Abstract
Cold stress is an important limiting factor affecting spring tea quality. This study analyzed the effects of foliar spraying of brassinolide (BR) at concentrations of 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, and 1 mg/L on the chlorophyll index, nitrogen balance index, quality, antioxidant defense system, and secondary metabolite profiles in leaves of Camellia sinensis cv. Fuding-dabaicha grown at 4 °C for 48 h. All exogenous BR treatments significantly increased leaf nitrogen balance index, with the highest effect at 0.1 mg/L, which also significantly increased leaf chlorophyll index. BR treatments distinctly increased tea polyphenol, catechin, amino acid, and caffeine levels at cold stress, with the greatest effect at 0.1 mg BR/L. Foliar spraying of BR showed no effect on the expression of CsGOGAT at cold stress, but it differentially regulated the expression of CsHMGR, CsGDH, and CsGs, accompanied by their expression being up-regulated under 0.1 mg BR/L treatment. BR-treated plants exhibited a low level of oxidative damage at cold stress based on malondialdehyde levels, which was associated with higher glutathione levels and CsCAT and CsSOD gene expression levels under BR concentrations of 0.05 mg/L and 0.1 mg/L. Non-targeted metabolomics found a total of 26,175 metabolites, the majority of which were lipids and lipid-like molecules (8.97%) and organic heterocyclic compounds (8.97%). BR treatments with 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, and 1 mg/L triggered 1181, 1997, 2414, and 1455 differential metabolites, respectively, accompanied by more differential metabolites being up-regulated. Among them, 18 differential metabolites were associated with tea quality. The enriched pathways of differential metabolites were mainly caffeine metabolism, amino acid synthesis and metabolism, alkaloid synthesis and metabolism, and flavonoid synthesis, depending on the BR concentrations used. Caffeine metabolism was an BR-inducible differential metabolite pathway. Taken together, foliar spraying of BR (0.1 mg/L) improved leaf antioxidant capacity and quality as well as modulated secondary metabolites and their pathways in cold-stressed tea.
1. Introduction
Tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Ktze.) is a perennial evergreen industrial crop with a preference for warm climates and a fear of cold stress [1]. Hence, temperature is one of the most important environmental factors affecting the distribution range, yield, and economic benefits of tea plants [2]. With the intensification of global climate change, tea plants are more and more susceptible to cold stress, high temperatures, drought, and other environmental impacts. The cultivated regions in southern China often suffer from cold stress in spring, which has a negative impact on spring tea production and tea quality [3]. March–May is the time of spring tea harvesting, and the spring cold is easy to cause tea buds to frostbite, freeze ripening, and even become black/brown until death, resulting in a decrease in tea leaf quality [4]. As a consequence, enhancing the resistance of tea plants to cold stress is an urgent problem in spring tea production.
In addition to affecting the plant phenotype, cold stress also negatively affects plant biochemical responses, as evidenced by the excessive accumulation of reactive oxygen species, which triggers oxidative damage [5]. Under cold stress, plants have antioxidant defense systems to mitigate oxidative damage, such as glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) [6]. In addition, cold stress heavily affects the production of secondary metabolites in plants [7]. A large number of secondary metabolites provide complex flavors and aromas with health-promoting properties in tea leaves, among which catechins, amino acids, flavonoids, caffeine, volatiles, and their derivatives are the key secondary metabolites affecting the quality of tea leaves [8].
Brassinolide (BR) is a highly efficient and non-toxic plant growth regulator [9]. BR improves plant resistance and plays an important role in resisting cold stress [10]. Zhou et al. [11] reported that 1.0 μmol/L BR treatment distinctly enhanced the antioxidant enzyme defense system in response to cold stress (4 °C) at an early stage of rice. In maize, exogenous BR (1.0 μmol/L) application dramatically increased plant height, glucose, starch, sucrose, and glycine betaine levels under cold stress [12]. Li et al. [13] found that spraying 2,4-epibrassinolide with 0.1 μmol/L could alleviate the inhibitory effect of cold stress on the growth of pepper plants, as evidenced by an increase in aboveground dry matter, root morphology, and antioxidant enzyme activity. Exogenous BR (0.05 mg/L) alleviated the photosynthetic inhibition and maintained the stability and integrity of the chloroplast in tung tree plants at low temperatures (8 °C) [14]. In tea plants, exogenous BR is also used to improve their low-temperature tolerance. In tea cultivar ‘Qiancha 1’, 0.01 mol/L BR treatment considerably mitigated cold stress (4 °C) damage through enhanced antioxidant enzyme activity and activated calcium signaling pathway [15]. Transcriptomics revealed that exogenous BR (0.05 mol/L) spraying affected the growth and development of tea plants mainly by regulating the biosynthesis pathways of starch, sucrose, and flavonoids [16]. These results imply that BR is able to modulate cold stress resistance in tea plants, but the intrinsic mechanism is not clear.
