Abstract
Sodium-based bentonite is used for drilling operations because of its high swelling capacity. This type of bentonite clay is not sourced locally in many oil- and gas-producing nations. However, low-swelling clays (calcium- and potassium-based) are in abundant quantities in most of these countries. Hence, there is a need to convert low-swelling bentonite clays to sodium-based bentonite. The method used to convert low-swelling clays is more applicable to calcium-based bentonite. This research investigated a thermochemical treatment method that converted potassium-based bentonite to sodium-based bentonite. The raw clay materials were sourced from Pindinga (P) and Ubakala (U) clay deposits in Nigeria. An X-ray diffractometer (XRD), an energy dispersive X-ray (EDX), and a scanning electron microscope (SEM) were used to characterize the raw clay samples. Mud slurry was prepared by mixing 22 g of the local raw clays, 3 wt.% soda ash, and MgO at concentrations between 1 and 3 wt.% and heating at 90 °C. The result showed that the viscosities of samples P and U increased from 6 to 26 and 8 to 35.5 cP before and after thermochemical treatment, respectively. Also, due to the thermochemical treatment, the samples’ yield point, consistency factor, consistency index, and thixotropy behavior were all significantly improved.
1. Introduction
Drilling fluid is any fluid used to carry cuttings from the wellbore to the surface during drilling operation [1,2]. The successful completion of oil and gas wells is highly dependent on the properties of drilling fluids [3,4,5]. The rheological properties of drilling fluid are one of the major properties of the fluid and are responsible for the suspension and carrying of cuttings. Water-based mud (WBM) is one of the most common types of drilling fluid. It is prepared by mixing water, clay, and additives. The American Petroleum Institute (API) stipulates that any WBM used to drill wells should have a minimum viscosity of 30 cP at 600 rpm. Meeting this requirement depends largely on the type of bentonite clay used to prepare the drilling fluid. There are three types of bentonite clay, namely potassium-based, sodium-based, and calcium-based bentonite. Potassium-based and calcium-based bentonite have very low swelling capability [6,7,8,9]. When these types of clays are used to prepare WBM, the viscosity of the mud is usually poor. Sodium-based bentonite clay on the other hand has a high swelling capability [10]. Hence, they are the type of clay used during drilling operations.
The majority of bentonite clay in Nigeria is either calcium- or potassium-based [2]. Numerous studies have been conducted to improve the swelling capacities of clay sourced from Nigeria using three different techniques. The first technique involved beneficiating the raw clays with sodium carbonate [11]. This was performed by mixing the raw clays with sodium carbonate to convert the clays to sodium-based bentonite. However, this method could not improve the swelling capacity of the clays as the authors did not subject the raw clays to the conditions necessary for ion exchange to take place between the clay and sodium carbonate. The factors necessary for the thermochemical treatment of low-swelling clay include temperature (70–90 °C), the concentration of bentonite clay, and the concentration of sodium carbonate. The second method involved the addition of viscosifiers such as carboxyl methyl cellulose, poly-anionic cellulose, hydroxyl ethyl cellulose, and gum arabic to improve the rheological properties of the mud prepared using the local raw clays [12,13,14]. This method improved the rheological properties of the mud. This occurred because of the addition of viscosifier to the mud samples. The third method involved the combination of the first two methods [15,16,17,18,19]. Researchers resorted to using this technique as a result of the failure recorded using the first technique [20].
There is still a need to treat the local raw clays through an activation route that will not involve the addition of a viscosifier. Thermochemical treatment of low-swelling clays is an activation route that does not involve the use of a viscosifier. It can be used to convert calcium- or potassium-based bentonite to sodium-based bentonite. It involves the use of heat and chemical (soda ash) to beneficiate the clay. The application of heat during this process is used to decompose the sodium carbonate into sodium oxide and carbon dioxide [21,22,23]. Calcium ions in the low-swelling clay will then be exchanged for sodium ions in sodium oxide [21]. Magzoub et al. [10] looked into how heat, agitation, and sodium carbonate affected the rheological and swelling capabilities of calcium-based bentonite colloidal dispersions. The authors noted that the slurry’s viscosity increased and satisfied the minimum level required by API after being heated and stirred simultaneously. The limitation of Magzoub et al. [10] was the length of time (6 h) needed to treat the clay. Also, this method of clay activation cannot be used to improve the swelling behavior of potassium-based bentonite [21]. This is because sodium (from sodium oxide) cannot displace the potassium present in potassium-based bentonite clay as a result of the positions of sodium and potassium in the electrochemical series.
