Abstract
Piezoelectric catalytic technology has attracted much attention in the field of dye wastewater treatment, in which inorganic piezoelectric materials have been widely studied. Its core mechanism involves utilizing the piezoelectric effect to generate positive and negative charges, which react with oxygen ions and hydroxyl radicals, respectively, to generate reactive oxygen species to degrade organic pollutants. Currently, while organic piezoelectric catalysts theoretically offer significant advantages such as low cost and high processability, there has been a notable lack of research in this area, which presents an innovative opportunity for the exploration of new organic piezoelectric catalytic materials. In this study, new research using natural nanocellulose (FC) suspension as an efficient organic piezoelectric catalyst is reported for the first time. The experimental results showed that the catalyst exhibited excellent degradation performance for Rhodamine B (RhB), Acid Orange 7 (AO7), and Methyl Orange (MO) under ultrasonic vibration (40 kHz, 200 W): the degradation rates reached 95.4%, 72.4%, and 31.2%, respectively, for 150 min, and the corresponding first-order reaction kinetic constants were 0.0205, 0.00858, and 0.00249 min−1, respectively. It is noteworthy that the RhB solution can achieve the optimal degradation efficiency without adjustment under neutral initial pH conditions, which significantly enhances the practical application feasibility. The experimental results showed that the catalyst, with a measurable piezoelectric coefficient (d33 = 4.4 pm/V), exhibited excellent degradation performance for Rhodamine B (RhB), Acid Orange 7 (AO7), and Methyl Orange (MO) under ultrasonic vibration (40 kHz, 200 W). This organic piezoelectric catalyst, based on renewable biomass, innovatively converts mechanical vibration energy in the environment into the power to degrade pollutants. It not only expands the application boundaries of organic piezoelectric materials but also provides a new solution for sustainable water treatment technology, demonstrating extremely promising application prospects in the field of green and environmentally friendly water treatment.
1. Introduction
The efficient removal of organic pollutants from environmental waters has become a global challenge. Organic chemicals (e.g., synthetic dyes, pesticides, etc.) discharged from industry and residual from agricultural fertilizers pose a serious threat to ecosystems and human health due to their high solubility and chemical stability [1,2]. Although traditional physical adsorption methods can achieve pollutant transfer, they cannot completely mineralize the toxic substances. Although the advanced oxidation technology represented by photocatalysis has made significant progress in dye degradation [3,4,5,6], its practical application is still limited by light-dependent and quantum efficiency bottlenecks—according to statistics, most of the current photocatalysts attenuate up to 89% or more of their activity under dark conditions, and the energy cost of UV-dependent system accounts for the total 60–75% of the operating cost [7]. Therefore, it is of great practical significance to develop non-light-dependent novel catalytic systems.
In recent years, breakthroughs in mechanical energy–chemical energy conversion technology have provided new ideas for wastewater treatment. Piezoelectric catalysis generates a piezoelectric potential through the force–electric coupling effect of materials, which can drive the free radical chain reaction to degrade pollutants, and its energy utilization efficiency is improved by 2–3 orders of magnitude compared with that of traditional photocatalysis [8,9,10]. Specifically, the piezoelectric material generates polarized charges under mechanical stress and reacts with H2O/O2 through interfacial charge transfer to generate active species such as hydroxyl radicals (·OH) and superoxide radicals (O2−) [11,12,13]. Current studies have focused on inorganic piezoelectric materials, such as ZnO [8,14,15,16], BaTiO3 [17,18,19,20], and PZT [21,22,23,24], but they suffer from inherent drawbacks such as high energy consumption for preparation (>800 °C sintering) and poor biocompatibility [15]. In contrast, although organic piezoelectric materials possess advantages such as being solution-processable and environmentally friendly [16], the existing reported piezoelectric coefficients are generally lower than 20 pC/N [17], which severely restricts their catalytic performance.
