first three species are widely recognized within the industry and commonly referred to as ‘Big Leaf Jiangzhenxiang,’ ‘Small Leaf Jiangzhenxiang,’ and ‘Shimuxiang’, respectively. The “Identification Method for Jiangzhenxiang (DB45/T 1914-2018),” published by the market supervision administration of Guangxi, China [26], enumerates these three prevalent sources and details their macroscopic and microscopic structural characteristics, as well as the thin-layer chromatographic profiles of the aromatic resinous wood.
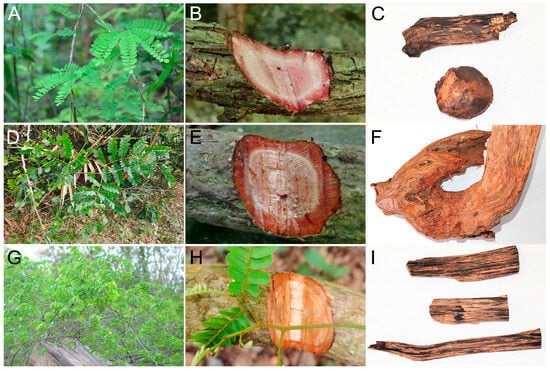
Figure 1.
Morphological characteristics of three Dalbergia species and their products under wounding. (A) Leaf of Dalbergia peishaensis; (B) wound stem of D. peishaensis; (C) products from D. peishaensis stem; (D) leaf of D. tsoi; (E) wound stem of D. tsoi; (F) products from D. tsoi stem; (G) leaf of D. pinnata; (H) wound stem of D. pinnata; (I) products from D. pinnata stem.
According to data from the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, 57 species of Dalbergia have been recognized in various pharmacopeias and herbal references worldwide. Notably, species such as D. benthamii, D. hancei, D. millettii, D. mimosoides, D. pinnata, and D. yunnanensis were identified as medicinal sources in the “Reference Collection of Traditional Chinese Medicine” and “Chinese Materia Medica”. With the exception of D. hancei, which is included in the Guangxi Medicinal Materials Standard, these species are yet to be formally recognized in the official Chinese medicinal material standards.
Research focusing on the characteristics and microscopic identification of these species [24,27] has been conducted. However, in the absence of official guidelines, the quality control of these medicinal materials remains inconsistent and under-regulated. This gap highlights the urgent need for the inclusion of these species in formal standards to ensure consistent quality and efficacy in their medicinal use.
Recent years have seen a significant surge in research focused on the chloroplast (cp) genomes of Dalbergia species. D. assamica, D. balansae, D. bariensis, D. benthamii, D. candenatensis, D. cochinchinensis, D. hainanensis, D. hupeana, D. millettii, D. mimosoides, D. hancei, D. obtusifolia, D. odorifera, D. oliveri, D. sissoo, and D. tonkinensis have had their complete chloroplast genomes successfully assembled [17,28,29,30]. The investigation into the cp genomes of Dalbergia reveals a typical quadripartite structure, which is remarkably conserved across different species in terms of genome size, structure, and gene content, while exhibiting minimal sequence variations. The cp genomes range between 155,698 bp and 156,698 bp in size, encompassing 110 to 129 genes. These include 75 to 84 protein-coding genes, 30 to 37 tRNA genes, four to eight rRNA genes, and two to three pseudogenes. These studies also identified several highly mutated gene regions, which include atpA-trnG, trnG-UCC-psbZ, trnK(UUU), psbA-trnK(UUU), trnL(UAA)-trnT(UGU), trnP(UGG)-psaJ, trnQ(UUG)-rps16, trnR(UCU)-trnG(UCC), trnS(GCU)-psbI, ndhE-ndhG, ndhF, ndhF-trnL, ndhG-ndhI, ndhH-rps15, petG-psaJ, rpc16, rps8-rpl14, rps12-clpP, rps15, rps16-accD, ycf1a, and ycf1b. These regions are proposed as candidate molecular markers or DNA barcodes for the identification of Dalbergia species, offering new tools for taxonomic and conservation efforts. Previous research has also proposed several multi-gene combinations with effective discrimination among Dalbergia taxa, including ITS2+trnH-psbA [31,32], rbcL+matK+ITS [33,34], and rbcL+matK+trnL [19]. However, DNA samples from heartwood or resin-containing wood often suffer from severe degradation and microbial interference, particularly when nuclear genes (ITS and ITS2) are used, complicating the acquisition of reliable results. These studies on the chloroplast genomes of Dalbergia species significantly enhance our understanding of their genetic architecture and evolutionary trajectories, while also offering potential applications for the conservation and sustainable utilization of these botanical resources.
Of the 29 chloroplast genomes of Dalbergia species, 11 of them have been classified as lianas or climbing shrubs, namely D. benthamii, D. pinnata, D. tsoi, D. peishaensis, D. hancei, D. millettii, D. candenatensis, D. yunnanensis, D. mimosoides, D. vietnamensis, and D. armata. Notably, D. tsoi and D. peishaensis are endemic to Hainan Island in China, while D. hancei, D. millettii, and D. mimosoides are found in China as a whole. D. vietnamensis plants are found in Vietnam and Cambodia [35], and D. armata is native to Africa [36]. Given these challenges, the comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes suggest that identifying high-resolution, short-segment DNA barcodes (under 300 bp) could offer a more effective method for species identification, thus representing a promising direction for future research.
This study utilizes next-generation sequencing technology to assemble and annotate the chloroplast (cp) genomes of three liana species within the Dalbergia genus, followed by comparative genomic analyses with related species. It aims to generate cp genome sequences for three medicinal liana species of Dalbergia while also conducting a comparative analysis of the phylogenetic relationships among closely related species within the genus, with a particular focus on clarifying the evolutionary connections between D. pinnata, D. tsoi, and D. peishaensis. Additionally, this study seeks to identify structural variations and chloroplast molecular markers suitable for species identification within Dalbergia, particularly for the authentication of ‘Jiangzhenxiang’. The findings are expected to provide a robust scientific foundation for species identification, phylogenetic research, variety selection, and the conservation and utilization of Dalbergia species, including their resinous medicinal and aromatic products.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and DNA Extraction
Specimens of Dalbergia peishaensis, D. pinnata, and D. tsoi were collected with the assistance of staff members from the Jiangfengling Branch of the Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park (18°20′~18°57′ N, 108°41′~109°12′ E). The collection took place between 6 May and 8 May 2022. All specimen collections were carried out with the appropriate permissions and were compliant with the legal requirements in the Hainan Province of China.
