Abstract
Root-knot nematodes are the major diseases in protected cultivation around the world. Bio-organic fertilizer has become a research hotspot, with a variety of microorganisms that control various vegetable soil-borne diseases. This study screened nematocidal microorganisms from fresh vermicompost, explored the inhibitory substances produced by biocontrol agents, and evaluated their potential biocontrol ability in the pot and field under greenhouse conditions. The highly effective antagonistic microbes of Meloidogyne incognita (M. incognita) were screened. Strains YL1 and YL31 were identified as Peribacillus frigoritolerans, and strain YL6 was identified as Lysinibacillus fusiformis. The three strains all produced chitinase and protease, which prevented the normal development of eggs and the second-stage juveniles (J2) by destroying their appearance. The three strains all improved potassium-dissolving ability, and the strains YL1 and YL6 also enhanced phosphorus-dissolving ability. Pot experiments showed that tomato root knots were reduced, and plant growth improved. Field tests showed that the root-knot index and nematode population were reduced significantly, and cucumber growth and yield were enhanced. Strain YL1 had the best control effect with 70.6%, and the yield increased by 14.9% compared with the control. Overall, this study showed the ability of antagonistic bacteria YL1, YL6, and YL31 to control root-knot nematodes, and these antagonistic bacteria could be developed as biocontrol agents for sustainable agriculture.
1. Introduction
In recent years, plant-parasitic nematodes have become one of the major factors restricting the development of the protected vegetable industry, causing economic losses of more than US$100 billion per year [1,2]. Among them, root-knot nematode is one of the most common and destructive soil-borne diseases in monoculture vegetable cropping, resulting in huge losses to the protected vegetable industry [3]. Many studies have been conducted on root-knot nematode control measures [4,5,6]. The research focuses on breeding resistant plant varieties and developing nematicides. Breeding resistant plant varieties can effectively reduce losses caused by nematodes; however, invasion by many other pathogens can lead to weakened resistance due to severe selection pressure on resistant plants [7]. Nematicides can effectively control nematodes, but their toxic residues affect the environment and human health [8,9]. In order to produce green vegetables, most nematicides are gradually banned or strictly restricted in use. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop alternative control strategies and long-term integrated approaches against nematode infestation to replace chemical nematicides [6,10].
Biological control has received close attention because it does not damage the agricultural ecological environment and avoids the harm of pesticides to human health. Biological control usually uses fungi, bacteria, and actinomycetes or their metabolites that feed on or parasitize nematodes [11,12], such as Bacillus [13], Arthrobotrys [14], and Streptomyces [15] These antagonistic microorganisms contain nematocidal compounds, or release nematicides during the process of acting on nematodes [16]. At present, most of the root-knot nematode antagonistic microorganisms commonly used in biological control are screened from crop soils, natural fertilizer, and compost. Organic fertilizers based on organic waste, such as livestock and poultry manure, sewage sludge, and solid and food waste, have many advantages, including low cost, easy availability, reuse of waste, and reduction of environmental pollution [17]. As a biological control agent, organic fertilizers not only can improve soil environment and promote plant growth but also contain abundant antagonistic microorganisms, which can effectively control soil-borne diseases [18].
Vermicompost is a product of the biodegradation of organic waste by earthworms and is a natural bio-organic fertilizer. Vermicompost is rich in microorganisms. These microorganisms not only can improve soil fertility and plant nutrition and enhance plant disease resistance but also regulate the microbial community in soil and indirectly stimulate nematode predators and parasites that depend on microorganisms [19]. It has been reported that vermicompost can effectively control many vegetables’ soil-borne diseases to a certain extent [20]. Vermicompost can significantly reduce plant-parasitic nematodes and decrease plants’ susceptibility [21,22]. Xiao et al. [23] showed that vermicomposting can help tomato plants, especially sensitive varieties, resist M. incognita infection. Field trials by Singh et al. showed that vermicompost can reduce the number of M. javanica in chickpea plants, promote plant growth, and increase yield [24]. However, these studies only demonstrated that vermicompost can prevent and control root-knot nematodes. The presence of the antagonistic microorganisms in vermicompost that can inhibit root-knot nematodes and their mechanism of action are still unclear. The aim of this study was to isolate and screen highly effective antagonistic bacteria against M. incognita from fresh vermicompost in pot and field conditions in a greenhouse setting.
The strains were identified based on their physiological and biochemical indices and molecular characteristics. The mechanism of effective antagonistic bacteria for controlling root-knot nematodes and promoting growth in plants was examined to provide new resources for the development and utilization of vegetable root-knot nematode antagonists.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms Isolated from Vermicompost
Fresh vermicompost samples were provided by the Scientific Research Foundation of Shenyang Agricultural University. These samples were obtained by feeding earthworms (Eisenia foetida) with semi-decomposed cow dung. A total of 157 isolates containing bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes were isolated from vermicompost. The isolated strains were inoculated into the corresponding nutrient medium and shaken at 28 °C and 180 r/min for 18 h, 48 h, and 96 h, respectively, to make seed liquid. The fermentation broth was prepared with 1% inoculum and cultured by shaking at 28 °C and 180 r/min for 2 d, 3 d, and 5 d, respectively. Finally, the concentration was adjusted to 109 CFU/mL for a stock solution and stored in a 4 °C refrigerator.
2.2. Preparation of Root-Knot Nematode Inoculum
Tomato tissue samples seriously infested by root-knot nematode were collected from greenhouses in Chaoyang, Liaoning, of China. The nematode infecting the tomato roots was identified as M. incognita [25]. The tomato roots infected by root-knot nematode were gently rinsed with distilled water, and the egg sacs were harvested with a sterile needle and placed into a 0.5% NaClO solution for disinfection for 5 min then rinsed with sterile water 3 times. They were then placed on a mesh screen of non-toxic filter paper. The egg sacs were placed in a petri dish filled with sterile water. They were then in an incubator at 28 °C for 4–7 days with replacement of sterile water daily. Newly hatched J2 were collected every 24 h. The concentration of nematodes was adjusted with sterile water to obtain about 500 nematodes/mL and stored in a 4 °C refrigerator for both in vitro and in vivo trials.
2.3. Screening of Antagonistic Bacteria against Root-Knot Nematode
The experiment was performed in a 24-well cell culture plate with 0.8 mL fermentation broth and 0.2 mL J2 suspension in each well. A well with sterile distilled water and blank medium was used as a control. The treatment was repeated 4 times, and the plate was placed in a 28 °C incubator. Mortality was checked after 24 h under a stereomicroscope. If the nematodes were still motionless and remained motionless when touched with a toothpick, they were considered dead. The fermentation liquid of strains with a nematode-corrected mortality rate higher than 90% was selected for re-screening. The fermentation broth was diluted 2 times, 3 times, and 5 times. The corrected mortality of J2 was checked after 12 h and 24 h with the same method. The mortality and corrected mortality of the second-stage juveniles (J2) after 24 h were calculated.
