Abstract
Pineapple translucency is a major physiological disorder in ‘Tainong 17’ (Golden Diamond) that severely impairs fruit quality, storability, and market value, yet its physiological basis remains poorly understood. To clarify the underlying mechanisms, we conducted two seasons of field surveys across 24 plots in eleven pineapple orchards in Hainan, China, comparing translucent and healthy fruits in terms of plant growth, nutrient status, fruit quality, cell wall composition, and soil properties. Our results showed that translucency significantly reduced fruit quality, with soluble solids and ascorbic acid contents decreasing by 9.7% and 16.3%, respectively. Translucent plants exhibited markedly increased biomass, whereas fruit dry matter was reduced by 21.6%. In addition, affected plants accumulated 40–70% more nitrogen in leaves, stems, and fruits, accompanied by 23% and 14% reductions in abscisic acid concentrations in leaves and fruits, respectively. Calcium and boron allocation to fruits was impaired, with fruit Ca and B contents decreasing by 25.1% and 50.4%, respectively, despite increased levels in vegetative organs. These nutrient imbalances coincided with a 16.4% decrease in protopectin, a 5.3% decrease in cellulose, and a 15.5% increase in soluble pectin, indicating cell-wall loosening. Collectively, our findings demonstrate that excessive nitrogen input disrupts carbon–nitrogen metabolism and ABA signaling, elevates fruit N/Ca ratios, and accelerates cell-wall remodeling, thereby predisposing fruits to translucency, particularly under humid or rainy conditions.
1. Introduction
Pineapple (Ananas comosus [Linnaeus] Merrill) ranks as the third most important tropical fruit globally, accounting for approximately 23% of total tropical fruit production [1]. Currently, pineapple cultivation spans over 90 countries and regions worldwide, with global trade steadily increasing [2]. As one of the world’s major pineapple producers, China has experienced sustained growth in pineapple production over the past five decades [2]. Among cultivated pineapple varieties, the ‘Tainong 17’ (Golden Diamond) elite hybrid from Taiwan is notable for its high yield, distinctive flavor, and superior fresh-eating quality, contributing to its widespread cultivation in southern China [3].
Translucency is a widespread physiological disorder in pineapple production, commonly occurring during fruit ripening. It is characterized by cell wall rupture, cell dehydration, and the development of water-soaked, translucent tissue, leading to significant deterioration in fruit quality and storability [4]. Increasing translucency severity leads to pronounced declines in soluble solids, vitamin C, and sugar content; moderately affected fruits (>23% affected area) show reductions of 14.2%, 39.5%, and 15.2%, respectively [5]. Severe cases render fruits commercially unacceptable, creating a major bottleneck for sustainable production of ‘Tainong 17’.
The occurrence of translucency arises from a complex interplay of internal factors—such as genetic traits and nutrient status—and external drivers, including climate and cultivation practices [6,7,8]. Among these, high temperature and humidity combined with imbalanced fertilization—particularly excessive nitrogen (N)—are recognized as major triggers [9]. While N is indispensable for protein, nucleic acid, and phospholipid synthesis, oversupply disrupts carbon–N metabolism, suppresses reproductive growth, and impairs fruit development. The growth cycle of ‘Tainong 17’ spans ~16 months, encompassing slow and rapid vegetative phases, floral induction, and fruit development. Although translucency symptoms appear during late fruit development, the underlying physiological shifts often occur much earlier. Normally, fruit development follows “source–sink” regulation, with assimilates transported from vegetative organs to fruits, accompanied by leaf senescence and plant aging. In contrast, translucent plants show excessive vegetative vigor—manifested as increased biomass, dark green leaves, and premature sucker formation at harvest—indicating disrupted vegetative–reproductive balance [10]. Empirical evidence further supports this link: in MD2 pineapples in the Philippines, foliar urea application during early fruit development increased translucency incidence to >20% at 35 kg N ha−1, compared with only 12.8% under 12 kg N ha−1 or zero N application [11].
Abnormal calcium (Ca) metabolism is another critical factor contributing to translucency. As a secondary messenger in plant signal transduction, Ca regulates growth, fruit quality, systemic defense, and physiological stability [12]. In fruit, most Ca is localized in the middle lamella and plasma membrane, where it forms calcium pectate with pectins to reinforce cell walls and intercellular adhesion, while also stabilizing membranes by binding to phospholipids and proteins. Ca deficiency disrupts these structures, causing membrane leakage and physiological disorders [13]. Such deficiency may result from inadequate soil Ca or physiological Ca deficiency, in which soil Ca is sufficient but fruit Ca remains low [14]. In tropical Ferralsols, severe weathering and leaching exacerbate Ca loss [15]. Although Ca fertilization is widely practiced, its effectiveness in preventing translucency remains limited, reflecting poor translocation to fruits. Ca transport relies on transpiration and auxin-mediated polar transport; thus, vigorous vegetative growth increases auxin levels and leaf transpiration, intensifying competition between leaves and fruits for Ca [16]. Moreover, fruits have intrinsically low transpiration and restricted phloem mobility of Ca, further limiting supply [16]. Consequently, Ca deficiency increases plasmodesmata permeability and disrupts cell wall metabolism, leading to middle lamella softening and rupture [17,18]. Evidence from apples corroborates this mechanism, showing that translucent fruit consistently contains lower Ca than healthy fruit, and Ca deficiency is a major cause of watercore formation [19,20].
Nitrogen availability strongly regulates Ca transport and metabolism. Under low N supply, limited vegetative growth reduces competition for Ca between leaves and fruits [21]. Conversely, excessive N disrupts Ca allocation by overstimulating shoot growth and enhancing transpiration-driven Ca flow toward leaves, thereby reducing Ca delivery to fruits [22,23,24]. Beyond transpiration effects, excess N disrupts carbon–nitrogen metabolism and hormonal balance, suppressing reproductive growth and sink strength, thereby weakening the fruit’s capacity to acquire assimilates and Ca [25]. Ammonium (NH4+) further competes with Ca2+ uptake, preferentially directing Ca to leaves rather than fruits, resulting in physiological Ca deficiency even when soil Ca is sufficient [26]. Excess N also modifies Ca partitioning and cell wall composition. In apples, N fertilization increased water-soluble Ca but decreased Ca bound to pectin, accompanied by reduced protopectin, elevated soluble pectin, and enhanced activity of cell wall-degrading enzymes [24]. Similar effects are reported in rice, where high N reduces cellulose and lignin deposition in stems [27]. Elevated NH4+ further acidifies the apoplast, destabilizing pectin polysaccharide networks and weakening cell walls [28].