Magzoub et al. [22] investigated the swelling kinetics of calcium-based bentonite clay using particle size analysis. The swelling of the clay was shown to be a kinetically controlled process that depended on time, temperature, sodium carbonate, and bentonite composition. It followed a second-order reaction. Mahmoud et al. [23] beneficiated calcium-based bentonite clay using sea water and soda ash. The bentonite was treated initially with sea water under simultaneous heating and stirring conditions. This process did not improve the swelling capacity of the clay. However, after the addition of soda ash to the mud, the swelling properties of the clay improved.
The method used by Magzoub et al. [22] and Mahmoud et al. [23] also had the same setbacks stated with the method used by Magzoub et al. [10]. There is still the need to utilize a thermochemical treatment method that can be used to beneficiate potassium-based bentonite. This treatment method will involve the use of reagents such as magnesium oxide. This will cause the substitutions of ions within the structure of the clay. Magnesium (from MgO) will substitute aluminum in the octahedral unit of the clay. This substitution process will create unbalanced charges that will attract sodium ions to the interlayer units of the clay [21,24,25]. When this occurs, the clay will be converted to sodium-based bentonite depending on the amount of sodium ions in the clay. This research, therefore, will employ this thermochemical treatment route for the improvement of the rheological properties of Nigerian raw clays (potassium-based).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
The materials used for the experiment include local raw clays, soda ash (Merck—99.9% purity), magnesium oxide (Merck—99.9% purity), distilled water, a spatula, a beaker (500 mL), and a measuring cylinder (1000 mL). The equipment used for the experiment include a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (Model-EVO®, Carl Zeiss Pvt. Ltd., Cambridge, UK), an energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) (Model-EVO® Carl Zeiss Pvt. Ltd., Cambridge, UK), an X-ray diffractometer (XRD) (Bruker-D8), a variable mud mixer (Ofite, Model 9B), a viscometer (Ofite, Model 800), a magnetic stirrer, an oven (U-Test GENO, DT104A), a jaw crusher (Retsch, BB 50), a weighing balance (OHAUS, Model AX124), and a mud balance (Ofite).
2.2. Material Collection and Preparation
Two locations in Nigeria were used to gather the regional raw clays. They were gathered in Ubakala (latitude 5°30′41″ N and longitude 7°28′32″ E), Abia State, and Pindinga (latitude 9°59′4″ N and longitude 10°57′8″ E), Gombe State. Prior research has demonstrated that the raw clay materials from these locations have subpar rheological properties [18,26,27,28]. The raw clay samples were taken at a depth of 1 m, and the moisture content was reduced by oven drying for 16 h at 70 °C. The dried clay samples were sieved using an API standard mesh size of 75 microns and crushed using a crusher [10].
2.3. Sample Characterization
The fine local raw clay materials were characterized using SEM, EDX, and XRD. A SEM was used to analyze the surface of the clay samples. The clay sample was placed inside the sample chamber of the SEM. The sample chamber was placed under vacuum conditions. This was performed to remove any gas particles inside the chamber. The electron beam was turned on and incident on the clay sample inside the sample chamber using an accelerating voltage of 25 kV. The interaction between the electrons and the clay sample generated signals that defined the surface morphology of the clay sample. The model of SEM used to analyze the clay sample also contained an EDX. When the clay sample was placed in the sample chamber in the SEM, the beam of electrons that was incident on the clay sample caused the clay sample to emit X-rays. The energy of the emitted X-ray was characteristic of the elements present in the clay material. The mineralogical composition of the clay samples was analyzed using a Bruker-D8 diffractometer. Cu Kα radiation was used for the analysis. The clay sample was placed in the sample holder of the diffractometer. A beam of electrons was incident on the clay sample with an accelerating voltage of 40 kV. The beam of electrons interacted with the clay sample and dislodged into the inner shell electrons to produce X-ray spectra that were characteristic of the clay sample.