Cellulose, as a renewable natural polymer with the richest reserves, has piezoelectric properties originating from the asymmetric arrangement of C2/C3 hydroxyl groups of glucose units and has the advantages of environmental friendliness, good processability, and low price, making it an ideal catalytic material [21,22,23,24,25]. Cellulose’s innate piezoelectricity, combined with nanostructure-enhanced charge separation, positions it as a sustainable, solution-processable catalyst. This study bridges a critical gap: while inorganic piezocatalysts dominate research, FC is the first purely organic system demonstrating broad-spectrum dye degradation under ambient conditions [26,27,28,29,30,31]. Recent studies have shown that the force–electric conversion properties of cellulose can be significantly enhanced by nanostructure engineering—Ram et al. [32] prepared cellulose nanocrystalline aerogels exhibiting a piezoelectric output density of 52 nW/cm2; Rajala et al. [33] fabricated a thin cellulose nanofibrous membrane and found that a 50 V/m electric field produced a maximum polarization of 0.15 C/cm2. Guan et al. [34] broke the symmetry of the crystal structure by introducing oxygen vacancy defects in the CNC lattice, which facilitated carrier segregation and produced good piezoelectric properties. It is worth noting that despite the progress of cellulose-based materials in the field of energy harvesting, their application in piezoelectric-catalyzed environmental remediation is still a gap, especially since the broad-spectrum degradation ability of multiple types of dyes and the reaction mechanism have not been clarified [35].
Therefore, in this study, metal-free and environmentally friendly FC was selected as the catalyst, and the piezoelectric catalytic performance of cellulose (FC) nanosuspension and its constitutive relationship were systematically investigated for the first time by adding several free radical scavengers. By constructing an ultrasound-triggered piezoelectric catalytic system, the efficient degradation of Rhodamine B (95.4%), Acid Orange 7 (72.4%), and Methyl Orange (31.2%) was realized, and the free radical-dominated reaction mechanism was revealed. This study provides a new paradigm for the development of green and efficient wastewater treatment technologies.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. FC Preparation
Through a series of cyclic chemical pretreatments, poplar wood particles were purified. The lignin of the sample should first be eliminated using acidified sodium chlorite at 75 °C for 1 h, and then it should be repeated 6 times. The sample was then removed from the sample by treating it for 2 h at 90 °C with 5.0 wt% potassium hydroxide. The sample was then exposed to 5.0 wt% potassium hydroxide for 2 h at 90 °C and acidified sodium chlorite for 2 h at 75 °C. After filtering the sample, it was washed with deionized water. Then, the 1.0 wt% FC suspension was created by passing the undried cellulose pulps through a high-intensity ultrasonic generator for 30 min [33].
2.2. Characterization
The structure of the FC was determined using an X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Smartlab 9 kw, Japan). The morphology of FC was observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM, EM30PLUS, Republic of Korea). The piezoelectric properties of the FC were analyzed by piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM, MFP-3D, USA). Vibration was exerted through an ultrasonic crusher (FS-1200pv, 240 W, 20 kHz, China, Shanghai). The determination of the RhB dye decomposition ratio was conducted using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (UV-Vis, UV2300 II, Shanghai, China).
2.3. Piezocatalysis Experiment
The following is the detailed experimental procedure for the piezocatalytic decomposition of dyes: First, 5 mL of the FC suspension was combined with 5 mL of the RhB solution (5 mg L−1). The dye solution was vibrated using an ultrasonic crusher (240 W, 20 kHz), while the temperature was maintained below 301 K. The heat from the ultrasonic vibrations was balanced by an ice-water bath. Approximately 3 mL of fluid was sampled after 30 min of shaking. After the supernatant was centrifugated, the absorption spectra of the catalytic decomposition products could be measured. Using an ultraviolet–visible spectrometer, the absorbance of the RhB dye was determined. The solutions of Methyl Orange (MO) and Acid Orange 7 (AO7) (5 mg L−1) were both decomposed by piezocatalysis. Piezocatalytic experiments were performed using NaOH or HCl to change the pH of the RhB solution.