The physiological metabolism of tea plants is highly susceptible to external environmental conditions [17,18]. Tea metabolites are important contributors to the resistance of tea plants to biotic and abiotic stresses and the flavor quality of tea leaves [19,20]. Metabolomics, a biotechnology for studying plant metabolites, is well able to detect metabolic changes in plants due to environmental stimuli [21]. Untargeted metabolomics is a reliable and systematic qualitative and quantitative analysis of small-molecule metabolites in biological systems, which can identify differential metabolites [22,23]. Zhou et al. [24] reported a significant effect on amino acids, flavonoids, and caffeine metabolism in green tea leaves after inoculated with Aspergillus sydowii, as per metabolomic analysis. There is no information about BR-triggered changes in secondary metabolite profiles of tea plants under cold stress. Hence, the aim of this study was to analyze the effects of spraying different BR concentrations on leaf quality and quality-related gene expression levels as well as secondary metabolite profiles of tea plants under cold stress.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Culture and Exogenous BR Treatments
The seeds of Camellia sinensis cv. Fuding-dabaicha were sterilized by a 75% alcohol solution, rinsed with distilled water, soaked in distilled water for two weeks, and then germinated in pre-autoclaved (0.11 MPa, 121 °C, 2 h) river sand at 28 °C/20 °C (day/night temperature) and 70% relative humidity in a greenhouse. On 30 May 2023, three-leaf-old tea seedlings were transplanted into plastic pots (15.2 cm × 10.5 cm × 13.5 cm) filled with the substrate of soil and sand (3:1, v/v). Each pot had four tea seedlings. After transplanting, the plants were placed at a day/night temperature of 28 °C/16 °C with a photon flux density of photosynthesis of 338–982 μmol/m2/s and a relative air humidity of 70%. Tea plants grew in such conditions until 19 August 2023. Then, a low-temperature treatment was initiated. On 19 August 2023, the day and night temperatures at which the tea seedlings were grown were changed to 4 °C, while other environmental conditions remained unchanged.
The exogenous BR treatment was also carried out at the same time as the low-temperature treatment. The BR reagent (CAS#72962-43-7; HPLC ≥ 95%) was provided by Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), and exogenous BR was formulated to the concentration of 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, and 1 mg BR/L based on the results of Sun et al. [25]. The set concentration of BR was foliar sprayed until the leaves were dripping. Exogenous BR treatment was carried out again after 24 h. The tea seedlings were subjected to such cold stress conditions for 2 days (48 h). The experiment ended on 21 August 2023, and the plants were harvested.
2.2. Experimental Design
The experiment was designed as a one-way arrangement with five treatments, including 0 mg BR/L (T0), 0.05 mg BR/L (T1), 0.1 mg BR/L (T2), 0.5 mg BR/L (T3), and 1 mg BR/L (T4). Each treatment was replicated six times for a total of 30 pots (2 seedlings/pot).
2.3. Analysis of Variables
Chlorophyll index (CHL) and nitrogen balance index (NBI) were determined using a Dualex portable plant polyphenol chlorophyll meter (Dualex Scientific+, Force A, Orsay, France) half an hour before harvest.
Some of the collected leaf samples were frozen by liquid nitrogen and then kept at −80 °C for RNA extraction and subsequent analysis of biochemical variables. The other leaf samples were treated at 105 °C for 30 min, oven-dried at 80 °C for 48 h, and ground for the determination of tea food quality-related indexes.
Leaf tea polyphenol content was determined by the ferrous tartrate coloring reaction [26], catechin by the 1% vanillin staining method [26], free amino acids by the ninhydrin coloring method [26], and caffeine by UV spectrophotometry [26]. Glutathione content was determined by the method described by Li et al. [27]. Malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration in leaves was carried out by the method outlined by Sudhakar et al. [28].
According to the results of Cao et al. [29] and Liu et al. [30], four quality-related genes, including the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene (CsHMGR), glutamate dehydrogenase (CsGDH), glutamine synthetase (CsGS), and glutamine oxoglutarate aminotransferase (CsGOGAT), and two antioxidant-related genes, catalase (CsCAT) and superoxide dismutase (CsSOD) genes, were selected, and their specific primer sequences (Supplementary Material Table S1) in qRT-PCR were designed based on the Primer Premier 5.0 software. Leaf total RNA was extracted using the TaKaRa MiniBEST Plant RNA Extraction Kit (9769, Takara, Otsu, Japan). After testing the concentration and purity of the total extracted RNA, the RNA was reverse transcribed to cDNA using the PrimeScriptTM RT Reagent Kit with the gDNA Eraser Kit (RR047A, Takara, Otsu, Japan). qRT-PCR was performed by the Real-Time PCR Detection System (CFX96, BIO-RAD, Hercules, CA, USA), where 10 μL of the SYBR GREEN PCR Master Mix Kit (Aidlab, Beijing, China), 0.4 μL of forward primer, 0.4 μL of reverse primer, 7.2 μL of ddH2O, and 2 μL of cDNA were included. The GADPH gene was used as the internal reference gene. The quantitative results were calculated with reference to the 2−ΔΔCt [31] and normalized by T0 treatment.
2.4. Non-Targeted Metabolome Assay
Fresh leaf samples (25 mg) were mixed with 500 μL of extraction solution (methanol/acetonitrile/water = 2:2:1, v/v), containing the mixture of isotopic (13C) labeling internal standard, which was grounded at 35 HZ for 4 min and then extracted by ultrasonic ice bath for 5 min. This process was repeated 3 times. The sample was left at −40 °C for 1 h and centrifuged at 13,800× g for 15 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was used for the Vanquish (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cleveland, OH, USA) Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatograph (UPLC) detection. The target compounds were separated using a Phenomenex Kinetex C18 column (2.1 mm × 50 mm, 2.6 μm). The A phase was the aqueous phase containing 0.01% acetic acid, and the B phase was the mixture of isopropanol and acetonitrile (1:1, v/v). The sample plate temperature was 4 °C, and the injection volume was 2 μL. The Orbitrap Exploris 120 mass spectrometer was capable of primary and secondary mass spectrometry data acquisition under the control of Xcalibur software (version 4.4, Thermo, Cleveland, OH, USA). The parameters were as follows: sheath gas flow rate of 50 Arb, aux gas flow rate of 15 Arb, capillary temperature of 320 °C, full ms resolution of 60,000, MS/MS resolution of 15,000, collision energy of SNCE 20/30/40, and spray voltage of 3.8 kV (positive) or 3.4 kV (negative) [32]. The screened metabolites were classified in the HMDB database. Differential metabolites were screened from sample substances containing p values (p-value) less than 0.05 and greater than 1. They were generated and analyzed by using R software (version 1.46.0) and ggplot2 (version 3.3.5). The metabolites were classified in the HMDB database.
