Abstract
This study investigated the effects of Trichoderma harzianum inoculation on the growth, physiological responses, and soil nutrient uptake of three turfgrass species cultivated on eco-concrete—Axonopus compressus (Sw.) Beauv., Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers., and Zoysia sinica Hance. A 2 × 2 factorial design was used to evaluate plant growth, physiological responses, and soil metrics under cement stress, incorporating T. harzianum inoculation (inoculated vs. control) and substrate composition (eco-concrete vs. pastoral soil). Our results indicate that inoculation with Trichoderma harzianum significantly enhanced the growth potential of the three turfgrass species compared to uninoculated controls. Furthermore, under cement stress conditions in vegetated concrete, inoculation with T. harzianum significantly alleviated the inhibition of growth and development. More specifically, in the vegetated concrete habitat, inoculated plants exhibited significantly increased root length and surface area. This enhancement promoted the uptake of available nitrogen (AN), available phosphorus (AP), and available potassium (AK) from the soil. Concurrently, inoculated plants showed higher leaf epidermal cell density, stomatal width, soluble sugar content, and antioxidant enzyme activity (SOD, POD, CAT, and APX). Additionally, significant reductions were observed in root activity, relative conductivity, and malondialdehyde (MDA) and proline contents. In conclusion, T. harzianum inoculation promotes the growth of the three turfgrass species under cement stress, likely by enhancing root development, increasing osmoregulatory substance accumulation, and elevating antioxidant enzyme activities.
1. Introduction
The rapid development of global infrastructure, including highways, railways, and water conservancy projects, has enhanced regional connectivity while simultaneously exacerbating ecological degradation and resource depletion [1]. Large-scale construction activities often lead to surface exposure, soil contamination from construction waste, and reduced erosion resistance, resulting in severe soil erosion and ecosystem disruption [2,3]. Among the emerging ecological restoration strategies, eco-concrete greening technology has gained prominence as a sustainable approach for rehabilitating damaged slopes [4,5]. Eco-concrete constitutes a multiphase material system containing size-graded mineral aggregates, water, reactive/inert additives, and cement-based binding matrices [6]. However, eco-concrete fundamentally differs from pastoral soil due to its incorporation of highly alkaline, high-grade cement. These properties—high hardness, poor water retention, and limited nutrient availability—impede root expansion, water absorption, and nutrient uptake, subjecting plants to significant cement stress [7]. Consequently, identifying stress-tolerant plant species and enhancing their adaptability to eco-concrete environments remains a critical research priority.
Axonopus compressus (Sw.) Beauv. (a perennial herb of the Poaceae family), Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. (a resilient perennial grass), and Zoysia sinica Hance (a robust perennial species with extensive root systems) are renowned for their soil stabilization capabilities and ecological benefits [8,9,10]. Despite these advantages, current eco-concrete projects predominantly utilize conventional species such as Festuca elata, Lolium perenne, and Poa annua, leading to limited biodiversity and monotonous landscapes [11]. To address this gap, our study selected three underutilized species—A. compressus, C. dactylon, and Z. sinica—for eco-concrete applications, aiming to expand the diversity of stress-resistant vegetation suitable for slope rehabilitation.
Microbial inoculants, particularly those containing beneficial microorganisms, have demonstrated significant potential in enhancing plant growth and improving soil quality [12,13]. Trichoderma harzianum, a fungal species in the Deuteromycotina, colonizes plant rhizospheres, suppresses pathogenic fungi, and enhances nutrient acquisition [14,15,16]. Several studies have confirmed that T. harzianum significantly promotes the growth of a variety of plants. More specifically, it can effectively promote the growth, development and regeneration process of Festuca arundinacea by enhancing its water and nutrient uptake and the transport capacity of its root system [17]. At the photosynthesis level, recent studies have shown that inoculation with T. harzianum significantly enhanced the net photosynthetic rate of Lolium perenne, which in turn accelerated the conversion efficiency of photosynthetic products and ultimately drove significant biomass accumulation [18]. In addition, T. harzianum not only effectively promotes the growth and development of Avena sativa and improves the physicochemical properties of soil [19] but also enhances soil enzyme activity and promotes organic matter conversion [20]. However, thus far, studies on T. harzianum’s beneficial effect on plant stress tolerance are lacking.
This study investigates the effects of T. harzianum inoculation on the growth performance, leaf epidermal morphology, and physiological responses of A. compressus, C. dactylon, and Z. sinica under eco-concrete conditions. By elucidating the synergistic mechanisms between microbial agents and turfgrasses, this research aims to advance sustainable strategies for slope restoration and ecological resilience.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
A. compressus, C. dactylon, and Z. sinica seeds were obtained from Jiangsu Jinzhao Seed Industry Co. Ltd. (Nanjing, China). T. harzianum inoculum (with CaCO3 as the carrier; 500 million spores/g) was provided by Weifang Shenneng Technology Co., Ltd. (Weifang, China). Two planting substrates were prepared: (1) eco-concrete (cement/gravel/sand/pastoral soil = 2:8:2:3; porosity = 25%; pH = 9.0) and (2) pastoral soil (pH = 6.5). Both substrates were sterilized via autoclaving (121 °C, 0.11 MPa, 2 h) to eliminate microbial contaminants prior to experimentation.