Despite the widespread occurrence of fruit translucency in tropical pineapple production, its underlying physiological mechanisms and environmental drivers remain poorly understood, limiting the effectiveness of current mitigation practices. To address these knowledge gaps, this study conducted extensive plant and soil surveys in Hainan Province, the main pineapple-producing region in China, to systematically assess the nutritional status and physiological traits of translucent versus healthy fruits. We also examined the role of soil environmental conditions in modulating translucency, aiming to identify key physiological and environmental drivers of this disorder. These efforts provide a basis for elucidating underlying mechanisms and guiding effective prevention strategies. Specifically, the study addressed three core questions: (I) What are the major physiological and nutritional differences between translucent and healthy pineapples? (II) How does N–Ca imbalance contribute to translucency formation? and (III) How do soil properties influence its occurrence?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
This study targeted the ‘Tainong 17’ pineapple cultivar widely cultivated in Hainan Province, China. Field surveys and systematic sampling of plants and soils were conducted during the fruit development and maturation stages in two separate periods: March to May 2022 across five counties/cities (Haikou, Chengmai, Lingao, Baisha, and Ledong), and March to May 2024 across another five counties/cities (Haikou, Chengmai, Lingao, Danzhou, and Dongfang) (Figure 1).
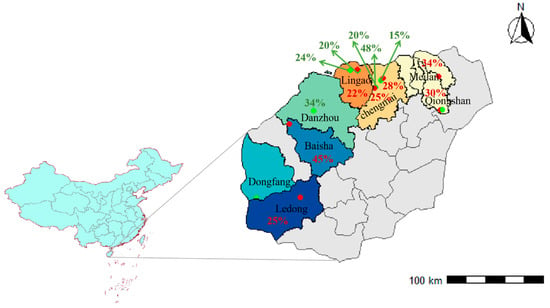
Figure 1.
Geographic distribution of sampling sites on Hainan Island during March–May 2022 and March–May 2024. Sampling locations from the two years are distinguished by color: red dots represent sites sampled in March–May 2022 with corresponding translucency incidence, and green dots represent sites sampled in March–May 2024 with corresponding translucency incidence.
A total of 24 plots with a relatively high occurrence of translucency during fruit maturation were selected from the northwestern region of Hainan Island, covering distinct ecological zones characterized by lateritic soils and varying topography from coastal lowlands to inland uplands. The region experiences a typical tropical monsoon climate, with mean annual temperatures of 24–26 °C and annual rainfall of 1200–1800 mm. As climatic differences among sites are relatively small, variation in soil and nutritional conditions is considered the primary factor contributing to translucency development. Among the selected plots, 13 plots were classified as translucency-affected and 11 as healthy controls. To ensure uniform maturity at sampling, fruits were selected at a specific ripening stage characterized by the yellowing of the first to third fruit eyes (counting from the base of the fruit), corresponding to early commercial maturity. From each plot, 160 mature fruits meeting this criterion and of uniform size were randomly harvested. Translucency occurrence was first assessed by trained personnel using a standardized empirical tapping method. Healthy fruits produced a clear, resonant sound when struck with a rubber mallet, whereas translucent fruits emitted a dull, solid sound. Fruits with dull acoustic responses were then longitudinally sectioned to visually confirm translucency symptoms [29,30].
Within the translucency-affected plots, the incidence of translucency—defined as the proportion of fruits exhibiting visible translucency symptoms—ranged from 15% to 40%, with affected surface areas exceeding 23% and translucency severity classified as grade II or higher [5]. In parallel, five representative plants were randomly selected from both healthy and affected plots, respectively. Stems, leaves, and fruits were separately collected and packaged. Soil samples from the 0–20 cm topsoil layer were simultaneously obtained.
2.2. Measurements and Methods
Half of the plant samples were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen for the determination of fruit quality and endogenous hormone contents, while the remaining samples were used for physicochemical and physiological analyses. For each plot, five representative plants were randomly selected to ensure spatial representativeness. Stems, leaves, and fruits were separately collected, packaged, and labeled. Green leaves were first heated at 105 °C for 30 min to inactivate enzymes, then oven-dried at 75 °C to constant weight and ground for subsequent analyses. Soil samples were collected from the 0–20 cm topsoil layer at multiple random points within each plot, composited to form a representative sample, air-dried, and sieved prior to analysis. The measurements included a range of fruit quality indicators such as soluble solids, soluble proteins, vitamin C, and titratable acidity, as well as plant biomass. Nutrient contents were determined for different organs, including nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), and boron (B), along with total N in soil. In addition, cell wall components—protopectin, soluble pectin, cellulose, and hemicellulose—were analyzed, together with endogenous hormones, mainly abscisic acid (ABA).
2.2.1. Fruit Quality Indicators
Fruit quality was assessed using fresh juice obtained by homogenizing and filtering fruit pulp. Total soluble solids (TSS) were measured with a handheld refractometer (PAL-1, Atago, Tokyo, Japan). Titratable acidity (TA) was determined by acid–base titration using 0.1 M NaOH (Xilong Scientific, Guangdong, China) [31]. Ascorbic acid content was measured by DCPIP titration after stabilizing juice with metaphosphoric acid (Xilong Scientific, Guangdong, China) [32]. Soluble protein content was determined by the Bradford method [33]. Frozen pulp (1.0 g) was homogenized in chilled phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.0), centrifuged (10,000× g, 15 min, 4 °C), and the supernatant reacted with Bradford reagent. Absorbance at 595 nm was measured with a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (UV-1800, Shimadzu, Japan), and protein content calculated from a bovine serum albumin (Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China) standard curve.
2.2.2. Nutrient Content
The concentrations of phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and boron in plant tissues were determined by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES, Jiangsu, China). Briefly, approximately 0.2 g of dried plant material was digested with a HNO3-HClO4 (Xilong Scientific, Guangdong, China) mixture following a standard method, and the digestate was analyzed by ICP-OES [34]. Total nitrogen in plant tissues (0.2–0.5 g sample) and soil (1 g sample) was determined using the Kjeldahl method [35]. The digestion for plant tissue employed concentrated H2SO4 and H2O2 (Xilong Scientific, Guangdong, China), while the soil digestion involved KMnO4 (Xilong Scientific, Guangdong, China), concentrated H2SO4, and reduced iron powder, as detailed in the method. All nutrient concentrations are expressed on a dry weight basis.
2.2.3. Fruit Pectin and Cellulose Content
Pectin fractions, including protopectin, water-soluble pectin (WSP), covalently bound pectin (CSP), and ionically bound pectin (ISP), were determined using the carbazole colorimetric method. Cellulose and hemicellulose contents were measured using colorimetric analysis [35].
2.2.4. Endogenous Hormone Content
Endogenous hormone contents (abscisic acid, ABA) were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). An ACCHROM S3000 (Acchrom Technologies Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) system equipped with an Alphasil VC-C18 column (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 µm) was used [36]. The injection volume was 10 µL, with a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min, column temperature 35 °C, run time 40 min, and detection at 254 nm.
