Machine Learning Approaches for Early Detection of Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament in Health Screening Settings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Data Collection
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Feature Selection via Random Forest
2.4. Model Development and Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Re-Estimation for Interpretability
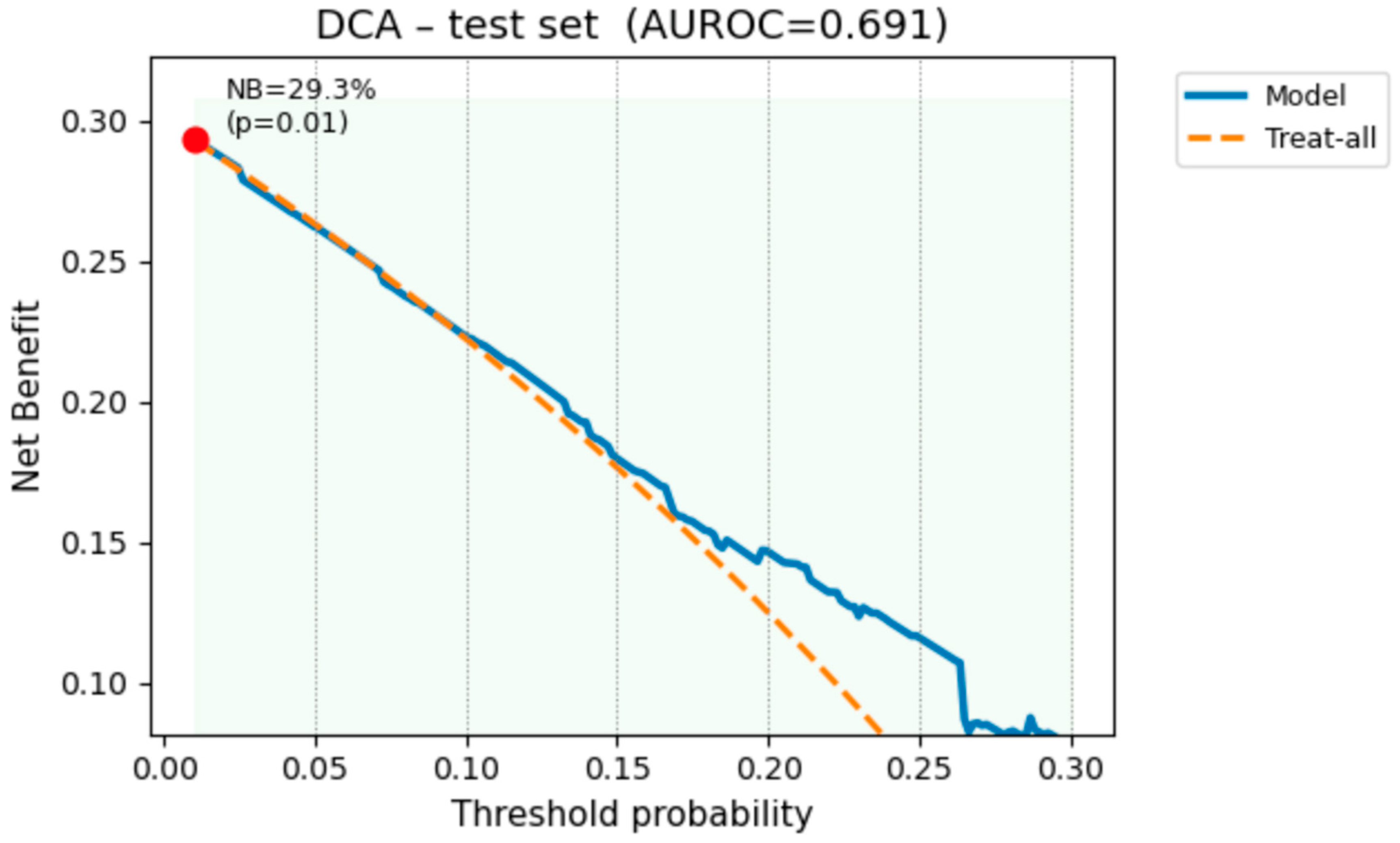
2.6. Decision-Curve Analysis
3. Results
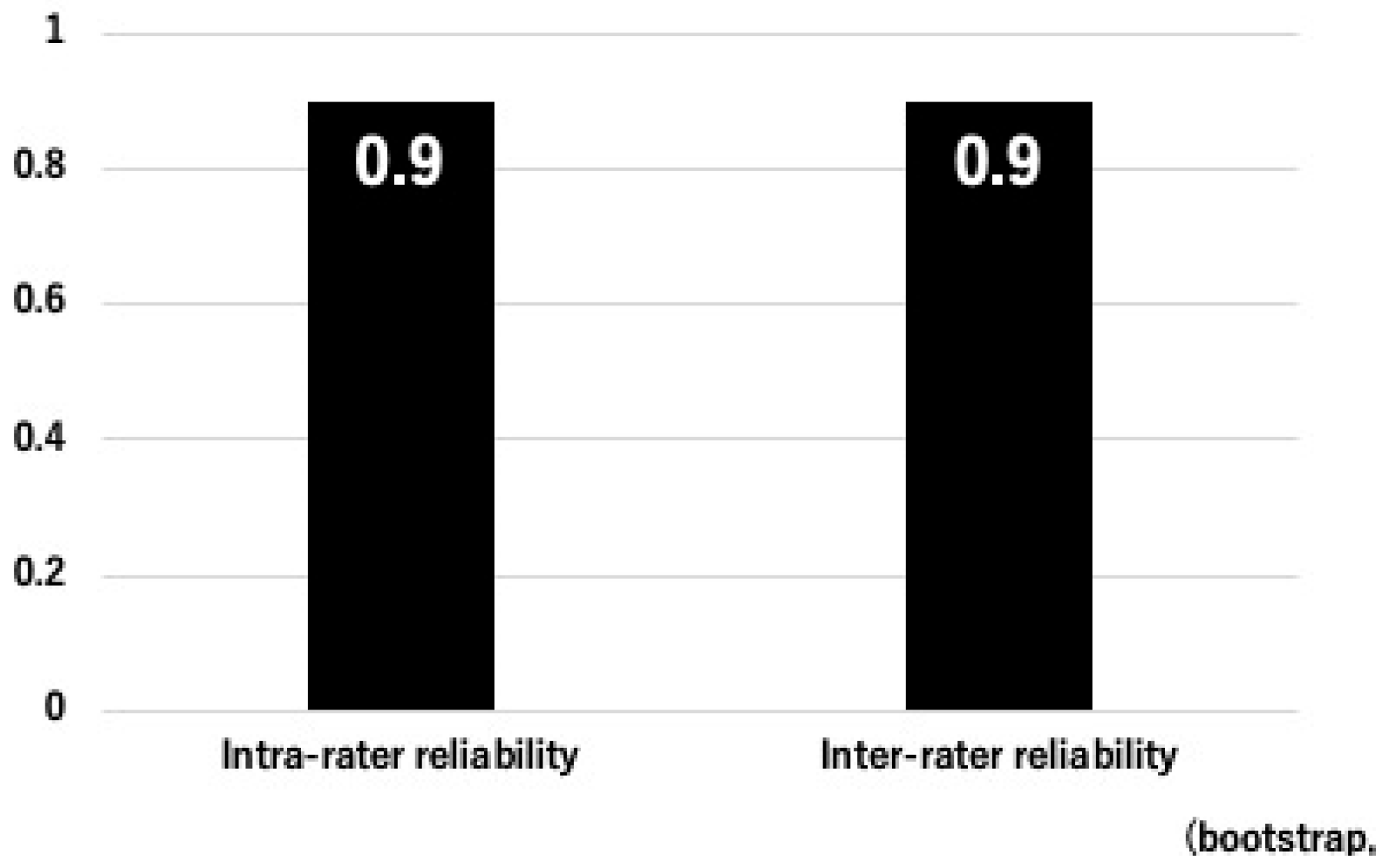
3.1. Inter- and Intra-Rater Reliability of OPLL
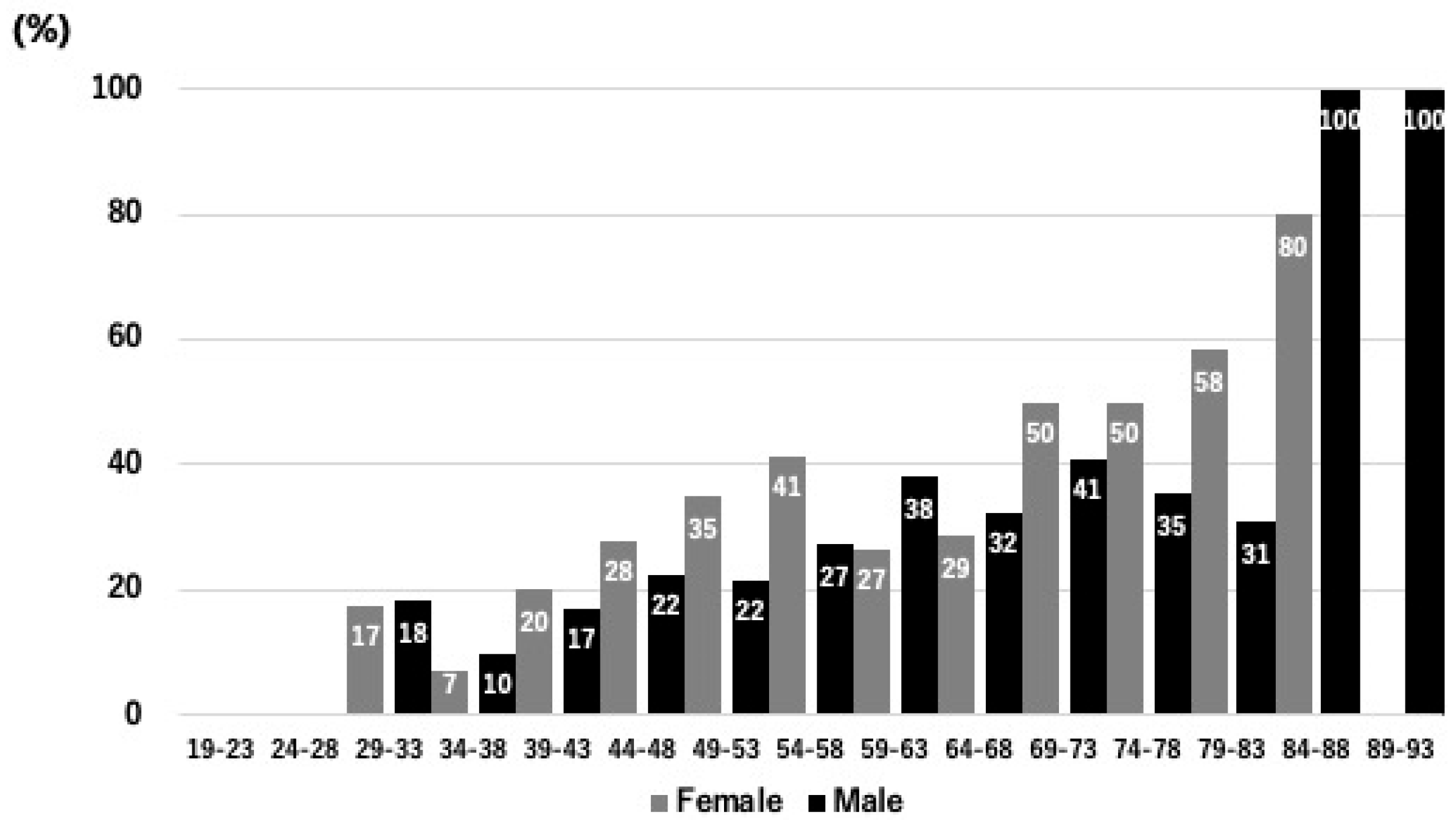
3.2. Participant Characteristics
3.3. Laboratory and Biochemical Parameters
3.4. Lifestyle, Dietary Habits, and Physical Activity
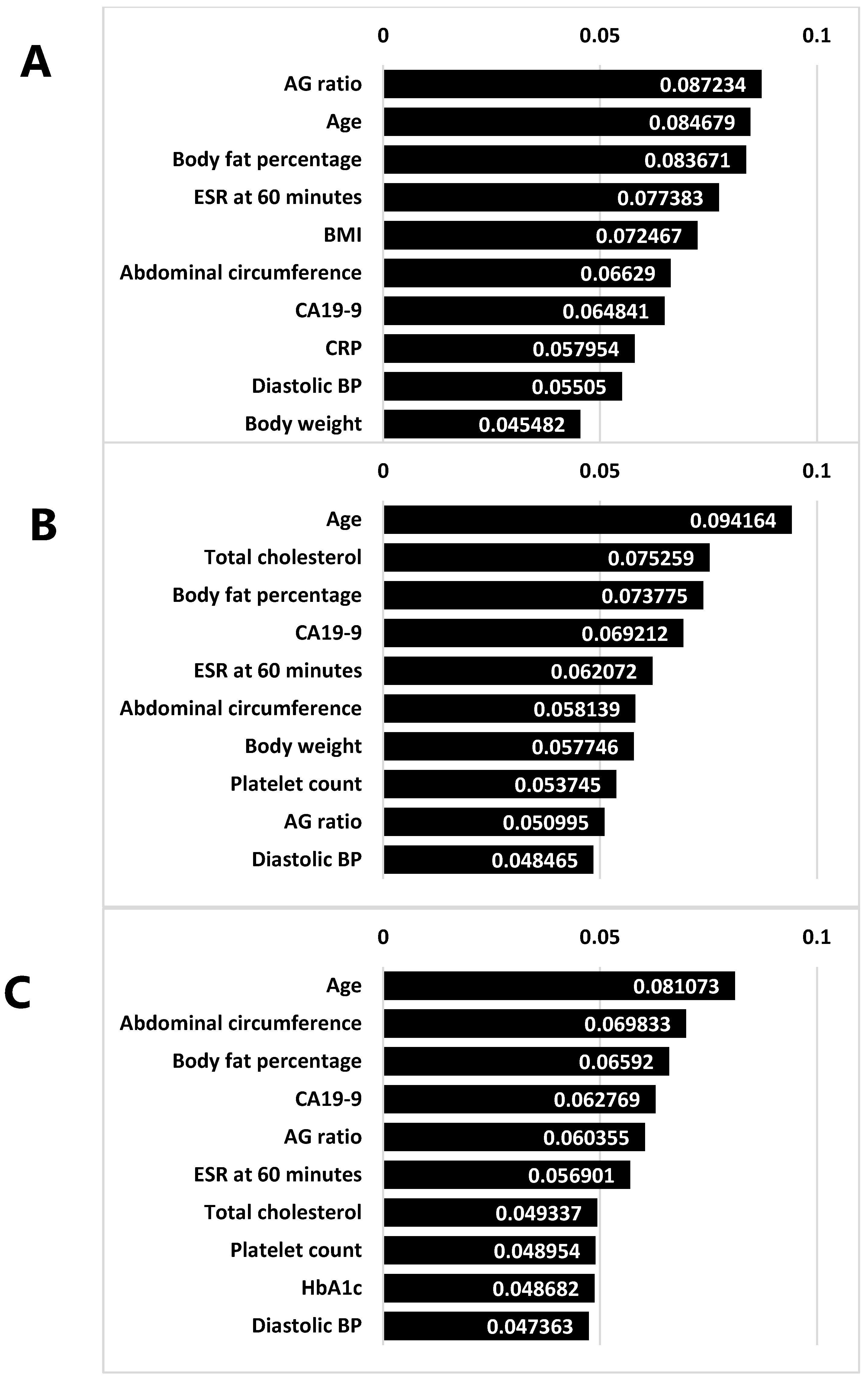
3.5. Feature Selection
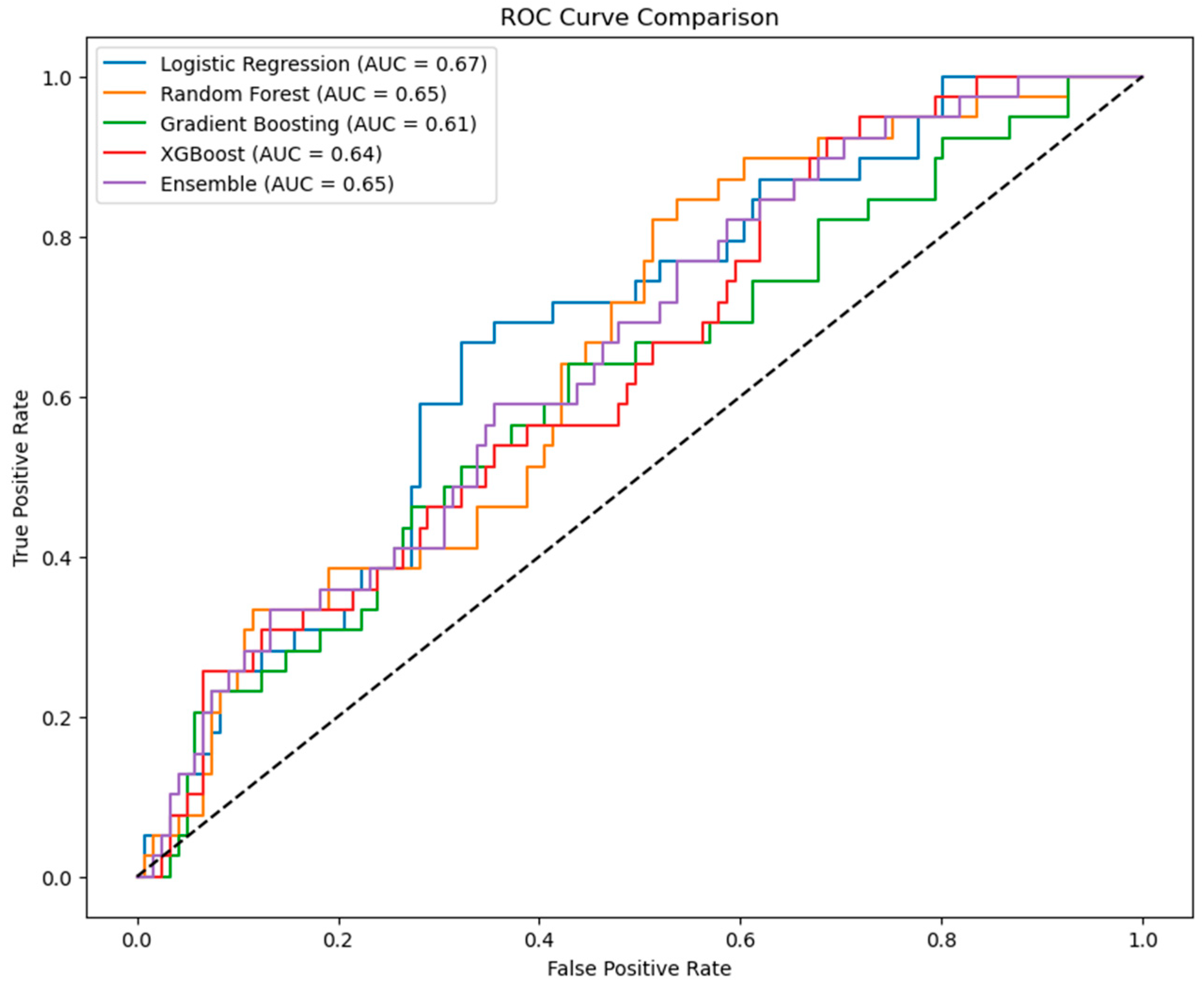
3.6. Model Performance
3.7. Statistical Re-Estimation of Logistic Regression Interpretation
3.8. Feature Importance in Tree-Based Models
3.9. Clinical Implications
3.10. Decision-Curve Analysis
3.11. Additional Analyses of CA19-9
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Prevalence and Implications for OPLL Detection
4.2. Risk Factor Analysis
4.3. Development and Validation of Predictive Models for OPLL Detection: Feature Selection and the Impact of Metabolic Risk Factors
4.4. Clinical Implications
4.5. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellaire, C.P.; Paulson, A.E.; Ani, C.F.; Benn, L.; Carroll, A.H.; Mesfin, A. Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament in the Cervical Spine: Etiology, Clinical Presentation, and Management. JBJS Rev. 2025, 13, e24.00161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Hirai, T.; Sakai, K.; Yamada, K.; Sakaeda, K.; Hashimoto, J.; Egawa, S.; Morishita, S.; Matsukura, Y.; Inose, H.; et