Uniform-sized seeds were selected and sown in sterilized substrate-filled pots (50 seeds per pot). Cultivation was conducted in a glass greenhouse at Yangtze University’s West Campus (Jingzhou, China), under controlled conditions (temperature: 18–25 °C; relative humidity: 80%; light intensity: 10,000 lx).
Preliminary dose–response trials (1, 2, 3, and 4 g/L) revealed optimal growth performance at a T. harzianum concentration of 3 g/L. Consequently, this concentration was selected for subsequent experimental treatments.
2.2. Experimental Design
The experiment employed a 2 × 2 factorial design with two primary factors: Factor 1 consisted of inoculation with T. harzianum and control watering, while Factor 2 included eco-concrete and pastoral soil substrates. This resulted in four treatment combinations (Table 1), each replicated three times with 6 pots per replicate, yielding a total of 18 pots per treatment to ensure statistical robustness.

Table 1.
Group settings.
The first treatment was carried out immediately after sowing. T. harzianum was dissolved in distilled water to make 100 mL of 3 g/L solution (150 million spores). This was added to each pot along the contact surface for the inoculated group, with an equal amount of distilled water for the uninoculated group. Subsequently, inoculation was performed every 5 days for a total of 6 treatments. Then, 30 days after sowing, each treatment group was randomly sampled.
2.3. Preparation of Freehand Sections for Leaf Subepidermal Structure Observations
For each treatment, ten potted samples were randomly selected. From each pot, 3 individual plants were randomly collected. A 1 cm segment from the middle portion of the third leaf of each plant was excised and rinsed with distilled water. Sections were prepared using the freehand sectioning method, as described by Cheng [21], and stained with acetocarmine solution. The sections were photographed under a light microscope (Olympus CX21, Shanghai, China), and the morphological characteristics of the lower epidermal cells and stomata in the middle leaf section—including parameters such as length and width—were measured and recorded using Image J 1.53t image analysis software. The cell and stomatal densities were then calculated [22]. Each index was measured at least 50 times, and the experiment was repeated thrice.
2.4. Measurement of Physiological and Biochemical Indicators
Root systems were scanned using an EPSON scanner (v3.771), manufactured by Epson Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan, and root morphological parameters (total length, surface area, and volume) were analyzed with Win RHIZO Pro 2007a.
Shimadzu’s UV-3600 UV-VIS-NIR (Kyoto, Japan) spectrophotometer was used to determine the following: root viability was determined using triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining [23]; malondialdehyde (MDA) content was determined using the thiobarbituric acid colorimetric method [24]; soluble sugar and free proline contents were determined using the anthrone colorimetry method and acid ninhydrin colorimetry, respectively; and contents of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), and ascorbate peroxidase (APX) were determined using the nitrogen blue tetrazolium (NBT), ultraviolet absorption, and guaiacol methods, respectively [25]. In addition, leaf relative electrical conductivity (REC) was determined using LEICI DDB-303A(Shanghai, China) [26]. Three biological replicates and three technical replicates were performed for each indicator.
The mulch on top of the soil was removed and the mixed soil samples were collected by 5-point sampling method using sterilized tools at a depth of 3~5 cm. These were naturally dried and then ground through a sieve, and available nitrogen (AN), available phosphorus (AP), and available potassium (AK) were measured according to the method of Wang Chao et al. [27].
2.5. Data Analysis
We organized our data using Microsoft Excel 2010. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed using SPSS 27.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA). Comparisons were analyzed using Duncan’s multiple range method, and differences were considered statistically significant if the p-value was less than 0.05. Graphs and images were processed using Graphpad Prism 9.0, Adobe Photoshop 2021, and Image J 1.53t.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Treatments on the Growth of Three Turfgrass Species
Under the different treatments, the growth of the three turfgrass species was visually and significantly different (Figure 1). The treatment group inoculated with T. harzianum in pastoral soil flourished overall, with longer and greener plant leaves. Plants in Eco-concrete showed dwarfing and wilting, with leaves showing tilting and curling phenomena or even drying out and dying, while the treatment group inoculated with T. harzianum in eco-concrete showed relatively less wilting, partially alleviating the negative effects of cement stress. Among the three turfgrass species, C. dactylon showed the best response to T. harzianum inoculation.
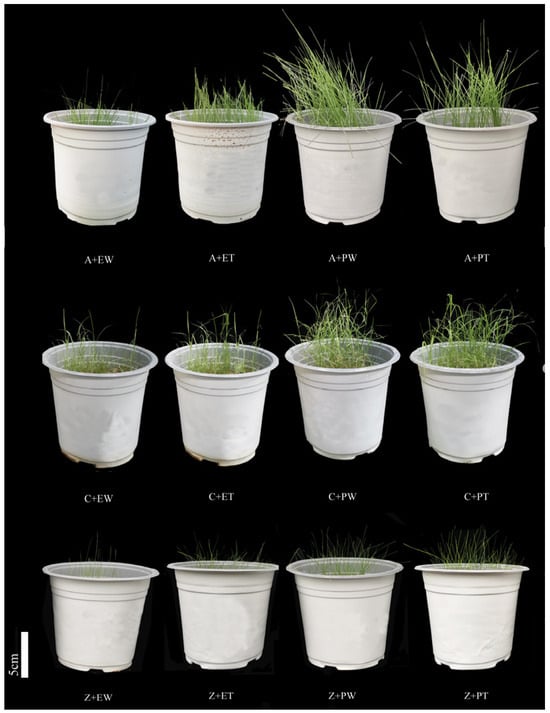

Figure 1.