2.2.5. Microscopic Structure Observation
Pulp sections (~3 mm × 1 mm) from healthy and translucent fruits were fixed overnight in tert-butanol at –20 °C, freeze-dried at –40 °C for 12 h, mounted on aluminum stubs, sputter-coated with gold (EIKO IB-3, Tokyo, Japan) for 60 s, and observed under a scanning electron microscope (Axia ChemiSEM, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.3. Data Analysis
Data analysis was conducted using Microsoft Excel 2019 and SPSS Statistics (Version 26.0). Intergroup differences were evaluated with Student’s t-test. Multivariate datasets were analyzed by principal component analysis (PCA), and bivariate relationships were examined via Pearson correlation analysis, both performed in SPSS. The correlation matrix and PCA biplots were visualized using OriginPro 2024. Structural equation modeling (SEM) was carried out in AmosGraphicsCLI, with all figures produced in OriginPro 2024.
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Fruit Quality
Fruit quality analysis across 24 fields over two survey seasons revealed that translucency significantly degraded pineapple quality. In affected fruits, soluble solids and ascorbic acid (vitamin C) were 14.1% and 78.1 mg/kg, representing highly significant reductions of 9.7% and 16.3%, respectively, relative to normal fruits (Figure 2a,b). Soluble protein, titratable acidity, and sugar–acid ratio were 2.0 mg/g, 0.6%, and 22.9, respectively, with soluble protein and sugar–acid ratio decreasing by 11.9% and 7.6%, while titratable acidity increased by 1.2% relative to normal fruits (Figure 2c–e). In 2022, translucency was associated with pronounced declines in soluble solids (14.1%, −12.5%), ascorbic acid (74.8 mg/kg, −20.4%), soluble protein (2.5 mg/g, −8.7%), and sugar–acid ratio (19.6, −19.5%), along with a significant increase in titratable acidity (+8.7%). In 2024, the same trends were observed, although the differences between translucent and normal fruits were not statistically significant. Collectively, these results confirm that translucency detrimentally affects both the nutritional and sensory quality of pineapple fruit.
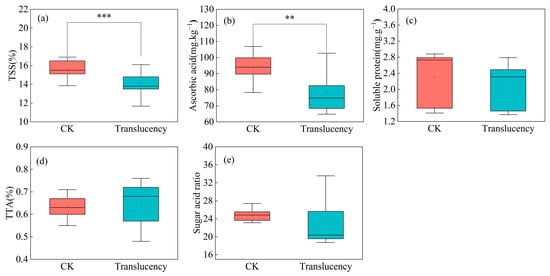
Figure 2.
Changes in fruit quality of translucent pineapple. Data represent the mean values from all surveyed plots over two seasons. (a) Soluble solids content; (b) Ascorbic acid; (c) Soluble protein; (d) Titratable acidity; (e) Sugar–acid ratio. Significance levels: ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
3.2. Changes in Fruit Cell Wall Components
The cell wall of mature pineapple fruit is primarily composed of a polysaccharide network including cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, and glycoproteins, and alterations in these components can modify cell wall structure and mechanical properties. Analysis of the major components pectin and cellulose showed pronounced changes in translucent fruit. Overall, protopectin content was extremely significantly reduced by 16.4% compared to normal fruit, whereas soluble pectin content was on average 15.5% higher. (Figure 3a). Cellulose content was 5.3% lower, while hemicellulose content was 5.1% higher, both at significant levels (Figure 3b). When analyzed by survey year, fruits from translucent fields in 2022 exhibited significant reductions in protopectin (−16.3%) and cellulose (−3.8%), together with marked increases in soluble pectin (+16.5%) and hemicellulose (+11%) (Figure 3c,d). In 2024, the changes followed the same trends as in 2022, although most did not reach statistical significance: protopectin decreased significantly by 16%, while soluble pectin increased significantly by 14.5%, cellulose, and hemicellulose showed similar trends but without statistical significance (Figure 3c,d). Furthermore, no significant differences in cell wall composition were detected between 2022 and 2024 for either normal or translucent fruits.
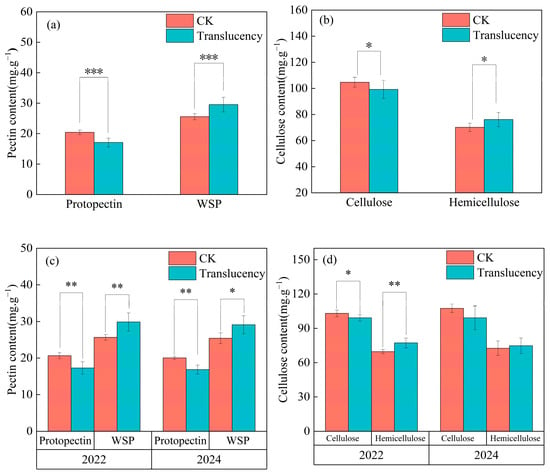
Figure 3.
Changes in cell wall components of translucent pineapple fruits. Panels (a,b) show combined analyses across both survey seasons, and panels (c,d) show results separated by season. (a,c) Pectin content; (b,d) Cellulose content. Significance levels: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
3.3. Changes in Fruit Cell Wall Microstructure
Scanning electron microscopy revealed pronounced differences in cell wall microstructure between healthy and translucent-affected pineapple fruits. In healthy fruits, the cell walls exhibited smooth and continuous surfaces without rupture or perforation, and the overall structural integrity was preserved (Figure 4a–c). Pulp cells were compactly arranged, with well-defined cellular inclusions and an orderly tissue organization. By contrast, translucent-affected fruits displayed severe structural disruption (Figure 4d–f). The cell walls underwent marked shrinkage and rupture, and the middle lamella was extensively degraded or completely lost. Cellular inclusions were largely absent, while cells appeared swollen, deformed, and irregularly arranged. These findings suggest that translucency is associated with cellular inactivation and loss of cell wall integrity, leading to impaired permeability, intercellular water accumulation, and eventual tissue breakdown.
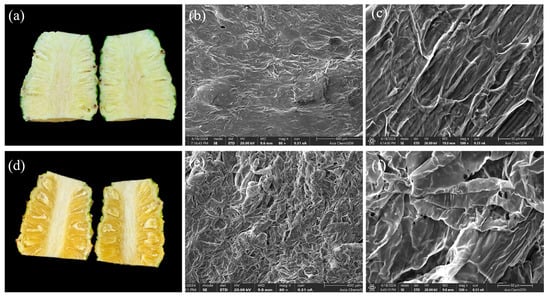
Figure 4.
Scanning electron micrographs of fruit cell walls in healthy and translucent-affected pineapples. (a) External appearance of healthy fruit; (b) cell wall microstructure at 80× magnification (scale bar = 400 μ); (c) cell wall microstructure at 500× magnification (scale bar = 50 μm); (d) external appearance of translucent-affected fruit; (e) cell wall microstructure at 80× magnification (scale bar = 400 μm); (f) cell wall microstructure at 500× magnification (scale bar = 50 μm).