The fresh and healthy leaves of three Dalbergia species were collected, immediately frozen with liquid nitrogen, and then stored in liquid nitrogen. Subsequently, they were preserved at −80 °C prior to DNA extraction. Plant samples were authenticated by Dr. Wang Jun, an Associate Professor of Plant Taxonomy at the Institute of Tropical Bioscience and Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences. The voucher specimens were labeled WJ202202 (D. peishaensis), WJ202203 (D. pinnata), and WJ202205 (D. tsoi), and were deposited at the herbarium of Institute of Tropical Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences.
High-quality genomic DNA was extracted using a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) method [37]. The quality and quantity of the DNA extracts were assessed via 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis and a NanoDrop One spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), respectively.
2.2. DNA Sequencing and De Novo Genome Assembly
The whole chloroplast genomes were amplified using long-range PCR and nine universal primer pairs, in accordance with the previous study. The purified PCR products were subsequently mixed and fragmented to construct DNA libraries (insert size measuring 390 bp in length) following the standard Illumina protocol. The paired-end libraries were then sequenced using the Illumina Hiseq X Ten platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) at Bio & Data Biotechnologies Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). The raw data of these three Dalbergia species were obtained with paired-end reads of 390 bp, and these raw data were filtered by using NGS QC Toolkit_v2.3.3 for high-quantity clean short reads. Then, the clean reads were trimmed according to their quality, removing bases from the 3′ and 5′ ends until no base with Q < 20 was found [38]. After that, the chloroplast genomes were assembled using the trial version of SOAPdenovo v2.04 [39], and these draft cp genomes were subsequently corrected based on GapCloser v1.12 [39].
2.3. Genome Annotation and Analysis
The Dual Organellar GenoMe Annotator (DOGMA, http://dogma.ccbb.utexas.edu/ (accessed on 19 December 2022)) was used for annotating the cp genomes and identifying the genes of the encoding proteins (mRNAs), transfer RNAs (tRNAs), and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) with the default settings. Then, the annotated genes and their encoding proteins were confirmed by using BLAST v2.2.28 within the Nr, String, and GO databases to verify the boundaries of the genes and exons [40]. Finally, the circular cp genome maps of D. peishaensis, D. pinnata, and D. tsoi were drawn with the Organellar Genome DRAW software (OGDRAW, v1.3.1) [41]. The assembled and annotated files of the three liana Dalbergia species chloroplast genome sequences were deposited in a public dataset on FigShare (https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/The_gbf_files_of_three_plant_cp_gnomes/29424275 (accessed on 27 June 2025)). The cp genomes downloaded from GenBank for the following comparative analysis were re-annotated using the same method.
2.4. Sequence Analyses
To determine the patterns of synonymous codon usage, relative synonymous codon usage values (RSCU) and codon usage were resolved using CondoW v 1.4.2. The simple sequence repeats (SSRs) were detected with MISA (http://pgrc.ipk-gatersleben.de/misa/ (accessed on 25 August 2024)). Tandem repeats of 1–6 nucleotides were considered as microsatellites. The minimum numbers of repeats were set to 10, 6, 5, 5, 5, and 5 for mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, and hexanucleotides, respectively. The repeat sequences were analyzed using the web-based Reputer software (http://bibiserv.techfak.uni-bielefeld.de/reputer/ (accessed on 25 August 2024)), which contains forward, reverse, palindromic, and complement repeats with an edit distance of less than 3 bp and minimal lengths of 30 bp.
2.5. Phylogenetic and ANI Analysis
For phylogenetic analysis, 26 complete cp genome sequences of the Dalbergia genus were downloaded from NCBI for phylogenetic tree construction with our three Dalbergia species sequenced in this study. The cp genomes of Pterocarpus indicus and Stylosanthes viscosa from Fabaceae were selected as the outgroup. All shared sequences were aligned separately using MAFFT v7.505 [42], and were then used for creating a phylogenetic tree with FastTree v2.1.10 [43]. The statistics method used was maximum likelihood (ML), and bootstrap analysis was conducted with 1000 replicates. Average nucleotide identity (ANI) analysis was performed using FastANI v1.34 [44] across a total of twenty-nine Dalbergia cp genomes, including the three Dalbergia species reported in this study.
2.6. Genome Comparison of cp Genomes from Dalbergia
The overall GC content and the GC content at the first, second, and third codon positions (GC1, GC2, and GC3, respectively) of the genomes were determined using the EMBOSS v6.4.0 [45]. The expansions and contractions of inverted repeats (IRs) and single-copy (SC) regions were visualized in 29 Dalbergia species. The IRscope web service (https://irscope.shinyapps.io/irapp (accessed on 3 September 2022)) was used to compare the four main (LSC/IRb/SSC/IRa) regions. Structural variations (SVs) were identified using MUMmer v3.1 [46] and SyRI v1.7.0 [47]. For the high-variation region analysis, all 29 cp genomes were aligned using MAFFT v7.505 with the default setting. DnaSP v6 software was used to identify nucleotide variability (Pi) values, with the step size and window length set as 25 and 100 bp, respectively [48].
3. Results
3.1. Genome Sequencing and Features of Assembled Chloroplast Genomes
The Illumina HiSeq platform generated between 16,579,278 and 19,625,290 high-quality paired-end reads for the three Dalbergia species, facilitating the de novo assembly of complete chloroplast (cp) genomes. The raw sequencing data were processed to remove adapter sequences and low-quality reads, resulting in high-quality clean data. The assembled cp genomes exhibited an average coverage ranging from 106.58× to 122.95×. Figure 2 illustrates the cp genome structures of the three Dalbergia species, and Table S1 summarizes their key characteristics. Of these species, the cp genome of D. pinnata is the largest with a length of 159,619 bp, while that of D. peishaensis is the smallest with a length of 155,553 bp. The GC content of these genomes ranges from 35.89% to 36.09%.
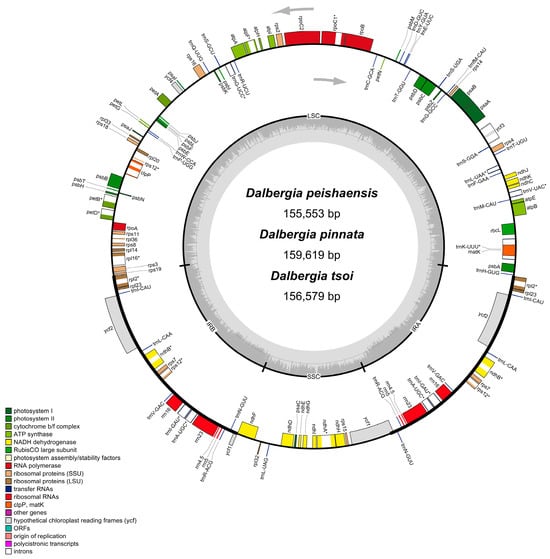
Figure 2.
Chloroplast genome maps of Dalbergia peishaensis, D. tsoi, and D. pinnata. The arrows represent the transcriptional direction of genes and * represent the multiple copy genes.
