Simple Summary
Toxoplasmosis is a disease caused by the parasite Toxoplasma gondii, which can infect humans and animals, including dogs. Dogs become infected by accidentally ingesting the parasite’s oocysts from the environment and eating infected rodents or other small animals. Following infection, dogs develop antibodies against T. gondii. The current study investigated the percentage of dogs living in Greece that have antibodies against the parasite as an indirect way to assess the level of environmental contamination with T. gondii oocysts. Blood samples were collected from 1282 dogs living in both urban and rural regions of Greece, including Attica and Thessaloniki. Overall, 47.6% of the dogs had antibodies against the parasite, indicating they had been exposed to T. gondii. Seropositive dogs were more commonly found in rural areas (53.8%) than in urban areas (43.9%) (p < 0.001). The findings of this study suggest that T. gondii infection is widespread in dogs across Greece, especially in rural regions, and the parasite is highly present in the environment, posing a potential risk for human exposure in these areas. Control measures are necessary to prevent dogs from being infected and to reduce this risk for dog owners. Dog owners should also follow basic hygiene practices, like washing their hands after petting their dogs, to protect themselves.
Abstract
Toxoplasmosis, caused by the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii, is a zoonotic disease that affects various animal species, including dogs, that can serve as sentinels for indirectly estimating the environmental contamination. The current study aimed to determine the seroprevalence of T. gondii IgG and IgM antibodies in dogs across different regions of Greece and assess their living area as a potential risk factor. In total, 1282 blood samples were collected from dogs in urban and rural areas of Greece, including Attica and Thessaloniki. Serum samples were tested for T. gondii-specific IgG and IgM antibodies using an indirect immunofluorescent antibody test. A chi-square test was performed to assess the association between seropositivity for T. gondii and geographical location (urban/rural). The overall T. gondii seroprevalence was 47.6%, while the seroprevalence of IgG and IgM antibodies was 34.3% and 22.2%, respectively. Dogs from rural areas exhibited a significantly higher seroprevalence (53.8%) than those from urban areas (43.9%) (p < 0.001), with the estimated odds ratio being equal to 1.49 (95% CI, 1.18 to 1.65) and the relative risk increased by 22.4%. Dogs in Greece are highly exposed to T. gondii, particularly in rural areas. Measures to prevent canine infections are necessary, and basic hygiene practices, such as hand washing after petting dogs, are required to reduce human infection risk and safeguard public health.
Keywords:
dogs; Greece; IFAT; IgG; IgM; public health; rural environment; seroprevalence; Toxoplasma gondii; toxoplasmosis 1. Introduction
Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoon that causes the zoonotic disease toxoplasmosis, affecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, including humans, cats, and dogs [1]. Felines are the sole definitive hosts, shedding oocysts with their faeces, while many other animal species serve as intermediate hosts [1]. Transmission occurs mainly via the ingestion of sporulated oocysts from the environment or bradyzoites in tissue cysts of raw or undercooked meat, and vertically from the mother to the foetus [2,3,4,5].
Canine toxoplasmosis is rarely a primary disease. Following infection, dogs seroconvert, while most remain asymptomatic and do not develop pathological lesions [6,7,8]. Clinical toxoplasmosis is mainly associated with immunosuppression and co-infection with other canine pathogens such as Ehrlichia canis or the canine distemper virus (CDV) [8,9,10]. Similarly, young dogs, immunosuppressed dogs, or those undergoing corticosteroid treatment or chemotherapy are more prone to develop clinical disease [8,9,10].
When dogs exhibit symptoms, they are generalised or typically concern the lungs, central nervous system (CNS), muscles, or alimentary tract [9]. Infection of the CNS can persist for many days up to months, while infection of the pulmonary system or liver can prove fatal in just seven days [9]. Generalised clinical signs are more common in dogs under 12 months of age, including pyrexia, dyspnoea, diarrhoea, tonsil inflammation, hepatocellular icterus, and vomitus [9]. Cardiac infections are usually asymptomatic, but older dogs can show congestive heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias [9]. As for infections during pregnancy, they can lead bitches to abort [3,5,11].