2.4. Sample Preparation
The local raw clay samples were treated thermochemically using heat, soda ash (sodium carbonate), and magnesium oxide. Previous studies have shown that soda ash acts as a good source of sodium ions compared to other sodium compounds used to beneficiate low-swelling clays [10,22,23]. MgO was used to aid the substitution of ions within the structure of the clay [24]. A sample of mud was prepared by mixing 22 g of raw clay from Pindinga with 350 cc of distilled water. 3 wt.% of soda ash and 1 wt.% of MgO were added to the mud sample and mixed thoroughly. Additional two samples of mud were prepared by mixing 22 g of raw clay from Pindinga with 350 cc of distilled water. An additional two samples of mud were prepared by mixing 22 g of raw clay from Pindinga and 3 wt.% of soda ash with 350 cc of distilled water. 1 wt.% and 2 wt.% of MgO were added to the two samples respectively and mixed.
Another three samples of mud were prepared using 22 g of raw clay from Ubakala, 3 wt.% of soda ash, and varying concentrations of MgO (1–3 wt.%), as shown in Table 1. Table 1 shows the samples of mud prepared for thermochemical treatment. The mud samples prepared using Pindinga and Ubakala raw clay materials were tagged as samples P and U, respectively. The subscripts indicate the concentration of MgO and soda ash in each of the samples. The first item of the subscript (1–3) was used to indicate the level of concentration of MgO while the second item represents the fixed concentration of soda ash (3 wt.%). For example, sample P1,3 was prepared using 22 g of Pindinga clay, 1 wt.% of MgO, and 3 wt.% of soda ash. Sample P3,3 was prepared using 22 g of Pindinga clay, 3 wt.% of MgO, and 3 wt.% of soda ash. Each of the samples was heated at 90 °C for one hour using a magnetic stirrer.

Table 1.
Mud samples prepared for thermochemical treatment.
2.5. Testing Procedure
The effect of the thermochemical treatment of the local raw clays on the rheological behavior of the mud was determined using API standard procedures for mud testing [10,27,29,30]. The plastic viscosity, yield point, power law index, and consistency factor of the samples were calculated using Equation (1) to Equation (4), respectively. The shear stress to shear rate relationship of the samples before and after the thermochemical treatment was determined. Also, the thixotropy behavior of the samples before and after the thermochemical treatment was determined using the thixotropy loop test [31,32]. The elemental composition of the thermochemically treated clays was determined using EDX.
where:
PV = θ600 − θ300
YP = θ300 − PV
n = 3.32 log (θ600/θ300)
K = θ300/(511)n
θ300 = Dial reading of the viscometer at 300 rpm;
θ600 = Dial reading of the viscometer at 600 rpm;
PV = Plastic viscosity;
YP = Yield point;
n = Power law index;
K = Consistency factor.
3. Discussion of Results
3.1. Characterization Results of the Local Clay Samples
The results obtained from the characterization of the clay samples are discussed in this section. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the surface morphologies of all the clay samples, as acquired from the SEM. The surface of all the clay samples look like a flake [33]. This is a unique characteristic of clay materials [24]. The raw clay materials contained small and large particles with irregular shapes. Table 2 shows the elemental composition of the clay samples. The clay sample from Pindinga contained the following elements: oxygen (4.50%), magnesium (2.97%), silicon (53.26%), aluminum (33.17%), potassium (3.50%), and calcium (2.60%). Potassium was the dominant cation present in this clay. The raw clay material from Ubakala contained the following elements: oxygen (5.42%), magnesium (4.41%), silicon (39.21%), aluminum (44.50%), calcium (3.68%), and potassium (2.78%). Calcium is the dominant cation present in this clay sample. None of the local raw clay samples contained sodium.

Figure 1.
SEM Images of the raw clay material from Pindinga.

Figure 2.
SEM Images of the raw clay material from Ubakala.

Table 2.
Elemental composition of the clay samples before and after thermochemical treatment using EDX.
The elemental analysis of the thermochemically treated clay is also shown in Table 2. The same elements (oxygen, sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, potassium, and calcium) were found in all the treated clay samples. The thermochemical treatment of the local raw clay materials had an impact on the chemical composition of the local clay materials. Initially, the raw clay material from Pindinga and Ubakala, respectively, did not contain sodium. However, after the thermochemical treatment of the raw clays, sodium was found in the clay samples. Also, the raw clays did not contain a lot of magnesium. However, after the thermochemical treatment, the composition of magnesium increased. This was due to the substitution of ions that occurred during the thermochemical treatment [21,25]. This process created some charges within the structure of the clay that attracted sodium ions (from soda ash).
Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the XRD analysis of all the clay samples. The raw clay material from Pindinga contained a high composition of montmorillonite and quartz, a low composition of feldspar and illite, and traces of calcite. The raw clay sample from Ubakala also contained a high composition of montmorillonite, a low composition of feldspar and quartz, and traces of illite and calcite. The elemental composition and XRD analysis of the acquired local raw clay materials showed that all the local raw clay materials were bentonite clay.
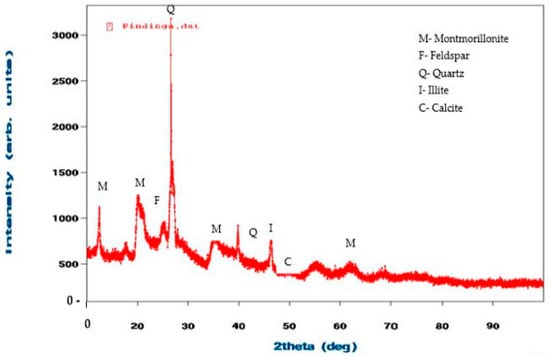
Figure 3.
XRD Images of the raw clay material from Pindinga.
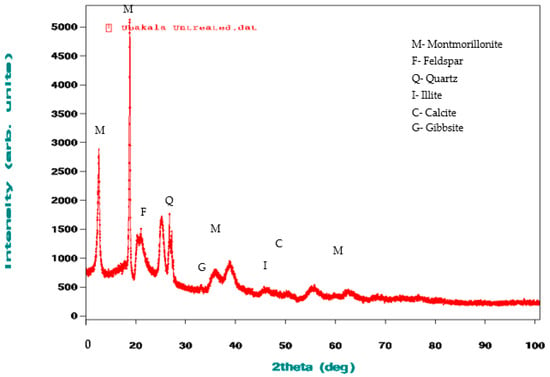
Figure 4.
XRD Images of the raw clay material from Ubakala.
3.2. Effect of the Thermochemical Treatment of the Local Raw Clay Materials
This section discusses the effect of the thermochemical treatment of the local raw clay materials on the properties of water-based mud.
3.2.1. Mud Viscosity
Figure 5 shows the effect of the thermochemical treatment of the local raw clays on the viscosity (600 rpm) of the samples. The thermochemical treatment of the raw clay materials has a strong effect on the viscosity of the samples prepared using Pindinga and Ubakala clays. The viscosity of samples P1,3 and P3,3 were improved from 6 to 14 cP and 8 to 26 cP, respectively, after the thermochemical treatment. The viscosity of samples U1,3 and U3,3 also improved from 6 to 10 cP and 8 to 35.5 cP, respectively. It was observed that the higher the concentration of MgO in the samples, the more the effect of the thermochemical treatment on the mud viscosity. The thermochemical treatment of Ubakala raw clay was able to improve the viscosity of the mud (sample U3,3) to the standard specified by API. API stipulated that the minimum viscosity of a mud sample should be 30 cP.
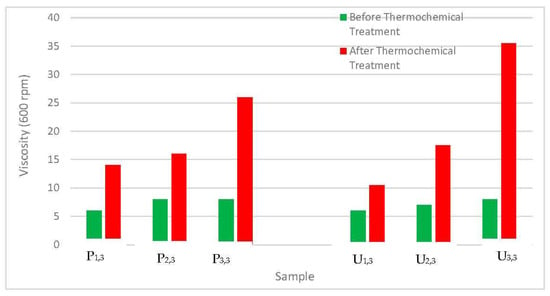
Figure 5.
Effect of the thermochemical treatment of the local raw clay materials on the mud viscosity at 600 rpm.
The thermochemical treatment of Pindinga clay improved the viscosity of the mud (sample P3,3) comparably with that of finished bentonite clay (26 cP) [34]. Hence, Pindinga raw clay can also be used for drilling operations after being treated thermochemically. The improvement in the mud viscosity after the thermochemical treatment of the local raw clay materials was a result of the substitution and exchange of ions that took place during the heating process [10,21].