After accounting for single copies and duplicated genes, the assembled cp genomes of the Dalbergia species each contained 130 genes, comprising 84–85 protein-coding genes, 37 tRNAs, and 8 rRNAs (Table S1). The rps16 gene is absent in D. peishaensis. The infA gene, previously unreported in any chloroplast genomes of this genus, was detected in all three species and was encoded by 180, 180, and 234 nucleotide acids in D. pinnata, D. tsoi, and D. peishaensis, respectively. Among the duplicated genes are four protein-coding genes, seven tRNA genes, four rRNA genes, one photosynthesis-related gene (ndhB), and two pseudogenes (ycf1 and ycf2). There are sixteen genes containing introns; thirteen of these genes have one intron, and three genes, namely pafI, rps12, and clpP1, contain two introns.
3.2. Repeat Sequence Analysis
Twenty-nine genera of Dalbergia were selected for SSR analysis, including D. peishaensis, D. tsoi, and D. pinnata. A total of 4533 SSRs were detected in these 29 Dalbergia cp genomes (Table 1). Seven motifs and three types of SSR were identified in this family, including mononucleotide repeats, dinucleotide repeats, and trinucleotide repeats. Mononucleotide repeats are the most abundant type of SSR, followed by dinucleotide repeats and trinucleotide repeats. Among the mononucleotide repeats, the A/T type was the most common. Dinucleotide repeats only consisted of AT/TA, and trinucleotide repeats consisted of AAT/ATT. The number of mononucleotide repeats ranged from 138 (D. obtusifolia) to 164 (D. sissoo). Dinucleotide repeats ranged from 6 (D. martinii) to 21 (D. bariensis).

Table 1.
Statistics of simple repeat sequences in cp genomes of Dalbergia species.
The cp genomes of D. peishaensis, D. pinnata, and D. tsoi exhibit distinct characteristics in terms of SSR content, motif distribution, and repeat types, reflecting varying degrees of genetic variability within the Dalbergia genus (Table 1). D. peishaensis contains 152 SSRs, with a motif distribution of 64 A, 66 T, 3 C, 4 G, 8 AT, 6 TA, and 0 TTA, and repeat types comprising 130 A/T, 7 C/G, 14 AT/TA, and 0 AAT/ATT. In comparison, D. pinnata harbors 153 SSRs, containing motifs distributed as 69 A, 63 T, 2 C, 3 G, 10 AT, 6 TA, and 0 TTA, and repeat types of 132 A/T, 5 C/G, 16 AT/TA, and 0 AAT/ATT. Meanwhile, D. tsoi possesses the highest SSR count of the three at 168, with motifs consisting of 77 A, 68 T, 2 C, 4 G, 9 AT, 8 TA, and 0 TTA, and repeat types including 145 A/T, 6 C/G, 17 AT/TA, and 0 AAT/ATT. All three species exhibit a predominance of A/T and AT/TA repeats, consistent with genus-wide patterns in Dalbergia cp genomes. However, D. peishaensis displays a relatively low SSR count, suggesting a more conserved cp genome structure, whereas D. pinnata shows slightly greater variability with a higher SSR count and an elevated number of AT/TA repeats (16 compared to 14 in D. peishaensis), which may indicate potential structural variation and supports its genetic divergence, observed in prior analyses. D. vietnamensis, with the highest SSR count and an increased presence of C/G motifs (ten compared to three in D. cochinchinensis), demonstrates the greatest variability, aligning with its status as a genetically divergent species within the genus. The high A/T repeat count (145) and the AT/TA repeats (17) in D. tsoi further underscore its unique genomic profile and distinct evolutionary trajectory compared to D. peishaensis and D. pinnata. Trinucleotide repeats were missing in the cp genomes of D. peishaensis, D. tsoi, and D. pinnata. These comparative insights into their SSR profiles highlight the diverse evolutionary dynamics of Dalbergia cp genomes, providing a foundation for further genetic and phylogenetic studies.
3.3. Relative Codon Preference Analysis
In these newly assembled chloroplast genomes of three Dalbergia species, codon usage patterns were analyzed to elucidate their genetic characteristics. Tryptophan (Trp) exhibited the least diversity, being encoded solely by the codon UGG. In contrast, a total of 26,051, 26,164, and 27,364 codons were identified in D. peishaensis, D. tsoi, and D. pinnata, respectively, encoding 21 amino acids. The codons for arginine (Arg), leucine (Leu), and serine (Ser) displayed the highest diversity, each represented by six distinct codon types. Leucine (Leu) was the most frequently utilized amino acid, constituting 10.5% of all codons (2746 codons) across the three species. Conversely, the termination codons UAG and UGA were the least frequently used (Table S2). Of the 65 codons encoding the 21 amino acids, 31 exhibited a usage preference (relative synonymous codon usage, RSCU > 1), while the codon for Trp (UGG) showed no preference (RSCU = 1) (Figure 3). Additionally, 33 codons were used less frequently (RSCU < 1), indicating a bias in codon usage within these chloroplast genomes (Figure 3). These findings provide insights into the molecular evolution and codon bias of Dalbergia species, with potential implications for future genetic and phylogenetic studies.
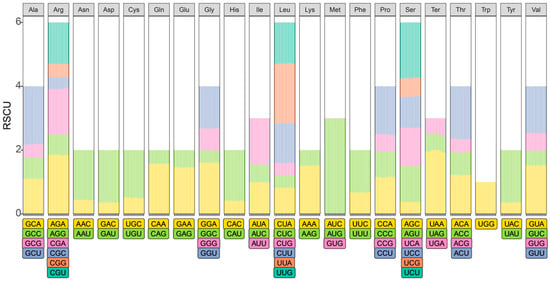
Figure 3.
Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) analysis of chloroplast genomes of Dalbergia peishaensis, D. pinnata, and D. tsoi.
