Abstract
Ultrasound is considered a physical technology that can be applied at various stages of food processing to optimise resources and reduce production time. In this study, the influence of ultrasonic treatments at different power levels (0 W, 100 W, 200 W, and 300 W) on three Isaño genotypes (yellow, yellow with purple eyes, and purple) during alcoholic fermentation was investigated. The main parameters assessed were yeast growth kinetics, ethanol production, and substrate consumption in an ultrasonic bath operating at a frequency of 50 kHz. The findings demonstrated enhanced yeast growth, accelerated substrate consumption, and increased ethanol production compared to the control (untreated sample). However, the impact of ultrasound on fermentation decreased as the power level increased. Notably, an ultrasonic power of 100 W applied over 84 h of fermentation resulted in the highest ethanol yield (10.36% v/v) in the purple Isaño genotype. In conclusion, ultrasonic treatment is a promising approach to improve the fermentation process of Isaño, potentially enabling its development as a functional beverage with both nutritional and therapeutic properties.
1. Introduction
The mashua or Isaño (Tropaeolum tuberosum) is a tuberous plant belonging to the family Tropaeolaceae [1]. This annual herbaceous plant is currently cultivated in the high Andean regions of Peru, Bolivia, Ecuador, Venezuela, Colombia, and Argentina [2,3]. There are several genotypes, the most common being yellow, purple, and yellow with purple eyes. Consumed as a staple food by Andean populations, mashua (Isaño) is also recognised for its medicinal properties [4]. Traditionally, it has been used in the treatment of venereal diseases, skin and respiratory disorders, urinary and prostate disorders, and for its hepatoprotective and nephroprotective effects. Additionally, it exhibits anticancer activity and functions as a diuretic agent [5,6,7]. These benefits are attributed to its rich composition of vitamins, amino acids, minerals, fibres, polyphenols, flavonoids, anthocyanins, antioxidants, fatty acids, glucosinolates, and alkamides [7,8,9,10,11,12]. Despite its potential, the industrial use of Isaño remains limited [13]. However, recent studies have investigated its use in food products, including bakery products [14], sausages [15], and beverages [16]. Previous research suggests that a promising approach to using Isaño is its transformation into a fermented alcoholic beverage known as “Isaño wine”, due to its high starch content (41.35 ± 1.60% dry basis) [17].
Traditionally, wine is produced from grapes [18]. However, wines have also been made from other fruits and tubers, including pineapple, nanche, pomegranate, papaya, and oca [19,20]. Driven by this diversity, our research group aims to explore the potential of an Andean crop for the production of a fermented beverage with consumer benefits. The fermentation of Isaño presents several challenges, particularly the conversion of starch into fermentable sugars and yeast inhibition due to the presence of glucosinolates and phenolic compounds. To overcome these obstacles, a physical, chemical, or enzymatic pretreatment, or a combination of these, must be applied to hydrolyse the starch and release simple sugars, such as glucose and maltose, which can be efficiently utilised by yeasts in winemaking [21]. Traditional wine fermentation is a process that typically requires long maturation times and significant storage space [22]. To optimise this process and reduce production time, several innovative technologies have been applied, including pulsed electric fields, gamma radiation, high pressure, and ultrasound [23]. While different approaches have been investigated, their practical application depends on various factors, such as equipment availability, process efficiency, and impact on microbial activity [24,25].
Among these techniques, ultrasound has emerged as a particularly promising approach in the food industry, as it not only accelerates fermentation but also improves the technological and functional properties of food products [26,27]. This technology is based on the cavitation effect, which consists of the implosion of air bubbles generated by ultrasonic waves at frequencies above the human hearing threshold (>16 kHz). This phenomenon facilitates the physical or chemical modification of food properties. Several studies have reported on the use of ultrasound in fermentation processes, highlighting that its effect depends on the growth phase of the yeast, as well as the frequency and power of the ultrasound applied. It has been reported that the application of ultrasound in the fermentation of cider with Hansenia sp., at a frequency of 40 kHz and a power of 100 W, accelerated the growth of the yeast, reaching values up to 10 times higher than those of the control group [28]. Similarly, in beer fermentation with Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ultrasonic treatment at 40 kHz and 120 W increased the glucose fermentation rate by 2.3 and 2.5 times at temperatures of 30 °C and 20 °C, respectively [29]. Other studies reported that the use of 40 kHz and 160 W improved ethanol production by 13.18% [30], while the use of 23 kHz and 120 W increased it by 19.33% [31]. On the other hand, treatment with low-frequency ultrasound in the range of 20–30 kHz and with power levels of 23.4–26.7 W reduced fermentation time by 6–9 h compared to controls [32]. Taken together, these results demonstrate that the use of ultrasound in fermentation reduces process time and improves product quality characteristics [26]. Furthermore, it is regarded as a green, sustainable, innovative, cost-effective, rapid, portable, and easy-to-use technology, and its non-destructive nature makes it highly suitable for fermentation processes [33]. However, its effectiveness depends on the type and frequency of ultrasound, the type of antinutrient, the duration of exposure, and the composition of the food. Therefore, the aim of this experimental study was to investigate the effect of ultrasound power and Isaño genotypes on fermentation kinetics parameters.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
Isaño genotypes (yellow, yellow with purple eyes, and purple) were cultivated in the agroecological zone of Yunguyo, Puno, Peru, at an altitude of 3880 m a.s.l., with latitude coordinates 15°38′30″ S and longitude 69°49′50″ W. Samples of each genotype were collected using a random sampling method and transported to the laboratory for further processing. Prior to processing, they were washed with tap water to remove any surface contaminants, then dried at room temperature and stored in a dark place at 25 ± 2 °C with a relative humidity of 68.1 ± 1.5%.