Toxoplasmosis is more prevalent in cats than dogs, with the latter more frequently affected by neosporosis. In fact, until the discovery of Neospora caninum in 1988, many cases of neosporosis in dogs were misdiagnosed as canine toxoplasmosis [9,12]. Both protozooses have similar clinical pictures and low morbidity and fatality rates [8,9]. Furthermore, clinical toxoplasmosis cases in dogs may have decreased in the last decades due to the routine vaccination of dogs for CDV [9].
Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis can be achieved with different methods, including the detection of specific anti-T. gondii IgG and IgM antibodies in the dog’s serum [13]. IgG antibodies indicate a chronic infection and persist throughout the dog’s life, while IgM indicate a recent infection [9]. Detecting both IgG and IgM in dogs provides a clearer picture regarding recent and past T. gondii infections [14]. The indirect immunofluorescent antibody test (IFAT) is one of the most commonly used methods for detecting IgG antibodies in dogs and other animals and is also used to detect IgM antibodies [1,13,15]. Until now, most seroprevalence studies for T. gondii have employed IFAT due to its high diagnostic accuracy [1,10]. In fact, IFAT is highly specific, and if appropriate cut-off thresholds are utilised, there is no cross-reaction with antibodies against other protozoans, such as N. caninum [1,10]. It is worth noting that no serological test can provide a conclusive diagnosis of toxoplasmosis, and there is no association between antibody titers and the intensity of the symptoms [9].
Infection in dogs is of epidemiological relevance. Estimating the levels of environmental contamination with T. gondii oocysts can be directly performed by measuring the number of oocysts in the environment. However, this approach remains challenging and impractical [16,17]. On the other hand, since dogs that have been exposed to T. gondii seroconvert, assessing the seroprevalence in this animal species can be used as an indirect indication of T. gondii presence in a specific area. Seropositivity in dogs can also be used to evaluate human infection risk in an area since it is suggestive of the dogs’ previous exposure to T. gondii in their living environment. This is relevant to human infection risk because dogs and humans usually live in close proximity. Moreover, studies have shown that seroprevalence rates in human and canine populations are positively associated [17,18,19,20,21].
Furthermore, investigating the T. gondii seroprevalence in dogs is essential since they are the most common pets in Greek households [22]. Oocyst production does not occur in dogs because they are dead-end intermediate hosts for this protozoon [23]. However, they can mechanically carry and spread T. gondii oocysts through two routes [6,24,25]. Firstly, they like rolling in soil, foul-smelling substances, and cat faeces (xenosmophilia), which may contain oocysts. This way, dogs pick oocysts up on their fur and carry them inside the house. As a result, humans who pet them may be exposed to T. gondii oocysts [6,24,25]. Secondly, dogs may contribute to environmental contamination by excreting oocysts following ingestion of infected cat faeces during coprophagy, a typical canine behaviour [6,20,24,25,26]. However, the epidemiological significance of the mechanical transmission of T. gondii by dogs may be questioned since it has been shown that oocysts do not sporulate on the dog’s coat, probably due to unfavourable temperature and humidity conditions [6]. On the other hand, viable oocysts have been recovered from dog faeces under experimental [6] and natural [26] infection conditions. These findings justify the recommendation of hand washing after [27] contact with dogs or dog faeces to prevent T. gondii infections in humans.
In addition to being the most popular pet animal in Greece [22], a significant part of the canine population is livestock guarding dogs and hunting dogs in rural and mountainous regions. Concurrently, there are many stray dogs in both rural and urban areas. Given the large and diverse canine population in Greece, the epidemiological role of dogs in a poorly studied area, as well as the lack of previous studies investigating the prevalence of antibodies against T. gondii in dogs in Greece [28], the current study aimed to (a) estimate the seroprevalence of IgG and IgM anti-T. gondii antibodies in dogs in the country, and (b) investigate the role of dogs’ living environment (urban vs. rural areas) as a potential risk factor for their exposure to T. gondii.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Sampling and Investigation Area
In 2023, 1282 blood samples were collected from dogs (Canis lupus familiaris) living in Attica, Thessaloniki, and other areas of Greece. Attica and Thessaloniki represent Greece’s two most densely populated urban areas, with approximately 4.9 million people (47% of the Greek population) [29], while all the other sampling regions were rural areas.