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
To investigate the evolutionary relationships of these three new Dalbergia species cp genomes in the Dalbergia genus, a maximum likelihood (ML) tree was constructed with FastTree using nucleic acid from the whole cp genome alignment. This phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that D. odorifera, D. hainanensis, and D. tonkinensis, which are famous for having dense wood and have been used for furniture manufacture since ancient times, were more distributed in the originated clade than other relative Dalbergia species. The results showed that D. peishaensis exhibited a close relationship with D. cultrata, which branched more recently than D. tsoi and D. pinnata. D. tsoi and D. pinnata were placed in the basic clade within the Dalbergia genus; D. tsoi and D. benthamii were clustered as a sub-branch, and D. pinnata and D. candenotensis were clustered as another sub-branch; however, these two sub-branches were located within a single branch and were thus the basic species in the Dalbergia genus (Figure 4A). To further confirm the taxonomic classification of the Dalbergia species, the average nucleotide identity (ANI) of the 29 of high-quality cp genomes was calculated, including the 3 new cp genomes from tropical regions (Figure 4B). D. peishaensis exhibited moderate to low genetic similarity with most species, with values ranging from 96 to 98. For instance, its similarity with D. hainanensis and other closely related species (e.g., D. odorifera and D. tonkinensis) was around 96–97, indicating significant genetic divergence. However, it exhibited a slightly higher similarity (around 98) with D. cultrata, suggesting a closer evolutionary relationship with these species. This placed D. peishaensis in a relatively distant position within the group, potentially indicating an earlier divergence (Figure 4B). Similarly, D. pinnata displayed low genetic similarity with most species, predominantly in the 96–97 range. It showed a similarity of 96 with D. hainanensis and its close relatives, as well as with D. tsoi. However, D. pinnata had a slightly higher similarity (around 98) with D. candatenensis and D. benthamii, hinting at a closer genetic connection with these species. This pattern suggests that D. pinnata is genetically distinct from the majority of the group, likely belonging to a separate evolutionary lineage (Figure 4B). Additionally, D. tsoi consistently shows the lowest similarity across the board, with values mostly at 96–97. Its similarity with D. hainanensis, D. peishaensis, and D. pinnata is 96, marking it as one of the most genetically divergent species in the dataset. Even in terms of similarity with D. benthamii, which also shows low similarity with other species, D. tsoi only reaches 97 (Figure 4B). This indicates that D. tsoi and D. Pinnata have a closer relationship to each other than with D. peishaensis.
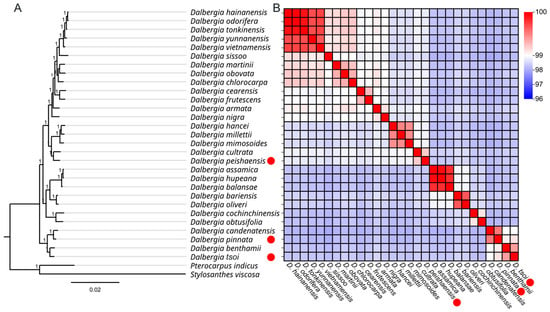
Figure 4.
A phylogenetic tree obtained using the maximum likelihood (ML) method for Dalbergia species based on whole plastid genomes and their average nucleotide identity (ANI). The red solid circles represent the three tropical Dalbergia species. (A) The evolutionary tree of 29 Dalbergia species; P. indicus and S. viscosa were set as outgroups. (B) ANI analysis between 29 Dalbergia species.
3.5. Comparative cp Genome Analysis
The plastid genomes of the 29 Dalbergia species showed several minor differences in the boundaries of the IR/LSC and IR/SSC regions (Figure 5). All the cp genomes displayed the typical quadripartite structure of angiosperms, with the large single-copy (LSC) region size varying between 84,965 bp and 85,834 bp, the inverted repeats (IRs) ranging from 25,697 bp to 29,165 bp, and the small single-copy (SSC) region varying between 15,810 bp and 19,311 bp. However, D. pinnata had longer IRs at 29,165 bp and a shorter SSC at 15,810 bp. In the LSC/IRb region, the gene order was rpl2–rps19. In most species of Dalbergia, the rps19 gene is entirely located within the LSC region, while it expands to the IRb region in D. hancei, D. milletii, and D. mimosoides. In the other species, the rps19 gene spanned the LSC/IRb border, with 1–8 bp extended into the LSC region and 17–30 bp extended into the IRb region. The ndhF genes of most species are located in the SSC region, varying from 2 bp to 37 bp away from the IRb region, except for in D. yunnanensis, D. hancei, D. mimosoides, D. peishaensis, and D. candenatensis. However, in the Dalbergia species, the ycf 1 pseudogene was located in the junction of the IRb/SSC region, with 1 bp to 162 bp of the ycf1 pseudogene extending into the SSC region. The ycf1 gene covered the junction of the IRa/SSC region, with 1414 bp to 4869 bp located in the SSC region and 463 bp to 3907 bp extending into the IRa region (Figure 5).
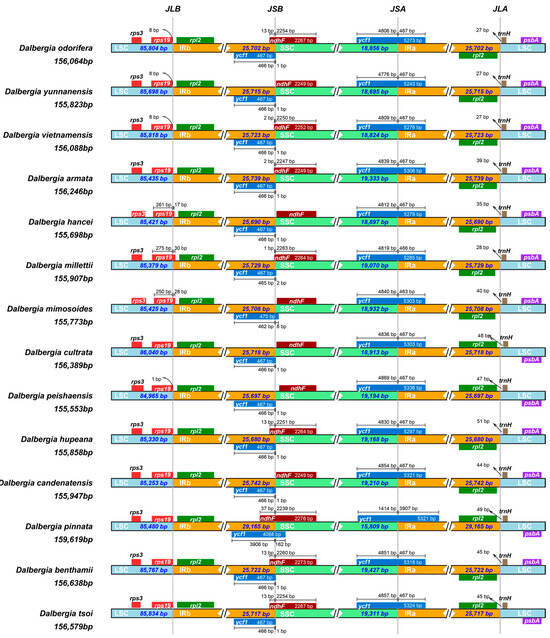
Figure 5.
Comparison of border distance between adjacent genes and junctions of LSC, SSC, and two IR regions among plastid genomes of Dalbergia species.
3.6. Structural Variations in cp Genomes of Dalbergia Species
MUMmer and SyRI were used to identify genomic variations among Dalbergia species by comparing reference and query chloroplast genomes based on their location in the phylogenetic tree. In brief, the species located above represent the reference cp genome, whereas the species located below represent the query cp genome. The genomic variations include the number of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), insertions, and deletions, as well as their lengths, in the reference and query cp genomes. The results show that significant genetic divergence still exists in Dalbergia cp genomes, despite them always presenting high conservation in other studies (Table 2 and Table S3).

Table 2.
Statistics of structural variations in cp genomes of Dalbergia species.
The cp genome of D. peishaensis shows significant genetic divergence, with 742 SNPs, 109 insertions, and 146 deletions when compared to the reference genome of D. cultrata, alongside a length of 1568 bp in the D. cultrata cp genome and a length of 495 bp in the D. peishaensis cp genome (Table 2 and Table S3). The cp genome of D. pinnata also displayed the highest genetic variation in this dataset, with 484 SNPs, 59 insertions, and 76 deletions. The structural variations in the length of the D. candenatensis cp genome are of 348 bp, but the length in the D. pinnata cp genome is notably longer at 4015 bp, indicating a significant discrepancy in genome size. This difference suggests potential genome expansion or rearrangement in the D. pinnata cp genome, possibly due to duplications or insertions (Table 2 and Table S3). The cp genome of D. tsoi exhibits 624 SNPs, 94 insertions, and 92 deletions, with a length of 532 bp in D. benthamii as the reference and a length of 498 bp in D. tsoi cp genome as the query. While its variation is less extreme than that of D. pinnata, the numbers still indicate notable divergence (Table 2 and Table S3). The high number of SNPs and indels (insertions and deletions) indicates substantial variation in its chloroplast genome, suggesting that the Dalbergia genus may have undergone considerable evolutionary changes. The structural variations in the cp genomes of the Dalbergia genus might contribute to the further development of identification markers.