2.4. Active Species Detection
From tests with radical scavengers, the main active components in the RhB dye decomposition using FC were discovered. Holes (h+) were tested using ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), hydroxyl radicals (OH) using tert-butyl alcohol (TBA), and superoxide radicals (O2−) using benzoquinone (BQ), respectively. The piezocatalytic experiment was repeated after adding 1 mL of the three reagents mentioned above in batches to a 50 mL RhB solution that contained 5 mL of catalyst.
3. Results and Discussion
As evidenced by the XRD analysis in Figure 1a, the FC sample exhibits characteristic cellulose Iβ crystalline structure, manifesting four distinct diffraction peaks at 12.26° (110), 15.1° (110), 22.3° (020), and 34.4° (004); the absence of amorphous halo and impurity peaks, coupled with peak profiles, confirms the high crystallinity and phase purity of the FC. Furthermore, SEM characterization (inset of Figure 1b) reveals a hierarchical nanofibrillar architecture, where individual fibers demonstrate uniform diameter distribution and length-to-aspect ratios exceeding 200:1, forming an interconnected three-dimensional conductive network. This well-defined nanostructure correlates with the XRD-derived crystallinity index, suggesting that the piezoelectric performance enhancement originates from both crystallographic anisotropy and nanoscale topological effects.
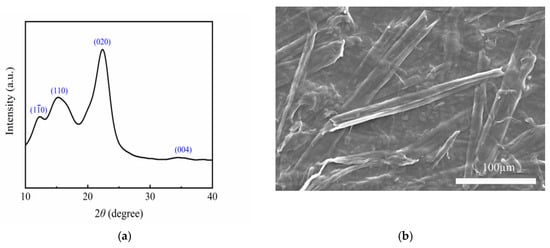
Figure 1.
(a) XRD pattern of the FC suspension; (b) SEM pattern of the FC suspension.
Complementary elemental analysis via energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS, Figure 2) quantifies the surface composition as C (24.6%), O (52.7%), S (11.6%), Na (7.1%), and N (4.0%). This atomic composition aligns with theoretical stoichiometric expectations for functionalized cellulose derivatives, confirming successful fibrillation without elemental contamination.

Figure 2.
HAADF-STEM of NFC revealing the EDS mapping region and corresponding (a) EDS mapping of (b) C; (c) N; (d) O; (e) Na; (f) S.
Piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM) characterization was conducted to evaluate the intrinsic piezoelectric properties of FC. As shown in Figure 3a,c, the phase contrast image demonstrates uniform polarization domains, while the amplitude mapping reveals consistent electromechanical response across the nanofibrillar structure, with corresponding surface topography confirming the material’s morphological integrity. The characteristic amplitude butterfly loop and 180° phase hysteresis behavior (Figure 3d) conclusively verify the piezoelectric nature of FC, yielding a measurable piezoelectric coefficient (d33 = 4.4 pm/V). The omnidirectional polarization of FC under ultrasound enables barrier-free charge transfer to solid–liquid interfaces via full surface charge exposure; concurrently, the inherently low carrier recombination rate substantially prolongs the generation cycle of active species (O2−/·OH), while continuous deformation driven by high-frequency ultrasound amplifies the local piezoelectric field through cumulative strain effects, yielding an equivalent high piezoelectric response despite the intrinsic low d33. These results fundamentally confirm the stress-induced charge separation capability of FC, establishing its viability as an organic piezoelectric catalyst for mechanochemical applications. Cellulose Iβ crystallinity promotes asymmetric charge separation under stress, as confirmed by PFM hysteresis (Figure 3d).
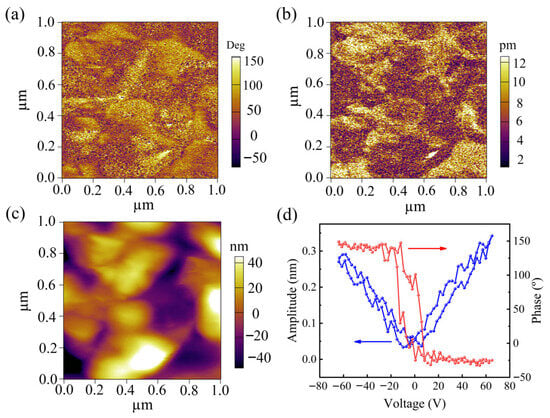
Figure 3.