2.2. Winemaking
The production of Isaño wine followed the procedure described by Nnaemeka et al. [34], with some modifications. Initially, the tubers were selected, with any damaged ones removed, washed with tap water, and disinfected with a sodium hypochlorite solution at 200 ppm. Subsequently, 100 g of Isaño tubers were cooked at 85 °C for 30 min. After cooking, the tubers were mixed with 900 g of water and crushed in a blender (Oster brand, model BLST4655-053, Mexico City, Mexico) for 5 min. The resulting mixture (must) was transferred to a 1 L glass bioreactor (PHIWE, Göttingen, Germany) equipped with seven connections and a heating coil for hot water circulation to maintain a constant temperature, and immersed in an ultrasonic bath fitted with a multi-frequency ultrasound generator (QX Ultrasonic, Beijing, China). The samples were then treated with α-amylase enzyme (LD Carlson Co., Kent, OH, USA) at a concentration of 0.21 g/L, with the pH adjusted to 5.5, and incubated at 37 °C for 60 min. Following this treatment, the samples were cooled, and the pH was adjusted to 3.25 using a citric acid solution to deactivate the α-amylase enzyme. Subsequently, the enzyme amyloglucosidase (Brewhaus brand, Fort Worth, TX, USA) was added at a concentration of 0.01 g/L, and the mixture was incubated at 60 °C for 6 h. After the enzymatic treatment, the soluble solids were adjusted to 16 °Brix, and the pH was set to 4.5. The hydrolysed must was inoculated with 0.20 g/L of Saccharomyces cerevisiae EC-1118 (LALVIN® brand, Lallemand Inc., Montreal, QC, Canada), which had been previously activated by dissolving it in the must at 30 °C with continuous stirring for 30 min. The bioreactor was connected to a container filled with water through a tube, allowing the release of CO2 while retaining water vapour and volatile alcohols. Additionally, 5 mL needles and syringes were inserted into one of the reactor’s channels to collect samples every 12 h without opening the bioreactor. Fermentation was carried out at 25 °C for 84 h at an ultrasonic frequency of 50 kHz, with variable powers of 100, 200, and 300 W, and an energy density of 6 W/cm2. A mixture without ultrasonic treatment was included as a control. The collected samples were centrifuged and analysed to determine ethanol concentration, biomass, and reducing sugars. All experiments were performed in triplicate, and the results are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
2.3. Analytical Determinations
2.3.1. Determination of Biomass
Microbiological analysis was carried out following the methodology described by Zhang et al. [31], with some modifications. Serial dilutions were prepared by mixing 1 mL of the Isaño wort sample with 9 mL of sterile distilled water to obtain the 10−1 dilution. From this, 1 mL was taken and mixed with an additional 9 mL of distilled water to prepare the 10−2 dilution, and so on. The diluted samples were properly homogenised before being plated onto Petri dishes containing OGYE Agar, a selective medium for yeasts and moulds. The plates were incubated at 20–25 °C for 48 h. Yeast colonies were counted using a colony counter.
2.3.2. Quantification of Ethanol Concentration
As described by Flores-Mendoza et al. [35], an oxidising solution was prepared by dissolving 0.85 g of potassium dichromate in 15 mL of distilled water. Then, 25 mL of concentrated sulphuric acid was measured, and the potassium dichromate solution was gradually added while maintaining the solution in a cold-water bath. The final volume was adjusted to 100 mL. Ethanol solutions were prepared at known concentrations, as shown in Table 1. A stock solution was made by dissolving 7 mL of 99.9% pure ethanol in 100 mL of distilled water. This stock solution was then diluted to the desired concentrations (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, and 3.0 mL in 50 mL of water), resulting in the final ethanol concentrations.

Table 1.
Quantities and concentrations for the preparation of standard solutions.
Then, 2 mL of each standard solution was added and reacted with 4 mL of potassium dichromate solution at 75 °C for 30 min, followed by cooling with cold water to stop the reaction. The absorbance was measured using a spectrophotometer (Genesys 20, Thermo Scientific, Mississauga, ON, Canada) at 587 nm. The same procedure was applied to the sample, where the standard ethanol solution was substituted with the sample.
2.3.3. Determination of Reducing Sugars
Reducing sugars were analysed according to the procedure described by Burgos [36]. The tests were performed by weighing 1 g of 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS), 1.6 g of NaOH, and 43.8 g of Na-K tartrate. NaOH was dissolved in 50 mL of distilled water, followed by the addition of Na-K tartrate and DNS, while protecting the reagent from light with aluminum foil. Next, the solution was made up to 100 mL with distilled water in a volumetric flask and left to stir overnight in an amber flask. The glucose standard solution was prepared with the following concentrations: 0, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9, 1.1, 1.3, 1.5, 1.7, and 2.0 g/L. To each screw-cap tube, 0.25 mL of each solution and 0.25 mL of DNS reagent were added, and the tubes were covered with aluminum foil to protect the reaction from light. The tubes were placed in a thermostatic bath at 92 °C for 5 min. The reaction was then stopped by cooling the tubes in ice for 5 min. Afterwards, 2.5 mL of distilled water was added to each tube, followed by shaking. The absorbance was measured at 540 nm using a spectrophotometer. For the fermentation samples, centrifugation was performed at 1700 g for 10 min, and the same procedure was followed, replacing the standard glucose solution with the sample.
2.3.4. Determination of °Brix
The °Brix value was determined using a tabletop Milwaukee MA871-BOX digital refractometer (Milwaukee Instruments, Inc., Rocky Mount, NC, USA). One or two drops of the must were placed on the prism, and the reading was taken immediately [37].
2.3.5. Determination of Kinetic Parameters
The experimental data were fitted using the Monod model (Equation (1)):
where μ represents the specific growth rate (h−1), μmax is the maximum growth rate (h−1), Ks is the saturation constant (g/L), and S is the limiting substrate concentration (g/L).
To determine the coefficients of the Monod equation, the rate of change in substrate concentration (ds/dt) was first calculated. Subsequently, the specific growth rate (μ) as a function of time was determined. The slope of the straight line obtained by linearising the Monod equation (by plotting 1/S vs. 1/μ) was calculated using Microsoft Excel. The maximum cell growth rate and the saturation constant during fermentation were estimated based on the °Brix data.
2.3.6. Fermentation Process Performance
The biomass yield YX/S (g biomass·g substrate−1) and product yield YP/S (g ethanol·g substrate−1) were calculated according to Equations (2) and (3), respectively:
where X0 and Xf are the initial and final biomass concentrations, P0 and Pf are the initial and final ethanol concentrations, and S0 and Sf are the initial and final substrate concentrations, respectively.
2.4. Experimental Design
The data were statistically analysed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) under a Completely Randomised Design. Table 2 presents the factors and levels used in the process. The means were compared using Tukey’s test at a significance level of 0.05, with the statistical analysis performed using Infostat software (version 2020, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina).