2.5. Data Analysis
SAS software (v8.1; SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) was used to analyze the analysis of variance (ANOVA) and significant differences between treatments with Duncan’s multiple range test (p = 0.05). Sigmaplot (v10.0; Systat Software, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) software was used for graphing. Differential metabolites were screened from samples containing p-values less than 0.05 and greater than 1. R software (version 1.46.0) and ggplot2 (version 3.3.5) were used to generate and analyze volume maps for differential metabolite classification and differential metabolite screening volcano maps and bubble maps for differential metabolites.
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Leaf Physiological Indexes
Foliar spraying of BR under cold stress conditions increased leaf NBI and CHL to some extent, with the most significant effect in T2 (Figure 1). T1, T2, T3, and T4 treatments significantly increased NBI by 92.42%, 129.26%, 40.40%, and 43.37%, respectively, compared with T0 treatment. However, none of the BR treatments significantly affected CHL, except for T2, which significantly improved CHL (74.75%), compared with T0 treatment.
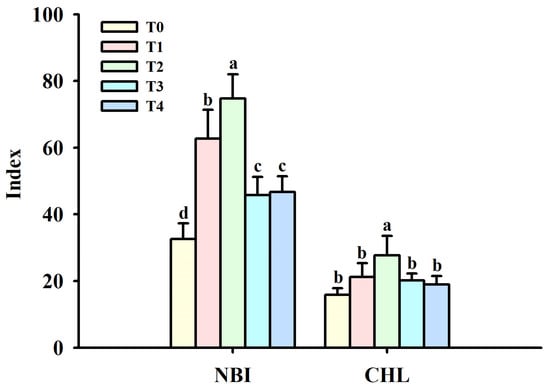
Figure 1.
Effects of foliar spraying of BR on leaf NBI and CHL at cold stress. Different letters above the bars indicate significant (p ≤ 0.05) differences. Abbreviation: BR, brassinolide; CHL, chlorophyll index; NBI, nitrogen balance index; T0, 0 mg BR/L; T1, 0.05 mg BR/L; T2, 0.1 mg BR/L; T3, 0.5 mg BR/L; T4, 1 mg BR/L.
3.2. Changes in Leaf Quality
Spraying BR under cold stress conditions showed positive effects on leaf polyphenol, catechin, free amino acid, catechin, and GSH levels in tea plants (Figure 2a,b). Compared with T0 treatment, T1, T2, T3, and T4 treatments significantly increased tea polyphenol levels by 66.74%, 118.67%, 50.27%, and 73.94%, and also boosted caffeine levels by 59.60%, 112.12%, 50%, and 44.45%, respectively. Among the four BR treatments, tea polyphenol and caffeine levels were significantly higher under T2 treatment than under the other three BR treatments, whereas there were no significant differences among the other three BR treatments. In addition, T1, T2, and T3 treatments significantly increased catechin levels by 31.63%, 39.10%, and 24.78% and free amino acid levels by 75.47%, 113.2%, and 53.77%, respectively, compared with T0 treatment, but T4 treatment did not present a significant effect on catechin and free amino acid levels.
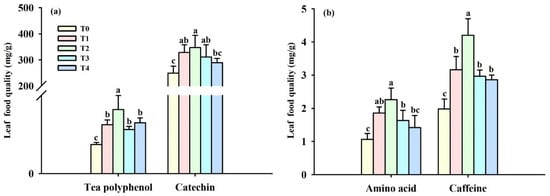
Figure 2.
Effects of foliar spraying of BR on leaf tea polyphenol (a), catechin (a), amino acid (b), and caffeine (b) levels at cold stress. Different letters above the bars indicate significant (p ≤ 0.05) differences. Abbreviation: BR, brassinolide; T0, 0 mg BR/L; T1, 0.05 mg BR/L; T2, 0.1 mg BR/L; T3, 0.5 mg BR/L; T4, 1 mg BR/L.
3.3. Changes in Leaf Quality-Associated Gene Expression
Compared with T0 treatment, T1 treatment significantly down-regulated the expression of CsHMGR gene, but T2 and T3 treatments up-regulated the expression of CsHMGR gene by 1.61- and 1.31-fold, respectively, followed by no significant effect between T4 and T0 treatments (Figure 3). Compared with T0 treatment, only T2 and T3 treatments significantly up-regulated the expression of CsGDH gene by 10.00- and 1.02-fold, respectively; T1, T2, and T4 treatments significantly increased the expression of CsGs gene by 1.10-, 2.30-, and 1.61-fold, respectively; and only T2 treatment significantly up-regulated the expression of CsGOGAT gene (0.37-fold).
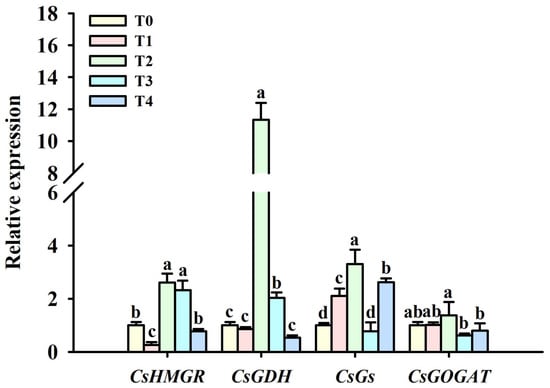
Figure 3.
