Abstract
Blood-derived autologous products are frequently used in both human and equine medicine to treat musculoskeletal disorders. These products, especially the platelet-rich plasma (PRP), may contain high concentrations of growth factors (GFs), and thus improve healing in several tissues. Nevertheless, the procedures for preparation of PRP are currently non-standardized. Several protocols, which are based on distinct centrifugation patterns (rotation speed and time), result in PRPs with different characteristics, concerning platelet and GFs concentrations, as well as platelet activation. The aim of the present study was to compare two different protocols for PRP preparation: protocol (A) that is based on a single-centrifugation step; protocol (B), which included two sequential centrifugation steps (double-centrifugation). The results here reported show that the double-centrifugation protocol resulted in higher platelet concentration, while leukocytes were not concentrated by this procedure. Although platelet activation and aggregation were increased in this protocol in comparison to the single-centrifugation one, the TGF-β1 concentration was also higher. Pearson’s correlation coefficients gave a significant, positive correlation between the platelet counts and TGF-β1 concentration. In conclusion, although the double-centrifugation protocol caused premature platelet aggregation, it seems to be an effective method for preparation of PRP with high platelet and TGF-β1 concentrations.
1. Introduction
In the last decade, hemoderivative therapeutics has become a suitable alternative to treat musculoskeletal disorders in both human and veterinary medicine. Particularly, the platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has shown beneficial effects on several joint diseases, which help to relieve pain and improve the articular structures (reviews in [1,2,3,4]).
A systematic review on the efficacy of PRP in equine and human orthopedic therapeutics [1] concluded that, although many equine studies yielded positive results, the same is not true for human clinical trials. Furthermore, beneficial results for both species were more frequently observed in studies with a high risk of bias, which lead the authors to conclude that the use of PRP has still not shown strong positive effects in clinical scenarios.
Campbell et al. [2] have demonstrated, through meta-analysis and systematic review, that many studies, including comprehensive and meticulous ones, lack detailed information regarding the procedure for PRP preparations (centrifugation steps) and their characteristics (platelet counts, growth factor concentrations, and administered volumes).
On the other hand, PRP is an accessible and inexpensive source of growth factors [5], especially transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1). Therefore, it seems that the standardization of protocols to prepare PRP, as well as the careful characterization of PRP, is worthwhile.
Different authors have used distinct centrifugation patterns (rotation force, time, and number of centrifugation steps) to prepare PRP, possibly resulting in different final products [6]. Some protocols include two centrifugation steps, the second at higher force g. In the final step, the platelets are resuspended in a reduced plasma volume [7]. The platelet count in PRP can reach 13 times that of filtered apheresis platelet concentrates from whole blood, and the TGF-β1 concentration also increases, reaching an excess of 50 ng/mL [8]. However, Argüeles et al. [7] reported that the TGF-β1 concentrations were similar in PRPs that were obtained by either single- or double-centrifugation methods.
Although TGF-β1 is not the only growth factor present in PRP, it plays a significant role in musculoskeletal disorders, and it will be emphasized here. TGF-β is a multifunctional cytokine that belongs to the TGF superfamily, which includes three different mammalian isoforms (TGF-β 1 to 3) and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP). The isoform TGF-β1 was first identified in human platelets as a protein of 25 kDa, with a potential role in wound healing. Most of the immune cells secrete TGF-β1 [9].
In vitro and in vivo studies revealed that TGF-β ameliorates the deleterious effects of IL-1 on the cartilage matrix, counteracting both the IL-1 induced proteoglycan degradation and the suppression of synthesis [10]. Additionally, TGF-β regulates chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation [11] and induces the production of type II collagen and aggrecan [12]. Increased TGF-β1 concentrations (up to 10 or 100 ng/mL) correlate to increased proteoglycan and hyaluronan synthesis in cartilage [13] and meniscal [14] explants.
However, the role of TGF-β in joints remains controversial [15]. While TGF-β1 seems to favor chondrogenesis [16], multiple intra-articular injections of TGF-β1 may also promote osteoarthritis [17]. There are evidences that indicate that high doses of TGF-β may stimulate synovial proliferation and fibrosis, attracting inflammatory leukocytes to the synovial membrane, and thus inducing osteophyte formation [18,19].
These controversial results emphasize the need to standardize PRP preparation and to characterize the products, aiming at high platelet counts and high TGF-β1 concentrations. This is usually achieved by increasing centrifugal force, and/or time, but a limiting point is that platelet activation and aggregation also increases by increasing these centrifugal patterns. Platelet activation leads to TGF-β1 release, and the resulting preparation could be rich in platelets, but poor in TGF-β1. Thus, careful characterization of PRP is necessary, especially when intended for intra-articular administration, concerning the TGF-β1 concentration, to minimize the adverse effects [15].