(a) PFM phase image. (b) PFM amplitude image. (c) PFM topography image. (d) Amplitude butterfly and phase hysteresis loops.
The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) survey spectrum of cellulose (Figure 4a) exhibits two predominant characteristic peaks corresponding to C 1s and O 1s core levels. High-resolution spectral analysis reveals distinct chemical states for each element. The O 1s spectrum (Figure 4b) displays a characteristic peak at 529.7 eV, attributable to lattice oxygen species. While the broad C 1s/O 1s peaks (Figure 4c) reflect inherent heterogeneity in biopolymer bonding, deconvolution identifies four carbon environments (284.7 eV: C-C; 286.6 eV: C-O; 287.9 eV: O-C-O; 288.6 eV: O-C=O) consistent with cellulose’s molecular structure. This binding energy progression corresponds to the characteristic carbon hybridization states in cellulose molecular structure.

Figure 4.
(a) is the full XPS spectrum of cellulose, (b) is the high-resolution spectrum of O 1s, and (c) is the high-resolution spectrum of C 1s.
The piezocatalytic degradation process of RhB was systematically investigated through time-dependent UV-vis spectral analysis. As shown in Figure 5a, the characteristic absorption peak at 554 nm exhibits progressive attenuation under ultrasonic vibration, with complete signal disappearance observed after 180 min, confirming thorough dye mineralization. Comparative kinetic studies (Figure 5b,c) reveal critical mechanistic insights: control experiments under non-vibratory conditions or in the absence of FC demonstrate negligible absorbance reduction (<8% after 180 min), effectively ruling out physical adsorption or mechanical cleavage as dominant mechanisms. The strict correlation between simultaneous vibration and catalyst presence highlights the essential role of piezoelectric polarization in driving the redox degradation pathway.
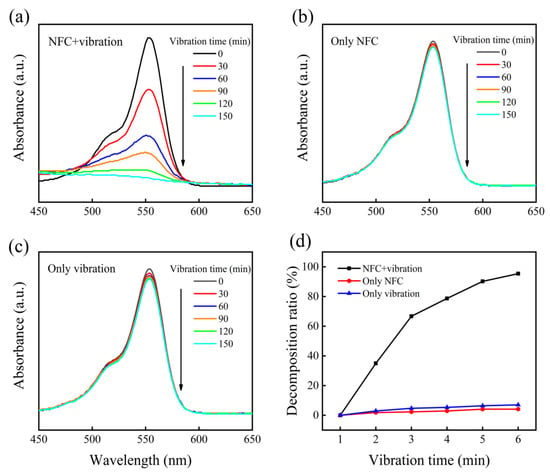
Figure 5.
The absorption spectra of RhB under different conditions. (a) Catalyst and vibration. (b) Only catalyst. (c) Only vibration. (d) The decomposition curve of RhB over various reaction conditions.
The initial absorbance value and the absorbance value over time are used to evaluate the decomposition ratio of RhB (D) in Equation (1) [36]:
where C0 and Ct are the concentrations of RhB solution defined at time 0 and time t, respectively. According to Equation (1), the dye decomposition ratios in Figure 5d for the three situations of catalyst only, vibration only, and vibration–catalyst are 4.1%, 7%, and 95.4%, respectively. This implies that FC suspension and vibration are required for the piezocatalytic decomposition of dyes. Furthermore, as the catalytic reaction progressed in Figure 5a,b, the maximum absorption peak of the RhB dye steadily decreased from 554 nm to 550 nm in wavelength. The N-demethylation intermediate created during the decomposition of RhB caused the “blue shift” effect [37].