3.2.2. Shear Stress to Shear Rate Relationship
Figure 6 show the effect of the thermochemical treatment of the local raw clay materials on the shear stress to shear rate relationship of the samples. All the mud samples exhibited a Bingham plastic fluid behavior. The shear stress to shear rate behavior of the samples before the thermochemical treatment was very poor. The higher the concentration of MgO in the samples, the more the impact of the thermochemical treatment. It improved the shear stress to shear rate behavior of the samples prepared using the raw clay from Pindinga and Ubakala. This was also observed in the research conducted by Magzoub et al. [35] where thermochemical treatment of calcium-based bentonite clay increased the shear stress behavior of the mud samples.
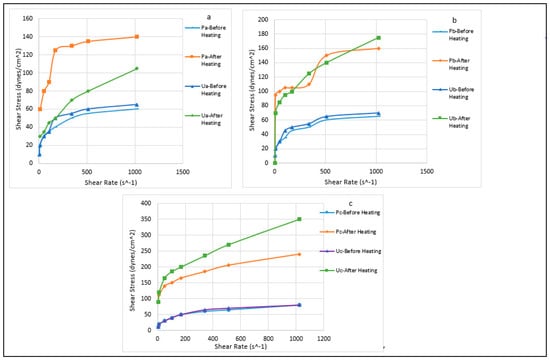
Figure 6.
Effect of the thermochemical treatment on the shear stress to shear rate relationship of the mud samples: (a). Samples P1,3 and U1,3. (b). Samples P2,3 and U2,3. (c). Samples P3,3 and U3,3.
3.2.3. Plastic Viscosity, Yield Point, Flow Behavior Index, and Consistency Factor
Table 3 shows the effect of the thermochemical treatment of the local raw clay materials on the plastic viscosity, yield point, flow behavior index, and consistency factor of the mud samples. The thermochemical treatment of the local raw clay materials also had some significant effects on the plastic viscosity, yield point, flow behavior index (n), and consistency factor (k) of most of the samples. The thermochemical treatment of the samples improved the plastic viscosity of the samples prepared with Pindinga and Ubakala clay, respectively. The plastic viscosity of samples P2,3 and P3,3 increased from 0.5 to 1 cP and 1.5 to 3.5 cP, respectively. The plastic viscosity of samples U2,3 and U3,3 increased from 0.5 to 3.5 cP and 1.0 to 8.0 cP, respectively.

Table 3.
Effect of the thermochemical treatment of the local raw clay materials on the plastic viscosity, yield point, flow behavior index, and consistency factor of the samples.
The thermochemical treatment improved the yield point of the samples prepared with Pindinga and Ubakala clay. The yield point of samples P1,3, P2,3, and P3,3 were increased from 1.0 to 13.0 lbf/100sq.ft, 5.0 to 14 lbf/100sq.ft, and 5.0 to 17 lbf/100sq.ft, respectively. The yield point of samples U2,3 and U3,3 were increased from 6.0 to 10.5 lbf/100sq.ft and 6.0 to 19.0 lbf/100sq.ft, respectively. The yield point of samples P3,3 and U3,3 after the thermochemical treatment met the API standard. API recommends that the yield point of any water-based drilling mud should be a minimum of three times its plastic viscosity. Magzoub et al. [35] also reported similar observations in their studies of thermochemical upgrading of calcium-based bentonite for drilling fluid applications. The thermochemical treatment improved the plastic viscosity and yield point of the mud samples prepared with calcium-based bentonite. The flow behavior index of the samples prepared with Pindinga and Ubakala clays was also affected after the thermochemical treatment. Despite the effect of the thermochemical treatment on the flow behavior index, the samples still behaved like a non-Newtonian fluid. The thermochemical treatment of the samples prepared using Pindinga and Ubakala clay also improved the consistency factor of the samples.
3.2.4. Thixotropy Behavior
Figure 7 and Figure 8 show the thixotropy behavior of the mud prepared with Pindinga clay before and after thermochemical treatment, respectively. The mud samples prepared before the thermochemical treatment did not exhibit any thixotropy behavior. The up-sheared curve and the down-sheared curve of all the samples coincided with each other during the 10-s and 10-min thixotropy tests. This is undesirable during drilling operations. The thermochemical treatment affected the thixotropy behavior of this sample. The down-sheared curve lay above the up-sheared curve before a shear rate of 51 s−1 during the 10-min thixotropy test. This shows that at very low shear rate conditions, the fluid exhibited negative thixotropy [30]. The structure developed in the sample after the 10-min rest period did not break down completely at low shear rate conditions. The sample also exhibited negative thixotropy between a shear rate of 170 s−1 and 340 s−1.