Effects of foliar spraying of BR on leaf CsHMGR, CsGDH, CsGs, and CsGOGAT gene expression levels at cold stress. Different letters indicate significant (p ≤ 0.05) differences. Abbreviation: BR, brassinolide; T0, 0 mg BR/L; T1, 0.05 mg BR/L; T2, 0.1 mg BR/L; T3, 0.5 mg BR/L; T4, 1 mg BR/L.
3.4. Changes in Leaf Antioxidant Defense Systems
Exogenous BR treatments also elevated GSH levels, as evidenced by a significant increase of 32.81% and 57.18% after T1 and T2 treatments, compared with T0 treatment (Figure 4a). Foliar spraying of BR also strongly affected CsCAT and CsSOD gene expression in leaves. In contrast to T0, T1 and T4 treatments, not T2 and T3 treatments, significantly up-regulated CsCAT gene expression by 2.24- and 1.22-fold, respectively (Figure 4b). Similarly, T3 and T4 treatments also significantly down-regulated CsSOD gene expression by 0.49-fold and 0.72-fold, respectively, while T1 up-regulated it by 0.42-fold compared to T0 treatment, along with no significant change between T0 and T2 treatments. All BR applications reduced leaf MDA content to varying degrees compared to T0 treatment, whereas only T2 and T3 treatments led to significantly lower MDA levels by 29.95% and 19.08%, respectively (Figure 4c).
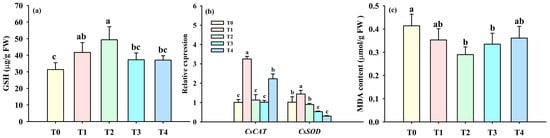
Figure 4.
Effects of foliar spraying of BR on leaf tea glutathione levels (a), CsCAT and CsSOD gene expression at cold stress (b), and malondiadehyde levels (c). Different letters indicate significant (p ≤ 0.05) differences. Abbreviation: BR, brassinolide; T0, 0 mg BR/L; T1, 0.05 mg BR/L; T2, 0.1 mg BR/L; T3, 0.5 mg BR/L; T4, 1 mg BR/L.
3.5. Changes in Leaf Secondary Metabolite Profiles
In this non-targeted metabolomics, the identified secondary metabolites were categorized according to the chemical classification attribution information. The secondary metabolites in this case were categorized into 14 classes, including lipids and lipid-like molecules (8.97%), organic heterocyclic compounds (8.97%), organic acids and derivatives (2.56%), phenylpropanoids and polyketides (2.56%), organic oxygen compounds (2.56%), and others (74.36%) (Figure 5). A total of 26,175 differential metabolites were identified in the leaves based on VIP > 1 and p < 0.05 from the leaf sample substance list. A total of 1181 differential metabolites were detected in T0 treatment versus T1 treatment (Figure 6a), with 605 up-regulated and 576 down-regulated. Similarly, there was a total of 1997 differential metabolites in T0 versus T2, with 1251 up-regulated and 746 down-regulated (Figure 6b). T3 treatment triggered a total of 2414 differential metabolites (1346 up-regulated and 1066 down-regulated) (Figure 6c), and T4 treatment resulted in a total of 1455 differential metabolites (1139 up-regulated and 316 down-regulated) (Figure 6d). In the T1 treatment versus T2 treatment, 638 differential metabolites were detected, 324 up-regulated and 314 down-regulated (Figure 6e). Similarly, in the T2 treatment versus T3 treatment, 1468 differential metabolites were detected, of which 636 were up-regulated and 832 were down-regulated (Figure 6f). In the T2 treatment versus T4 treatment, 1397 differential metabolites were detected, with 963 up-regulated and 434 down-regulated species (Figure 6g).
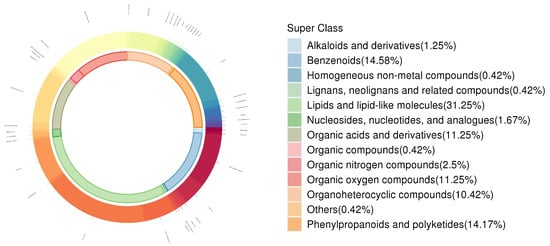
Figure 5.
Metabolite classification and their proportion.
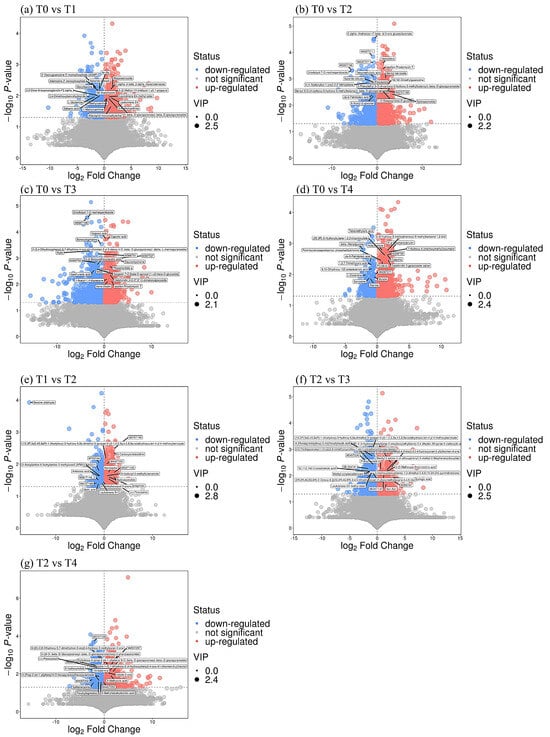
Figure 6.