To evaluate the catalytic versatility of FC, systematic comparative experiments were performed on piezocatalytic degradation of structurally diverse dyes under ultrasonic activation. Figure 6 systematically compares the degradation efficiencies of representative anionic (MO) and azo-type (AO7) dyes. The FC suspension exhibits broad-spectrum piezocatalytic activity, showing distinct degradation efficiencies under identical operational conditions. Notably, the system demonstrated a hierarchical degradation profile, achieving 95.4%, 72.4%, and 31.2% removal rates for RhB, AO7, and MO, respectively. This differential degradation behavior correlates with the molecular structure and redox potentials of the target pollutants, confirming the selective nature of piezoelectric-driven redox reactions. The dye decomposition complies with the pseudo-first-order kinetic Equation (2):
ln (C0/C) = k t

Figure 6.
Absorption spectra and decomposition ratios of different dyes. (a) MO dye. (b) AO7 dye. (c) Decomposition ratio. (d) The negative logarithm of C/C0.
Here, C0 and Ct follow Equation (1). The ratio constant and reaction time, respectively, are denoted by k and t. Kinetic analysis reveals distinct degradation rate constants (k) for the target dyes, with RhB exhibiting the highest value (0.02053 min−1), followed by AO7 (0.00858 min−1) and MO (0.00249 min−1), as shown in Figure 6d. This degradation selectivity primarily arises from molecular structural variations among the dye compounds. Mechanistically, the degradation process involves cleavage of characteristic chemical bonds: RhB contains readily cleavable C-C/C-N bonds requiring lower activation energy, resulting in superior degradation efficiency. Conversely, MO and AO7 possess conjugated azo bonds (N=N) and imine linkages (C=N) with higher bond dissociation energies, consequently demonstrating reduced degradability. The structure–activity relationship confirms that bond dissociation energy constitutes the rate-determining factor in piezoelectric catalytic degradation processes [38].
The effectiveness of piezocatalysis is examined regarding the effect of solution pH in making the FC suspension applicable to practical dye wastewater treatment. As a result, Figure 7a examines how the FC suspension performs at different pH levels. HCl and NaOH are used in the experiments to adjust the pH of the solution. When pH is 7, the FC suspension exhibits excellent piezocatalytic decomposition activity for RhB dye decomposition. When the pH is adjusted to 3, 5, 9, and 11, the decomposition performance is partially suppressed with decomposition ratios of 48.5%, 53.1%, 66.3%, and 57.7%, respectively. The pH-dependent study (Figure 7a) highlighted a key practical advantage: FC achieved optimal RhB degradation (95.4%) without chemical adjustment at neutral pH. This is in contrast to traditional catalysts (e.g., ZnO and PZT) that require acidic pH regulation, reducing the complexity and cost of actual wastewater production. The main cause could be that, under acidic conditions, the presence of a large amount of H+ ions in the solution, along with the presence of RhB dyes in the solution as cations, may lead to an electrostatic repulsion effect between RhB and the catalyst, resulting in a lower decomposition ratio. On the other hand, when under alkaline conditions, the ∙OH concentration in the solution is elevated, resulting in the reunion of the ∙OH and a significant reduction in the piezocatalytic RhB decomposition ratio. As a result, under acidic and alkaline circumstances, the FC suspension is not suitable for high-frequency ultrasonic vibration dye decomposition.

Figure 7.
(a) Decomposition ratio corresponding to different pH levels of RhB solutions. (b) The RhB decomposition ratio with the different scavengers.
To explore the mechanism of piezocatalysis, radicals that play a significant role in the dye decomposition process are examined. The findings of the radical quenching experiments are shown in Figure 7b. With the addition of BQ, EDTA, and TBA, the decomposition ratios are suppressed with the different decompositions, and the RhB decomposition ratios in the presence of BQ, TBA, and EDTA are only 28.5%, 29.7%, and 55%, respectively, which are lower than the decomposition ratios in the absence of scavengers. These results indicate that ∙OH radicals, ∙O2− radicals, and holes play a crucial role in piezocatalysis.