All dogs were selected using simple random sampling, meaning that a subset of dogs was randomly selected from the total number of dogs admitted to the various private veterinary practices for routine examinations involving blood sampling. They were apparently healthy, older than 6 months old, and belonged to different breeds and both sexes. The cephalic, jugular, or saphenous vein was punctured in each dog to draw 2 mL of blood, which was subsequently placed into tubes with a clot activator. After allowing the blood to clot, the tubes were centrifuged at 1500× g for 10 min to obtain the serum. Serum samples were stored at −20 °C until further examination.
2.2. Serological Antibody Testing
Each sample was examined using a commercially available indirect immunofluorescent antibody test kit (IFAT) to detect IgG and IgM antibodies. Sera were diluted 2-fold from 1:100 to 1:1600 in Phosphate Buffer Solution (PBS) (P3812-10PAK, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and tested on commercial coated slides with T. gondii antigens (MegaFLUO® TOXOPLASMA g., Art.-No. 826S50FK1, MEGACOR, Hörbranz, Austria) using manufacturer’s instructions, except replacing conjugate with anti-dog IgG FITC conjugated antibody (F7884-2ml, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) diluted 1:200 in PBS. The anti-canine IgM FITC conjugated antibody (CJ-F-CANM-AP-10ML, VMRD, Pullman, WA, USA) was used for the IgM detection. Tests were evaluated under a fluorescence microscope with a filter system for FITC (iScope, Euromex, Arnhem, The Netherlands). The cut-offs employed were 1/200 for IgG and 1/100 for IgM. Each IFAT was carried out by the same experienced person who was blinded to each sample’s origin. Both positive and negative controls included in the kit were used in each analysis.
2.3. Statistical Analyses
For the estimation of the prevalence rates and their 95% confidence intervals (CI 95%), the Epitools (ausvet.com.au) and the Wilson score interval methods were used. Chi-square tests were performed using SPSS v23, with Cramér’s V values (φc), odds ratios, and relative risks being estimated to assess the association between the region (urban/rural) and the serological status with regard to IgG, IgM, or either of them. Statistical significance was set at the 0.05 level.
3. Results
The overall seropositivity in either IgG and/or IgM was 47.6% (610/1282, 95% CI: 44.9 to 50.3%), with 34.3% (440/1282, 95% CI: 31.8 to 37.0%) of samples being seropositive for IgG and 22.2% (284/1282, 95% CI: 20.0 to 24.5%) of samples seropositive for IgM. In addition, 8.9% (114/1282, 95% CI: 7.5 to 10.6%) of dogs were seropositive for both IgG and IgM antibodies. The IgG titers ranged from 1/100 to 1/1600, and the IgM titers ranged from 1/100 to 1/800.
Regarding sampling areas, the seropositivity in Attica was 46.4% (209/450, 95% CI: 41.9 to 51.1%) in Thessaloniki, 40.7% (144/354, 95% CI: 35.7 to 45.9%), and 53.8% (257/478, 95% CI: 49.3 to 58.2%) in the rest of rural Greece when considering either IgG or IgM. The seroprevalence for each antibody test in each area is summarised in Table 1, and the overall seroprevalence rates (IgG and/or IgM) in the different regions examined are illustrated in Figure 1. When considering urban and rural areas, dogs originating from urban areas had a seroprevalence of 43.9% (353/804, 95% CI: 40.5 to 47.4%), while in rural areas, seropositivity was 53.8% (257/478, 95% CI: 49.3 to 58.2%) in either IgM or IgG tests. In rural areas, dogs were more likely to be found seropositive for antibodies against T. gondii (IgG, IgM, or both) (ϕc = 0.091, and p < 0.001) compared to dogs in urban areas, with the estimated odds ratio being equal to 1.49 (95% CI, 1.18 to 1.65) and the relative risk increased by 22.4%. When seropositivity was separately considered for IgM and IgG, no significant differences were observed concerning IgM positivity between dogs in urban and rural areas, contrary to IgG positivity, where in rural areas, dogs were more likely to be found positive (ϕc = 0.064, and p = 0.021) compared to dogs in urban areas with the estimated odds ratio being equal to 1.32 (95% CI, 1.04 to 1.67) and the relative risk increased by 19.8%.