3.4. Changes in Nutrient Status of Translucent Pineapple Fruits
3.4.1. Dry Matter Accumulation in Fruits
Across both survey years, pineapple plants affected by translucency exhibited significantly higher aboveground biomass compared to healthy plants, but fruit dry matter accumulation was markedly reduced. The aboveground fresh and dry weights (including leaves, stems, and fruit) of affected plants reached averages of 6255.7 g/plant and 756 g/plant, respectively, representing a 20% increase in total fresh weight and a 10% decrease in total dry matter compared to healthy plants (Figure 5a,b). Although the fruit fresh weight of affected plants was 12.1% higher than that of healthy fruits, their dry matter content was extremely significantly reduced, averaging 21.6% lower than in translucent fruits. The mean water content of translucent fruits was 88.6%, 6% higher than that of healthy fruits. In 2022, affected plants exhibited enhanced vegetative growth, with aboveground fresh and dry weights increased by 23.1% and 7.1%, respectively, compared with healthy plants. Fruit fresh weight was significantly higher (+17.8%), whereas fruit dry weight decreased markedly by 17.5%. In 2024, a similar pattern was observed: aboveground fresh biomass increased substantially by 23.4%, but dry biomass declined by 21.7%. Fruit fresh weight showed no significant difference, while fruit dry weight was reduced by 24.6% (Figure 5c,d).
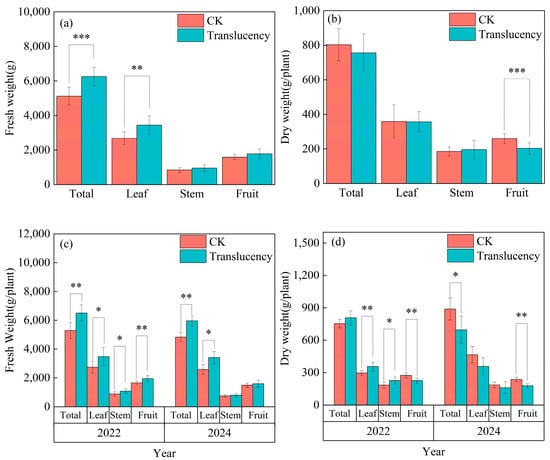
Figure 5.
Biomass accumulation in translucent-affected pineapple plants. (a,b) Combined analysis of two survey seasons; (c,d) separate analyses for 2022 and 2024. (a,c) Fresh weight; (b,d) dry matter content. Significance levels: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
3.4.2. Nutrient Uptake
Among the nutrients analyzed, nitrogen (N), calcium (Ca), and boron (B) were the only elements that exhibited significant differences between translucent-affected and healthy pineapple plants in all analyzed organs, whereas other nutrients showed no notable variation. Overall, affected plants accumulated higher levels of N, Ca, and B compared with healthy plants, but their distribution among different organs was markedly altered across the two survey years.
On average, the N concentrations in the leaves, stems, and fruits of affected plants were 3.2 g/kg, 1.6 g/kg, and 3.0 g/kg, representing increases of 40.3%, 53.1%, and 70% relative to healthy plants (Figure 6a). Similarly, total Ca uptake was significantly enhanced in affected plants; however, the Ca concentration in fruits was markedly reduced (3.3 g/kg, −25.1%) (Figure 6b), suggesting impaired Ca translocation from vegetative organs to reproductive tissues. For B, although total uptake was slightly higher (+3.0%), fruit B concentration was dramatically decreased (0.06 g/kg, −50.4%) (Figure 6c).
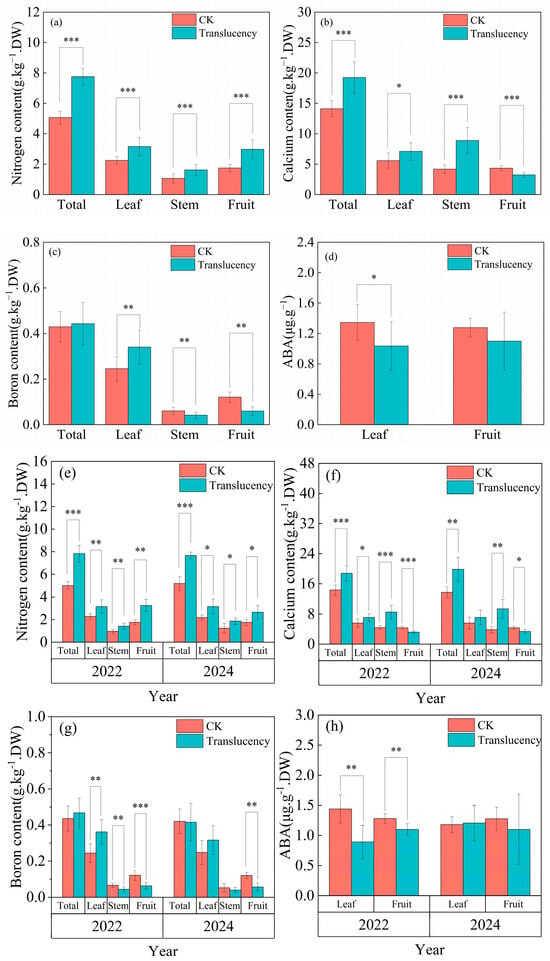
Figure 6.
Nutrient content and abscisic acid (ABA) changes in translucent-affected pineapple plants. (a–d) Combined analysis of two survey seasons; (e–h) separate analyses for 2022 and 2024. (a,e) Nitrogen content; (b,f) Calcium content; (c,g) Boron content; (d,h) Abscisic acid (ABA) content. Significance levels: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Year-specific analyses confirmed these trends. In 2022, N concentrations in leaves, stems, and fruits of affected plants were elevated by 38.0%, 48.2%, and 85.6%, respectively, compared with healthy controls (Figure 6e). Ca concentrations increased by 26.9% in leaves, 93.2% in stems, but decreased by 26.9% in fruits (Figure 6f). Similarly, B concentrations increased by 47.9% in leaves, while stems and fruit B concentration declined by 32.6% and 48.2% (Figure 6g). In 2024, affected plants again exhibited elevated N concentrations (+44.5% in leaves, +50.1% in stems, +51.7% in fruits) (Figure 6e). Ca levels were higher in whole plants (+44.1%), but fruit Ca concentration was reduced by 22.9% (Figure 6f). For B, no significant differences were detected in total, leaf, or stem concentrations, yet fruit B concentration remained significantly lower (−52.8%) compared with healthy fruits (Figure 6g).
3.5. Endogenous Abscisic Acid (ABA)
Analysis of endogenous abscisic acid (ABA) revealed significant differences in hormone distribution between translucent-affected and healthy pineapple plants. On average, the ABA concentration in the leaves of affected plants was significantly lower by 23.0% compared with healthy plants (Figure 6d). Fruit ABA concentrations were also reduced in affected plants, although the overall difference across years was less pronounced.