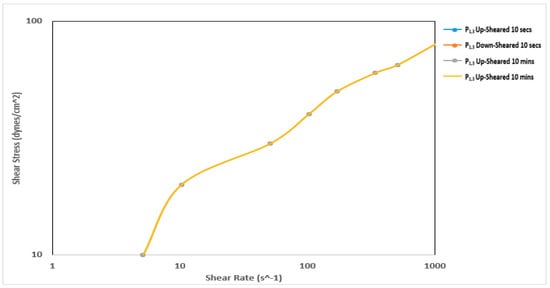
Figure 7.
Thixotropy behavior of the mud prepared with Pindinga clay before thermochemical treatment.
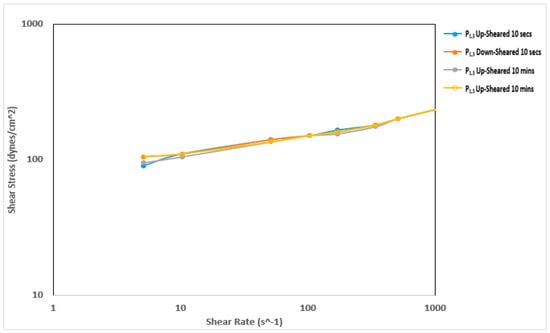
Figure 8.
Thixotropy behavior of the mud prepared with Pindinga clay after thermochemical treatment.
Figure 9 and Figure 10 show the thixotropy behavior of the mud prepared with Ubakala clay before and after thermochemical treatment, respectively. Initially, this sample did not exhibit any thixotropy behavior. However, after the thermochemical treatment, the sample exhibited prominent thixotropy behavior. The sample exhibited a negative thixotropy before a shear rate of 1022 s−1 during the 10-min thixotropy test. The down-sheared curve was lying above the up-sheared curve [30]. This implies that the structure developed during the 10-min rest period did not break down. The thermochemical treatment affected the thixotropy behavior of the samples prepared using Pindinga and Ubakala clay, respectively. It made the fluid samples exhibit negative thixotropy behavior. It also improved the shear stress required to shear the fluid. The structure generated during the rest period was a result of the improvement in the fluid viscosity during the treatment of the local raw clay materials.
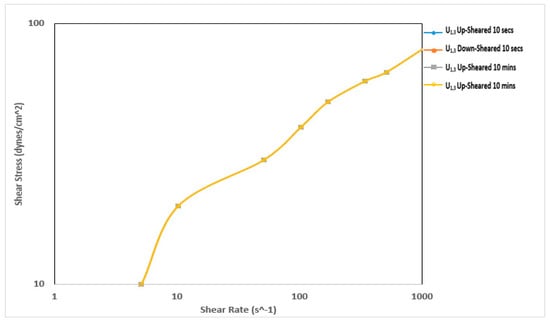
Figure 9.
Thixotropy behavior of the mud prepared with Ubakala clay before thermochemical treatment.
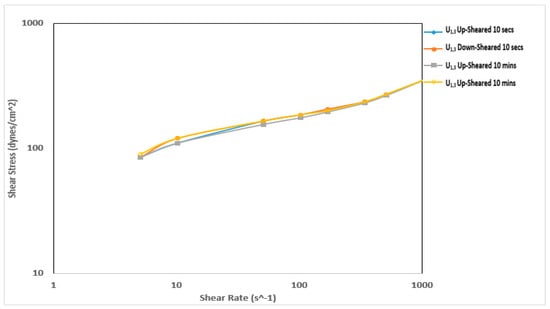
Figure 10.
Thixotropy behavior of the mud prepared with Ubakala clay after thermochemical treatment.
4. Conclusions
The thermochemical treatment of the clay samples improved the rheological properties of the mud prepared with Pindinga and Ubakala clay, respectively. The viscosity (600 rpm) of the mud samples prepared with Pindinga and Ubakala clay was improved from 8 to 26 cP and 8 to 35.5 cP, respectively. It also improved the yield point, consistency factor, and consistency index of the mud samples to the standard recommended for drilling operations.