al. Comparison of Postoperative Complications and Outcomes in Anterior Cervical Spine Surgery: Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Versus Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Clin. Spine Surg. 2024, 37, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, H.; Kanemura, T.; Satake, K.; Ito, K.; Ouchida, J.; Morita, D.; Ando, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Ishiguro, N.; Imagama, S. Reoperation for Late Neurological Deterioration After Laminoplasty in Individuals With Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy: Comparison of Cases of Cervical Spondylosis and Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament. Spine 2020, 45, E909–E916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odate, S.; Shikata, J.; Soeda, T.; Yamamura, S.; Kawaguchi, S. Surgical results and complications of anterior decompression and fusion as a revision surgery after initial posterior surgery for cervical myelopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2017, 26, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobashi, G.; Washio, M.; Okamoto, K.; Sasaki, S.; Yokoyama, T.; Miyake, Y.; Sakamoto, N.; Ohta, K.; Inaba, Y.; Tanaka, H.; et al. High body mass index after age 20 and diabetes mellitus are independent risk factors for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine in Japanese subjects: A case-control study in multiple hospitals. Spine 2004, 29, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, S.; Yoshii, T.; Okawa, A.; Fushimi, K.; Fujiwara, T. Perioperative complications of anterior decompression with fusion versus laminoplasty for the treatment of cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: Propensity score matching analysis using a nation-wide inpatient