Table 2.
Experimental design for Isaño fermentation.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Behaviour of the Biomass Concentration of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae During Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation in Three Isaño Genotypes
Figure 1 illustrates the growth kinetics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae during ultrasound-assisted fermentation of yellow, yellow with purple eyes, and purple Isaño must over a fermentation period of 0 to 84 h. Rapid yeast growth was observed between 2 and 60 h of fermentation, followed by a deceleration phase between 60 and 84 h in the ultrasound-treated samples. In contrast, the control sample (0 W) did not exhibit this deceleration by the end of the 84 h period.
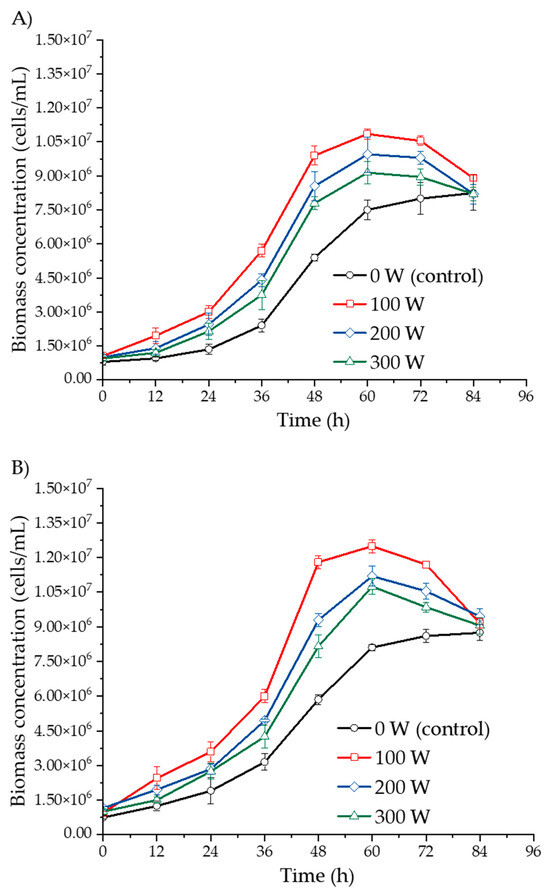
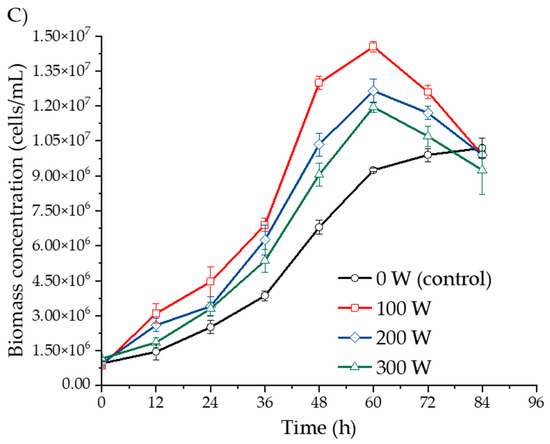
Figure 1.
Biomass concentration kinetics of S. cerevisiae in three Isaño genotypes: (A) yellow, (B) yellow with purple eyes, and (C) purple.
In Figure 1A, biomass concentrations in ultrasound-treated yellow Isaño must were significantly higher than those in the control samples. Similar trends were observed in yellow Isaño must with purple eyes (Figure 1B) and the purple Isaño must (Figure 1C). Across all samples, Isaño must provided a favourable environment for yeast growth during fermentation, attributed to its high starch content of 41.35 ± 1.60% on a dry basis [17]. The increase in biomass can primarily be explained by glucose consumption derived from starch, as yeasts metabolise sugars to produce ethanol and other metabolites [38]. Moreover, yeast growth is influenced by additional factors such as sugar concentration, fermentation temperature, inoculum density, nitrogen and oxygen availability, the presence of inhibitory or stimulating substances from yeast or bacterial growth, fungicide residues, and the addition of sulphur dioxide [39]. In the purple Isaño must, ultrasound at 100 W demonstrated the most efficient promotion of S. cerevisiae growth, followed by 200 W, 300 W, and the control (0 W) at 60 h of fermentation. The higher biomass observed in purple Isaño must may be attributed to its superior nutritional and functional properties, including a high antioxidant content [40]. Additionally, ultrasound has been shown to enhance the extraction of phenolic compounds, which could further contribute to biomass growth [41]. These findings are consistent with prior studies that highlight the positive effects of ultrasound on fermentation. For instance, Al Daccache et al. [28] reported that ultrasound accelerated growth kinetics by 52% during the logarithmic phase, with a 10-fold increase in the biomass growth rate compared to the untreated sample. Similarly, Klomklieng and Prateepasen [42] reported that ultrasound enhanced ethanol production and reduced fermentation time by 6 to 9 h compared to the control. The observed increase in biomass concentration could be attributed to the stimulation of cell division induced by low-power ultrasound [39]. However, Cao et al. [43] cautioned that high-power ultrasound may cause cellular damage and even cell death. Huang et al. [44] suggested that ultrasound promotes microbial growth by disaggregating cell clusters and increasing membrane permeability, thereby enhancing cellular functions and component activity. This increased permeability facilitates the exchange of intracellular and extracellular materials, accelerating the material and energy metabolism of S. cerevisiae [26,31]. Taken together, these results highlight the beneficial effects of ultrasound, particularly at moderate power levels, on the growth and metabolism of S. cerevisiae during fermentation, ultimately reducing fermentation time.