Year-specific analyses showed that in 2022, both leaf and fruit ABA concentrations of affected plants were markedly reduced by 38.1% and 14.1%, respectively, compared with healthy controls. In contrast, in 2024 no significant differences were detected in either leaves or fruits.
3.6. Soil Conditions
Among soil properties analyzed, total nitrogen (N), bulk density, and water content showed significant differences between translucent-affected and healthy pineapple plots (Figure 7a,b). Across the two survey years, the average total N content in the surface soil (0–20 cm) of affected plots was 2.5%, significantly higher by 50.7% compared with healthy plots (Figure 7a), consistent with the elevated N levels observed in plant tissues (Figure 6a,e). Moisture content and soil bulk density were also significantly greater in affected plots, averaging 20.9% (+16.8%) and 1.3 g.cm−3 (+11.6%), respectively (Figure 7b,c). These results suggest that compacted soils with higher water retention and reduced aeration may predispose pineapple plants to translucency.
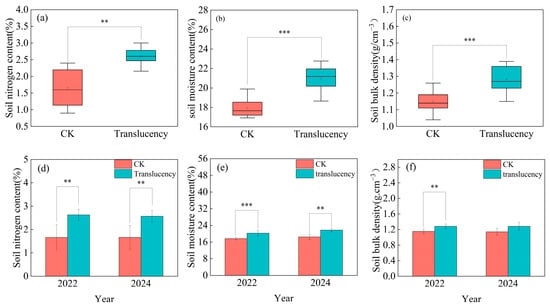
Figure 7.
Changes in basic soil properties in translucency-affected pineapple plots. (a–c) Combined analysis of two survey seasons; (d–f) separate analyses for 2022 and 2024. (a,d) Soil total nitrogen content; (b,e) Soil moisture content; (c,f) Soil bulk density. Significance levels: ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Year-by-year analysis further confirmed these patterns. In 2022, affected plots exhibited markedly higher soil total N (+38.1%), water content (+14.9%), and bulk density (+11.3%) compared with healthy plots (Figure 7d–f). In 2024, soil total N (+54.6%) and water content (+17.9%) remained significantly elevated in affected plots, while bulk density showed no significant difference (Figure 7d–f).
3.7. Key Factors Influencing the Occurrence of Pineapple Translucency
The incidence of pineapple translucency was found to be closely linked to multiple physiological and environmental factors. Principal component analysis (PCA) distinguished healthy from translucent-affected pineapples based on nutritional quality, cell wall composition, plant nutrient status, and soil physicochemical properties, indicating that these traits collectively contribute to the disorder (Figure 8a).
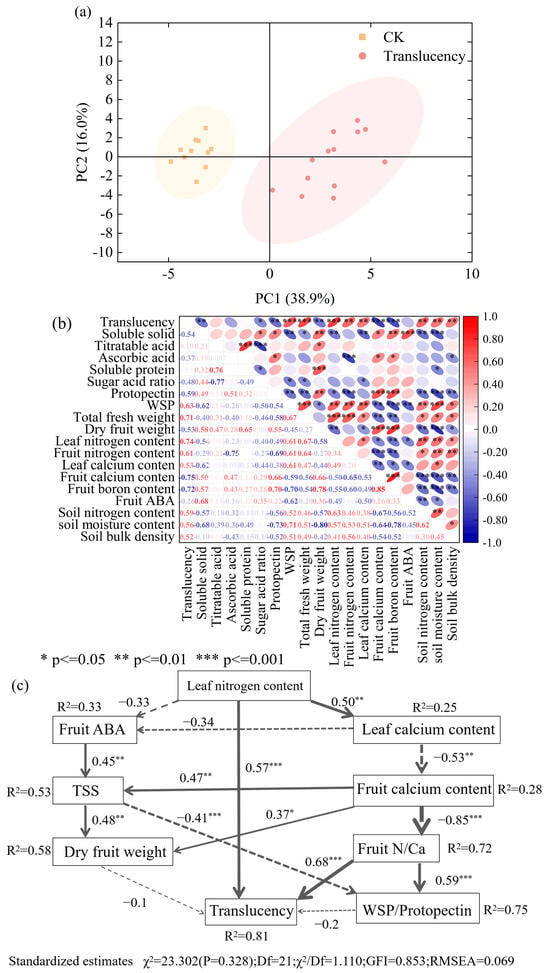
Figure 8.
Multivariate and mechanistic analyses of factors associated with pineapple translucency. (a) Principal component analysis (PCA) of physiological, biochemical, and soil variables; (b) correlation heatmap among key variables; (c) Structural equation model (SEM) illustrating direct and indirect pathways affecting translucency. TSS, total soluble solids; WSP, water-soluble pectin. Solid arrows: positive path coefficients; dashed arrows: negative path coefficients.
Correlation analysis further revealed that translucency incidence was positively associated with fruit and leaf nitrogen concentrations, fruit soluble pectin, plant fresh biomass, and soil N, moisture, and bulk density, while it was negatively correlated with fruit soluble solids, protopectin, dry matter content, and fruit Ca and B concentrations (Figure 8b). Among these factors, nutrient status, particularly of N, Ca, and B, exhibited strong effects on both fruit cell wall composition and translucency incidence, with significant correlations also observed among these nutrients themselves and with endogenous ABA. Specifically, higher fruit N was positively associated with water-soluble pectin (WSP) but negatively with protopectin, whereas fruit Ca and B displayed the opposite trends, suggesting that nutrient imbalances directly disrupt cell wall stability. Moreover, fruit Ca and B contents were negatively correlated with both leaf and fruit N contents, yet Ca and B themselves were strongly and positively correlated. In addition, endogenous ABA displayed associations with nutrient status similar to Ca and B, showing a negative relationship with N but positive associations with Ca and B. Meanwhile, strong positive correlations were observed between soil properties (total nitrogen, moisture content, and bulk density) and translucency incidence, further suggesting that these edaphic conditions contribute to the development of the disorder.
Structural equation modeling (SEM) provided mechanistic insights into these interactions (Figure 8c). Leaf N enrichment not only exerted a direct positive effect on translucency incidence but also indirectly contributed through several pathways. Elevated leaf N suppressed ABA synthesis in fruits, thereby reducing soluble solids accumulation and dry matter deposition, which are critical for fruit quality formation. At the same time, excessive leaf N promoted Ca retention in leaves while limiting Ca translocation to fruits, resulting in an elevated fruit N/Ca ratio.
4. Discussion
4.1. Prevalence and Characteristics of Pineapple Translucency
Pineapple translucency is a common physiological disorder worldwide that significantly reduces fruit quality and market value. Its incidence varies among cultivars and regions. For example, translucency in ‘MD-2’ in Hawaii can reach 62.5% [37], Smooth Cayenne in Thailand exhibits 10–20% translucency at maturity [38], and in Trinidad and Tobago, Smooth Cayenne reaches over 50% translucency at 35–70% maturity [39]. Traditional cultivars typically show lower incidences, around 19.2% [9,37]. In southern China, cultivars such as ‘Tainong 17’, ‘Golden Pineapples’, and ‘Bali’ also display moderate-to-high translucency rates. Globally, this indicates that translucency is a widespread concern, particularly in cultivars with high vegetative vigor.