database. Spine J. 2019, 19, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, S.; Koike, Y.; Endo, T.; Takahata, M.; Sudo, H.; Kadoya, K.; Kanayama, M.; Fujita, R.; Fukada, S.; Terkawi, M.A.; et al. Visceral fat obesity predicts ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: Annual health examination data-based evidence. Spine J. 2025, 25, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, E.; Ono, A.; Yokoyama, T.; Wada, K.; Tanaka, T.; Kumagai, G.; Iwasaki, H.; Ishibashi, Y.; Takahashi, I.; Umeda, T.; et al. Prevalence and symptom of ossification of posterior longitudinal ligaments in the Japanese general population. J. Orthop. Sci. 2014, 19, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Yoshii, T.; Hirai, T.; Iwanami, A.; Takeuchi, K.; Yamada, T.; Seki, S.; Tsuji, T.; Fujiyoshi, K.; Furukawa, M.; et al. Prevalence and distribution of ossification of the supra/interspinous ligaments in symptomatic patients with cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine: A CT-based multicenter cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Kuharski, M.; Balmaceno-Criss, M.; Diebo, B.G.; Daniels, A. Hyperlipidemia, Obesity, and Diabetes, and Risk of Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament. World Neurosurg. 2024, 188, e642–e647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, Y.W.; Chang, J.S.; Yoon, S.Y. Quantification of Risk Factors for Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament in Korean Populations: A Nationwide Population-based Case-control Study. Spine 2019, 44, E957–E964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liawrungrueang, W.; Cho, S.T.; Cholamjiak, W.; Sarasombath, P.; Twinprai, N.; Twinprai, P.; Han, I. Performance and clinical implications of machine learning models for detecting cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: A systematic review. Asian Spine J. 2025, 19, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, D. Applied Predictive Analytics: Principles and Techniques for the Professional Data Analyst, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Obermeyer, Z.; Emanuel, E.J. Predicting the Future—Big Data, Machine Learning, and Clinical Medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Huang, T.; Lu, C.; Lu, L.; Li, D. Machine Learning and Network Methods for Biology and Medicine. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 2015, 915124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukada, S.; Endo, T.; Takahata, M.; Kanayama, M.; Koike, Y.; Fujita, R.; Suzuki, R.; Murakami, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Terkawi, M.A.; et al. Dyslipidemia as a novel risk for the development of symptomatic ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine J. 2023, 23, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, T.; Takahata, M.; Koike, Y.; Fujita, R.; Suzuki, R.; Hisada, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Yamada, K.; Iwata, A.; et al. Association between obesity and ossification of spinal ligaments in 622 asymptomatic subjects: A cross-sectional study. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2022, 40, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, T.; Takahata, M.; Fujita, R.; Koike, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Hasegawa, Y.; Murakami, T.; Ishii, M.; Yamada, K.; Sudo, H.; et al. Strong relationship between dyslipidemia and the ectopic ossification of the spinal ligaments. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Total | OPLL (−) | OPLL (+) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male, female) | 1442 (842:600) | 1010 (601:409) | 432 (241:191) | 0.200 |