The thermochemical treatment also had an impact on the thixotropy behavior of the mud samples. It made the fluid samples exhibit negative thixotropy behavior. The time to treat the samples thermochemically to attain acceptable rheological properties was one hour. This is shorter than other treatment times observed in the literature.
It is recommended that further studies should be carried out to reduce the temperature requirement for thermochemical treatment of potassium-based bentonite clay. This will help to reduce the cost of treating potassium-based bentonite clay.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: O.O., A.O.A., P.N. and S.O.; Methodology: O.O., A.O.A., P.N. and S.O.; Result Analysis: O.O., A.O.A., P.N., C.C.O. and S.O.; Writing—original draft preparation, review, and editing: O.O., A.O.A., P.N., C.C.O. and S.O.; Supervision: A.O.A., P.N., C.C.O. and S.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the African Development Bank (AfDB) for the offer of a Ph.D. scholarship to the first author. Peter Ngene acknowledges support from NLNG Nigeria LTD in the form of the Nigerian Prize for Science 2018.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Agwu, O.E.; Okon, A.N.; Udoh, F.D. A review of Nigerian bentonitic clays as drilling mud. Society of Petroleum Engineers—SPE Niger Annu. In Proceedings of the SPE Nigeria Annual International Conference and Exhibition, Lagos, Nigeria, 4–6 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nlemedim, P.U.; Chime, T.O.; Omotioma, M.; Archibong, F.N.; Ajah, S.A. Comparative study of bentonite and Ikwo clay for oil-based drilling mud formulation. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 229, 212089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, R.O.; Orodu, O.D.; Efeovbokhan, V.E. Properties and application of Nigerian bentonite clay deposits for drilling mud formulation: Recent advances and future prospects. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.; Kamal, M.S.; Al-Harthi, M. Polymeric and low molecular weight shale inhibitors: A review. Fuel 2019, 251, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oseh, J.O.; Mohd, N.M.N.A.; Gbadamosi, A.O.; Agi, A.; Blkoor, S.O.; Ismail, I.; Igwilo, K.C.; Igbafe, A.I. Polymer nanocomposites application in drilling fluids: A review. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 222, 211416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewu, B.B.; Arabi, S.A.; Oladipo, M.O.; Funtua, I.I.; Mohammed-Dabo, I.A.; Muhammad, A.M. Improvement of rheological properties of bentonitic clays using sodium carbonate and a synthetic viscosifier. Int. Arch. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2011, 2, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Akinwumi, A. Beneficiation of Nigeria Local Clay to Meet API Standard Specification for Drilling Fluid Formulation. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2015, 5, 16–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wilfred, O.C.; Akinade, A.E. Comparative Study of Basic Properties of Mud Prepared with Nigerian Local Clay and Mud Prepared with Foreign Clay: A Case Study of Abbi Clay Deposit. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2016, 8, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agwu, O.; Okon, A.; Akpanika, O. Activation of Local Bentonitic Clays for Use as Viscosifiers in Water-based Drilling Fluids. J. Sci. Res. Rep. 2016, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magzoub, M.I.; Hussein, I.A.; Nasser, M.S.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Sultan, A.S.; Benamor, A. Effects of sodium carbonate addition, heat and agitation on swelling and rheological behavior of Ca-bentonite colloidal dispersions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 147, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, O.O.; Mesubi, M.A.; Adekola, F.A.; Odebunmi, E.O.; Adekeye, J.I. Beneficiation and characterization of a bentonite from North-Eastern Nigeria. J. North Carol. Acad. Sci. 2008, 124, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Olatunde, A.O. Improvement of Rheological Properties of Drilling Fluid Using Locally Based Materials. Petrol. & Coal. 2012, 54, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Akinwumi, E.A.; Omolola, A. Suitability of Using Agbarha Clay for Drilling Mud Formulation in Oil and Gas Industry. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 5, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Salawudeen, T.O.; Arinkoola, A.O.; Jimoh, M.O.; Salam, K.K.; Ogunmola, E.O. Effect of inert fibre on performance of B. Eurycoma as rheology and filtration control additive in water-based drilling fluid. Int. J. Pet. Eng. 2016, 2, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apugo-Nwosu, T.U.; Mohammed-Dabo, I.A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Abubakar, G.; Alkali, A.S.; Ayilara, S.I. Studies on the suitability of Ubakala bentonitic clay for oil well drilling mud formulation. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udoh, D.F.; Okon, N.A. Formulation of Water-Based Drilling Fluid using Local Materials. Asian J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 14, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Dewu, B.B.M.; Oladipo, M.O.A.; Funtua, I.I.; Arabi, S.A.; Mohammed-Dabo, I.A.; Muhammad, A.A. Evaluation of Rheological and Other Physical Properties of Bentonite Clays from Fika Formation in Parts of North-Eastern Nigeria. Pet. Technol. Dev. J. 2012, 1, 885324. [Google Scholar]