Mortality = numbers of dead J2S/numbers of tested J2S × 100%
Corrected mortality = (mortality of fermentation broth − control mortality)/(1 − control mortality) × 100%
2.4. Identification of Antagonistic Bacteria in Root-Knot Nematode
The screened high-efficiency antagonistic bacteria of root-knot nematodes were transferred to the beef peptone medium plate and cultivated in a 28 °C incubator for 24–48 h. After the colonies grew vigorously into single colonies, colony size, color, texture, shape, and humidity were monitored. Gram staining and spore staining were also monitored/recorded. Physiological and biochemical identification was conducted, including indole, methyl red, V-P, and starch hydrolysis on root-knot nematode antagonistic bacteria following general physiological and biochemical methods in the Common Bacterial System Identification Manual [26].
Genomic DNA extraction of root-knot nematode antagonistic bacteria was carried out following the instructions of the Ezup Column Bacteria Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China). Using the extracted genomic DNA as a template, the partial sequence of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified by PCR utilizing universal primers 27F (5′-AGA GTT TGA TCC TGG CTC AG-3′) and 1492R (5′-ACG GCT ACC TTG TTA CGA CTT-3′) [27]. After the PCR reaction products were detected by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, they were sent to Shanghai Bioengineering Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). for sequencing. The measured 16S rDNA sequence was submitted to GenBank database of NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) for BLAST comparison analysis (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). The sequence of strain type with high homology was selected, and phylogenetic analysis was carried out with Mega7.0 and ITOL software (http://itol.embl.de/).
2.5. Research on the Functions and Growth-Promoting Properties of Antagonistic Bacteria
2.5.1. Detection of the Protease and Chitinase Production Capacity of Antagonistic Bacteria
Antagonistic bacteria were incubated on gelatin solid medium (10.00 g gelatin, 5.00 g peptone, 0.50 g K2HPO4, 0.2 g MgSO4∙7H2O, 15 g agar, distilled water 1000 mL, pH 7.0–7.2) and chitin solid medium (200 mL colloidal chitin, 0.3 g KH2PO4, 0.7 g K2HPO4, 0.01 g FeSO4, 0.5 g MgSO4, 0.1 g NH4Cl, 0.1 g NaCl, 20 g agar, 1000 mL distilled water, pH 7) and inverted at 30 °C for 24 h and 48 h. The growth status was monitored. The diameter of the hydrolysis circle (D) and the diameter of the colony (d) were measured, and the ratio of D/d was calculated.
2.5.2. Phosphorus-Dissolving and Potassium-Dissolving Ability Tests of Antagonistic Bacteria
Antagonistic bacteria were inoculated on the phosphorus-dissolving solid medium (10.00 g glucose, 0.50 g (NH4)2SO4, 0.5 g yeast extract powder, 0.3 g NaCl, 0.3 g MgSO4∙7H2O, 0.03 g FeSO4∙7H2O, 0.03 g MnSO4, 5.00 g Ca3(PO4)2, 0.3 g KCl, 15 g agar powder, 1000 m distilled water, pH 7.0–7.5) and the potassium-dissolving solid medium (5 g glucose, 0.50 g MgSO4∙7H2O, 0.1 g CaCO3, 0.006 g FeCL3, 2 g Ca3(PO4)2, 20 g agar powder, 1000 mL distilled water, pH 7.0, 2 mL of 0.5% bromothymol blue (BTB) per 100 mL of culture medium were added before use) and incubated at 30 °C for 5 and 7 d at a constant temperature, and the growth status of the bacteria was monitored. The diameter (D) and colony diameter (d) of the phosphorus-dissolving circle and potassium-dissolving circle were measured. The ratio of D/d was calculated.
2.6. Effects of Antagonistic Bacteria on the Development of Root-Knot Nematode Eggs and J2
Ten fresh worm eggs were extracted with a pipette and placed into the cell culture plate. A total of 20 μL of the fermentation broth of strain YL1, strain YL6, and strain YL31 was added, using a sterile culture broth as a control, and this was repeated 5 times for each treatment. The normal egg hatching process was observed as a control. Samples were taken every 12 h, and the eggs were sucked up on a glass slide with straw. The development process of the eggs was monitored and photographed under an optical microscope. The method for observing the effects of antagonistic bacteria on the development of J2 was the same as above. The samples were taken and observed at 12 h and 24 h.
2.7. Pot Experiment
Root-knot nematodes were collected from a greenhouse seriously infested with tomatoes in Chaoyang, Liaoning, of China. The soil in the plough layer at a depth of 0–20 cm was taken and then sieved with a 5 mm screen. This was done to remove coarse plant debris and particles. It was thoroughly mixed and used for pot experiments. Healthy soil was collected in the same area and not infected with root-knot nematodes. The tomato variety tested was L-402. Five treatments were used: (1) healthy soil CK0; (2) infested soil CK1; (3) infested soil + antagonistic bacteria YL1; (4) infested soil + antagonistic bacteria YL6; and (5) infested soil + antagonistic bacteria YL31. During the three-leaf stage, tomato seedlings were transplanted into 15 cm × 13 cm pots filled with 1 kg of soil each. The antagonistic bacteria fermented liquid was taken from a stock solution, diluted 10-fold and 50-fold. The dose was 10 mL with root irrigation, and each treatment was repeated three times. The potted plants were randomly placed in a constant temperature light incubator at 28 °C and cultivated under 16 h light/8 h dark conditions. Without any additional fertilizer, the potted plants were wetted in a timely and quantitative manner.
Forty-five days after transplantation, the tomato plants were harvested by gently shaking the soil around the roots to obtain intact plant roots, followed by rinsing them with water to remove the soil from the root surface. Tomato plant height, stem thickness, root fresh weight, aboveground fresh weight, and root knot number were measured. A total of 100 g of soil around the tomato plant roots was taken, and the nematode population in the soil was detected under a microscope. The disease grade was recorded [28]. The root-knot index and relative effect were assessed as follows:
Root-knot Index = Σ (Number of Diseased Plants at All Levels × Corresponding Level Value)/(Total Number of Investigated Plants × Highest Level) × 100%
Control Effect = [(Root-knot Index with Control − Root-knot Index with Treatment)/Root-knot Index with Control] × 100%
2.8. Field Tests
Field experiments were conducted in a cucumber greenhouse with severe nematode occurrence in Shenyang, Liaoning Province, China. The initial population density of nematodes was determined to be 1095.0 ± 26.5 J2/100 g soil using the Baermann funnel method [29,30]. The temperature range was 15~30 °C, and the cucumber variety was Jinyou 30. Four treatments were used: (1) control CK with water; (2) antagonistic bacteria YL1; (3) antagonistic bacteria YL6; and (4) antagonistic bacteria YL31. Each treatment was repeated 4 times, the plot area was 2.4 m2, and 9 seedlings were planted in each plot using a random block arrangement. The three kinds of bacterial fermentation broth (1 × 109 CFU/mL) and the same amount of water were inoculated on the cucumber seedlings after transplantation for 7 days. The dose was 100 mL with root irrigation. Routine management was performed in the greenhouse during the test.