Despite these regional and varietal differences, the physiological changes associated with translucency are remarkably consistent: with affected fruits displaying higher water content alongside significant reductions in soluble solids, sugars, organic acids, and dry matter accumulation [5]. These characteristics underscore the importance of identifying the underlying causes and developing effective mitigation strategies.
4.2. Effects of Nitrogen Status on Translucency Occurrence
Our study demonstrated that N nutritional status plays a central role in both the direct and indirect development of pineapple translucency, primarily through disrupting carbon-N metabolism, hormonal regulation, and cell wall formation. As fundamental processes in plant growth, carbon and N metabolism are tightly coupled: N provides essential substrates for protein, nucleic acid, and chlorophyll synthesis, whereas carbon metabolism supplies the skeletons and energy required for N assimilation [40,41]. Maintaining a balance between these pathways is critical for coordinating vegetative and reproductive growth. Excessive N input disrupts this balance, often promoting luxuriant vegetative growth at the expense of reproductive development. Consistent with this, translucency-affected pineapples in our study exhibited significantly higher N content in organs and greater total plant biomass compared to healthy plants, while fruit dry matter, soluble solids, and vitamin C content were markedly reduced, indicating impaired assimilate allocation to reproductive sinks. Comparable responses have been observed in apples, where high N application reduces fruit carbohydrate content while increasing soluble proteins and amino acids, ultimately compromising fruit quality [42,43].
Excessive N can also indirectly facilitate pineapple translucency by disrupting endogenous ABA dynamics. ABA is a key regulator of the vegetative–reproductive transition, assimilate partitioning, and sugar transport during fruit development [42,44]. In our study, translucency-affected plants exhibited significantly lower ABA concentrations in both leaves and fruits in 2022, consistent with reduced sink strength, limited sugar accumulation, and impaired dry matter deposition. Although differences were less pronounced in 2024, the overall trend supports a role for N-induced hormonal imbalance in facilitating translucency. Emerging evidence suggests that the nitrate transceptor NRT1.1B can interact with ABA signaling; under high-N supply, nitrate may compete with ABA for binding, dampening ABA-responsive transcription [45]. This provides a plausible mechanistic context for our observations of lower ABA and altered carbon allocation under excess N.
Beyond metabolic effects, excessive N may also compromise fruit mechanical strength by altering calcium and boron nutrition. Calcium stabilizes cell walls via calcium pectate formation, while boron cross-links pectin molecules through borate diester bonds, jointly enhancing structural integrity [46]. Our results showed that although N-rich pineapple plants accumulated higher total Ca and B, their fruit Ca and B contents were significantly reduced compared to healthy controls, leading to elevated fruit N/Ca ratios. This imbalance disrupts pectic–calcium cross-links, inducing depolymerization and degradation of pectin, compromising intercellular adhesion and cell wall integrity, and thereby predisposing fruit to translucency. Consistently, fruit N was positively associated with soluble pectin (WSP) but negatively with protopectin, whereas fruit Ca and B showed the opposite trends, suggesting that disrupted N–Ca–B interactions directly weaken fruit cell wall stability [47]. These findings align with observations in apples, where Ca deficiency is linked to increased watercore incidence [48,49,50]. Concomitantly, decreases in protopectin and cellulose along with increases in soluble pectin suggest enhanced degradation of pectic substances mediated by polygalacturonase (PG) and pectin methyl esterase (PME), loosening the cell wall network and predisposing fruits to translucency, particularly under stress conditions such as high humidity or heavy rainfall.
The antagonistic effects of N on Ca and B uptake observed in other crops, including canola and citrus [51,52,53], appears to extend to pineapple, although the underlying physiological mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Moreover, emerging evidence suggests cross-talk between ABA and Ca signaling, whereby ABA may modulate Ca transport and vice versa [54,55]. Accordingly, N-induced reductions in ABA could exacerbate fruit Ca deficiency, further increasing the risk of translucency. Our structural equation modeling (SEM) further supports this mechanism, showing that leaf N enrichment directly promotes translucency and indirectly affects fruit ABA, N/Ca ratio, and cell wall metabolism, ultimately weakening fruit mechanical strength and facilitating disorder onset.
4.3. Potential Measures
Excessive nitrogen input disrupts the balance between vegetative and reproductive growth and adversely affects the synthesis of key cell wall components, making rational N management essential for reducing translucency incidence. Optimizing both the rate and timing of N application is particularly critical. Current studies indicate that N requirements vary among pineapple cultivars: for example, ‘Tainong 17’ requires approximately 5.01 kg of N per 1000 kg of fruit yield, which is comparable to ‘Golden Pineapples’ (5.01 kg) and ‘Caine’ (5.27 kg), but lower than for ‘Bali’ (7.22 kg per 1000 kg fruit) [56,57,58]. Accordingly, the recommended N application rate for commercial pineapple cultivation generally ranges from 300 to 500 kg N ha−1 [56,59,60]. In contrast, surveys show that the average N input in Hainan exceeds 900 kg N ha−1 [15], far surpassing the recommended threshold and increasing the risk of physiological disorders such as translucency. Other major pineapple-producing regions report lower N input levels, such as 720 and 857 kg N ha−1 in Malaysia and 450 kg N ha−1 in Hawaii (USA) [60,61,62], underscoring the need for region-specific nutrient management tailored to cultivar traits and local practices. Although cultivars differ among these regions and Hainan, their nutrient uptake characteristics are generally similar, and thus variations in management practices, soil fertility, and production systems should be the main considerations for adapted nutrient management approaches.
Proper timing of N application is equally important. Adequate N supply during early vegetative growth supports leaf expansion and canopy establishment, while N inputs should be reduced during the first three months after flower induction to promote a smooth transition from vegetative to reproductive growth and enhance flowering success [63]. During fruit development, moderate N supplementation is required to support fruit growth while avoiding excessive vegetative regrowth [58].
When vegetative growth remains excessive during or after the reproductive transition, interventions to redirect assimilate allocation toward reproductive organs may be necessary. Artificial defoliation is one effective strategy: studies on ‘Smooth Cayenne’ in Hawaii demonstrated that removing two-thirds of the leaves prior to harvest reduced translucency incidence by up to 65% without affecting fruit weight or soluble solids content [9]. Moreover, reported that defoliating two-thirds of the leaves four weeks before harvest or complete defoliation three weeks before harvest decreased translucency incidence by up to 19-fold [9]. These findings suggest that defoliation, when precisely timed and properly managed, can serve as a practical auxiliary measure when vegetative growth is excessive, provided it is carefully timed and executed.