Table 1.
Toxoplasma gondii IgG, IgM, and overall (IgG or IgM) seroprevalence in dogs from different areas of Greece.
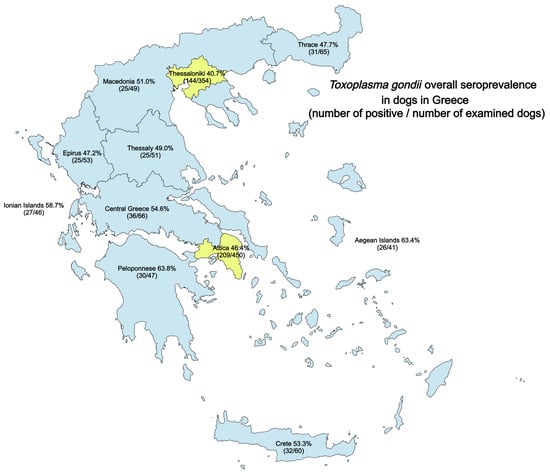
Figure 1.
Toxoplasma gondii overall seroprevalence (IgG and/or IgM) in dogs from different geographic regions of Greece. The parentheses include the numbers of positive/numbers of examined dogs in each region. Thessaloniki and Attica represent the urban areas of the current study and are painted in a different colour.
4. Discussion
In the current study, the overall T. gondii seropositivity of dogs was 47.6%, indicating that a large percentage of dogs in Greece have been exposed to T. gondii. Canine seroprevalence rates in similar studies from other countries range from 1.0% in China [10] to 98.0% in Egypt [30]. In comparison to nearby countries, dogs in Albania and Turkey displayed slightly higher overall seropositivity rates than in the current study, at 51.7% (owned dogs) and 54.3% (unspecified ownership), respectively [31]. The canine seroprevalence in some other Mediterranean countries has been estimated at 29.2% in a recent survey in Italy (owned dogs) [32] and at 58.7% in a study in Spain (kennel dogs) [33]. Seropositivity in dogs from different studies can vary because of different diagnostic methods, serum dilutions employed, sampling area climate, dog origin (stray, client-owned, or hunting dogs), the study inclusion criteria, and the oocyst environmental contamination levels [10,14,34,35].
Anti-T. gondii IgG antibodies were detected in 34.3% of dogs, while 22.2% were seropositive for IgM. The lower seroprevalence of IgM compared to IgG antibodies is unsurprising because, as mentioned above, IgM immunoglobulins in dogs persist for a couple of months post-infection [36], indicating an acute/recent or active infection [9]. In contrast, IgG antibodies can be detected lifelong after exposure, indicating a chronic infection [9]. Therefore, more dogs are expected to be seropositive for IgG than IgM antibodies. Our findings are in concordance with previous seroprevalence studies in dogs that also demonstrated higher seropositivity for IgG than IgM anti-T. gondii antibodies [14,37,38,39]. The fact that 8.9% of dogs were seropositive for both IgG and IgM indicates that these dogs were recently infected with T. gondii a few weeks before sampling and prior to becoming seronegative for IgM. Alternatively, these dogs may have already been seropositive for IgG from an old exposure to the parasite and were recently reinfected with T. gondii, causing a new increase in IgM antibodies [1].
Concerning living areas, it has been established that dogs from rural regions are expected to have higher seropositivity rates than those from urban regions [1,10,14,21,35,38,40]. Generally, rural areas tend to have higher levels of environmental contamination with oocysts compared to urban ones [14,21]. This may be attributed to the fact that wild and domestic cats are more prevalent in rural regions, there is more soil where oocysts are commonly found, and also prey animals, which represent an additional infection source, are more abundant in rural areas. These conditions increase the probability of rural dogs being exposed to T. gondii oocysts [14]. Moreover, people living in rural regions are more likely to feed offal to their dogs, which may contain T. gondii tissue cysts [35]. Our findings align with the aforementioned studies, since dogs from rural areas had a significantly higher overall seroprevalence than dogs from urban areas, and they were 1.49 times more likely to be positive for T. gondii. Correspondingly, in an analogous study conducted on the feline population in Greece, cats in rural areas had a significantly higher infection risk than cats in urban areas [2]. Again, these similarities imply higher levels of environmental contamination with T. gondii oocysts in the country’s rural areas.