3.7. Potential Markers for Identification of Dalbergia Species
Highly variable sequences were calculated using DNASP version 6 with the window length and step size set as 100 and 25 bp, respectively (Figure 6). The divergent hotspot region in the plastid genome of Dalbergia was mainly distributed in the LSC and SSC regions. The nucleotide diversity (Pi) values ranged from 0.00143 to 0.13791. Six variable hotspots (Pi > 0.08) were detected, namely trnL-UAA, trnL-UAA—trnT-UGU, trnS-UGA—psbC, trnR-UCU—trnG-UCC, psbB—psbT, and ndhG—ndhI, of which five hotspots were located in the LSC region and one hotspot was distributed in the SSC region, and only the region between ndhG and ndhI was identified as being of high variation (Pi > 0.1).
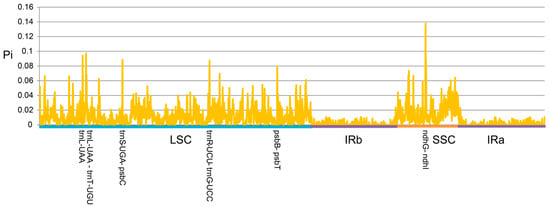
Figure 6.
Nucleotide diversity of three tropical liana Dalbergia cp genomes based on sliding window analysis.
4. Discussion
The identification of plants or seedlings has traditionally relied on taxonomy, which utilizes morphological characteristics such as leaves, flowers, and fruits [49]. For instance, D. pinnata is characterized by its asymmetric leaf base; D. tsoi and D. peishaensis are distinguished by numerous small leaflets; and the legumes of this genus typically present with shapes that are oblong, ligulate, or strap-shaped, with the exception of D. candenatensis, whose legumes have a half-moon shape. The legume colors range from reddish-brown in D. tsoi to uniformly brown in other species. However, identifying resinous heartwood in the market can prove challenging. Traditionally, anatomical analysis is employed, but this method is limited when applied to closely related species as differences are often quantitative rather than qualitative. For example, statistical analysis reveals no significant differences in the wood anatomy among the three species comprising ‘Jiangzhenxiang’ (i.e., D. benthamii, D. pinnata, and D. tsoi) as per the DB45/T 1914-2018 standard. Furthermore, databases such as the International InsideWood Database [50] and the CITESwoodID Database [51,52] primarily contain data on tree species, with scant information on the lianas or climbing shrubs of Dalbergia.
Among the lianas of Dalbergia identified as sources of ‘Jiangzhenxiang’—specifically D. benthamii, D. pinnata, and D. tsoi—the resinous wood of these species has been the subject of extensive study regarding its chemical composition and pharmacological properties (Figure 1). Research conducted by various scholars has demonstrated that the primary volatile component in the resinous wood of these three species is elemicin [53,54,55,56,57]. Elemicin exhibits notable antibacterial and antifungal activities [58,59] and has been reported to possess antipneumonia and vasodilatory effects [60]. Additionally, other chemical components of ‘Jiangzhenxiang’ have exhibited α-glucosidase-inhibitory activity [61] and the potential to accelerate wound healing [62]. Research on D. peishaensis remains limited, being discussed only in a single study, which reported the presence of elemicin in its resinous wood [54]. The relationship between D. tsoi and D. peishaensis extends beyond mere morphological differences; notable distinctions are evident in their fruit coloration—reddish brown in D. tsoi and brown in D. peishaensis. Additional disparities can be observed in their wood anatomy. For example, D. tsoi exhibits homocellular rays, primarily multiseriate and occasionally uniseriate, whereas D. peishaensis displays heterocellular rays, predominantly uniseriate with occasional Kribs-type heterogeneous I. There are also differences in the width of the wood rays, with D. tsoi generally being 3–4 cells across compared to the 1–2 cells typically seen in D. peishaensis. Vessel density further distinguishes the two, with D. tsoi exhibiting a density of 3–4 vessels per mm2 and D. peishaensis a density of 13–15 vessels per mm2 [63]. However, it is still difficult to classify these species in scientific research or on the market. Chloroplast genome sequencing represents an opportunity to overcome this problem in species identification. This study also revealed a significant difference in the length of their chloroplast genomes: D. tsoi has a genome of 159,619 bp, while D. peishaensis has one of 155,553 bp, a difference of 4066 bp (Figure 2). Phylogenetically, they are distinctly separated, clustering on different branches of the evolutionary tree (Figure 4A), and their ANI is 98.36, whereas that of D. tsoi and D. benthamii is 99.38 and the ANI score of D. peishaensis and D. cultrata is 99.21 (Figure 4B). These findings do not support the results of a previous study, which advocated that D. peishaensis should be recognized as a distinct species [64].
Although high-throughput sequencing has revolutionized the analysis of plant chloroplast genomes and provided substantial benefits despite encountering distinct challenges [28,30], its extant methodologies are still limited, especially for the identification of the clean reads and assembly completeness. It is possible that integrant reads were overlooked in the final assembly, resulting in an incomplete gene predication. In this study, the infA gene was detected in the cp genomes of three liana medicinal plants from the genus Dalbergia which had not been reported in previous studies of Dalbergia species [65]. In higher plants, infA encodes roughly 70 amino acids of the translation initiation factor IF1, a crucial component of protein synthesis initiation in organelles [19]. The infA gene is notably dynamic in the evolution of chloroplast DNA, having been lost in 24 angiosperm lineages, yet it remains intact in the majority of angiosperm species [66]. Additionally, infA is considered the most mobile gene in plant chloroplast DNA, experiencing multiple transfers throughout evolutionary history [67]. Previous studies reported the loss of both the infA and rpl22 genes in all studied Dalbergia chloroplast genomes, a trait otherwise common among legumes [65]. TOC (the protein translocon at the outer envelope membrane of chloroplasts) and TIC (the protein translocon at the inner envelope membrane of chloroplasts) had been identified as two successive protein translocons in their double-envelope membranes that import thousands of nucleus-encoded proteins synthesized in cytosol [68,69]. As the member of the TIC complex, TIC214 is predicted to possess at least six transmembrane helices in its amino-terminal domain, which protein unexpectedly encoded by the previous enigmatic ycf1 gene in chloroplasts [70]. In this study, the ycf1 gene and the ycf1 pseudogene were also identified in these three cp genomes of Dalbergia species. The ycf1 pseudogene of D. pinnata in the IRb/SSC region is significantly longer at 4068 bp compared to the other species, which range from 467 bp to 470 bp. In the IRa/SSC region, while the length of ycf1 is similar to other Dalbergia species at 3907 bp in the IRa region (compared to 463 bp to 467 bp in others), it spans only 1414 bp in the SSC region, whereas the other species range from 4776 bp to 4869 bp (Figure 5). However, this is also part of a traditional quadripartite structure analysis of plant cp genomes.