After 75 days of planting, the root situation of the cucumber plants was observed, the root-knot index was investigated, and the control effect was calculated according to method 2.7. The fresh weight and dry weight of the aboveground part, the fresh weight and dry weight of the underground part, and the yield were measured.
2.9. Data Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) with SPSS 22.0 statistical software and Microsoft Office Excel 2019. Significant differences among treatments were determined according to Duncan’s multiple range test (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Root-Knot Nematode Antagonistic Bacteria
A total of 157 strains were isolated from vermicompost. Through the nematocidal activity of the fermentation broth, six strains with a corrected mortality rate of more than 90% were selected for further screening (Table S1). Antagonistic bacteria YL1, YL6, and YL31 with stable and efficient nematocidal effect at three dilutions of different concentrations were selected as follow-up research objects (Table S2).
The morphology and biochemical characterization of strains YL1, YL6, and YL31 are shown in Figure 1A,B. The three isolates are Gram-positive. The sizes of 16S rDNA gene fragments of strains YL1, YL6, and YL31 were 1458 bp, 1454 bp, and 1458 bp, respectively. The 16S rDNA gene sequences of the three strains were compared, and the phylogenetic analysis of the sequences showed that strains YL1 and YL31 belonged to the same branch as Peribacillus frigoritolerans, and strain YL6 had the highest similarity with Lysinibacillus fusiformis. Based on the results of strain morphology, physiology, biochemistry, and molecular identification, strains YL1 and YL31 were identified as Peribacillus frigoritolerans, and strain YL6 was identified as Lysinibacillus fusiformis. These sequences of strains YL1, YL6, and YL31 were submitted to the GenBank database under accession numbers PP565075, PP565089, and PP565091.
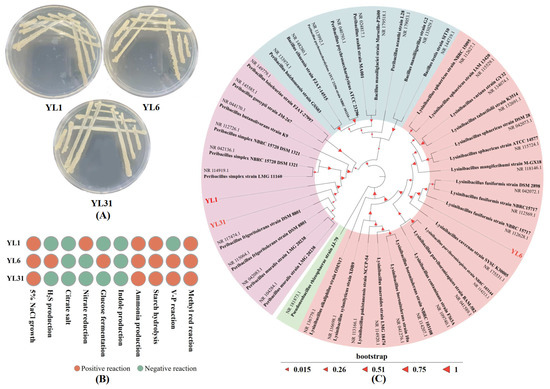
Figure 1.
Identification of antagonistic bacteria YL1, YL6, and YL31. (A): Morphological characteristics; (B): Physiological and biochemical characteristics; (C): 16S rDNA system circle developmental tree. YL1, YL6, and YL31 represent three antagonistic bacteria against root-knot nematodes isolated from vermicompost.
3.2. Functions and Growth-Promoting Properties of Antagonistic Bacteria
3.2.1. Protease and Chitinase Production Capacity of Antagonistic Bacteria
As shown in Figure 2, all three strains have collagenase activity. Compared with strains YL6 and YL31, strain YL1 has the smallest colony diameter and relatively slow growth, but the ratio of its hydrolysis circle diameter to the colony diameter is the largest among all strains. Strain YL6 has the fastest growth rate, but its hydrolyzed collagen activity is low. These results indicated that under the same culture conditions, the growth rate of the strain was not necessarily related to enzyme production activity.
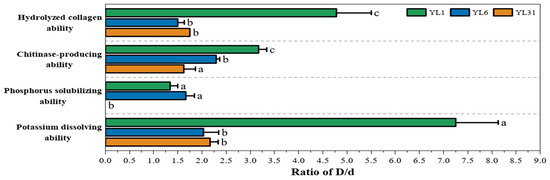
Figure 2.
The ability of antagonistic bacteria to inhibit nematodes and promote growth. YL1, YL6, and YL31 represent three antagonistic bacteria against root-knot nematodes isolated from vermicompost. D/d: The ratio of hydrolysis zone (D) to colony (d) diameter. Different letters represent a significant difference at p < 0.05 by Duncan’s test.
All three strains can have chitinase activity and degrade colloidal chitin to form a transparent circle (Figure 2). Compared with strains YL6 and YL31, strain YL1 has the smallest colony diameter and relatively slow growth, but the size of the transparent circle is not different from the other strains, and the ratio of the diameter of its water hydrolysis circle to the diameter of the colony is the largest. Therefore, strain YL1 had the strongest ability to produce chitinase.
3.2.2. Phosphorus-Dissolving and Potassium-Dissolving Ability of Antagonistic Bacteria
Apart from strain YL31, both strain YL1 and strain YL6 can dissolve phosphorus (Figure 2). The growth rate of strain YL6 is greater, the transparent circle is larger, and the ratio of the transparent circle to the colony diameter is also higher, but its phosphorus-dissolving ability is not significantly different from that of strain YL1.
The experiment of releasing potassium showed that each bacterial strain produces yellow halos of different sizes on the screening medium plate containing bromothymol blue. This indicates that all three strains can produce acid and have a certain ability to dissolve potassium. Among them, strain YL1 showed the largest halo, and the D/d ratio was significantly greater than that of other strains, indicating that strain YL1 had the most effective acid production effect and the strongest potassium-decomposing ability.
3.3. Effects of Antagonistic Bacteria on Root-Knot Nematode
3.3.1. Root-Knot Nematode Egg Development
The normal development process of the untreated root-knot nematode eggs was shown in Figure S1A. Figure S1B–D showed the destructive effects on root-knot nematode eggs at the various stages after the treatment with the fermentation broth of the three strains. After the treatment with the fermentation broth of strain YL1, the protoplasm of the eggs in the single-cell stage is blurred and unevenly distributed; in the twin-cell and triple-cell stages, scattered uneven lumpy materials were formed. During the four-cell and blastocyst stages, vacuoles of different sizes were formed; The outline of the eggshell was blurred during the gastrula stage. The contents of the embryo severely disintegrated and gradually disappeared and finally became a dead egg that stops developing (Figure S1B). After strain YL6 was treated with the fermentation broth, vesiculation occurred in the twin-cell stage. The protoplasm in the blastocyst stage shrank toward the middle and was severely separated from the eggshell, and the root-knot nematode in the larval stage was severely disintegrated (Figure S1C). The eggs treated with the fermentation broth of strain YL31 also had a similar situation, that is, uneven distribution of protoplasm, vesicles, and plasmolysis. From the blastocyst stage, the egg appeared concave, and the protoplasm in the egg gathered toward the middle, gradually disintegrated, and disappeared (Figure S1D).