| Age (year) | 57.48 ± 12.84 | 55.71 ± 12.97 | 61.50 ± 11.49 | <0.001 * |
| Blood Type (A; AB; B; O) | 221; 441; 121; 280; 379 | 153; 312; 90; 193; 259 | 65; 129; 31; 87; 120 | 0.752 |
| Height (cm) | 164.40 ± 8.78 | 165.02 ± 8.53 | 162.93 ± 9.20 | <0.001 * |
| Weight (kg) | 64.60 ± 13.64 | 63.81 ± 13.30 | 66.38 ± 14.27 | <0.001 * |
| Body Fat Percentage (%) | 26.46 ± 7.32 | 25.55 ± 7.02 | 28.60 ± 7.61 | <0.001 * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.75 ± 3.82 | 23.27 ± 3.61 | 24.85 ± 4.06 | <0.001 * |
| Abdominal Circumference (cm) | 86.73 ± 10.24 | 85.51 ± 10.00 | 89.53 ± 10.23 | <0.001 * |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 126.03 ± 18.70 | 124.95 ± 18.78 | 128.48 ± 18.32 | <0.001 * |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 77.31 ± 12.15 | 77.14 ± 11.92 | 77.69 ± 12.74 | 0.219 |
| Heart Rate (beats/min) | 71.79 ± 10.98 | 71.52 ± 11.09 | 72.43 ± 10.76 | 0.076 |
| Building Samples | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support | AUC (95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | OPLL (−) | 0.82 | 0.63 | 0.71 | 808 | 0.697 (0.66–0.76) |
| OPLL (+) | 0.44 | 0.68 | 0.53 | 345 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.65 | 1153 | ||||
| Macro average | 0.63 | 0.66 | 0.62 | 1153 | ||
| Weighted average | 0.71 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 1153 | ||
| Random Forest | OPLL (−) | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 808 | 0.998 (0.97–1.00) |
| OPLL (+) | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 345 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.98 | 1153 | ||||
| Macro average | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 1153 | ||
| Weighted average | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 1153 | ||