- Arinkoola, A.O.; Salawudeen, T.O.; Salam, K.K.; Jimoh, M.O.; Abidemi, G.O.; Atitebi, Z.M. Optimization of Water-Based Drilling Fluid Produced Using Modified Nigerian Bentonite and Natural Biopolymers: Reduced Experiment and Response Surface Methodology. Iran. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 16, 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- Udeagbara, S.G.; Ogiriki, S.O.; Afolabi, F.; Bodunde, E.J. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Local Clay from Ebonyi State, Nigeria as a Substitute for Bentonite in Drilling Fluids. Int. J. Pet. Gas Eng. Res. 2019, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Aghamelu, O.P.; Okogbue, C.O. Characterization of some clays from Nigeria for their use in drilling mud. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 116–117, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, N.S.; Olayiwola, T.; Elkatatny, S. A review on clay chemistry, characterization and shale inhibitors for water-based drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 206, 109043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magzoub, M.I.; Hussein, I.A.; Nasser, M.S.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Sultan, A.S.; Benamor, A. An Investigation of the Swelling Kinetics of Bentonite Systems Using Particle Size Analysis. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 41, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.; Mohamed, A.; Kamal, M.S.; Sultan, A.S.; Hussein, I.A. Upgrading Calcium-Bentonite to Sodium-Bentonite Using Seawater and Soda Ash. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 10888–10894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochieng, O. Characterization and classification of clay minerals for potential applications in Rugi Ward, Kenya. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Tanskanen, J.T.; Hirvi, J.T.; Kasa, S.; Schatz, T.; Pakkanen, T.A. Molecular dynamics study of montmorillonite crystalline swelling: Roles of interlayer cation species and water content. Chem. Phys. 2015, 455, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, A.S.; Dewu, B.B.M.; Oladipo, M.O.A.; Funtua, I.I. Mineralogy and rheology of raw and activated Turonian to Coniacian clays from Benue Trough, Northeastern Nigeria. Egypt. J. Pet. 2017, 27, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, A.S.; Dewu, B.B.M.; Funtua, I.I.; Oladipo, M.O.A.; Tukur, M.; Bilal, S.; Babale, S.I. Morphology, rheology and thermal stability of drilling fluid formulated from locally beneficiated clays of Pindiga Formation, Northeastern Nigeria. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgoyne, A.D.; Chenevert, M.E.; Millhelm, K.K.; Young, F.S., Jr. Applied Drilling Engineering; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- American Petroleum Institute (API). Specification for Drilling Fluid Materials, 5th ed.; API: Houston, TX, USA, 1993; Standard No. API 13A. [Google Scholar]
- Maxey, J. Thixotropy and Yield Stress Behavior in Drilling Fluids. In Proceedings of the 2007 AADE National Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, TX, USA, 10–12 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tehrani, A. Thixotropy in Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Ann. Trans. Nordic Rheol. Soc. 2008, 16, 103653. [Google Scholar]
- Gholami, R.; Elochukwu, H.; Fakhari, N.; Sarmadivaleh, M. A review on borehole instability in active shale formations: Interactions, mechanisms and inhibitors. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 177, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, I.; Mahmoud, M. Stimulating illitic sandstone reservoirs using in-situ generated HF with the aid of thermochemicals. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 190, 107089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogolo, O.; Arinkoola, A.; Osisanya, S.; Egede, F.; Chior, T.J. Rheological impact and economic implications of partial to total substitution of imported bentonite clay for oil and gas drilling operations in Nigeria. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2020, 11, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magzoub, M.; Mahmoud, M.; Nasser, M.; Hussein, I.; Elkatatny, S.; Sultan, A. Thermochemical Upgrading of Calcium Bentonite for Drilling Fluid Applications. ASME J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2018, 141, 042902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).