3.3.2. J2 of Root-Knot Nematode Development
The bodies of the nematodes that died normally were stiff, and there was no significant difference in the internal structure of the nematodes before death (Figure S2). The epidermis of the nematodes was smooth, and the outline was clear and complete. The size of the protoplasm in the body was uniform. After treatment with the fermentation broth of strain YL1 for 12 h, the internal structure of the nematodes disintegrated, the protoplasm decreased, and vesicles appeared. After 24 h, the nematodes were severely deformed, the epidermis deteriorated and gradually disappeared, and the internal materials were lost, forming large vesicles. After 12 h of treatment with the strain YL6 fermentation broth, the distribution of protoplasm in the nematodes was uneven, and a small number of vesicles appeared. After 24 h, the epidermis of the nematodes became thinner, and some of them completely disintegrated and disappeared. The protoplasm in the body was seriously damaged, forming rough lumps of different sizes. Similarly, vesicle formation, body wall disintegration, and complete disappearance occurred in the nematode bodies treated with the fermentation broth of the bacterial strain YL31.
3.4. Efficacy in Controlling Nematodes of Tomato
3.4.1. Effects of Antagonistic Bacteria on Root-Knot Nematodes
In the pot experiments (Figure S3A), compared with the control, the number of tomato root knots treated with different concentration dilutions of all strains was significantly reduced, but the inhibitory effect gradually weakened with the increase of fermentation broth dilution (Figure 3A,B). The strain YL1 stock solution had the most significant reduction in root knots with 76.4%, followed by the stock solution of YL6 with 65%. Under the 50-fold dilution, the inhibitory effects of strains YL6 and YL31 on the number of tomato root knots decreased significantly, and the difference between the two strains was not significant. There was no significant difference in control efficiency between the stock solution and the 10-fold dilution of strain YL31, and when it was diluted to 50 times, its control efficacy significantly weakened to 30.0% (Figure 3C). The control efficacy of strains YL1 and YL6 significantly weakened with the increase in dilution factors; however, the 50-fold dilution of strain YL1 could still achieve a control efficacy of 43.2%, suggesting that YL1 has a better biocontrol potential.
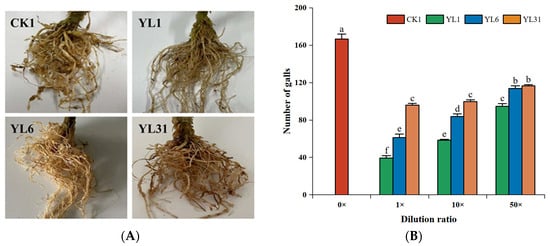
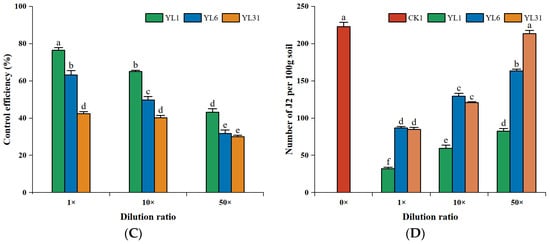
Figure 3.
Effects of different dilution factors of antagonistic bacteria on tomato root-knot nematodes. (A): Roots of tomato plants impacted by antagonistic strains; (B): Number of tomato root knots; (C): Control effect of root-knot nematodes in tomato plants; (D): Nematode population in 100 g soil. CK1: Infested soil uninoculated bacteria. YL1, YL6, and YL31: Three antagonistic bacteria against root-knot nematodes isolated from vermicompost. 0×, 1×, 10×, and 50× represent control, strain stock solution, and 10-fold and 50-fold dilutions, respectively. Different letters represent statistical significance at p < 0.05 by Duncan’s test.
Compared with the control, all strains reduced the population of nematodes in the tomato rhizosphere at different concentrations of stock dilution, but their inhibitory effect increased with lesser dilution (Figure 3D). The strain YL1 stock solution had the most significant inhibitory effect, and the population of rhizosphere nematodes was reduced by 85.7% compared with the control; the inhibitory effect of the 10-fold and 50-fold dilutions of strain YL1 on rhizosphere soil nematodes was significantly decreased, but the 50-fold dilution was still significantly different from the control, with an inhibition rate of 63.1%. The population of rhizosphere nematodes treated with the strains YL6 and YL31 stocks decreased by 61.1% and 62.0%, respectively, compared with the control. The 10-fold dilution of the two strains still had a significant inhibitory effect on the population of rhizosphere nematodes, and the inhibitory effect was similar. Under a 50-fold dilution, strain YL31 had no significant inhibitory effect on the population of rhizosphere nematodes. Except for the 50-fold dilution of strain YL31, various stock dilutions of strains YL1 and YL6 inhibited the reproduction of root-knot nematodes in the tomato rhizosphere to varying degrees.
3.4.2. Effects of Antagonistic Bacteria on Tomato Growth
The results of the analysis of tomato biomass and agronomic traits showed that the growth of tomato plants was inhibited after being infected by root-knot nematodes. Tomato height, stem diameter, and fresh weight of aboveground biomass all decreased (Figure 4A–C), while the fresh weight of roots infected with nematodes was either slightly or significantly higher than that of non-infected tomato plants (Figure 4D). After the fermentation broth of strains YL1, YL6, and YL31 were applied to the root-knot nematode-infected soil, compared with the uninoculated infected soil (CK1), the three strains all promoted tomato growth to varying degrees, but their growth-promoting effects differed. Among them, the stem diameter and the fresh weight of the aboveground biomass treated with the stock solution of strain YL1 increased by 68.8% and 100.8%, respectively, compared with CK1, which was close to the growth of the healthy soil (CK0).
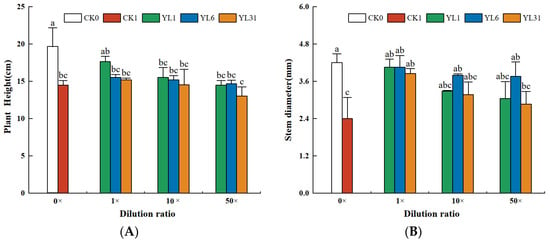
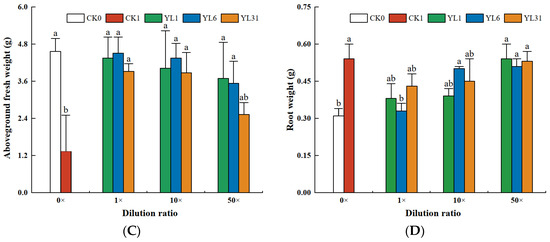
Figure 4.