The platelet-poor plasma (PPP) is the supernatant, which is usually discharged during PRP preparation. This fraction can be considered to be a byproduct and it has demonstrated positive effects when used in subcutaneous tissue during orthopedic surgery [20,21] and also as a single injection for chronic plantar fasciitis [22]. Nevertheless, PPP has been poorly explored in veterinary practice [23].
Therefore, the aim of the present study was to compare PRP that was prepared by two different protocols: a “single-centrifugation protocol”, based on one centrifugation step, and a “double-centrifugation protocol”, based on two centrifugation steps, in sequence. The PRP and PPP preparations were analyzed for platelet counts, platelet activation, and TGF-β1 concentration.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
The present study was approved by the Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia of the Universidade de São Paulo’s Ethics Committee on Animal Use (CEUA/USP; 1209080715), and it was carried out in accordance with EC Directive 86/609/EEC for animal experiments http://ec.europa.eu/environment/chemicals/lab_animals/legislation_en.htm. Twelve gelding male horses, aged between three and five years, which were clinically healthy and free of any drugs for 15 days prior to the study, were included in the present study.
The sample size calculation was determined to provide an 80% statistical power mainly for TGF-β1, and platelet concentration to detect a difference of 30% between the groups, with a two-sided alpha level of 0.025 and β = 0.20 based on two-way analysis of variance.
2.2. Blood Collection
Blood was collected from jugular vein following aseptic preparation of the site. For the single centrifugation protocol (see below), blood was collected while using a 21-gauge needle and a 10 mL syringe, and transferred to a Falcon tube (15 mL) containing 1 mL of 3.8% sodium citrate as anticoagulant. For the double centrifugation protocol, a 21-gauge needle and seven vacutainer tubes containing 3.8% sodium citrate were used (4.5 mL; final dilution blood:anticoagulant was 9:1). After harvesting and homogenization of the blood, the final volume was aliquoted and transferred to three Falcon tubes (15 mL), 10.5 mL each.
2.3. Platelet Rich Plasma Preparation
Two different protocols were used for PRP preparation: a single and a double centrifugation procedure, as schematized in Figure 1. The products were analyzed.
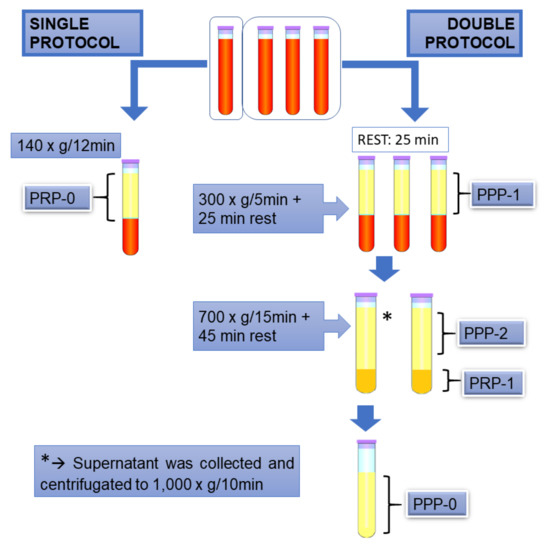
Figure 1.
Illustrative scheme of the protocols used in the present study. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP)-0, PRP obtained by the single protocol; platelet-poor plasma (PPP)-1, platelet poor plasma obtained in the first centrifugation step of double protocol; PPP-2, supernatant of the second centrifugation step of double protocol; PRP-1: PRP obtained by the double protocol; PPP-0, supernatant after centrifugation of PPP-2.
The single centrifugation protocol that was used here was adapted from Ottaiano et al. [24], in which premature platelet aggregation is avoided. In brief, blood was collected in one tube and centrifugated at 140× g for 12 min. (room temperature), and the supernatant was collected was named “PRP-0”.
For the double centrifugation protocol [4], three 15 mL tubes were used, containing 10.5 mL of blood each. After collection, the blood samples were incubated at room temperature for 25 min., and then were centrifugated at 300× g for 5 min., followed by another 25 min. “rest period”. It was empirically observed that less platelet activation occurred when these “rest period” were included. The supernatants were collected, and one of them was reserved and named “PPP-1”, while the other two were submitted to a second 700× g, 15 min. centrifugation, followed by another “rest period” of 45 min. The supernatant from the second tube was collected, reserved, and named “PPP-2”. The pellet and remaining volume were gently homogenized using a pipette and named “PRP-1”. The supernatant of the third tube, named “PPP-0”, was collected and cleared by centrifugation at 1000× g for 10 min., to assure minimal platelet counting in the supernatant. This was use as a sample with 100% light transmission in aggregometry testing, as described below.