On this basis, the piezocatalytic decomposition mechanism of the RhB dye is proposed in Figure 8. An imbalance between the compensatory and polarization charges results from the spontaneous polarization of the FC suspension changing during vibration. For the purpose of maintaining the electrical neutrality of the FC suspension, the additional compensating charges will interact directly with the dye molecules or with oxygen or hydroxyl present in the solution, generating reactive radicals in the dye molecules. These radicals play an essential role in the decomposition of RhB dyes. The process of piezoelectric-catalyzed dye decomposition reaction is represented by Equations (3)–(6):
As schematized in Figure 8, Equation (3) represents the stress-induced charge separation in fibrillated cellulose (NFC), where ultrasonic vibration generates polarized surface charges (q+/q−). These drive redox reactions (Equations (4) and (5)) with adsorbed H2O/O2, producing ∙O2− (via q− reduction) and ∙OH (via q+ oxidation). In addition to the excellent piezocatalysis reported in this work, cellulose also has excellent photocatalysis performance. Li et al. [39] have reported ZnO/NFC (nanofibrillated cellulose) composites with a good network structure, and under UV light irradiation, the decomposition ratio of MO for 9 h is 100%. Dai et al. [40] have found a nanofibriform C-modified catalyst for Nb2O5 (F-C/Nb2O5) synthesized by niobium oxalate and NFC. F-C/Nb2O5 has decomposed about 90% of RhB after 30 min of light exposure. Synergistic catalysis is an effective strategy to increase the decomposition ratio of dyes. Ma et al. [41] have reported that ZnO nanorods have decomposed AO7 at 100% within 80 min while being vibrated and exposed to UV light, which is higher than 57% for only photocatalysis or 37% for piezocatalysis; in the future, it will ultimately be feasible to increase the dye decomposition ratio of the NFC catalyst by simultaneously harvesting light and vibration in the environment on the basis of the synergistic catalysis of piezocatalysis and photocatalysis. The ‘compensating charges’ in Figure 8 originate from piezoelectric polarization reversal under cyclic stress, enabling sustained radical generation. This aligns with the PFM hysteresis (Figure 3d), confirming reversible dipole reorientation.

Figure 8.
The schematic diagram of the enhanced piezocatalysis in the NFC.
4. Conclusions
In summary, this experiment unequivocally demonstrates that FC vibration causes the piezocatalytic performance. Under 150 min of vibration, the FC can decompose RhB dyes in a ratio of 95.4%. The FC’s piezocatalysis is broadly applicable. For MO and AO7 dye, the piezocatalytic decomposition ratio can reach 31.2% and 72.4%, respectively. It has been established through studies of active substances that the active compounds are ∙OH, ∙O2−, and holes. This study provides a potential application of organic materials for the processing of dye effluent through piezocatalysis. While this study focuses on catalytic efficiency, the robust piezoelectric response of FC under prolonged ultrasonic exposure and its intrinsic structural durability suggest favorable stability. Reusability studies—though beyond this work’s scope—will be prioritized in future applications, leveraging cellulose’s renewable nature and mechanical resilience.
Compared with traditional inorganic piezocatalysts such as ZnO, BaTiO3, and PZT reported in previous studies, although our FC system may not achieve the highest degradation rate for certain dyes, it exhibits unique advantages: it can achieve efficient degradation of RhB (95.4%) under neutral initial pH conditions without adjustment, avoiding the complex pH regulation process required by many inorganic catalysts; meanwhile, as a renewable biomass material, it has better environmental friendliness and lower preparation cost and can utilize ambient mechanical vibration energy, which significantly reduces the dependence on external energy input. These characteristics make the FC-based piezocatalytic system have strong practical application potential in sustainable water treatment, especially in the field of treating dye wastewater with near-neutral pH.