3.2. Ethanol Production Behaviour in Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation of Three Isaño Genotypes
Figure 2 shows the effect of ultrasound-assisted fermentation at different power levels on the ethanol content in the must of three Isaño genotypes. In Figure 2A, it is evident that ethanol production in the yellow Isaño must treated with ultrasound increased significantly compared to the control sample (0 W). A similar pattern was observed in the yellow-purple Isaño fermentation must (Figure 2B) and the purple Isaño must (Figure 2C). In the purple Isaño must, the ethanol concentration reached 10.36 ± 0.33% (v/v) at 84 h with an ultrasonic power of 100 W. At power levels of 200 W, 300 W, and in the control (0 W), the ethanol content in the purple Isaño must was 8.70 ± 0.41%, 8.18 ± 0.07%, and 7.07 ± 0.38% (v/v), respectively. In comparison, the yellow-purple and yellow Isaño musts reached 9.27 ± 0.58% (v/v) and 8.51 ± 0.60% (v/v), respectively. These results are consistent with previous studies. Klomklieng and Prateepasen [42] demonstrated that low-power ultrasound improves ethanol production and reduces fermentation time by 6 to 9 h compared to the control. Similarly, Choi et al. [30] reported that the use of indirect ultrasound (ultrasonic bath) at a power of 160 W and a frequency of 40 kHz in barley-based beer fermentation enhanced ethanol production and shortened fermentation time. Pulidindi et al. [29] also found that ultrasound at 120 W and 40 kHz improved ethanol production. Finally, Al Daccache et al. [28] highlighted that low-intensity ultrasound significantly increases biomass growth, glucose consumption, and ethanol production during apple juice fermentation. Ultrasound treatment increases ethanol production in S. cerevisiae by promoting yeast growth through enhanced membrane permeability and enzymatic activities [45]. Ultrasound intensity affects cellular ultrastructure. Previous studies have shown that, in samples without ultrasonic treatment, cells remain intact and maintain a uniform morphology, with the cytoplasm and organelles homogeneously distributed, along with a clearly visible nuclear region. However, when ultrasonic treatment is applied at 102.8 W for 10 min, the cellular structure becomes irregular, with no visible organelles in the cytoplasm, the presence of vacuoles, and signs of plasmolysis in some cells. At a higher intensity of 288 W over the same duration, significant damage is observed, with evidence of plasmolysis [46].
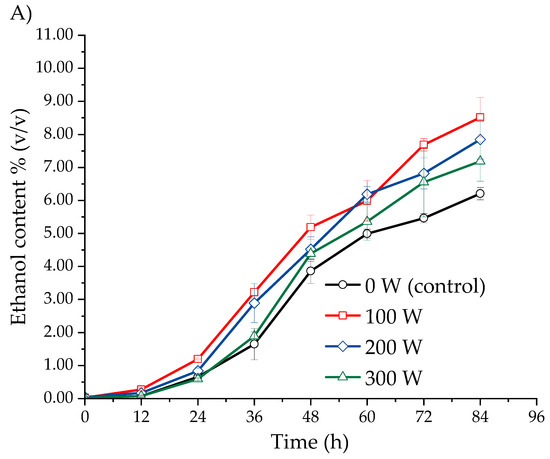
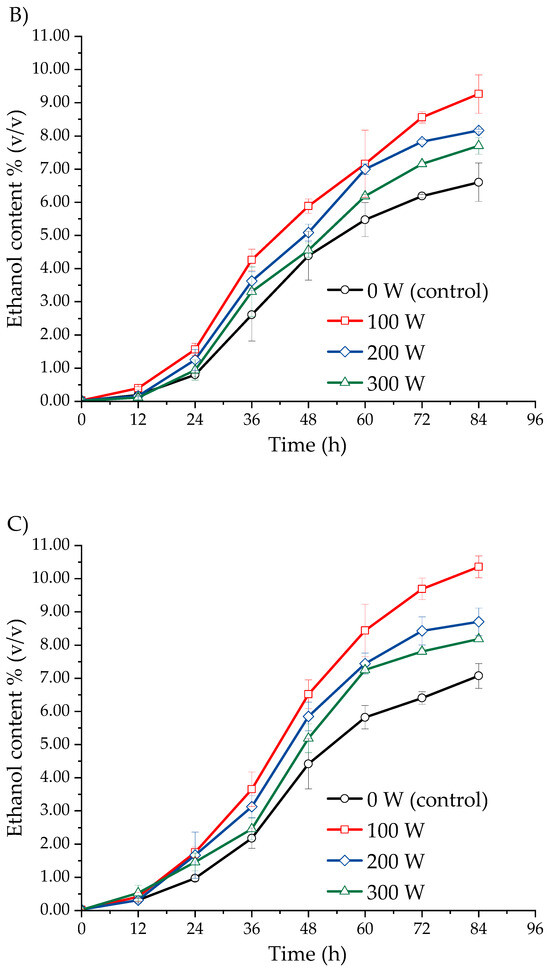
Figure 2.
Ethanol production kinetics in three Isaño genotypes: (A) yellow, (B) yellow with purple eyes, and (C) purple.
The higher ethanol production observed in the purple Isaño must, compared to the yellow and yellow-purple genotypes, can be attributed to its unique nutritional and functional properties. Purple Isaño is a rich source of antioxidants, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, with an antioxidant capacity eight to ten times greater than that of yellow Isaño [40,47]. These characteristics provide a favourable environment for the growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae during fermentation [38]. Consequently, the results demonstrate that ultrasonic treatments during fermentation not only increase ethanol production but also optimise the process by reducing the time required to reach significant concentrations of this metabolite.
3.3. Behaviour of Reducing Sugars in the Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation Process Evaluated in Three Isaño Genotypes
Figure 3 shows the effect of ultrasound-assisted fermentation, applied at different power levels, on the reducing sugar content in the fermentation must of three Isaño genotypes over a period of 0 to 84 h. The samples subjected to ultrasonic treatment exhibited a greater reduction in reducing sugar content compared to the non-sonicated samples over the same time period. The reducing sugar content progressively decreased as fermentation time increased, with the most significant reduction rate observed at an ultrasonic power of 100 W, followed by 200 W, 300 W, and finally 0 W. This trend was consistent across all three Isaño genotypes. In the case of purple Isaño, the reducing sugar content reached 2.62 ± 0.03 g/L at 84 h. These findings correlate with the increase in biomass concentration and ethanol content observed during fermentation (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Furthermore, the effects observed with ultrasound treatments align with previous studies, which have reported that ultrasound improves fermentation efficiency by reducing sugar content more rapidly, increasing ethanol production speed, and shortening the overall fermentation time [29]. One potential explanation for these observations is that ultrasound may facilitate the transfer of oxygen in the liquid medium, thereby promoting faster sugar consumption after its application [31].The must provides a favourable environment for microbial growth, enabling yeast to metabolise the available sugars during fermentation. As the process progresses, the reduction in available sugars, coupled with the increase in ethanol concentration, eventually limits yeast population growth and halts fermentation [38]. In conclusion, the application of ultrasound was beneficial for the growth and fermentation activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Among the power levels tested, the 100 W treatment proved to be the most effective, outperforming the 200 W and 300 W treatments.