According to a recent report, the total number of dogs in Greece is 1.42 million, with more than half (54%, 760,500) of the dog population being stray or shelter dogs [22]. The number of dogs examined in the current study (n = 1282) is among the highest compared to similar seroprevalence surveys in dogs from other countries [10]. Therefore, extrapolating the seropositivity rate of the current study (47.6%) in the canine population in the country, it is likely that more than 650,000 dogs in Greece may have come in contact with T. gondii at some point during their lifetime.
Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence has been investigated in other animal species in Greece, including pigs, wild boars, sheep and goats, cattle, birds, hares and most recently, cats [2,28]. The seroprevalence in dogs in the current study was higher than the previously recorded seroprevalences in all other animal species except sheep and goats [28]. Indeed, T. gondii seropositivity was up to 90% in sheep from specific regions and 61.3% in goats in Greece [28]. Therefore, it becomes evident that various animal species are exposed to T. gondii in the country, with dogs and small ruminants presenting the highest seropositivity rates. This is of specific importance for sheep and goats since infection with T. gondii may lead to abortions and production losses [41].
As for the seropositivity in dogs, it is a great indicator for T. gondii occurrence and distribution in an area. The high seropositivity reported herein indirectly reflects the environmental contamination levels of T. gondii oocysts in Greece [18]. In the present study, dogs living in Thessaloniki had a lower seroprevalence than dogs living in Attica. In the same context, in another study on feline toxoplasmosis in Greece, cats living in Macedonia, an area including Thessaloniki, had a lower seroprevalence than cats living in Central Greece, an area including Attica [2]. These findings suggest lower environmental contamination and T. gondii oocyst burden in Thessaloniki and Macedonia than in Attica and Central Greece. In contrast, another recent T. gondii seroprevalence study on chickens revealed a higher seropositivity in chickens from Central Greece-Attica compared to those from Central Macedonia, but the difference was not statistically significant [42].
The results of this study also suggest that dogs in both urban and rural regions are exposed to T. gondii. Dogs acquire infection by ingesting oocysts, hunting infected prey, or eating undercooked meat [17,18]. The existence of two horizontal transmission routes in dogs may also contribute to the higher seroprevalence in this animal species compared to others that are typically exposed to T. gondii through one pathway [17]. For instance, production animals are not omnivores, and cats are not typically coprophagous [43]. It is worth noting that current evidence suggests that most dogs acquire T. gondii infection horizontally after birth and not transplacentally [10]. This further supports the theory that coprophagy and rubbing in soil, cat faeces, and foul substances play an essential role in canine infections [6]. Considering that a cat eating an infected mouse can expel more than a billion oocysts during patency [44], it becomes clear that dogs who regularly ingest cat faeces have a considerably increased infection risk [32]. In this frame, based on their high seropositivity, dogs represent great sentinels in Greece for assessing the distribution of T. gondii oocysts in the environment [18].
To exacerbate the above, regarding human infection, some studies have identified dog ownership as a potential risk factor, particularly in rural areas and in young children [45,46]. As mentioned earlier, dogs can serve as transport hosts for T. gondii oocysts, especially when cats are present in the same household [45]. Acknowledging the high seroprevalence rate of the dogs examined in the current study, canine owners, and particularly young children, should employ hygiene measures to avoid the accidental ingestion of oocysts. These include washing their hands after petting their dogs and after disposing of dog faeces, as well as limiting dogs’ access to cat faeces and litterboxes. Dogs’ fur, limbs, mouth, and faeces may harbour T. gondii oocysts [6,10,20,24,25,26], while the oocysts also remain viable after passing through the dog’s gastrointestinal tract. However, it should be noted that the prevalence of T. gondii oocysts in dog faeces is expected to be very low [26]. Moreover, dogs should be fed commercial food or properly cooked meat (>60 °C for 10 min) [47], and owners should also control their dogs’ hunting instincts so as not to prey on intermediate hosts (i.e., birds or small mammals) that might harbour T. gondii tissue cysts, representing an additional source of infection [9].