2.4. Platelet and Leukocyte Counts
A complete blood count was performed on each blood sample. Leukocyte (WBC) counts were completed in the PRP-0, PRP-1, and PPP-1 sample while using a flow cytometry hematology system (ADVIA 2120i, Siemens – Erlangen, Germany).
Platelet counts were performed in whole blood (baseline values) samples and in the PRP-0, PRP-1, PPP-1, and PPP-2 samples while using a Neubauer chamber. Platelet concentrations were described as a ratio between platelet count for each sample and the platelet count for the whole blood sample.
2.5. Aggregometry Test
Platelet aggregation responses were evaluated while using an aggregometer (Chrono-Log Corporation, model 700) and monitored by the turbidimetric method developed by Born and Cross [25] using Agrolink software (Chrono-Log Corporation, Havertown, Pennsylvania, USA). Prior to this test, the PPP-0 was used as sample with 100% light transmission. To perform this test, 500 µL of PPP-0 was used as a blank. Likewise, 498 µL of each sample were placed in a 6-mm-wide siliconized cuvette with a stirring bar magnet and maintained at 37 °C. The samples were then identified with the software and baselines were adjusted to 0%. Two µL of agonist collagen type I (Chrono-Log Corporation) were added to the cuvettes, which were agitated. The aggregation curve was then observed for a 6-min. period.
This test was performed in all samples, except PPP-2, because, due to its low platelet counts, PPP-2 did not gave reliable results. The agonist alone was added as a control. All of the samples were stored at −80 °C until further analysis and TGF-β1 determination.
2.6. Determination of TGF-β1 Concentrations
TGF-β1 concentrations were quantified in all samples by ELISA, while using a commercially available human TGF-β1 kit (Quantikine ELISA, R&D Systems, Inc; Minneapolis, MN, USA, DB100B), previously validated for use in equine samples [26,27], in accordance with manufacturer instructions. All of the samples were run in duplicates.
After thawing and homogenization, TGF-β1 of each sample was activated: aliquots (20 µL) were placed in microcentrifuge tubes (200 μL), and 10 µL of 1 M HCl were added, which were then homogenized and incubated at room temperature. After 10 min., 10 µL of 1.2 M NaOH and 160 µL of RD5-53 diluent (R&D Systems, Inc; Minneapolis, MN, USA, part #895587) were added to each sample. RD5-53 diluent (50 µL) was added to all the wells of a 96-well anti-TGF-β1 antibody coated plate (TGF-β1 plate). Standards or samples (50 µL) were then added to the appropriate wells and then incubated for 2 h at room temperature with gentle agitation. The solution was discarded and the plate was washed four times with wash buffer solution (R&D Systems, Inc; Minneapolis, MN, USA, part #895126). Next, 100 µL of anti-TGF-β1 polyclonal antibody conjugated with HRP (R&D Systems, Inc; Minneapolis, MN, USA, part #893003) were added to each well, which were then covered by a film and then incubated again for 2 h at room temperature. The washing procedure was repeated, as previously described, and then 100 µL of substrate solution were added to each well. The plate was then covered with aluminum foil and incubated for 30 min. at room temperature. Finally, 100 µL of stop solution was added to each well. The wells were homogenized and absorbances were read while using a microplate reader at 450 nm.
2.7. Statistical Analyses
The data were analyzed for normality while using Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests. Afterwards, an analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Tukey-Kramer or Bonferroni tests, were used to compare parametric data. Non-parametric data were analyzed via the Friedman test. Correlation analyses were performed while using coefficients of determination and Pearson’s correlation coefficients. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Instat 3 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Statistical significance was set to p < 0.05 and confidence interval (CI) of 95%.
3. Results
3.1. Platelet and Leukocyte Counts and Platelet Concentration Times
The baseline platelet counts for the horses that were used in the present study was 180 × 103/μL. Figure 2 shows that the platelet counts were significantly increased in PRP-0, obtained by the single-centrifugation protocol, and also in the products that were obtained by the first and the second centrifugation steps in the double-centrifugation protocol (PPP-1, and PRP-1, respectively) (p = 0.0001). For PRP-0, the mean platelet count was 494 ± 157 × 103/μL (2.7 times the baseline), while for PPP-1 and PRP-1, the platelet counts were 756 ± 228 × 103/μL (4.2 times) and 1371 ± 423 × 103/μL (7.6 times), respectively. These data show that higher platelet counts were obtained in the products that were prepared by the double-centrifugation protocol (PPP-1 and PRP-1), as compared to the lower values that were obtained by the single centrifugation procedure (PRP-0). As expected, the platelet counts in PPP-2 (supernatant of the second centrifugation step) was lower than the baseline.