Changes of differential metabolites of tea after spraying BR at low temperature. Abbreviation: BR, brassinolide; T0, 0 mg BR/L; T1, 0.05 mg BR/L; T2, 0.1 mg BR/L; T3, 0.5 mg BR/L; T4, 1 mg BR/L.
Among the differential metabolites, 18 substances were associated with tea quality (Table 1), namely L-glutamine, rutin, 7-methylxanthine, 3-methylxanthine, chlorogenic acid, catechin, epicatechin, 7-methyluric acid, 1-methyluric acid, baclofen, N-acetyl-L-glutamate, 5-semialdehyde, N-acetylglutamic acid, kaempferol, phloretin, astragalin, eriodictyol, γ-glutamylmethionine, and N-methyl-D-aspartic acid. Among them, T1 treatment down-regulated L-glutamine and rutin concentrations, T2 treatment up-regulated caffeine and caffeine degradation products (7-methylxanthine and 3-methylxanthine), T3 treatment increased chlorogenic acid and down-regulated L-glutamine and rutin concentrations, and T4 boosted catechin and epicatechin levels and down-regulated L-glutamine concentrations, as compared with T0 treatment.

Table 1.
Differential metabolites associated with tea quality in tea leaves at cold stress after foliar spraying of BR.
3.6. Changes in Differential Metabolite Pathways
The metabolic pathways of the differential metabolites were analyzed. A total of 260 differential metabolic pathways were found in T1 versus T0 treatment (Figure 7a), which were mainly enriched in caffeine metabolism, alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, nitrogen metabolism, etc. A total of 66 differential metabolic pathways were identified in T2 versus T0 treatment (Figure 7b), mainly enriched in pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis, caffeine metabolism, vitamin B6 metabolism, etc. A total of 232 differential metabolic pathways were observed in the T3 versus T0 treatment (Figure 7c), primarily enriched in β-alanine metabolism, flavone and flavonol biosynthesis, etc. There were a total of 584 differential metabolic pathways in T4 versus T0 treatment (Figure 7d), mainly enriched in caffeine metabolism, amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism, fructose and mannose metabolism, etc. In addition, a total of 40 differential metabolic pathways were detected in T1 versus T2 treatment (Figure 7e), mainly enriched in caffeine metabolism and glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism. A total of 161 differential metabolic pathways were detected in T2 versus T3 treatment (Figure 7f), mainly enriched in arginine and proline metabolism; 114 differential metabolic pathways were detected in T2 versus T4 treatment (Figure 7g), mainly enriched in flavone and flavonol biosynthesis and caffeine metabolism.
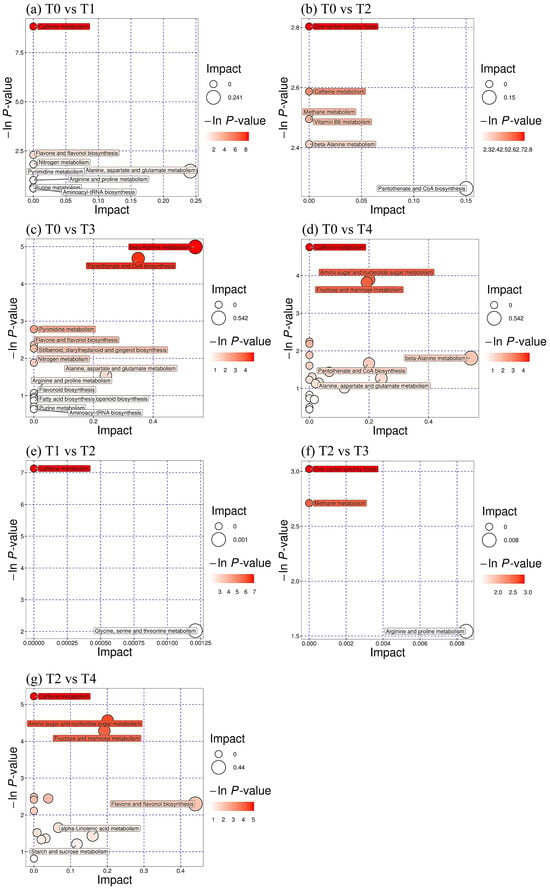
Figure 7.
Changes in differential metabolite pathways in tea leaves at cold stress after foliar spraying of BR. Abbreviation: BR, brassinolide; T0, 0 mg BR/L; T1, 0.05 mg BR/L; T2, 0.1 mg BR/L; T3, 0.5 mg BR/L; T4, 1 mg BR/L.
4. Discussion
Cold stress is one of the important environmental stresses negatively affecting the growth, yield, and quality of tea [2]. BR is thought to improve plant tolerance to cold stress [10,11,12,13,14,15]. This study assessed the effect of foliar spraying BR on physiological response and second metabolite profile in tea leaves exposed to cold stress only. Leaf chlorophyll content can directly affect the photosynthetic capacity of plants, which in turn affects the quality of tea leaves [33]. NBI is an indicator of crop growth as well as N availability [34]. The present study showed that at cold stress, spraying BR treatments increased NBI, with 0.1 mg/L BR having the highest effect, and 0.1 mg/L BR treatment also significantly increased CHL. This is consistent with the study of Li et al. [35] that spraying 0.10 mg/L EBR significantly increased the chlorophyll content of tomato leaves. In fact, exogenous BR can effectively improve the relative structural integrity of chloroplasts at cold stress, so that the bilayer is obvious, the plasma membrane and the matrix are tightly attached, and the matrix area is significantly increased [36].