In recent decades, the methodologies of plant whole-genome sequencing (WGS) and analysis have developed rapidly, along with the emergence of a variety of excellent software that can also be used in cp genome analysis [71]. In this study, fastANI, MUMmer, and SyRI, which are usually used for WGS data analysis, were integrated into the comparative analysis of the Dalbergia genus cp genomes. Subsequently, our results suggested that average nucleotide identities (ANIs) present slightly differently within the genus than is observed using traditional or molecular taxonomy, which is consistent with our constructed phylogenetic tree (Figure 4). More refined structural variations were identified with MUMmer and SyRI, such as SNPs and the sites of insertion or deletion, which could contribute to the further species classification (Table 2). The nucleotide diversity analysis, which was carried out for population genomics, also provided new insights into the divergence and evolution in the Dalbergia genus. Six plastid genome regions from 29 Dalbergia species, trnL-UAA, trnL-UAA–trnT-UGU, trnR-UCU–trnG-UCC, psbB–psbT, trnS-UGA–psbC, and ndhG–ndhI, were identified as having higher Pi values, which is indicative of variability. Notably, ndhG–ndhI exhibited the most significant changes, suggesting its potential utility as a candidate molecular marker for identifying resinous wood in the future (Figure 6).
Liana species are distributed worldwide and are usually located in a specific ecological niche [72]. For instance, the liana Vitis vinifera has distinctive features and grows principally in tropical forests [73]. Unlike tree foliage, the species of V. vinifera uniquely expands both vertically and horizontally within forests. V. vinifera leaves typically exhibit higher nutrient concentrations, shorter lifespans, and faster decomposition rates [74]. Moreover, V. vinifera stems display a range of flexible and adaptive structural strategies, such as cambial variants that facilitate bending growth, self-repair after damage, and modifications in vessel diameter and morphology that enhance transport efficiency [75]. Research has shown that liana species possess advantages in terms of light interception, photosynthetic rate, water use, and growth in arid forest settings, demonstrating remarkable adaptability [76]. Consequently, Dalbergia lianas might also significantly contribute to rapid biodiversity restoration during the initial stages of forest vegetation recovery, and should thus be examined in future research. Furthermore, this study examined the challenging scarcity of genetic resources for medicinal plants, which is compounded by their slow growth rates, prolonged heartwood formation, and the limited developmental scope of Dalbergia tree species.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we sequenced and assembled the chloroplast genomes of three medicinal liana species from the genus Dalbergia (D. peishaensis, D. pinnata, and D. tsoi) native to the tropical regions of Hainan Province, China. The cp genome sizes ranged from 155,553 bp to 159,619 bp, displaying a typical quadripartite structure with large single-copy (LSC), small single-copy (SSC), and two inverted repeat (IR) regions. Gene content across the Dalbergia chloroplast genomes was highly conserved; however, the IR boundaries exhibited significant variability, accompanied by a notable abundance of simple sequence repeats (SSRs). A key finding was the presence of intact infA genes in all three liana species, a novel observation within the genus, as previous studies reported infA to be absent in other Dalbergia species. Additionally, the ycf1 gene in D. pinnata displayed distinct length variations compared to other Dalbergia species, suggesting potential functional divergence. Phylogenetic analysis of 29 Dalbergia species, including the 3 studied here, revealed two distinct clades within the liana group, challenging the synonymity of D. peishaensis with D. tsoi and supporting their taxonomic distinction. Six highly variable regions were identified as potential molecular markers for species identification within Dalbergia. These findings enhance the genomic resources available for Dalbergia and facilitate the development and validation of genetic markers for wood identification, particularly for ‘Jiangzhenxiang’ (i.e., D. benthamii, D. pinnata, and D. tsoi) and other liana or climbing shrub species within the genus. The methodologies applied to characterize structural variations in this study provide a potential framework for future research on comparative genomics and conservation efforts in the chloroplast genomes. Therefore, future studies are needed to investigate the accuracy and reliability of this framework based on whole-population cp genomes, such as all released the cp genomes of the Dalbergia genus.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae11070799/s1, Table S1: Statistics of annotated genes in three tropical Dalbergia species; Table S2: Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) in three chloroplast genomes from Dalbergia genus; Table S3: Statistics of structural variations in cp genomes of Dalbergia species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.D. and J.W.; Methodology and Software, X.D.; Writing—Original Draft, X.D. and J.W.; Writing—Review and Editing, S.Z., X.S. and L.W.; Supervision, X.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 322RC768).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Huanqiang Chen from the Jianfengling Branch of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park Management Bureau for plant sample collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Adema, F.; Ohashi, H.; Sunarno, B. Notes on Malesian Fabaceae (Leguminosae-Papilionoideae) 17. The genus Dalbergia. Blumea-Biodivers. Evol. Biogeogr. Plants 2016, 61, 186–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaingoson, F.R.; Oyebanji, O.; Stull, G.W.; Zhang, R.; Yi, T.S. A dated phylogeny of the pantropical genus Dalbergia L.f. (Leguminosae: Papilionoideae) and its implications for historical biogeography. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.Y.; Hu, H.Z.; Li, X.F.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Q.L.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, N.N.; Lin, W.; Xu, D.P. Physiological and biochemical mechanisms of drought regulating the size and color of heartwood in Dalbergia odorifera. Tree Physiol. 2025, 45, tpae157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, A.N.; Warrier, R.R.; Kher, M.M.; da Silva, J.A.T. Indian rosewood (Dalbergia latifolia Roxb.): Biology, utilisation, and conservation practices. Trees 2022, 36, 883–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Shilpi, J.A.; Mondal, H.; Hossain, F.; Anisuzzman, M.; Hasan, M.M.; Cordell, G.A. Ethnomedicinal, phytochemical, and pharmacological profile of the genus Dalbergia L. (Fabaceae). Phytopharmacology 2013, 4, 291–346. [Google Scholar]