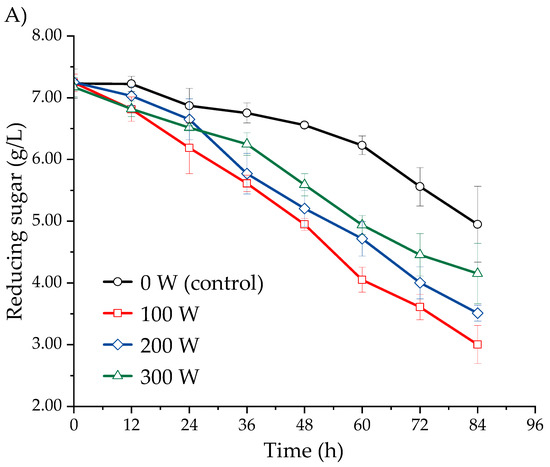
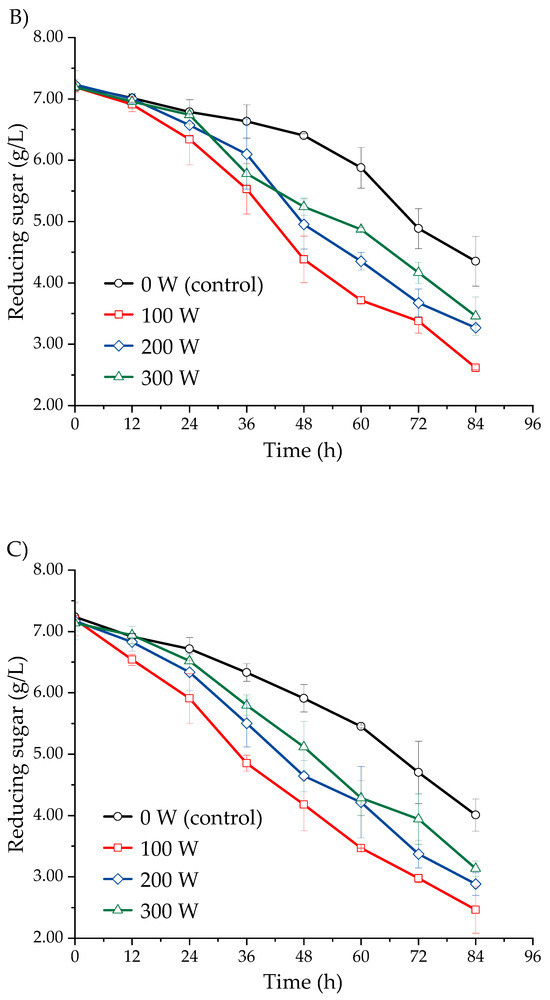
Figure 3.
Kinetics of reducing sugars, evaluated in three Isaño genotypes: (A) yellow, (B) yellow with purple eyes, and (C) purple.
3.4. Behaviour of Soluble Solids in the Fermentation Process
Figure 4 presents the effect of ultrasound, applied at different power levels, on the soluble solids content (°Brix) in the fermentation must of S. cerevisiae from three Isaño genotypes, observed over a period of 0 to 84 h. The ultrasonicated samples exhibited a greater decrease in soluble solids content compared to the non-sonicated samples. The soluble solids content decreased as fermentation time progressed, with the most rapid reduction occurring at an ultrasonic power of 100 W, followed by 200 W, 300 W, and finally the control (0 W). This trend was consistent across all three Isaño genotypes evaluated. In the case of purple Isaño, the °Brix decreased from 16.0 to 4.3 ± 0.3 at 84 h of fermentation. The decrease in °Brix is associated with the consumption of sugars by S. cerevisiae during the fermentation process, which continues until the sugars are exhausted and microbial activity ceases [38,48]. However, high-power ultrasound may have an adverse effect on cell growth, which could explain the slower rate of reduction in °Brix observed at higher power levels [30]. Based on the results obtained, it can be concluded that ultrasound treatment at 100 W significantly enhances the fermentation process, with purple Isaño showing the best fermentation performance.
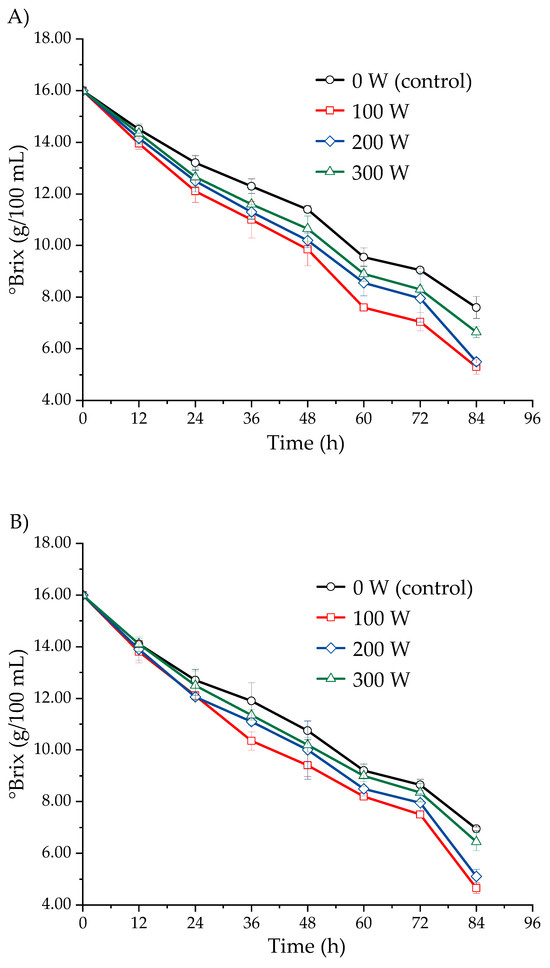
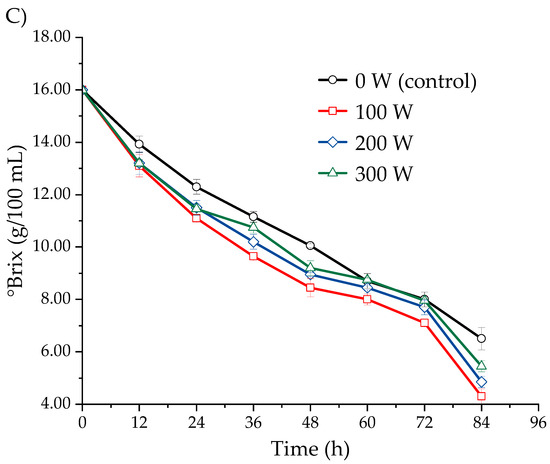
Figure 4.
