Influence of Probiotic Administration in Canine Feed: A Comprehensive Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
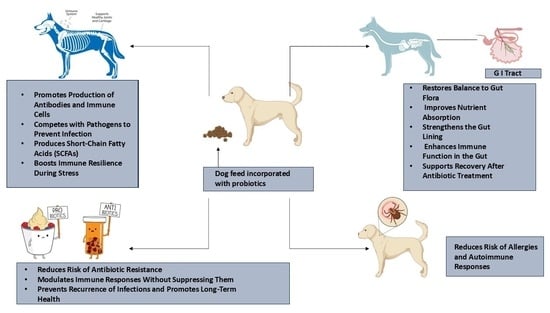
2. Utilization of Probiotic Strains in Dog Food
2.1. Role of Lactobacillus Acidophilus in Gut Health
2.2. Role of Saccharomyces boulardii in Immune System
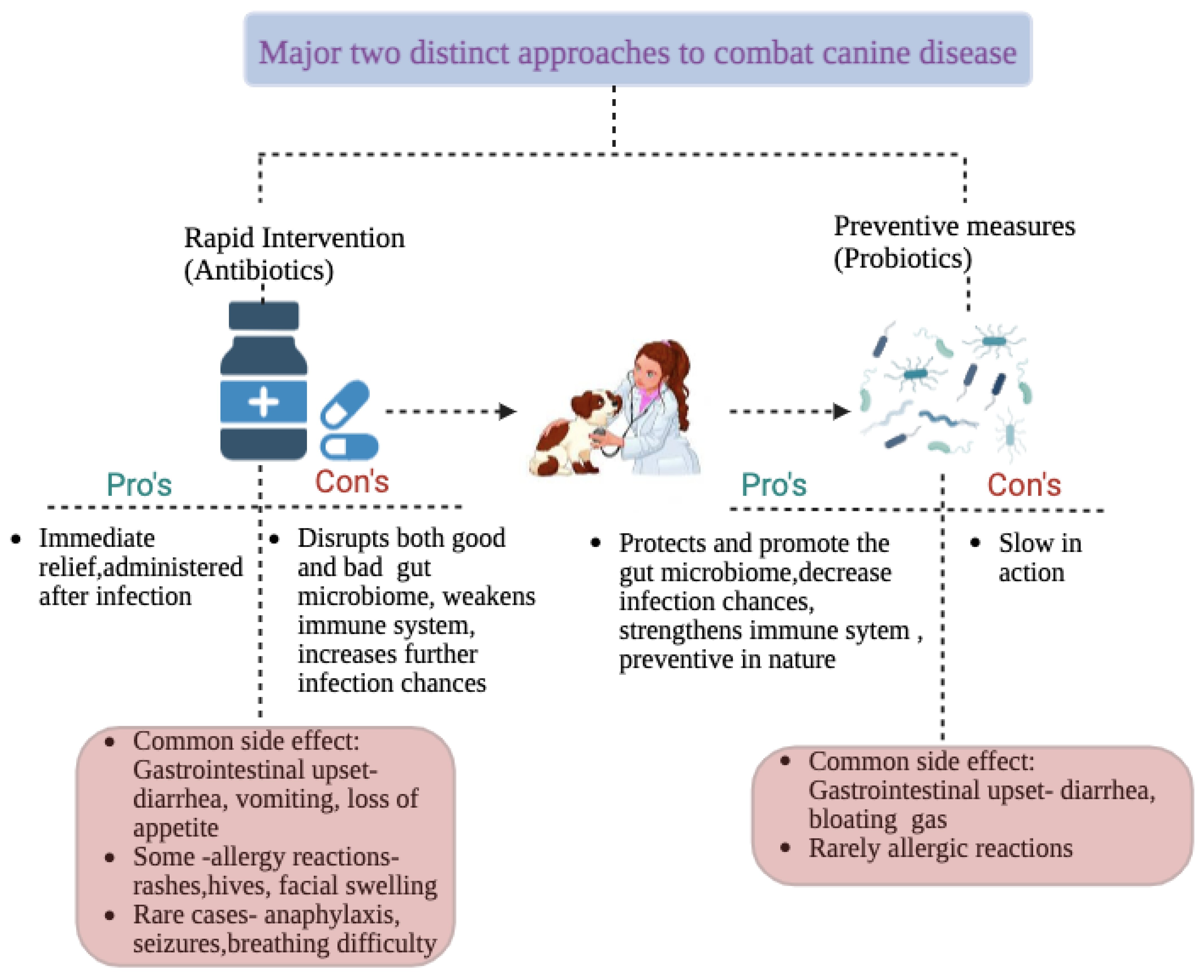
3. Canine Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy and Probiotics
4. Obesity in Dogs and Probiotics
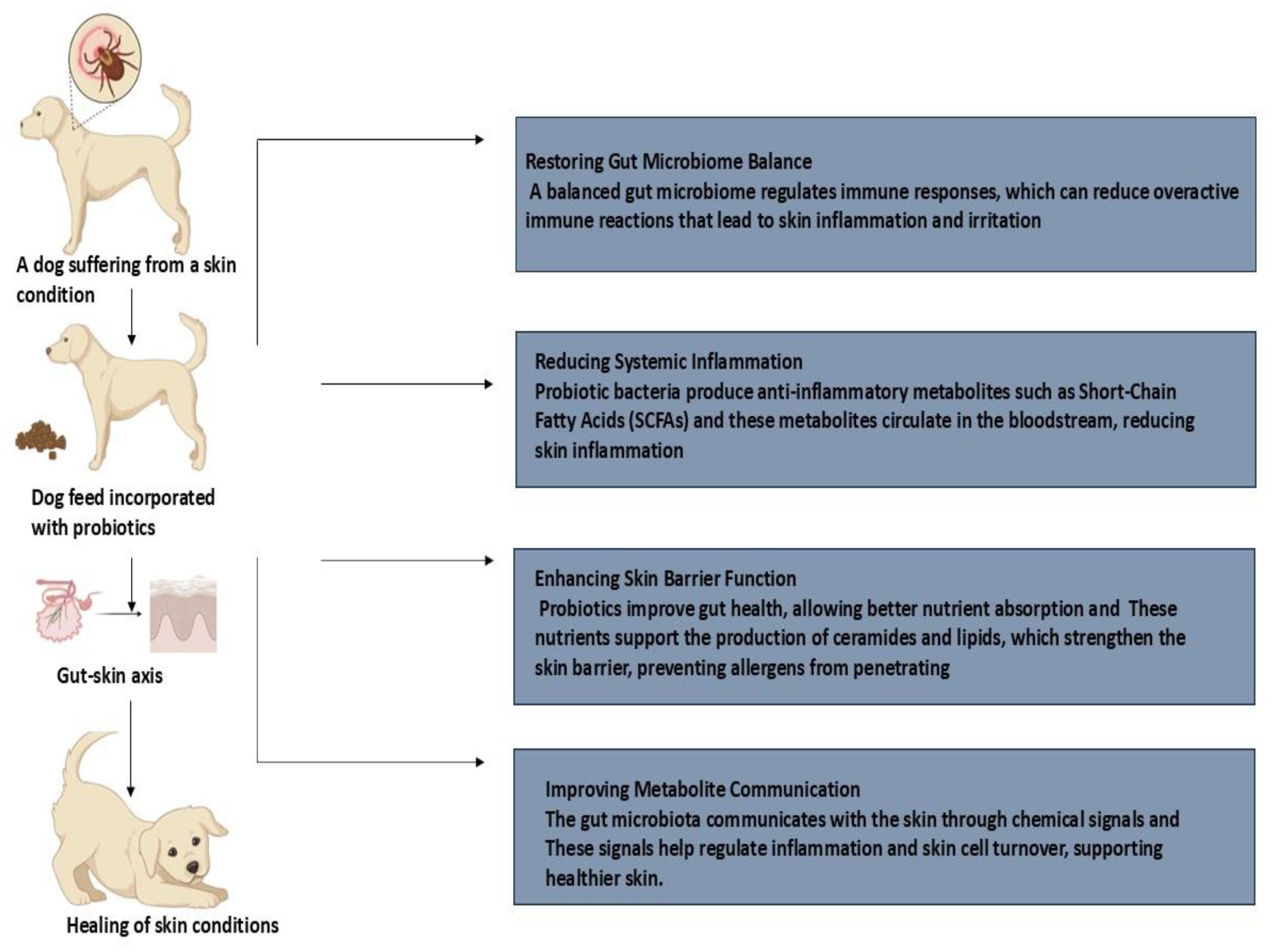
5. Atopic Dermatitis and Probiotics
6. Technologies Used to Incorporate Probiotics in Dog Feed to Ensure Maximum Effectiveness
| Technology Used | Benefits | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Microencapsulation | Enhancing the survival of probiotic cells through gastrointestinal digestion and boosting their stability. | [49] |
| Edible Films and Coatings Functionalization by Probiotic Incorporation | Edible coatings and films provide an eco-friendlier and consumer-oriented alternative to conventional food packaging. | [54] |
| Freeze-Drying | Compared to other drying techniques, freeze-drying probiotics uses less energy while maintaining their original physical and chemical properties. | [52] |
| Fermentation Technologies | Continuous culture and immobilized cell systems are two examples of fermentation technologies that may increase the effectiveness of probiotic strains, improve gut function, increase the number of strains accessible, and expand the uses of products. | [55] |
| Encapsulation with Liposomes | It forms a protective barrier around the bacteria, shielding them while permitting small molecules to pass through. | [56] |
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Castro Santos Melo, C.; Da Silva Freire, A.; Galdeano, M.A.; Da Costa, C.F.; De Oliveira Gonçalves, A.P.D.; Dias, F.S.; Menezes, D.R. Probiotic potential of Enterococcus hirae in goat milk and its survival in canine gastrointestinal conditions simulated in vitro. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 138, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Wu, Z. Gut probiotics and health of dogs and cats: Benefits, applications, and underlying mechanisms. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasaly, N.; de Vos, P.; Hermoso, M.A. Impact of bacterial metabolites on gut barrier function and host immunity: A focus on bacterial metabolism and its relevance for intestinal inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 658354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Yan, W.; Ma, Y.; Fang, J. The impact of probiotics on gut health via alternation of immune status of monogastric animals. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marelli, S.P.; Fusi, E.; Giardini, A.; Martino, P.A.; Polli, M.; Bruni, N.; Rizzi, R. Effects of probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus D2/CSL (CECT 4529) on the nutritional and health status of boxer dogs. Vet. Rec. 2020, 1874, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Pattanaik, A.K.; Jadhav, S.E. Potent health-promoting effects of a synbiotic formulation prepared from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCDC15 fermented milk and Cichorium intybus root powder in Labrador dogs. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2021, 3, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Chaiyasut, C. Influence of probiotic supplementation on health status of the dogs: A review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillon, M.L.; Marshall-Jones, Z.V.; Butterwick, R.F. Effects of probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus strain DSM13241 in healthy adult dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2004, 65, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascher, M.; Hellweg, P.; Khol-Parisini, A.; Zentek, J. Effects of a probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus strain on feed tolerance in dogs with non-specific dietary sensitivity. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 62, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, V.H.; Bandara, H.M.; Ishikawa, K.H.; Mayer, M.P.; Samaranayake, L.P. The role of probiotic bacteria in managing periodontal disease: A systematic review. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2016, 14, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, I.; Mahiddine, F.Y.; Park, H.; Kim, M.J. Lactobacillus acidophilus novel strain, MJCD175, as a potential probiotic for oral health in dogs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 946890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegh, C.A.M.; Geerlings, S.Y.; Knol, J.; Roeseler, G.; Belzer, C. Postbiotics and their potential applications in early life nutrition and beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelesidis, T.; Pothoulakis, C. Efficacy and safety of the probiotic Saccharomyces boulardii for the prevention and therapy of gastrointestinal disorders. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2012, 5, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meineri, G.; Martello, E.; Atuahen, D.; Miretti, S.; Stefanon, B.; Sandri, M.; Biasato, I.; Corvaglia, M.R.; Ferrocino, I.; Cocolin, L.S. Effects of saccharomyces boulardii supplementation on nutritional status, fecal parameters, microbiota, and mycobiota in breeding adult dogs. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grellet, A.; Heilmann, R.M.; Lecoindre, P.; Feugier, A.; Day, M.J.; Peeters, D.; Freiche, V.; Hernandez, J.; Grandjean, D.; Suchodolski, J.S.; et al. Fecal calprotectin concentrations in adult dogs with chronic diarrhea. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2013, 74, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, S.; Fracassi, F.; Bresciani, F.; Galuppi, R.; Diana, A.; Linta, N.; Bettini, G.; Morini, M.; Pietra, M. Effect of Saccharomyces boulardii in dogs with chronic enteropathies: Double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. Vet. Rec. 2017, 182, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, Q.; Mugnier, A.; Chastant, S.; Sicard, F.; Martin, J.C.; Svilar, L.; Castex, M.; Ramis-Vidal, M.G.; Rovere, N.; Michaud, L.; et al. The supplementation of female dogs with live yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae var boulardii CNCM I-1079 acts as gut stabilizer at whelping and modulates immunometabolic phenotype of the puppies. Front. Nutr. 2024, 12, 1366256. [Google Scholar]