- Nikum, R.D.; Nehete, J.Y. Review on traditionally medicinal importance, morphology, phytochemistry and pharmacological activities of Dalbergia sisso. Int. J. Pharmacogn. 2021, 8, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.I.S.; Ferreira, A.F.; Costa, M.A.P.D.C.; Silva, F.D.L.; Estevinho, L.M.; Carvalho, C.A.L.D. Phytochemical study and antioxidant activity of Dalbergia ecastaphyllum. Rodriguésia 2020, 71, e00492019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburger, M.O.; Cordell, G.A.; Tantivatana, P.; Ruangrungsi, N. Traditional medicinal plants of Thailand, VIII. Isoflavonoids of Dalbergia candenatensis. J. Nat. Prod. 1987, 50, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheenpracha, S.; Karalai, C.; Ponglimanont, C.; Kanjana-Opas, A. Candenatenins A−F, Phenolic Compounds from the Heartwood of Dalbergia candenatensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1395–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasolomampianina, R.; Bailly, X.; Fetiarison, R.; Rabevohitra, R.; Bena, G.; Ramaroson, L.; Raherimandimby, M.; Moulin, L.; De Lajudie, P.; Avarre, J.C. Nitrogen-fixing nodules from rose wood legume trees (Dalbergia spp.) endemic to Madagascar host seven different genera belonging to α- and β-Proteobacteria. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 4135–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernusak, L.A.; Aranda, J.; Marshall, J.D.; Winter, K. Large variation in whole-plant water-use efficiency among tropical tree species. New Phytol. 2007, 173, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, R.V. Climbing plant diversity in Australia: Taxonomy, biogeography and functional traits. Ecol. Lianas 2015, 9, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.H.; Zheng, Y.; Ke, M.Q. Study on the effects of vacuum heat treatment on the physical, mechanical, and chemical properties of Dalbergia latifolia Roxb. wood. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, L.C.A.; Longui, E.L.; Muszynski, L. A quest for a sustainable alternative wood species to produce world class clarinets. BioResources 2021, 16, 6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhung, N.P.; Thu, P.Q.; Chi, N.M.; Dell, B. Vegetative propagation of Dalbergia tonkinensis, a threatened, high-value tree species in South-east Asia. South. For. A J. For. Sci. 2019, 81, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, D.T.; Tang, D.V.; Hien, V.T.T.; Ton, N.D.; Hai, N.V. Nucleotide diversity of a nuclear and four chloroplast DNA regions in rare tropical wood species of Dalbergia in Vietnam: A DNA barcode identifying utility. Asian J. Appl. Sci. 2014, 2, 116–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.Y.; Wong, K.H.; Kong, B.L.H.; Siu, T.Y.; But, G.W.C.; Tsang, S.S.K.; Lau, D.T.W.; Shaw, P.C. Comparative analysis of chloroplast genomes of Dalbergia species for identification and phylogenetic analysis. Plants 2022, 11, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Wappler, T.; Labandeira, C.; Huang, J.; Song, A.; Xie, S.P.; Jia, L.B.; Deng, W.Y.D.; Su, T. Cenozoic Dalbergia (Fabaceae) plant fossils from Southwest China: Biogeographic implications and plant-insect interactions. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2024, 647, 112260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassold, S.; Lowry, P.P.; Bauert, M.R.; Razafintsalama, A.; Ramamonjisoa, L.; Widmer, A. DNA barcoding of Malagasy rosewoods: Towards a molecular identification of CITES-listed Dalbergia species. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Xu, M.F.; Wang, L.Z.; Chen, D.K. Overview of the pharmacy characteristics of climbing ancient Jiangzhenxiang. Strait Pharm. J. 2020, 32, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.X.; Huang, Y.H.; Tu, X.W.; Liu, Y.L.; Yang, X.; Chen, Y.Q.; Li, K.; Xie, Y.Q. Characteristics of traditional medicine of Li nationality in Hainan. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharm. 2022, 31, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.C.; Li, Y.H.; Li, S.Y. Original plant of Chinese herb Jiangxiang. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 1996, 19, 550–553. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Y.; Liu, X.C. Further textual research on Herb Rosewood. Strait Pharm. J. 1996, 9, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Gao, S.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.N.; Mo, W. Identification of original plant varieties of national Jiangzhenxiang conventionally used as medicine and incense in Hainan. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2016, 44, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.B.; Ni, X.J.; Tian, L.W.; Zeng, Y.; Li, S.Y. A new study on the Materia Medica of Jiangxiang. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2017, 40, 982–985. [Google Scholar]
- DB45/T 1914-2018; Identification Method of Jiangzhenxiang. Markert Supervision Administration of Guangxi: Nanning, China, 2018.
- Yu, X.Q.; Huang, Y.; Chen, R.; Wei, J.H.; Huang, M.C. Pharmacognosy Research of Dalbergia benthamii Prain. Popul. Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xu, J.; Li, W.M.; Li, M.F. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome sequence of Dalbergia species and its phylogenetic implications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Lin, F.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, P. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome sequences of six Dalbergia species and its comparative analysis in the subfamily of Papilionoideae (Fabaceae). PeerJ 2022, 10, e13570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Zhu, C.J.; Yang, J.B.; Vatanparast, M.; Schley, R.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, D.Y.; Tu, T.Y.; Klitgård, B.B.; Zhang, D.X. Comparative analysis of complete plastid genome reveals powerful barcode regions for identifying wood of Dalbergia odorifera and D. tonkinensis (Leguminosae). J. Syst. Evol. 2022, 60, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Jiao, L.C.; Yu, M.; Guo, J.; Jiang, X.M.; Yin, Y.F. DNA barcoding authentication for the wood of eight endangered Dalbergia timber species using machine learning approaches. Holzforschung 2018, 73, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Ma, R.; Qiao, M.; Fu, Y. The DNA barcode identification of Dalbergia odorifera T. Chen and Dalbergia tonkinensis Prain. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartvig, I.; Czako, M.; Kjaer, E.D.; Nielsen, L.R.; Theilade, I. The use of DNA barcoding in identification and conservation of rosewood (Dalbergia spp.). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.W.; Wu, J.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Lian, X.M.; Wu, F.L.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Z.B.; Zhu, S. The phylogenetic analysis of Dalbergia (Fabaceae: Papilionaceae) based on different DNA barcodes. Holzforschung 2017, 71, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J. Dalbergia in Asia; Sience Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 1–371. [Google Scholar]
- Lachenaud, O.; van der Maesen, L.J.G. Notes on African Dalbergia (Leguminosae–Papilionoideae) with the description of two new species from Atlantic Central Africa. Symb. Bot. Ups. 2016, 38, 167–194. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.P.; Mei, W.L.; Lin, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Peng, S.Q.; Li, H.L.; Zhu, J.H.; Li, W.; Wang, P.; et al. Genome sequence of the agarwood tree Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Spreng: The first chromosome-level draft genome in the Thymelaeceae family. GigaScience 2020, 9, giaa013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.P.; Chen, H.Q.; Huang, S.Z.; Yu, M.; Dai, H.F.; Mei, W.L. Characterization of complete chloroplast genome of the tertiary relict tree Cephalotaxus hainanensis (Cephalotaxaceae), an endangered species endemic to China. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 824–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.B.; Liu, B.H.; Xie, Y.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Huang, W.H.; Yuan, J.Y.; He, G.Z.; Chen, Y.X.; Liu, Y.J.; Cheung, D.W.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 2012, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. BLAST: Improvements for better sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W6–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, M.; Drechsel, O.; Kahlau, S.