| Gradient Boosting | OPLL (−) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 808 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) |
| OPLL (+) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 345 | ||
| Accuracy | 1.00 | 1153 | ||||
| Macro average | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1153 | ||
| Weighted average | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1153 | ||
| XGBoost | OPLL (−) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 808 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) |
| OPLL (+) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 345 | ||
| Accuracy | 1.00 | 1153 | ||||
| Macro average | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1153 | ||
| Weighted average | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1153 | ||
| Ensemble | OPLL (−) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 808 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) |
| OPLL (+) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 345 | ||
| Accuracy | 1.00 | 1153 | ||||
| Macro average | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1153 | ||
| Weighted average | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1153 |
| Testing Samples | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support | AUC (95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | OPLL (−) | 0.79 | 0.60 | 0.69 | 202 | 0.691 (0.66–0.76) |
| OPLL (+) | 0.51 | 0.69 | 0.61 | 87 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.65 | 289 | ||||
| Macro average | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 289 | ||
| Weighted average | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.67 | 289 | ||
| Random Forest | OPLL (−) | 0.79 | 0.76 | 0.77 | 202 | 0.700 (0.63–0.76) |
| OPLL (+) | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.51 | 87 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.69 | 289 | ||||
| Macro average | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 289 | ||
| Weighted average | 0.70 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 289 | ||
| Gradient Boosting | OPLL (−) | 0.76 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 202 | 0.692 (0.63–0.76) |
| OPLL (+) | 0.49 | 0.40 | 0.44 | 87 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.69 | 289 | ||||
| Macro average | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 289 | ||
| Weighted average | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 289 | ||
| XGBoost | OPLL (−) | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.78 | 202 | 0.679 (0.62–0.74) |
| OPLL (+) | 0.47 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 87 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.69 | 289 | ||||
| Macro average | 0.61 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 289 | ||
| Weighted average | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.67 | 289 | ||
| Ensemble | OPLL (−) | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0.84 | 202 | 0.703 (0.66–0.77) |
| OPLL (+) | 0.43 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 87 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.74 | 289 | ||||
| Macro average | 0.61 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 289 | ||
| Weighted average | 0.7 | 0.74 | 0.71 | 289 |
| Predictor | Coefficient | Odds Ratio | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (kg) | 0.077 | 1.079 [0.214–0.925] | 0.925 |
| Abdominal circumference (cm) | −0.233 | 0.792 [0.541–1.157] | 0.228 |
| Age (year) | 0.468 | 1.596 [1.271–2.001] | <0.001 * |
| Height (cm) | −0.103 | 0.902 [0.387–2.101] | 0.812 |