Author Contributions
Writing—review and editing, Z.Y. (Zhaoning Yang); writing—original draft preparation, Z.Y. (Zhaoning Yang) and Z.Y. (Zihao Yang); conceptualization, X.S.; data curation, W.C.; supervision, J.L.; visualization, K.C.; project administration, Y.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Data Availability Statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, W. (1−x)Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–xBiFeO3 solid solutions with enhanced piezocatalytic dye degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Singh, G.; Vaish, R. Ag-nanoparticles-loaded Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.9Zr0.1O3 for multicatalytic dye degradation. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 145716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Yu, X.; Huang, D.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y. Piezocatalytic performance of Fe2O3-Bi2MoO6 catalyst for dye degradation. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2023, 17, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.B.; Rajesh, P.; Ramasamy, P. Enhanced optical, thermal and piezoelectric behavior in dye doped potassium acid phthalate (KAP) single crystal. J. Cryst. Growth 2017, 468, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yein, W.T.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, X. Piezoelectric potential induced the improved micro-pollutant dye degradation of Co doped MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets in dark. Catal. Commun. 2019, 125, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masimukku, S.; Hu, Y.C.; Lin, Z.H.; Chan, S.W.; Chou, T.M.; Wu, J.M. High efficient degradation of dye molecules by PDMS embedded abundant single-layer tungsten disulfide and their antibacterial performance. Nano Energy 2018, 46, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; He, Q.; Wu, M.; Xu, Y.; Sun, P.; Dong, X. Piezoelectric polarization promoted spatial separation of photoexcited electrons and holes in two-dimensional g-C3N4 nanosheets for efficient elimination of chlorophenols. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Sun, C.; He, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Z.; Lü, Z.; et al. Piezoelectricity-driven structural stabilization and electrochemical enhancement in silicon anodes: A novel force-electric coupling framework. J. Energy Chem. 2025, 109, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Sun, H.; Xiao, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Synergetic piezo-photocatalytic effect in a Bi2MoO6/BiOBr composite for decomposing organic pollutants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 560, 150037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Wu, J.M. Synergistically catalytic activities of BiFeO3/TiO2 core-shell nanocomposites for degradation of organic dye molecule through piezophototronic effect. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Sun, Y.G.; Chang, W.E.; Lee, J.T. Piezoelectricity induced water splitting and formation of hydroxyl radical from active edge sites of MoS2 nanoflowers. Nano Energy 2018, 46, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.L.; Lai, S.N.; Wu, J.M. Strain-induced ferroelectric heterostructure catalysts of hydrogen production through piezophototronic and piezoelectrocatalytic system. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16106–16117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Qin, N.; Lin, E.; Yuan, B.; Kang, Z.; Bao, D. Synthesis of Bi4Ti3O12 decussated nanoplates with enhanced piezocatalytic activity. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 21128–21136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, F.; Lei, R.; Jiang, C.; Feng, W.; Liu, P. Tuning piezoelectric field for optimizing the coupling effect of piezo-photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 278, 119291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Bhardwaj, U.; Kushwaha, H.S. ZnO hollow pitchfork: Coupled photo-piezocatalytic mechanism for antibiotic and pesticide elimination. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Hao, A.; Cao, Y.; Jia, D. Boosting piezocatalytic performance of Ag decorated ZnO by piezo-electrochemical synergistic coupling strategy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 566, 150730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Tan, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Yin, R.; Meng, H.; Su, Y.; Qiao, L.; Bai, Y. Ultrahigh piezocatalytic capability in eco-friendly BaTiO3 nanosheets promoted by 2D morphology engineering. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2021, 596, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.; Kang, Z.; Wu, J.; Huang, R.; Qin, N.; Bao, D. BaTiO3 nanocubes/cuboids with selectively deposited Ag nanoparticles: Efficient piezocatalytic degradation and mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 285, 119823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.D.; Jin, C.C.; Liu, D.M.; Zhang, J.T.; Zhang, L.X. Strain engineering to boost piezocatalytic activity of BaTiO3. ChemCatChem. 2023, 15, e202201316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, A.; Chauhan, V.S.; Vaish, R. Porous BaTiO3 ceramic with enhanced piezocatalytic activity for water cleaning application. Surf. Interf. 2023, 36, 102497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Liu, D.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, L.; Zhuge, F. The role of microstructure in piezocatalytic degradation of organic dye pollutants in wastewater. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ling, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cao, F.; Li, H.; Bian, Z. Engineering spherical lead zirconate titanate to explore the essence of piezo-catalysis. Nano Energy 2017, 40, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Sharma, M.; Halder, A.; Vaish, R. Effect of poling on piezocatalytic and electrochemical properties of Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 ceramics. Surf. Interf. 2022, 30, 101827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Shao, W.; Lin, Q.; Tan, J.; Gao, S.; et al. Sm-Doped (1–x)Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-xPbTiO3 Nanostructures for Piezocatalytic Dye Degradation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 5, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Zhao, F.; Fan, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Ling, S.; Yu, H.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; et al. A Nanostructured Moisture-Absorbing Gel for Fast and Large-Scale Passive Dehumidification. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, Y.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose Nanocrystals: Chemistry, Self-Assembly, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogai, A. Emerging nanocellulose technologies: Recent developments. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2000630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.A.; Davoudpour, Y.; Islam, M.N.; Mustapha, A.; Sudesh, K.; Dungani, R.; Jawaid, M. Production and modification of nanofibrillated cellulose using various mechanical processes: A. review. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 99, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, B.; Zeng, J.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Gao, W.; Chen, K. Chiral Photonic Liquid Crystal Films Derived from Cellulose Nanocrystals. Small 2021, 17, 2007306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solhi, L.; Guccini, V.; Heise, K.; Solala, I.; Niinivaara, E.; Xu, W.; Mihhels, K.; Kröger, M.; Meng, Z.; Wohlert, J.; et al. Understanding nanocellulose–water interactions: Turning a detriment into an asset. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 1925–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csoka, L.; Hoeger, I.C.; Rojas, O.J.; Peszlen, I.; Pawlak, J.J.; Peralta, P.N. Piezoelectric effect of cellulose nanocrystals thin films. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, F.; Biswas, B.; Torris, A.; Kumaraswamy, G.; Shanmuganathan, K. Elastic piezoelectric aerogels from isotropic and directionally ice-templated cellulose nanocrystals: Comparison of structure and energy harvesting. Cellulose 2021, 28, 6323–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, S.; Siponkoski, T.; Sarlin, E.; Mettanen, M.; Vuoriluoto, M.; Pammo, A.; Juuti, J.; Rojas, O.J.; Franssila, S.; Tuukkanen, S. Cellulose nanofibril film as a piezoelectric sensor material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15607–15614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Jia, Y.; Chang, T.; Ruan, L.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, G.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, G. Highly efficient piezo-catalysis of the heat-treated cellulose nanocrystal for dye decomposition driven by ultrasonic vibration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.T.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.Y.; Yuan, Z.Y. High-entropy alloys in electrocatalysis: From fundamentals to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 8319–8373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.Y.; Liu, H.B.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhao, Y.W.; Yang, S.; Lyu, S.Y.; Xing, A.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, X.Y. Ferroelectric polarization-enhanced photocatalytic performance of heterostructured BaTiO3@TiO2 via interface engineering. J. Cent. South Univ. 2021, 28, 3778–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Mohamood, T.; Ma, W.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J. Oxidative decomposition of rhodamine B dye in the presence of VO2+ and/or Pt(IV) under visible light irradiation: N-deethylation, chromophore cleavage, and mineralization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 26012–26018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Yang, F.; Li, R.; Ai, C.; Lin, C.; Lin, S. Improving hydrogen evolution activity of perovskite BaTiO3 with Mo doping: Experiments and first-principles analysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 11695–11704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S.; Ma, J. Cellulose controlled zinc oxide nanoparticles with adjustable morphology and their photocatalytic performances. Carbohyd. Polym. 2021, 259, 117752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Yuan, B.; Guo, M.; Zhang, K.; Chen, X.; Song, Z.; Nguyen, T.T.; Wang, X.; Lin, S.; Fan, J.; et al. A novel nano-fibriform C-modified niobium pentoxide by using cellulose templates with highly visible-light photocatalytic performance. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 13210–13218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Z.; You, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Wang, F. High piezo-photocatalysis of BaTiO3 nanofibers for organic dye decomposition. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 48, 104308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).