The growth of tomato plants impacted by antagonistic bacteria. (A–D): Effect of different treatments on plant height, stem diameter, aboveground fresh weight, and root weight of tomato plants. CK0: Healthy soil. CK1: Infested soil uninoculated bacteria. YL1, YL6, and YL31: Three antagonistic bacteria against root-knot nematodes isolated from vermicompost. Different letters represent statistical significance at p < 0.05 by Duncan’s test.
The plant height and the fresh weight of the root with the stock solution of strain YL1 varied from those of CK0 and CK1, showing its improvement over the disease-infected soil but statistically insignificant. The 10-fold and 50-fold dilutions of the stock solution from strain YL1 could still significantly improve the tomato stem thickness and shoot fresh weight with little effect on plant height and root fresh weight. The stock solution of strain LY31 increased tomato stem diameter and shoot fresh weight, and its 10-fold dilution increased shoot fresh weight, while a 50-fold dilution had no positive effect on tomato growth.
3.5. Efficacy in Controlling Nematodes of Cucumber
During field experiments on cucumber plants (Figure S3B), inoculation with strains YL1, YL6, and YL31 considerably suppressed root-knot nematode infection (Table 1). Compared with the control, all treatments significantly reduced the root-knot index of the root-knot nematode population. The root-knot index for tomato plants treated with the control (CK) was 71.9%. The treatments of tomato plants with strains YL1, YL6, and YL31 reduced the root-knot index to 21.1%, 30.4%, and 43.3%, respectively. The control effects of antagonistic bacteria YL1, YL6, and YL31 were 70.6%, 57.8%, and 39.7%, respectively. Among them, strain YL1 had the highest control effect, followed by strain YL6. Compared with the control (CK), the nematode population in the soil treated with strains YL1, YL6, and YL31 was reduced by 65.9%, 43.9%, and 36.1%, respectively.

Table 1.
Effect of antagonistic bacteria on M. incognita of the cucumber plants in field experiment.
The three antagonistic bacteria also improved plant growth and yield (Table 2). The aboveground fresh weight and dry weight of cucumber plants were significantly increased with all bacteria treatments, and strain YL1 increased by 76.0% and 33.4%, respectively, compared with the control (CK). The underground fresh weight and dry weight of cucumber plants were not significantly affected by strain YL31 inoculation. Furthermore, compared with the control (CK), strains YL1, YL6, and YL31 enhanced the yield by 14.9%, 6.8%, and 4.3%, respectively.

Table 2.
Effect of antagonistic bacteria on cucumber growth with M. incognita in field experiment.
4. Discussion
Root-knot nematode disease is one of the most serious soil-borne diseases worldwide and can cause dramatic yield losses in vegetable crops [31]. Although chemical controls with nematicides have achieved remarkable results, inappropriate use of the same pesticide over a long period of time not only makes pathogens resistant to pesticides but also leads to environmental pollution [32].
Vermicompost is a natural ecological organic fertilizer. Studies have shown that vermicompost has a good control ability against root-knot nematodes [16,33]. In this study, 70 strains of bacteria, 38 strains of fungi, and 49 strains of actinomycetes were isolated from vermicompost, and the nematicide activity of their fermentation liquid was determined. After primary and secondary screening, three efficient and stable root-knot nematode antagonistic strains (YL1, YL6, and YL31) were discovered. Strains YL1 and YL31 were identified as Peribacillus frigoritolerans, and strain YL6 was identified as Lysinibacillus fusiformis. The hydrolysis zones formed by the three strains on gelatin and chitin plates reflected their potential to utilize collagen and chitin. The outer epidermis of root-knot nematodes is mainly composed of collagen protein. The eggshell is mainly composed of three parts, of which the middle layer is a protein-chitin cross-linked layer, accounting for 80% of the entire eggshell composition, providing strength support for the entire egg structure and being an important barrier to prevent infection from foreign microorganisms [34,35]. The effect of the antagonistic bacteria solution on the growth and development of root-knot nematode egg embryos and J2 was observed under a dissecting microscope. All three antagonistic bacteria resulted in severe disintegration and shedding of the epidermis of J2. Strains YL1 and YL6 resulted in lysis and disappearance of the epidermis of eggs. Although strain YL31 did not cause obvious peeling on the surface of the eggs, the internal structure of the eggs was seriously damaged due to the action of antagonistic bacteria and the phenomenon of vesiculation and loss of protoplasm. These results show that some proteases, hydrolytic enzymes, and small molecular metabolites produced by the three strains isolated from vermicompost can degrade or penetrate the epidermis of root-knot nematode eggs, hinder the normal development of eggs, destroy the morphological structure of J2, and lead to suppressing eggs and killing insects. There have been many reports on the control of root-knot nematodes by antagonistic metabolites. Among them, Paecilomyces lilacinus, which has been investigated the most, can produce chitinase and protease, which alter the internal structure of eggs, result in follicle cystization, and inhibit the normal hatching of eggs [36]. Trichoderma harzianum has been reported to be able to control root-knot nematode disease, and a protease produced by it plays an important role in the control of root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne incongnita) [37]. Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus can also produce one or several proteases or other secondary metabolites, which severely damage the eggshell [38,39,40]. Fallahzadeh et al. [41] obtained a strain of Bacillus wiedmannii and reported that the control of root-knot nematodes depends mainly on producing highly active chitinase, which destroys the eggs and eggshells of J2.