| HbA1c (%) | 0.122 | 1.130 [0.900–1.418] | 0.290 |
| CA19-9 (U/mL) | 0.212 | 1.236 [1.004–1.351] | 0.029 * |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 0.102 | 1.107 [0.947–1.294] | 0.198 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | −0.154 | 0.857 [0.743–0.989] | 0.035 * |
| ESR at 60 min | 0.187 | 1.206 [-0.066–0.441] | 0.147 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.591 | 1.805 [0.513–6.297] | 0.354 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mizukoshi, R.; Maruiwa, R.; Ito, K.; Isogai, N.; Funao, H.; Fujita, R.; Yagi, M. Machine Learning Approaches for Early Detection of Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament in Health Screening Settings. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070749
Mizukoshi R, Maruiwa R, Ito K, Isogai N, Funao H, Fujita R, Yagi M. Machine Learning Approaches for Early Detection of Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament in Health Screening Settings. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(7):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070749
Chicago/Turabian StyleMizukoshi, Ryo, Ryosuke Maruiwa, Keitaro Ito, Norihiro Isogai, Haruki Funao, Retsu Fujita, and Mitsuru Yagi. 2025. "Machine Learning Approaches for Early Detection of Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament in Health Screening Settings" Bioengineering 12, no. 7: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070749
APA StyleMizukoshi, R., Maruiwa, R., Ito, K., Isogai, N., Funao, H., Fujita, R., & Yagi, M. (2025). Machine Learning Approaches for Early Detection of Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament in Health Screening Settings. Bioengineering, 12(7), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070749