Addressing calcium and boron deficiencies, which weaken fruit cell wall integrity, is also crucial. Supplementary fertilization during the reproductive phase has proven effective. For instance, spraying 2% calcium chloride (CaCl2) on ‘Smooth Cayenne’ in Hawaii reduced translucency incidence by 50% [9]. Similarly, foliar applications of a 6% calcium plus 2% boron solution (30 L ha−1) during early fruit development reduced translucency incidence in ‘Golden Pineapples’ in the Philippines by 12.8% [11]. However, varietal differences, climate, and cultivation practices necessitate further research to optimize fertilizer formulations, concentrations, and application timings for different production regions.
This integrated approach—combining optimized N management, timely vegetative control, and targeted Ca/B supplementation—offers a practical framework for reducing pineapple translucency and improving fruit quality.
5. Conclusions
Pineapple translucency has become increasingly prevalent across major production regions worldwide, substantially compromising fruit nutritional quality, sensory attributes, and market value. Affected fruits exhibit lower levels of soluble solids, sugars, and vitamin C, higher soluble acid content, and an imbalanced sugar–acid ratio. Morphologically, they show tissue disruption, loss of cell wall structure, reduced inclusions, waterlogging, swelling, and cellular disorganization.
Our findings identified excessive nitrogen input as a principal driver of translucency. High N availability disrupts endogenous abscisic acid (ABA) regulation, impairs reproductive growth, and alters assimilate allocation, limiting sugar accumulation, dry matter, and inclusion deposition, thereby reducing plant stress resilience. Excessive N also interferes with calcium and boron uptake and their translocation to fruits, elevating fruit N/Ca ratios and inducing physiological calcium deficiency. This nutrient imbalance further compromises cell wall formation, decreasing protopectin and cellulose while increasing soluble pectin, weakening fruit mechanical strength and structural stability. The N/Ca ratio emerges as a critical determinant, underscoring the importance of nutrient balance in preventing disorder onset.
Mitigating pineapple translucency requires integrated management strategies. These could include optimizing N application rates and timing to balance vegetative and reproductive growth, implementing appropriately timed defoliation to redirect assimilates toward fruit development, and targeted calcium and boron supplementation during the reproductive stage to restore cell wall integrity. Coupling these measures with improved fertilizer application practices can enhance nutrient use efficiency and effectively reduce translucency incidence.
Author Contributions
T.L. was responsible for conceptualization, supervision, and writing—review and editing. J.Y. and Z.H. carried out the investigation, performed formal analysis, and contributed to writing—original draft. F.L. and S.H. assisted with investigation and data curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Cooperation Agreement on Building Green Pineapple Brand and Training of Innovative Talents (Grant No. RH2100006535) and the Key Lab of Crop Specific Fertilizer, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, China (Grant No. RH2200004932). The Article Processing Charge (APC) was funded by the latter.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author (T.L.).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Cooperation Agreement on building green pineapple brand and training of innovative talents (RH2100006535), and Key Lab of Crop Specific Fertilizer Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affair, China (RH2200004932).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, Q.R.; Sun, G.M. Development Status of Pineapple Industry in the World. Chin. J. Trop. Agric. 2012, 32, 72–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome. 2021. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Su, W.Q.; Liu, Y.Q.; Ren, H.; Ou, G.L.; Li, J.J.; Luo, R.H.; Lu, Y.Y. Introduction and Performance of the new pineapple variety Tainong No. 17 introduced in Nanning, Guangxi. China Fruits 2011, 5, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.H.; Lua, A.P. Occurrence and Control Measures of Pineapple Water Core and Fruit Cracking. Sci. Plant. Breed. 2019, 7, 40–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.l.; Fu, Q.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.M.; Zhang, X.M. Changes of Physiological Indexes and Endogenous Hormone Content of Watercore Pineapple Fruit. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2021, 42, 2587–2593. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paull, R.E.; Reyes, M.E.Q. Preharvest weather conditions and pineapple fruit translucency. Sci. Hortic. 1996, 66, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, K.; Chen, N.J.; Paull, R.E. Pineapple crown and slip removal on fruit quality and translucency. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 283, 110087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.B.; Yao, Y.L.; Li, C.I.; He, J.J.; Fu, Q.; Yang, Y.Q.; Lin, S.P.; Zhang, X.M. Effects of Preharvest High Temperature Stress on Physiological Characteristics and Fruit Quality in Pineapple. South China Fruits 2025, 1007–1431. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C. Effects of Fruit Temperature, Calcium, Crown and Sugar-Metabolizing Enzymes on the Occurrence of Pineapple Fruit Translucency. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu, HI, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Paull, R.E.; Chen, N.J. Pineapple translucency and chilling injury in new low-acid hybrids. In Proceedings of the II Southeast Asia Symposium on Quality Management in Postharvest Systems, Vientiane, Laos, 4–6 December 2013; Volume 1088, pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayondon, R.R.; Valleser, V.C. Effects of Urea and Calcium-Boron Applied at Flower-Bud Stage on ‘Md2’ Pineapple Fruit. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2018, 8, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wang, C.; Gao, Q.; Li, L.; Luan, S. Calcium spikes, waves and oscillations in plant development and biotic interactions. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.T.; Waldron, K.W. Physiology and Biochemistry of Plant Cell Walls; Springer Science Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, H. Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms of Calcium Absorption, Transport and Metabolism in Plants. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2007, 24, 762–778. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Hong, X.; Liu, S.; Wu, X.; Fu, S.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Song, X.; et al. Cropland degradation and nutrient overload on Hainan Island: A review and synthesis. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 313, 120100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, H. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995; pp. 285–299. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.B. Occurrence and Control of Apple Watercore Disease. Hebei Fruits1 2011, 1, 36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.B.; Wang, Z.H.; Jin, C.S. Research progress on pathogenesis of watercore in apple. China Fruits 2022, 1, 8–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perring, M.; Pearson, K.; Martin, K. The distribution of calcium in apples with watercore. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1984, 35, 1326–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Lin, Q.; Luo, Z.; Ban, Z.; Li, X.; Reiter, R.J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Liang, Z.; Qi, M.; et al. Ongoings in the apple watercore: First evidence from proteomic and metabolomic analysis. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniak, J.; Stasiak, A.; Latocha, P.; Łata, B. Seasonal Changes in Macronutrients in the Leaves and Fruit of Kiwiberry: Nitrogen Level and Cultivar Effects. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 50, 2913–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larocca, G.N.; Baldi, E.; Toselli, M. Understanding the Role of Calcium in Kiwifruit: Ion Transport, Signaling, and Fruit Quality. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschi, K.D. The Calcium Conundrum. Both Versatile Nutrient and Specific Signal. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2438–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z. Effect of Nitrogen Application and Interstem Rootstock on Calcium Absorption and Fruit Quality of Fuji Apples; Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, J.; Jiang, Y.M.; Wei, S.C.; Ge, S.F.; Li, H.N.; Men, Y.G.; Zhou, L. Annual utilization and allocation of urea-13C by M. hupehensis Rehd. under different N rates. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2015, 21, 800–806. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, D.S. Calcium regulation in plant cells and its role in signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1995, 46, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, L.; Ding, Y.; Yao, X.; Wu, X.; Weng, F.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Tang, S.; Ding, C.; et al. Nitrogen fertilizer application affects lodging resistance by altering secondary cell wall synthesis in japonica rice (Oryza sativa). J. Plant Res. 2017, 130, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, K.; Cakmak, T.; Cooper, A.; Lager, I.; Rasmusson, A.G.; Escobar, M.A. Distinct signalling pathways and transcriptome response signatures differentiate ammonium- and nitrate-supplied plants: Transcriptome signatures of ammonium and nitrate responses. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duprat, F.; Grotte, M.; Pietri, E.; Loonis, D.; Studman, C.J. The acoustic impulse response method for measuring the overall firmness of fruit. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1997, 66, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.W.; Bhat, S.A.; Huang, N.F.; Chang, C.Y.; Chan, P.C.; Elepano, A.R. Artificial intelligence-based real-time pineapple quality classification using acoustic spectroscopy. Agriculture 2022, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Official Method 942.15: Acidity (Titratable) of Fruit Products. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 20th ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2023; p. C37-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) in Vitamin Preparations and Juices, Official Method 967.21. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 20th ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2023; p. C45-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.268-2025; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Multi-Elements in Foods. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2025.