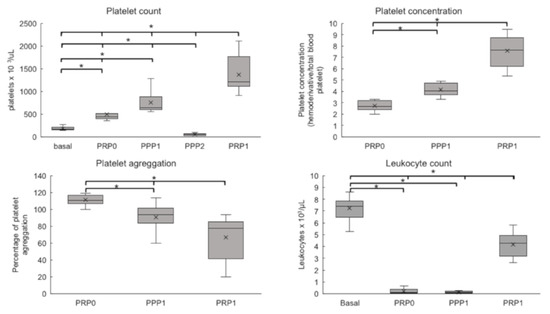
Figure 2.
Platelet counts, Platelet concentrations, Platelet aggregation (%), and Leukocyte counts of PRP and PPP preparations. The figure shows results as Box plots, representing medians (horizontal central lines), means (x), 25th and 75th percentiles (rectangles, first and third quartiles), and minimal and maximal values (vertical lines) for each experimental group. Basal, whole blood; PRP0, PRP obtained by the single protocol; PPP1, platelet poor plasma obtained in the first centrifugation step of double protocol; PPP2, supernatant of the second centrifugation step of double protocol; PRP1, PRP obtained by the double protocol; PPP0, supernatant obtained after centrifugation of PPP2. * Differences statistically significant (p < 0.05).
In contrast, the leukocyte counts decreased in all analyzed products (PRP-0, PRP-1, and PPP-1) relative to the baseline (Figure 2), which indicated that the platelet-rich plasma was not leukocyte-rich.
3.2. Platelet Aggregation
Aggregometry tests revealed significant differences among the groups (Figure 2). PRP-0 have shown high aggregation (110%, relative to baseline), with small variations among different samples. This indicates that this protocol did not induce previous platelet activation. In contrast, the aggregation response was significantly lower (p = 0.0001) in the samples that were prepared by the double-centrifugation protocol: PPP-1 = 90.9% and PRP-1 = 66.8%. This indicates that a certain degree of platelet activation/aggregation had already occurred during the experimental procedure.
3.3. TGF-β1 Concentrations
Figure 3A shows that the PRP-1 samples contained TGF-β1 concentrations that were significantly higher (12,407 pg/mL) than those that were found in PRP-0, PPP-1, and PPP-2 (p = 0.0001). The mean TGF-β1 concentrations in PRP-0 (5537 pg/mL) and PPP-1 (5539 pg/mL) were similar to each other, while PPP-2 presented the lowest concentrations (mean 2942 pg/mL) (Figure 3A).
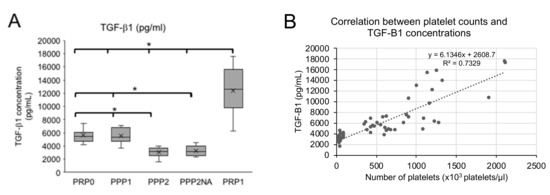
Figure 3.
Transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) concentrations (A) and correlation between Platelet counts and TGF-β1 concentrations (B). The results in (A) are shown as Box plots, representing medians (horizontal central lines), means (x), 25th and 75th percentiles (rectangles, first and third quartiles), and minimal and maximal values (vertical lines) for each experimental group. PRP0, PRP obtained by the single protocol; PPP1, platelet poor plasma obtained in the first centrifugation step of double protocol; PPP2, supernatant of the second centrifugation step of double protocol; PPP2NA, PPP2 with no agonist; PRP1, PRP obtained by the double protocol. * Differences statistically significant (p < 0.05).
Figure 3B shows that there is a positive correlation between platelet count and TGF-β1 concentrations (R2 = 0.74; Pearson’s correlation coefficient = 0.86).
Table 1 shows that the TGF-β1 concentration was proportional to the platelet counts in PRP-0, PPP-1, and PRP-1. The only exception was PPP-2 (the supernatant of double centrifugation protocol), which presented low platelet counts and relative higher TGF-β1 concentrations.

Table 1.
Ratio between TGF-β1 concentrations and platelet counts obtained from platelet-rich plasma 0 (PRP-0) and 1 (PRP-1), and platelet-poor plasma 1 (PPP-1) and 2 (PPP-2).