Effects of different treatments on the growth of three turfgrass species. Abbreviations: A—A. compressus, C—C. dactylon, Z—Z. sinica, EW—eco-concrete–water, ET—eco-concrete–T. harzianum, PW—pastoral soil–water, PT—pastoral soil–T. harzianum. Scale = 5 cm.
3.2. Effects on the Root Development and Root Viability of Three Turfgrass Species
Eco-concrete limited the growth of the root systems of the three turfgrass species, and inoculation with T. harzianum mitigated this negative effect (Figure 2A). Among the different treatments, the root system of the group planted in pastoral soil without T. harzianum was long and slender with fewer lateral roots, while that of the treatment group watered with T. harzianum was weak and slender but had more lateral roots. The most obvious differences in root morphology were between the group planted in eco-concrete without T. harzianum and others which exhibited a strong, short, and sparse root system. In contrast, the roots of the samples watered with T. harzianum were slender, short, and more lateral.
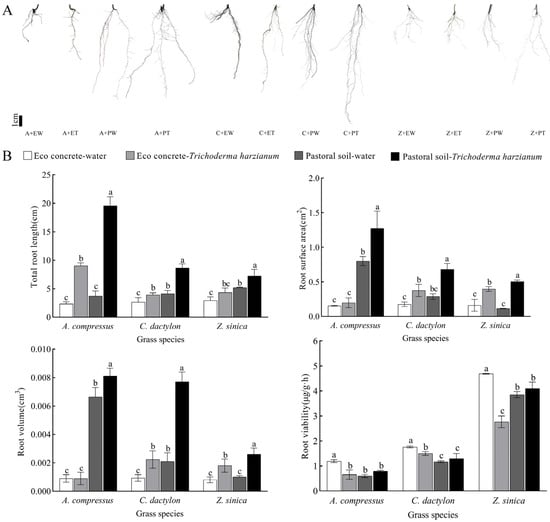
Figure 2.
Effects of different treatments on root morphology and development of three turfgrass species. (A) The root morphology of plants. Abbreviations: A—A. compressus, C—C. dactylon, Z—Z. sinica, EW—eco-concrete–water, ET—eco-concrete–T. harzianum, PW—pastoral soil–water, PT—pastoral soil–T. harzianum. Scale = 1 cm. (B) The total root length, root surface area, root volume, and root viability of three turfgrass species under different treatments. The data are presented as the means ± SEs (n = 5); different letters above the bars indicate significant (p < 0.05) differences.
Inoculation with T. harzianum significantly affected the root growth characteristics of the three turfgrass species (Figure 2B). In eco-concrete, the total root lengths of A. compressus, C. dactylon, and Z. sinica decreased by 74.05%, 35.68%, and 43.67%, respectively, compared to pastoral soil but increased by 36.73%, 32.03%, and 32.47%, respectively, after inoculation with T. harzianum. Regarding root surface area, carpet grass decreased by 80.78% in eco-concrete compared to pastoral soil but increased by 27.58% after T. harzianum inoculation, while C. dactylon and Z. sinica showed increases of 114.16% and 145.05%, respectively. In eco-concrete, the root volume of three turfgrass species was significantly reduced. However, C. dactylon and Z. sinica increased by 139.29% and 125%, respectively, after T. harzianum inoculation. Notably, cement stress in the eco-concrete led to a significant increase in root viability in the three turfgrass species and a significant decrease in root viability after inoculation with T. harzianum; however, in the pasture soil, inoculation with T. harzianum led to an increase in root viability.
3.3. Effects of Different Treatments on Lower Epidermal Characteristics of Three Turfgrass Species
As shown in Figure 3A, in the eco-concrete environment, the leaf epidermal cells of the three turfgrass species gradually shriveled and dehydrated, and stomatal closure was observed. Both abaxial epidermal cell density and stomatal density per unit area decreased. However, after inoculation with T. harzianum, epidermal cell shriveling was slightly alleviated, accompanied by a moderate increase in both epidermal cell density and stomatal density. The results are shown in Figure 3B.
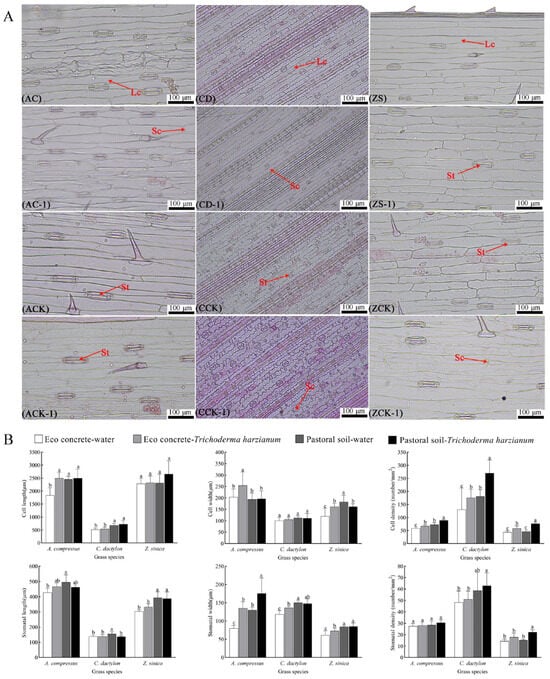
Figure 3.