Tea quality can be negatively affected by cold stress [37]. In this study, under cold stress, BR increased tea polyphenols, free amino acids, caffeine, and catechin levels in tea leaves in a concentration-dependent way, with 0.1 mg/L having the most significant effect. While a BR concentration of 1 mg/L only significantly increased the levels of tea polyphenol and caffeine. This suggests that a BR concentration of 0.1 mg/L can be used to improve the tea quality under cold stress. These changes are related to the fact that BR modulates the expression levels of quality-related genes. Amino acids are the main chemical constituents of tea leaves that regulate and balance the bitterness and viscosity in tea [38], and GS, GOGAT, and GDH are key enzymes in the amino acid biosynthesis pathway [29]. HMGR catalyzes the conversion of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A into mevalonate, which has a significant impact on the level of terpenoids in plants [39]. In the present study, at cold stress, both 0.1 mg/L and 0.5 mg/L BR treatments up-regulated the expression of GsGDH and CsGDH, with 0.1 mg/L being the most significant, suggesting that spraying BR at cold stress modulated the expression of CsHMGR and CsGDH to promote terpenoid levels [29]. The BR concentrations of 0.05 mg/L, 0.1 mg/L, and 1 mg/L up-regulated the expression of CsGS, suggesting that glutamate was converted more into amides such as glutamine and theanine by glutamine synthetase after BR spraying [40]. These implied that BR treatment promoted amino acid formation in relation to its induced expression of CsGDH and CsGs at cold stress, independent of CsGOGAT.
When plants are exposed to cold stress, there is a burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS), resulting in oxidative damage to plant cells [41]. In the present study, the reduction in MDA shows that BR spraying within a concentration range of 0.1–0.5 mg/L clearly reduces the oxidative damage in cold-stressed tea plants. This is in line with the results of Kumar and Manish [42] on Brassica species sprayed with 24-epibrassinolide at 4 °C and Sun et al. [25] on Zea mays sprayed with brassinolide at chilling stress. The change in MDA levels is correlated with changes in BR-induced GSH levels and CsCAT and CsSOD gene expression levels. In this study, leaf GSH levels were significantly increased after foliar spraying 0.05 and 0.1 mg/L BR, and leaf CsCAT and CsSOD gene expression levels were up-regulated after foliar spraying 0.05 mg/L BR. Pre-treatment with 28-homobrassinolide (1 nmol/L) significantly up-regulated SOD and CAT expression in Brassica juncea at 4 °C [43]. Therefore, this concluded that BR-treated tea plants activate antioxidant defense systems (GSH, SOD, and CAT) to remove more reactive oxygen species against cold stress, resulting in low oxidative damage, where a BR concentration of 0.05 mg/L mainly induced CsCAT and CsSOD gene expression levels and GSH levels, and a BR concentration of 0.1 mg/L mainly increased GSH levels. However, it is not known whether the effects of BR on the antioxidant systems of tea plants are also present at normal temperature.
Non-targeted metabolomics allow for the analysis of the overall pattern in changes of all metabolites in an organism, which in turn leads to the discovery of new metabolites and metabolic pathways following abiotic stress [44,45]. Moreover, we used non-targeted metabolomics to identify 33 differential compounds in different tea cultivars, including epicatechin, theanine, theobromine, chlorogenic acid, adenine, and chrysin. In this study, non-targeted metabolomic analysis was performed on Fuding-Dabaicha leaves, and a total of 26,175 differential metabolites were identified. Among the differential metabolites, there were 18 substances associated with the tea leaf quality, including caffeine, flavonoids, amino acids, and so on [46]. Meanwhile, the differential metabolites appeared more under 0.1 mg/L BR treatment versus 0 mg/L BR treatment, where 1997 differential metabolites (1251 up-regulated and 746 down-regulated) were identified after foliar spraying 0.1 mg/L BR. All of the obtained differential metabolites were more up-regulated after the 0.1 mg/L BR treatment, which showed a boosting benefit of BR. This is consistent with the result that leaf quality variables were the highest after a BR concentration of 0.1 mg/L. In addition, the enriched pathways for differential metabolites were variable after foliar spraying BR, showing that this was BR concentration-dependent. Moreover, the enriched pathways of the differential metabolites were also different when 0.1 mg/L BR was compared to the other BR concentrations, but various amino acid metabolisms were evident, e.g., glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism after 0.1 mg/L BR versus 0.05 mg/L BR and arginine and proline metabolism after 0.1 mg/L BR versus 0.5 mg/L BR. Further analysis of the enriched pathways of differential metabolites revealed that they were mainly amino acid synthesis and metabolism, alkaloid synthesis and metabolism, and nutrient metabolism. BR improved the photosynthetic efficiency of the plant by increasing the Calvin cycle and acting as a regulator of the secondary metabolites [47]. However, caffeine metabolism was found after BR concentrations of 0.05 mg/L, 0.1 mg/L, and 1 mg/L as well as 0.1 mg/L BR versus 0.05 mg/L BR and 0.1 mg/L BR versus 1 mg/L BR, showing that caffeine synthesis and degradation are a differential metabolic pathway susceptible to BR induction. Caffeine is a typical purine alkaloid found in more than 60 different plants, including coffee and tea [48]. Its synthesis and degradation pathways have been well characterized and are susceptible to various environmental factors [49]. This is consistent with the significant increase in leaf caffeine levels after BR spraying. Additional in-depth studies on the differential metabolites obtained and their enriching pathways are needed to support BR regulation of tea quality at cold stress.