Bacillus-like bacteria are ubiquitous in various habitats in nature, and they have strong environmental adaptability. They are a valuable type of biocontrol bacteria for plant diseases and insect pests and can effectively promote the growth and development of plants [42,43]. The action mechanism of Bacillus in controlling plant root-knot nematodes is (1) to compete for nutrients and space; (2) to alter the action mode of root exudates and nematodes; (3) to produce toxic substances that are fatal for root-knot nematodes; and (4) to generate secondary metabolites that inhibit egg hatching and larval development [44]. Currently, Bacillus has been isolated and screened for the control of root-knot nematodes, including Bacillus thuringiensis [38], Bacillus amyloliquefaciens [45], Bacillus subtilis [46], Bacillus simplex [47], Bacillus firmus [48], Bacillus pumilus [49], Bacillus mycoides [50], and Bacillus megaterium and Bacillus cereus [9]. Peribacillus frigoritolerans is a multifunctional strain with the characteristics of preventing and controlling soil-borne diseases, promoting plant growth, and tolerating low temperature and saline-alkali environments [51]. Lu et al. [52] isolated a strain of Peribacillus frigoritolerans from a biogas slurry, and the control effect on tomato incognita was more than 80%. In this study, the Peribacillus frigoritolerans YL1 isolated from vermicompost has a control effect of 76.4% on tomato root-knot nematodes. Lysinibacillus widely exists in soil, oceans, plants, and animals, with a variety of physiological and metabolic characteristics, and can resist various harsh environments in nature. Ling et al. [53] discovered Lysinibacillus mangiferahumi isolated from the rhizosphere soil of mango plants, which produced nematiocidal volatile compounds with activities against M. incognita. Cheng et al. [54] screened a strain of Lysinibacillus macroides from soil and observed that it had a poisonous effect on M. incognita and could promote plant growth. In most cases, Lysinibacillus fusiformis has been isolated from soil, water, and plants. The research focus has been limited to the production of biosurfactants [55] and exopolysaccharides [48], degradation of crude oil [56], soil pollution remediation [57], inhibition of fungi [53], algae-lytic activity, and productivity of microalgae [58]. However, there are few reports on the control of nematode diseases. In this study, the high-efficiency nematicide of Lysinibacillus fusiformis was discovered from vermicompost, which is a practical strain resource for the biological control of root-knot nematodes.
Phosphorus and potassium are essential nutrients for plants [59], and the deficiency of phosphorus and potassium will reduce plant growth. However, most of the phosphorus and potassium in the soil is in the form of insoluble phosphorus and potassium, which cannot be directly absorbed by plants [60,61]. Thus, most crops require applications of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers to promote crop growth and improve crop quality and yield. However, the utilization rate of these chemical fertilizers is low, which is vulnerable to resulting in environmental pollution and waste of resources. Studies have shown that the insoluble phosphorus and potassium in the soil can be converted into available phosphorus and potassium through microorganisms and inoculants that can be utilized by plants, thereby promoting plant growth and quality improvement [62,63]. In this study, the three strains isolated and screened from vermicompost, except for strain YL31, which has no phosphorus-dissolving effect, can dissolve phosphorus and potassium. Moreover, the results of the greenhouse pot and field test also showed that the three bacterial strains not only have good control effects on root-knot nematodes but also promote crop growth. It has been shown in the literature that Peribacillus frigoritolerans and Lysinibacillus fusiformis both have a certain ability to dissolve phosphorus and potassium. Costa et al. [64] screened Peribacillus frigoritolerans from cambic calcisol soil, which has a high ability to solubilize phosphorus and potassium. Jha et al. [65] isolated Lysinibacillus fusiformis from the roots of Suaeda nudiflora, which can effectively improve plant growth by enhancing the dissolution of phosphorus in the soil. Santosh et al. [66] isolated and screened a strain of Lysinibacillus fusiformis with high ability to dissolve potassium from the rhizosphere soil of cotton. The three antagonistic bacteria screened in this study not only have a strong inhibitory effect on root-knot nematode incognita but also possess phosphorus- and potassium-dissolving abilities. These strains of bacteria have great potential to prevent and control root-knot nematodes and can be used for further investigation as a useful biological control agent for practical application.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we isolated three strains from vermicompost. The three antagonistic isolates displayed nematocidal activity as well as plant growth-promoting characteristics and were found to be efficient in controlling root-knot nematodes on tomato and cucumber crops. The results reveal the potential of the three isolates for microbial applications and commercial use as biocontrol agents in the field. There is an urgent need for more robust examinations under field conditions. The ability of the three isolates screened from this study to colonize in the rhizosphere, their interactions with other soil microorganisms, and nematocidal biological control of other crops all need to be studied further.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae10040407/s1: Table S1: Mortality of microorganism isolated from vermicompost to Meloidogyne incognita (24 h).; Table S2: Inhibitory effects of antagonistic microorganism on Meloidogyne incognita associated with different dilution factors; Figure S1: Effects of antagonistic bacteria on various development stages of root-knot nematode eggs; Figure S2: Effects of antagonistic bacteria on J2.; Figure S3: Pictures of tomato pot experiment (A) and cucumber field experiment (B).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Y. and C.L.; methodology, G.Z.; software, C.L.; validation, Y.W. and X.N.; formal analysis, F.D.; investigation, D.Y.; resources, L.Y.; data curation, J.S.; writing—original draft preparation, C.L.; writing—review and editing, L.Y.; visualization, C.L.; supervision, Y.W.; project administration, L.Y.; funding acquisition, L.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Program of Distinguished Professor of Liaoning Province China (01062920001).
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all those who provided helpful suggestions on this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mesa-Valle, C.M.; Garrido-Cardenas, J.A.; Cebrian-Carmona, J.; Talavera, M.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Global Research on Plant Nematodes. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, G.C.; Egnin, M.; Bonsi, C. The Impact of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes on Agriculture and Methods of Control. In Nematology—Concepts, Diagnosis and Control; Shah, M.M., Mahamood, M., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; pp. 121–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, D.L.; Cortada, L.; Dalzell, J.J.; Claudius-Cole, A.O.; Haukeland, S.; Luambano, N.; Talwana, H. Plant-Parasitic Nematodes and Food Security in Sub-Saharan Africa. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inácio, M.L.; Faria, J.M.S.; Haukeland, S. Editorial: Novel approaches for sustainable crop yield and management of plant-parasitic nematodes. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1274757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.T.; Haegeman, A.; Danchin, E.G.J.; Gaur, H.S.; Helder, J.; Jones, M.G.K.; Kikuchi, T.; Manzanilla-López, R.; Palomares-Rius, J.E.; Wesemael, W.M.L.; et al. Top 10 Plant-Parasitic Nematodes in Molecular Plant Pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 946–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, F.N. Development of Alternative Strategies for Management of Soilborne Pathogens Currently Controlled with Methyl Bromide. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2003, 41, 325–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubertot, J.N.; West, J.S.; Bousset-Vaslin, L.; Salam, M.U.; Barbetti, M.J.; Diggle, A.J. Improved Resistance Management for Durable Disease Control: A Case Study of Phoma Stem Canker of Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus). Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 114, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damalas, C.A.; Eleftherohorinos, I.G. Pesticide Exposure, Safety Issues, and Risk Assessment Indicators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 1402–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antil, S.; Kumar, R.; Pathak, D.V.; Kumar, A.; Panwar, A.; Kumari, A. Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria—Bacillus Cereus KMT-5 and B. Megaterium KMT-8 Effectively Suppressed Meloidogyne Javanica Infection. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 174, 104419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiddin, F.A.; Khan, M.R. Efficacy of newly developed biopesticides for the management of wilt disease complex of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Legume Res. 2019, 42, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, F.E.d.F.; Aguilar-Marcelino, L.; Braga, F.R. Editorial: Nematophagous fungi as nematode control agents. Front. Fungal Biol. 2024, 4, 1353132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.; Vicente, C.S.L.; Menéndez, E.; Faria, J.M.S.; Rusinque, L.; Camacho, M.J.; Inácio, M.L. The Fight against Plant-Parasitic Nematodes: Current Status of Bacterial and Fungal Biocontrol Agents. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqsood, A.; Aslam, M.N.; Khaliq, H.; Shakeel, M.T.; Wu, H.Y.; Fahad, S. Endophytic Bacillus spp. Mediated Plant Growth Promotion of Tomato Seedlings and Suppression of Meloidogyne incognita and Fusarium oxysporum Disease Complex. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 43, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D. Effectiveness of various nematode-trapping fungi for biocontrol of the Meloidogyne incognita in tomato (Lycopersicion esculentum Mill.). Rhizosphere 2024, 29, 100845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogollón-Ortiz, A.M.; Monteiro, T.S.A.; de Freitas, L.G.; de Queiroz, M.V. Potential of different species of actinobacteria in the management of Meloidogyne javanica. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A.A.; Shakeel, A.; Waqar, S.; Handoo, Z.A.; Khan, A.A. Microbes vs. Nematodes: Insights into Biocontrol through Antagonistic Organisms to Control Root-Knot Nematodes. Plants 2023, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, K.W.; Chia, S.R.; Yen, H.W.; Nomanbhay, S.; Ho, Y.C.; Show, P.L. Transformation of Biomass Waste into Sustaina ble Organic Fertilizers. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghman, R.; Bhatti, M.T.; Najabat, Z.; Hyder, S.; Rizvi, Z.F.; Gondal, A.S.; Zafar, Z.; Malik, S.; Iqbal, R.; Hafeez, A.; et al. Organic amendments: A natural way to suppress phytopathogens, a sustainable approach to go green. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2023, 47, 602–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; De Castro, F.; Aprile, A.; Benedetti, M.; Fanizzi, F.P. Vermicompost: Enhancing Plant Growth and Combating Abiotic and Biotic Stress. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, S.; Asri, F.O. Importance of Vermicompost in Tomato Plant Cultivation and Improvement of Some Soil Properties. Compost. Sci. Util. 2023, 29, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhair, R.; Moustafa, Y.T.A.; Mustafa, N.S.A.; El-Dahshouri, M.F.; Zhang, L.X.; Ageba, M.F. Efficacy of amended vermicompost for bio-control of root knot nematode (RKN) Meloidogyne incognita infesting tomato in Egypt. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 27, 102397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikoria, R.; Ohri, P. Application of neem waste vermicompost in compensating nematode induced stress and upregulating physiological markers of tomato plants under glass house conditions after 10 days of exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2023, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Liu, M.; Jiang, L.; Chen, X.; Griffiths, B.S.; Li, H.; Hu, F. Vermicompost Increases Defense against Root-Knot Nematode (Meloidogyne Incognita) in Tomato Plants. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 105, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Devindrappa; Hazra, K.K.; Singh, U.; Gupta, S. Eco–Friendly Management of Meloidogyne Javanica in Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Using Organic Amendments and Bio–Control Agent. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.A.M.; Phillips, M.S.; Blok, V.C. Molecular diagnostic key for identification of single juveniles of seven common and economically important species of root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.). Plant Pathol. 2007, 56, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.Z.; Cai, M.Y. Identification System Manual of Common Bacteria; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.N.; Mohandas, C.; Nambisan, B. Purification, structural elucidation and bioactivity of tryptophan containing diketopiperazines, from Comamonas testosteroni associated with a rhabditid entomopathogenic nematode against major human-pa-thogenic bacteria. Peptides 2014, 53, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, K.R. Design of greenhouse and microplot experiments for evaluation of plant resistance to nematodes. In Plant Nematology Laboratory Manual; Zuckerman, B.M., Mai, W.F., Harrison, M.B., Station, M.A.E., Eds.; University of Massachusetts Amherst: Amherst, MA, USA, 1985; pp. 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, K.; Amir, K.; Asgar, A.; Saba, F.; Ahmad, S.M. Root-Knot Nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.): Biology, Plant-Nematode Interactions and Their Environmentally Benign Management Strategies. Gesunde Pflanz. 2023, 75, 2187–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, W. A rapid centrifugal flotation technique for extracting nematodes from soil. Plant Dis. Report. 1964, 48, 692. [Google Scholar]
- Botelho, A.O.; Campos, V.P.; Da Silva, J.C.P.; Freire, E.S.; de Pinho, R.S.C.; Barros, A.F.; Oliveira, D.F. Physicochemical and biological properties of the coffee (Coffea arabica) rhizosphere suppress the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne exigua. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2019, 29, 1181–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Q.X.; Song, B. Chemical nematicides: Recent research progress and outlook. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12175–12188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Cao, Y.; Dong, Q.E.; Tong, J.Y.; Mo, M.H. Vermicomposting of Pleurotus eryngii spent mushroom substrates and the possible mechanisms of vermicompost suppressing nematode disease caused by Meloidogyne incognita. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, D. Nematode Egg-Shells. Parasitology 1980, 81, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgwyn, B.; Nagel, B.; Ryerse, J.; Bolla, R.I. Heterodera Glycines: Eggshell Ultrastructure and Histochemical Localization of Chitinous Components. Exp. Parasitol. 2003, 104, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardi, N.S.; Sosa, A.L.; Etcheverry, M.G.; Passone, M.A. In vitro characterization bioassays of the nematophagous fungus Purpureocillium lilacinum: Evaluation on growth, extracellular enzymes, mycotoxins and survival in the surrounding agroecosystem of tomato. Fungal Biol. 2022, 126, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nafady, N.A.; Sultan, R.; El-Zawahry, A.M.; Mostafa, Y.S.; Alamri, S.; Mostafa, R.G.; Hashem, M.; Hassan, E.A. Effective and Promising Strategy in Management of Tomato Root-Knot Nematodes by Trichoderma harzianum and Arbuscular Mycorrhizae. Agronomy 2022, 12, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Pang, C.Y.; Zheng, Z.Q.; Zhou, W.; Guo, Z.Q.; Xiao, D.Y.; Du, H.W.