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 263–282. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tansupo, P.; Suwannasom, P.; Luthria, D.L.; Chanthai, S.; Ruangviriyachai, C. Optimised separation procedures for the simultaneous assay of three plant hormones in liquid biofertilisers. Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 21, 157–162. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.J.; Paull, R.E. Production and postharvest handling of low acid hybrid pineapple. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1166, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joomwong, A. Impact of Cropping Season in Northern Thailand on the Quality of Smooth Cayenne Pineapple. II. Influence on Physico-chemical Attributes. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2006, 8, 330–336. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228728029_Impact_of_cropping_season_in_Northern_Thailand_on_the_quality_of_Smooth_Cayenne_pineapple_II_Influence_on_physicochemical_attributes (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Mohammed, D.M. Optimizing Postharvest Handling and Maintaining Quality of Fresh Pineapples (Ananas cosmosus (L.)); Inter-American Institute for Cooperation on Agriculture: San Isidro, Costa Rica, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, C.; Palacios-Rojas, N.; Feil, R.; Stitt, M. Regulation of secondary metabolism by the carbon-nitrogen status in tobacco: Nitrate inhibits large sectors of phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 46, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranjuelo, I.; Tcherkez, G.; Molero, G.; Gilard, F.; Avice, J.C.; Nogués, S. Concerted changes in N and C primary metabolism in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) under water restriction. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Sha, J.; Chen, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Ge, S.; Jiang, Y. Exogenous Abscisic Acid Regulates Distribution of 13C and 15N and Anthocyanin Synthesis in ‘Red Fuji’ Apple Fruit Under High Nitrogen Supply. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F. The Mechanism of High Nitrogen Regulating Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism in Apple Fruit and Nitrogen Regulation Techniques. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an, China, 2021. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, L. Understanding the multifaceted role of ABA signaling in orchestrating plant developmental transition. Stress Biol. 2025, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, C.; Zhu, W.; Shi, B.; Yang, W.; Su, H.; Wang, X.H.; et al. NRT1.1B acts as an abscisic acid receptor in integrating compound environmental cues for plants. Cell 2025, 188, 5231–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Hématy, K.; Höfte, H. Growth Control and Cell Wall Signaling in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 381–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, D.T.; Hanson, J.B. The mineral. nutrition of higher plants. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1980, 31, 239–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Yin, X.N.; Zhao, C.Z.; Zhang, H.Y. Effects of Foliar Nutrition Supplementation on Apple Watercore Disease. Hebei Fruits 2005, 5, 4–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Yin, X.N.; Liu, X.Y.; Niu, J.J.; Li, K.Y. Study on the Relationship Between Boron and Apple Watercore Disease. China Fruits 2009, 10, 1000–8047. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.M.; Wang, W.H.; Hang, B.; Tong, W.; Wang, Z.H.; Jia, X.H. Relationship of Carbohydrate, Mineral Content, Reactive Oxygen Species Metabolism and ‘Fuji’ Apple Watercore Occurred. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2015, 42, 2023–2030. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Xu, F.S. Advances and prospects of boron nutrition in plants. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2007, 24, 789–798. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepaskhah, A.R.; Maftoun, M. Seedling growth and chemical. composition of two pistachio cultivars as affected by boron and nitrogen application. J. Plant Nutr. 2008, 17, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, A.Q.; Naeem, A.; Sagervanshi, A.; Wimmmer, M.A.; Mühling, K.H. Boron uptake and distribution by oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) as affected by different nitrogen forms under low and high boron supply. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 161, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B.; Davydov, O.; Knight, H.; Galon, Y.; Knight, M.R.; Fluhr, R.; Fromm, H. Rapid transcriptome changes induced by cytosolic Ca2+ transients reveal ABRE related sequences as Ca2+responsive cis elements in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2733–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, T.; Tan, Q.; Li, S.; Mazars, C.; Galaud, J.P.; Zhu, X. Interactions between calcium and ABA signaling pathways in the regulation of fruit ripening. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 256, 153–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.Y. Investigation and Gold Pineapple Fertilization Nutritional: Properties and Weight Loss Technology Research. Master’s Thesis, Hainan University, Hai’kou, China, 2019. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Q. Effects of Soil Nutrient Status and Soil Amendments on Nutrient Accumulation, Yield and Quality of Tainong 17 Pineapple. Master’s Thesis, Hainan University, Hai’kou, China, 2019. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, X. Integrative transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis of D-leaf of seven pineapple varieties differing in N-P-K% contents. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Lu, M.; Deng, Y. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilization on perfumed pineapple and suitable application amounts. Trop. Crops 2021, 42, 1619–1624. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomew, D.P.; Rohrbach, K.G.; Evans, D.O. Pineapple cultivation in Hawaii. Fruits Nuts 2002, 7, 1–8. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10125/2444 (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Razzaque, A.H.M.; Musa, M.H.; Abd Rahim, A.; Hanif, A.H.M. Pineapple response to nitrogen application on tropical peat: II. Effect on fruit yield and quality. Fruits 2000, 55, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew, D.P.; Hawkins, R.A.; Lopez, J.A. Hawaii Pineapple: The Rise and Fall of an Industry. Hort. Sci. 2012, 47, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.R. General Theory of Soil and Fertilizer; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 178–180. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).