- Lonigro, N.; Perondi, F.; Bruni, N.; Bigliati, M.; Costale, A.; Pagani, E.; Lippi, I.; Melocchi, A.; Zema, L.; Meineri, G.; et al. How Does Saccharomyces cerevisiae DSM 34246 (Canobios-BL) var. boulardii Supplementation Impact the Fecal Parameters of Healthy Adult Dogs? Vet. Sci. 2025, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidori, M.; Corbee, R.J.; Trabalza-Marinucci, M. Nonpharmacological treatment strategies for the management of canine chronic inflammatory enteropathy—A Narrative Review. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.M.; Pinchbeck, G.; McIntyre, K.M.; Nuttall, T.; McEwan, N.; Dawson, S.; Williams, N.J. Routine antibiotic therapy in dogs increases the detection of antimicrobial-resistant faecal Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 3305–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, S.; Suchodolski, J. Understanding the canine intestinal microbiota and its modification by pro-, pre- and synbiotics-what is the evidence? Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 2, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.S.; Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Reime, R.A.; Reid, G.; Verbeke, K.; Scott, K.P.; Holscher, H.D.; Azad, M.B.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of synbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez-Brito, M.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Gómez-Llorente, C.; Gil, A. Probiotic mechanisms of action. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidori, M.; Rueca, F.; Massacci, F.R.; Diaferia, M.; Giontella, A.; Caldin, M.; Furlanello, T.; Corbee, R.J.; Mannucci, G.; Pezzotti, G.; et al. The use of Ascophyllum nodosum and Bacillus subtilis C-3102 in the management of canine chronic inflammatory enteropathy: A pilot study. Animals 2021, 11, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herstad, K.M.V.; Vinje, H.; Skancke, E.; Næverdal, T.; Corral, F.; Llarena, A.; Heilmann, R.M.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M.; Nyquist, N.F. Effects of Canine-Obtained Lactic-Acid bacteria on the fecal microbiota and inflammatory markers in dogs receiving Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory treatment. Animals 2022, 12, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwoha, I.O. A review on trypanosomosis in dogs and cats. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 6432–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Cui, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Deng, B.; Han, S. The function of probiotics and prebiotics on canine intestinal health and their evaluation criteria. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washabau, R.J. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis. In Elsevier eBooks; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Hobi, S.; Bęczkowski, P.M.; Mueller, R.; Tse, M.; Barrs, V.R. Malassezia dermatitis in dogs and cats. Vet. J. 2024, 304, 106084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truglio, M.; Sivori, F.; Cavallo, I.; Abril, E.; Licursi, V.; Fabrizio, G.; Cardinali, G.; Pignatti, M.; Toma, L.; Valensise, F.; et al. Modulating the skin mycobiome-bacteriome and treating seborrheic dermatitis with a probiotic-enriched oily suspension. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda, L.J.; Perper, M.; Keri, J.E. Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis: A comprehensive review. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2019, 30, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, N.D.; Craigon, P.J.; Shaw, S.C.; Blott, S.C.; England, G.C.W. Behavioural differences in dogs with atopic dermatitis suggest stress could be a significant problem associated with chronic pruritus. Animals 2019, 9, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umborowati, M.A.; Damayanti, D.; Anggraeni, S.; Endaryanto, A.; Surono, I.S.; Effendy, I.; Prakoeswa, C.R.S. The role of probiotics in the treatment of adult atopic dermatitis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2022, 41, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.E.; Shofer, F.S.; Laster, L. Association of age and body weight with periodontal disease in North American dogs. J. Vet. Dent. 1994, 11, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heseltine, J.C.; Panciera, D.L.; Saunders, G.K. Systemic candidiasis in a dog. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 223, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenplas, Y. Bacteria and yeasts in the treatment of acute and chronic infectious diarrhea. Part II: Yeasts. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 1999, 5, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciňáková, M.; Simonová, M.; Strompfová, V.; Lauková, A. Oral application of Enterococcus faecium strain EE3 in healthy dogs. Folia Microbiol. 2006, 51, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahraman, O.; Gurbuz, E.; Inal, F.; Arık, H.D.; Alatas, M.S.; Inanc, Z.S.; Ahmed, I. Effects of Bacillus subtilis C-3102 addition on nutrient digestibility, faecal characteristics, blood chemistry and faecal Lactobacilli spp., Enterococci spp., and Escherichia coli in healthy dogs. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 22, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Cho, J.H.; Cho, W.; Gang, S.; Park, S.; Jung, B.; Kim, H.B.; Song, K.H. Effects of synbiotic preparation containing Lactobacillus gasseri BNR17 on body fat in obese dogs: A pilot study. Animals 2022, 12, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoran, D.L. Obesity in dogs and cats: A metabolic and endocrine disorder. The Veterinary clinics of North America. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 40, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, A.; Kwakm, M.; Lee, D.J.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, M.K.; Song, M.; Lee, M.; Yang, J.; Oh, S.; Kim, Y. Dietary supplementation with probiotics promotes weight loss by reshaping the gut microbiome and energy metabolism in obese dogs. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0255223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, A.J. The growing problem of obesity in dogs and cats. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1940S–1946S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; So, D.; An, S.; Cho, E.; Lim, S.; Lee, H. Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum CBT LP3 and Bifidobacterium breve CBT BR3 supplementation on weight loss and gut microbiota of overweight dogs. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milosevic, I.; Vujovic, A.; Barac, A.; Djelic, M.; Korac, M.; Spurnic, A.R.; Gmizic, I.; Stevanovic, O.; Djordjevic, V.; Lekic, N.; et al. Gut-Liver Axis, gut microbiota, and its modulation in the management of liver diseases: A review of the literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsella, R.; Santoro, D.; Ahrens, K. Early exposure to probiotics in a canine model of atopic dermatitis has long-term clinical and immunological effects. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 146, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, M.; Bahar, A.; Keikha, M.; Karbalaei, M.; Kobyliak, N.; Yousefi, B. Probiotics function and modulation of the immune system in allergic diseases. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2020, 48, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Yun, T.; Ham, J.; Lee, W.; Kang, J.; Yang, M.; Kang, B. Clinical trial of oral administration of Bifidobacterium longum in dogs with atopic dermatitis. Korean J. Vet. Res. 2020, 60, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuff, H.G.; Aldrich, C. Acuff, H.G.; Aldrich, C. A review of application strategies and efficacy of probiotics in pet food. In Antibiotics and Probiotics in Animal Food-Impact and Regulation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vivek, K.; Mishra, S.; Pradhan, R.C.; Nagarajan, M.; Kumar, P.K.; Singh, S.S.; Manvi, D.; Gowda, N.N. A comprehensive review on microencapsulation of probiotics: Technology, carriers and current trends. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 3, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbehat, M.; Mauriello, G.; Altamimi, M. Microencapsulation of probiotics for food functionalization: An update on literature reviews. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foongsawat, N.; Sunthornthummas, S.; Rangsiruji, A.; Sarawaneeyaruk, S.; Insian, K.; Pringsulaka, O. In vitro survival of microencapsulated canine-specific probiotics under simulated gastrointestinal tract conditions and during storage. J. Curr. Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Han, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Ye, Z.; Li, P.; Gu, Q. Research progress on improving the freeze-drying resistance of probiotics: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.; Janfaza, S.; Tasnim, N.; Gibson, D.L.; Hoorfar, M. Microencapsulating polymers for probiotics delivery systems: Preparation, characterization, and applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, O.L.; Pop, C.R.; Dufrechou, M.; Vodnar, D.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Dulf, F.V.; Minervini, F.; Suharoschi, R. Edible films and coatings functionalization by probiotic incorporation: A review. Polymers 2019, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, C.; Yildirim, S. Fermentation technologies for the production of probiotics with high viability and functionality. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Yin, S.; He, Y.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, C. Biomaterials and encapsulation techniques for Probiotics: Current status and future prospects in biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name of the Diseases | Symptoms | Probiotic Used | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| African trypanosomiasis | When trypanosomes penetrate the epidermal barrier, a localized inflammatory response known as chancre development is triggered. | Lactobacillus reuteri | [26] |