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M.; Sun, M.; et al. Aminopeptidase MNP-1 triggers intestine protease production by activating daf-16 nuclear location to degrade pore-forming toxins in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, I.; Van Rensburg, P.J.J.; Claassens, S. Effect of cultivation media and temperature on metabolite profiles of three nematicidal Bacillus species. Nematology 2022, 24, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Y.; Wang, P.Y.; Yang, L.L.; Rang, X.; Zhou, W.Z.; Liu, Y.J. Chemotaxis of Meloidogyne incognita Response to Rhizosphere Bacteria. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahzadeh-Mamaghani, V.; Shahbazi-Ezmareh, R.; Shirzad, A.; Moslehi, S. Possible mechanisms of action of Bacillus wiedmannii AzBw1, a biocontrol agent of the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne arenaria. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2023, 33, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacic, V.; Miljakovic, D.; Marinkovic, J.; Ignjatov, M.; Milosevic, D.; Tamindzic, G.; Ivanovic, M. Bacillus Species: Excellent Biocontrol Agents against Tomato Diseases. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Manzano, F.E.; Amora, D.X.; Martínez-Gómez, A.; Moelbak, L.; Escobar, C. Biocontrol of Meloidogyne spp. in Solanum lycopersicum using a dual combination of Bacillus strains. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1077062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.H. Application Effect of Bacillus in Tomato Root Knot Nematode Disease Control. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2024, 18, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, A.P.A.; Pankaj, D.; Singh, D.; Singh, A.K.; Sowmya, R. Nematicidal potential of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria against Meloidogyne incognita infesting tomato under protected cultivation. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2022, 32, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinardo-Miranda, L.L.; Miranda, I.D.; Silva, H.D.S.; Fracasso, J.V. Biological control of phytoparasitic nematodes in sugarcane fields. Pesqui. Agropecuária Trop. 2022, 52, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wen, C.; Liu, W.; Dong, D.; Qiu, J.; Liu, T. Screening and Identification of Biocontrol Bacterial Against Root-Knot Nematode. North. Hortic. 2016, 9, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settu, V.; Annaiyan, S.; Mannu, J. Revealing the genetic arsenal of Bacillus firmus TNAU1: Unleashing nematicidal and plant growth promotion traits. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 129, 102177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.-M.; Liu, R.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.-P.; Song, W.-W.; Zhang, J.; Liang, C.; Zhao, H.-H.; Shi, Q.-Q. Volatile Organic Compounds of Bacillus pumilus Strain S1-10 Exhibit Fumigant Activity Against Meloidogyne incognita. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 3057–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, M.; Tan, J.; Xiang, B.K.; Shi, H.L.; Chen, H.H.; Peng, W.X.; Yin, Z.C. Effects of different Bacillus on bacterial community of tobacco rhizosphere soil and control of root-knot nematodes. Tob. Sci. Technol. 2022, 55, 8–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Isolation and Identification of Salt-Tolerant Growth-Promoting Bacteria and the Effects on Brassica Campestris under Salt-Alkali Conditions. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian City, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.H.; Ruan, Z.Y.; Zhao, B.Q.; Wang, H.M.; Zhao, J.C.; Zhao, W.Y.; Liu, H.; Sou, Z.; Wang, Y.W.; Liu, X.F. The Applications of Brevibacterium frigoritolerans and Microbial Agents. CN 103952348 B, 11 January 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.-L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, L.; Mo, M.-H.; Li, W.-J.; Yang, F.-X. Lysinibacillus mangiferahumi sp. nov., a new bacterium producing nematicidal volatiles. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2012, 102, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, D.W.; Cheng, F.X.; Zhu, C.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Shi, X.B.; Zheng, L.M.; Su, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.Y. Isolation, identification and application of a strain of Lysinibacillus macrolides against Meloidogyne incognita. J. South. Agric. 2021, 52, 2765–2775. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, Q. Using large-scale multi-module NRPS to heterologously prepare highly efficient lipopeptide biosurfactants in recombinant Escherichia coli. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 159, 110068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathivanan, K.; Chandirika, J.U.; Vinothkanna, A.; Govindarajan, R.K.; Meng, D.; Yin, H. Characterization and Biotechnological Functional Activities of Exopolysaccharides Produced by Lysinibacillus fusiformis KMNTT-10. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 1742–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, P.A.; Ebudola, A.N.; Olusebi, Y.K.; Rafi, N.; Fawzhia, O.S.J.; Oluwaseun, O.I. Hydrocarbon Utilizing and Metal Tolerant Bacteria Simultaneously Degrade Hydrocarbons and Detoxify Metals in Petroleum Contaminated Soil. Geomicrobiol. J. 2023, 40, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, N.R.; Zavala, J.; Gil-Kodaka, P.; Diringer, B. Evaluation of bacterial strains to improve the productivity of microalgae used in bivalve hatcheries in Peru. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2022, 53, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trukhachev, V.I.; Belopukhov, S.L.; Grigoryeva, M.; Dmitrevskaya, I.I. Study of the Sustainability of Ecological and Chemical Indicators of Soils in Organic Farming. Sustainability 2024, 16, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreshizadeh, S.; Calvo-Pena, C.; Ruiz-Munoz, M.; Otero-Suarez, R.; Coque, J.J.R.; Cobos, R. Pseudomonas taetrolens ULE-PH5 and Pseudomonas sp. ULE-PH6 Isolated from the Hop Rhizosphere Increase Phosphate Assimilation by the Plant. Plants 2024, 13, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumare, A.; Sarr, D.; Diedhiou, A.G. Potassium sources, microorganisms and plant nutrition: Challenges and future research directions. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, D.; López, J.E.; Saldarriaga, J.F. Plant Growth-Promoting and Biocontrol Potential of Aspergillus tubingensis and Talaromyces islandicus. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.J.; Xiao, L.H.; Guo, X.L.; Zhu, Y.Z.; An, X.L.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, D.L. Effects of inoculating different mycorrhizal fungi on rhizosphere soil fungi and nutrient uptake of blueberry. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2024, 65, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.N.; Gil, T.; Teixeira, R.; dos Santos, A.S.R.; Romão, I.R.; López, C.S.; Vílchez, J.I. Combined Use of a Bacterial Consortium and Early-Colonizing Plants as a Treatment for Soil Recovery after Fire: A Model Based on Los Guajares (Granada, Spain) Wildfire. Biology 2023, 12, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, Y.; Mohamed, H.I. Inoculation with Lysinibacillus fusiformis Strain YJ4 and Lysinibacillus sphaericus Strain YJ5 Alleviates the Effects of Cold Stress in Maize Plants. Gesunde Pflanz. 2023, 75, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosh, S.; Velmourougane, K.; Idapuganti, R.G.; Manikandan, A.; Blaise, D. Potassium Solubilizing Potential of Native Bacterial Isolates from Cotton Rhizosphere of Rainfed Vertisols. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2022, 45, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).