Anatomy of the leaf epidermis of three turfgrass species. (A) Lower epidermal structure of the leaves under a light microscope. Abbreviations: A—A. compressus, C—C. dactylon, Z—Z. sinica, EW—eco-concrete–water, ET—eco-concrete–T. harzianum, PW—pastoral soil–water, PT—pastoral soil–T. harzianum. (B) Parameters (length, width, and density) related to lower epidermal cells and stomata. The data are presented as the means ± SEs (n = 30); different letters above the bars indicate significant (p < 0.05) differences.
The leaf epidermal cells and stomatal of the three turfgrass species were influenced by the application of T. harzianum, as illustrated in Figure 3B. All the relevant indices of the three turfgrass species grown in eco-concrete were lower than those in the pastoral soil habitat. After the application of T. harzianum, the cell densities of the three turfgrass species increased significantly, by 15.59%, 34.06%, and 35.40%, respectively, and the stomatal widths significant increased by 68.72%, 14.966%, and 19.21%, respectively. In pastoral soil, inoculation with T. harzianum increased the cell densities of the three turfgrass species significantly, by 22.62%, 49.54%, and 64.41%, respectively. Moreover, the cell lengths increased to a certain degree; however, they did not reach statistical significance.
3.4. Effects of Different Treatments on Cell Membrane Permeability and Osmoregulatory Substances of Three Turfgrass Species
Changes in cell membrane permeability and osmoregulatory substances are critical indicators of plant stress responses (Figure 4). Under vegetated concrete conditions, the relative electrical conductivity (REC) of the three turfgrass species increased significantly by 77.91%, 13.73%, and 15.64%, respectively, compared to pastoral soil conditions. However, inoculation with T. harzianum effectively reduced these values by 60.72%, 45.22%, and 39.16%, respectively. Similarly, malondialdehyde (MDA) content showed substantial increases of 65.00%, 187.08%, and 34.18% in vegetated concrete compared to pastoral soil, while T. harzianum treatment significantly decreased these levels by 11.01%, 70.58%, and 23.27%, respectively. In pastoral soil, both REC and MDA contents were reduced following T. harzianum application.
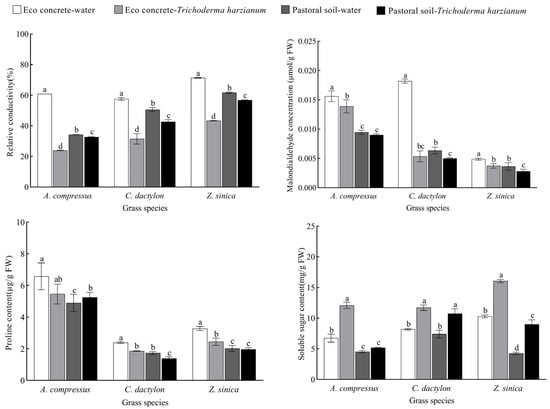
Figure 4.
Effects of different treatments on cell membrane permeability and osmoregulatory substances in three turfgrass species. The data are presented as the means ± SEs (n = 3); different letters above the bars indicate significant (p < 0.05) differences.
Regarding osmoregulatory substances, proline (Pro) and soluble sugar (SS) contents in vegetated concrete exceeded those in pastoral soil. Notably, inoculation with T. harzianum significantly altered these concentrations: compared to untreated controls, Pro content decreased by 17.20%, 22.18%, and 25.45%, while SS content increased by 78.77%, 42.94%, and 56.31%, respectively. In pastoral soil, inoculation with T. harzianum increased SS content by 14.29%, 45.00%, and 110.87% in the three turfgrass species, respectively.
3.5. Effects of Different Treatments on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities of Three Turfgrass Species
The application of T. harzianum significantly influenced the antioxidant enzyme activities of three turfgrass species (Figure 5). To assess the physiological impact of T. harzianum, we measured the activities of key antioxidant enzymes—superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), catalase (CAT), and ascorbate peroxidase (APX). The results demonstrated that turfgrasses cultivated in eco-concrete exhibited substantially higher SOD, POD, CAT, and APX activities compared to those grown in pastoral soil; further increases in antioxidant enzyme activities were observed after inoculation with T. harzianum. In contrast, no consistent trend was observed in the antioxidant enzyme activities of turfgrasses inoculated with T. harzianum in pastoral soil. All antioxidant enzyme activities showed a decreasing trend, except those of SOD and POD, which increased in Z. sinica.
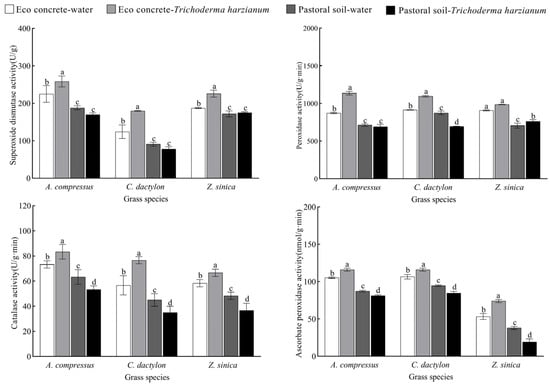
Figure 5.