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, exposure to T. gondii is prevalent in the canine population across Greece, with dogs living in rural areas exhibiting a higher infection risk than their counterparts in urban areas. The substantial IgM seropositivity rate of 22.2% suggests that recent or active infections are common in the examined population. Considering the high overall seroprevalence at 47.6%, T. gondii appears ubiquitous throughout Greece’s urban and rural regions. Consequently, this high environmental contamination indicates that humans and other animals are at risk of exposure to T. gondii oocysts [16]. Therefore, to mitigate the infection risk, dog owners should take preventative measures to avoid accidental ingestion of oocysts, such as washing their hands after petting their dogs and properly disposing of their pet’s faeces. Further hygienic measures, including the thorough cooking of meat intended for dog consumption, are necessitated to reduce the risk of T. gondii infection in dogs and safeguard public health.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.S. and E.P.; methodology, G.S., A.I.G., and E.P.; software, G.S., A.I.G., and P.A.; validation, G.S., A.I.G., D.B., and E.P.; formal analysis, G.S., A.I.G., I.S., C.N.T., and E.P.; investigation, G.S., P.A., and D.B.; resources, G.S., A.I.G., and E.P.; data curation, G.S. and A.I.G.; writing—original draft preparation, G.S., A.I.G., I.S., and C.N.T.; writing—review and editing, G.S., A.I.G., I.S., C.N.T., P.A., D.B., and E.P.; visualisation, G.S. and E.P.; supervision, E.P.; project administration, E.P.; funding acquisition, E.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in compliance with the national animal welfare regulations. The applied diagnostic veterinary procedures were not within the context of the relevant EU legislation for animal experimentations (Directive 86/609/EC) and may be performed to diagnose animal diseases and improve animal welfare. No suffering was caused during the blood sample collection.
Informed Consent Statement
Consent was ensured by the owners or registered veterinarians.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sioutas, G.; Symeonidou, I.; Gelasakis, A.I.; Tzirinis, C.; Papadopoulos, E. Feline Toxoplasmosis in Greece: A Countrywide Seroprevalence Study and Associated Risk Factors. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, K.D.S.; Costa, A.J.; Toniollo, G.H.; Sabatini, G.A.; Moraes, F.R.; Paulillo, A.C.; Ferraudo, A.S. Experimental toxoplasmosis in pregnant bitches. Vet. Parasitol. 1999, 86, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qassab, S.; Reichel, M.P.; Su, C.; Jenkins, D.; Hall, C.; Windsor, P.A.; Dubey, J.P.; Ellis, J. Isolation of Toxoplasma gondii from the brain of a dog in Australia and its biological and molecular characterization. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 164, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresciani, K.D.S.; Costa, A.J.; Toniollo, G.H.; Luvizzoto, M.C.R.; Kanamura, C.T.; Moraes, F.R.; Perri, S.H.V.; Gennari, S.M. Transplacental transmission of Toxoplasma gondii in reinfected pregnant female canines. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 104, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, D.S.; Dubey, J.P.; Butler, J.M.; Blagburn, B.L. Mechanical transmission of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts by dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 73, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, D.S.; Dubey, J.P.; Butler, J.M.; Blagburn, B.L. Experimental tissue cyst induced Toxoplasma gondii infections in dogs. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1996, 43, 25659464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero-Berna, R.; Gennari, S.M. Clinical toxoplasmosis in dogs and cats: An update. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Lindsay, D.S.; Lappin, M.R. Toxoplasmosis and Other Intestinal Coccidial Infections in Cats and Dogs. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2009, 39, 1009–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Yang, Y.; Su, C. Toxoplasma gondii infections in dogs: 2009–2020. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 287, 109223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, T.P.; Lopes, W.D.Z.; Ferreira, R.M.; Pieroni, J.S.P.; Pinto, V.M.R.; Sakamoto, C.A.; da Costa, A.J. Toxoplasma gondii: Evidence for the transmission by semen in dogs. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 123, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Carpenter, J.L.; Speer, C.A.; Topper, M.J.; Uggla, A. Newly recognized fatal protozoan disease of dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1988, 192, 1269–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Huertas-López, A.; Cantos-Barreda, A.