Kinetics of the decrease in soluble solids (°Brix) during fermentation at 25 °C, evaluated in three Isaño genotypes: (A) yellow, (B) yellow with purple eyes, and (C) purple.
3.5. Application of the Monod Kinetic Model Based on the °Brix Parameter in Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation of Yeast
Table 3 presents the kinetic parameters of maximum cell growth rate (μmax) and saturation constant (Ks) of the Monod model, along with the biomass yield (Yx/s) and product yield (Yp/s) for the ultrasound-assisted fermentation process. These parameters were evaluated in three Isaño genotypes (yellow, yellow with purple eye, and purple) under different ultrasonic power levels (0 W, 100 W, 200 W, and 300 W). In the sample without ultrasonic treatment (control), the μmax values were 0.007 ± 0.004 h−1, 0.017 ± 0.001 h−1, and 0.028 ± 0.007 h−1, while the Ks values were 13.829 ± 11.115 g/L, 30.773 ± 13.535 g/L, and 27.801 ± 9.927 g/L for the yellow, yellow-purple, and purple fermentation musts, respectively. Comparatively, these μmax values are higher than those reported by Llacsa and Cucho [49] for quinoa chicha fermentation (0.004 h−1) and similar to those obtained by Pari [50] for banana peel fermentation (0.0278 h−1).

Table 3.
Kinetic parameters of the Monod model and the yield of the fermentation process.
When applying ultrasonic treatment, μmax showed significant variations depending on the power level and genotype. For yellow Isaño, μmax increased from 0.006 ± 0.003 h−1 to 0.029 ± 0.013 h−1 as the power decreased from 300 W to 100 W. In the case of yellow Isaño with purple eyes, μmax initially decreased, followed by an increase from 0.167 ± 0.190 h−1 to 0.211 ± 0.257 h−1. For purple Isaño, the growth was more consistent, with μmax increasing from 0.015 ± 0.001 h−1 to 0.064 ± 0.059 h−1 as the power increased from 100 W to 300 W. Specifically, it was observed that the depletion of soluble solids occurred more rapidly at 100 W in the purple Isaño must, with μmax of 0.015 ± 0.001 h−1 and Ks of 16,088 ± 20,360 g/L. The Yp/s was 0.899 ± 0.016, and Yx/s ranged between 7.60 × 105 ± 8.79 × 104 and 9.84 × 105 ± 6.81 × 103.
Overall, biomass yields per gram of glucose consumed were significantly higher in ultrasound-treated cultures (100, 200, and 300 W) compared to the control (0 W). These results are consistent with those reported by Al Daccache et al. [28], who found that the maximum growth rate in ultrasound-assisted samples was up to 10 times higher than in untreated samples. Similarly, studies on yeast have shown that ultrasound treatment increases ethanol production and biomass yield. For instance, He et al. [45] observed a 30.79% increase in ethanol production and a 24.10% increase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae biomass at 28 kHz ultrasonic frequency, which they attributed to improved cell membrane permeability and increased enzymatic activity. Another study by Yang et al. [51] reported that ultrasonic treatment at 28 kHz, 180 W/L for 24 h increased ethanol yield by 34.87%, which was associated with changes in gene expression and cellular metabolism. In conclusion, ultrasonic treatments improve cell membrane permeability by generating micropores that facilitate substrate transfer and stimulate cell growth. These effects are reflected in increased biomass and ethanol yields in the three Isaño genotypes studied.
4. Conclusions
This study shows that ultrasonic treatment significantly improves the fermentation process of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in musts from yellow, yellow with purple eyes, and purple Isaño genotypes compared to untreated samples. When the power was increased from 100 W to 300 W, the rates of yeast growth, ethanol production, and substrate consumption improved considerably. Optimal fermentation efficiency was achieved with an ultrasonic power of 100 W, a frequency of 50 kHz, and a fermentation duration of 84 h, particularly in the purple Isaño must. Under these conditions, ethanol production reached 10.36% (v/v), with a maximum microbial growth rate (μmax) of 0.015 h−1 and a saturation constant (Ks) of 16.088 g/L.