Table 2 shows the TGF-β1 concentrations in the final volume of each product analyzed (across samples PRP-0, PRP-1, PPP-1, and PPP-2).

Table 2.
TGF-β1 concentrations (pg) in total volume (mL) obtained in platelet-rich plasma 0 (PRP-0), 1 (PRP-1), and platelet-poor plasma 1 (PPP-1) and 2 (PPP-2).
4. Discussion
The aim of the present study was to establish a protocol to prepare PRP with high platelet counts, as well as high TGF-β1 concentration. PRPs with such characteristics are supposed to be more useful for intra-articular administration in treating joint diseases.
Two different protocols were tested, and the products thus obtained were characterized, concerning platelet counts, TGF-β1 concentrations, and premature platelet activation/aggregation.
Our results have shown that the first protocol, based on a single centrifugation step, avoided premature platelet activation/aggregation, but resulted in a preparation with relatively low platelet and TGF-β1 concentrations (PRP-0).
In contrast, the final product that was obtained by the double-centrifugation protocol—PRP-1—presented high platelet counts and high TGF-β1 concentration, but some degree of premature platelet activation occurred. Leukocyte counts were not concentrated.
PPP-1, the product of the first centrifugation step in the double centrifugation protocol, was similar to PRP-0. This product could be considered to be a “PRP”, since it presents the minimum platelet concentration required to be considered a “PRP” by Fortier et al. [19] (4.2 times).
Table 3 summarizes the main characteristics of our preparations and of the preparations described in the literature.

Table 3.
PRP characterization.
The platelet concentrations in PPP-1 and PRP-1 were higher than many other preparations for equines [7,28,29,31], and was also higher than the concentration that was obtained by Hessel et al. [30] while using the E-PET ® device.
The PRP-1, obtained after the second centrifugation step, resulted in a platelet concentration of 7.6 times the baseline. This concentration was higher than most of other studies, both in equines and human (Table 3), but it was slightly lower than those reported by Textor et al., using double centrifugation [32] that achieved weight times concentration, and Sutter et al. [8] that achieved 13 times and nine times concentrations, respectively, by apheresis/filtration and buffy coat methods. Nevertheless, apheresis only gave lower platelet concentrations (5 times) [8].
The presence of leukocytes in PRP may be useful or harmful, depending on the planned use and treatment objective [38]. In the present study, PRP was aimed for intra-articular injection. In this case, leukocytes are undesirable, because it is already known that patients who receive leukocyte-rich PRP present more joint swelling and pain [39], besides other deleterious effects [2,33]. Leukocyte were not concentrated in none of our products—PRP-0, PPP-1, and PRP-1. Nevertheless, it is important to note that the leukocytes count in PRP-1 were higher than those that were observed by Vendruscolo et al. [29] in their study of ten different protocols for double centrifugation. We also found higher leukocyte counts than those that were reported by Pereira et al. [35]. These results might be explained by differences in the plasma collection after centrifugation (although always avoiding the “buffy coat”).
The leukocyte concentration in our PRP-0 was also very low, in contrast to the results that were reported by Fontenot et al. [28], who also used a single-centrifugation protocol, but at higher speed, resulting in leukocytes-rich plasma. Of course, the growth factor composition of PRP is affected by the presence of other cell types [34].
In PRP preparation, besides the concentration of platelets, its functionality is also an issue, because platelets that were prematurely activated have possibly released their growth factors. This point was evaluated here by an aggregometry test, which was induced by collagen as exogenous agonist. By the single-centrifugation protocol, the platelets were not activated, in contrast to the double-centrifugation protocol, in which 90% of platelets responded after the first centrifugation step (PPP-1), and only 66.8% responded after the second centrifugation step (PRP-1). These results suggest that increased centrifugation speed and time could lead to platelet activation, which is in agreement with other authors [40]. Argüeles et al. [7] observed higher platelet activation after the first centrifugation step, which was possibly due to the presence of red blood cells in these samples, while Kingston et al. [41] have shown that sodium citrate partially inhibits platelet aggregation.
In the present study, collagen was used as exogenous agonist. Reversible responses are obtained [42], although other agonists may be also used, such as epinephrine and ADP, in contrast to collagen that induces irreversible aggregation and release of growth factors, mainly TGF-β1 and PDGF-BB in a dose-dependent fashion, up to 10% of the estimated total platelet content [32].
The TGF-β1 concentrations were similar in PRP-0 (single-centrifugation) and PPP-1 (first centrifugation step in the double-centrifugation protocol), despite their differences in platelet counts. This could be due to the premature platelet activation and partial TGF-β1 release in the preparation of PPP-1.