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Martínez-Carrasco, C.; Ibáñez-López, F.J.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cerón, J.J.; Álvarez-García, G. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the validation of serological methods for detecting anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in humans and animals. Vet. Parasitol. 2024, 328, 110173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Ahmed, H.; Irum, S.; Qayyum, M. Seroprevalence of IgG and IgM antibodies and associated risk factors for toxoplasmosis in cats and dogs from sub-tropical arid parts of Pakistan. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 31, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davidson, M.G. Toxoplasmosis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2000, 30, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Fu, L.L.; Yue, C.L.; Tang, R.X.; Liu, Y.S.; Lv, L.; Shi, N.; Zeng, P.; Zhang, P.; Wang, D.H.; et al. Stray dogs as indicators of Toxoplasma gondii distributed in the environment: The first report across an urban-rural gradient in China. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meireles, L.R.; Galisteo, A.J.; Pompeu, E.; Andrade, H.F. Toxoplasma gondii spreading in an urban area evaluated by seroprevalence in free-living cats and dogs. Trop. Med. Int. Heal. 2004, 9, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas-López, A.; Sukhumavasi, W.; Álvarez-García, G.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cano-Terriza, D.; Almería, S.; Dubey, J.P.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Cerón, J.J.; Martínez-Carrasco, C. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in outdoor dogs and cats in Bangkok, Thailand. Parasitology 2021, 148, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salb, A.L.; Barkema, H.W.; Elkin, B.T.; Thompson, R.C.A.; Whiteside, D.P.; Black, S.R.; Dubey, J.P.; Kutz, S.J. Dogs as sources and sentinels of parasites in humans and wildlife, Northern Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, J.; Mayer, D.C.G. Toxoplasma gondii and Giardia duodenalis infections in domestic dogs in New York City public parks. Vet. J. 2016, 211, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Vázquez, C.; Maldonado-López, L.; Vitela-Mendoza, I.; Medina-Esparza, L.; Aguilar-Marcelino, L.; de Velasco-Reyes, I. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Associated Risk Factors in Different Populations of Dogs from Aguascalientes, Mexico. Acta Parasitol. 2023, 68, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MARS PETCARE State of Pet Homelessness Project—Greece. Available online: https://cms.stateofpethomelessness.com/s3media/2024-01/soph-greece.pdf?VersionId=Fy9UvabEEBAbDRxH0FhSM.XB6b889fl (accessed on 11 May 2024).
- Cong, W.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhou, N.; Peng, P.; Qin, S.Y.; Meng, Q.F.; Qian, A.D. Prevalence of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in pets and their owners in Shandong province, Eastern China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, J.K.; Parker, B.B. An apparent role of dogs in the transmission of Toxoplasma gondii. The probable importance of xenosmophilia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1996, 791, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, J.K.; Lindsay, D.S.; Parker, B.B.; Dobesh, M. Dogs as possible mechanical carriers of Toxoplasma, and their fur as a source of infection of young children. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 7, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schares, G.; Pantchev, N.; Barutzki, D.; Heydorn, A.O.; Bauer, C.; Conraths, F.J. Oocysts of Neospora caninum, Hammondia heydorni, Toxoplasma gondii and Hammondia hammondi in faeces collected from dogs in Germany. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1525–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, J.K. Prevention of Toxoplasma infection in pregnant women and their fetuses. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 20, 727–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symeonidou, I.; Sioutas, G.; Lazou, T.; Gelasakis, A.I.; Papadopoulos, E. A Review of Toxoplasma gondii in Animals in Greece: A FoodBorne Pathogen of Public Health Importance. Animals 2023, 13, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellenic Statistical Authority Population-Housing Census in Greece. 2021. Available online: https://elstat-outsourcers.statistics.gr/Booklet_AποτελεσματαΠληθυσμου2023_II GR_FINAL2_WEB.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2024).
