Layer Inoculation as a New Technology to Resist Volatile Fatty Acid Inhibition during Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion: Methane Yield Performance and Microbial Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrates and Inoculum
2.2. Experimental Design and Set-up
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Microbial Diversity Analysis
2.4.1. Sample Collection
2.4.2. Deoxyribonucleic Acid Extraction and Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification
2.4.3. Illumina MiSeq Sequencing and Processing of Sequencing Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion Performance
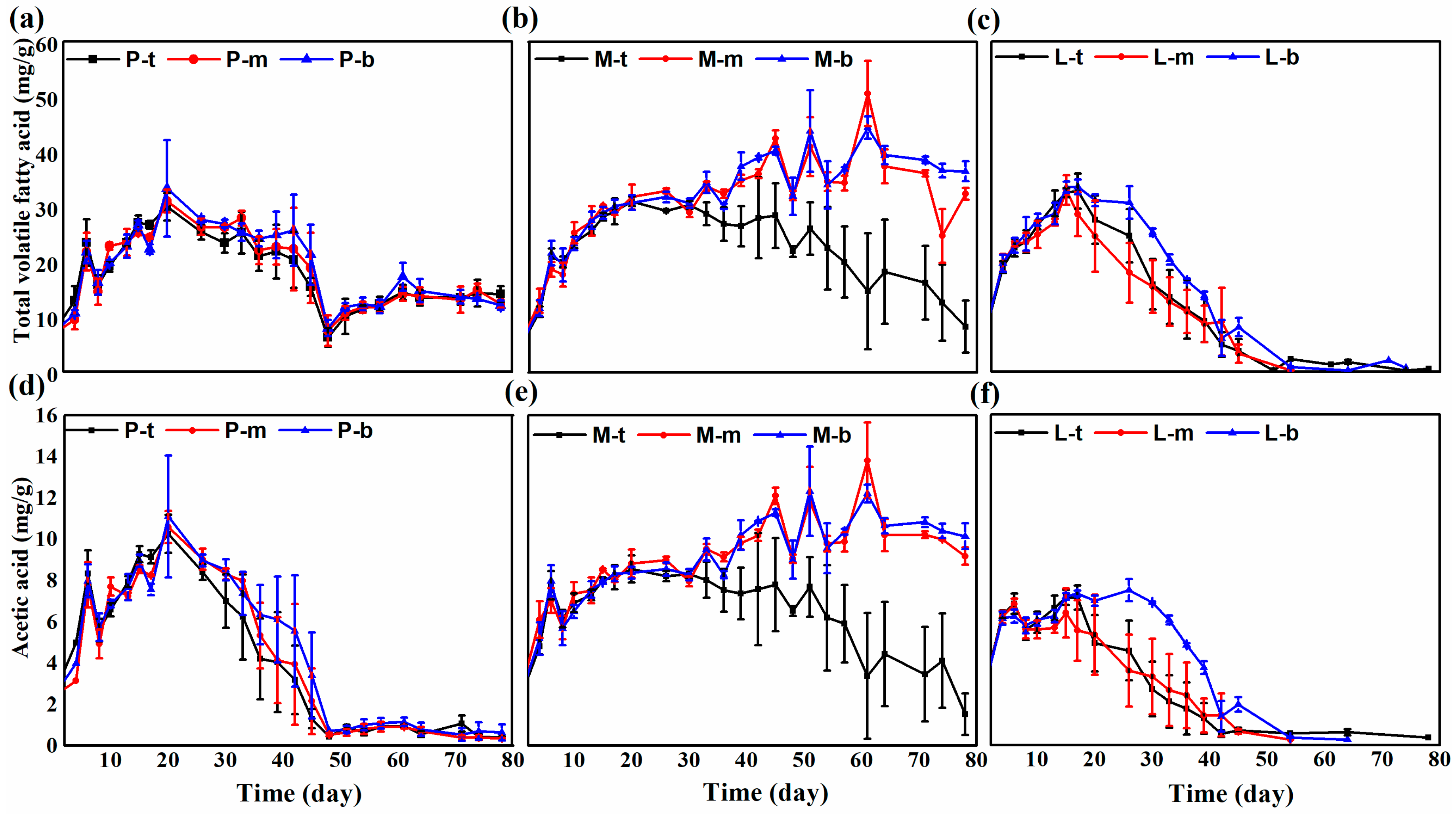
3.2. Volatile Fatty Acid Concentrations during Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion
3.3. Ammonia Concentration during Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion
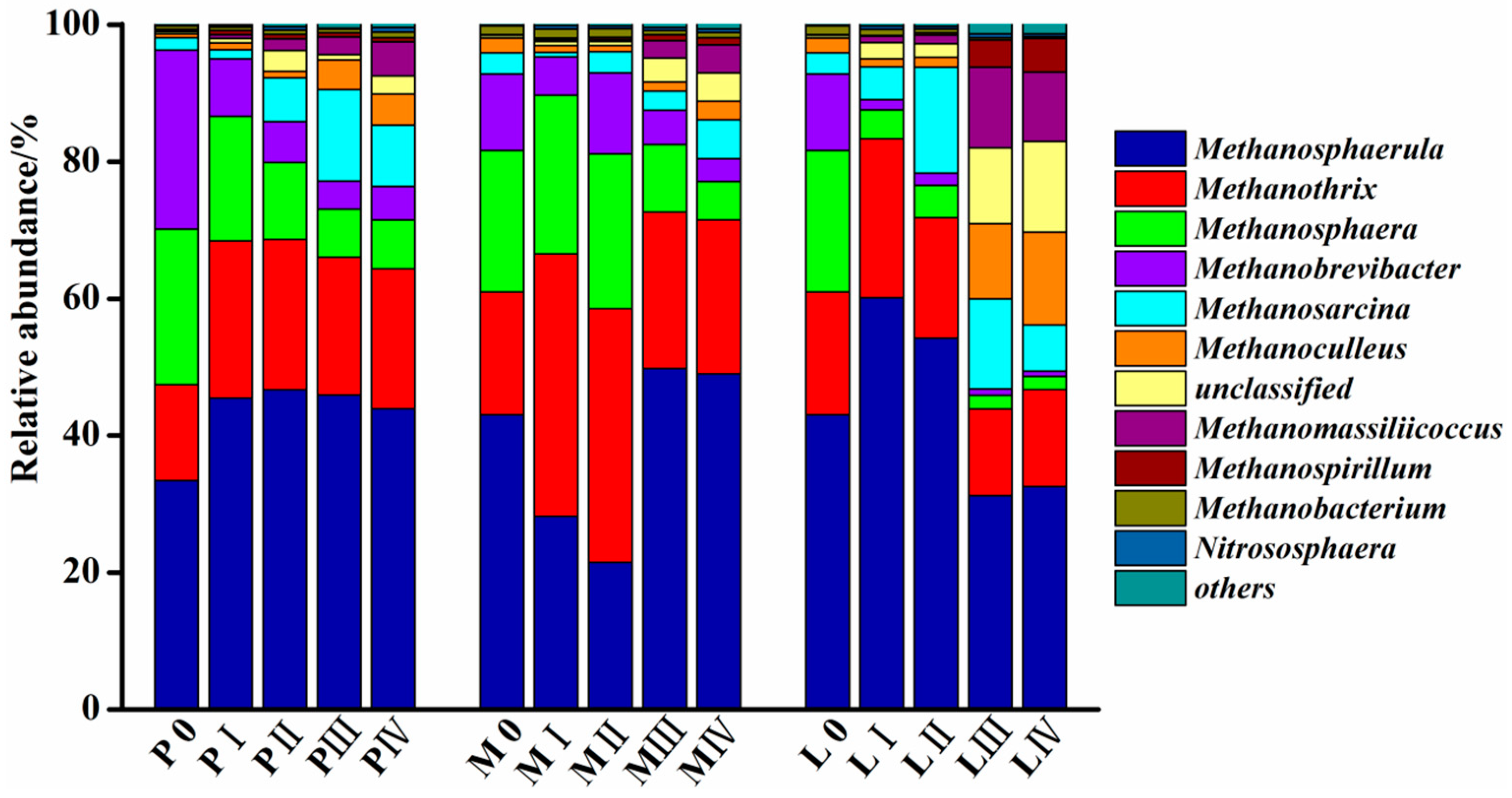
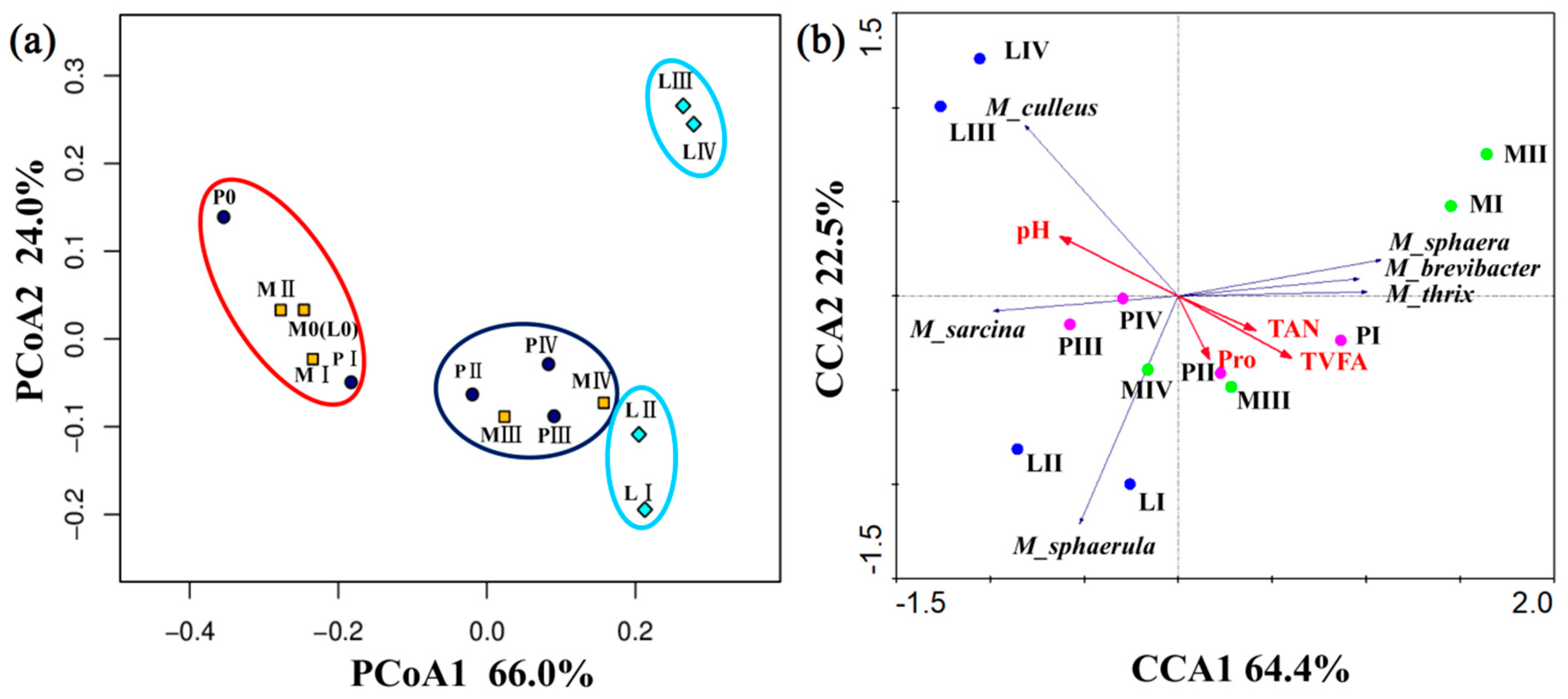
3.4. Changes in the Methanogenic Archaea Community during Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | English Full Name |
| AD | Anaerobic digestion |
| TS | Total solids |
| Ss-AD | Solid-state anaerobic digestion |
| L-AD | Liquid anaerobic digestion |
| VFA | Volatile fatty acid |
| VS | Volatile solids |
| PM | Pig manure |
| MS | Maize straw |
| AV | Average value |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| C/N | Carbon-to-nitrogen ratio |
| TCD | Thermal conductivity detector |
| SCOD | Soluble chemical oxygen demand |
| TAN | Total ammonia nitrogen |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| OTU | Operational taxonomic unit |
| SMY | Specific methane yield |
| HM | Hydrogenotrophic methanogens |
| AM | Acetotrophic methanogens |
| PCoA | Principal coordinates analysis |
| CCA | Canonical correspondence analysis |
References
- Gu, X.; Du, H.; Khan, J. Disentangling the heterogeneous effects of different support policies on livestock and poultry farmers’ willingness to utilize manure resources: Evidence from central China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1070423. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Huang, R.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Han, Y.; Xiao, B.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, B.; Yu, G. Biohythane production and microbial characteristics of two alternating mesophilic and thermophilic two-stage anaerobic co-digesters fed with rice straw and pig manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Liu, R.H.; Sun, C. A review of methane production from agricultural residues in China. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2016, 54, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Jia, S.; Song, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, J.; Cui, Z.; Han, Y.; et al. Methane production from the co-digestion of pig manure and corn stover with the addition of cucumber residue: Role of the total solids content and feedstock-to-inoculum ratio. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Park, S.Y.; Zhu, J.Y. Solid-state anaerobic digestion for methane production from organic waste. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2011, 15, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlottenburg, A.; Rosenheim, H. Anaerobic digestion. Eur. Bioplastics e.V. 2015, 8. Available online: https://docs.european-bioplastics.org/publications/bp/EUBP_BP_Anaerobic_digestion.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Di Maria, F.; Gigliotti, G.; Sordi, A.; Micale, C.; Zadra, C.; Massaccesi, L. Hybrid solid anaerobic digestion batch: Biomethane production and mass recovery from the organic fraction of solid waste. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, Z.W.; Tang, L.; Li, Y. A mass diffusion-based interpretation of the effect of total solids content on solid-state anaerobic digestion of cellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.R.; Benbelkacem, H.; Bollon, J.; Bayard, R.; Escudie, R.; Buffiere, P. Influence of moisture content on the specific methanogenic activity of dry mesophilic municipal solid waste digestate. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 1032–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y. Influence of total solid and stirring frequency on performance of dry anaerobic digestion treating cattle manure. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 79, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbassi-Guendouz, A.; Brockmann, D.; Trably, E.; Dumas, C.; Delgenés, J.P.; Steyer, J.P.; Escudié, R. Total solids content drives high solid anaerobic digestion via mass transfer limitation. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riya, S.; Suzuki, K.; Meng, L.Y.; Zhou, S.; Terada, A.; Hosomi, M. The influence of the total solid content on the stability of dry-thermophilic anaerobic digestion of rice straw and pig manure. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Mathematical modeling of solid-state anaerobic digestion. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2015, 51, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.; Li, Y. Solid state anaerobic co-digestion of yard waste and food waste for biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 127, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ge, X.; Li, Y. Solid-state anaerobic co-digestion of spent mushroom substrate with yard trimmings and wheat straw for biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, L.; Durante, M.; Pauss, A.; Lespinard, O.; Ribeiro, T.; Lamy, E. Quantifying physical structure changes and non-uniform water flow in cattle manure during dry anaerobic digestion process at lab scale: Implication for biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Hu, Y.Y.; Wang, S.F.; Cao, Z.P.; Li, H.Z.; Fu, X.M.; Wang, K.J.; Zuo, J.E. Effects of thermal treatment on high solid anaerobic digestion of swine manure: Enhancement assessment and kinetic analysis. Waste Manag. 2017, 62, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, F.; Ge, X.; Li, Y. Challenges and strategies for solid-state anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motte, J.C.; Escudie, R.; Bernet, N.; Delgenes, J.P.; Steyer, J.P.; Dumas, C. Dynamic effect of total solid content, low substrate/inoculum ratio and particle size on solid-state anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, F.; Lin, L.; Li, Y. Comparison of digestate from solid anaerobic digesters and dewatered effluent from liquid anaerobic digesters as inocula for solid state anaerobic digestion of yard trimmings. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, F.; Li, Y. Solid-state anaerobic co-digestion of hay and soybean processing waste for biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 154, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.D.; Zhao, L.X.; Feng, J.; Yao, Z.L.; Huang, K.M.; Luo, J.; Wei, S.M.; Chen, J.K. Sequencing batch dry anaerobic digestion of mixed feedstock regulating strategies for methane production: Multi-factor interactions among biotic and abiotic characteristics. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 284, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagbohungbe, M.O.; Dodd, I.C.; Herbert, B.M.J.; Li, H.; Ricketts, L.; Semple, K.T. High solid anaerobic digestion: Operational challenges and possibilities. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2015, 4, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation, W.E.; Association, A. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.H.; Hai, F.I.; Zhan, X.M.; Guo, W.S.; Ngo, H.H.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Anaerobic co-digestion: A critical review of mathematical modelling for performance optimization. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 498–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. Comparison of premixing methods for solid-state anaerobic digestion of corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Hydrogen–methane production from swine manure: Effect of pretreatment and VFAs accumulation on gas yield. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stronach, S.; Rudd, T.; Lester, J.N. Anaerobic Digestion Processes in Industrial Waste Water Treatments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Li, G.X.; Chi, M.H.; Sun, Y.B.; Zhang, J.X.; Jiang, S.X.; Cui, Z.J. Effects of co-digestion of cucumber residues to corn stover and pig manure ratio on methane production in solid state anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Gómez, X.; Otero, M.; Morán, A. Anaerobic digestion of solid slaughterhouse waste (SHW) at laboratory scale: Influence of co-digestion with the organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW). Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 40, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Dong, B.; Wu, B.; Dai, X. High-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge under mesophilic conditions: Feasibility study. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, H.T.; Qiu, Y.Q.; Ren, L.H.; Jian, B. Microbial characteristics in anaerobic digestion process of food waste for methane production–A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Yu, Z.H.; Lu, J.X.; Li, D.Y.; Wang, G.Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.Y.; Xu, F.Q.; et al. Effect of inoculum and substrate/inoculum ratio on the performance and methanogenic archaeal community structure in solid state anaerobic co-digestion of tomato residues with dairy manure and corn stover. Waste Manag. 2018, 81, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiman, W.B.; Rainey, F.; Kämpfer, P.; Trujillo, M.; Chun, J.; DeVos, P.; Hedlund, B.; Dedysh, S. Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; p. 410. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.M.; Li, L.H.; Yuan, Z.H. Acclimation of acid-tolerant methanogenic propionate-utilizing culture and microbial community dissecting. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.; Lanjekar, V.B.; Dhakephalkar, P.K.; Dagar, S.S. Cultivation of multiple genera of hydrogenotrophic methanogens from different environmental niches. Anaerobe 2018, 50, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Yang, H.N.; Zheng, D.; Pu, X.D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Deng, L.W. Methanogenic activity and microbial communities characteristics in dry and wet anaerobic digestion sludges from swine manure. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 152, 1073–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| AV ± SD | Total Solid (TS)% | Volatile Solid (VS)% | Total Organic Carbon (TOC)% | Total Nitrogen (TN)% | Carbon-to-Nitrogen Ratio (C/N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM | 27.5 ± 0.7 | 22.0 ± 0.3 | 39.4 ± 0.2 | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 10.1 |
| MS | 90.0 ± 0.2 | 81.3 ± 0.1 | 77.0 ± 0.8 | 1.3 ± 0.0 | 59.2 |
| Inoculum | 20.9 ± 0.1 | 10.4 ± 0.2 | 32.0 ± 0.4 | 3.5 ± 0.0 | 9.3 |
| Reactor | P | M | L |
|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate | PM | PM + MS a | PM + MS a |
| Substrate/inoculum | 3:1 | 3:1 | 3:1 |
| Inoculation method | Mixed b | Mixed b | Layer c |
| Feeding (kg TS) | 10.2 | 10.2 | 10.2 |
| Total solid (TS) (%) | 20.3 | 20.3 | 20.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Kong, D.; Gao, W.; Liang, J.; Liu, F.; Du, L. Layer Inoculation as a New Technology to Resist Volatile Fatty Acid Inhibition during Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion: Methane Yield Performance and Microbial Responses. Fermentation 2023, 9, 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060535
Gao X, Li Z, Zhang K, Kong D, Gao W, Liang J, Liu F, Du L. Layer Inoculation as a New Technology to Resist Volatile Fatty Acid Inhibition during Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion: Methane Yield Performance and Microbial Responses. Fermentation. 2023; 9(6):535. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060535
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xingliang, Zhuowu Li, Keqiang Zhang, Dewang Kong, Wenxuan Gao, Junfeng Liang, Fuyuan Liu, and Lianzhu Du. 2023. "Layer Inoculation as a New Technology to Resist Volatile Fatty Acid Inhibition during Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion: Methane Yield Performance and Microbial Responses" Fermentation 9, no. 6: 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060535
APA StyleGao, X., Li, Z., Zhang, K., Kong, D., Gao, W., Liang, J., Liu, F., & Du, L. (2023). Layer Inoculation as a New Technology to Resist Volatile Fatty Acid Inhibition during Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion: Methane Yield Performance and Microbial Responses. Fermentation, 9(6), 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060535