The highest TGF-β1 concentrations were found in PRP-1 (double-centrifugation procedure), again demonstrating a correlation between platelet counts and TGF-β1 concentration. This result agrees with other studies on PRP in equines [8,33,34,36]. PPP-2, which is the supernatant of the double-centrifugation protocol, contained low platelet counts and high TGF-β1 concentrations, possibly due to the premature platelet activation and TGF-β1 release during the second centrifugation step.
Table 3 also shows that other authors [32,37] obtained preparations with high platelet counts, but low TGF-β1 concentrations in comparison to ours. According to Textor and Tablin [37], treatment with bovine thrombin as agonist or with 10% calcium chloride increased TGF-β1 concentrations, which indicated that TGF-β1 was released by platelet activation. Argüelles et al. [7] obtained a preparation with low platelet counts, but high TGF-β1 concentrations (after 10% calcium chloride activation), and the authors concluded that single centrifugation was “more efficient”, meaning that less premature platelet activation occurred. This result is similar to ours.
Pereira et al. [35] compared seven different double-centrifugation protocols, which concentrated the platelets from 4.1 to 5.4 times, and the TGF-β1 concentrations achieved our PRP-1 values in only one of the protocols (Table 3). The values that were obtained in all of these studies, as well as in the present report, were lower than those that were reported by Sutter et al. [8] by apheresis, followed by filtration.
As platelet activation is necessary to release growth factors, the avoidance of premature activation guarantees the presence of growth factors at the time of PRP use. Most of the growth factors have short half-lives after release (minutes to a few hours). If activated platelets are not used in an adequate timeframe, the growth factors become inactivated before application to the target tissue [43]. Consequently, premature platelet activation or a delay in use can result in poor therapeutic efficacy.
It should be emphasized that the procedures described here permit the preparation of PRPs with different characteristics, which could be useful in treating different clinical joint conditions. For example, PRP-0 may be useful to treat large joints, in which the injection volume is not an issue, while PRP-1, whereas more laborious and time-consuming, may be appropriate to treat small joints.
5. Conclusions
The present study has compared two procedures for preparation of PRP, one that is based on a single-centrifugation step and one based on double-centrifugation. In the single-centrifugation procedure, no premature platelet activation occurred, but platelets and TGF-β1 were less concentrated. The double-centrifugation protocol resulted in high platelet and TGF-β1 concentrations, but a certain degree of activation occurred, which was evidenced by both aggregometry tests and the presence of TGF-β1 in supernatant. All of our preparations were platelet-rich but not leukocyte-rich. Taken together, these results emphasize the need to carefully characterize the PRP obtained by any procedure, to produce reliable and reproducible results.
Author Contributions
The conceptualization of the experiment was initiated by S.R.T.S. and R.Y.A.B.; Methodology, S.R.T.S., C.P.V., J.J.M., J.F. and T.F.O.; Validation of data was performed by S.R.T.S., T.F.O., M.L.V.O., Y.M.M. and R.Y.A.B.; Formal analysis was done by R.Y.A.B.; Investigation was done by S.R.T.S. and T.F.O.; Resources were looked up by S.R.T.S. and R.Y.A.B.; Curation and preparation, visualization of data and writing original draft preparation was performed by S.R.T.S. and R.Y.A.B.; Supervision and writing of the review was done by all co-authors; Editing was done by Y.M.M. and R.Y.A.B.; Project was administrated by S.R.T.S. and R.Y.A.B.
Funding
This research was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that have no conflict of interest.