Effects of different treatments on antioxidant enzyme activities (SOD, POD, CAT, and APX) of three turfgrass species. The data are presented as the means ± SEs (n = 3); different letters above the bars indicate significant (p < 0.05) differences.
3.6. Effects of Different Treatments on AN, AP, and AK of Three Turfgrass Species Grown in Soil
The application of T. harzianum significantly altered the available nitrogen (AN), available phosphorus (AP), and available potassium (AK) contents in turfgrasses cultivation systems (Figure 6). Under unstressed conditions, T. harzianum inoculation increased AN, AP, and AK levels compared to the non-inoculated control. Similarly, soil amendment with cement enhanced these nutrient contents across the three turfgrass species. However, in the eco-concrete system, T. harzianum treatment resulted in varying degrees AN, AP, and AK content reduction.
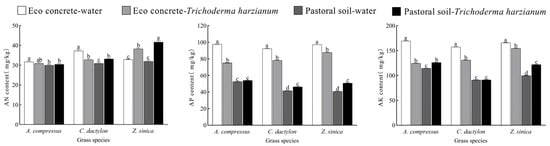
Figure 6.
Soil AN, AP, and AK contents in different treatment groups. The data are presented as the means ± SEs (n = 3); different letters above the bars indicate significant (p < 0.05) differences.
4. Discussion
While eco-concrete inhibits plant growth to a certain degree, it still serves as an effective approach for slope restoration and ecological rehabilitation [28,29,30]. The cement component exposes plants to combined drought and saline stress, which restricts the development of the root system and the capacity for nutrient uptake [31]. In the current study, A. compressus, C. dactylon, and Z. sinica displayed growth inhibition when subjected to cement stress within eco-concrete habitats, along with symptoms of wilting and yellowing. However, inoculation with T. harzianum mitigated the damage, consistent with the findings of Marina et al. [32]. Notably, root viability was higher in eco-concrete habitats. This might be attributed to the development of thicker and shorter roots under cement stress, a morphological adaptation that supports aboveground growth while limiting soil penetration. The observed decrease in root viability following T. harzianum treatment might reflect alleviated stress, thereby reducing the physiological demands on the root system. In addition, C. dactylon showed the greatest increase in root surface area after inoculation with T. harzianum in eco-concrete, suggesting that its root system is more morphologically plastic and that adaptation to poor substrates can be enhanced by rapidly adjusting root conformation.
Under cement-induced stress, plants prioritize water homeostasis through the synergistic inhibition of cell elongation and active reduction of stomatal aperture [33,34]. More specifically, inhibiting cell elongation reduces cell volume, thereby diminishing the effective surface area for transpiration [35]. Concurrently, actively constricting stomatal apertures or inducing stomatal closure directly restricts water dissipation pathways [36]. Our results demonstrate that cement stress significantly suppresses both cell elongation and stomatal opening parameters. T. harzianum application effectively mitigated these adverse effects; it significantly enhanced epidermal cell elongation, increased cell density, and augmented both stomatal width and stomatal density. These findings suggest that T. harzianum may assist plants in maintaining superior growth and physiological function under stressful conditions by enhancing stress tolerance and alleviating the suppression of cell expansion and stomatal development mediated by stress signaling. Among them, Z. sinica had the most significant stomatal regulation, suggesting a more flexible regulation of stomatal opening, favoring CO2 uptake and reducing water loss.
Environmental stressors trigger the substantial accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in plants [37,38]. This surge induces oxidative damage, mainly through membrane lipid peroxidation [39]. Malondialdehyde (MDA), a terminal byproduct of polyunsaturated fatty acid peroxidation, serves as a key biomarker of membrane deterioration [40]. Concurrently, increased relative electrolyte conductivity (REC) signifies compromised membrane semi-permeability due to ion leakage from damaged phospholipid bilayers [41]. In this study, eco-concrete exposure induced significant elevation in MDA and REC across all turfgrass species, confirming severe oxidative membrane injury. T. harzianum inoculation, however, markedly suppressed MDA and REC relative to stressed controls. These results demonstrate T. harzianum’s capacity to preserve membrane architecture and minimize permeability under cement stress. This is consistent with the finding that T. harzianum inoculation reduces the MDA content of Satureja hortensis under saline stress, thereby enhancing its salinity tolerance [42].
Proline (Pro) and soluble sugars (SSs) function as essential compatible osmolytes, mitigating osmotic stress by stabilizing subcellular structures (e.g., enzymes, membranes) and maintaining protoplasmic hydration via cytoplasmic osmotic adjustment [43,44]. Proline scavenges hydroxyl radicals, buffers cellular redox potential, and protects protein quaternary structure [45], while SSs preserve membrane integrity through vitrification and direct ROS detoxification [46]. Under alkaline cement stress, turfgrasses exhibited significant Pro and SS accumulation, consistent with active osmoprotective responses [47]. T. harzianum application induced a distinct osmolyte strategy: while consistently enhancing SS accumulation (aligning with Mona et al. [48]), it paradoxically reduced Pro levels in vegetated concrete. This suggests that T. harzianum promotes a preferential shift toward SS-dominated osmoregulation.