These results confirm the potential of ultrasound technology to optimise the production of Isaño wine, a crop well-adapted to the extreme conditions of the Peruvian Altiplano. This product could be positioned as a functional beverage with nutritional properties and potential health benefits.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C. and U.A.; methodology, A.C. and M.M.-M.; formal analysis, U.A. and M.M.-M.; investigation, M.M.-M. and H.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.C.; writing—review and editing, U.A., C.V.-S. and W.C.C.P.; supervision, A.C. and U.A.; funding acquisition, A.C., N.C.R. and J.M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to the Universidad Nacional del Altiplano and the Instituto de Investigacion e Innovación en Producción, Seguridad Alimentaria y Agroindustria—IPSAA, Puno, Perú, for allowing us to use their laboratory and equipment during the execution of the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Aruquipa, R.; Trigo, R.; Bosque, H.; Mercado, G.; Condori, J. El Isaño (Tropaeolum uberosum) Un Cultivo de Consumo y Medicina Tradicional En Huatacana Para El Beneficio de La Población Boliviana. RIIARn 2017, 3, 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Valle-Parra, M.; Pomboza-Tamaquiza, P.; Buenaño-Sánchez, M.; Guevara-Freire, D.; Chasi-Vizuete, P.; Vásquez, C.; Pérez-Salinas, M. Morphology, Phenology, Nutrients and Yield of Six Accessions of Tropaeolum tuberosum Ruiz y Pav (Mashua). Trop. Subtrop. Agroecosystem 2018, 21, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Freire, D.; Valle-Velástegui, L.; Barros-Rodríguez, M.; Vásquez, C.; Zurita-Vásquez, H.; Dobronski-Arcos, J.; Pomboza-Tamaquiza, P. Nutritional Composition and Bioactive Components of Mashua (Tropaeolum tuberosum Ruiz and Pavón). Trop. Subtrop. Agroecosystems 2018, 21, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, L.; Pagán, M.J.; Martínez-Monzó, J.; García-Segovia, P. Propiedades Funcionales de Tuberculos Andinos de La Región Andina de Chimborazo (Ecuador): Una Revisión. Rev. Esp. Nutr. Comunitaria 2016, 22, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, D.; Chirinos, R.; Gálvez Ranilla, L.; Pedreschi, R. Bioactive Potential of Andean Fruits, Seeds, and Tubers, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 84. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar-Galvez, A.; Pedreschi, R.; Carpentier, S.; Chirinos, R.; García-Ríos, D.; Campos, D. Proteomic Analysis of Mashua (Tropaeolum tuberosum) Tubers Subjected to Postharvest Treatments. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 125485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaza, L.; Tena, V.; Serban, A.M.; Alonso, M.J.; Rumbero, A. Alkamides from Tropaeolum tuberosum Inhibit Inflammatory Response Induced by TNF–α and NF–ΚB. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaza Ticona, L.N.; Tena Pérez, V.; Bermejo Benito, P. Local/Traditional Uses, Secondary Metabolites and Biological Activities of Mashua (Tropaeolum tuberosum Ruíz & Pavón). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 247, 112152. [Google Scholar]
- Chirinos, R.; Pedreschi, R.; Rogez, H.; Larondelle, Y.; Campos, D. Phenolic Compound Contents and Antioxidant Activity in Plants with Nutritional and/or Medicinal Properties from the Peruvian Andean Region. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 47, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticona, L.A.; Sánchez, Á.R.; Gonzáles, Ó.O. Antimicrobial Compounds Isolated from Tropaeolum tuberosum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 35, 4698–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaza, T.L.; Peña-Rojas, G.; Andía-Ayme, V.; Durán, B.; Rumbero, A. Anti-Glycative and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Macamides Isolated from Tropaeolum tuberosum in Skin Cells. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 1, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, M.T.; Escribano-Bailón, M.T.; Moreno, F.J.; Villamiel, M.; Dueñas, M. Determination by HPLC-DAD-ESI/MSn of Phenolic Compounds in Andean Tubers Grown in Ecuador. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 84, 103258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores Mamani, E.; Apaza Ticona, J.; Calsina Ponce, W.C.; Quille Calizaya, G.; Huanca Rojas, F.; Coloma Paxi, A.; Inquilla Mamani, J.; Huata Panca, P.; Zayra Churata, A. Conocimiento Ancestral En La Curación de La Próstata a Base de Isaño (Tropaeolum tuberosum Ruiz y Pavón). Idesia 2020, 38, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásconez-Barrera, F.; Oleas-López, J.; Bonilla-Lucero, M.; Benítez-Santillán, L. Homemade Bread Made with Mashua and Wheat Flour: Added Value to the Raw Material and Nutritional Contribution to the Health of Children and Adults. Surv. Fish. Sci. 2023, 10, 348–358. [Google Scholar]
- González, M.; Georgina, M.; Georgina, M. Determining the Nutritional Value of Sausages Made with Llama and Alpaca Meat with the Addition of Goose Flour and Mashua. ESPOCH Congr. Ecuadorian J. S.T.E.A.M. 2022, 2, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez-barreto, F.F.; Ramírez Tixe, E.; Chuquilín Goicochea, R.; Aliaga-barrera, I. Optimization of the Functional Properties of a Drink Based on Tubers of Purple Mashua (Tropaeolum tuberosum Ruíz y Pavón). Agroindustrial Sci. 2020, 10, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcárcel-Yamani, B.; Rondán-Sanabria, G.G.; Finardi-Filho, F. The Physical, Chemical and Functional Characterization of Starches from Andean Tubers: Oca (Oxalis tuberosa Molina), Olluco (Ullucus tuberosus Caldas) and Mashua (Tropaeolum tuberosum Ruiz & Pavón). Brazilian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 453–464. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreyra, M.M.; Schvab, M.d.C.; Gerard, L.M.; Zapata, L.M.; Davies, C.V.; Hours, R.A. Alcoholic Fermentation of Orange Juice with S. Cerevisiae. Cienc. Docencia Tecnol. 2009, 39, 143–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ronquillo, A.; Lazcano, V.; Pérez, I.; Cabrera, S.; Lazcano, M. Elaboracion y Caracterización de Vino de Frutas e Infusión de Hierbas. Investig. Desarro. Cienc. Tecnol. Aliment. 2016, 1, 366–371. [Google Scholar]
- Oré, F.; De la Cruz, R.; Montalvo, J.; Muñoz, K. Evaluation of the Acceptability and Alcohol Content of Goose Wine (Oxalis tuberosa) of Five Varieties. J. Agro-Industry Sci. 2019, 1, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.R.; Basak, N. Enhancing Biohydrogen Production by Optimization of Waste Potato Concentration in Dark and Photo Fermentation. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 494, 145000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, N.; Mor, R.S.; Kumar, K.; Sharanagat, V.S. Advances in Application of Ultrasound in Food Processing: A Review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 70, 105293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.A.; Wang, T.T. Effect of Ultrasound Irradiation on the Evolution of Color Properties and Major Phenolic Compounds in Wine during Storage. Food Chem. 2017, 234, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galván-D’Alessandro, L.; Carciochi, R.A. Fermentation Assisted by Pulsed Electric Field and Ultrasound: A Review. Fermentation 2018, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Gai, L.; Niu, D. Potential Applications of Pulsed Electric Field in the Fermented Wine Industry. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Mei, Z.; Zhou, X.; Yu, H. Potential Use of Ultrasound to Promote Fermentation, Maturation, and Properties of Fermented Foods: A Review. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Lopez, L.M.; Garcia-Galicia, I.A.; Tirado-Gallegos, J.M.; Sanchez-Vega, R.; Huerta-Jimenez, M.; Ashokkumar, M.; Alarcon-Rojo, A.D. Recent Advances in the Application of Ultrasound in Dairy Products: Effect on Functional, Physical, Chemical, Microbiological and Sensory Properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Daccache, M.; Koubaa, M.; Salameh, D.; Maroun, R.G.; Louka, N.; Vorobiev, E. Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation for Cider Production from Lebanese Apples. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 63, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulidindi, I.; Gedanken, A.; Schwarz, R.; Sendersky, E. Mild Sonication Accelerates Ethanol Production by Yeast Fermentation. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 2352–2356. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, E.J.; Ahn, H.; Kim, M.; Han, H.; Kim, W.J. Effect of Ultrasonication on Fermentation Kinetics of Beer Using Six-Row Barley Cultivated in Korea. J. Inst. Brew. 2015, 121, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiong, F.; Wang, Y.; Dai, C.; Xing, Z.; Dabbour, M.; Mintah, B.; He, R.; Ma, H. Fermentation of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae in a One Liter Flask Coupled with an External Circulation Ultrasonic Irradiation Slot: Influence of Ultrasonic Mode and Frequency on the Bacterial Growth and Metabolism Yield. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 54, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomklieng, W.; Prateepasen, A. Using Low-Power Ultrasonic for Enhancing Saccharomyces Cerevisiae M30 Productivity for Ethanol Producing from Molasses. Int. Proc. Chem. Biol. Environ. Eng. 2011, 9, 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Sanaei Nasab, S.; Tahmouzi, S.; Feizollahi, E.; Mollakhalili-Meybodi, N. Impacts of Novel Non-Thermal Processing (NTP) on Anti-Nutritional Compounds of Food Grains and Seeds. Food Control 2024, 162, 110469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnaemeka, I.C.; Egbuna Samuel, O.; Onoh Maxwell, I.; Christain, A.O.; Chinelo S, O. Optimization and Kinetic Studies for Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Fermentation of Colocynthis Vulgaris Shrad Seeds Shell for Bioethanol Production. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Mendoza, L.; Osorio-Lorenzo, P.V.; Pérez-San Juan, A.R.; Sánchez-Rosas, D.L.; Rodríguez-Puertos, T. Elaboración de Una Bebida Fermentada Tipo Cerveza Artesanal a Base de Malta Adicionada Con Tallo de Maíz (Zea mays) y Mexale. Rev. Cient. Pakamuros 2019, 3, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Montañez, L.J.B. Cuantificación de Azúcares Reductores Del Sustrato En Residuos de Piña Con El Método Del Ácido 3,5-Dinitrosalicílico. Fund. Univ. Am. 2020, 13, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, R.T.S.; Biasoto, A.C.T.; Rybka, A.C.P.; Castro, C.D.P.C.; Aidar, S.T.; Borges, G.S.C.; Silva, F.L.H. Physicochemical Characterization, Bioactive Compounds, in Vitro Antioxidant Activity, Sensory Profile and Consumer Acceptability of Fermented Alcoholic Beverage Obtained from Caatinga Passion Fruit (Passiflora cincinnata Mast.). Lwt 2021, 148, 111714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onofre, C. Efecto Del Proceso de Fermentación Alcohólica de La Chicha de Quinua (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) Sobre Su Contenido de Antioxidante, Vitaminas y Minerales. Licentiate Thesis, Universidad Nacional de San Agustin, Arequipa, Peru, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Englezos, V.; Cravero, F.; Torchio, F.; Rantsiou, K.; Ortiz-Julien, A.; Lambri, M.; Gerbi, V.; Rolle, L.; Cocolin, L. Oxygen Availability and Strain Combination Modulate Yeast Growth Dynamics in Mixed Culture Fermentations of Grape Must with Starmerella Bacillaris and Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Food Microbiol. 2018, 69, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, D.; Aguilar-Galvez, A.; García-Ríos, D.; Chirinos, R.; Limaymanta, E.; Pedreschi, R. Postharvest Storage and Cooking Techniques Affect the Stability of Glucosinolates and Myrosinase Activity of Andean Mashua Tubers (Tropaeolum tuberosum). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, P.; Bel, A.; Jurado, R.; Encarna, G. Combining High-Power Ultrasound and Enological Enzymes during Winemaking to Improve the Chromatic Characteristics of Red Wine. LWT 2022, 156, 113032. [Google Scholar]
- Klomklieng, W.; Prateepasen, A. Molasses Fermentation to Ethanol by Saccharomycescerevisiae M30 Using Low Ultrasonic Frequency Stimulation. KKU Res. J. 2012, 17, 950–957. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Hu, Z.; Pang, B. Optimization of Postharvest Ultrasonic Treatment of Strawberry Fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2010, 55, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, S.; Dai, C.; Sun, L.; Sun, W.; Tang, Y.; Xiong, F.; He, R.; Ma, H. Effects of Ultrasound on Microbial Growth and Enzyme Activity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 37, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Ren, W.; Xiang, J.; Dabbour, M.; Kumah Mintah, B.; Li, Y.; Ma, H. Fermentation of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae in a 7.5 L Ultrasound-Enhanced Fermenter: Effect of Sonication Conditions on Ethanol Production, Intracellular Ca2+ Concentration and Key Regulating Enzyme Activity in Glycolysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 76, 105624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, L.; Li, B.; Xu, Z. Effect of Ultrasound Treatment Conditions on Saccharomyces Cerevisiae by Response Surface Methodology. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, A.; Mera, J. Elaboracion Del Tuberculo Mashua (Tropaeolum tuberosum) Troceada En Miel y Determinacion de La Capacidad Antioxidante. Wild 2014, 2007–2010. [Google Scholar]
- Apaza, R.M.; Atencio, Y.J. Tecnología Para La Elaboración de Una Cerveza Artesanal Tipo Ale, Con Sustitutción Parcial de Malta (Horden vulgare) Por Guiñapo de Maiz Morado (Zea mays); Universidad Nacional de San Agustin: Arequipa, Peru, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Llacsa, J.D.; Cucho, A. Cinética de Fermentación de La Chicha de Quinua Evaluado En Tres Variedades de Quinua (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Licentiate Thesis, Universidad Nacional del Altiplano, Puno, Peru, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pari, E. Cinética de Conversión de Los Carbohidratos Presentes En La Cáscara de Plátano (Musa cavendishi) Para La Obtención de Etanol. Licentiate Thesis, Universidad Nacional del Altiplano, Puno, Peru, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, W.; Xu, H.; Cheng, L.; Dapaah, M.F.; He, R.; Ma, H. Incorporating Transcriptomic-Metabolomic Analysis Reveal the Effect of Ultrasound on Ethanol Production in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 79, 105791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).