References
- Brossi, P.M.; Moreira, J.J.; Machado, T.S.L.; Baccarin, R.Y.A. Platelet-rich plasma in orthopedic therapy: A comparative systematic review of clinical and experimental data in equine and human musculoskeletal lesions. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.A.; Saltzman, B.M.; Mascarenhas, R.; Khair, M.M.; Verma, N.N.; Bach, B.R.; Cole, B.J. Does Intra-articular Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection Provide Clinically Superior Outcomes Compared with Other Therapies in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis? A Systematic Review of Overlapping Meta-analyses. Arthroscopy 2015, 31, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filardo, G.; Kon, E.; Roffi, A.; Di Matteo, B.; Merli, M.L.; Marcacci, M. Platelet-rich plasma: Why intra-articular? A systematic review of preclinical studies and clinical evidence on PRP for joint degeneration. Knee Surg. Sport Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2015, 23, 2459–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendruscolo, C.P.; Alves, A.L.G.; Brossi, P.M.; Baccarin, R.Y.A. Uso do soro autólogo condicionado e do plasma rico em plaquetas na terapia ortopédica de equinos. Semina 2014, 35, 2607–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, L.A.; Barker, J.U.; Strauss, E.J.; McCarrel, T.M.; Cole, B.J. The Role of Growth Factors in Cartilage Repair. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 2706–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Doda, V.; Kotwal, U.; Dogra, M. Quantification of platelets and platelet derived growth factors from platelet-rich-plasma (PRP) prepared at different centrifugal force (g) and time. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2016, 54, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argüelles, D.; Carmona, J.U.; Pastor, J.; Iborra, A.; Viñals, L.; Martínez, P.; Bach, P.; Prades, M. Evaluation of single and double centrifugation tube methods for concentrating equine platelets. Res. Vet. Sci. 2006, 81, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutter, W.W.; Kaneps, A.J.; Bertone, A.L. Comparison of hematologic values and transforming growth factor-β and insulin-like growth factor concentrations in platelet concentrates obtained by use of buffy coat and apheresis methods from equine blood. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2004, 65, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubkowska, A.; Dolegowska, B.; Banfi, G. Growth factor content in PRP and their applicability in medicine. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2012, 26, 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Van Beuningen, H.M.; Van Der Kraan, P.M.; Arntz, O.J.; Van Den Berg, W.B. Protection from interleukin 1 induced destruction of articular cartilage by transforming growth factor β: Studies in anatomically intact cartilage in vitro and in vivo. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1993, 52, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kraan, P.M.; Blaney Davidson, E.N.; Blom, A.; Van den Berg, W.B. TGF-beta signaling in chondrocyte terminal differentiation and osteoarthritis. Modulation and integration of signaling pathways through receptor-Smads. Osteoarthr. Cartilage 2009, 17, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freyria, A.M.; Mallein-Gerin, F. Chondrocytes or adult stem cells for cartilage repair: The indisputable role of growth factors. Injury 2012, 43, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, T.I.; Roberts, A.B. Transforming growth factor β regulates the metabolism of proteoglycans in bovine cartilage organ cultures. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 12828–12831. [Google Scholar]
- Imler, S.M.; Doshi, A.N.; Levenston, M.E. Combined effects of growth factors and static mechanical compression on meniscus explant biosynthesis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2004, 12, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugé, C.; Girard, N.; Lhuissier, E.; Bazille, C.; Boumediene, K. Regulation and Role of TGFβ Signaling Pathway in Aging and Osteoarthritis Joints. Aging Dis. 2014, 5, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denker, A.E.; Nicoll, S.B.; Tuan, R.S. Formation of cartilage-like spheroids by micromass cultures of murine C3H10T1/2 cells upon treatment with transforming growth factor-β1. Differentiation 1995, 59, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beuningen, H.M.; Glansbeek, H.L.; Van Der Kraan, P.M.; Van Den Berg, W.B. Osteoarthritis-like changes in the murine knee joint resulting from intra-articular transforming growth factor-β injections. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2000, 8, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaney Davidson, E.N.; Van der Kraan, P.M.; Van den Berg, W.B. TGF-β and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2007, 15, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, L.A.; Hackett, C.H.; Cole, B.J. The Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Cartilage: Basic Science and Clinical Application. Oper. Tech. Sports Med. 2011, 19, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Floryan, K.; Berghoff, W. Intraoperative use of autologous platelet-rich and platelet-poor plasma for orthopedic surgery patients. AORN J. 2004, 80, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadil, D.P.; Satterlee, C.C.; Costigan, J.M.; Holt, D.W.; Shostrom, V.K. Autologous platelet gel and platelet-poor plasma reduce pain with total shoulder arthroplasty. J. Extra Corpor. Technol. 2007, 39, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malahias, M.A.