The enzymatic antioxidant system constitutes a coordinated defense cascade against ROS. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) catalyzes the dismutation of O2− to H2O2 and O2, while peroxidases (POD, APX) and catalase (CAT) detoxify H2O2 into H2O and O2 [49,50]. APX utilizes ascorbate as an electron donor and operates in the ascorbate–glutathione cycle, crucial for H2O2 removal in chloroplasts and cytosol, whereas CAT primarily scavenges H2O2 in peroxisomes [51]. Sustained stress typically upregulates antioxidant gene expression and enhances antioxidant enzymes activities [52,53,54]. In this study, the turfgrasses exhibited the significant upregulation of SOD, POD, CAT, and APX activities in eco-concrete, indicating the systemic activation of enzymatic ROS-scavenging pathways. Critically, T. harzianum symbiosis further amplified these activities, suggesting that fungal induction potentiates the host’s endogenous antioxidant capacity; this is consistent with studies of tobacco and roses [55,56]. The synergistic elevation of four core enzymes signifies a robust, multi-layered antioxidant response essential for mitigating cement-induced oxidative injury.
Soil organic matter serves as a vital reservoir of essential plant nutrients, including nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). The bioavailability of these elements, released through mineralization, is a key indicator of soil fertility governing plant growth [57,58,59]. Consistent with its recognized role in soil amelioration [60], in this study, T. harzianum inoculation significantly increased the levels of available nitrogen (AN), available phosphorus (AP), and available potassium (AK) in pasture soils. Notably, cement stress led to an unexpected increase in soil AN, AP and AK contents, which could be attributed to the sharp rise in soil pH triggered by the Ca2+ produced during cement decomposition, resulting in a strongly alkaline environment, which inhibited nutrient uptake by the plant root system [61]. However, T. harzianum treatment effectively mitigated these negative effects of cement stress on nutrient acquisition. Consequently, the restoration of plant AN, AP, and AK uptake following T. harzianum application not only confirms its efficacy in alleviating cement stress but also demonstrates its capacity to modify the soil environment to improve nutrient accessibility [62].
However, there are some limitations to this study. These include the following: (i) the difference between the anthropogenically controlled greenhouse conditions and the natural environment; (ii) the short-term experimental indicators ignored long-term microbial community dynamics; (iii) the nutrient concentration in the plant could be a more direct reflection of the plant’s physiological use efficiency. In future studies, priority can be given to multi-season experiments under actual stress conditions to reveal the regulatory mechanism of nutrient uptake by T. harzianum in combination with the accumulation of effective nutrients in the substrate and plant tissues. Such studies could aid in deciphering the specific mechanism of microbial enhancement in plant resilience by combining soil microbiome analyses and plant genomics studies.
5. Conclusions
Cement stress severely constrains root elongation in A. compressus, C. dactylon, and Z. sinica within vegetation concrete systems, impairing water and nutrient acquisition, triggering epidermal cell shrinkage and osmotic imbalance, and exacerbating oxidative damage. Critically, T. harzianum inoculation counteracts these deleterious effects through multifunctional mechanisms: promoting root thickening to overcome physical constraints, enhancing soil nutrient extraction capacity (elevated AN, AP, AK), and activating integrated stress resilience. This integrated stress resilience includes amplified osmoregulatory substance (Pro, SS) accumulation, elevated antioxidant enzyme activities (SOD, POD, CAT, APX), and reduced cellular water loss. Notably, C. dactylon exhibited the most pronounced response, demonstrating superior improvement across all parameters: root architecture (length, surface area, volume, viability), leaf structural integrity (cell density, stomatal width), membrane stability (REC, MDA), and, ultimately, the synergistic enhancement of cement stress tolerance.