| Colitis | Large-bowel diarrhea is marked by symptoms such as the presence of mucus in the stool, fresh blood (hematochezia), a frequent urge to defecate (tenesmus), and sometimes discomfort or pain during bowel movements. | Lactobacillus acidophilus | [27] |
| Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency | This disorder is brought on by insufficient pancreatic digesting enzymes in the small intestine. Symptoms typically include weight loss, large, soft stools, and an increased appetite. | Lactobacillus reuteri | [28] |
| Malassezia dermatitis | They are usually marked by redness (erythema), flaking (scaling), and/or oily discharge. In long-term cases, thickening of the skin (lichenification) and darkening of the skin (hyperpigmentation) may also occur. | Lacticaseibacillus paracasei | [29] |
| Seborrheic dermatitis | Small, thin patches coated with oily scales are the hallmark of seborrheic dermatitis, which is most frequently observed in regions including the scalp, face, chest, back, and skin folds that have a high density of sebaceous glands. | Lactobacillus crispatus | [30,31] |
| Stress-Induced Dermatitis | Comfort-seeking, grooming, less trainability, fear- and anxiety-related behaviors, aggression, excitability, and attention-seeking. | Lactobacillus plantarum | [32,33] |
| Canine Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy | Vomiting and diarrhea. | Ascophyllum nodosum and Bacillus subtilis C-3102 | [24] |
| Halitosis | Bad breath. | Lactobacillus acidophilus | [11] |
| Periodontal Disease | Gum inflammation and infection, foul breath, and tooth loss are among the symptoms. | Lactobacillus acidophilus | [11,34] |
| Candidiasis | Debris accumulation in one or both ears that is yellow, brown, or black is one of the signs. An excessive amount of head shaking and scratching of the ears or other body parts. | Saccharomyces boulardii | [35,36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karukayil Gopalakrishnan, N.; Pappuswamy, M.; Meganathan, G.; Shanmugam, S.; Pushparaj, K.; Balasubramanian, B.; Kim, I.H. Influence of Probiotic Administration in Canine Feed: A Comprehensive Review. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050449
Karukayil Gopalakrishnan N, Pappuswamy M, Meganathan G, Shanmugam S, Pushparaj K, Balasubramanian B, Kim IH. Influence of Probiotic Administration in Canine Feed: A Comprehensive Review. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(5):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050449
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarukayil Gopalakrishnan, Niranjana, Manikantan Pappuswamy, Gomathy Meganathan, Sureshkumar Shanmugam, Karthika Pushparaj, Balamuralikrishnan Balasubramanian, and In Ho Kim. 2025. "Influence of Probiotic Administration in Canine Feed: A Comprehensive Review" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 5: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050449
APA StyleKarukayil Gopalakrishnan, N., Pappuswamy, M., Meganathan, G., Shanmugam, S., Pushparaj, K., Balasubramanian, B., & Kim, I. H. (2025). Influence of Probiotic Administration in Canine Feed: A Comprehensive Review. Veterinary Sciences, 12(5), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050449