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; Nikolaou, V.S.; Megaloikonomos, P.D.; Kazas, S.T.; Chronopoulos, E.; Babis, G.C. Similar effect of ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma versus platelet-poor plasma injections for chronic plantar fasciitis. Foot 2019, 38, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, I.; Marukawa, E.; Takahashi, Y.; Omura, K. Effects of platelet-poor plasma, platelet-rich plasma, and platelet-rich fibrin on healing of extraction sockets with buccal dehiscence in dogs. Tissue Eng. A 2014, 20, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottaiano, T.F.; Andrade, S.S.; De Oliveira, C.; Silva, M.C.C.; Buri, M.V.; Juliano, M.A.; Girão, M.J.B.C.; Sampaio, M.U.; Schmaier, A.H.; Wlodawer, A.; et al. Plasma kallikrein enhances platelet aggregation response by subthreshold doses of ADP. Biochimie 2017, 135, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Born, G.V.R.; Cross, M.J. The aggregation of blood platelets. J. Physiol. 1963, 168, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tablin, F.; Walker, N.J.; Hogle, S.E.; Pratt, S.; Norris, J.W. Assessment of platelet growth factors in supernatants from rehydrated freeze-dried equine platelets and their effects on fibroblasts in vitro. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2008, 69, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Textor, J.A.; Willits, N.H.; Tablin, F. Synovial fluid growth factor and cytokine concentrations after intra-articular injection of a platelet-rich product in horses. Vet. J. 2013, 198, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontenot, R.L.; Sink, C.A.; Were, S.R.; Weinstein, N.M.; Dahlgren, L.A. Simple tube centrifugation for processing platelet-rich plasma in the horse. Can. Vet. J. 2012, 53, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vendruscolo, C.P.; De Carvalho, A.M.; Moraes, L.F.; Maia, L.; Queiroz, D.L.; Watanabe, M.J.; Yamada, A.L.M.; Alves, A.L.G. Avaliação da eficácia de diferentes protocolos de preparo do Plasma Rico em Plaquetas para uso em Medicina Equina. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2012, 32, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessel, L.N.; Bosch, G.; Van Weeren, P.R.; Ionita, J.C. Equine autologous platelet concentrates: A comparative study between different available systems. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, J.U.; Argüelles, D.; Climent, F.; Prades, M. Autologous Platelet Concentrates as a Treatment of Horses with Osteoarthritis: A Preliminary Pilot Clinical Study. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2007, 27, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Textor, J.A.; Norris, J.W.; Tablin, F. Effects of preparation method, shear force, and exposure to collagen on release of growth factors from equine platelet-rich plasma. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2011, 72, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarrel, T.; Fortier, L. Temporal growth factor release from platelet-rich plasma, trehalose lyophilized platelets, and bone marrow aspirate and their effect on tendon and ligament gene expression. J. Orthop. Res. 2009, 27, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundman, E.A.; Cole, B.J.; Fortier, L.A. Growth Factor and Catabolic Cytokine Concentrations Are Influenced by the Cellular Composition of Platelet-Rich Plasma. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.C.D.F.; Zacarias, G.V.F.; Cantarelli, C.; Corrêa, M.M.B.; Silva, G.B.; Barbosa, A.L.T.; Brass, K.E.; De La Côrte, F.D. Avaliação De Sete Protocolos De Obtenção De Plasma Rico Em Plaquetas. Ciência Rural 2012, 43, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, J.; Plevin, S. Temporal release of growth factors from platelet-rich Fibrin (PRF) and Platelet-rich Rlasma (PRP) in the horse: A comparative in vitro analysis. Int. J. Appl. Res. Vet. Med. 2014, 12, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Textor, J.A.; Tablin, F. Activation of equine platelet-rich plasma: Comparison of methods and characterization of equine autologous thrombin. Vet. Surg. 2012, 41, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansdown, D.A.; Fortier, L.A. Platelet Rich Plasma: Formulations, Preparations, Constituents, and Their Effects. Oper. Tech. Sports Med. 2016, 25, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filardo, G.; Kon, E.; Pereira Ruiz, M.T.; Vaccaro, F.; Guitaldi, R.; Di Martino, A.; Cennachi, A.; Fornasari, P.M.; Marcacci, M. Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular injections for cartilage degeneration and osteoarthritis: Single- versus double-spinning approach. Knee Surg. Sport Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2012, 20, 2082–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausset, O.; Giraudo, L.; Veran, J.; Magalon, J.; Coudreuse, J.M.; Magalon, G.; Dubois, C.; Serratrice, N.; Dignat-George, F.; Sabatier, F. Formulation and storage of platelet-rich plasma homemade product. Biores. Open Access 2012, 1, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, J.K.; Bayly, W.M.; Sellon, D.C.; Meyers, K.M.; Wardrop, K.J. Effects of sodium citrate, low molecular weight heparin, and prostaglandin E1 on aggregation, fibrinogen binding, and enumeration of equine platelets. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, D.; Monreal, L.; Espada, Y.; Pastor, J.; Mayós, I.; Homedes, J. Assessment of a platelet function analyser in horses: Reference range and influence of a platelet aggregation inhibitor. Vet. J. 2005, 170, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.; Vavken, P.; Kevy, S.; Jacobson, M.; Zurakowski, D.; Murray, M.M. Platelet activation by collagen provides sustained release of anabolic cytokines. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).