Author Contributions
X.C. carried out the experimental plan and wrote the rough draft of the article. X.Z. reviewed the rough draft. D.H. and Y.F. revised all versions of the manuscript. D.H. planned the research, obtained financial support for the whole research project, and reviewed and revised the rough draft of the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the General Program of the Hubei Province Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2017CFB390).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, X.; Dong, F.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Y. Transport infrastructure, high-quality development and industrial pollution: Fresh evidence from china. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Duan, H.; Sun, P.; Li, J.; Zuo, J.; Mao, R.; Liu, G.; Niu, Y. Characterizing the generation and environmental impacts of subway-related excavated soil and rock in china. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, B.; Ilyass, O.; Amor-Ben, F.; Francis, L.; Jean-Michel, T. Reuse potential of dredged river sediments in concrete: Effect of sediment variability. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Shi, J.; Gong, C.; Dai, J.; Huo, L.; Lu, L.; Cheng, X. Study on green restoration of exposed mountain: Effect of isobutylidene diurea on slow-release of total nitrogen and physiological characteristics of euonymus fortune in planted eco-concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 359, 129460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhart, J.; Autischer, M.; Sakoparnig, M.; Krüger, M. The Realization of Clinker-Reduced, Performance-Based Sustainable Concrete by the Micro-Filler, Eco-Filler Concept. Materials 2021, 14, 4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundin, M.; Hedlund, H.; Cwirzen, A. Eco-Concrete in High Temperatures. Materials 2023, 16, 4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Rong, S.; Zhang, C.; Chu, H.; Wei, P.; Tao, S. Mesocosm experimental study on sustainable riparian restoration using sediment-modified planting eco-concrete. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Li, L.; Azeem, F.; Shabbir, S.; Zohaib, A.; Ashraf, U.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z. Insight of transcriptional regulators reveals the tolerance mechanism of carpet-grass (Axonopus compressus) against drought. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Fu, Q.; Song, Y.; Deng, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, K.; Li, S.; Fu, J. Research progress and prospects of molecular breeding in bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shao, A.; Xu, X.; Fan, S.; Fu, J. Comparative genomics reveals the molecular mechanism of salt adaptation for zoysiagrasses. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Jia, Y.; Yuan, L.; Qiu, J.; Xie, C. Experimental study on the vegetation characteristics of biochar-modified vegetation concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 206, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, L.; Zou, Y.; Wu, Q. Root-associated endophytic fungi modulate endogenous auxin and cytokinin levels to improve plant biomass and root morphology of trifoliate orange. Hortic. Plant J. 2023, 9, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Deng, X.; Song, R.; Song, X. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria promote growth of seedlings, regulate soil microbial community, and alleviate damping-off disease caused by rhizoctonia solani on Pinus sylvestris var. Mongolica. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, PDIS11212562RE. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Li, W.; Gao, L.; Liu, G. Strain improvement of Trichoderma harzianum for enhanced biocontrol capacity: Strategies and prospects. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1146210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Lü, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Shen, X.; Yin, C.; Mao, Z. Mixed application of raw amino acid powder and Trichoderma harzianum fertilizer for the prevention and management of apple replant disease. J. Integr. Agric. 2025, 24, 1126–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, A.; Mohamed, A.; Attia, M. Protective role of Claroideoglomus etunicatum and Trichoderma harzianum to improve growth and physiological immune responses of Olea europaea tolerance against fusarium solani. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2025, 136, 102593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tao, W.; Bai, J.; Shi, L.; Que, P.; Jia, D.; Han, H. Different Microorganisms on Growth Regulation Characteristics of Festuca arundinacea. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2025, 56, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cao, Y.; Qu, J.; Chen, C.; Wu, C. Effects of Trichoderma harzianum on Gas Exchange and Growth of Lolium perenne L. North. Hortic. 2023, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Shi, J.; Cai, Z.; Gao, P.; Li, F. Effect of Bacterial Manure Combined with Organic Fertilize on Oat Growth and Soil Characteristics in High Altitude Areas. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2025, 1–16. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3362.S.20250509.1033.002.html (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- Wang, J.; Mu, H.; Liu, S.; Qi, S.; Mou, S. Effects of Trichoderma harzianum on Growth and Rhizosphere Microbial Community of Continuous Cropping Lagenaria siceraria. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Qiu, Y.; Ye, D.; Tian, Z. Leaf structure analysis of Lolium perenne. J. Yangtze Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) Agric. Sci. Vol. 2010, 7, 23–26+95+111. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Guo, P.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, D. Responses of leaf epidermis, anatomical structure and photosynthetic characteristics of Poa pratensis to different nitrogen application level. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2023, 32, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liang, M.; Ma, Y. A review report on the experiments for the determination of root activity by TTC method. Guangdong Chem. Ind. 2020, 47, 211–212. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Kuang, J.; Ge, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Overexpression of SmLEA enhances salt and drought tolerance in Escherichia coli and Salvia miltiorrhiza. Protoplasma 2014, 251, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J. Plant Physiology Experiment Instruction; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Barranco, D.; Ruiz, N.; Gomes, M. Frost tolerance of eight olive cultivars. HortScience 2005, 40, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, M.; Song, W.; Wen, S.; Wang, B.; Zhu, C.; Shen, R. Impact of 25 years of inorganic fertilization on diazotrophic abundance and community structure in an acidic soil in southern china. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 113, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smrutirekha, M.; Kirtikanta, S.; Kundan, S. Progress in sustainable vegetation eco-concrete technology: A review on materials, applications and challenges. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 104, 112354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xia, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Cong, R.; Shi, M. Research and application progress of vegetation porous concrete. Materials 2023, 16, 7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Chen, C.; Pang, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yin, C. Research progress on vegetation restoration of road slopes in china. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 3437–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ji, L.; Gong, C.; Lu, L.; Cheng, X. Ceramsite vegetated concrete with water and fertilizer conservation and light weight: Effect of w/c and fertilizer on basic physical performances of concrete and physiological characteristics of Festuca arundinacea. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 236, 117785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marina, E.; Sergio, I.; Fernanda, C.; Verónica, F. Trichoderma harzianum enhances root biomass production and promotes lateral root growth of soybean and common bean under drought stress. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2024, 185, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caine, R.; Harrison, E.; Sloan, J.; Flis, P.; Fischer, S.; Khan, M.; Nguyen, P.; Nguyen, L.; Gray, J.; Croft, H. The influences of stomatal size and density on rice abiotic stress resilience. New Phytologist. 2023, 237, 2180–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamani, A.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Amin, A.S.; Wang, G.; Xiaojun, S.; Zain, M.; Gao, Y. Linking exogenous foliar application of glycine betaine and stomatal characteristics with salinity stress tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) seedlings. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haworth, M.; Marino, G.; Materassi, A.; Raschi, A.; Scutt, C.P.; Centritto, M. The functional significance of the stomatal size to density relationship: Interaction with atmospheric [co2] and role in plant physiological behaviour. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, L.; Caine, S.; Gray, J. Impact of Stomatal Density and Morphology on Water-Use Efficiency in a Changing World. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, A.; Mittler, R.; Suzuki, N. ROS as key players in plant stress signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittler, R.; Zandalinas, S.; Fichman, Y.; Van Breusegem, F. Reactive oxygen species signalling in plant stress responses. Nature reviews. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliane, M.; Antônio, N.; Josefa, B.; Rodrigo, R.; Djair, A.; Tancredo, S.; Diego, S. Lipidomics in Plants Under Abiotic Stress Conditions: An Overview. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, K.; Hirt, H. Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jia, H.; Peng, M.; Zhu, T.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J. Effects of Cd treatment on morphology, chlorophyll content and antioxidant enzyme activity of Elymus nutans Griseb., a native plant in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Plant Signal. Behav. 2023, 18, 2187561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzi-Nojadeh, M.; Pouresmaeil, M.; Amani, M.; Younessi-Hamzekhanlu, M.; Maggi, F. Colonization of Satureja hortensis L. (Summer savory) with Trichoderma harzianum alleviates salinity stress via improving physio-biochemical traits and biosynthesis of secondary metabolites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 208, 117831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, M.; Turkyilmaz Unal, B.; García-Caparrós, P.; Khursheed, A.; Gul, A.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Osmoregulation and its actions during the drought stress in plants. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeel, A.; Muhammad, F.; Xie, X.; Liu, X.; Muhammad, F. Antioxidant defense system and proline accumulation enables hot pepper to perform better under drought. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 140, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, C.; Huang, Q.; Rady, M.; Wang, L.; Ihtisham, M.; El-Awady, H.; Seif, M.; Alazizi, E.; Eid, R.; Yan, K.; et al. Integrative application of silicon and/or proline improves Sweet corn (Zea mays L. saccharata) production and antioxidant defense system under salt stress condition. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Hu, W.; Qin, X.; Fei, Y.; Hu, D. Effects of serendipita indica on the morphological and physiological characteristics of Agrostis stolonifera L. Under drought stress. Agronomy 2025, 15, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Passioura, J.B.; Colmer, T.D.; Byrt, C.S. Osmotic adjustment and energy limitations to plant growth in saline soil. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mona, S.; Hashem, A.; Abd, A.; Alqarawi, A.; Soliman, D.; Wirth, S.; Egamberdieva, D. Increased resistance of drought by Trichoderma harzianum fungal treatment correlates with increased secondary metabolites and proline content. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 16, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Novel insight into functions of ascorbate peroxidase in higher plants: More than a simple antioxidant enzyme. Redox Biol. 2023, 64, 102789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Han, C.; Wang, S.; Bai, M.; Song, C. Reactive oxygen species: Multidimensional regulators of plant adaptation to abiotic stress and development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2024, 66, 330–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Fartyal, D.; Agarwal, A.; Shukla, T.; James, D.; Kaul, T.; Negi, Y.; Arora, S.; Reddy, M. Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants: Myriad Roles of Ascorbate Peroxidase. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 20, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, S.; Kang, W.; He, L. Enriched endogenous free Spd and Spm in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) under drought stress enhance drought tolerance by inhibiting H2O2 production to increase antioxidant enzyme activity. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 291, 154139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.; Gu, Z.; Yang, R. NaCl stress on physio-biochemical metabolism and antioxidant capacity in germinated hulless barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Meng, R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Jiang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; Fang, W.; Chen, F.; et al. Heterografted chrysanthemums enhance salt stress tolerance by integrating reactive oxygen species, soluble sugar, and proline. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhi, C.; Ao, L.; Amit, J.; Meng, Q. Rhizosphere growth-promoting fungi of healthy Nicotiana tabacum L.: A systematic approach to boosting plant growth and drought resistance. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, A.; Miao, R.; Sui, D.; Baloch, A.; Chang, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhang, R. Changes in antioxidant enzyme activities, hormone levels and growth traits of rose induced by three native strains of Trichoderma harzianum. Pak. J. Bot. 2020, 52, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, J. Enhancing soil health to minimize cadmium accumulation in agro-products: The role of microorganisms, organic matter, and nutrients. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 348, 123890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Katoh, M. Root response and phosphorus acquisition under partial distribution of phosphorus and water-soluble organic matter. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 40, e13038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, A.; Cotrufo, M. Organic nitrogen storage in mineral soil: Implications for policy and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, K. Saline-alkaline stress in growing maize seedlings is alleviated by Trichoderma asperellum through regulation of the soil environment. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 11152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Rui, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Xue, B.; Yi, H. Bio-mineralization induced by Bacillus mucilaginosus in crack mouth and pore solution of cement-based materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 126, 112120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, T.; Wu, B.; Xia, Z.; Xu, W.; Gao, J. Soil carbon emissions and influential factors across various stages of vegetation succession in vegetated concrete. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).