- El Behairy, A.M.; Choudhary, S.; Ferreira, L.R.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Hilali, M.; Su, C.; Dubey, J.P. Genetic characterization of viable Toxoplasma gondii isolates from stray dogs from Giza, Egypt. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 193, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, K.; Yasa Duru, S.; Yagci, B.B.; Babur, C.; Ocal, N.; Gurcan, S.; Karaca, S. Seroprevalence of Neospora caninum and coexistence with Toxoplasma gondii in dogs. Turkiye Parazitol. Derg. 2009, 33, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Dini, F.M.; Stancampiano, L.; Poglayen, G.; Galuppi, R. Risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii infection in dogs: A serological survey. Acta Vet. Scand. 2024, 66, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezón, O.; Millán, J.; Gomis, M.; Dubey, J.P.; Ferroglio, E.; Almería, S. Kennel dogs as sentinels of Leishmania infantum, Toxoplasma gondii, and Neospora caninum in Majorca Island, Spain. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 1505–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.P.; Granada, S.; Oliveira, A.C.; Brancal, H.; Dubey, J.P.; Cardoso, L.; Vilhena, H. Toxoplasmosis in dogs: First report of Toxoplasma gondii infection in any animal species in Angola. Pathog. Glob. Health 2014, 108, 339–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strital, A.D.; Igarashi, M.; Muraro, L.S.; Aguiar, D.M.; Pacheco, T.A.; Garcia, J.L.; Freitas, S.H.; Amude, A.M. Epidemiological study and evaluation of risk factors for infection with Toxoplasma gondii and clinical and pathological findings of acute infection in dogs admitted at a Veterinary School Hospital. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2016, 36, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.A.O.; Silva, N.M.; Mineo, T.W.P.; Pajuaba Neto, A.A.; Ferro, E.A.V.; Mineo, J.R. Heterologous antibodies to evaluate the kinetics of the humoral immune response in dogs experimentally infected with Toxoplasma gondii RH strain. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 107, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.S. Seroprevalences to Toxoplasma gondii in privately-owned dogs in Taiwan. Prev. Vet. Med. 1998, 35, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Brito, A.F.; De Souza, L.C.; Vieira Da Silva, A.; Langoni, H. Epidemiological and serological aspects in canine toxoplasmosis in animals with nervous symptoms. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2002, 97, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sedlak, K.; Bartova, E. The prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii IgM and IgG antibodies in dogs and cats from the Czech Republic. Vet. Med. 2006, 51, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, A.d.N.; Gonçalves, D.D.; Nino, B.d.S.L.; Caldart, E.T.; Freire, R.L.; Navarro, I.T. Seroepidemiology of Toxoplasmosis in Humans and Dogs from a Small Municipality in Parana, Brazil. Ciência Anim. Bras. 2017, 18, e-42102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Giadinis, N.D.; Terpsidis, K.; Diakou, A.; Siarkou, V.; Loukopoulos, P.; Osman, R.; Karatzias, H.; Papazahariadou, M. Massive toxoplasma abortions in a dairy sheep flock and therapeutic approach with different doses of sulfadimidine. Turkish J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2011, 35, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreopoulou, M.; Schares, G.; Koethe, M.; Chaligiannis, I.; Maksimov, P.; Joeres, M.; Cardron, G.; Goroll, T.; Sotiraki, S.; Daugschies, A.; et al. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in different types of poultry in Greece, associated risk factors and co-existence with Eimeria spp. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 122, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrion, A.S.; Schnyder, M.; Wichert, B.; Deplazes, P. Toxocara eggs shed by dogs and cats and their molecular and morphometric species-specific identification: Is the finding of T. cati eggs shed by dogs of epidemiological relevance? Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 177, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Frenkel, J.K. Cyst-Induced Toxoplasmosis in Cats. J. Protozool. 1972, 19, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etheredge, G.D.; Michael, G.; Muehlenbein, M.P.; Frenkel, J.K. The roles of cats and dogs in the transmission of Toxoplasma infection in Kuna and Embera children in eastern Panama. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica/Pan Am. J. Public Health 2004, 16, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Frenkel, J.K.; Hassanein, K.M.; Hassanein, R.S.; Brown, E.; Thulliez, P.; Quintero- Nunez, R. Transmission of Toxoplasma gondii in Panama City, Panama: A five-year prospective cohort study of children, cats, rodents, birds, and soil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 53, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nawawi, F.A.; Tawfik, M.A.; Shaapan, R.M. Methods for inactivation of Toxoplasma gondii cysts in meat and tissues of experimentally infected sheep. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2008, 5, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).