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW—A suite of tools for generating physical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes and visualizing expression data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W575–W581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Zan, X.; Chu, L.; Su, Y.; Xu, P.; Liu, W. Study of the error correction capability of multiple sequence alignment algorithm (MAFFT) in DNA storage. BMC bioinform. 2023, 24, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2–approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European molecular biology open software suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marçais, G.; Delcher, A.L.; Phillippy, A.M.; Coston, R.; Salzberg, S.L.; Zimin, A. MUMmer4: A fast and versatile genome alignment system. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1005944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.; Sun, H.; Jiao, W.B.; Schneeberger, K. SyRI: Finding genomic rearrangements and local sequence differences from whole-genome assemblies. Genome biol. 2019, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, J.M. Botany: Taxonomy, morphology and physiology of fruits, leaves and flowers. In Citrus; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 30–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, E.A. Inside Wood-A web resource for hardwood anatomy. IAWA J. 2011, 32, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, G.; Richter, H.G.; Schmitt, U. Design and application of CITESwoodID computer-aided identification and description of CITES-protected timbers. IAWA J. 2011, 32, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Palacios, P.; Esteban, L.G.; Gasson, P.; García-Fernández, F.; de Marco, A.; García-Iruela, A.; García-Esteban, L.; González-de-vega, D. Using lenses attached to a smartphone as a macroscopic early warning tool in the illegal timber trade, in particular for CITES-listed species. Forests 2020, 11, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.B.; Zhang, D.Y.; Xu, Z.C.; Mo, W. Study on composition and antioxidant activity of volatile oil from Dalbergia pinnata. Trad. Chin. Drug Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 28, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Wang, L.Z. Textual research on Materia Medica of Jiangxiang and Jiangzhenxiang. Asia-Pac. Trad. Med. 2019, 15, 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.S.; Wei, J.H.; Chen, R.; Huo, L.N.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wu, G. GC-MS analysis of volatile oil from Dalbergia benthamii Prain of different producing areas by supercritical carbon dioxide extraction. Technol. Dev. Chem. Ind. 2020, 49, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; He, Y.X.; Lei, X.L.; Liao, L.K.; Fu, T.K.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, X.B.; Zou, L.Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Ruan, R.; et al. Chemical composition and evaluation of antioxidant activities, antimicrobial, and anti-melanogenesis effect of the essential oils extracted from Dalbergia pinnata (Lour.) Prain. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 254, 112731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.D.; Fan, Z.Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Ban, M.M.; Yang, L. Species identification and chemical composition analysis of Shimuxiang. Trad. Chin. Drug Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 32, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasinghe, L.; Kumarihamy, B.M.M.; Nishantha Jayarathna, K.H.R.; Gayathri Udishani, N.W.M.; Ratnayake Bandara, B.M.; Hara, N.; Fujimoto, Y. Antifungal constituents of the stem bark of Bridelia retusa. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, P.G.; Bao, L.; Luciani, A.; Panighi, J.; Desjobert, J.M.; Costa, J.; Casanova, J.; Bolla, J.M.; Berti, L. (E)-Methylisoeugenol and elemicin: Antibacterial components of Daucus carota L. essential oil against Campylobacter jejuni. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7332–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, I.D.; Rogers, K.L.; Griffiths, L.R. Isolation of bioactive compounds that relate to the anti-platelet activity of Cymbopogon ambiguous. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2010, 2011, 467134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.H.; Zhao, W.B.; Zhang, D.Y.; Li, S.J.; Fan, Z.Y.; Lin, R.Y. Macroscopic and microscopic identification of Hainan Li medicine Dalbergia benthamii Prain. Pharm. Today 2020, 30, 324–327. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, R.X.; Li, C.Q.; Chen, Y.; Xia, T.Y.; Peng, M.M.; Ren, Z.L.; Zhao, H.; et al. Identification of active compounds and molecular mechanisms of Dalbergia tsoi Merr. & Chun to accelerate wound healing. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 112990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Wood Anatomy of Seven Species of Vine or Climbing Plant of Dalbergia L.f. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2022, 45, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, F.; Tu, T.Y.; Li, S.J.; Zhang, D.X. A new synonym of Dalbergia tsoi Merr. et Chun. J. Trop. Subtr. Bot. 2013, 21, 225–228. [Google Scholar]
- Magee, A.M.; Aspinall, S.; Rice, D.W.; Cusack, B.P.; Sémon, M.; Perry, A.S.; Stefanović, S.S.; Milbourne, D.; Barth, S.; Palmer, J.D.; et al. Localized hypermutation and associated gene losses in legume chloroplast genomes. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, K.H.; Morden, C.W.; Ems, S.C.; Palmer, J.D. Rapid evolution of the plastid translational apparatus in a nonphotosynthetic plant: Loss or accelerated sequence evolution of tRNA and ribosomal protein genes. J. Mol. Evol. 1992, 35, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millen, R.S.; Olmstead, R.G.; Adams, K.L.; Palmer, J.D.; Lao, N.T.; Heggie, L.; Kavangh, T.A.; Hibberd, J.M.; Gray, J.C.; Morden, C.W.; et al. Many parallel losses of infA from chloroplast DNA during angiosperm evolution with multiple independent transfers to the nucleus. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenkert, S.; Soll, J.; Bölter, B. Protein import into chloroplasts—How chaperones feature into the game. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, P.; López-Juez, E. Biogenesis and homeostasis of chloroplasts and other plastids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, M. The TIC complex uncovered: The alternative view on the molecular mechanism of protein translocation across the inner envelope membrane of chloroplasts. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2015, 1847, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Mei, W.; Wang, H.; Zeng, J.; Dai, H.; Ding, X. Comprehensive Analysis of NAC Transcription Factors Reveals Their Evolution in Malvales and Functional Characterization of AsNAC019 and AsNAC098 in Aquilaria sinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzer, S.A. Testing ecological theory with lianas. New Phytol. 2018, 220, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballé, G. Liana structure, function and selection: A comparative study of xylem cylinders of tropical rainforest species in Africa and America. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1993, 113, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Kitching, R.L.; Cao, M. Lianas as structural parasites: A re-evaluation. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isnard, S.; Silk, W.K. Moving with climbing plants from Charles Darwin’s time into the 21st century. Am. J. Bot. 2009, 96, 1205–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Vega, J.A.; Bongers, F.; Poorter, L.; Schnitzer, S.A.; Sterck, F.J. Lianas have more acquisitive traits than trees in a dry but not in a wet forest. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 2367–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).