5. Conclusions
The antioxidant defense system of tea seedlings at 4 °C was improved by exogenous BR treatments, resulting in low oxidative burst, especially under 0.05 mg/L and 0.1 mg/L BR spraying. Spraying BR also increased leaf quality of tea plants under cold stress, especially most pronounced in the 0.1 mg/L BR spraying, which was associated with the up-regulation of the expression levels of quality-related genes. Non-targeted metabolomics also revealed a large number of secondary metabolites involved in the BR treatment, among which 18 quality-related differential metabolites were identified. The enriched pathways of differential metabolites were focused on amino acid synthesis and metabolism, flavonoid synthesis, and caffeine metabolism, suggesting that exogenous BR improves the tea quality at cold stress. These results clearly indicate that 0.1 mg BR/L can enhance leaf resistance and quality of tea plants under cold stress. In the future, it also needs to be clear whether 0.1 mg BR/L can also have such an effect on tea plants at normal temperature.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae10060639/s1. Table S1: The specific primers of selected genes designed for qRT-PCR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.-B.G. and Q.-S.W.; data curation, Y.W. and A.-Q.L.; investigation, Y.W. and A.-Q.L.; methodology, A.-Q.L.; resources, X.-B.G. and Q.-S.W.; supervision, X.-B.G. and Q.-S.W.; writing—original draft, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, A.H., E.F.A., X.-B.G. and Q.-S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Local Science and Technology Development Project Fund guided by the Central Committee in Guizhou Province ([2022]4052). The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Construction of Modern Agriculture (tea) Industry Technology System (CARS-19) (China) and the Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSP2024R356), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Data Availability Statement
All the data supporting the findings of this study are included in this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSP2024R356), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q. Requirements of environmental conditions for tea plant growth and development. Sichuan Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, 12, 28–29, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.C.; Wang, L.; Hao, X.Y.; Li, N.N.; Ding, C.Q.; Huang, J.Y.; Yang, Y.J. Progress and prospective of cold resistance mechanism in tea plants. J. Tea Commun. 2022, 49, 139–148, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.Y.; LI, X.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, L. Prevention and control technology of “cold spell in later spring” in tea garden. China Tea 2018, 40, 9–12, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Liu, Y.P.; Gu, X.P.; Hu, J.M.; Yu, F.; Zhang, B. Effects of low temperature on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of tea (Camellia sinensis L.). Crops 2018, 3, 155–161, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Nadeem, M.; Galagedara, L.; Thomas, R.; Cheema, M. Recent insights into cell responses to cold stress in plants: Signaling, defence, and potential functions of phosphatidic acid. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 203, 105068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritonga, F.N.; Chen, S. Physiological and molecular mechanism involved in cold stress tolerance in plants. Plants 2020, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akula, R.; Ravishankar, G.A. Influence of abiotic stress signals on secondary metabolites in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 1720–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Song, C.; Zhao, J.; Xia, E.; Wen, W.; Zeng, L.; Benedito, V.A. Editorial: Secondary metabolites and metabolism in tea plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1143022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clouse, S.D.; Sasse, J.M. Brassinosteroids: Essential regulators of plant growth and development. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1998, 49, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadura, I.; Janeczko, A. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of brassinosteroid-induced tolerance to high and low temperature in plants. Biol. Plant. 2018, 62, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.J.; Wu, W.P.; Tang, C.B.; Xiao, Z.F.; Chen, G.H.; Wang, Y. Effect of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on germination and physiological characteristics of rice seedlings under chilling stress. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occid. Sin. 2020, 29, 1410–1416, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Singh, I.; Kumar, U.; Singh, S.K.; Gupta, C.; Singh, M.; Kushwaha, S.R. Physiological and biochemical effect of 24-epibrassinoslide on cold tolerance in maize seedlings. Physiol. Mol. Boil Plants 2012, 18, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, P.; Xie, J.M.; Yu, J.H. Effects of 2,4-epibrassinolide on growth and antioxidant enzymes system in pepper roots under chilling stress. J. Nuclear Agric. Sci. 2015, 29, 1001–1008, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Lu, K.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Li, Z. Effects of low-temperature stress and brassinolide application on the photosynthesis and leaf structure of tung tree seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 497266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, K.; Shen, W.; Zhao, Y. External application of brassinolide enhances cold resistance of tea plants (Camellia sinensis L.) by integrating calcium signals. Planta 2023, 258, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tian, N.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, S. Transcriptomics analysis reveals the signal transduction mechanism of brassinolides in tea leaves and its regulation on the growth and development of Camellia sinensis. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.Y.; Huang, J.G.; Li, X.; Li, Z.X.; Ahammed, G.J.; Yan, P.; Stepp, J.R. Altitudinal effects on the quality of green tea in east China: A climate change perspective. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Griffin, T.S.; Kraner, D.; Schaffner, M.K.; Sharma, D.; Hazel, M.; Leitch, A.R.; Orians, C.M.; Han, W.Y.; Stepp, J.R.; et al. Environmental factors variably impact tea secondary metabolites in the context of climate change. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.; Wang, B.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Chang, M.M.; Xia, T.; Shi, X.Z.; Xu, G.W. A comprehensive strategy for studying protein-metabolite interactions by metabolomics and native mass spectrometry. Talanta 2019, 194, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaleckis, R.; Meister, I.; Zhang, P.; Wheelock, C.E. Challenges, progress and promises of metabolite annotation for LC-MS-based me tabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 55, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.N.; Liang, Q.L. Advance in metabolomics based on Mass Spectrometry. J. Instrum. Anal. 2017, 36, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.T.; Li, X.N.; Wang, J.; Ling, X.M. Metabonomics and its analytical technique. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2010, 30, 1792–1799, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.M.; Cheng, H.T.; Xue, M. Recent development of LC-MS-based analytical procedures and techniques in metabonomics. J. Int. Pharm. Res. 2011, 38, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Ma, C.; Ren, X.; Xia, T.; Li, X. LC–MS/MS-based metabolomic analysis of caffeine-degrading fungus Aspergillus sydowii during tea fermentation. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; He, Y.; Irfan, A.R.; Liu, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, D. Exogenous brassinolide enhances the growth and cold resistance of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings under chilling stress. Agronomy 2020, 10, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.S. Experimental Guideline in Plant Physiology; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.S.; Xie, Y.C.; Rahman, M.M.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Wu, Q.S. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and endophytic fungi activate leaf antioxidant defense system of lane late navel orange. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhakar, C.; Lakshmi, A.; Giridarakumar, S. Changes in the antioxidant enzymes efficacy in two high yielding genotypes of mulberry (Morus alba L.) under NaCl salinity. Plant Sci. 2001, 161, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.L.; Shao, Y.D.; Zou, Y.N.; Wu, Q.S.; Yang, T.Y.; Kuča, K. Inoculation with Clariodeoglomus etunicatum improves leaf food quality of tea exposed to P stress. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2021, 49, 12166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; WU, Q.S.; Yang, Y.T.; Kuča, K. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improve the antioxidant capacity of tea (Camellia sinensis) seedlings under drought stress. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2020, 48, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doppler, M.; Kluger, B.; Bueschl, C.; Schneider, C.; Krska, R.; Delcambre, S.; Karsten, H.; Lemmens, M.; Schuhmacher, R. Stable isotope-assisted evaluation of different extraction solvents for untargeted metabolomics of plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Z.; Liu, Y.F.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, L.Y.; Zeng, Y.X.; Song, S.X.; Zhao, E.; Qing, Z. Effect of different light ratio on physiology and main amino acid accumulation of Fuding-dabaicha leaf. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 29–35, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.L.; Lu, Y.L.; AO, J.H.; Chen, D.W.; Huang, Y.; Shen, D.C.; Huang, H.J.; Jiang, Y. Effect of compound bacterial manure on the growth of sugarcane. Sugarcane Canesugar 2016, 6, 14–17, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Shu, S.; Guo, S.R.; Du, J.; Wang, J.W. Effect of 24-brassinolides on photosynthetic characteristics and fruit quality of cherry tomato. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2015, 35, 138–145, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Quan, M.P.; Xu, J.H.; Yin, J.M.; Yang, Z.K.; Tan, W.M. The physiological mechanisms of exogenous brassinolide regulating abiotic stresses in plants: A review. J. Plant Prot. 2023, 50, 22–31, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.C. Study on Cold Resistance of Different Tea Cultivars Introduced in Linyi Area. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, China, 2007. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Li, Y.; Ma, T.T. Influences of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on quality and related gene expression of Liubao tea. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2022, 50, 157–163, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chu, W.; Liu, Y.Y.; LI, Y.B.; Chu, X.S. Advances on plant 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase (HMGR) genes. Curr. Biotechnol. 2018, 8, 93–102, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.G.; Wan, X.C. Review on enzymatic biosynthesis of theanine. J. Tea Sci. 2011, 31, 1–10, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Cao, M.A.; Kuča, K.; Alqahtani, M.D.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Wu, Q.S. Cloning of CAT genes in Satsuma mandarin and their expression characteristics in response to environmental stress and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.S.; Manish, K. Effect of 24-Epibrassinolide on lipid peroxidation and proline in three Brassica species under temperature stress. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 9, 376–384. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, H.; Sirhindi, G.; Bhardwaj, R.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Ahmad, P. 28-homobrassinolide regulates antioxidant enzyme activities and gene expression in response to salt- and temperature-induced oxidative stress in Brassica juncea. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, A.Q.; Zhou, J.H.; Rong, Z.Y.; Alqahtani, M.D.; Gao, X.B.; Wu, Q.S. Mycorrhiza-triggered changes in leaf food quality and secondary metabolite profile in tea at low temperatures. Rhizosphere 2024, 29, 100840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.F.; Liu, J.H.; Yin, H.Y.; Liu, D.M.; Guo, X.M.; Yang, Y.G.; Wang, H.F.; Yu, Y.J. Study on difference of tea cultivars planted in Xinyang by non-targeted metabolomics with chemometrics based on Ultrahigh Performance Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. J. Instrum. Anal. 2022, 41, 149–155, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Paiva, L.; Lima, E.; Motta, M.; Marcone, M.; Baptista, J. Variability of antioxidant properties, catechins, caffeine, L-theanine and other amino acids in different plant parts of Azorean Camellia sinensis. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2020, 3, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.P.; REN, G.X.; Xiang, Y.; Zang, Y.M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.S. Effect of exogenous brassinolide on morphological characters and contents of seven chemical constituents of Glycyrrhiza uralensis. China J. Chin. Mat. Med. 2016, 41, 197–204, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ashihara, H.; Crozier, A. Biosynthesis and metabolism of caffeine and related purine alkaloids in plants. Adv. Bot. Res. 1999, 30, 118–205. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanpuria, P.; Kumar, V.; Yadav, S.K. Tea caffeine: Metabolism, functions, and reduction strategies. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).